Genetics Review: Mutations, DNA Repair, and Recombination
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is a forward mutation?
A forward mutation is a genetic change that alters a wild-type allele to a mutant allele.

What is a reverse (reversion) mutation?
A reverse mutation is a genetic change that restores a mutant allele back to the wild-type allele.
What is a substitution mutation?
A substitution mutation is a type of mutation where one base pair is replaced by another base pair in the DNA sequence.
What is an insertion mutation?
An insertion mutation is a type of mutation where one or more nucleotide base pairs are added into the DNA sequence.
What is a deletion mutation?
A deletion mutation is a type of mutation where one or more nucleotide base pairs are removed from the DNA sequence.
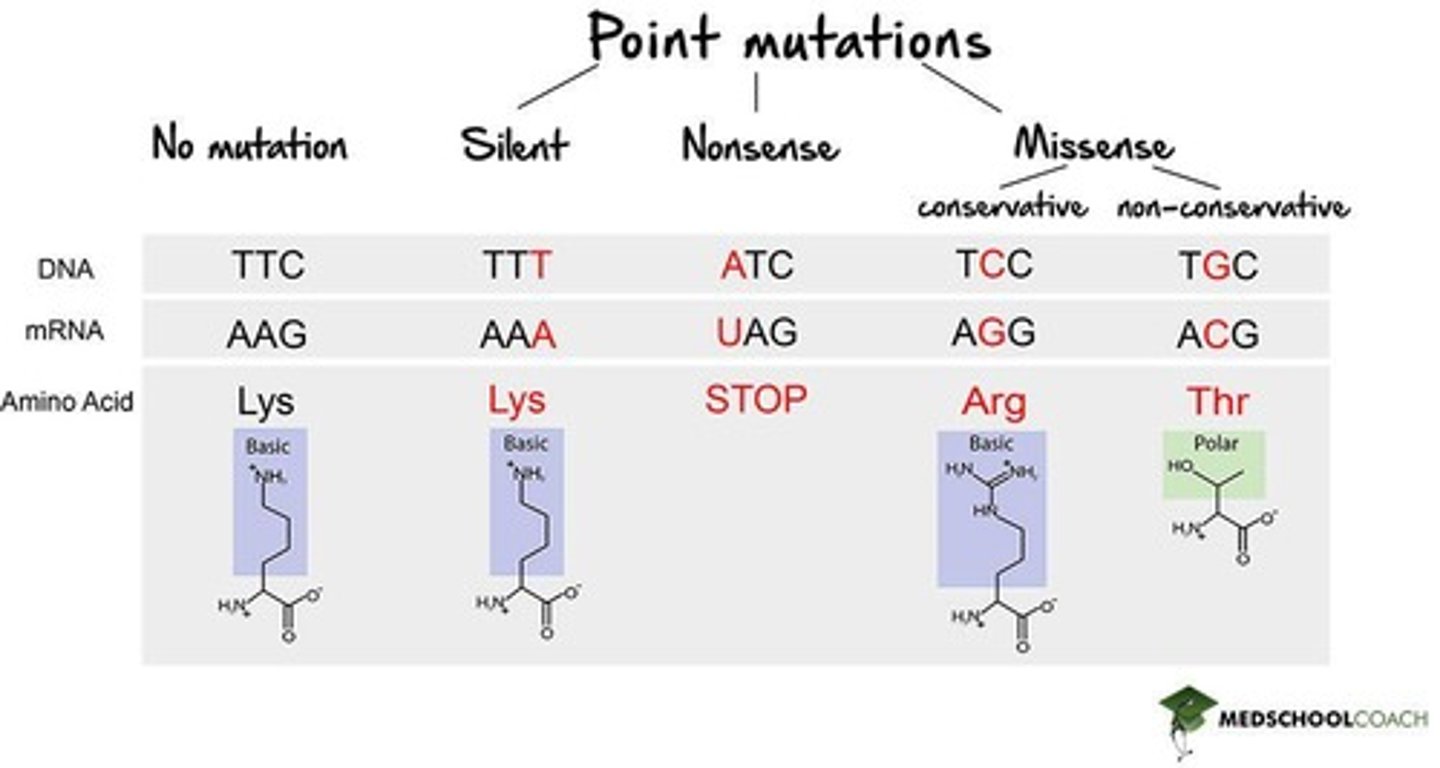
What are three point mutations?
Three point mutations include silent mutations (no change in amino acid), missense mutations (change in one amino acid), and nonsense mutations (creation of a stop codon).
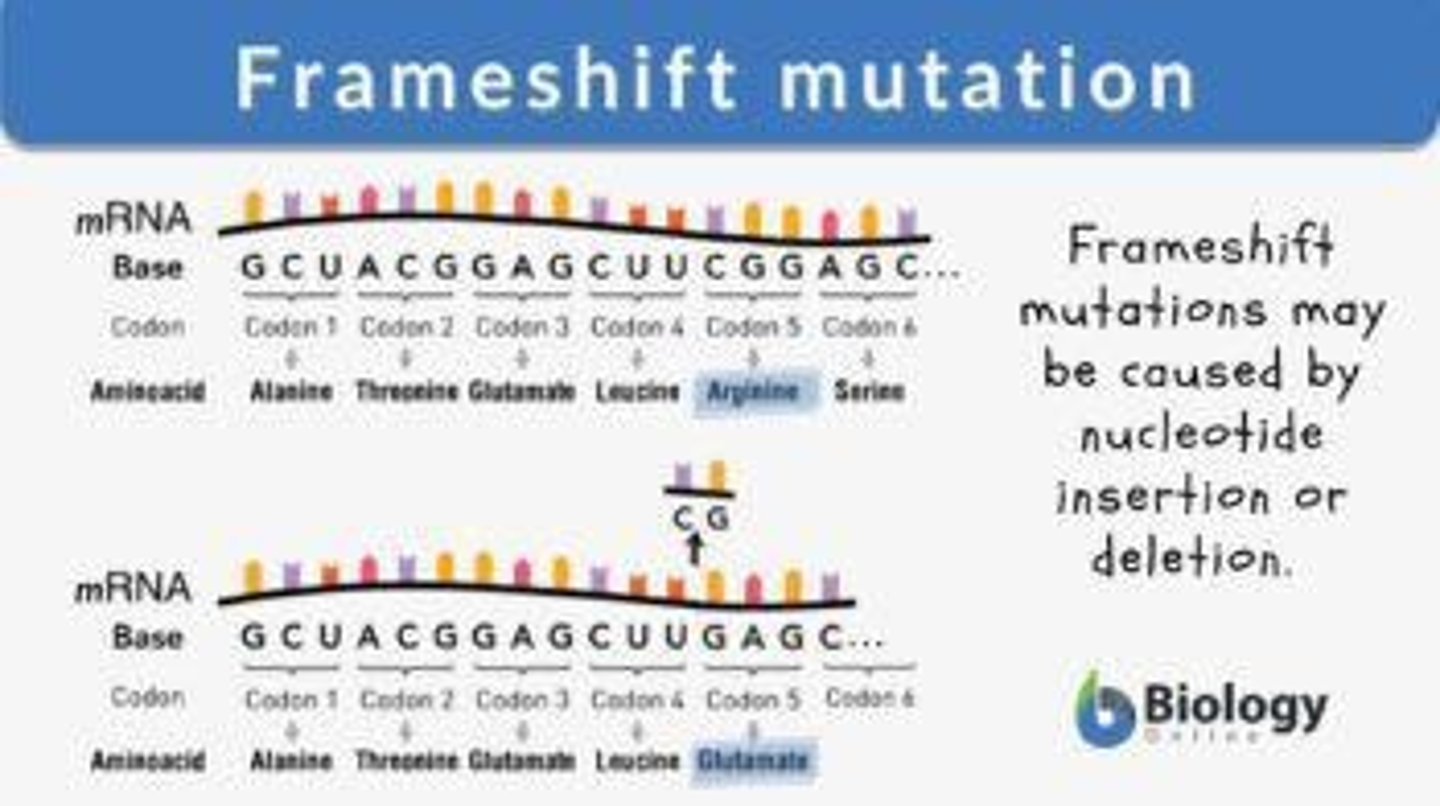
What is a frameshift mutation?
