Headaches
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Quickly and effectively resolving acute headache symptoms (abortive or preventative?)
Abortive therapy
Decreasing frequency and severity of future headaches (abortive or preventative?)
Preventative therapy
Unilateral
Throbbing
Nausea, vomiting
Sensitivity to light, sound, movement
With or without aura
Symptoms of migraine headache
Do migraines have common triggers?
Yes
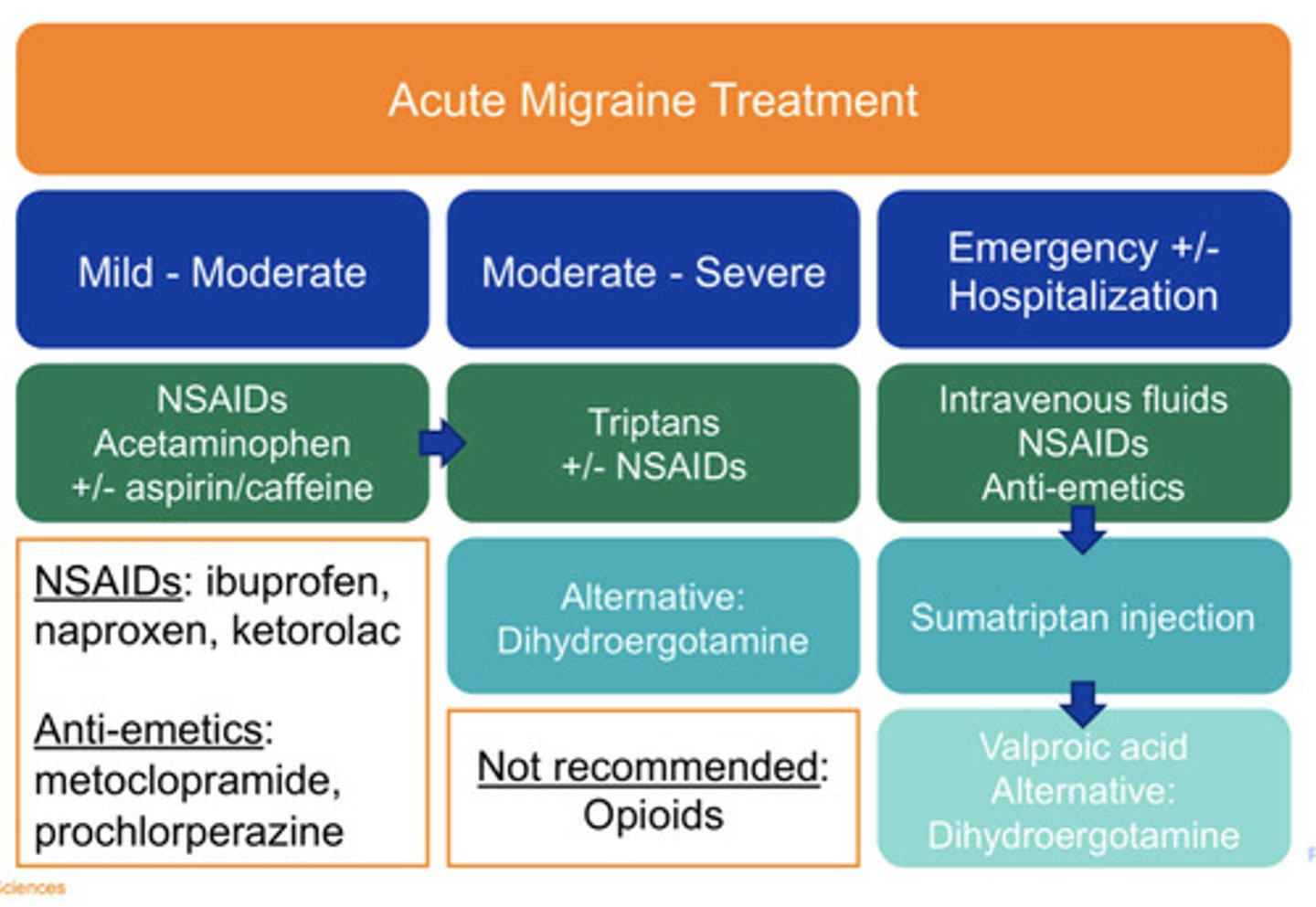
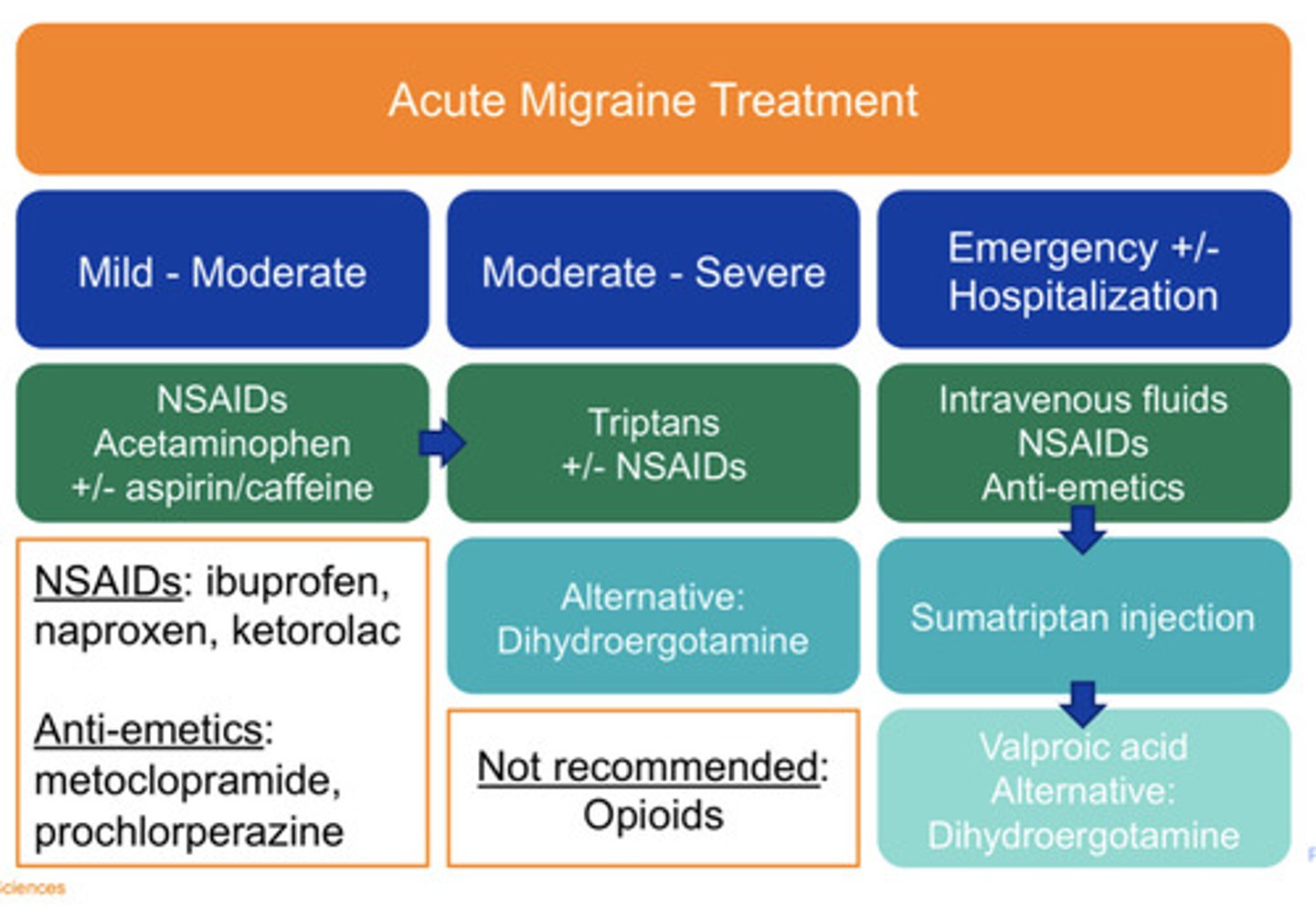
