Evolution (DAT Booster)
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
Which of the following best defines evolution at a genetic level?
A.The passing of genetic traits from parents to offspring through genes
B.The increase in population size over time
C.Changes in allele frequencies in a population over time
D.An individual adapting to their environment
E.The formation of a new species
C.Changes in allele frequencies in a population over time
Evolution is defined as the gradual changes populations undergo over time. At the genetic level, evolution refers to the change in allele frequencies within a population over generations. These changes in allele frequencies drive evolution, leading to certain genetic traits becoming more or less common.
All of the following are mechanisms of microevolution EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A.Genetic drift
B.Natural selection
C.Gene flow
D.Adaptive radiation
E.Mutation
D.Adaptive radiation
Microevolution involves small changes in allele frequencies within a population over short periods of time. Mechanisms like genetic drift, natural selection, gene flow, and mutation drive these changes, leading to variations in traits within the population. Adaptive radiation is an example of macroevolution, where a single ancestral species gives rise to multiple distinct species, making it the exception in this case.
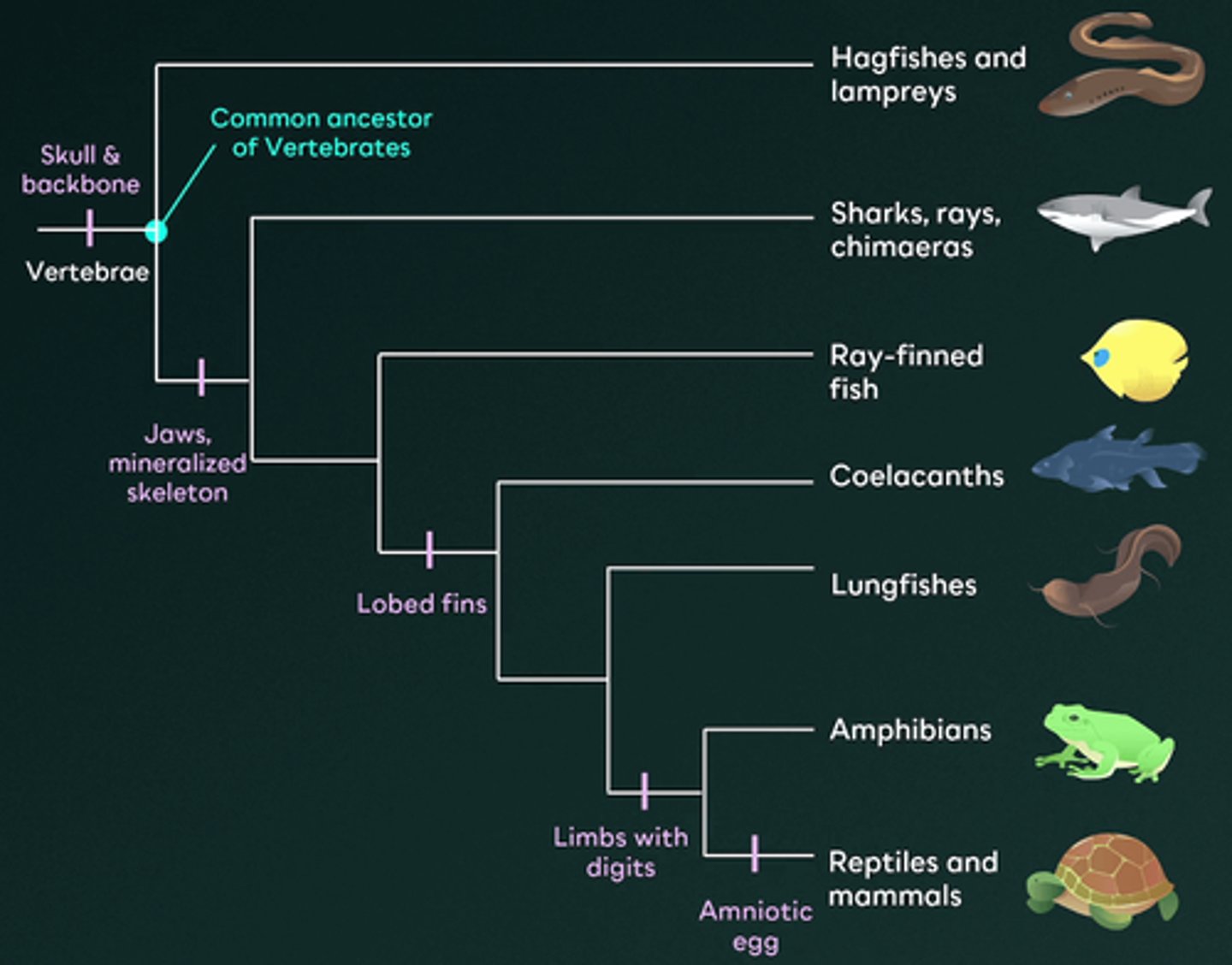
What information can be determined from a phylogenetic tree?
A.The population size of each species
B.Evolutionary relationships among organisms
C.The geographical distribution of species
D.The relationship between organisms within a population
E.The physical traits of all organisms
B.Evolutionary relationships among organisms
A phylogenetic tree illustrates the evolutionary relationships between organisms at the macroevolutionary level. It shows the common ancestors shared by different species and traces the evolutionary paths they have followed over time.

What is the primary benefit of evolution?
A.Increased population size
B.Preservation of original traits
C.Decreased competition among species
D.Increased biodiversity
E.Increased lifespan of all individuals
D.Increased biodiversity
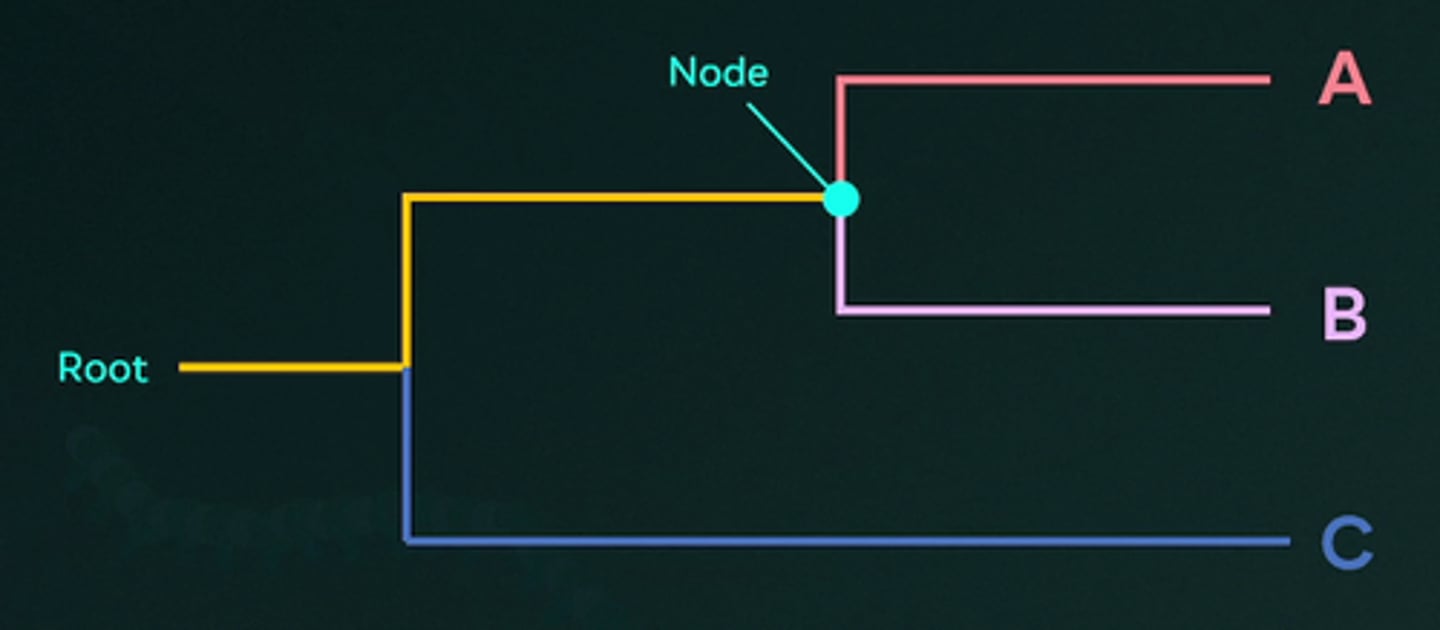
What does a node represent on a phylogenetic tree?
A.The physical traits of an organism
B.A shared trait by different species
C.The geographical location of species
D.The point at which a species went extinct
E.A common ancestor shared by different species
E.A common ancestor shared by different species
A node on a phylogenetic tree represents a common ancestor shared by different species. It indicates the point at which a single lineage splits into two or more lineages, leading to the divergence and branching off of different species.
What is a cladogram primarily based on?
A.Shared characteristics
B.Chronological sequence of evolutionary events
C.Genetic similarities
D.Ecological niche of organisms
E.Behavioral traits
A.Shared characteristics
A cladogram is a visual diagram that represents hypothesized relationships between groups of organisms based on shared characteristics. Unlike phylogenetic trees, cladograms do not provide information about the amount of change or the time scale over which these changes occurred.
Which of the following best describes the composition of Earth's early reducing atmosphere?
A.High levels of oxygen
B.A mixture of inorganic molecules
C.Large amounts of amino acids
D.Abundance of sulfur dioxide
E.Presence of the ozone layer
B.A mixture of inorganic molecules
The early Earth’s atmosphere was made up of gasses released by volcanoes, including hydrogen, ammonia, methane, and water vapor. The atmosphere was highly reducing because it lacked free oxygen. This allowed the molecules to donate electrons easily, promoting the formation of larger compounds that were essential for the development of life later on.
Which of the following best describes Oparin & Haldane's hypothesis regarding the formation of organic molecules on early Earth?
A.Organic molecules were synthesized by early autotrophic organisms
B.Organic molecules formed during the condensation of water vapor
C.Organic molecules were formed spontaneously in the presence of an oxidizing atmosphere
D.Organic molecules were created within volcanic environments
E.Organic molecules formed from inorganic molecules interacting with lightning & UV radiation
E.Organic molecules formed from inorganic molecules interacting with lightning & UV radiation
Oparin and Haldane’s hypothesis suggests that organic molecules formed from inorganic molecules interacting with lighting and UV radiation. Haldane further hypothesized that organic molecules accumulated in Earth’s primordial oceans, forming a “prebiotic soup” that would gradually evolve toward life.
