Phase 1/2 Chemical Reactions
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is the difference between phase 1 and phase 2 metabolic reactions?
Phase 1 reactions add functional groups to create a more polar molecule.
Phase 2 reactions modify existing functional groups by introducing a new group to further increase polarity.
Three types of biotransformations in phase one are
Oxidation
Reduction
Hydrolysis
What is oxidation? How can you tell when it has happened to a molecule?
Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state of an atom or molecule. Most often, a gain of oxygen, loss of hydrogen, loss of an alkyl group, and/ or the loss of a heteroatom will signify oxidation.
How does steric hinderance play a role in the oxidation of aromatic rings during aromatic hydroxylation?
Unsubstituted phenyl rings are usually hydroxylated at the para position to avoid steric hinderance with the rest of the molecule.
How does steric hinderance play a role in the oxidation of benzylic carbons?
The less substituted/ less hindered carbon will undergo oxidation (in a situation with multiple benzylic carbons)
What is the omega carbon?
The omega carbon is the last carbon in an aliphatic carbon chain.
What is the omega-1 carbon?
The penultimate carbon in an aliphatic chain.
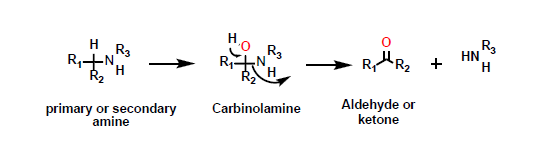
What is this reaction?
Oxidative deamination
What is required for oxidative deamination?
the alpha carbon of the amine must be attached to at least one hydrogen.
What is the intermediate of oxidative deamination?
carbinolamine
What is the product of oxidative deamination?
an aldehyde or a ketone, depending on the nature of the groups attached to the amine.
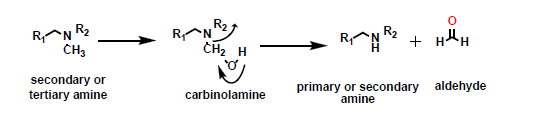
What is this reaction?
Oxidative N-dealkylation
What is the substrate for an oxidative N-dealkylation reaction?
A secondary or tertiary amine, or amide.
What is reduction? How can you tell when it has happened to a molecule?
Reduction involves the gaining of electrons and the decrease of oxidation state. Generally, gaining a hydrogen and/or losing oxygen is indicative of reduction.
What are some functional groups that commonly undergo reduction?
Azo groups and nitro groups are the two primary recipients of reduction
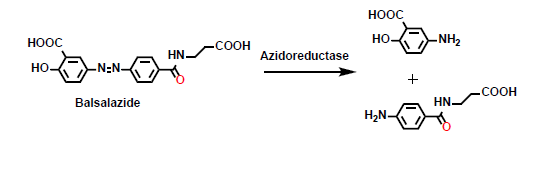
What is this reaction?
This is a reduction reaction involving an azo group.
What is hydrolysis?
The breakage of a bond by introducing water into the system.
What functional groups readily undergo hydrolysis?
Esters, amides, and their cyclic analogs: lactones and lactams.
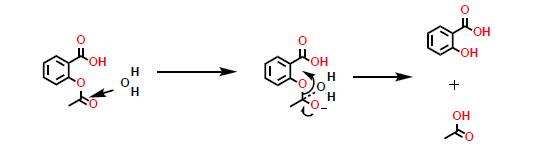
What kind of reaction is this?
a hydrolysis reaction
How does steric hinderance affect hydrolysis?
Esters and amides that are easily accessible are hydrolyzed to a greater extent than those located in the middle of a molecule or surrounded by other functional groups.
How is the rate of hydrolysis different between amides / lactams and esters and lactones?
Amides and lactams are hydrolyzed at a slower rate than esters and lactones.