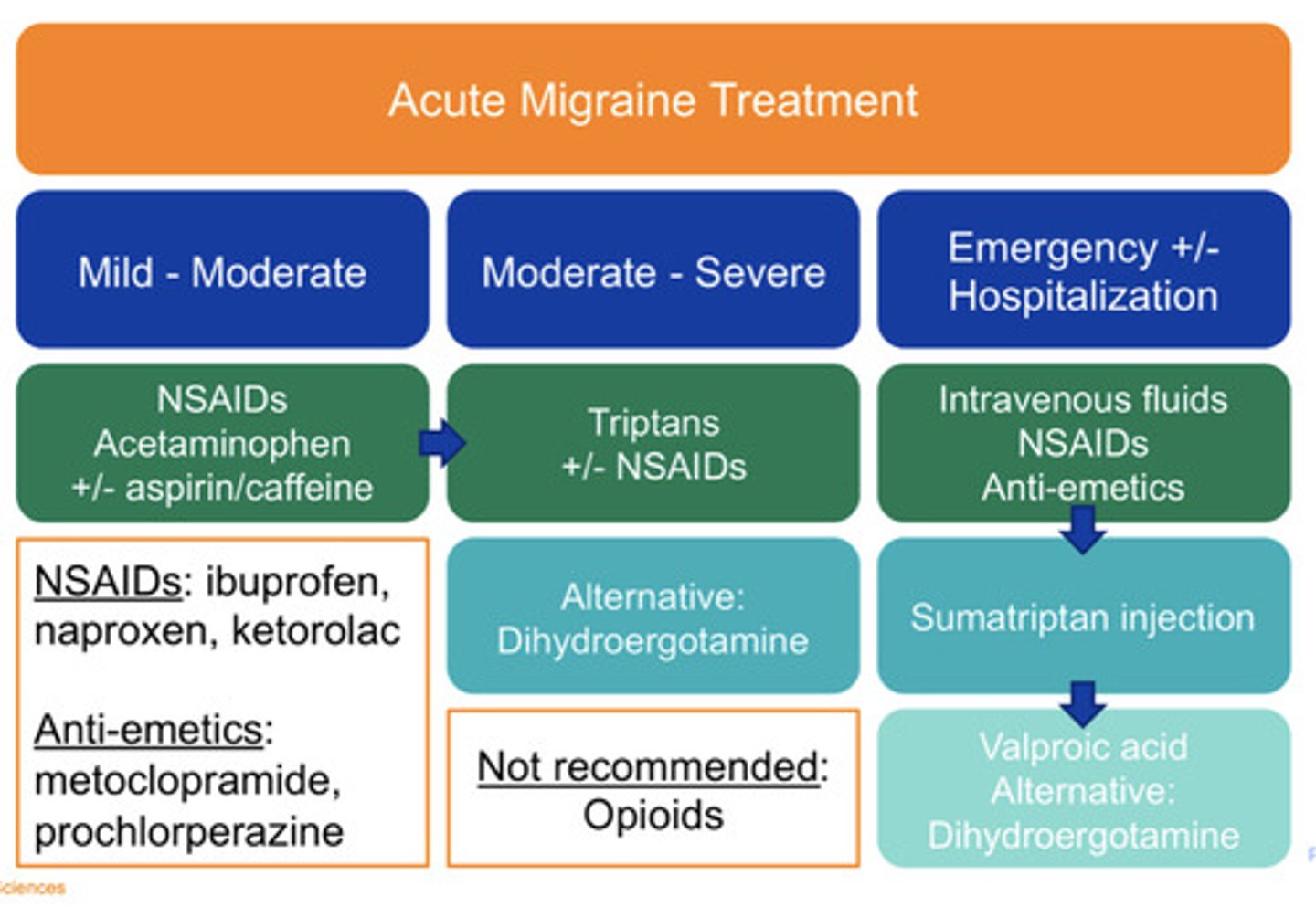
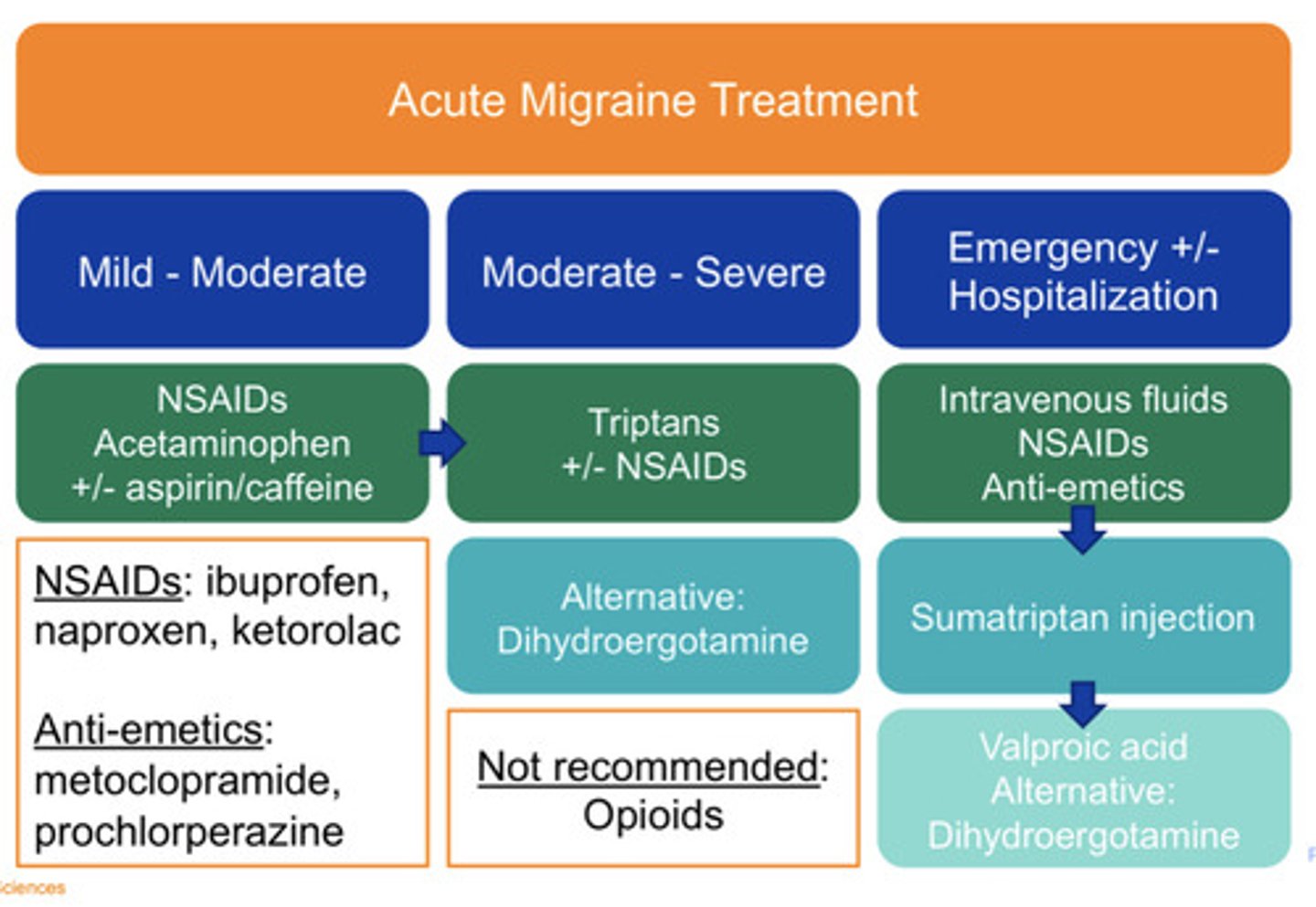
Mild/moderate acute migraine treatment
NSAIDs
Acetaminophen
+/- aspirin and caffeine
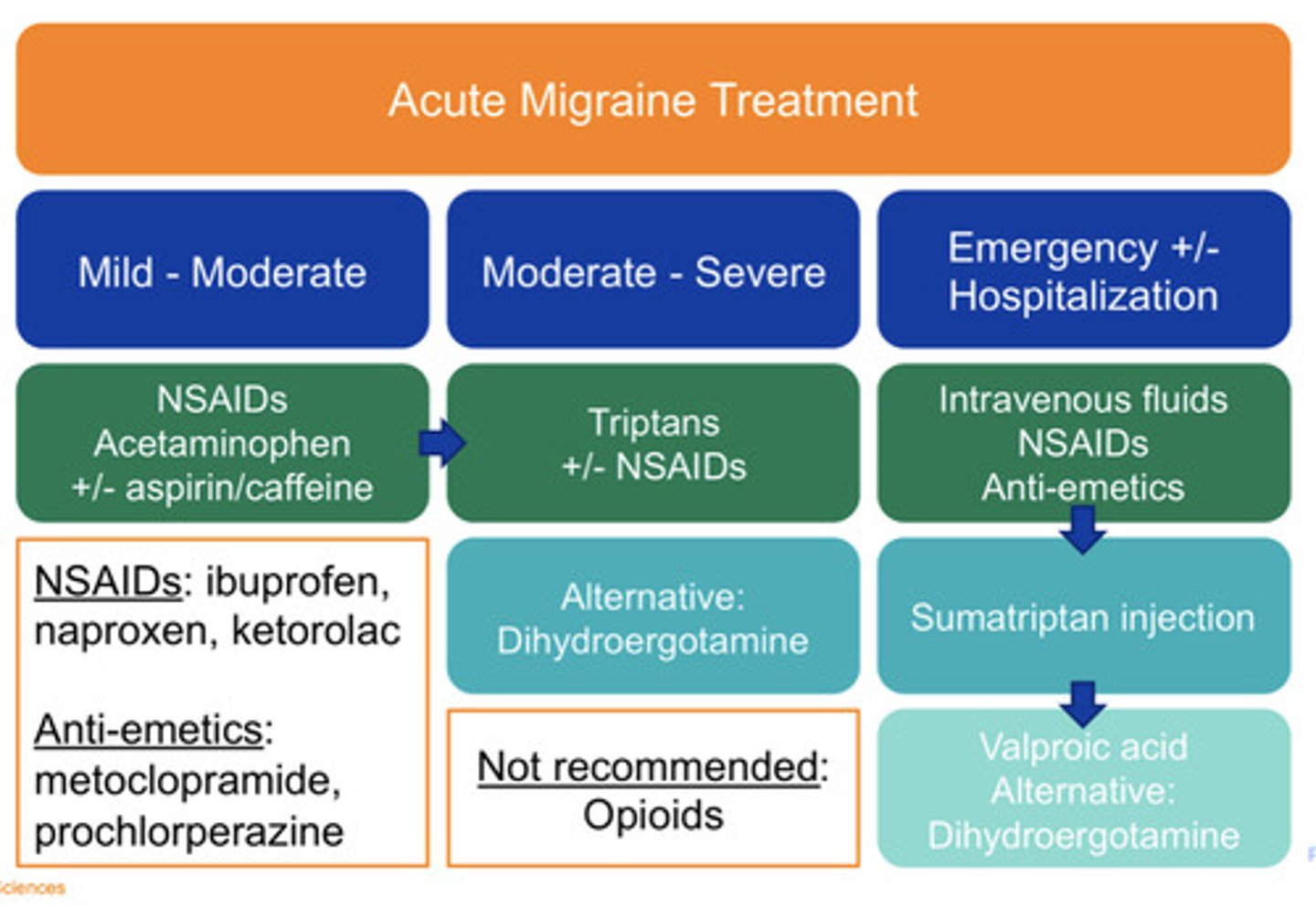
Moderate/severe acute migraine treatment
