Basic Chem/Ph/Water practice
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
subatomic particles
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
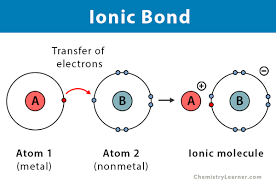
Ionic Bond
A bond formed when one atom donates an electron to another atom.
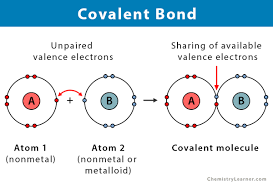
Covalent Bond
A bond formed when two atoms share electrons.
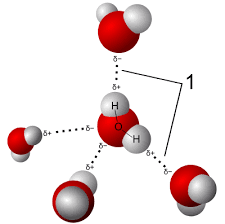
Hydrogen Bond
Weak attraction between water molecules due to the partial positive and partial negative charges.
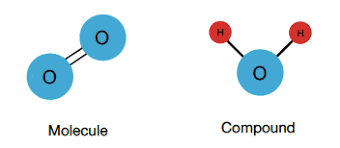
Molecule
Two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
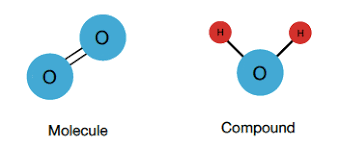
Compound
A substance made up of two or more atoms of different elements.
Chemical Change
A reaction that forms new products
Physical change
Matter changes form but not chemical identity
pH
Power of Hydrogen; a measure of hydrogen ion concentration.
Acids
Increase the hydrogen ion concentration of a water solution
Bases
Decrease the hydrogen ion concentration of a water solution.
pH Scale
Ranges from 0-14. Any pH value above 7 is a Base, any pH value below 7 is an acid.
Buffers
Any compound(s) that can both increase or decrease hydrogen ion concentration to maintain homeostasis.
Carbonic Acid
Bicarbonate Buffer System
Properties of water
Universal Solvent, Cohesion, Adhesion, High Specific Heat, High Heat of Vaporization, Density Changes
Dissociate
Compound breaks into ions in a solution
Cohesion
Water is attracted to other water molecules due to hydrogen bonding. Causes high surface tension.
Adhesion
Water is attracted to other substances that are polar/charged.
Capillary action
Water sticks to the walls of plant cell capillaries and travels up the plants
High specific heat
Water temperature changes slowly and holds temperature well.
High heat of vaporization
Water requires a lot of energy to change state.
Density Changes
Ice floats - solid water molecules form a lattice that is less dense than liquid water and therefore floats.