Exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:32 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
1
New cards
Concentration Gradient
the process of particles moving through a solution from an area with a higher # of particles to an area of a lower # of particles
2
New cards
Electrochemical Gradient
a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane.
3
New cards
What determines membrane potential?
the differences in ion concentration of the intracellular and extracellular fluids (potassium-sodium pump)
4
New cards
How is ion channel activity recorded?
patch clamp technique
5
New cards
Patch Clamp Technique
* Technique used to record electrical currents through individual ion channels in cells.
* Involves placing a glass pipette on the cell membrane and applying suction to form a tight seal
* Allows for precise measurement of ion flow and can be used to study the effects of drugs on ion channels
* Involves placing a glass pipette on the cell membrane and applying suction to form a tight seal
* Allows for precise measurement of ion flow and can be used to study the effects of drugs on ion channels
6
New cards
Cell Attached (Patch Type)
almost never used
7
New cards
Whole Cell Patch Clamping
useful for recording ion channels in a cell
8
New cards
Inside Out Patch
inside of cell is out in both
9
New cards
Outside-Outside Patch
this is usually the valuable patch for recording a single ion channel after drug
10
New cards
Design an experiment to see if drug XYZ can increase voltage-gated calcium ion channel
starting mem. potential of \~ -60mV → then record current through all of the channcels
11
New cards
Find out if your drug affects a single Ca++ ion channel
drug is really lipophilic and gets inside the cell well → inside out patch
12
New cards
How is resting membrane potential maintained?
the sodium-potassium pump
13
New cards
What ions are prevalent on the inside of the cell
K+
14
New cards
What ions are prevalent on the outside of the cell
Cl-, Na+, Ca++
15
New cards
Sodium-Potassium ATPase
* helps maintain equilibrium and membrane potential in cells
* keep K+ high inside, this is what cells need at rest
* why & what
* maintain resting membrane potential
* 3 Na+ in → out
* ATP hydrolysis → phosphorylation of pump
* 2 K+ out → in
* keep K+ high inside, this is what cells need at rest
* why & what
* maintain resting membrane potential
* 3 Na+ in → out
* ATP hydrolysis → phosphorylation of pump
* 2 K+ out → in
16
New cards
What’s the best patch to use if you want to record currents from all of the ion channels in cell?
whole cell patch clamping
17
New cards
Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
takes an electrical change in the membrane potential to open
18
New cards
Ligand-Gated (extra or intracellular) Ion Channels
molecule acts as a key to open the door
19
New cards
Mechanically Gated Ion Channels
physically pull door open
20
New cards
What does the Nernst equation help a mathematically-minded electrophysiologist figure out before ever having to patch clamp a cell?
helps scientists figure out what the membrane potential of any membrane is
21
New cards
Uniporters Transporters
transport a single species of substrate across a cell membrane
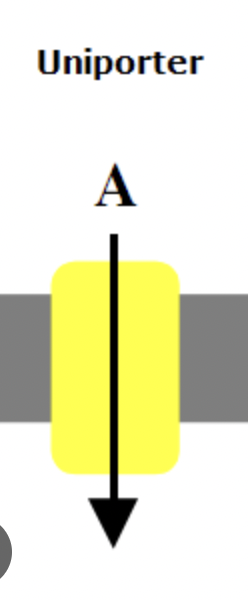
22
New cards
Symporters Transporters
proteins that simultaneously transport two molecules across a membrane in the same direction
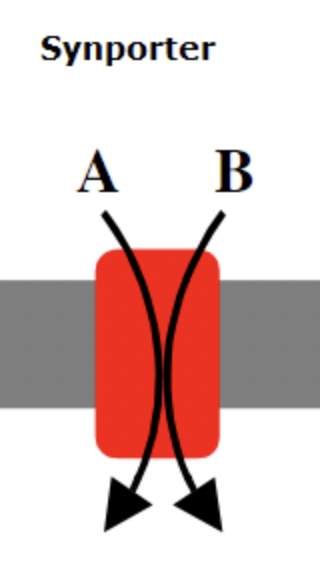
23
New cards
Antiporters Transporters
transport of two or more different molecules or ions across a phospholipid membrane
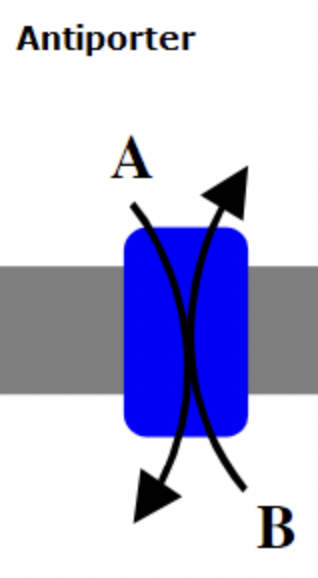
24
New cards
how many NADH are produced by glycolysis?
2 NADH
25
New cards
how many H+ are produced by glycolysis?
2 H+
26
New cards
how many CO2 are produced by glycolysis?
0 CO2
27
New cards
how many net ATP are produced by glycolysis?
2 net ATP
28
New cards
how many GTP are produced by glycolysis?
0 GTP
29
New cards
how many FADH2 are produced by glycolysis?
0 FADH2
30
New cards
how many pyruvates are produced by glycolysis?
2 pyruvates
31
New cards
how many NADH are produced between glycolysis & CAC?
2 NADH
32
New cards
how many H+ are produced between glycolysis & CAC?
