L12 Homeostasis in the Nervous Tissue II (Imported from Quizlet)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Terminate, tripartite
Neurons and astrocytes ___________ neurotransmission at the __________ synapse
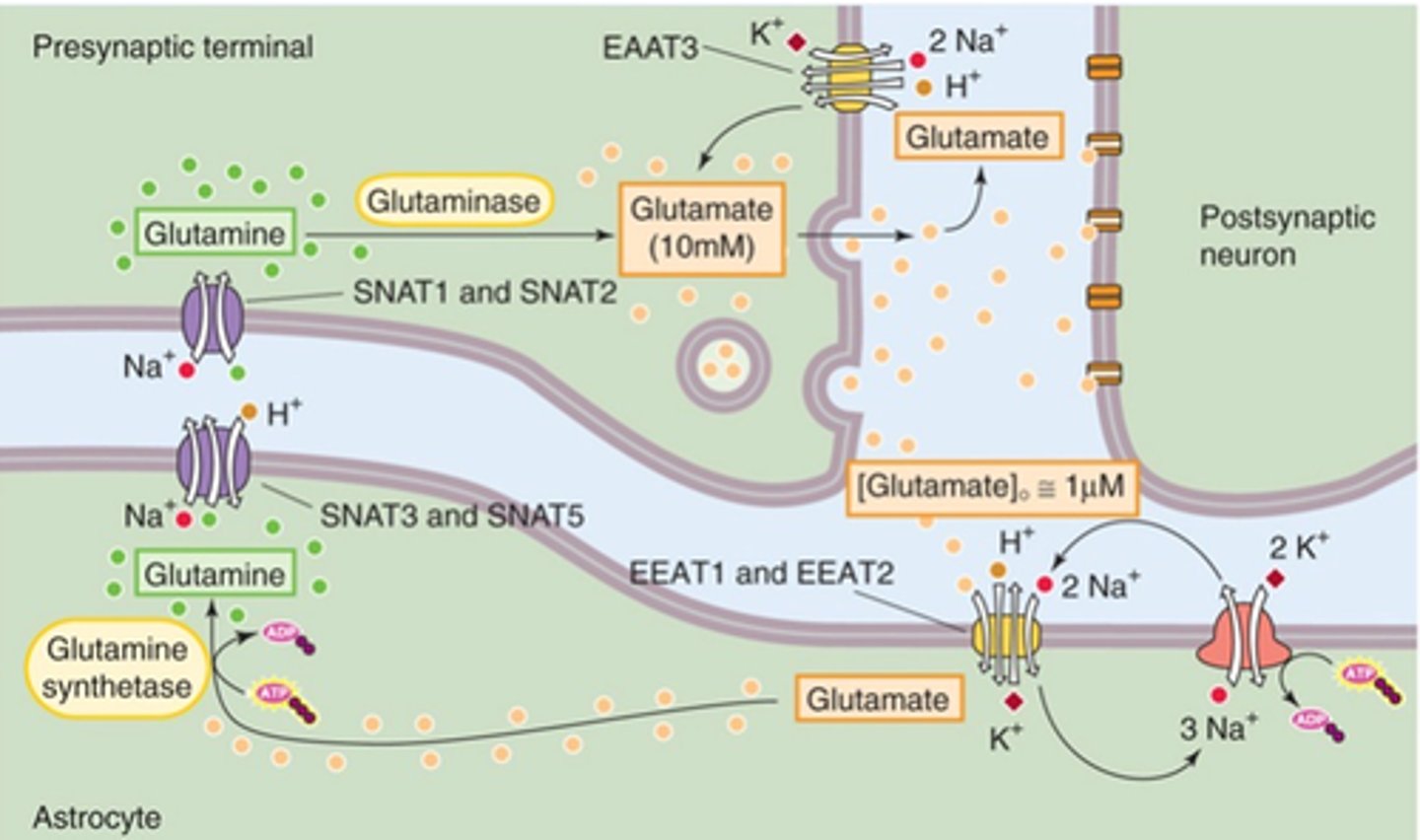
EAAT3 takes glutamate back into the the presynaptic terminal and EEAT1 and EEAT2 take glutamate back into the astrocyte and sends it to the presynaptic terminal
How do they terminate neurotransmission?

Recycle, presynaptic terminals
Neurons and astrocytes can ____________ neurotransmitters to ________________ __________
K+, extracellular space
Neurons and astrocytes remove __ from the ______________ ______
Because we don't want an increase in membrane potential as extracellular potassium increases
Why do they remove K+ from the extracellular space?
Astrocyte function
Increases in extracellular K+ affect what?