A frameshift mutation occurs when nucleotides are inserted or deleted from the DNA sequence, altering the reading frame of the genetic code.
What was the Lederberg Experiment?
The Lederberg Experiment demonstrated that mutations occur randomly and are not a direct response to environmental changes.
What is depurination?
Depurination is a chemical assault on DNA where purine bases (adenine or guanine) are removed, leading to potential mutations.
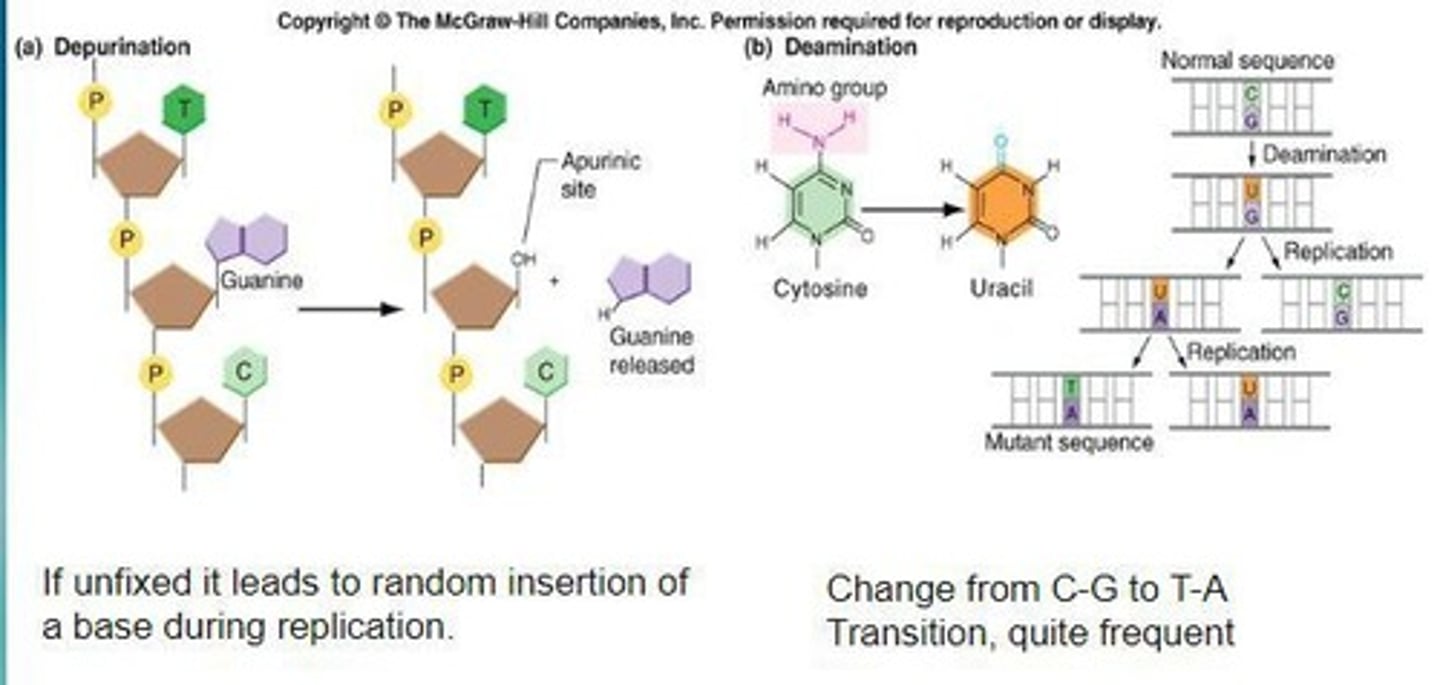
What is deamination?
Deamination is a chemical process that removes an amino group from a nucleotide, potentially leading to mutations.