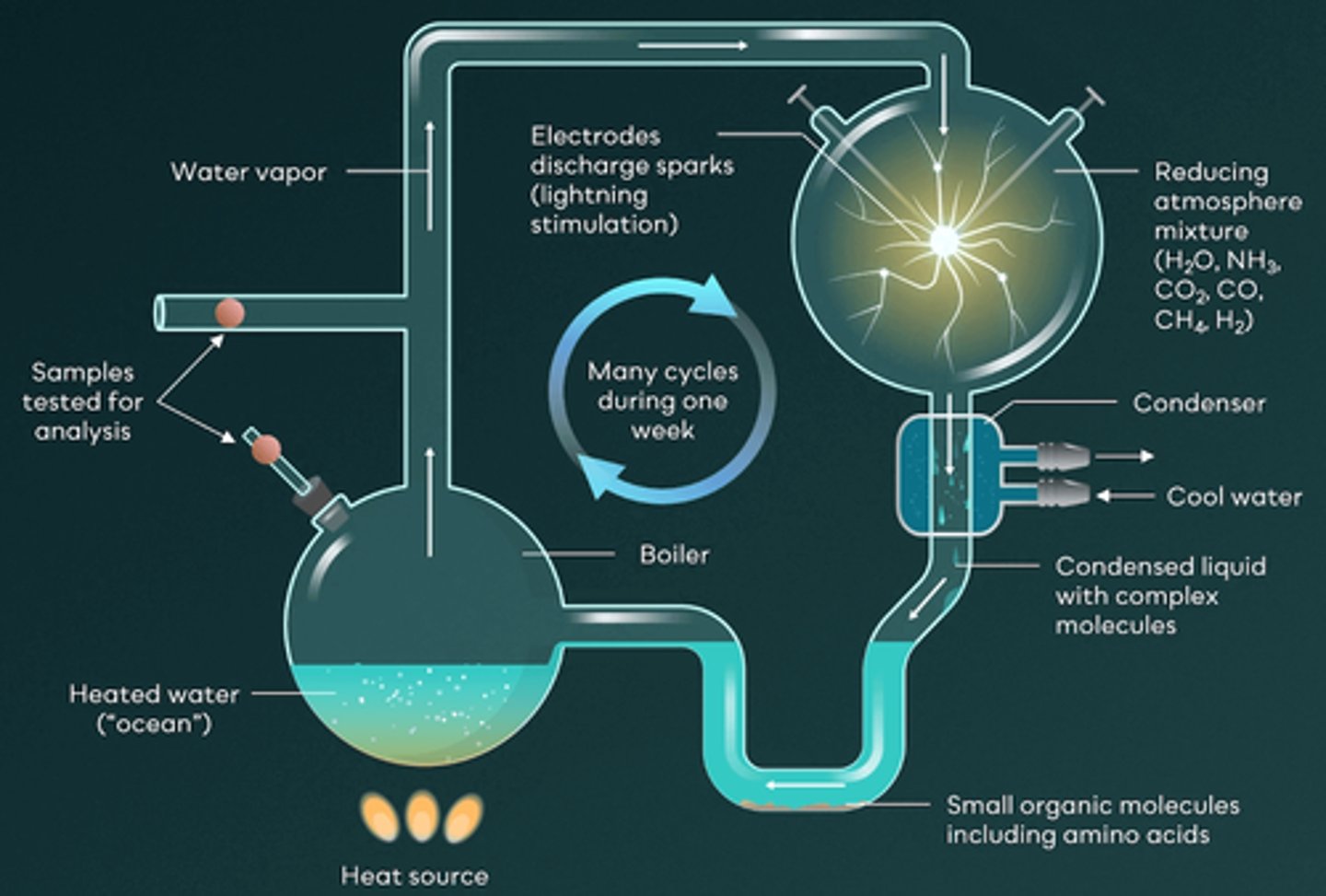
In Miller and Urey's famous experiment, what product formed that confirmed the hypothesis of Oparin and Haldane?
A.Nucleic acids
B.Carbohydrates
C.Amino acids
D.Virus
E.RNA
C.Amino acids
In Miller and Urey’s experiment, they sealed chemicals (ammonia, methane, hydrogen) and water (to mimic the ocean) in a flask and heated it. As the water vaporized, it mixed with the gases to simulate early Earth’s atmosphere. They then introduced electrical sparks to represent lightning as the energy source. Using a condenser, they collected the resulting gas and found that, with the help of the simulated lightning, the inorganic molecules had transformed into organic molecules – specifically amino acids. This experiment and the formation of amino acids provided strong support for the hypothesis about how the earliest organic molecules were formed.
Which of the following were the first living organisms on Earth?
A.Aerobic autotrophic eukaryotes
B.Anaerobic heterotrophic prokaryotes
C.Anaerobic autotrophic prokaryotes
D.Aerobic heterotrophic prokaryotes
E.Aerobic heterotrophic eukaryotes
B.Anaerobic heterotrophic prokaryotes
The first forms of life on Earth were anaerobic heterotrophic prokaryotes. With little to no oxygen available in the Earth’s early atmosphere, these organisms had to be anaerobic. They were also heterotrophic, relying on consuming organic substances for energy, as the more complex pathways used by autotrophs to harness energy from sunlight had not yet evolved. Additionally, they were prokaryotes, which are simpler and evolved earlier than eukaryotes.
What was the significance of the formation of the ozone layer for evolution?
A.Provided organisms with a direct energy source
B.Lowered atmospheric oxygen levels
C.Promoted the evolution of anaerobic organisms
D.Absorbed UV radiation
E.Cooled the Earth's overall temperature
D.Absorbed UV radiation
The ozone layer formed as a result of increasing oxygen levels in the atmosphere, produced by autotrophic prokaryotes as a byproduct of photosynthesis. This oxygen interacted with UV light, leading to the creation of the ozone layer. The ozone layer played a pivotal role in evolution by absorbing harmful UV radiation from the sun, creating a less harsh environment that allowed new forms of life to evolve and thrive on land.
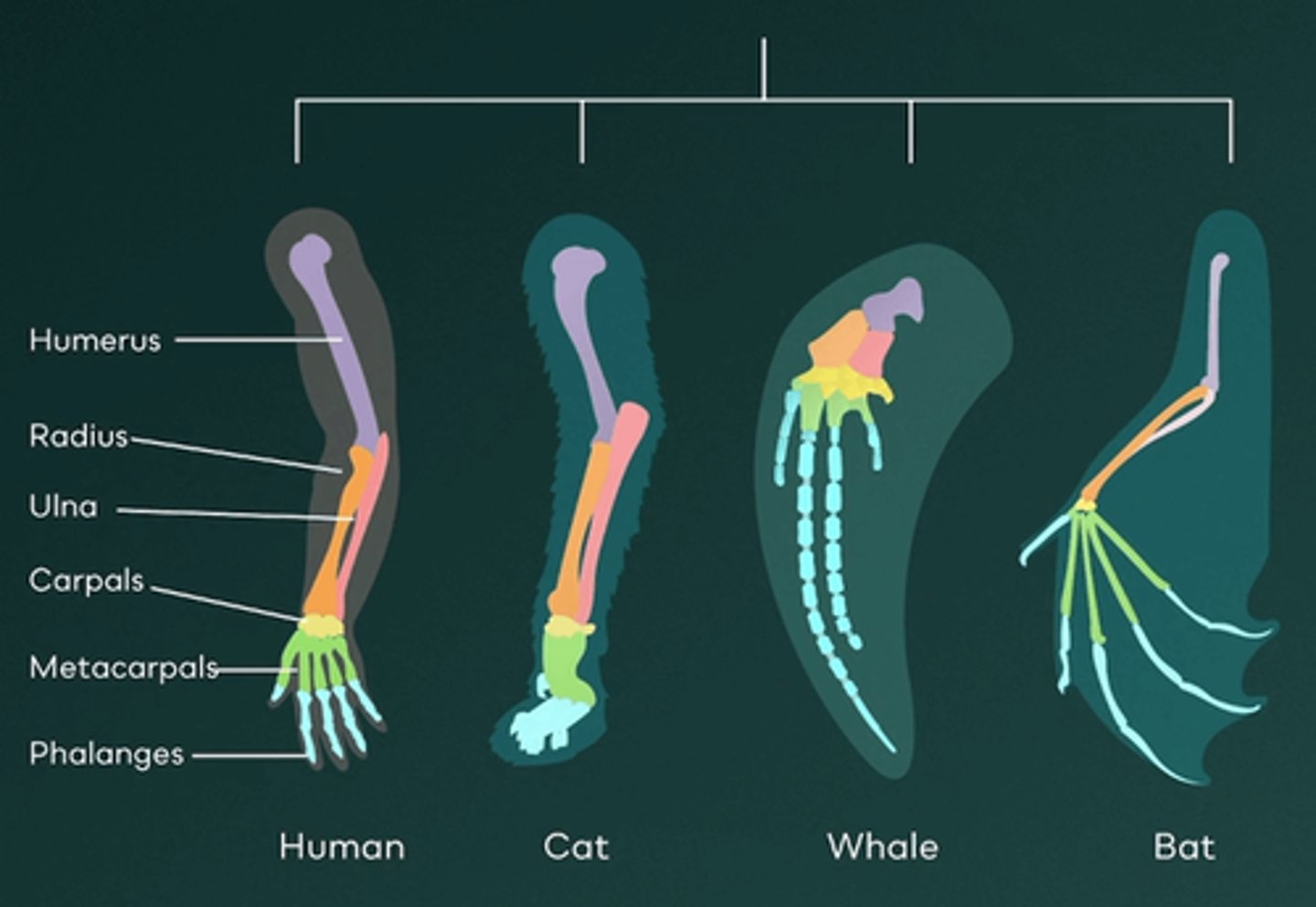
Which of the following is true regarding homologous structures?
A.They develop in unrelated species exposed to similar environments
B.They are only found in mammals
C.They must share the same function
D.They have significant structural differences
E.They have similar underlying anatomy due to a common ancestor
E.They have similar underlying anatomy due to a common ancestor
Homologous structures are anatomical features found in different species that originate from a common ancestor. These features share a similar underlying structure but may serve different functions. For example, a whale’s flipper and a bat’s wing have different functions, but since both are mammals that share a common ancestor, they are considered homologous structures.
Which of the following is an example of analogous structures?