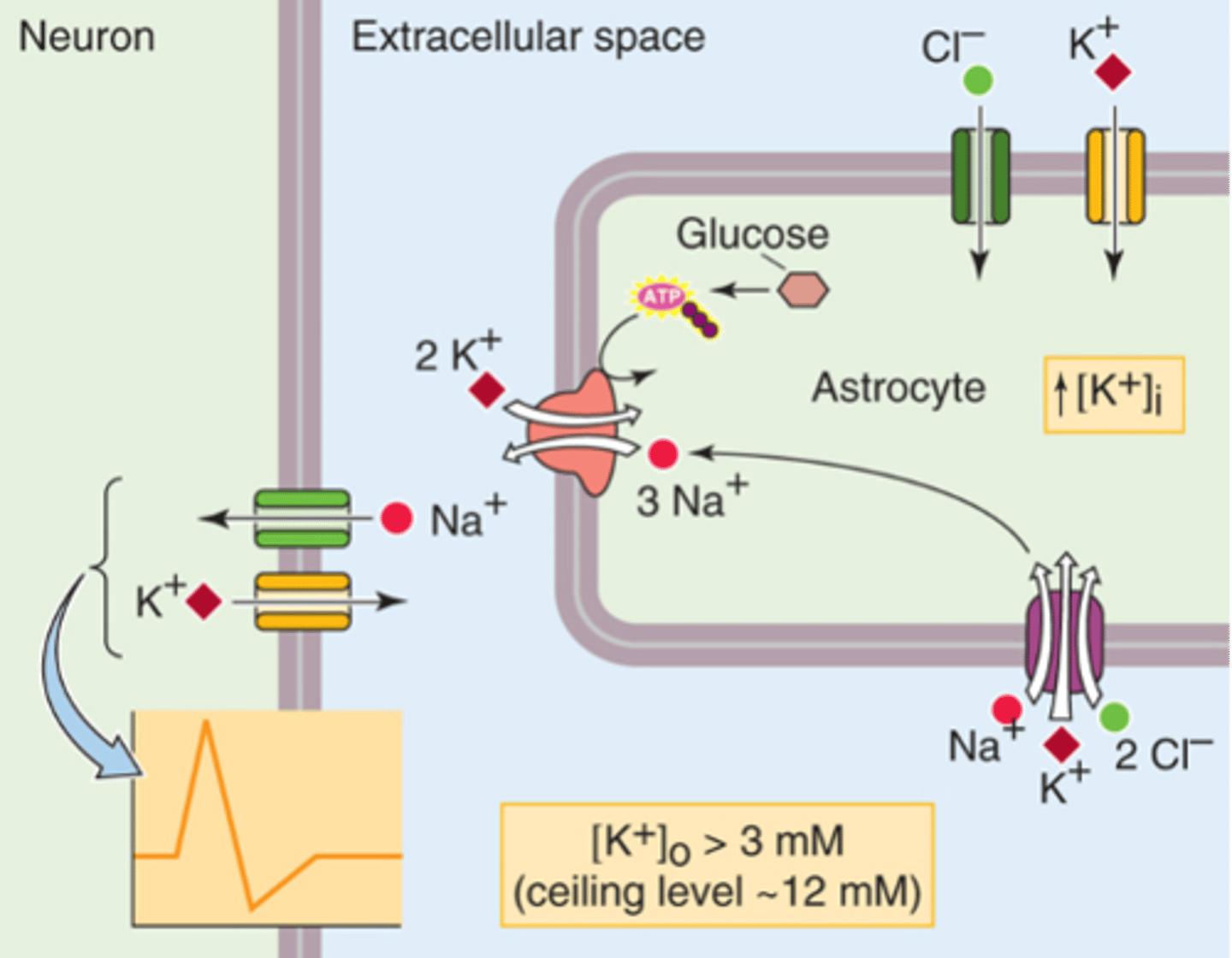
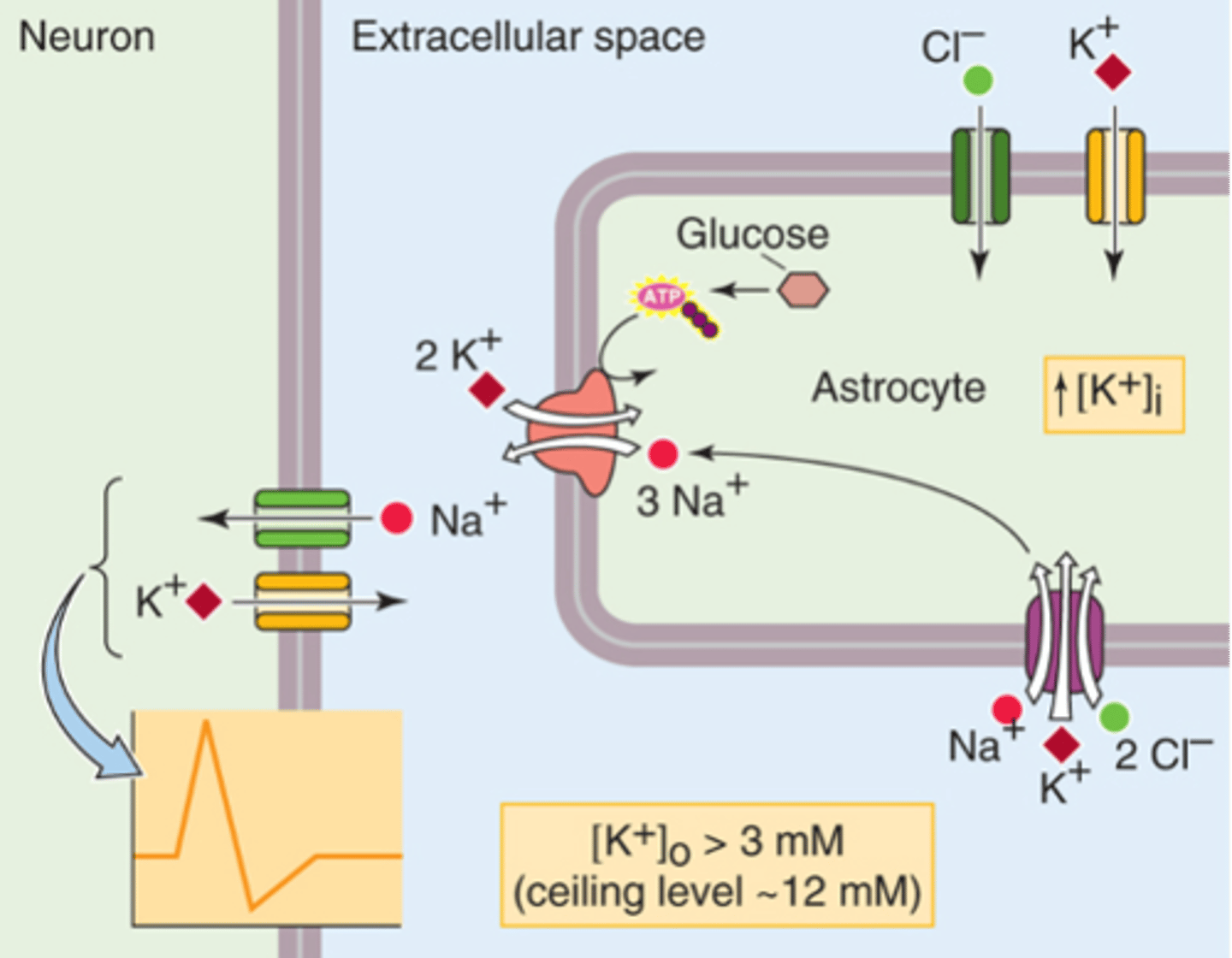
Increased glucose metabolism (more ATP which causes the sodium potassium ATP to bring in more potassium)
