Exam 1: OT Interventions and Documentation
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Evaluation
-process to determine what pt wants and needs to do, currently able to do, and what supports and barriers influence occupational performance and participation
-addresses whether a child will benefit from OT
-helps determine goals and intervention plan, including the scope and frequency of tx
-used to gather baseline data and develop tx plans
Screening
-quick method to determine if a comprehensive evaluation is needed
-can be formal or informal
-can also be completed at any time during the treatment process (i.e. your pt suddenly starts covering their ears with loud noises or they suddenly stop responding to any noise so then we use a quick screening tool to asses for hearing deficits, etc.)
Areas of occupation include _____________.
-occupations
-performance skills
-performance patterns
-client factors
-contexts and environment
Performance skills
observable, goal-directed actions that contribute to occupational engagement
motor skills: gripping a pencil, transporting toys to toy box, coordinating 2 sides of body to use scissors
process skills: sequencing steps to tie shoes, organizing school supplies, responding to signals to change classes
communication and interaction skills: positioning self appropriately next to peers, expressing anger appropriately at school, taking turns on a swing
Performance patterns
habits, routines, roles, and rituals that shape occupational performance and participation
ex: writing in a planner, bedtime routine, attending church weekly
Client factors
values, beliefs, body structures, and body functions that shape occupational performance and participation
ex: recognizing letter shapes (body fxn), shifting attention bw listening to teacher and talking to a friend (body fxn)
Contexts/environment
social, built, and natural environment where occupations take place
ex: home, school, playgrounds, malls, clinics, church
OT process includes _____________.
1) development of occupational profile
2) analysis of occupational performance
3) method of evaluation
4) development of recommendations based on the results
Development of occupational profile involves
-identifying patients occupational history, interests, values, patterns of engagement and participation, and areas of concern
Analysis of occupational performance involves
-identification of child's strengths and potential problems
-child's performance skills, performance patterns, context and environment, client factors, activity demands
Methods of evaluation includes
-observations
-assessment tools (standardized and non-standardized assessments)
-interviews
What should you consider when selecting methods for evaluation?
-child's age (consider chronological age & corrected age)
-presenting problems (neuromotor, dyspraxia, impaired FM, GM, visual etc.)
-parent's priorities
-availability of evaluation tools
-type of service delivery model (which theoretical FOR most appropriate for eval of child)
-amount of time and resources available
-the purpose of the eval
-requirements of the agency
-identify available resources (caregiver, other professionals, time and space, instruments and test materials)
Standardized assessments
-uniform procedures for administration and scoring
-may be norm-referenced or criterion-referenced
-help determine eligibility of OT services
-help to monitor progress
-help to make intervention decisions
-measurements of performance in specific areas (standard score)
What are the 5 reasons why we use standardized tests?
1) to assist in the determination of a medical or educational diagnosis (insurance agencies use results to determine if child will get OT)
2) to document a child's developmental, functional, and participation status (can compare progress to recent/past assessments)
3) to aide the planning of an intervention program (tests show you current level of function which is an indicator of where to start your interventions)
4) to measure outcomes of progress (comparing to baseline)
5) to measure variables in research
What are the different types of standardized assessments?