A.Human arm and cat paw
B.Bat wing and whale flipper
C.Whale flipper and fish fin
D.Human hand and chimpanzee hand
E.Cat paw and bat win
C.Whale flipper and fish fin
Analogous structures are anatomical features that have a similar function but do not share a common ancestor. These structures result from similar adaptations to similar environments, but their underlying anatomy is fundamentally different. In this example, a whale’s flipper and a fish’s fin both aid in swimming, but because a whale is a mammal and a fish is an aquatic vertebrate, their underlying structures differ significantly due to their separate evolutionary origins.
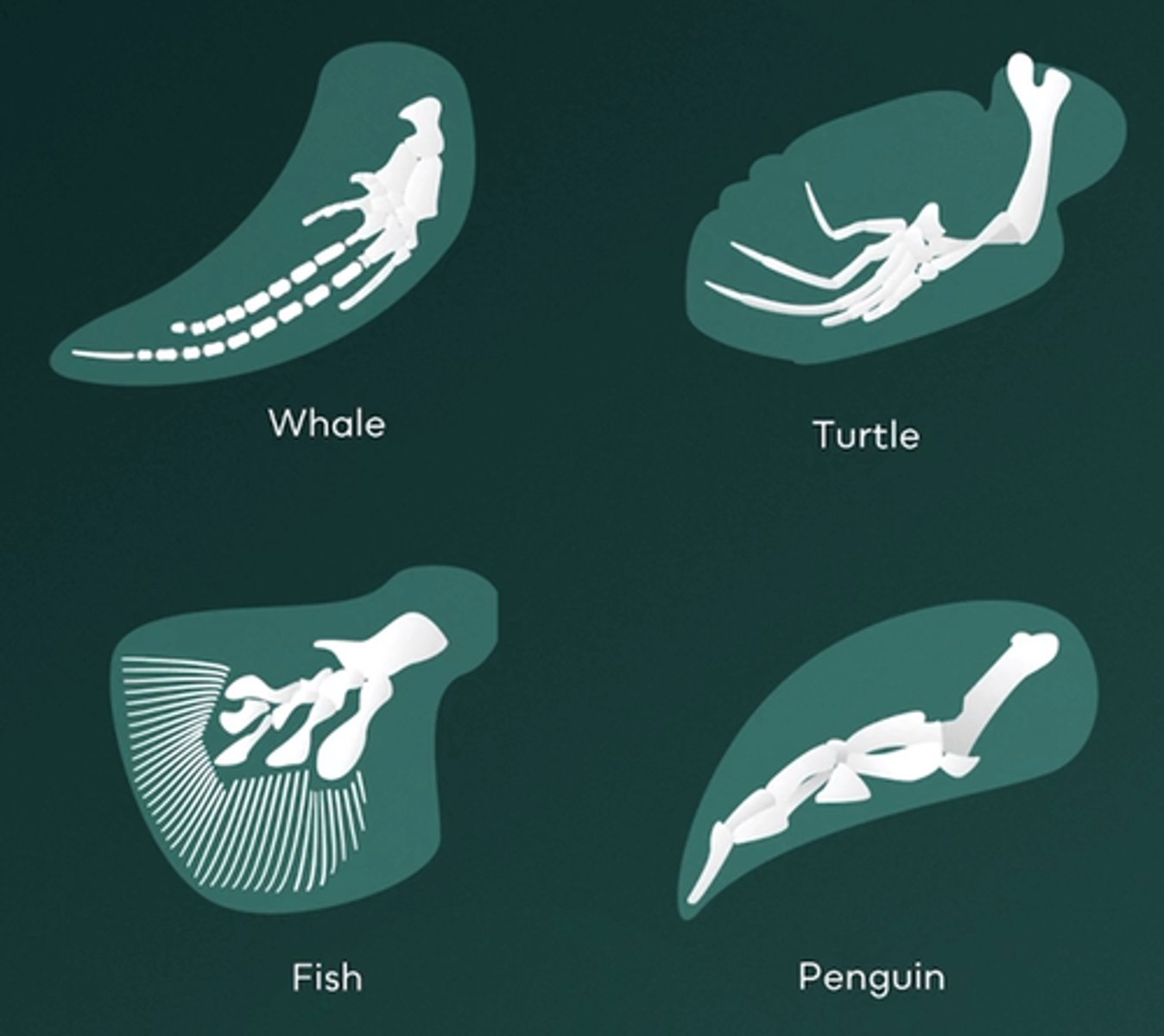
Which of the following is the best definition of a vestigial structure?
A.Structures that are specific to a particular species
B.Structures that perform different functions but have the same anatomical origin
C.Structures that have lost their primary function but were once functional in an ancestor
D.Structures that are vital to an organism's survival
E.Structures that are similar in all species with a shared environment
C.Structures that have lost their primary function but were once functional in an ancestor
Vestigial structures are features that seem to serve no current purpose but had a functional role in ancestors. Examples of vestigial structures in humans include wisdom teeth, the piloerector (goosebump) reflex, and the appendix.
According to Lamarck's theory of evolution, how would a population of elephants develop longer trunks over time?
A.Elephants with naturally longer trunks had better survival rates and reproduced more successfully, leading to longer trunks in future generations
B.A random genetic mutation resulted in elephants with longer trunks
C.A catastrophic event wiped out elephants with shorter trunks, leaving only those with longer trunks to survive and pass on their genes
D.Elephants that frequently stretched and used their trunks to reach food gradually developed longer trunks, passing this trait to their offspring
E.Elephants with shorter trunks eventually died out, leaving only those with longer trunks to survive
D.Elephants that frequently stretched and used their trunks to reach food gradually developed longer trunks, passing this trait to their offspring
Lamarck’s theory, known as the Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics, has been disproven. His theory was based on the concept of "use and disuse," which suggested that traits that were frequently used would develop and strengthen over time while unused traits would diminish. Lamarck believed that these acquired traits could be passed on to offspring. In this example, he would have argued that elephants that used their trunks more would develop longer trunks during their lifetime, and this trait would then be inherited by their offspring.
Which theory suggests that sudden, violent, large-scale events have shaped Earth's geological features and influenced evolution?
A.Natural transformation of species
B.Natural selection
C.Catastrophism
D.Uniformitarianism
E.Genetic flowism
C.Catastrophism
Georges Cuvier proposed the theory of Catastrophism, suggesting that Earth’s history was shaped by major geological catastrophes, such as meteor impacts and super volcanoes. He believed that most changes to Earth occurred through sudden, violent, large-scale events over short periods of time. These catastrophic events led to mass extinctions, drastically altering ecosystems and influencing the course of evolution.
All of the following statements regarding Neo-Darwinism are true EXCEPT for one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A.Selection pressure increases fitness
B.Reproductively advantageous genes are passed on more frequently
C.Competition for resources influences survival
D.Genetic mutations produce variation within a population
E.Individuals adapt via natural selection
E.Individuals adapt via natural selection
Neo-Darwinism combines Darwin’s theory of natural selection with modern genetics – this is the modern understanding of evolution. It explains how genetic mutations create variation within populations and how advantageous genes, rather than traits, are passed onto future generations. Neo-Darwinism also highlights how environmental pressures, like competition, increase fitness and drive population adaptation. The statement that individuals adapt due to natural selection is incorrect. Adaptation and evolution occur over generations at the population level, not within a single individual’s lifetime.
All of the following are considered selection pressures EXCEPTION one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A.Predation
B.Resource scarcity
C.Environmental change
D.Random genetic mutations
E.Introduced species
D.Random genetic mutations
Selection pressures are elements within an environment that prompt organisms to adapt. All of the following are examples of selection pressures, except random genetic mutations, which are not pressures themselves but rather the source of new genetic variation.
What is the source of variations that exist within populations?
A.Differences in alleles
B.Differences in learned behavior
C.Differences in morphology
D.Differences in reproductive strategy
E.Differences in diet
A.Differences in alleles
The source of variation within a population is differences in alleles. Individuals in a population may carry different alleles for the same trait, leading to genetic diversity. Other factors, such as morphology, diet, and reproductive strategies, are influenced by this genetic variation that arises from differences in alleles.
Giraffes with longer necks are able to reach food more effectively than individuals with shorter necks. Over time, giraffes with longer necks are more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to an increased proportion of long-necked individuals in the population. What type of selection is being displayed?
A.Stabilizing
B.Disruptive
C.Use and disuse
D.Artificial
E.Directional
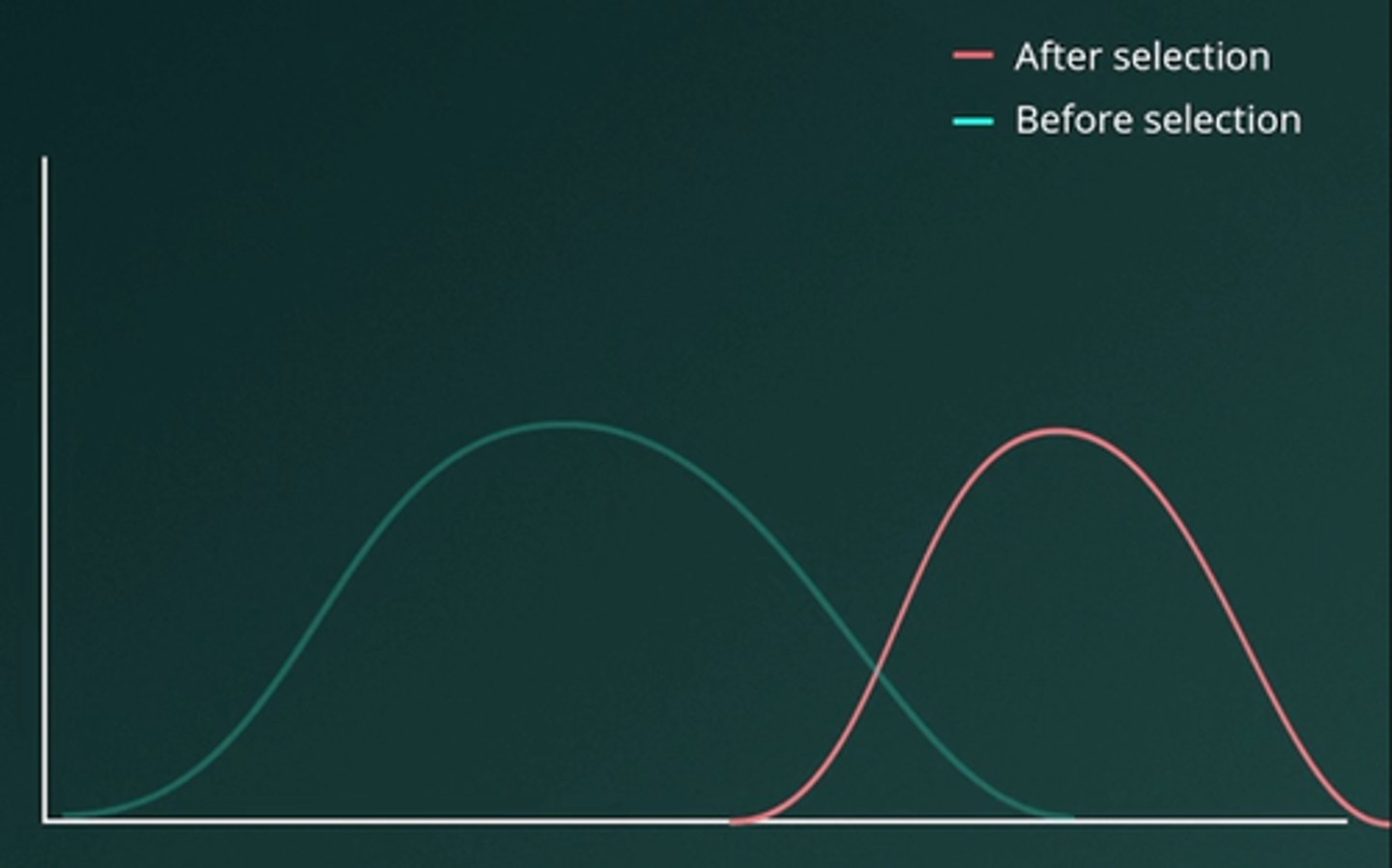
E.Directional
Directional selection occurs when one extreme phenotype is favored, leading to a shift in the population towards that trait. In this example, the giraffe population shows directional selection as the proportion of long-necked individuals increases. Giraffes with longer necks had a survival advantage, allowing them to reproduce and pass on their genes, resulting in more long-necked giraffes over time.