Increased K+ uptake (increases intracellular potassium concentration and this can drive and increase glucose metabolism)
What are the astrocyte functions affected by an increase in extracellular K+?
About -90mV
What is the equilibrium potential for K+ in both neurons and glia?
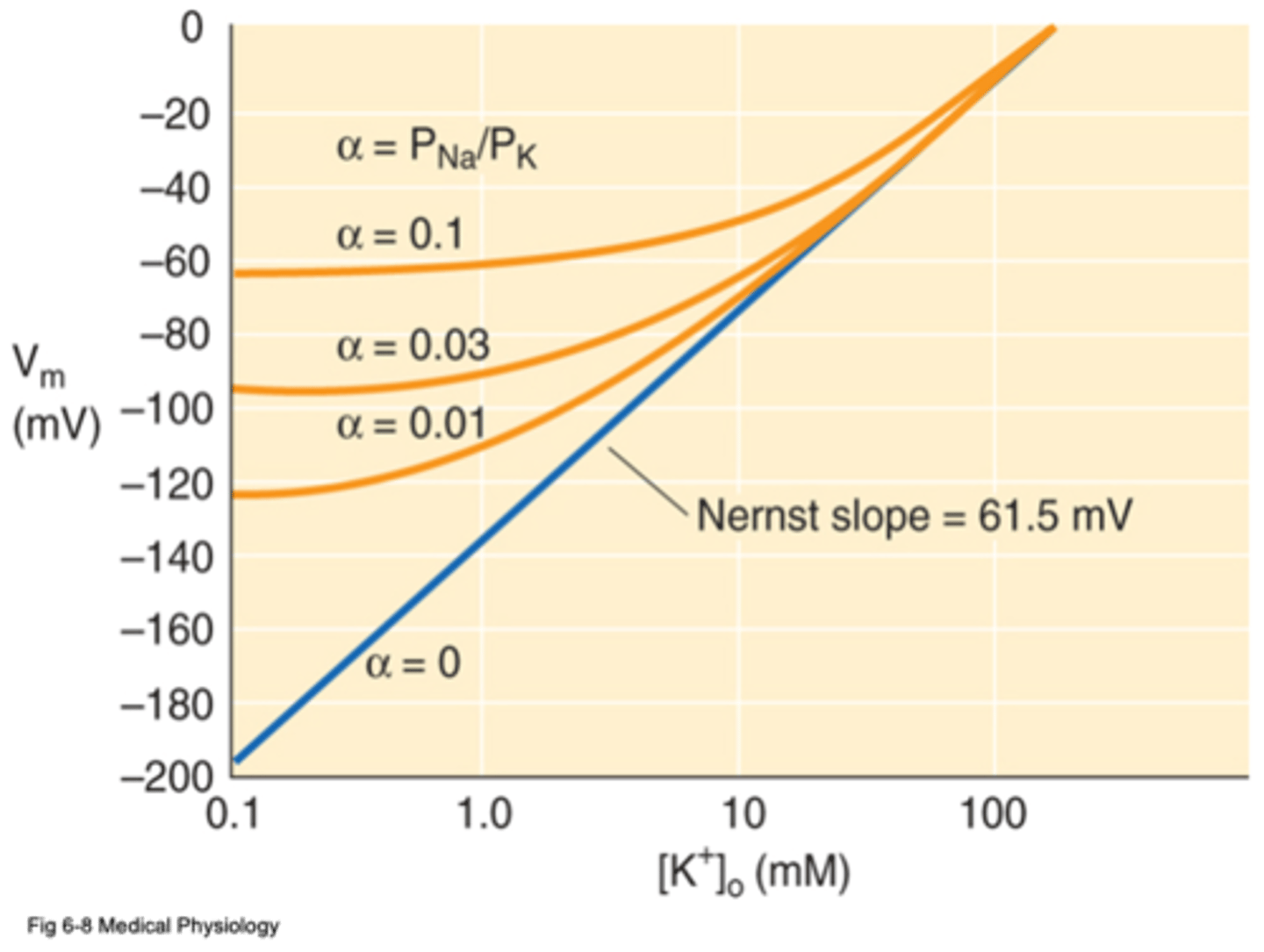
Permeability
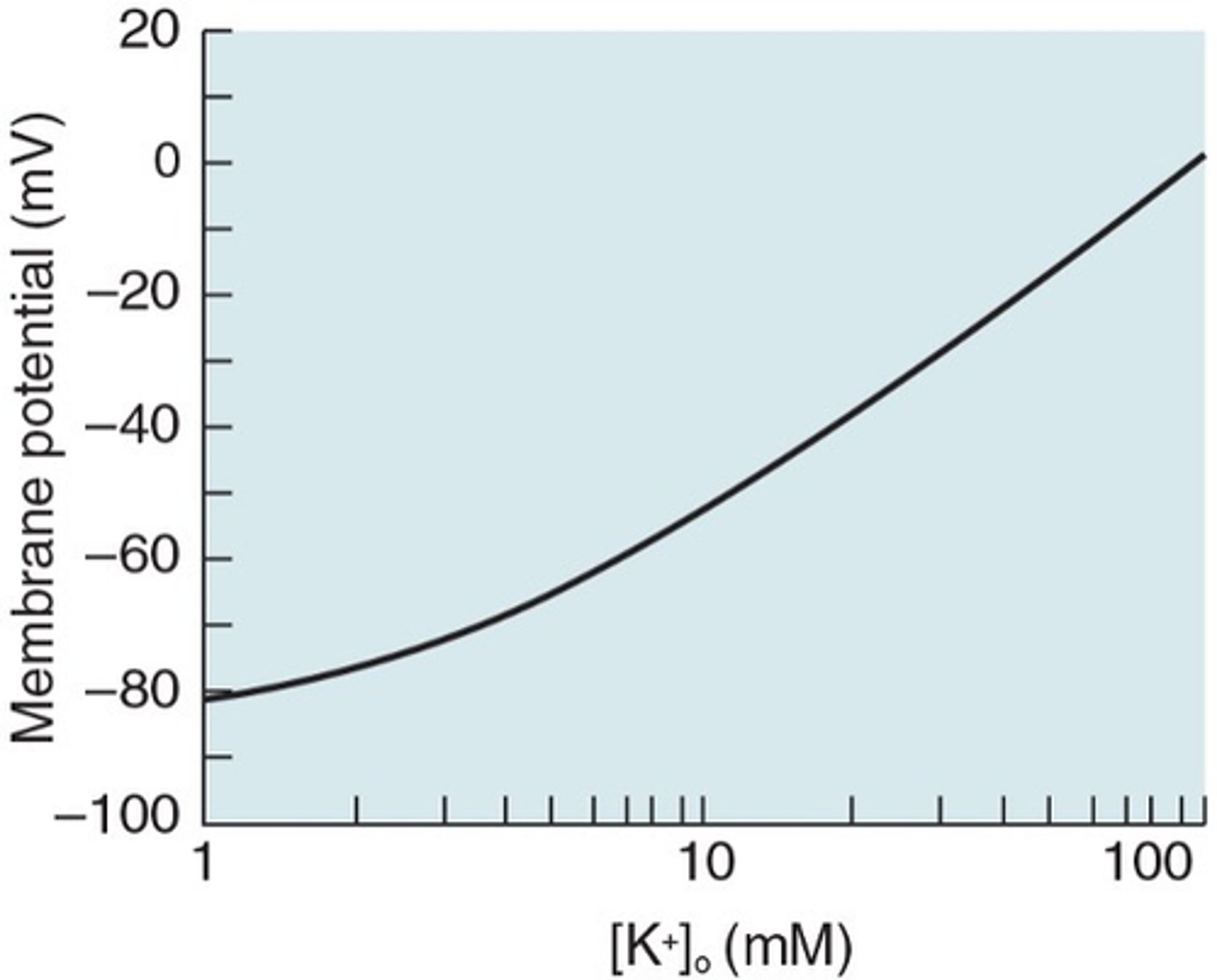
What does α refer to in this image?