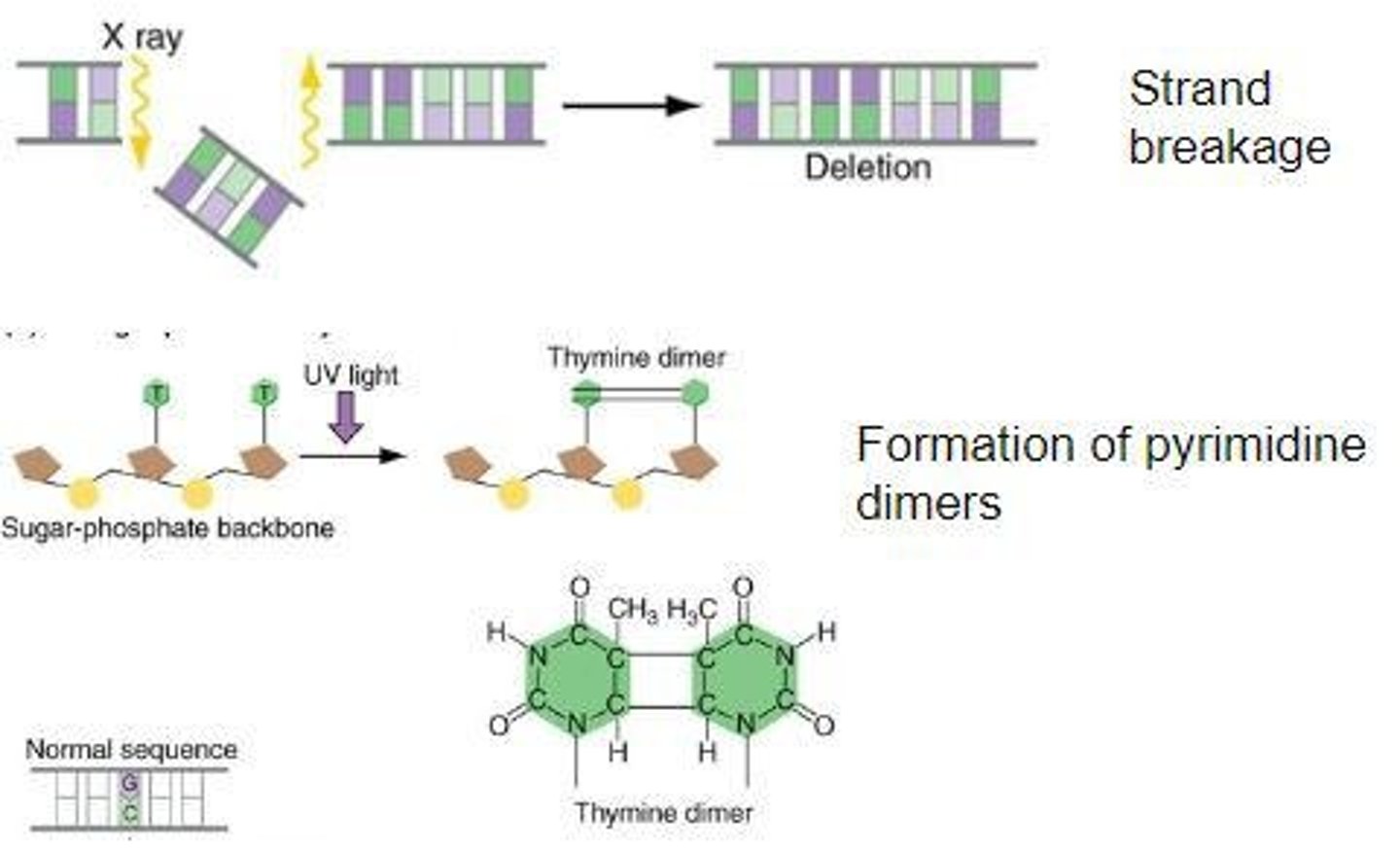
What effect does radiation have on genetic material?
Radiation can cause DNA damage, leading to mutations such as breaks in the DNA strands or the formation of thymine dimers.
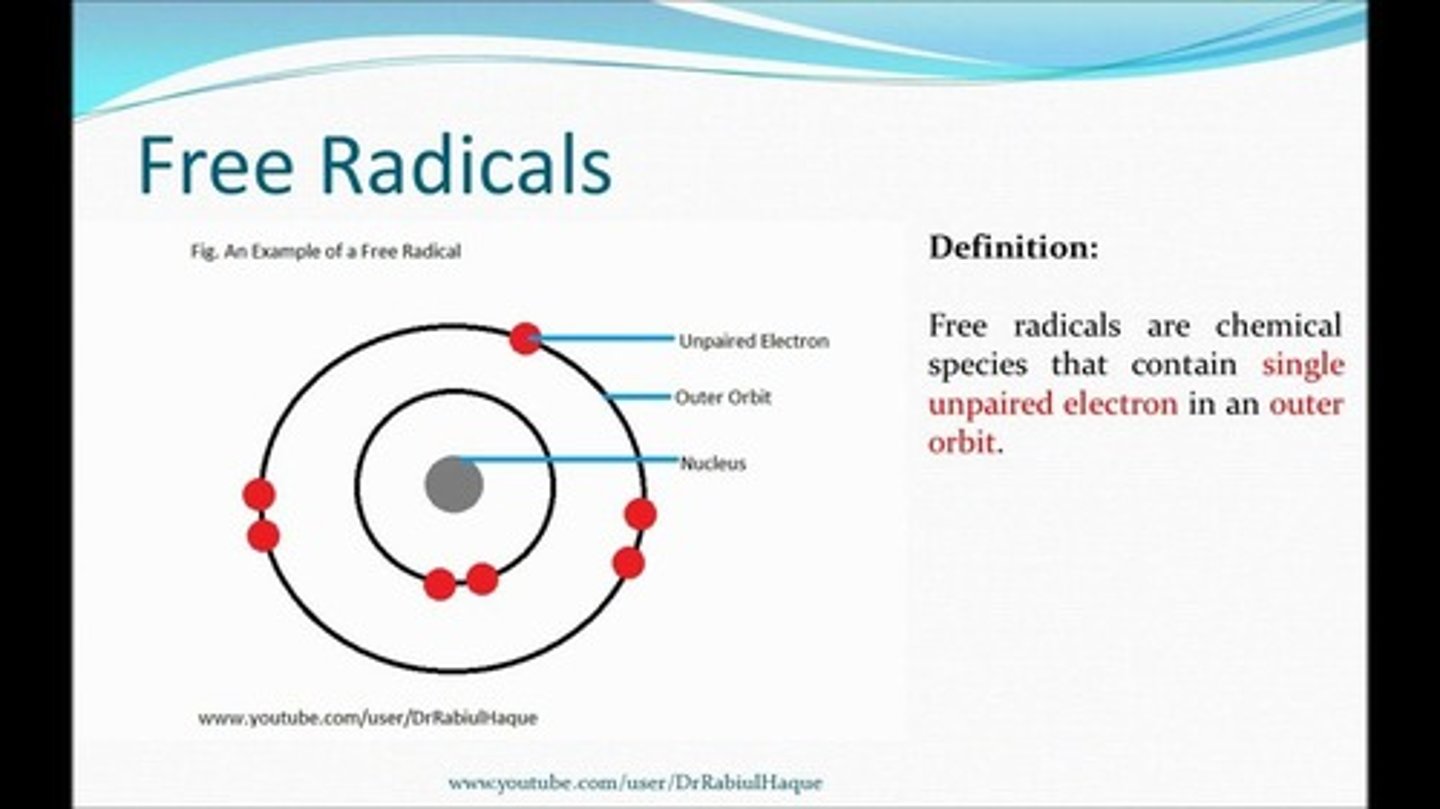
What is a free radical?
A free radical is an unstable atom or molecule that has unpaired electrons, which can cause oxidative damage to DNA.