In a species of deer, males have large antlers used for battling over mates, while females do not have antlers. This difference in physical traits between males and females is an example of which concept?
A.Disruptive selection
B.Intersexual selection
C.Speciation
D.Homologous structures
E.Sexual dimorphism
E.Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is a term used to describe differences in the appearance between male and female members of the same species. In this example, males have large antlers, while females do not, which is an example of sexual dimorphism.
Male elephant seals engage in fierce battles with other males to establish dominance and secure control over a group of females. The larger and more aggressive males typically win these contests and gain access to multiple mates. What type of selection is being displayed in this scenario?
A.Disruptive selection
B.Intrasexual selection
C.Stabilizing selection
D.Polygyny selection
E.Intersexual selection
B.Intrasexual selection
Intrasexual selection occurs between individuals of the same sex competing for access to mating opportunities. The scenario describes direct competition among male elephant seals for access to females, making this an example of intrasexual selection. Intrasexual selection is more commonly seen in males and allows the stronger males to reproduce and pass on their genes.
While studying in the Galápagos, Darwin observed that finches with small beaks were better at handling soft seeds, while finches with large beaks were better at cracking hard seeds. Finches with medium-sized beaks were less efficient at either task or had lower survival rates. What type of selection is being displayed in this scenario?
A.Disruptive selection
B.Directional selection
C.Intrasexual selection
D.Stabilizing selection
E.Intersexual selection
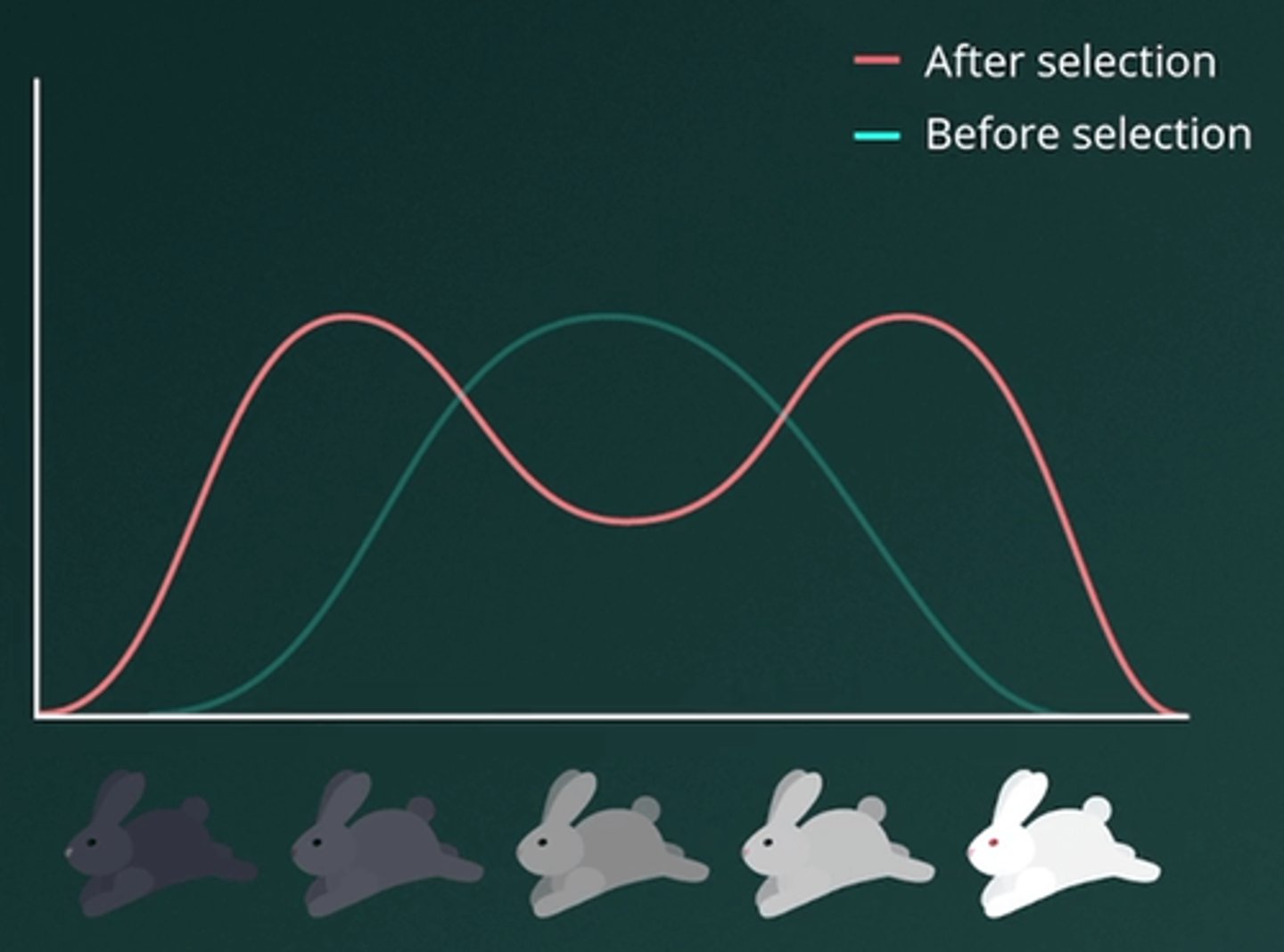
A.Disruptive selection
Disruptive selection occurs when individuals with extreme traits on both ends of the spectrum are favored over those with intermediate traits. In this example, Darwin observed that finches with either small or large beaks were more successful at gathering food, while medium-beaked finches had lower survival rates. This scenario illustrates disruptive selection, where the two extreme traits (small and large beaks) are favored, leading to their increased prominence in the population.
Which of the following individuals has the highest fitness?
A.A bird that lays 4 eggs, all of which live to adulthood
B.A rabbit that produces 12 offspring, with 6 surviving to adulthood
C.A frog that lays 300 eggs, with 100 surviving to adulthood
D.A fish that lays 500 eggs, with 200 surviving to adulthood
E.A bear that has one offspring, which lives to adulthood
D.A fish that lays 500 eggs, with 200 surviving to adulthood
Which of the following best defines allele frequency?
A.The total number of alleles present in a population
B.The percentage of homozygous individuals in a population
C.The proportion of a certain allele in a population
D.The number of offspring born each year in a population
E.The rate at which new alleles are introduced into a population
C.The proportion of a certain allele in a population
Allele frequency refers to how often a certain version of a gene (allele) occurs in a population. A higher allele frequency means that the version of the gene is more common in the population. Note that different versions of a gene are called alleles, and all the alleles present in a population make up the gene pool.
A small group of squirrels from a larger population migrate to a previously uninhabited area to establish a new colony. What is this an example of?
A.Natural selection
B.Gene flow
C.Bottleneck effect
D.Non-random mating
E.Founder effect
E.Founder effect
The founder effect is a form of genetic drift that occurs when a small group of individuals becomes separated from a larger population and establishes a new population. This new population often has reduced genetic diversity compared to the original group. In the example, the small group of squirrels migrating to a new area to form a new colony describes the founder effect.
A few blue butterflies leave their population and join a nearby population of yellow butterflies. They breed with the yellow butterflies and stay in the new population. What is this an example of?
A.Genetic drift
B.Founder effect
C.Gene flow
D.Natural selection
E.Bottleneck effect
C.Gene flow
Gene flow refers to the movement of alleles between populations due to migration. In this example, the blue butterflies migrate to a neighboring population of yellow butterflies, and by breeding with them, they introduce new alleles into the population. This example illustrates gene flow, as it describes the movement of individuals and their genetic material between populations.
A forest fire wipes out half of a deer population, reducing its genetic diversity and causing a significant shift in allele frequencies due to the loss of many individuals. What does this scenario best illustrate?
A.Gene flow
B.Founder effect
C.Natural selection
D.Disruptive selection
E.Bottleneck effect
E.Bottleneck effect
The bottleneck effect is a type of genetic drift that occurs when a population undergoes a significant reduction in size due to a natural catastrophe. These events often result in a shift in allele frequencies and a decrease in genetic diversity as individuals and their alleles are lost. In this example, the deer population loses half of its members due to a forest fire, making it an example of the bottleneck effect.
Which population would genetic drift impact the most?
A.A population of 20 sheep
B.A population of 500 deer
C.A population of 1000 birds
D.A population of 20,000 fish
E.A population of 500,000 ants
A.A population of 20 sheep
Genetic drift is the random fluctuation of allele frequencies due to chance events in a single population. The smaller the population, the greater the impact of genetic drift. Larger populations can better withstand random fluctuations in allele frequencies, while smaller populations are much more affected by these changes. In this question, the population of 20 sheep will be impacted by genetic drift the most due to their small population size.