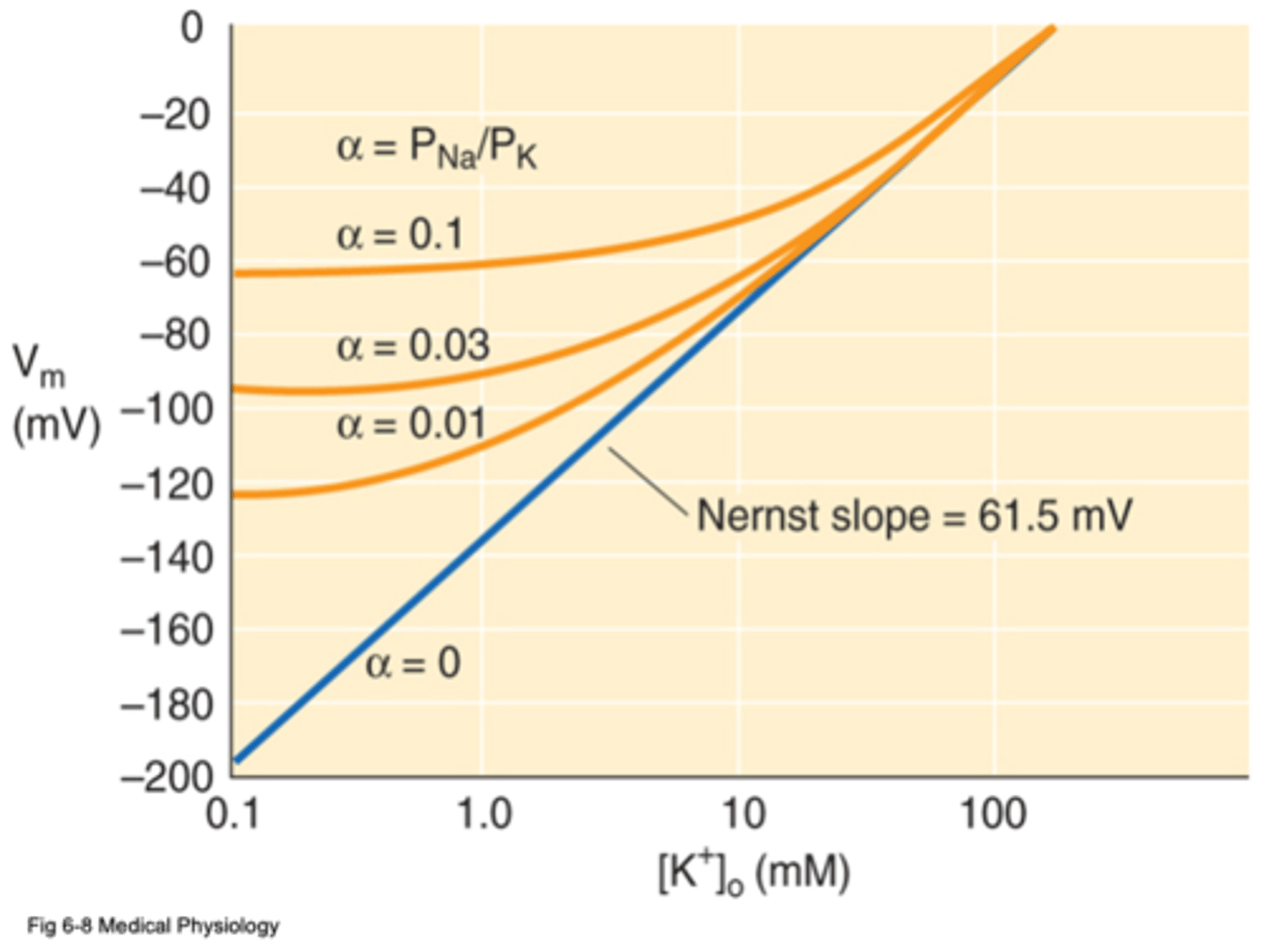
Neuronal membranes are more permeable to Na+ than astrocytic membranes
Astrocytes have higher K+ selectivity than neurons
Astrocytes are more sensitive to extracellular K+ changes
So why do neurons have resting membrane potentials of ~-65mV and glia (particularly astrocytes) have resting membrane potentials of ~-85mV?
Extracellular K+ will influence Vm
The more selective a membrane is to K+, the more ...?
Spatial buffering
Astrocytic syncytium allows what?
Gap junctions
What creates a syncytium?
Lots of astrocytes joined together by gap junctions
What is a syncytium?