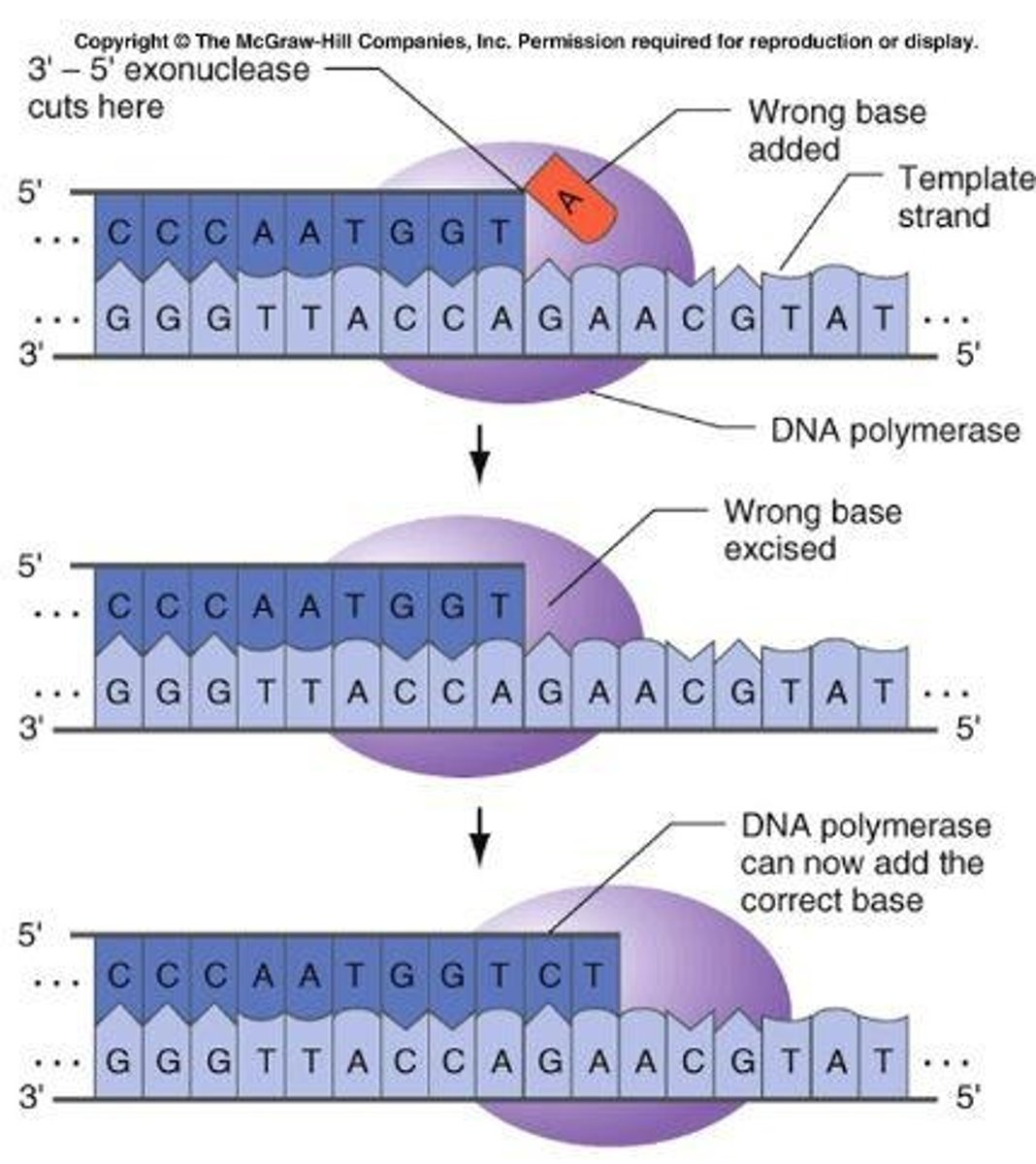
What is the proofreading direction of DNA polymerase?
DNA polymerase proofreads in the 3' to 5' direction, allowing it to remove incorrectly paired nucleotides.
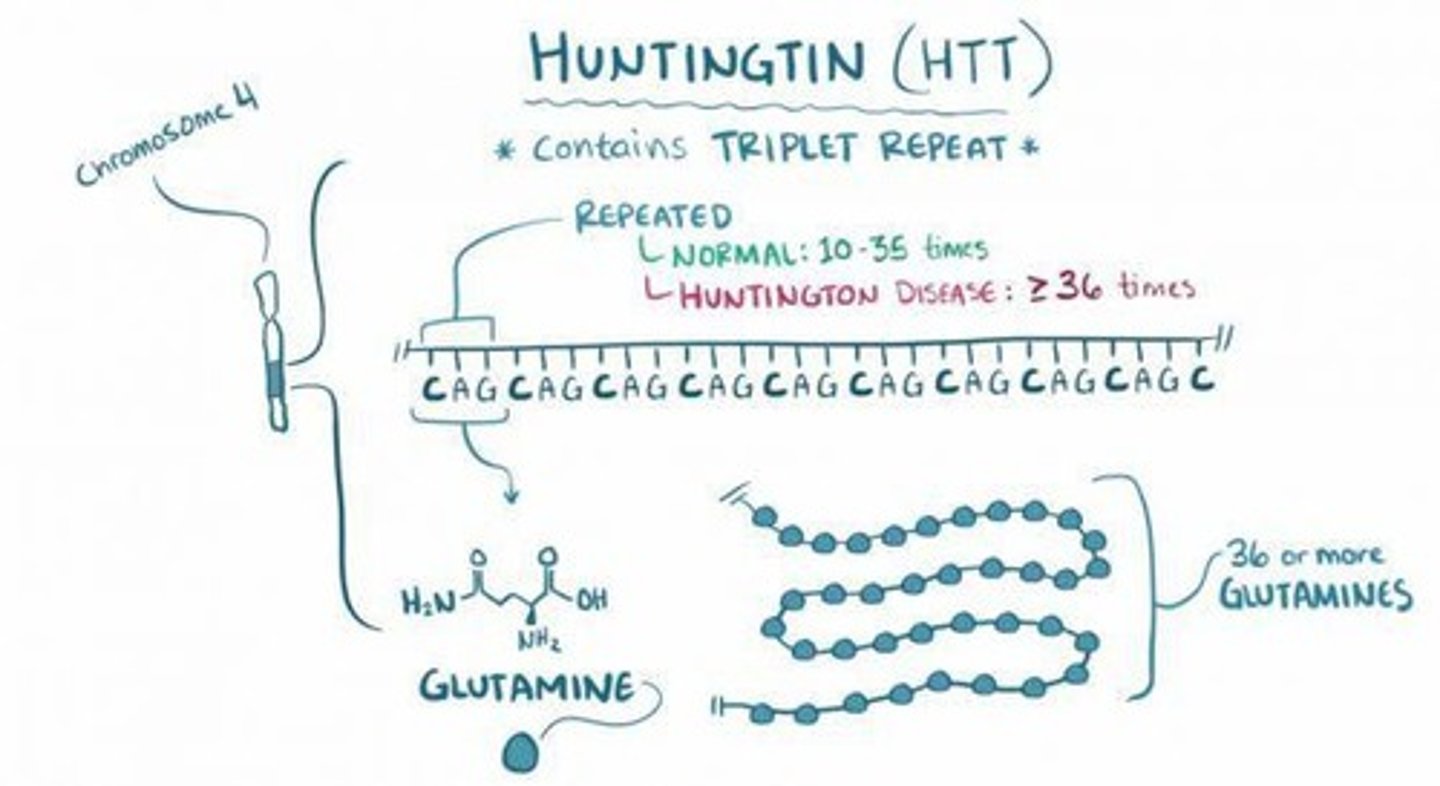
What are trinucleotide expansions?