norm-referenced and criterion referenced
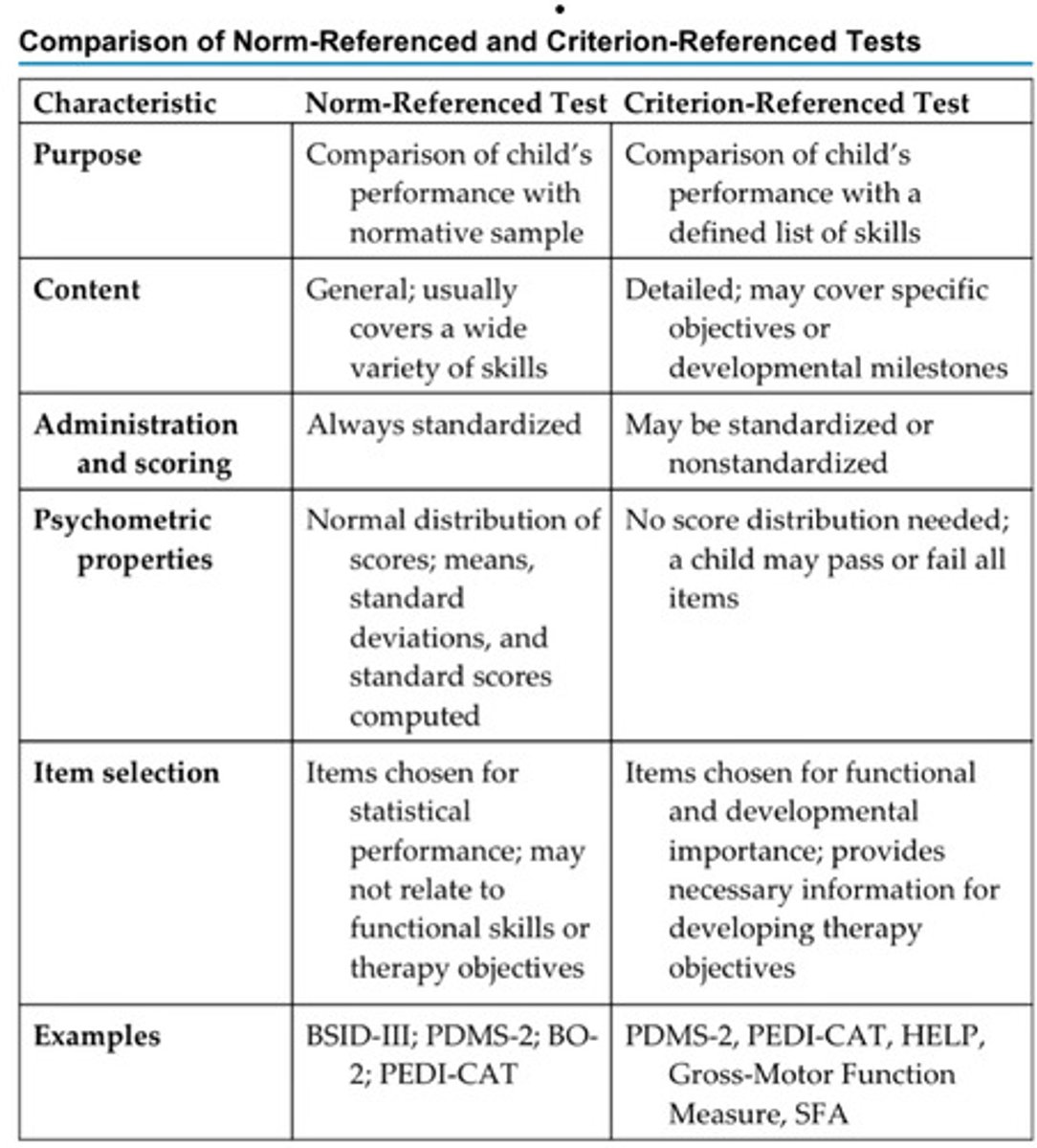
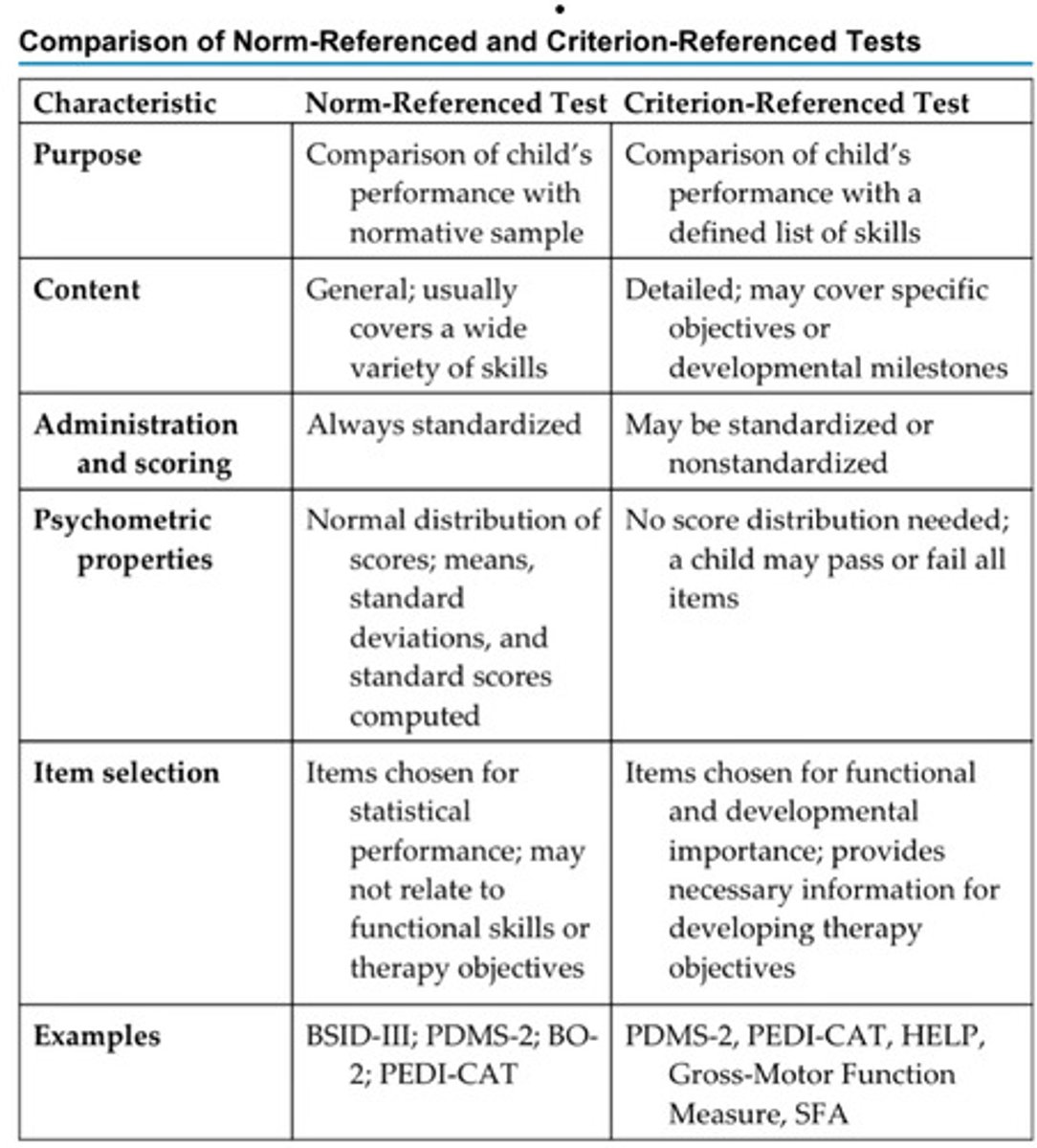
Norm-referenced tests
-standardized tests that compare an individual child's score to the average score of others their age
-test developed through the administration to large groups of children
-average scores are derived from norm samples
-address one or more areas of behavior with subtests
-include standardized protocols for administration and scoring
-analyzed by statisticians
The BOT is an example of what type of standardized test?
a) norm-referenced
b) criterion-referenced
a) norm-referenced
Criterion-referenced tests
-determines how the child performs a task
-determines which skill a child can and cannot accomplish
-compares performance to performance required for a particular skill
-does not compare to an average sample
-may take the form of a checklist
The HELP is an example of what type of standardized test?
a) norm-referenced
b) criterion-referenced
b) criterion-referenced
Non-standardized assessments
-commercially available
-NO FORMAL PROCESS
-do NOT require standardized instructions or materials to administer
ex: rating scales, inventories
Scoring and interpretation is a vital part of the evaluation process because ____________.
it helps to create detailed decisions about what OT services are to be provided
When scoring and interpreting results, the OT reflects on questions including ____________.
-will the child benefit from OT?
-if so, what are the appropriate outcomes for the OT services?
-what models/FOR will be used?
-what context (environment) will the OT sessions take place?
-is more info needed from parents, caregivers, other disciplines?
-does the child need to be referred for services (other than OT)?
The technical aspects of evaluation process include ____________.
