Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cellular Level of Organization
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Q: What is the primary function of the cell membrane/plasma membrane?
A: It provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
Q: What are the molecular components of the cell membrane?
A: Mainly phospholipids (in a bilayer), cholesterol, and proteins.
Q: Describe the structure of a phospholipid.
A: A phospholipid has a hydrophilic (water-loving) phosphate head and two hydrophobic (water-fearing) fatty acid tails.
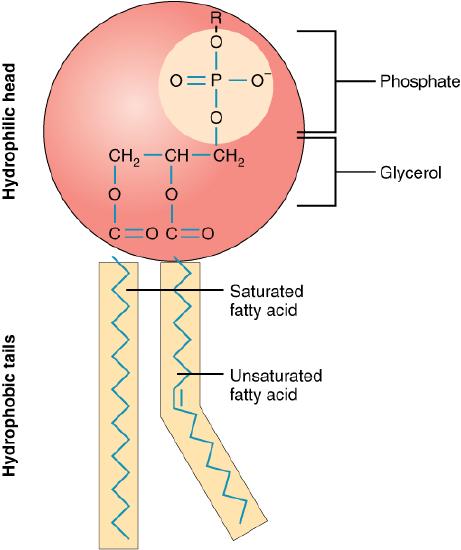
Q: Why is the cell membrane described as ‘amphipathic’?
A: Because phospholipids have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Q: What is the significance of membrane fluidity?
A: Lipids and proteins are not rigidly locked in place, allowing flexibility and movement within the membrane.
Q: What is selective permeability in relation to the cell membrane?
A: It allows only certain substances to cross the membrane unaided, usually small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Q: What types of proteins are found in the cell membrane, and what are their roles?
A: Integral proteins (embedded; includes channel and recognition proteins) and peripheral proteins (surface-associated; often enzymes).
Q: What is the glycocalyx?
A: A fuzzy coating around the cell made from glycoproteins and other carbohydrates, helping with cell recognition and protection.
Q: Name three extensions of the plasma membrane and their functions.
A: Microvilli (increase surface area), cilia (movement of materials), flagella (cell movement).
Q: What is passive transport?
A: Movement of substances across the membrane without using cellular energy (includes diffusion and facilitated diffusion).
Q: What is active transport?
A: Movement of substances across the membrane using energy from ATP, often against their concentration gradient.
Q: What is endocytosis and its types?
A: Endocytosis is when the cell engulfs materials: phagocytosis (“cell eating”), pinocytosis (“cell drinking”), and receptor-mediated endocytosis (highly selective).
Q: What is exocytosis?
A: The process where a cell exports material using vesicles that fuse with the membrane.
Q: How does cystic fibrosis relate to the cell membrane?
A: It results from a defective membrane ion channel (CFTR) affecting chloride transport, leading to thick mucus buildup especially in lungs.