"Triptans"
+/- NSAIDs
Alt: Dihydroergotamine
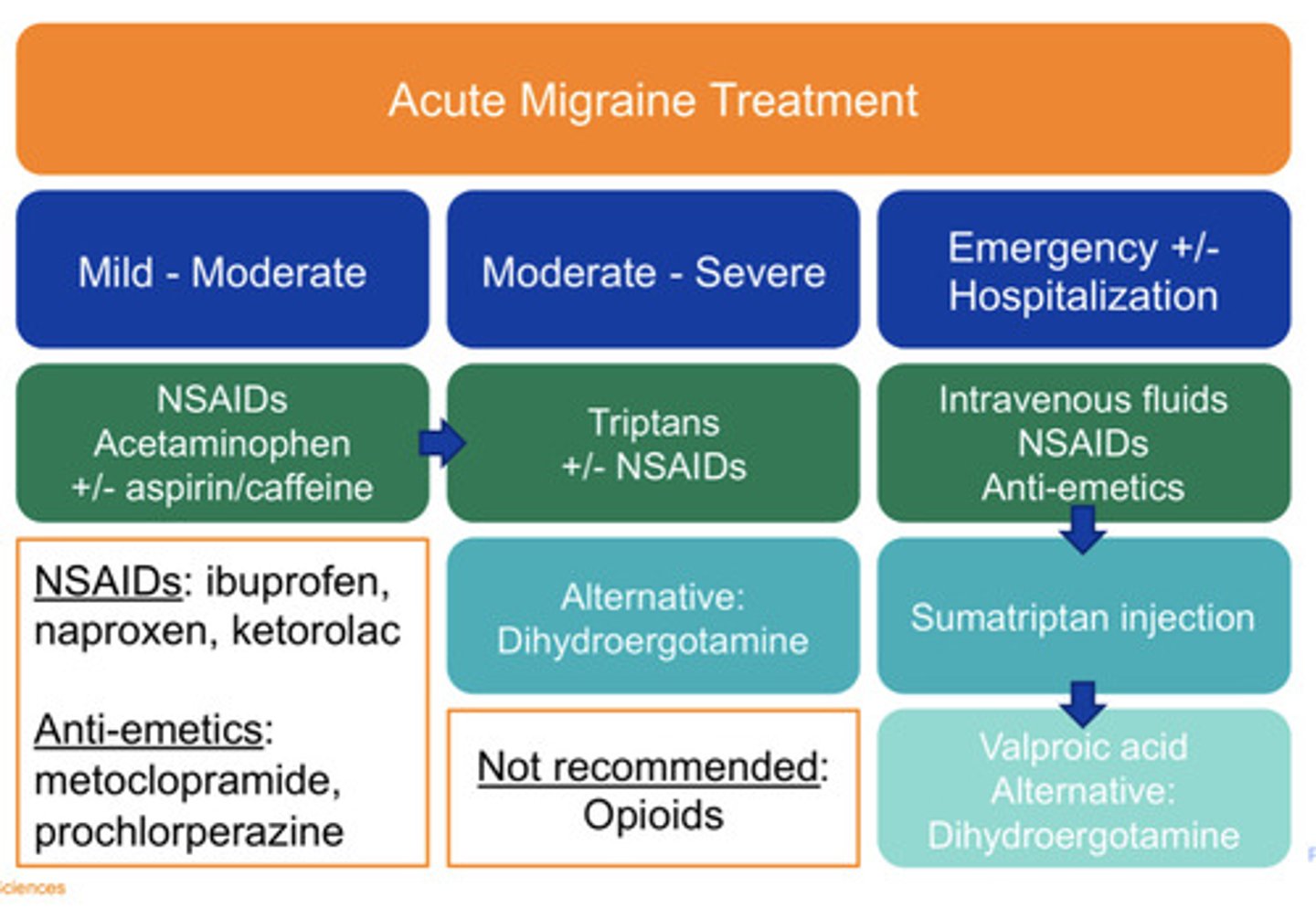
Emergent/hospitalization acute migraine treatment
-IV fluids
-NSAIDs
-Anti-emetics
Persistent symptoms: Sumatriptan injection then Valproic acid
Alternative Dihydroergotamine