Trinucleotide expansions are mutations where a sequence of three nucleotides is repeated multiple times, associated with diseases like Huntington's disease and Fragile X syndrome.
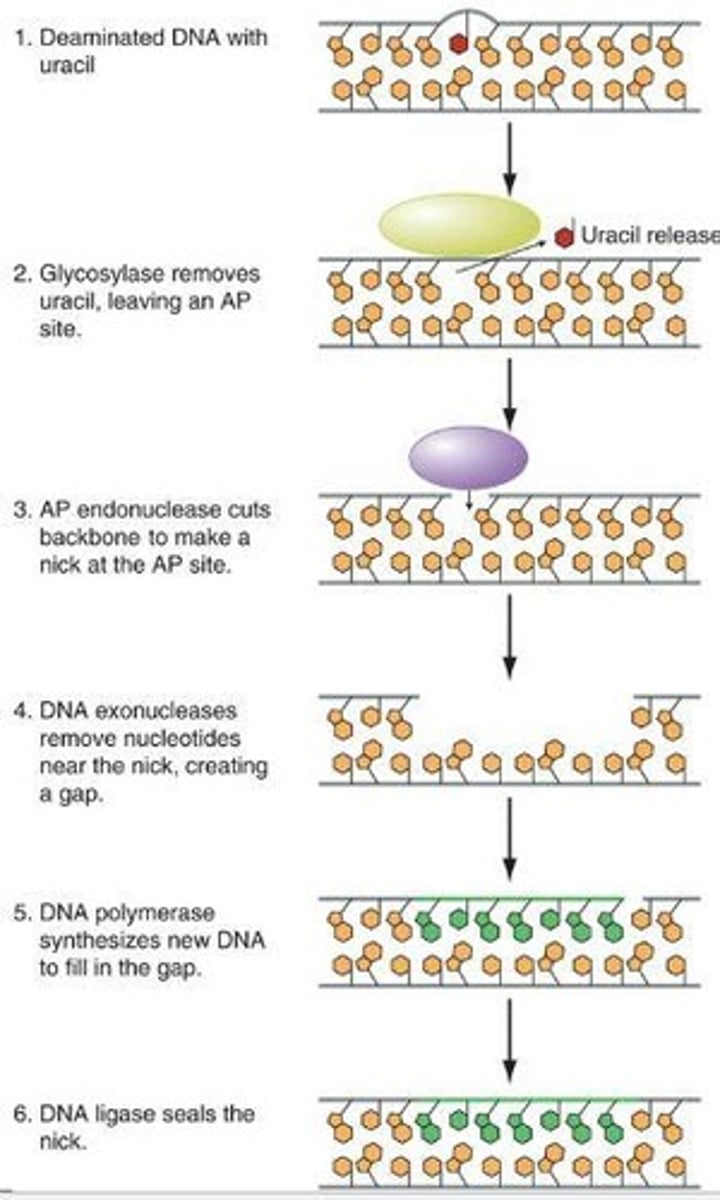
What is base excision repair?
Base excision repair is a DNA repair process that removes and replaces damaged or non-canonical bases in the DNA.
What is nucleotide excision repair?