-descriptive statistics
-standard scores
-reliability
-validity
Descriptive statistics
-statistics that summarize or describe the data collected in a study
-provide information about where members of a group are located on a normal curve
-help describe characteristics of a particular group (this is how we get a bell curve)
What are the 2 types of descriptive statisitics?
central tendency and variability
Central tendency
-the middle point of distribution in a bell curve for a group, or sample, of children
(we use mean and median)
What is the preferred measure of central tendency?
median
Variability
-in a set of numbers, how widely dispersed the values are from each other and from the mean
-determines how much of the performance group as a whole deviates from the mean
-used to compute the standard scores used in standardized tests
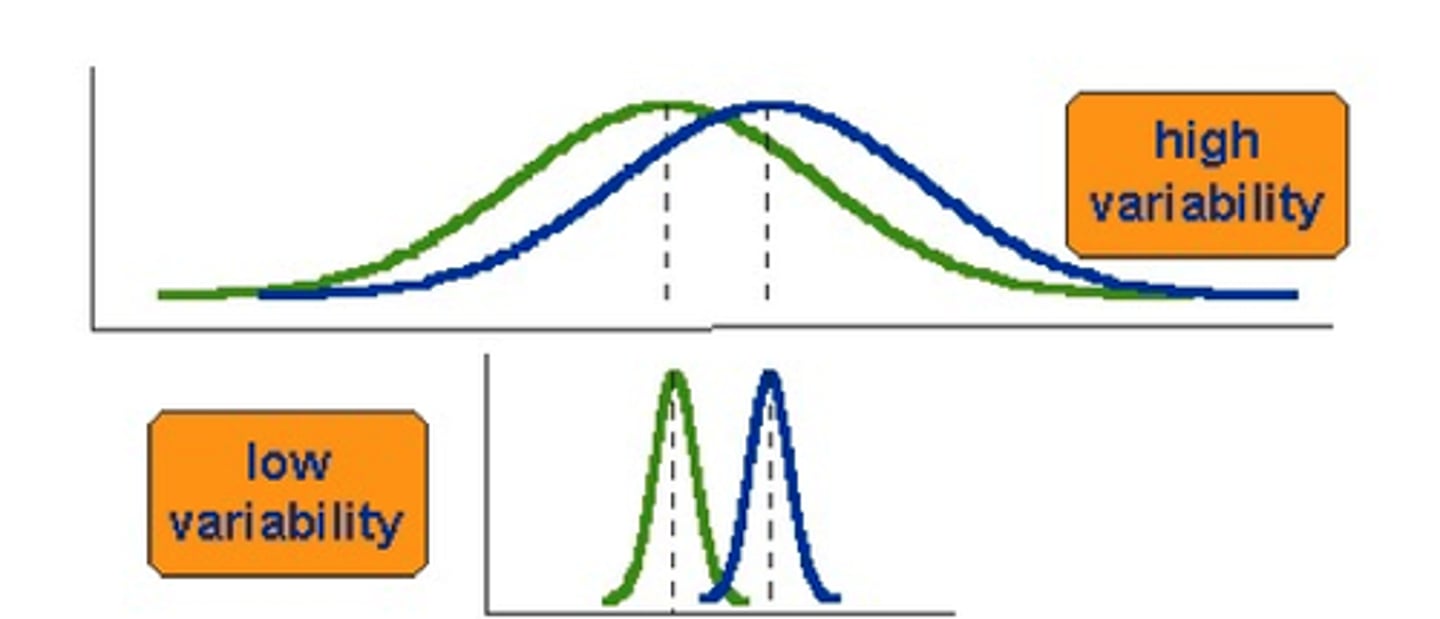
Standard score
-test score indicating how far a student's performance is from the mean with respect to standard deviation units
-a raw score converted to standard deviation units to help us see where the score lands in the bell curve in respect to the mean/average
-z score
-represents how far or close the child scores on the test in comparison to the average
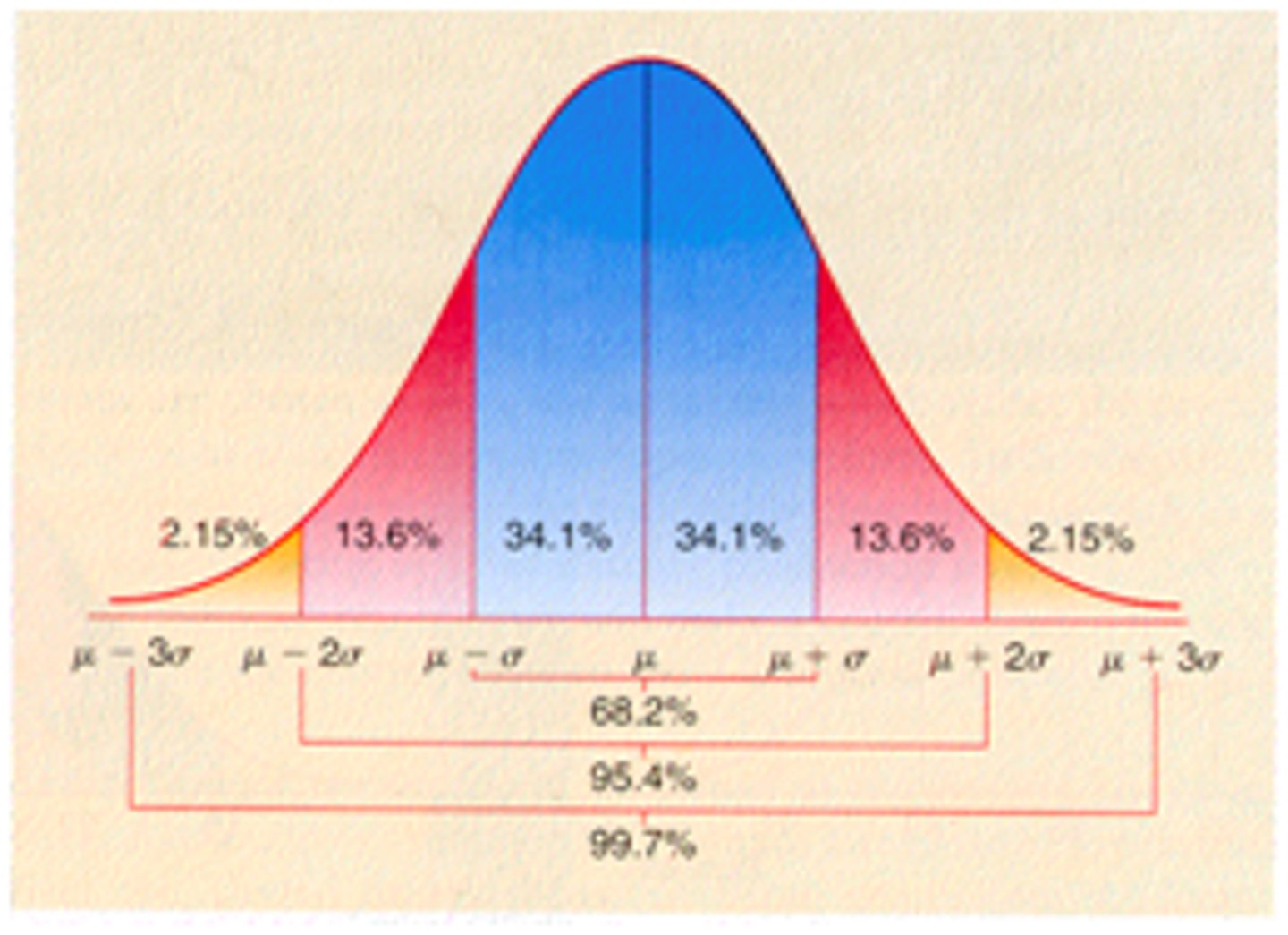
T or F: A child should be not be more than 2 SD away from the mean.
true
T or F: 68% of people will score within 1 SD and 95% of people will score within 2 SD.
true
Reliability
-ability of a test to yield very similar scores for the same individual over repeated testings
-consistency of two scores obtained by one individual when tested on two different occasions with different sets of items or under other examining conditions
If a child is given a test and receives a score of 50 and two days later is given the same test and receives a score of 75 this means that the ___________ of the test is questionable.
reliability
Validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to

Construct related validity
the extent to which the test may be said to measure a theoretical construct or trait
Content related validity
extent to which the items on a test accurately sample a particular behavior domain
Criterion related validity
ability of a test to predict how an individual performs on other measurements or activities
the test scores are checked against a criterion, an independent measure of what the test is designed to predict
Documentation includes compiling ____________
-evaluation report
-tx planning
-STGs and LTGs
-SOAP notes
-intervention planning
The evaluation report generally includes _______________.
-referral source
-relevant client info (dx, medical hx)
-description of occupational profile
-process and assessment tools used
-summary of findings (scores, etc.)
-interpretation of results
-recommendations
-clinician signature
When developing the evaluation report, the OT should be sure to ______________.
-use strength-focused documentation
-present scores objectively
-use appropriate terminology and define medical jargon
-justify opinions with data
The treatment plan generally includes ____________.
-recommendations
-referrals
-intervention methods
-goals: LTG and STG