2 H+
33
New cards
how many CO2 are produced between glycolysis & CAC?
2 CO2
34
New cards
how many net ATP are produced between glycolysis & CAC?
0 net ATP
35
New cards
how many GTP are produced between glycolysis & CAC?
0 GTP
36
New cards
how many FADH2 are produced between glycolysis & CAC?
0 FADH2
37
New cards
how many acetyl CoA are produced between glycolysis & CAC?
2 acetyle CoA
38
New cards
how many NADH are produced in CAC?
6 NADH
39
New cards
how many H+ are produced in CAC?
6 H+
40
New cards
how many CO2 are produced in CAC?
4 CO2
41
New cards
how many net ATP are produced in CAC?
0 net ATP
42
New cards
how many GTP are produced in CAC?
2 GTP
43
New cards
how many FAHD2 are produced in CAC?
2 FADH2
44
New cards
how many HS-CoA are produced in CAC?
2 HS-CoA
45
New cards
What was wrong with Patrick?
* He had a single-base pair mutation that resulted in a lack of pyruvate dehydrogenase
* Without this enzyme, his cells couldn't convert pyruvate into acetyl CoA, instead making more lactase, leading to lactic acid buildup
* Without this enzyme, his cells couldn't convert pyruvate into acetyl CoA, instead making more lactase, leading to lactic acid buildup
46
New cards
Why did this problem mean that he did not make ATP efficiently?
* without pyruvate dehydrogenase, his cells couldn't continue with aerobic metabolism
* without the enzyme, acetyl CoA couldn't be made, meaning the step between glycolysis and CAC didn't happen, and neither did the CAC and oxidative phosphorylation, meaning no ATP production
* without the enzyme, acetyl CoA couldn't be made, meaning the step between glycolysis and CAC didn't happen, and neither did the CAC and oxidative phosphorylation, meaning no ATP production
47
New cards
Why was he in pain?
* He was in pain due to the lactic acid buildup in his cells (lactate acidosis)
* The acidosis lead to hyperventilation, muscle pain & weakness, and abdominal pain & nausea
* The acidosis lead to hyperventilation, muscle pain & weakness, and abdominal pain & nausea
48
New cards
What treatments might have helped Patrick and why?
* a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet might have helped Patrick because fats skip through the portion of glycolysis that Patrick's cells couldn't undergo (they jumped directly to acetyl CoA, instead of having to go through glycolysis and be turned from pyruvate to acetyl CoA).
* use dichloroacetate (DCA), which blocks the enzyme that converts PDH from active to inactive forms.
* This says that Patrick had some of the enzyme and doctors would have kept what he had active - the "make the most of what you've got" strategy
* use dichloroacetate (DCA), which blocks the enzyme that converts PDH from active to inactive forms.
* This says that Patrick had some of the enzyme and doctors would have kept what he had active - the "make the most of what you've got" strategy
49
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 1
action potential zips down motor neuron
50
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 2
at the terminal end of the axon, voltage gate Ca++ ion channels open
51
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 3
the influx of calcium makes vesicles dock & dump out neurotransmitter → acetylcholine (Ach)
52
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 4
Ach is received by receptors on muscle cell membrane AchR
53
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 5
Whoosh Na+ rushes into the muscle cell through the nAchR channels
54
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 6
zip action potential zooms down the muscle cell membrane down into t-tubules
55
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 7
this makes ryanodine receptors on the sarcoplasmicreticulum (SR) organelle open
56
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 8
Ca++ comes rushong out of the SR
57
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 9
Ca++ binds to troponin
58
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 10
making tropomyosin move out of the way of myosin/actin cross bridging sites
59
New cards
Muscle Contractions Step 11
ATP hydrolysis on myosin heads allows cross bridging & power-stroke for sliding filament contractions
60
New cards
Cell News Adela
* Christmas Island rat extinct, bring back?
* CRISPR edit the Norway brown rat to make it “Christmasy”
* 95% identity b/w the two rats
* identity → identical DNA bases
* homology → about bases but more about functional products
* CRISPR edit the Norway brown rat to make it “Christmasy”
* 95% identity b/w the two rats
* identity → identical DNA bases
* homology → about bases but more about functional products
61
New cards
Cell News Brooke
* developed “cyborg” cells
* infused artificial polymers into bacteria → what does this mean?
* bacteria with a hydrogel inside still “alive” but not replicating
* infused artificial polymers into bacteria → what does this mean?
* bacteria with a hydrogel inside still “alive” but not replicating
62
New cards
Cell News Lloyd
* human collin interacting?
* this enzyme can postpone aging → p53 was used as a marker of aging
* b/c it was affecting transcription → Δ histone meth
* this enzyme can postpone aging → p53 was used as a marker of aging
* b/c it was affecting transcription → Δ histone meth
63
New cards
Cell New Joelle
* anti-aging from weeds?
* cocklebure plant has materials that help with wound healing and wrinkle reduction
* cocklebure plant has materials that help with wound healing and wrinkle reduction
64
New cards
Cell News Hannah
* kidney stones (calcium oxalate)
* can lemon juice actually work?
* lemon extract nanoparticles ; soften stones but didn’t stop
* can lemon juice actually work?
* lemon extract nanoparticles ; soften stones but didn’t stop
65
New cards
Cell News Mylee
* endometriosis antibody therapy
* interleukin-8
* tested in primates (1x/month injections)
* interleukin-8
* tested in primates (1x/month injections)