lecture 1
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Chromosomes
Bacillus bodies found in the nuclei of eukaryotes during the roles of cell division
Chromosome Theory
Chromosome carry genes
Cell Cycle
A four-stage process in which the cell increases in size, copies its DNA, prepares to divide, and divides
Interphase include
G1,S, and G2
The cell spends most of its time in
Interphase
G1 phase
Protein, enzymes, and types of RNA are formed
S phase
DNA replication / DNA synthesis
G2 phase
Complete the mitosis need of proteins and prepare for the mitotic processes
Where are chromosomes studied in plants
root-tip
Where are chromosome studied in animals
Embryos, cells of the blood, and spinal cord
Why can we only study chromosomes from young non mature cells
The cells are active in either mitosis or meiosis
Somatic cells
Diploid (2n) , pairs of 2 homologous chromosomes
Sex cells
Haploid (1n), present in a mono state
The best phase to study sex cells
Prophase 1
The best phase to study somatic cells
Metaphase
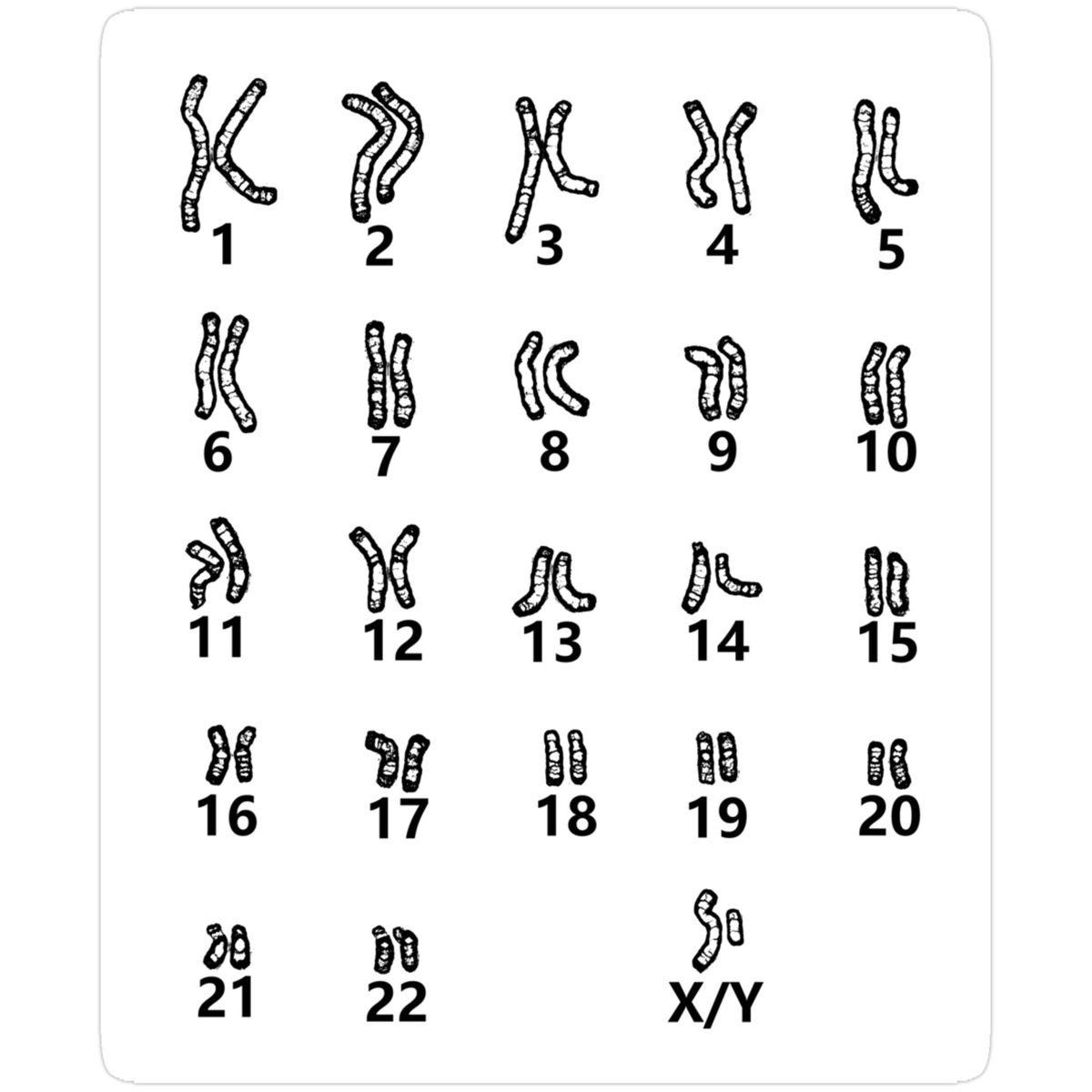
Karyotype
Normal karyotype in humans has
23 pairs
which number is the sex chromosome in a Human karyotype
23
Characteristics of a chromosome in a chromosome group study
Size
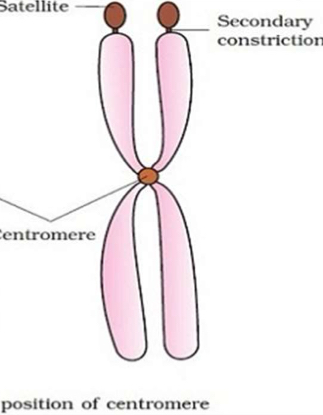
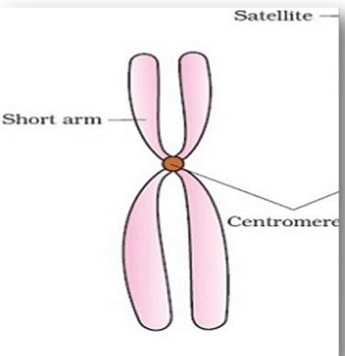
Centromere
Secondary constriction
Satellite
Chromomeres
Heterophknosis
Chromosome bands
Long chromosome
30 microns
where are long chromosome found
Onions
Short chromosomes
1 micron
Where are short microns found
Fungus
What’s the avg size of chromosomes
6 microns
Centromeres
A specialized DNA sequence of a chromosome that links a pair of sister chromatids