How does diploidy contribute to genetic variation within a population?
A.It minimizes the effects of mutations
B.It allows for the expression of only dominant alleles
C.It allows organisms to carry a second set of genetic information
D.It eliminates harmful alleles
E.It ensures all individuals express the same traits
C.It allows organisms to carry a second set of genetic information
Diploidy refers to the presence of two copies of each gene in an organism. It contributes to genetic variation by allowing individuals to carry two sets of genetic information. This enables recessive alleles to be carried without being expressed in heterozygous individuals, preserving genetic diversity. Additionally, this increases the potential for variation within the population if environmental conditions change and favor different traits.
In a population of worms, an uncommon recessive allele that causes yellow coloration helps these worms evade predation by birds, which usually identify the dominant, brown-colored worms. As yellow worms become more common and birds adapt to recognizing them, brown worms start to survive better. What is this scenario an example of?
A.Genetic drift
B.Heterozygous advantage
C.Disruptive selection
D.Frequency-dependent selection
E.Bottleneck effect
D.Frequency-dependent selection
In this scenario, frequency-dependent selection is described, which is a type of balanced polymorphism. Balanced polymorphism refers to the maintenance of multiple alleles in a population, with each allele being advantageous under certain conditions. In frequency-dependent selection, the fitness of a particular phenotype changes based on how common it is. Initially, when yellow worms were rare, birds were more accustomed to hunting the more common brown worms. As the brown worms decreased and the yellow worms became more numerous, the birds adapted to hunting yellow worms. This is an example of frequency-dependent selection, where the advantage of being yellow-colored shifted as their frequency increased.
Which of the following leads to the greatest amount of genetic variation in a population?
A.Balanced polymorphism
B.Natural selection
C.Bottleneck effect
D.Inbreeding
E.Founder effect
A.Balanced polymorphism
Of all the options, balanced polymorphism is the only one that directly promotes genetic variation. Balanced polymorphism works by maintaining multiple alleles in a population, as having both alleles can provide an advantage. This allows diverse alleles to persist in the gene pool. In contrast, processes like natural selection, the bottleneck effect, inbreeding, and the founder effect usually reduce genetic variation
How does the fast reproduction rate of prokaryotes lead to increased genetic variation within their population?
A.Allows for mutations to accumulate quickly
B.More sexual reproductive opportunities
C.Reduces the occurrence of harmful mutations
D.Results in more frequent mitosis
E.Prevents inbreeding from occurring
A.Allows for mutations to accumulate quickly
A faster reproduction rate contributes to genetic variation because more generations in a shorter time frame lead to a higher number of mutations. Since prokaryotes reproduce rapidly, any mutations that occur are passed onto future generations, causing mutations to accumulate quickly. This increase in mutations directly enhances genetic variation within a population. Prokaryotes are also subject to natural selection more rapidly due to their shorter lifespan and higher reproductive rates, and their large population sizes can further increase their genetic variation.
Which of the following best describes hybrid vigor?
A.It is the breeding of two individuals, both of whom carry genetic mutations
B.It is the breeding of closely related individuals to maintain genetic purity
C.It leads to offspring that are weaker and more prone to genetic disorders due to genetic incompatibility
D.It is the crossbreeding of two different individuals that results in sterile offspring
E.It is outbreeding that results in higher quality offspring with superior traits compared to either parent species
E.It is outbreeding that results in higher quality offspring with superior traits compared to either parent species
Hybrid vigor, also called heterosis, refers to the phenomenon where the offspring of genetically diverse parents exhibit superior traits compared to either parent individually. In other words, outbreeding leads to higher quality offspring. A common example of hybrid vigor is seen in mules, the hybrid offspring of a female horse and a male donkey, two genetically distinct species. Their combination of traits makes them more useful than either parent species alone.
All of the following are requirements for the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A.Large population size
B.No mutations
C.Random mating
D.Natural selection
E.No gene flow
D.Natural selection
The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium describes a state of genetic equilibrium within a population, where allele and genotype frequencies remain constant from one generation to the next. The five conditions for maintaining genetic equilibrium are a large population size, random mating, no mutations, no gene flow, and no natural selection. These conditions are the opposite of those required for evolution, and if any are not met, the population is no longer in genetic equilibrium, as evolution is taking place.
In a population of rabbits, the allele for black fur is dominant over the allele for white fur. If the frequency of the recessive allele is 0.30, what is the percentage of homozygous dominant individuals in the population?
A.0.09
B.0.21
C.0.42
D.0.49
E.0.70
D.0.49

In a population of beetles, green is the dominant color, and red is recessive. If the frequency of the red allele is 0.40, what is the proportion of heterozygous individuals?
A.0.16
B.0.24
C.0.36
D.0.48
E.0.60
D.0.48

A population of flowers has different colors: the homozygous dominant are white, the heterozygotes are pink, and the homozygous recessive are red. If there are 122 white, 46 pink, and 32 red flowers, what is the frequency of the recessive allele?
A.0.16
B.0.36
C.0.40
D.0.48
E.0.60
C.0.40

In dogs, short hair is dominant, while long hair is recessive. In a population of 200 dogs, the percentage of long-haired (homozygous recessive) dogs is 0.64. What is the frequency of the dominant allele in this population?
A.0.04
B.0.20
C.0.32
D.0.40
E.0.80
B.0.20

In beetles, green shells are dominant, while yellow shells are recessive. In a population of 1000 beetles, 0.49 of the beetles have yellow shells (homozygous recessive). How many beetles in the population are heterozygous?
A.90
B.300
C.420
D.490
E.700
C.420

All of the following are prezygotic isolation mechanisms EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A.Differences in mating behaviors
B.Physical incompatibility during mating attempts
C.Offspring that fails to develop properly after fertilization
D.Mating in different habitats
E.Inability of sperm to fertilize the egg
C.Offspring that fails to develop properly after fertilization
Reproductive isolation mechanisms are classified into two categories: prezygotic and postzygotic isolation. Prezygotic isolation prevents the formation of a zygote, meaning fertilization does not occur. In contrast, postzygotic isolation occurs after a zygote has formed but there are mechanisms that prevent the zygote from developing properly or reproducing successfully. In option C, the zygote forms but fails to develop properly, making this an example of postzygotic isolation, not prezygotic.
Which of the following is an example of temporal isolation?
A.Two species of squirrels are separated by a mountain range
B.Two species of frogs live in the same habitat, but one breeds in the spring and the other breeds in the summer
C.Two species of birds have different courtship dances to attract mates, preventing them from mating
D.Two breeds of dogs have different body sizes and structures, preventing successful mating between them
E.Two species of fish inhabit the same pond, but are unable to breed because their sperm and eggs are incompatible due to differences in proteins
B.Two species of frogs live in the same habitat, but one breeds in the spring and the other breeds in the summer
Temporal isolation is a form of prezygotic isolation that prevents two species from mating because they are active or reproduce at different times. This can involve species that mate in different seasons or at different times of day. Option B describes temporal isolation, as the frogs share the same habitat but do not breed together due to differences in their mating seasons.
A horse and a donkey mate and produce a mule, a strong and viable hybrid. Although the mule is physically healthy and possesses beneficial traits, it is unable to produce offspring when bred with another mule. What type of reproductive isolation mechanism does this describe?
A.Gametic isolation
B.Mechanical isolation
C.Hybrid sterility
D.Hybrid inviability
E.Hybrid breakdown
C.Hybrid sterility
When a horse and a donkey mate, they produce a hybrid offspring known as a mule. Mules are physically healthy and live to adulthood, however they cannot reproduce with each other. The inability of the hybrid offspring to reproduce with each other is an example of postzygotic isolation known as hybrid sterility.
Two different species of grasshoppers successfully mate, producing viable and fertile hybrid offspring. However, when the hybrid offspring mate with each other, the second-generation offspring show reduced fitness and are unable to reproduce. What type of reproductive isolation mechanism does this describe?
A.Gametic isolation
B.Hybrid sterility
C.Mechanical isolation
D.Hybrid inviability
E.Hybrid breakdown
E.Hybrid breakdown
Two different species of grasshoppers successfully mate, producing viable and fertile hybrid offspring. However, when these hybrids mate, their second-generation offspring have reduced fitness and are unable to reproduce. This is an example of hybrid breakdown, a postzygotic isolation mechanism where the first-generation hybrids are fertile, but subsequent generations experience reproductive issues, leading to the breakdown of future viability and fertility.
A population of lions and a population of panthers inhabit the same desert. The lions use loud roaring as a mating ritual, while the panther population signals readiness to mate with specific tail movements. Due to these differences in mating rituals, the two populations do not interbreed. What type of isolation mechanism is this?
A.Behavioral isolation
B.Mechanical isolation
C.Temporal isolation
D.Gametic isolation
E.Habitat isolation
A.Behavioral isolation
A population of lions and a population of panthers live in the same habitat but do not interbreed because of differences in their mating rituals. This is an example of a prezygotic barrier called behavioral isolation. In behavioral isolation, species or populations are prevented from mating due to differences in behaviors, such as mating calls, displays, or rituals, that signal readiness to mate. Even though they occupy the same space, these differences in mating behavior prevent them from interbreeding. Mating rituals are important to ensure that only members of the same species attempt to mate.
Sympatric speciation can occur due to all of the following EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A.Geographical isolation
B.Polyploidy
C.Sexual selection
D.Habitat differentiation
E.Behavioral isolation
A.Geographical isolation
Sympatric speciation occurs when a single species splits into two without the presence of a physical or geographical barrier. Factors such as sexual selection, polyploidy, and habitat differences can drive sympatric speciation. If a geographical barrier were involved, leading to speciation, this would be classified as allopatric speciation, also known as geographic speciation.
Which of the following best defines adaptive radiation?
A.The continuous increase in population size of a single species without any evolutionary changes
B.The gradual accumulation of mutations in a population over time leads to a new species
C.The development of similar traits in unrelated species due to similar environmental pressures
D.Environmental pressures cause the rapid evolution of multiple species from a single ancestor, allowing them to adapt to different niches
E.When two separate species are able to mate and merge into a single population
D.Environmental pressures cause the rapid evolution of multiple species from a single ancestor, allowing them to adapt to different niches
Adaptive radiation is a pattern of rapid evolution that occurs when a species is introduced to a new habitat or faces new environmental pressures. The new environment, with its diverse resources and niches, leads the original species to diversify into multiple species, each adapted to different aspects of the new environment.
