Acids, Bases and Salts
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CSEC Chemistry - Grade 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is the Bronsted-Lowry definition of an acid?
An acid is a proton donor.
It releases hydrogen ions (H⁺) in aqueous solution.
List 5 general characteristics of acids.
Sour taste pH less than 7
They change blue litmus to red
They are corrosive
They are electrolytes (they conduct an electric current)
Hydrochloric acid

Nitric acid

Sulfuric acid
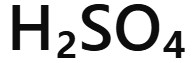

Perchloric acid

Hydrofluoric acid
Carbonic acid
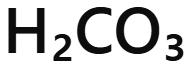
Ethanoic (acetic) acid

Methanoic (formic) acid
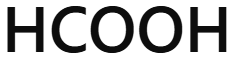
Phosphoric acid

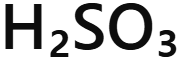
Sulfurous acid
ALL acids have this in their formula
Hydrogen ions (H+)

Acid + Base →
Salt + Water
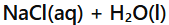
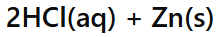
Acid + Metal →
Salt + Hydrogen gas
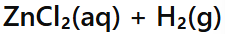

Acid + Metal Carbonate →
Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
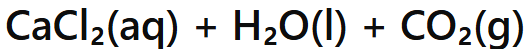

Acid + Metal Hydrogen Carbonate →
Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
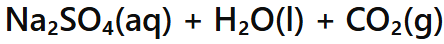
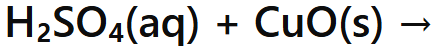
Acid + Metal Oxide →
Salt + Water
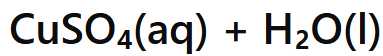
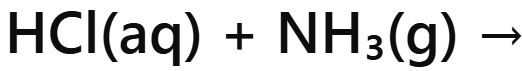
Acid + Ammonia →
Ammonium Salt

Name the type of reaction which occurs when acids react with bases.
Neutralization
What is basicity/proticity of an acid?
It is the number of moles of H+ ions that one molecule of an acid can donate when in aqueous solution.
Basicity tells how many protons an acid can release per molecule.

Monobasic acids release one H+ ion per molecule when dissolved in water. List 4 monobasic acids.
HCl - hydrochloric acid
HNO3 - nitric acid
HF - hydrofluoric acid
HClO4 - perchloric acid
HCOOH - methanoic acid
CH3COOH - ethanoic acid
Dibasic acids release two H+ ions per molecule when dissolved in water. List 3 dibasic acids.
H₂SO₄ - sulfuric acid
H₂SO₃ - sulfurous acid
H₂CO₃ - carbonic acid
Tribasic acids release three H+ ions per molecule when dissolved in water. Name one tribasic acid.
H₃PO₄ - phosphoric acid
Define acid anhydride
A substance (a non-metal oxide) that reacts with water to form an acid.
E.g. SO3, CO3, N2O5
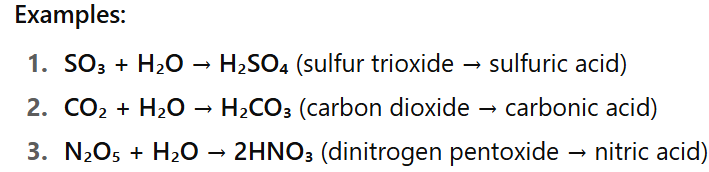
What is a dilute acid?
It is one that contains a lot of water.
What is a concentrated acid?
It is one that contains very little water.

What is a strong acid?
An acid which is fully ionized when dissolved in water e.g. hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid.