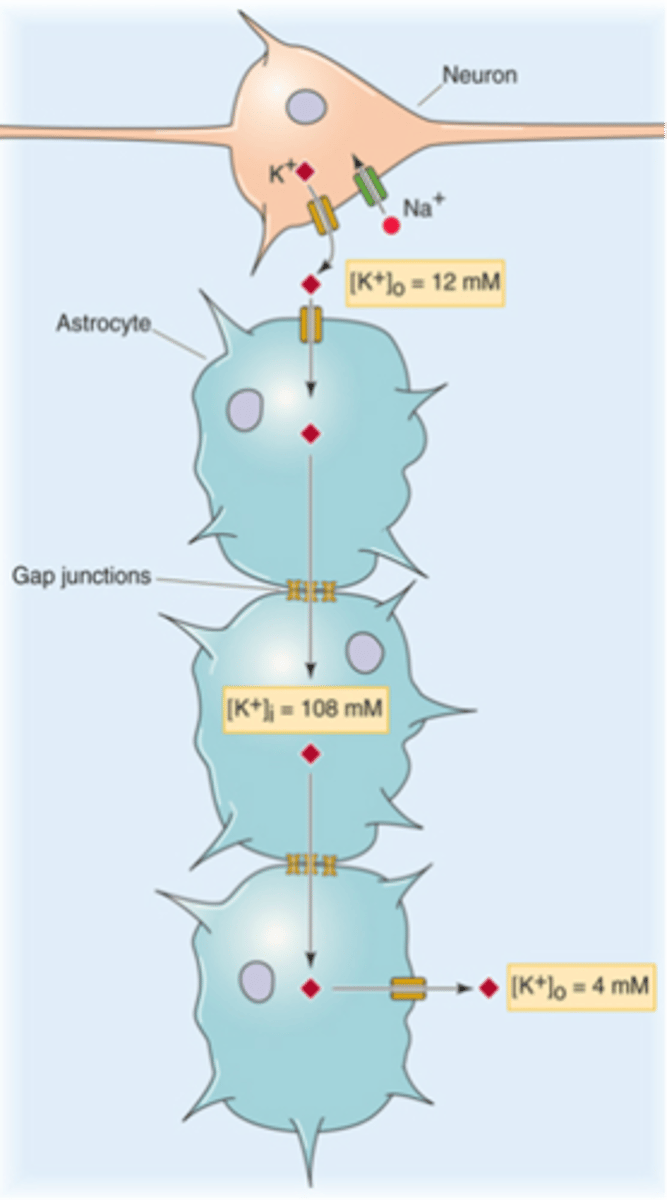
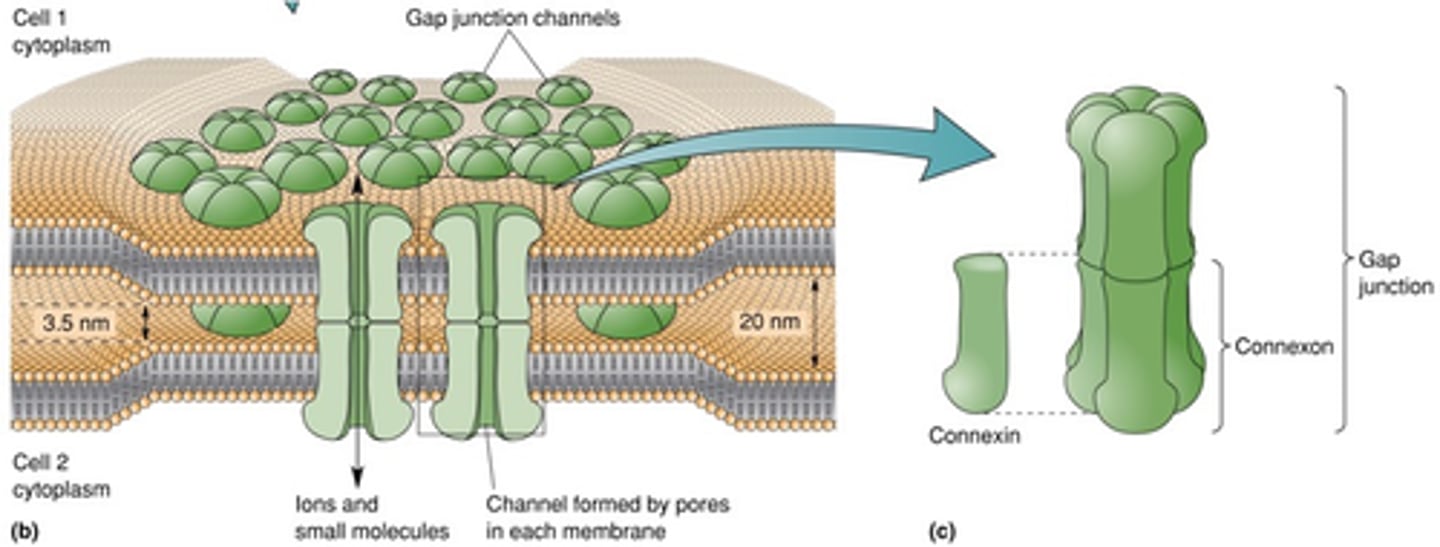
Connexons (composed of connexins)
What is in the membrane of each astrocyte that allows the movement of ions and small molecules in and out of the cell?