In a population of polar bears, the sea ice that they inhabit splits, separating the population into two groups. Over time, as the polar bears adapt to their new environments, they accumulate changes that prevent them from mating with each other even if they come into contact again. What scenario does this describe?
A.Allopatric speciation
B.Genetic drift
C.Sympatric speciation
D.Temporal isolation
E.Adaptive radiation
A.Allopatric speciation
In this scenario, the population of polar bears becomes geographically separated and develops changes that prevent them from mating, resulting in reproductive isolation and the formation of new species. Since this speciation is caused by geographic separation from the ice break, it is an example of allopatric speciation.
In a forest, a population of moths consists of both light and dark-colored individuals. The moths develop a mating preference for others of the same color. Over time, this leads to reproductive isolation between the two color groups. What does this describe?
A.Allopatric speciation
B.Sympatric speciation
C.Mechanical isolation
D.Adaptive radiation
E.Temporal isolation
B.Sympatric speciation
Sympatric speciation occurs when a single species splits into two new species without a geographic barrier. In this case, the population of moths develops a mating preference based on color, leading to reproductive isolation between the light and dark-colored groups. This sexual selection isolation prevents interbreeding and eventually results in the formation of two distinct species. The example described sympatric speciation, as the reproductive isolation occurs without any physical separation between the groups.
In a population of tulips, a mutation during cell division results in some tulips having double the normal number of chromosomes. These tulips can no longer breed with those that have the normal number of chromosomes. What type of speciation mechanism does this describe?
A.Hybrid inviability
B.Sexual selection
C.Hybrid breakdown
D.Polyploidy
E.Habitat differentiation
D.Polyploidy
Polyploidy occurs when an organism has more than the typical two sets of chromosomes. This can lead to sympatric speciation because individuals with polyploidy become genetically incompatible with those that have the normal number of chromosomes, causing reproductive isolation and eventually speciation. In this scenario, the tulips with polyploidy cannot breed with those that have a normal chromosome count and would only be able to breed with other tulips that have the same type of polyploidy, leading to speciation. Note that speciation due to polyploidy occurs primarily in plants, as most organisms with polyploidy are not viable.
The sugar glider and the flying squirrel do not share a common ancestor but have developed similar traits, such as gliding membranes, due to similar environments. The development of these similar traits, despite being unrelated, is known as __________.
A.Convergent evolution
B.Parallel evolution
C.Coevolution
D.Gradualism
E.Divergent evolution
A.Convergent evolution
Convergent evolution occurs when unrelated species, without a recent common ancestor, independently evolve similar traits due to adaptation to similar environments. In this example, the sugar glider and flying squirrel, which do not share a common ancestor, both developed gliding membranes that help them move between dense trees to avoid predators.
Cheetahs have evolved into exceptionally fast predators, able to sprint at high speeds to catch prey such as gazelles. In turn, gazelles have evolved to become faster and more agile to evade cheetahs, with only the fittest gazelles surviving. This continual back-and-forth adaptation between cheetahs and gazelles is an example of ________.
A.Convergent evolution
B.Mutualism
C.Parallel evolution
D.Coevolution
E.Divergent evolution
D.Coevolution
The ongoing back-and-forth adaptation between cheetahs and gazelles is an example of coevolution in a predator-prey relationship. Coevolution occurs when adaptations in one species drive adaptations in another. In this case, gazelles have evolved to become faster and more agile to evade cheetahs. In response, cheetahs must adapt to maintain their ability to catch the swift gazelles. Coevolution is commonly observed in predator-prey relationships, as both species must continuously adapt to each other in order to survive.
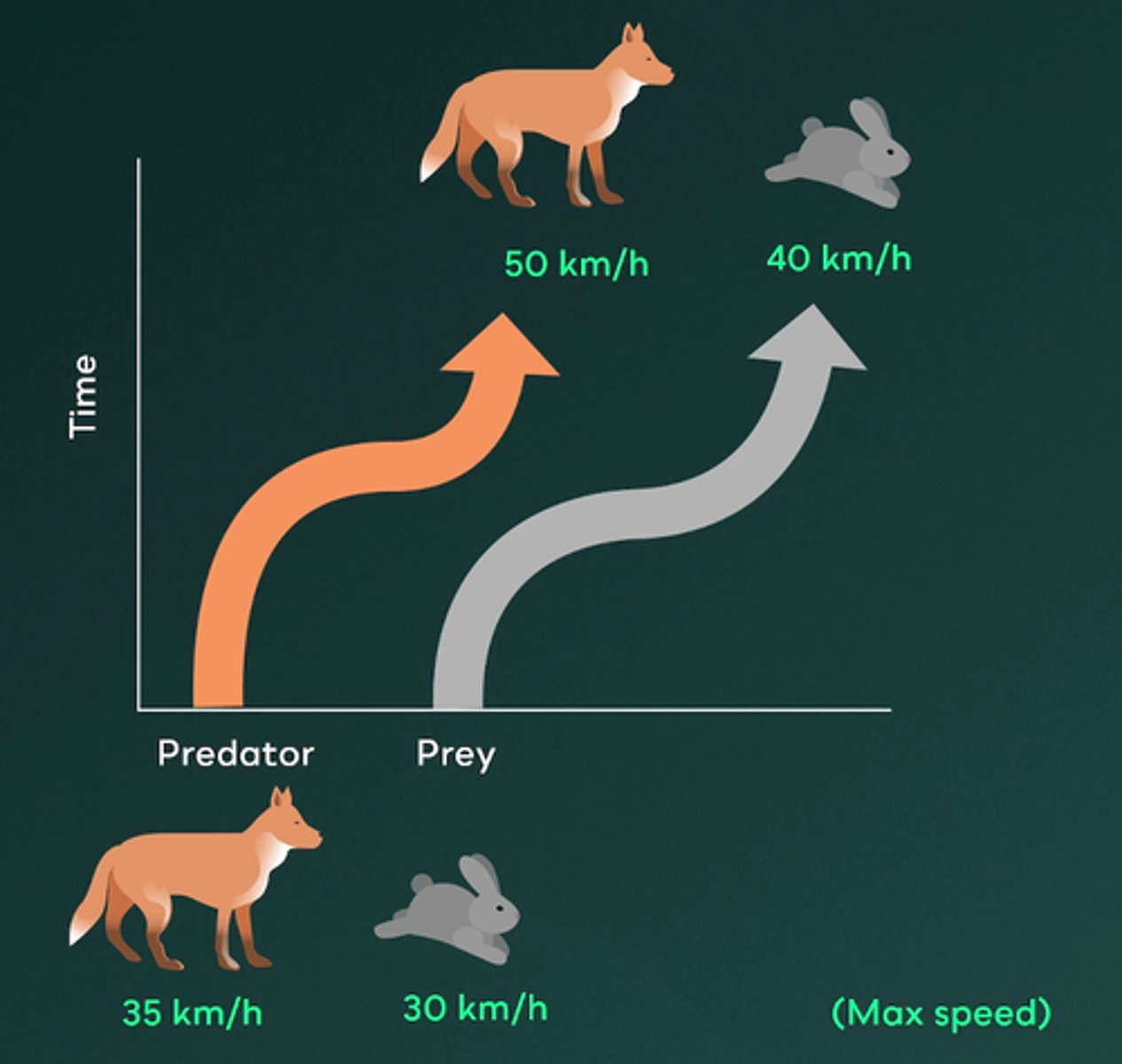
Darwin observed finches on the Galapagos Islands over an extended period and noted that they developed distinct beak sizes and shapes to adapt to the food sources on each island. They eventually became reproductively isolated from one another. The formation of multiple species from a common ancestor is an example of ________.
A.Convergent evolution
B.Founder effect
C.Divergent evolution
D.Coevolution
E.Parallel evolution
C.Divergent evolution
The formation of multiple species from a common ancestor is called divergent evolution. As the finches adapted to the habitats on their specific islands, they developed distinct traits and behaviors, becoming increasingly different from finches on other islands. Over time, this led to reproductive isolation, resulting in the finches being classified as distinct species from their common ancestor.
Which of the following is an example of coevolution?
A.Dolphins and sharks evolve fins because they occupy similar ecological niches
B.Barnacles attaching to whales, where the barnacles benefit while the whale is unaffected
C.A drought causes a bird population to adapt by developing longer beaks to access water reservoirs, eventually leading to the formation of a new species
D.Bees have evolved long structures to access nectar from deep flowers, while the flowers evolved specific tube shapes and nectar to attract bees for pollination
E.Penguins develop blubber to keep warm in icy waters, while arctic foxes develop thick fur to survive in freezing temperatures
D.Bees have evolved long structures to access nectar from deep flowers, while the flowers evolved specific tube shapes and nectar to attract bees for pollination
Coevolution happens when two or more species influence each other’s evolutionary path. This often occurs in species that closely interact, such as in predator-prey relationships or mutualistic pollinator interactions. In this question, option D is an example of coevolution. Bees have evolved long, specialized structures to access nectar from deep flowers, while the flowers have evolved tube shapes and nectar to attract bees. Over time, bees and flowers become more specialized for each other, benefiting both species.

