Hormones and the regulation of blood glucose concentration
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the features of hormones?
produced in glands - secrete hormone directly into the blood
carried in the blood plasma to the target cells - have specific receptors on their cell-surface membrane that are complementary to a specific hormone
effective in low concentration but have widespread and long-lasting effects
What is the second messenger model?
adrenaline binds to a transmembrane proteins receptor within the cell-surface membrane of a liver cell
binding of adrenaline causes the protein to change shape
protein changing shape activates adenyl cyclase - converts ATP to cyclic AMP
cAMP acts as as second messenger that binds to kinase, changing its shape and activating it
activated kinase catalyses the conversion of glycogen to glucose
How does the glucose move into the blood?
moves out of the liver cell by facilitation diffusion and into the blood through channel proteins
The pancreas is made up of groups of hormone-producing cells which are known as what?
islets of Langerhans
What are the cells of the islets of Langerhand?
Alpha cells - larger cells that produce glucAgon
beta cells - smaller and produce insulin
What 3 processes that regulate blood sugar take place in the liver?
glycogenesis
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
What is glycogenesis?
glucose → glycogen
(when blood glucose is higher than normal)
What is glycogenolysis?
glycogen → glucose
(when blood glucose concentration is lower)
What is gluconeogensis?
the production of glucose from sources other than carbohydrates (e.g glycerol and amino acids)
(when glycogen supply is exhausted)
Why is regulating blood glucose concentration important?
glucose is a substrate for respiration - source of energy
if too low, cells will be deprived of energy and die
if too high, lowers the water potential of the blood which can lead to dehydration
Blood glucose comes from where?
diet
hydrolysis in the small intestine of glycogen (glycogenolysis)
gluconeogenesis
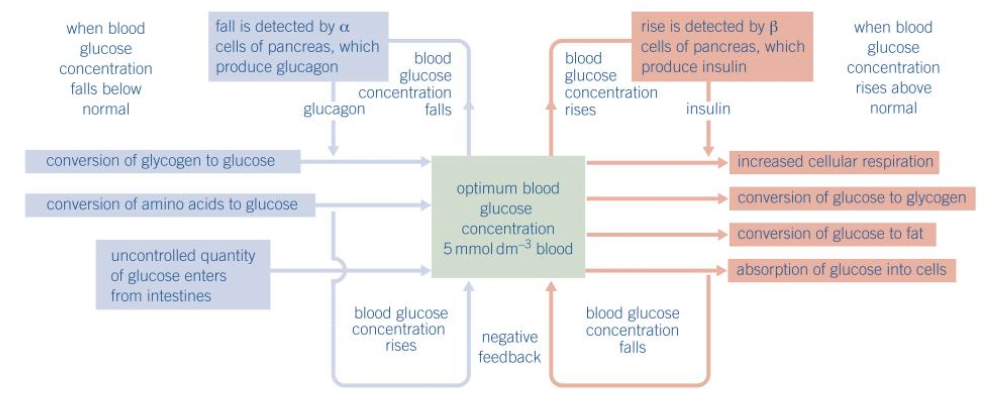
What happens when blood glucose concentration rises above normal?
receptors on beta cells detect increase and secrete insulin directly into the blood plasma
What are found on almost all body cells, except red blood cells?
glycoprotein receptors on their cell-surface membranes that bind specifically with insulin molecules
Blood glucose concentration is lowered in what ways?
increased cellular respiration
ACTIVATION OF ENZYMES THAT CAUSE THE:
conversion of glucose to glycogen
conversion of glucose to fat
absorption of glucose into cells
How is a fall in blood glucose concentration detected?
by the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans - which secretes glucagon directly into the blood plasma
How does glucagon increase blood glucose concentration?
attaching to specific protein receptors on the cell-surface membrane of liver cells
activating enzymes that convert glycogen to glucose
activating enzymes involved in to the conversion of amino acids and glycerol into glucose (gluconeogenesis)
How does adrenaline increase blood glucose concentration?
attaching to protein receptors on the cell-surface membrane of target cells
activating enzymes that cause the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver
What is a summary of the regulation of blood glucose concentration?
Why is there high glucose concentration in the urine of those with diabetes?
high glucose concentration in the blood/ filtrate
so not all glucose is reabsorbed at the proximal convoluted tubule
as all the carrier proteins are saturate / working at the maximum rate
What role does glucagon play in gluconeogenesis?
Attaches to receptors on target cells and activates/stimulates enzymes
so glycerol/amino acids are converted to glucose
How does insulin lower blood glucose other than activating enzymes?
STIMULATES UPTAKE OF GLUCOSE BY CHANNEL PROTEINS