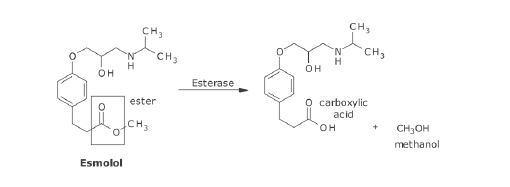
What metabolic transformation is occuring?
hydrolysis
What are the substrates of glucoronidation?
phenols, alcohols, hydroxylamines, and carbobxylic acids
What is the enzyme for glucoronidation?
glucuronyltransferase
What are the substrates for sulfate conjugation?
phenols, alcohols, arylamines, and N-hydroxy compounds
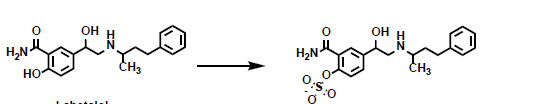
What phase 2 reaction is being shown here?
sulfate conjugation
What functional group is the target for amino acid conjugation?
carboxylic acids can be conjugated into amino acids.
How does glutathione operate?
Glutathione binds to powerful electrophiles that are often produced by metabolic processes, or are present in exogenous/ endogenous compound.
What is the function of acetylation?
to deactivate the drug
What functional groups are targets for acetylation?
primary amino groups, sulfonamides, hydrazines, and hydrazides.
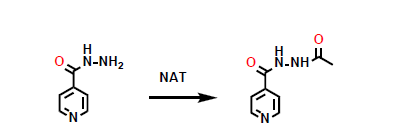
What metabolic phase 2 reaction is shown here?
acetylation of a primary amine.
What are the targets of methylation?
amines, thiols, and phenols
Methylation is a minor conjugation pathway for drug metabolism, where is it more commonly utilized in the body?
in the catabolism of norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, and histamine, as well as modulating the activity of proteins and nucleic acids.
Most phase 2 reactions are carried out in the cytosol, except one. Which phase 2 reaction is the exception and where does it occur?
glucuronidation occurs on the luminal side of the ER.
What is typically faster: phase two reactions, or the activity of CYPs?
phase two reactions tend to be faster than the activity of CYPs
What is UGT?
UDP-glucuronyltransferase
What is GST?
glutathione-S-transferases
What is SULT?
sulfotransferase
What is NAT?
N-acetyltransferase
What is TPMT?
thiopurine methyltransferase
What is a genetic condition that can occur as a result of reduced UGT expression?
Gilbert’s syndrome syndrome, results in increased bilirubin
Why do some neonates experience jaundice
due to increased bilirubin as a result of delayed UGT expression.
What enzymes are responsible for sulfation?
sulfotransferases (SULTS)
What is the result of sulfation?
products are more water soluble.
What amino acids tend to be used in amino acid conjugation?
glycine and/or glutamate
What enzyme is responsible for amino acid conjugation?
amino acid N-actyltransferases
What enzyme catalyzes glutathione conjugation?
glutathione S-transferases
What are the two variants of NATs?
NAT1 and NAT2
What is the typical result of an n-acetylation reaction?
typically the product is less water-soluble
What is a consequence of slow acetylators?
Slow acetylators, that express variants of NAT2, have a higher concentration of unchanged drugs. This results in an increased risk of nervous system damage and hepatotoxicity via CYP-mediated reactions

What is the answer to this question?
Phase 1 is primarily oxidation, and phase 2 is primarily glucuronidation.
What is the methyl group donor for methyltransferases?
the amino acid methionine.
What are the target functional groups for methylation?
phenols, thiols, and amines.
What are two examples of methyltransferases?
COMT (catechol-o-methyltransferase) and TPMT (thiopurine methyltransferase)
What enzyme for methylation has clinically significant polymorphisms?
TPMT. ~15% of Caucasians carry decreased activity variants.
What is enterohepatic recycling?
the process by which a drug or its metabolite is excreted into the bile, and enters the intestines, and is then reabsorbed into the bloodstream. This process can extend a drug/ metabolite’s presence in the body.
What kind of UGTs display clinically significant polymorphism?
UGT1A1 displays clinically significant polymorphism and may result in Gilbert’s syndrome (increase in bilirubin)
What enzymes responsible for glutathione conjugation have clinically significant polymorphisms?
GSTM1 and GSTT1