During treatment for an emergent, acute migraine with persistent symptoms (after IV fluids, NSAIDs, anti-emetics) what can you administer?
Sumatriptan injection then Valproic acid
Alternative treatment for migraine treatment
Dihydroergotamine
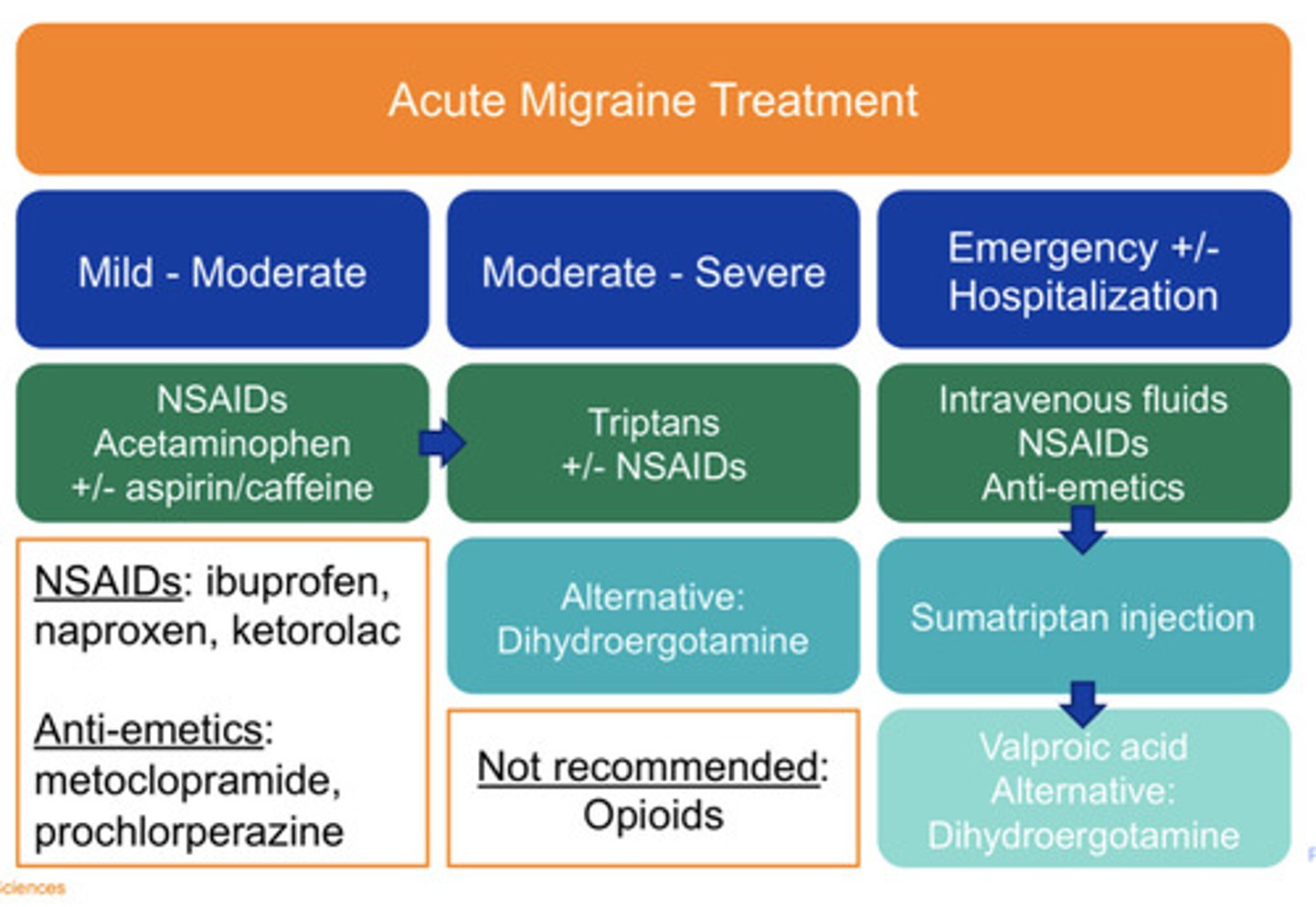
NOT recommended acute migraine treatment
Opioids
Ibuprofen, naproxen, ketorolac
NSAIDs
Metoclopramide, Prochlorperazine
Anti-emetics
Are triptans used as abortive or preventative therapy for migraines?