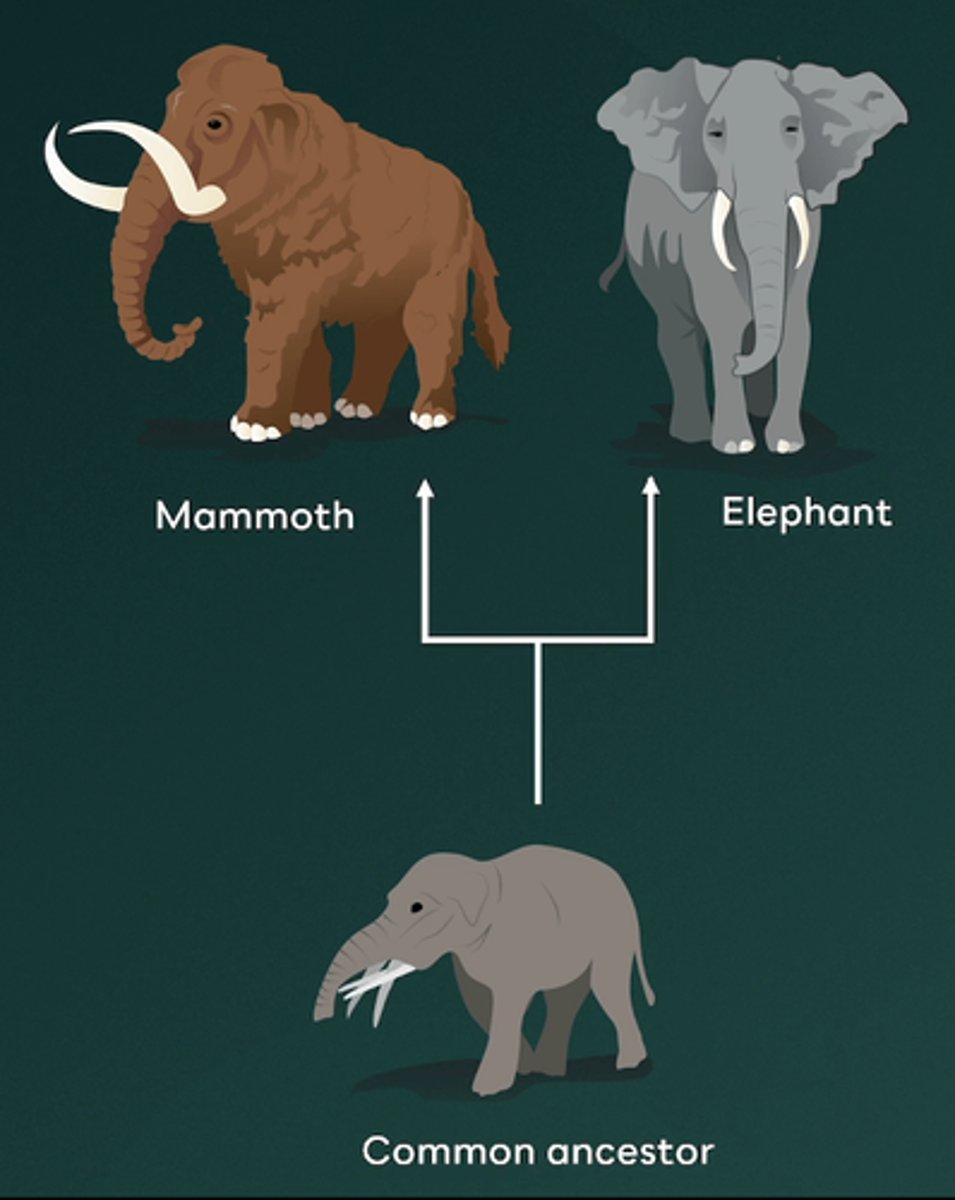
Which of the following best defines parallel evolution?
A.Unrelated species develop similar traits due to filling similar ecological niches
B.Two species evolve in response to each other's adaptations in a mutualistic relationship
C.Related species evolve similar traits independently after diverging from a common ancestor
D.Individuals evolve traits that help them compete for mates within the same population
E.Related species evolve different traits after diverging from a common ancestor
C.Related species evolve similar traits independently after diverging from a common ancestor
Parallel evolution occurs when related species independently evolve similar traits after diverging from a common ancestor. An example is the Woolly mammoth and modern elephant. After splitting from a common ancestor, they both developed similar traits like large bodies and tusks in response to similar environmental pressures, despite inhabiting different regions.
Which of the following is an example of Batesian mimicry?
A.A harmless milk snake resembles a venomous rattlesnake
B.A butterfly develops bright colors to warn predators of its toxicity
C.A venomous coral snake and a venomous scarlet king snake both evolve similar color patterns to warn predators of their danger
D.Two species of butterflies evolve similar coloration to blend into their environment
E.A caterpillar transforms into a butterfly, developing bright colors as it reaches adulthood
A.A harmless milk snake resembles a venomous rattlesnake
Batesian mimicry occurs when a harmless species mimics the appearance of a harmful or dangerous species. In option A, the milk snake is harmless but resembles the venomous rattlesnake, making it an example of Batesian mimicry. This resemblance helps the milk snake avoid predation by deceiving predators into thinking it is dangerous.

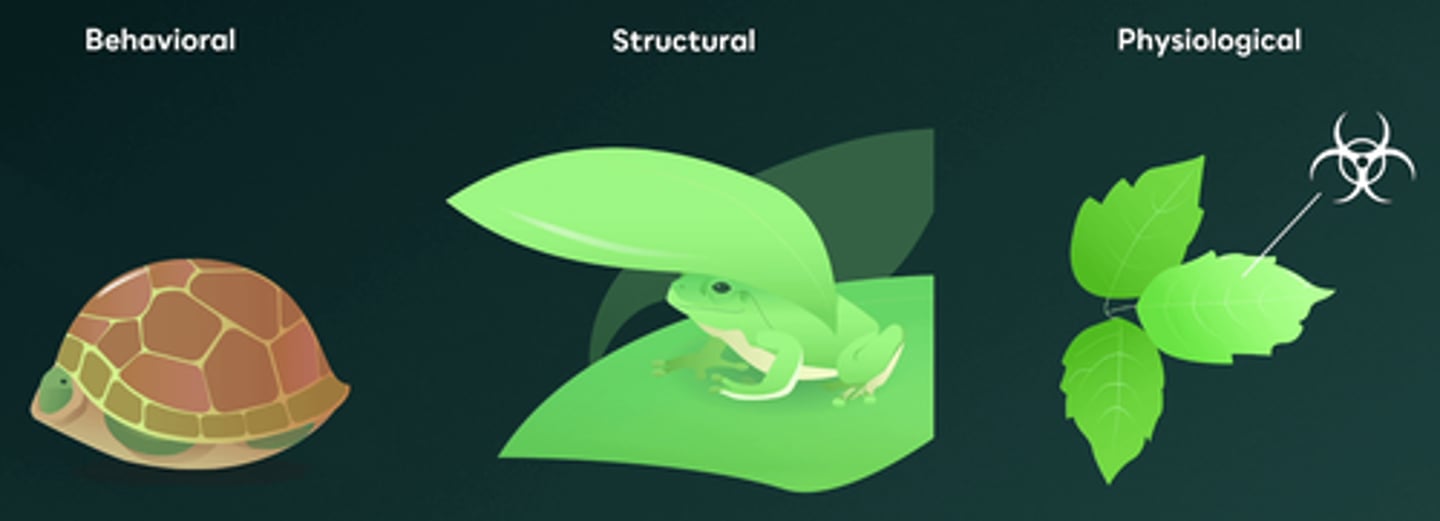
Which of the following are examples of behavioral adaptations?
I. Cockroaches scurrying away from light to avoid being seen
II. Squirrels collecting and storing acorns to ensure they have food during the winter months
III. Penguins having thick layers of blubber to survive cold temperatures
IV. Birds migrating to warmer climates during the winter to find food and avoid harsh conditions
V. Plants producing tannins to make their leaves taste bitter and deter herbivores
A.I and III
B.II and III
C.I, II, and IV
D.I, IV, and V
E.I, II, III, IV and V
C.I, II, and IV
There are three main types of survival adaptations: behavioral, structural, and physiological. Behavioral adaptations involve actions or behaviors that organisms perform to improve their chances of survival, which can be either instinctive or learned. Statements I, II, and IV describe behavioral adaptations, where the organisms engage in specific behaviors to enhance their survival. Statements III and V are structural adaptations and physiological adaptations respectively.

Poisonous dart frogs are known for their vibrant colors, like red and black, which act as warning signals to predators. Given this information, which of the following best describes a species exhibiting Mullerian mimicry?
A.A harmless species of frog that mimics the red and black coloration of the poisonous frogs to avoid predation
B.A poisonous species of frog that evolves dull, brown coloration to avoid attracting predators
C.A species of frog that develops sharp, spiny projections on its skin to deter predators
D.A species of frog that is nocturnal, reducing its chances of being seen by predators
E.A poisonous species of frog that evolves similar red and black coloration to warn predators
E.A poisonous species of frog that evolves similar red and black coloration to warn predators
Mullerian mimicry occurs when two or more species resemble each other and share the same type of defense mechanism. This shared warning signal causes predators to avoid both species. Predators also benefit by learning to avoid them more quickly. For example, if a dart frog has red and black coloration, another species with Mullerian mimicry would also be red and black and also poisonous.

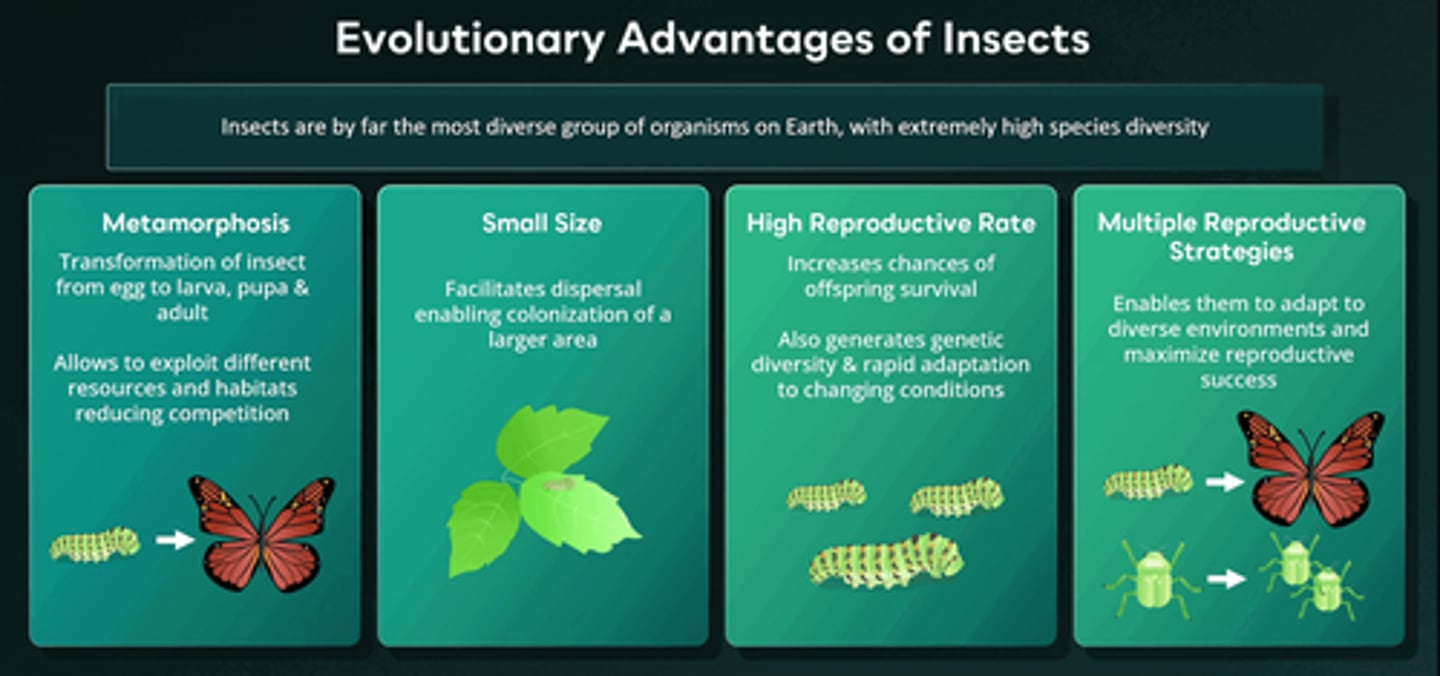
All of the following are evolutionary advantages that insects possess EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A.Having multiple reproductive strategies
B.Ability to undergo metamorphosis
C.High reproductive rate
D.Ability to thermoregulate
E.Small body size
D.Ability to thermoregulate
Insects are the group with the greatest species diversity. Several key evolutionary advantages have contributed to this diversity, including their ability to undergo metamorphosis, their small size, high reproductive rate, and a variety of reproductive strategies. However, insects are ectothermic, meaning their body temperature is controlled by the external environment, thus they cannot thermoregulate.