What is a weak acid?
An acid which is only partially ionised when dissolved in water e.g. carbonic acid and ethanoic acid.
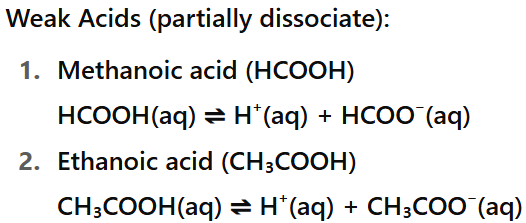
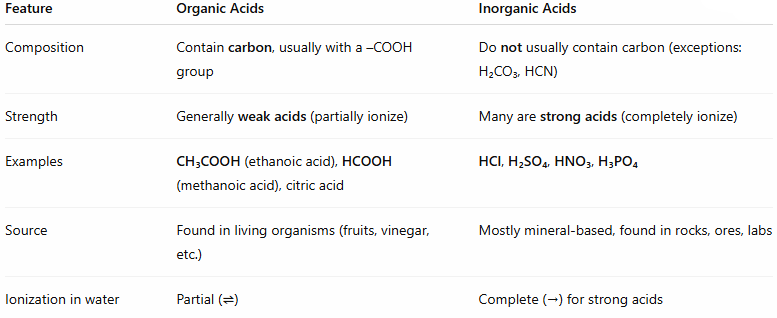
Differentiate between inorganic and organic acids.
Organic acids contain carbon, usually with a –COOH group. They are generally weak acids (partially ionize in water)
Inorganic acids do not usually contain carbon (exception H2CO3). Most of them are strong acids. They completely ionize in water.
Where can ascorbic acid/vitamin C (C6H8O6) be found naturally?
In many foods, e.g. citrus fruits, West Indian cherries, sweet peppers, tomatoes, green leafy vegetables.
Where can methanoic acid (HCOOH) be found naturally?
In the venom of bee and ant stings
Where can lactic acid(C3H6O3) be found naturally?
Produced in muscle cells during strenuous activity
Where can ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) be found ?
In vinegar
Where can citric acid(C6H8O7) be found?
In citrus fruits, e.g.limes
What is the result of vitamin C deficiency in the diet?
Scurvy
What happens to vitamin C during cooking?
Vitamin C is destroyed by becoming oxidised.
Why is sodium hydrogen carbonate sometimes added to fruits and vegetables?
It causes them to improve their appearance and texture since it neutralizes any vitamin C present thereby reducing the vitamin C content.
Stings can be treated by applying a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate or calamine lotion which contains zinc hydrogen carbonate. Why?
These neutralize methanoic acid.
Why can vinegar be used to preserve certain food items?
Being acidic, it has a low pH, which denatures (destroys) the enzymes that cause decay and inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi.
Why can limes be used to remove rust stains from clothing?
The acid in the lime juice reacts with the iron(III) oxide(Fe2O3) in the rust making a soluble compound which can be washed out of the clothes. Fe2O3(s) + 6H+(aq) -> 2Fe2+ (aq) + 3H20(l)
What is the Bronsted-Lowry definition of a base?
A proton(H+) acceptor.
It is a substance that releases hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in aqueous solution
What is a alkali?
A base which dissolves in water to form a solution containing OH- ions
Distinguish between a strong alkali and a weak alkali.
Strong alkali - Fully ionized when dissolved in water e.g. KOH and NaOH
Weak alkali - Partially ionized when dissolved in water e.g. NH3
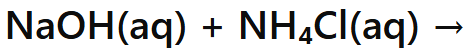
Base + Ammonium salt
Salt + Water + Ammonia Gas
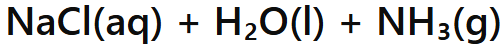
What are amphoteric oxides?
A substance which can react with both acids and alkali to form salt and water. Examples: Al₂O₃, PbO, ZnO
What are acidic oxides?
Oxides of certain non-metal which react with alkalis to form salt and water
Examples: CO2, SO3
What are basic oxides?
Oxides of metals which react with acids to form a salt and water
What are neutral oxides?
Oxides of certain non-metals which do not react with acids or alkali
Examples: CO, NO, N₂O
What is a salt?
A compound formed when some or all of the replaceable hydrogen ions in an acid are replaced by metal or ammonium ions
What is a normal salt?
A salt formed when ALL of the replaceable hydrogen ions in an acid are replaced by metal or ammonium ions. All acids can form normal salts
What is an acid salt?
A salt formed when the replaceable hydrogen ions in an acid are only partially replaced by metal or ammonium ions. Only dibasic and tribasic acids can form acid salts.
What is a hydrated salt?
Salts with fixed number of water molecules in their crystal lattice/salts containing water of crystallization
What is an anhydrous salt?
Salts without water of crystallization
What is ionic precipitation?
The reaction of two soluble salts in solution to form an insoluble salt. One solution contains the cation of the desired salt, the other solution contains the anion of the desired salt
Outline the steps involved in preparing an insoluble salt using direct combination.
Choose two soluble salts, one containing the cations required to make the salt the other containing the anions required
Dissolve the two salts in water to make solutions
Mix the two solutions to form the insoluble salt as a precipitate
Filter the mixture and collect the precipitate as the residue
Wash the residue with distilled water while it is still in the filter funnel and leave it to dry
Complete the solubility rule:
All nitrates are _______
soluble
Complete the solubility rule:
All Group 1 salts are ________
soluble
List 3 main ways of preparing soluble salts
Direct combination
React a reactive metal/insoluble carbonate/insoluble base with an acid
React an alkali and an acid using titration method
Describe the flow chart used to determine method of salt preparation.
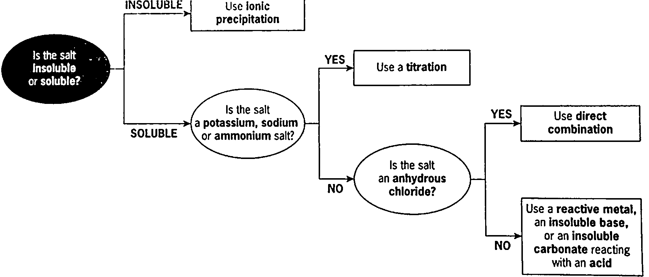
Outline the steps involved in the titration method of salt preparation.
Choose an appropriate alkali or soluble carbonate to provide the cations and an appropriate acid to supply the anions
Measure a fixed volume of the aqueous alkali or carbonate using a pipette. Run it into a conical flask and a few drops of an indicator solution e.g. phenolphthalein
Place the acid in a burette and take the initial burette reading
Add the acid to the aqueous alkali or carbonate until the neutralization point is reached ( indicator changes color)
Take a final burette reading and determine the volume of acid added
Repeat the titration of acid until you have three volumes of acid with precise readings. Average these volumes to determine the volume if acid needed
Add this volume of acid to the fixed volume of aqueous alkali or carbonate without the indicator
Evaporate the water from the solution
This salt is used as an ingredient in baking powder
Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3)
This salt is used to soften hard water
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3)
This salt is used in the manufacture of cement for use in the construction industry
Calcium carbonate
This salt has various medicinal and therapeutic uses
Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4)- Epsom salt
Three salts used in food preservation
Sodium chloride(NaCl), sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2), sodium benzoate
This salt is used in the manufacture of plaster of Paris, which is used when setting broken bones and as a building material
Calcium sulfate - gypsum
State one danger of consuming NaCl
Excessive consumption can lead to hypertension (high blood pressure)
State one danger of consuming NaNO3 and NaNO2
May increase a risk for developing cancer. Has been linked to causing brain damage in children
State one danger of consuming sodium benzoate
Has been linked to increasing hyperactivity and asthma in children. May increase a person's risk of developing cancer