Abortive therapy (resolve acute headache symptoms)
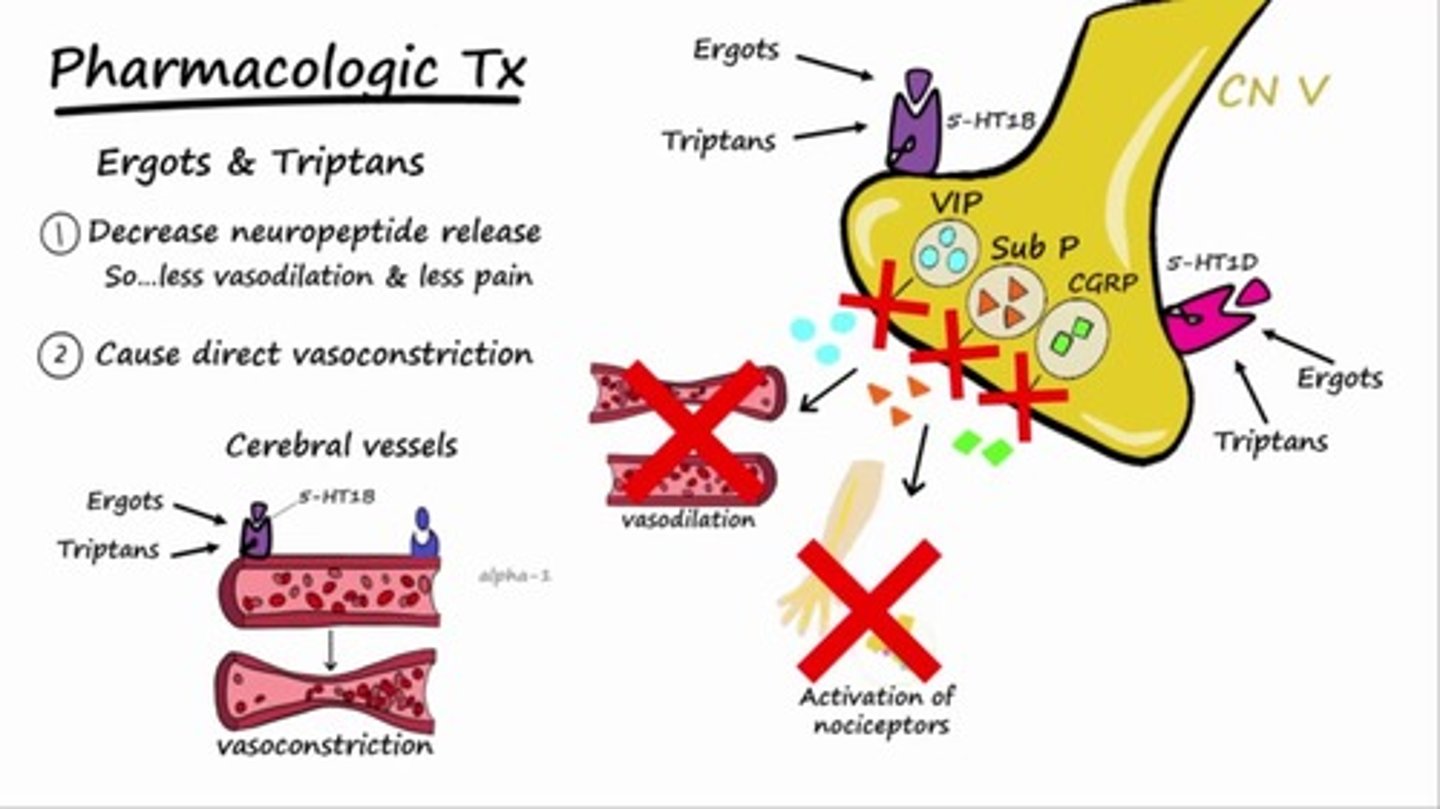
Serotonin 1b/1d agonists —> promotes vasoconstriction and blocks pain pathways in brain
Triptans
Triptans are available as PO, Nasal, and IV. Order from fastest onset to slowest?