Another name for Centromeres
Primary Constriction
Why are centromeres one of the most important part of chromosomes
controls the movement of chromosome to the poles of the cell during its division by attaching to the spindle fibers
What happens if a centromere region of a chromosome is lost
The chromosome cannot move (doesn’t go to the poles) which leads to It becoming a chromosomal fragment
Metacentric chromosome
Submetacentric chromosome
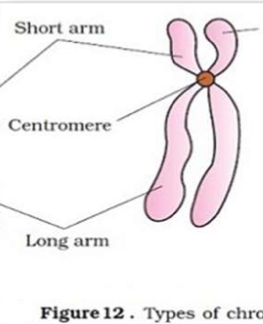
Acrocentric chromosome
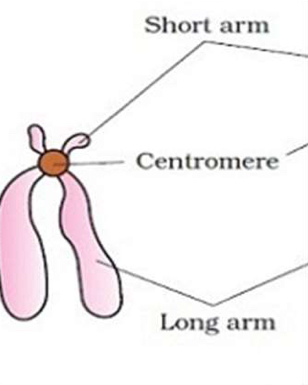
Telocentric chromosome
Dicentric chromosome
Contains 2 centromeres
Secondary constriction
Narrow region found at any point of the chromosome other than that of centromere
Secondary constriction function
The disappearance and formation of the nucleus (in a region called nuclear organizing region )
Distinguish between chromosomes
Chromosomal Satellite
Part of the end of a chromosome that is separated from the rest of the chromosome by a secondary constriction
Who coined the term chromosomal satellite
Muller in 1938
Chromomeres
Spherical granules are arranged on the chromosome
Where do chromomeres appear
Prophase 1 (meiosis)
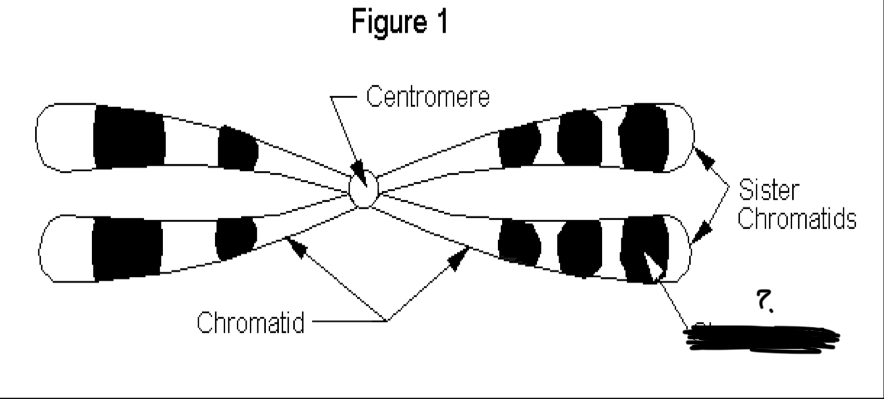
Chromomere
Heteropyknosis
The ability to distinguish regions on a chromosome according to the interaction of the chemical components contained in these regions with specific pigments
What specific pigments can be distinguished
Hematoxylin
Feulgen
Carmen
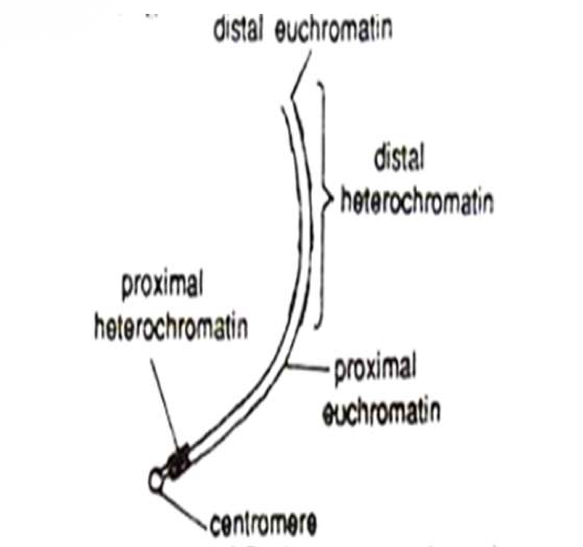
Euchrematin
Do not take up the dye directly ( region of active chromatin ) - contain genes.