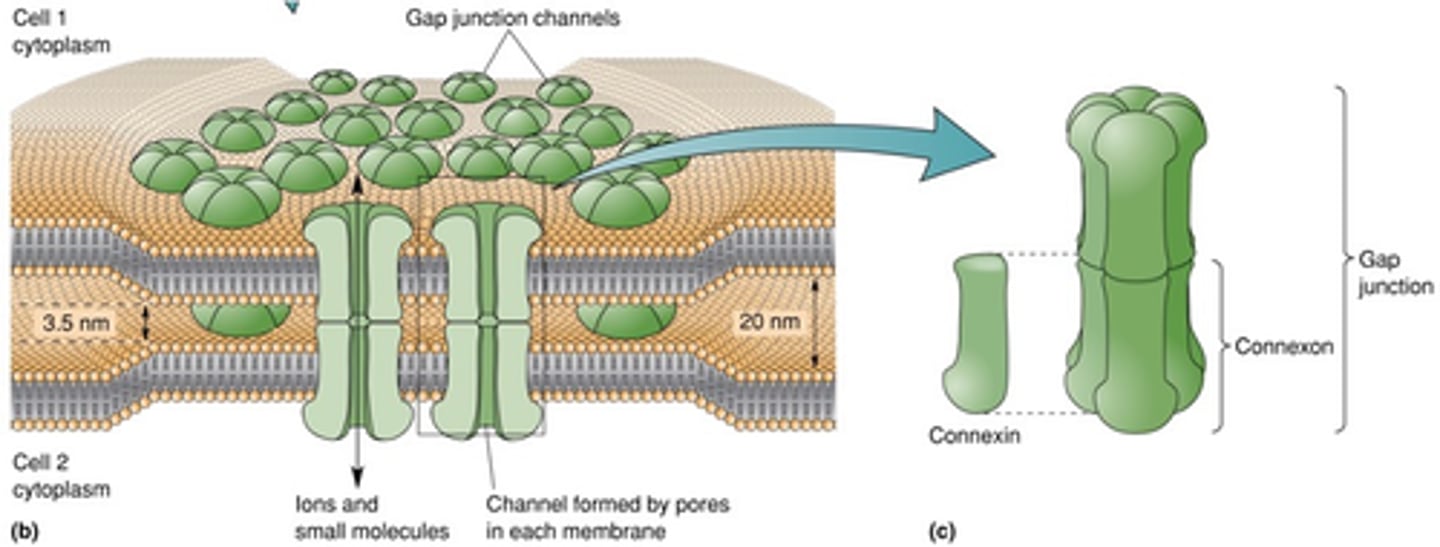
Redistribute K+ to areas of decreased activity and it can also transport sugars, amino acids, cAMP, Ca2+
Depending on the connexon, what can it do?
Joining of activity of neurons to the vasculature
What is neurovascular coupling?
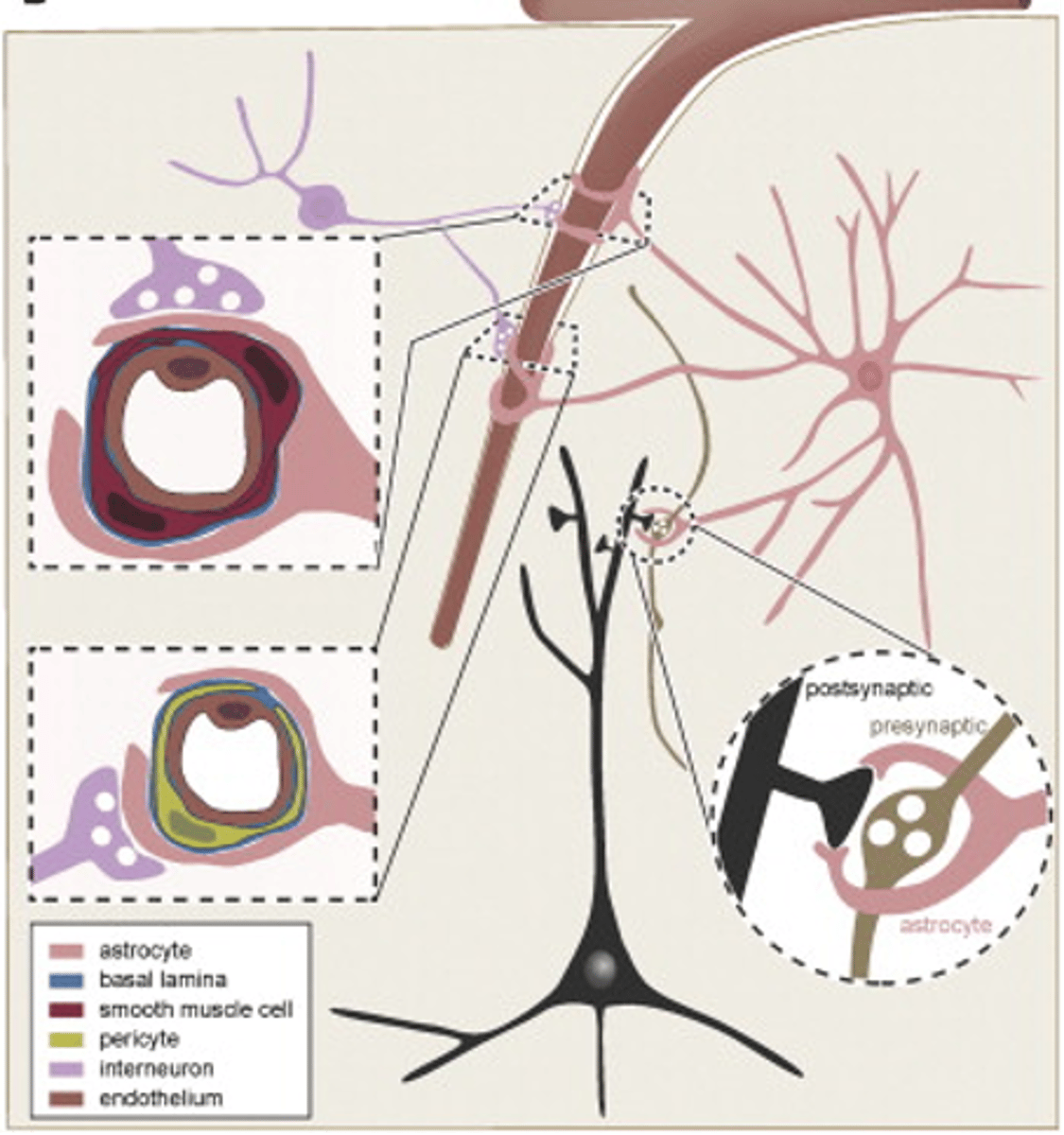
Astrocyte calcium
An increase in neuron firing rate causes an increase in what?