Nucleotide excision repair is a DNA repair mechanism that removes bulky DNA adducts and replaces them with the correct nucleotides.
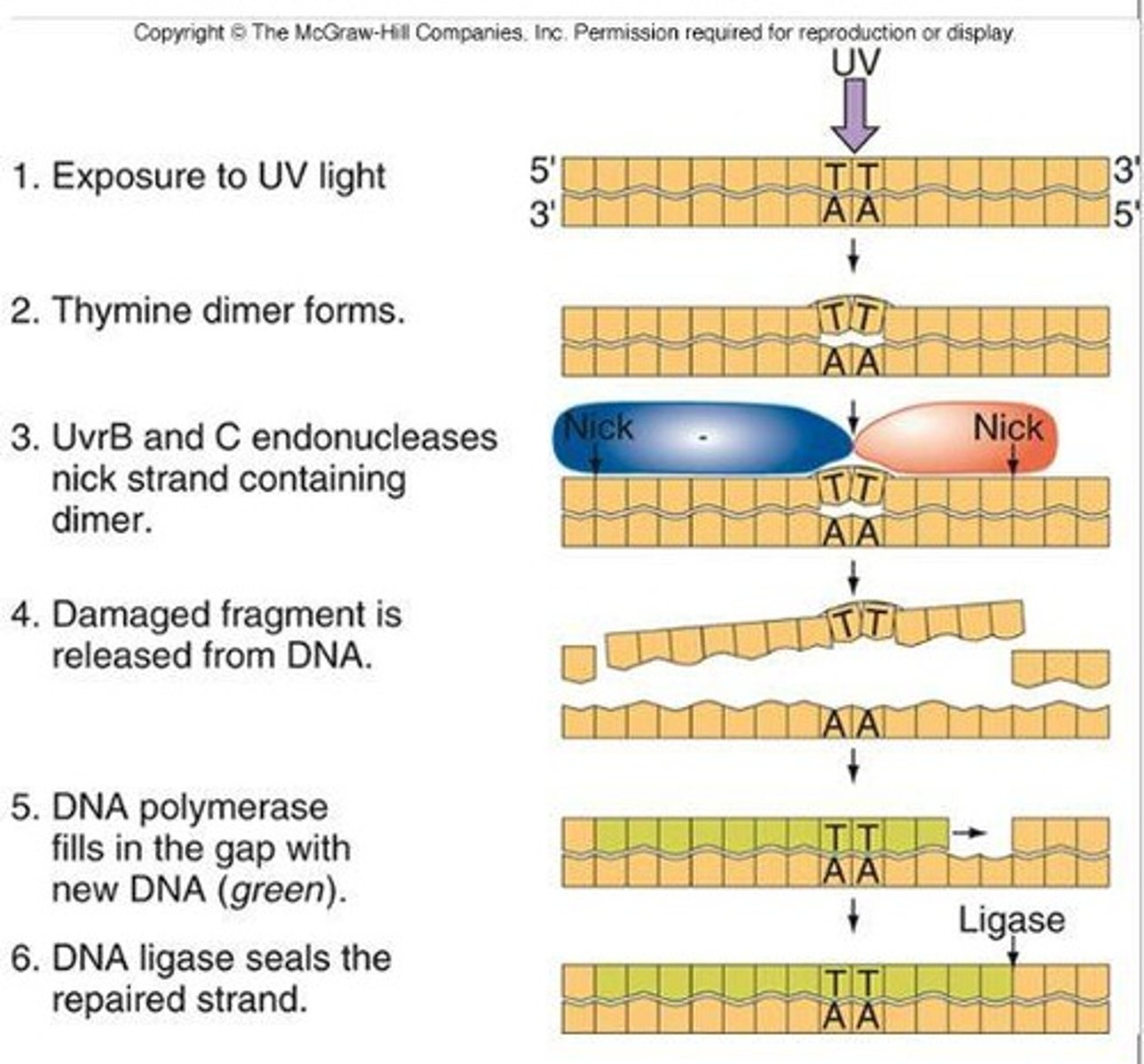
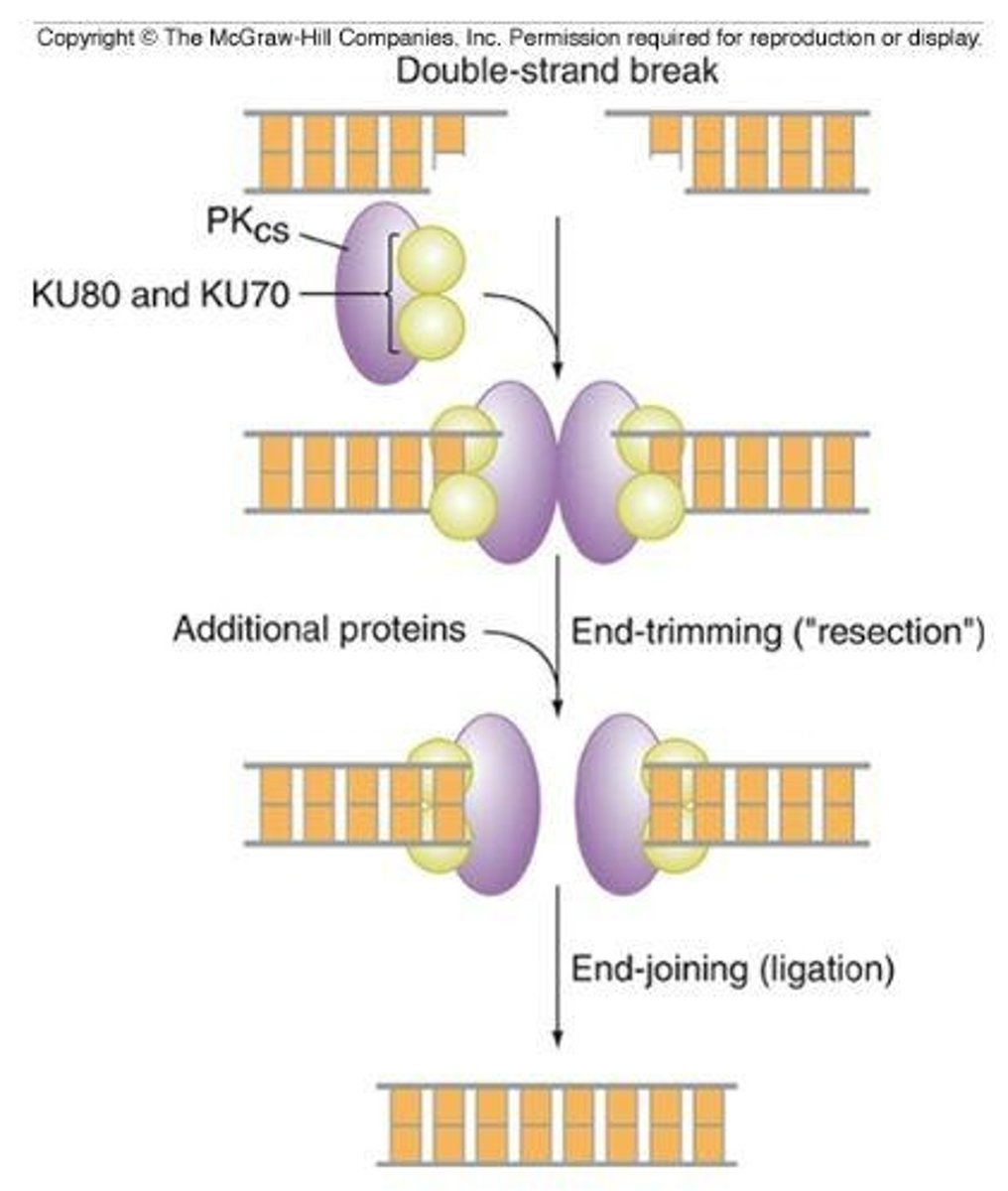
What is non-homologous end joining?
Non-homologous end joining is a DNA repair process that directly joins the ends of broken DNA strands without the need for a homologous template.
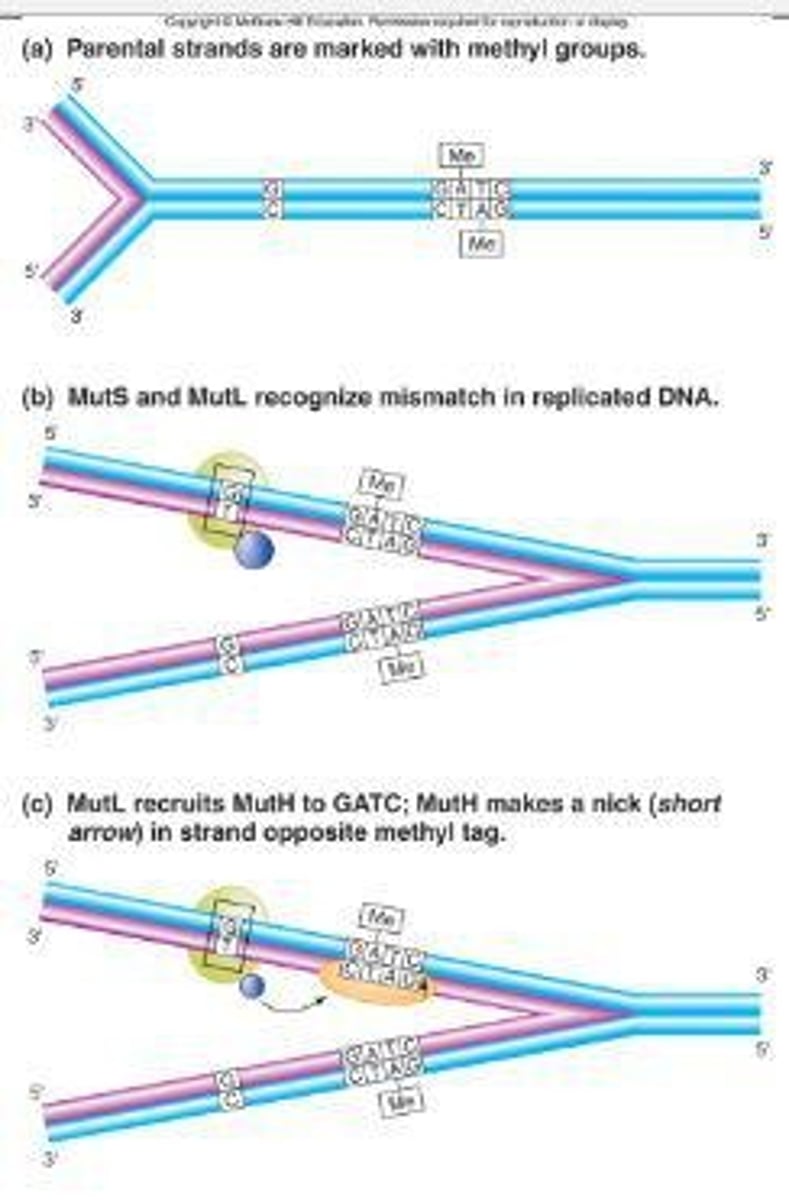
What is methyl-directed mismatch repair?