IV > nasal spray > oral
When should you take a triptan so that it is MOST effective?
Taken at onset of early/mild symptoms, do not "wait" until symptoms are severe
Chest pressure
Flushing
Serotonin syndrome (rare)
Adverse effects of triptans
Occurs when you take medications that cause high levels of the chemical serotonin to accumulate in your body. Symptoms usually occur within several hours of taking a new drug or increasing the dose of a drug you're already taking.
Serotonin syndrome

Cannot give Triptans within 24 hours of...
Dihydroergotamine (DHE)
When should you avoid triptans?
Avoid when vasoconstriction would be hazardous (e.g. MI, stroke, uncontrolled HTN, vascular disease)
Agonist at serotonin, NE, and DA receptors —> vasoconstriction
DHE (Dihydroergotamine)
When administering DHE, pre-medicate with...
Anti-emetic (e.g metoclopramide)
Contraindications of DHE include the same as triptans (avoid where vasoconstriction would be hazardous) plus...
Pregnancy
When should you add a preventative migraine therapy?
> or = 4 headache days per month
Debilitating headaches
Acute therapy adverse effects, contraindication, failure, or overuse
What are the goals of preventative migraine therapy?
50% decrease in headache days
Decrease attack severity, duration, disability
Improved response to acute therapy
With preventative migraine therapy, are max effects quick or slow?
Delayed/slow
Divalproex, valproate, topiramate
Anti-epileptic
Preventative migraine therapies include...
Anti-epileptic meds (Divalproex, valproate, topiramate)
Beta blockers (Propranolol)
TCAs (Amitryptaline)
Botulism toxin injections
Test 2: A 32 year-old female with a history of migraines had been successfully managed with the occasional abortive agent, but now reports 4-6 migraines per month over the last few months. Assuming no contraindications, which of the following would be a potential migraine prophylaxis agent?
Propranolol
Which anti-epileptic drugs can you NOT use in pregnancy?
Divalproex
Valproate
Topiramate
Divalproex, Valproate (neural tube defects)
Fatigue, sexual dysfunction, negative effects on reactive airway diseases
Beta blockers
Emerging preventative migraine meds
CGRP (calcitonin gene related peptide) agents
Expensive and reserved for those who have failed or are intolerant to other migraine therapies
CGRP
Ubrogepant and monoclonal antibodies - "mab" drugs
CGRP agents
Tension type HA treatment
NSAIDs
APAP (acetaminophen)
+/- aspirin/caffeine
(Note - same as mild migraine treatment)
Cluster HA acute treatment
SQ or nasal triptans and/or oxygen
Unilateral but with presentation of lacrimation/rhinorrhea
Cluster HA
Generally defines the overuse of any med for HA
> or = 10-15 days per month
If overuse HA, when should you try discontinuing the offending agent?
As able and abruptly as possible
How would you counsel a patient regarding the timing of triptan administration?
Take immediately upon onset of symptoms
Which triptan formulation has the fastest onset of action?
Injectable sumatriptan
Oral naratriptan
Nasal zolmitriptan
Oral rizatriptan
Injectable sumatriptan (speed of onset from fastest to slowest is injection, nasal, oral)