Meterochromatine
Region that accept the dye the most ( region of inactive chromatin.) - Doesn't contain genes
Chromosome bands
Each chromosome arm is divided into region, that can be seen using a microscope and special stain
Q -band
Quinacrine pigment - lack continuous fluorescence of chromosomal bundles
G-band
Gems pigments - continuous fluorescence of chromesomal bundles
R-band
Modified giemsa dye- became more visible

Polytene Chromosome
Polytene Chromosome
Large chromosome which have thousands of DNA strands (Known as giant chromosomes)
Where are polytene chromosome found
Salivary glands of insects
How are polytene chromosomes formed
Repeated rounds of DNA replication without cell division
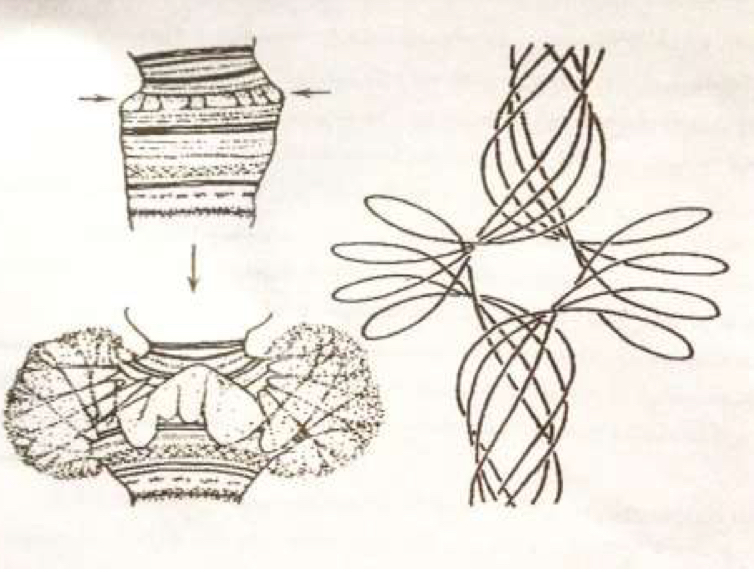
Super Chromosome
Super Chromosome
Consist of about a million adherent chromatids, and the amount of DNA these chromosomes contain may be 32 times that of normal cells
Where are Super chromosome found
Salivary glands of some insects after being infected with one of the micro-parasite ( genus thelophania)
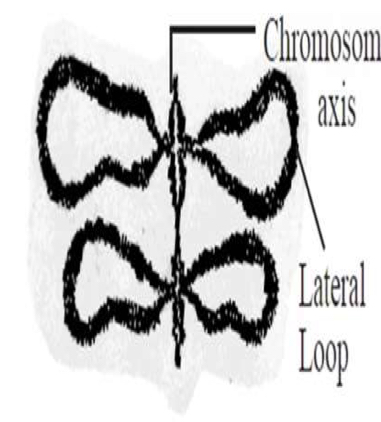
Lamp brush chromosomes
When does lamp brush chromosome appears
Prophase 1 stage of meiosis (especially in diplotine stage)
B-Chromosome
B-chromosome
Accessory chromosome that are mostly inactive chromatin, they carry no genetic information. They have no fixed number in the cells (1 to 30)
Where are B-Chromosome found
Corn