Methyl-directed mismatch repair is a DNA repair system that corrects mismatches based on the methylation pattern of the parent strand.
How do chemicals cause intercalation?
Chemicals can intercalate by inserting themselves between the base pairs of DNA, disrupting normal base pairing and leading to mutations.
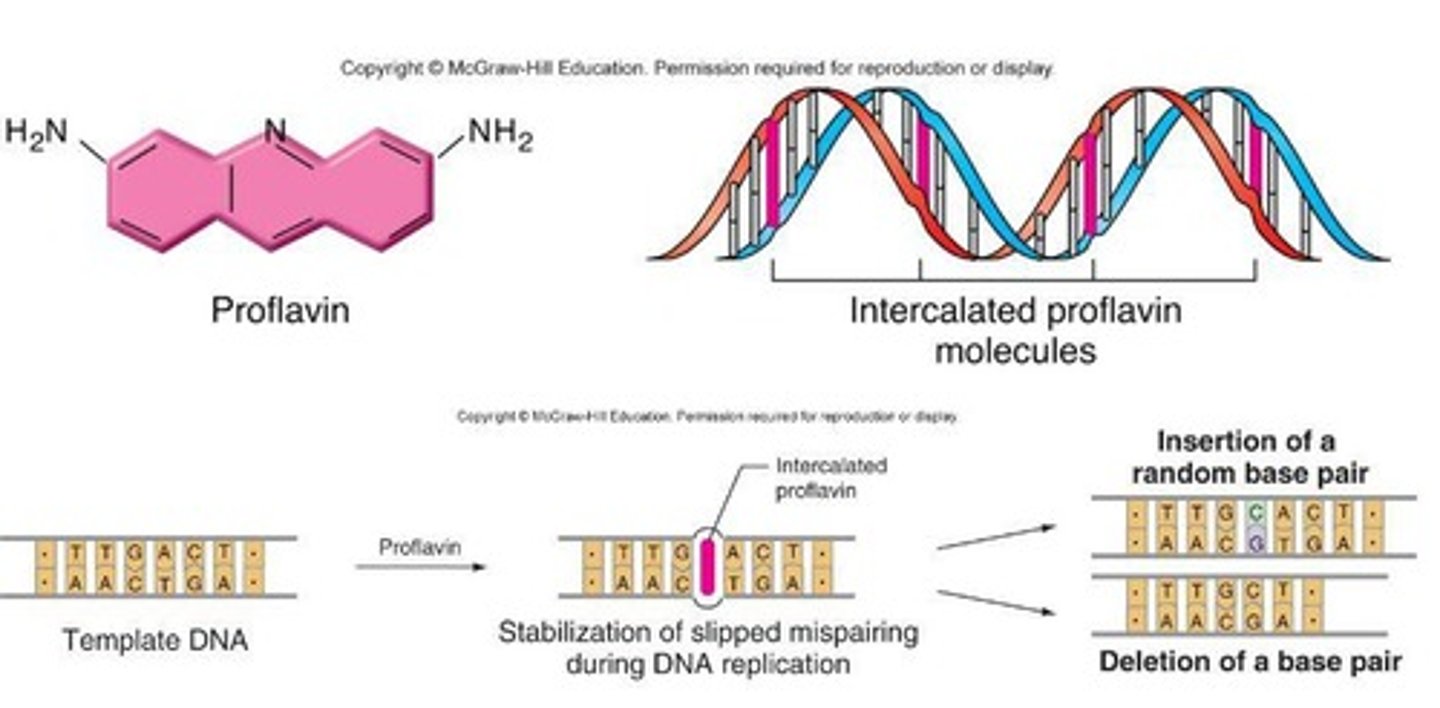
What are two other ways chemicals can alter genetic material?
Chemicals can alter genetic material by replacing bases or modifying base structures and properties.
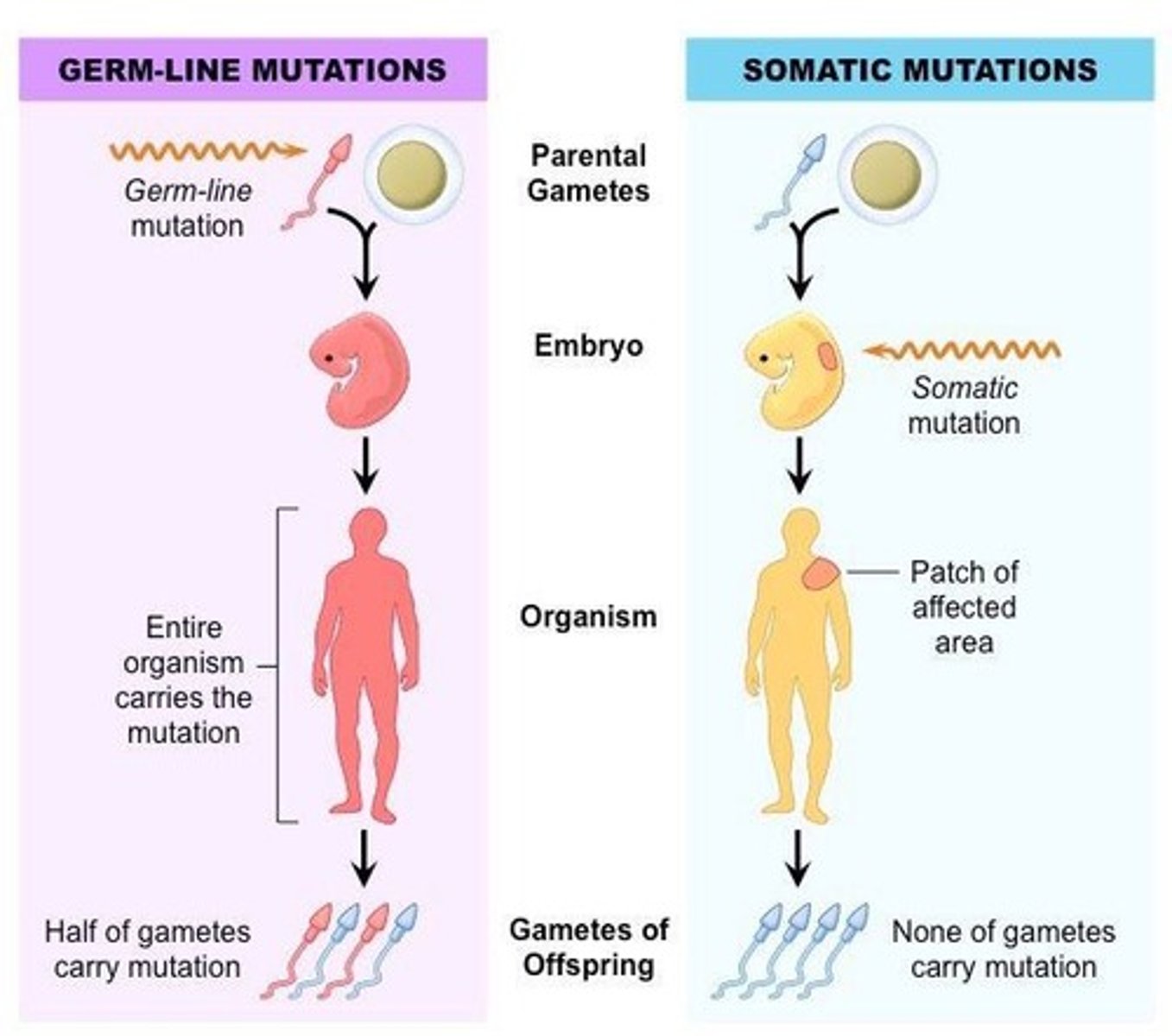
What is the difference between germline and somatic mutations?
