Atkinson-Shiffrin Multi-Store Model of Memory
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Memory
is the processing, storage and retrieval of information acquired through learning
Memory process
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
.
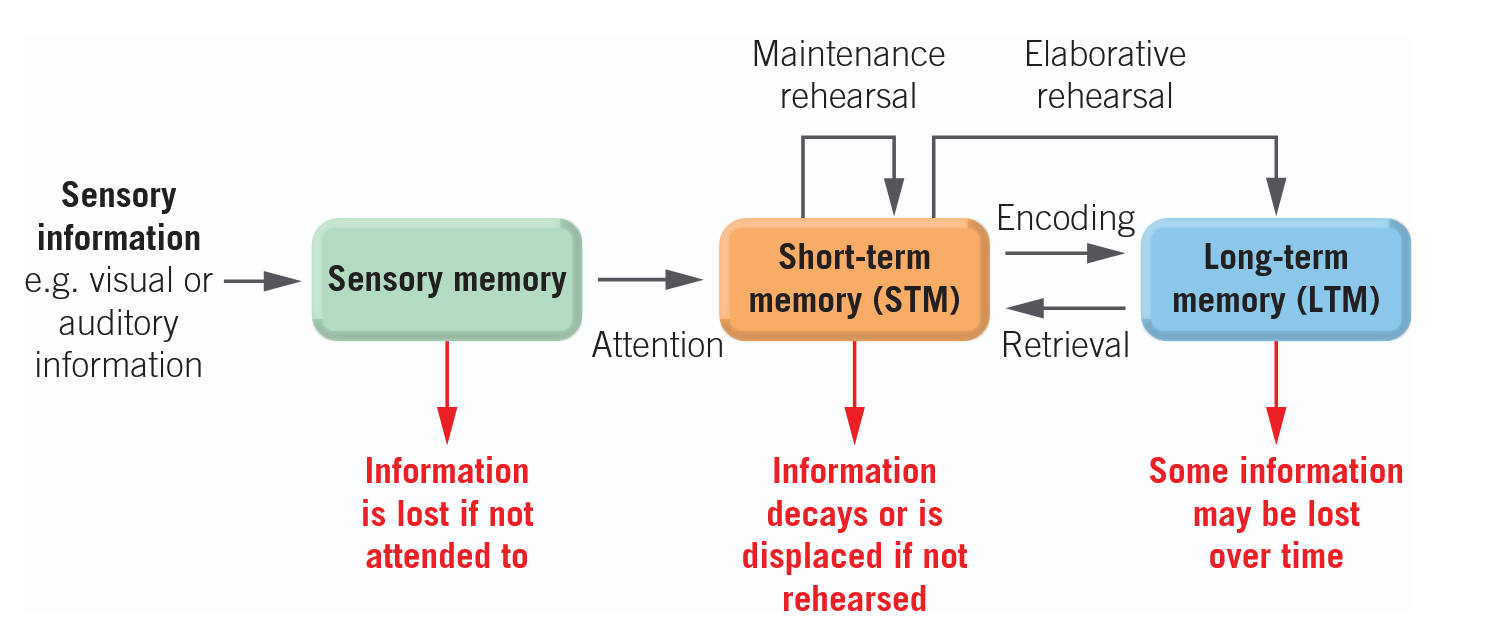
Atkinson-Shiffrin multi-store model
Sensory Memory Function
The entry point of memory where new information is stored for a very brief period
Sensory Memory Duration
Momentary, up to 10 seconds
Capacity
Vast, potentially unlimited
Iconic sensory memory
Replica of visual information that lasts 0.3 to 0.5 seconds with an unlimited capacity
Echoic sensory memory
Replica of auditory information that lasts 3 to 4 seconds with an unlimited capacity
Short term memory function
Information received into short term memory is encoded and stored for a brief period unless a conscious effort is made to keep it there longer
Short term memory duration
18 - 30 seconds
Capacity
5 - 9 items at a time
Displacement
When short term memory is full with items, new items can only enter through pushing one item out
Decay
reached duration of term memory and gotten forgotten
Maintenance rehearsal
when you repeat the information being remembered and it stays in short term memory
Elaborate rehearsal
involves giving meaning to new information and making associations with other information already stored in your long-term memory
Long term memory function
Information storage for re-access and use at a later time
Long term memory duration
Potentially permanent
Long term memory capacity
Potentially unlimited
Explicit memory
involves memory that occurs when information can be consciously or intentionally retrieved and stated.
Explicit components
Episodic
Semantic
Episodic
The memory of personally experienced events
Semantic
The memory of facts and knowledge about the world
Implicit memory
does not require conscious or intentional retrieval
Implicit components
Procedural
Classically conditioned
Procedural
The memory of motor skills and actions that have been learned previously
Classically conditioned
They are unconscious and involuntary associations between stimuli therefore it is implicit
Strengths vs Limitations of Model
One of the strengths is its ability to explain distinct short-term and long-term memory stores, supported by research on rehearsal and different storage capacities. However, the model is criticized for being too simplistic, lacking nuance in explaining memory distortion or individual differences, and potentially overemphasizing rehearsal