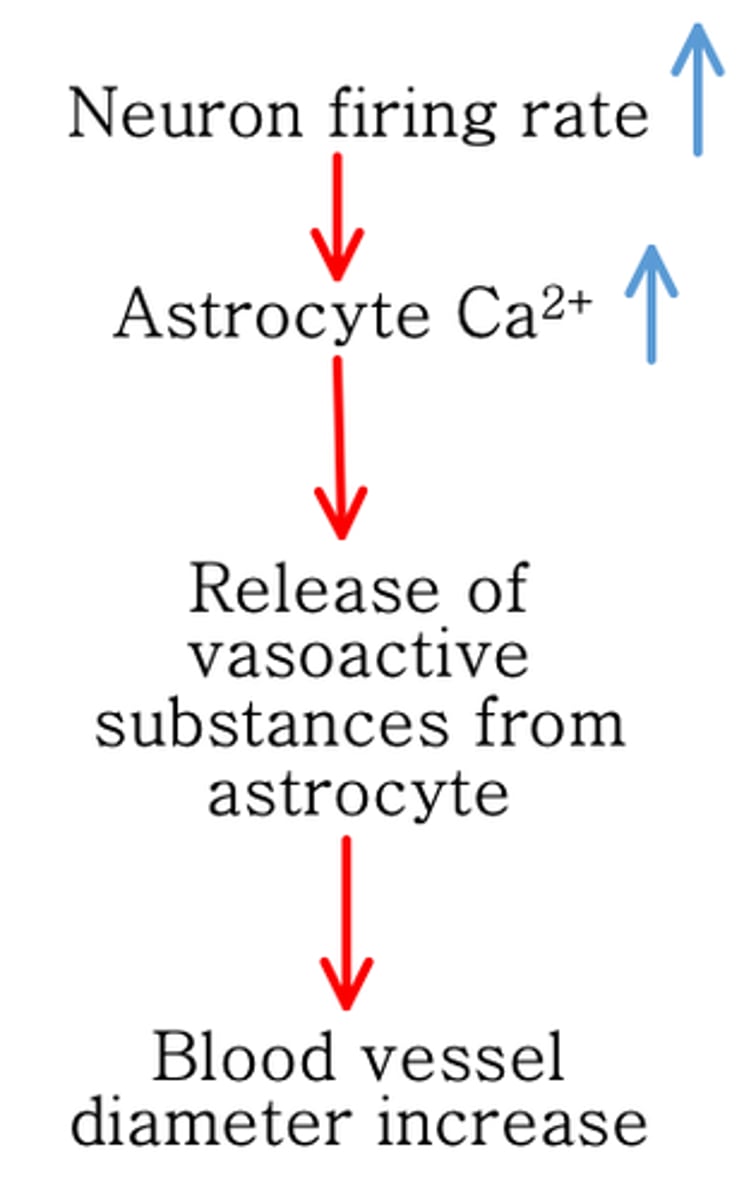
Active neurons need more glucose and oxygen
More blood is directed to these areas
Two techniques detect changes the subsequent changes in blood flow
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allow 3D structural images of the brain ... but what about techniques that measure activity?
Glucose use
What does Positron Emission Tomography (PET) exploit?
Oxygen use
What does Functional Magnetic Resonance Imagining (fMRI) exploit?
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
What are the two techniques that detect changes the subsequent changes in blood flow?
Uses an electromagnetic wave to disrupt hydrogen atom state
What does an MRI use and do?
Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent
What does BOLD stand for?
The magnetic resonance properties of hydrogen atoms differently
Oxyhaemoglobin and deoxyhaemoglobin distort what?
The local BECF
What do neurons and astrocytes regulate?
Syncytium, extracellular K+
Astrocytes act as a ___________ to buffer _____________ ___
Neurovascular coupling
Astrocytes enable what?
Oxygenated blood, active
fMRI uses changes in levels of ____________ ________ to identify ______ areas