Germline mutations occur in reproductive cells and can be passed to offspring, while somatic mutations occur in non-reproductive cells and are not inherited.
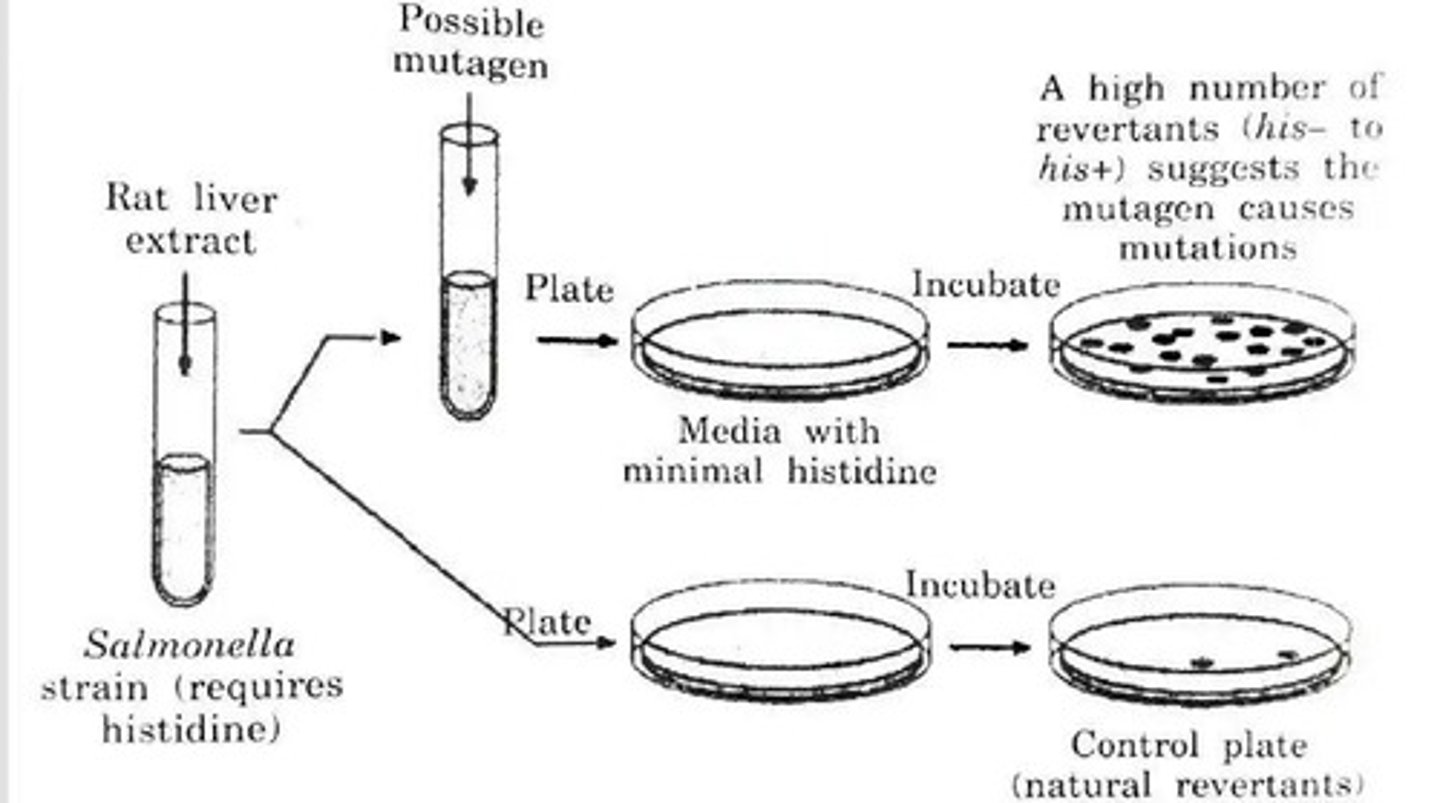
What is the Ames test?
The Ames test is a biological assay that assesses the mutagenic potential of chemical compounds using bacteria; auxotrophs cannot grow without specific nutrients, while prototrophs can.
How many basic amino acids are there?
There are 20 standard amino acids, with 9 considered essential for humans.
What direction do proteins follow during synthesis?
Proteins are synthesized from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, and peptide bonds are formed between amino acids during this process.
What are the levels of protein structure?
The levels of protein structure include primary (amino acid sequence), secondary (alpha helices and beta sheets), tertiary (3D shape), and quaternary (multiple polypeptide chains).
What is the purpose of the Meselson-Stahl Experiment?
The Meselson-Stahl Experiment demonstrated the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication, showing that each new DNA molecule consists of one old and one new strand.
How many replication forks are formed at one origin of replication?
Two replication forks are formed at one origin of replication during DNA replication.
What are the two main DNA polymerases in bacteria?
The two main DNA polymerases in bacteria are DNA polymerase I and DNA polymerase III.
What are the key components involved in crossing over?
Key components in crossing over include homologous chromosomes, the enzyme Spo11, and proteins like Rad51 that facilitate strand invasion and exchange.
What allele ratios indicate gene conversion?
In gene conversion, the expected 2:2 ratio of alleles may deviate to 3:1 or 1:3 due to the conversion process.