Which of the following is an example of a structural adaptation for survival?
A.Polar bears have thick fur and fat layers to survive freezing temperatures
B.Spiders that carry egg sacs containing many offspring
C.Bears hibernating during the winter to conserve energy
D.Snakes use venom to incapacitate their prey
E.A plant producing nicotine in its leaves to deter herbivores from eating it
A.Polar bears have thick fur and fat layers to survive freezing temperatures
Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive condition. A normal woman with no affected alleles marries a man with hemophilia. What is the probability of having a hemophilic son?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
A.0%
Hemophilia is a condition where the ability of the body to form blood clots is severely reduced. A normal woman, without hemophilia, will have the genotype XHXHand a man with hemophilia will have the genotype XhY. The offspring of these individuals will be 50% XHXhand 50% XHY. Therefore, there is a 0% chance of having a son with hemophilia.
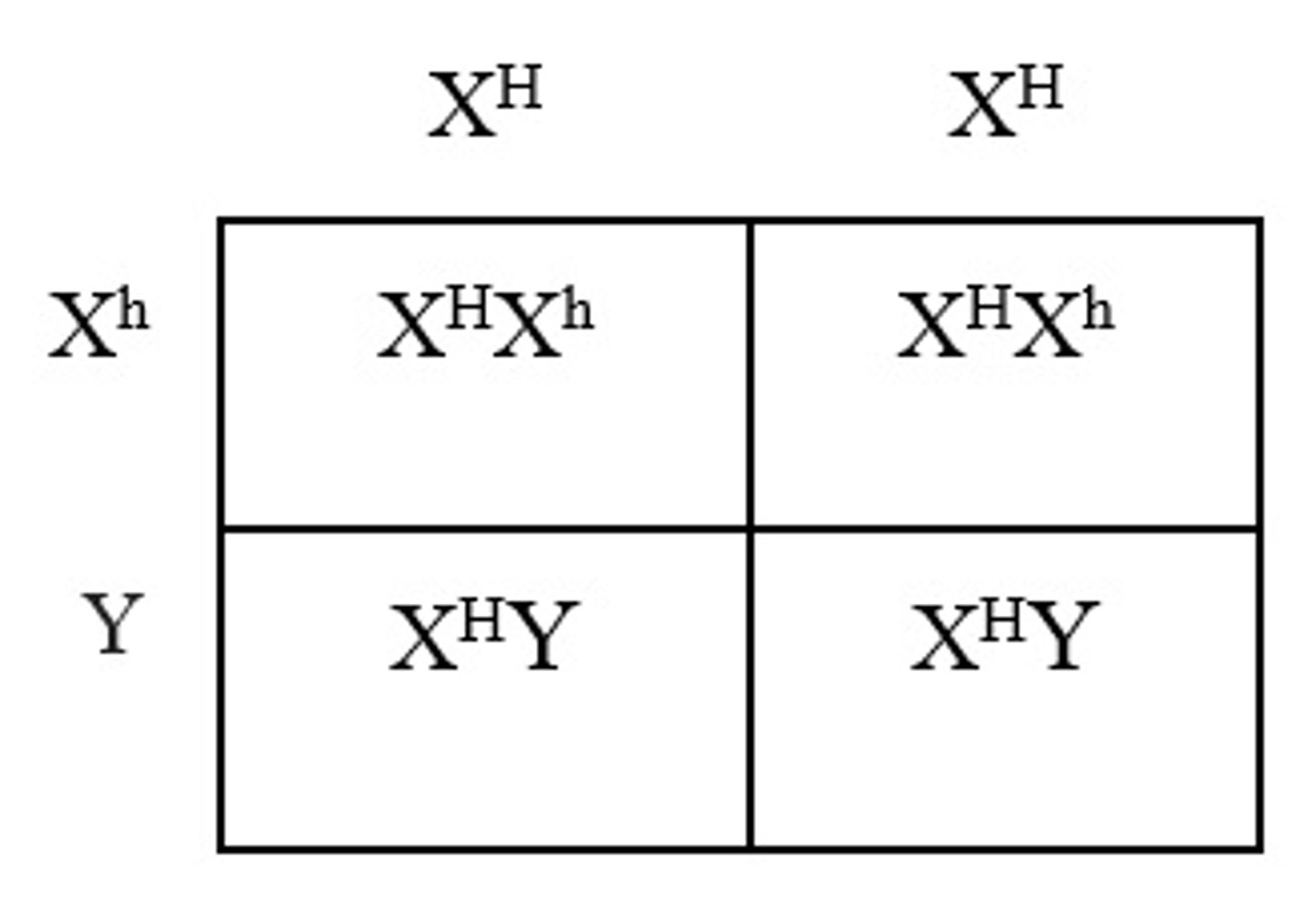
Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive condition. A normal woman (who is NOT a carrier for the disease) marries a man with hemophilia. What is the probability of having a hemophilic daughter?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
A.0%
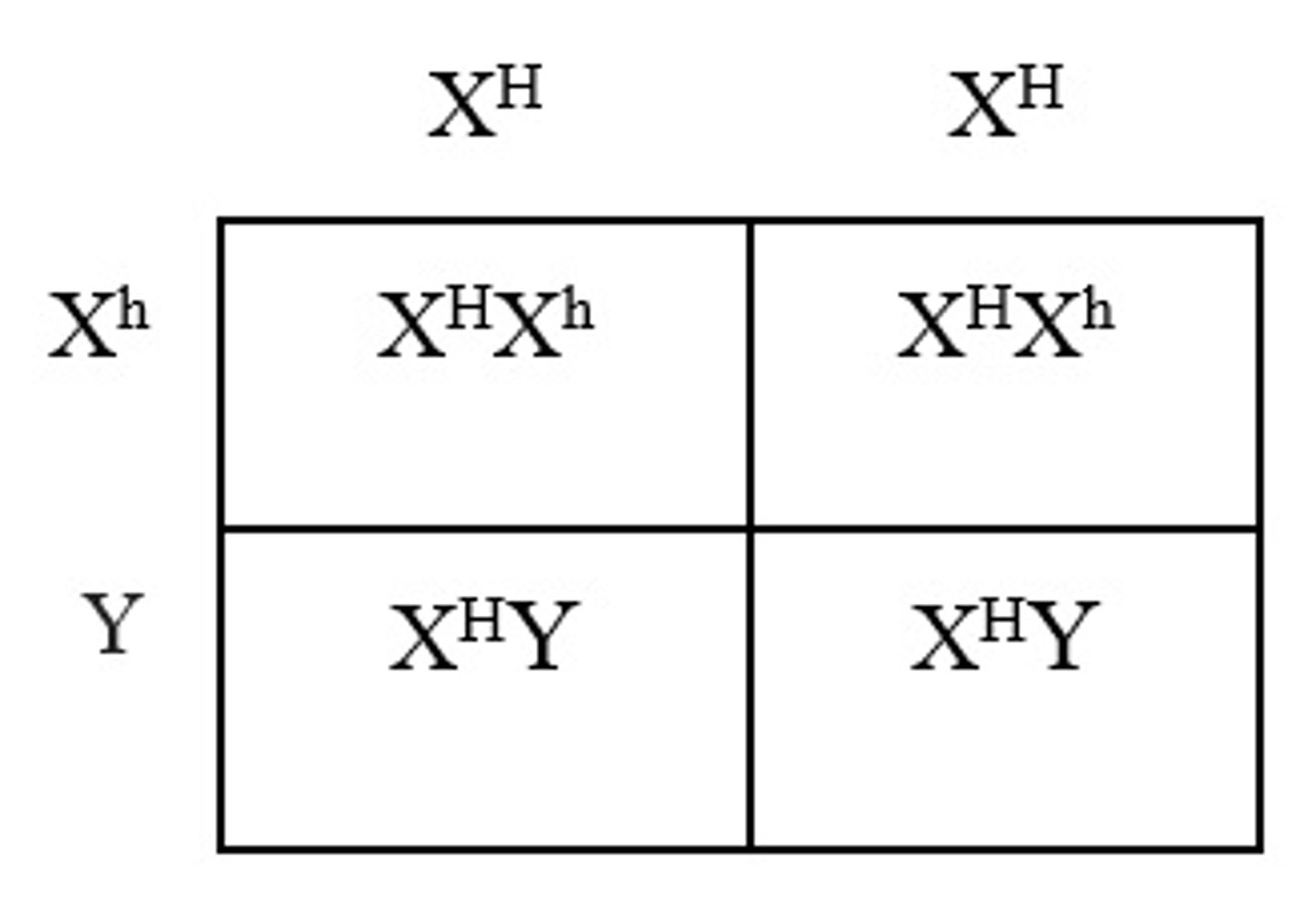
Hemophilia is a condition where the ability of the body to form blood clots is severely reduced. A normal woman, without hemophilia, will have the genotype XHXHand a man with hemophilia will have the genotype XhY. The offspring of these individuals will be 50% XHXhand 50% XHY. Therefore, there is a 0% chance of having a daughter with hemophilia.
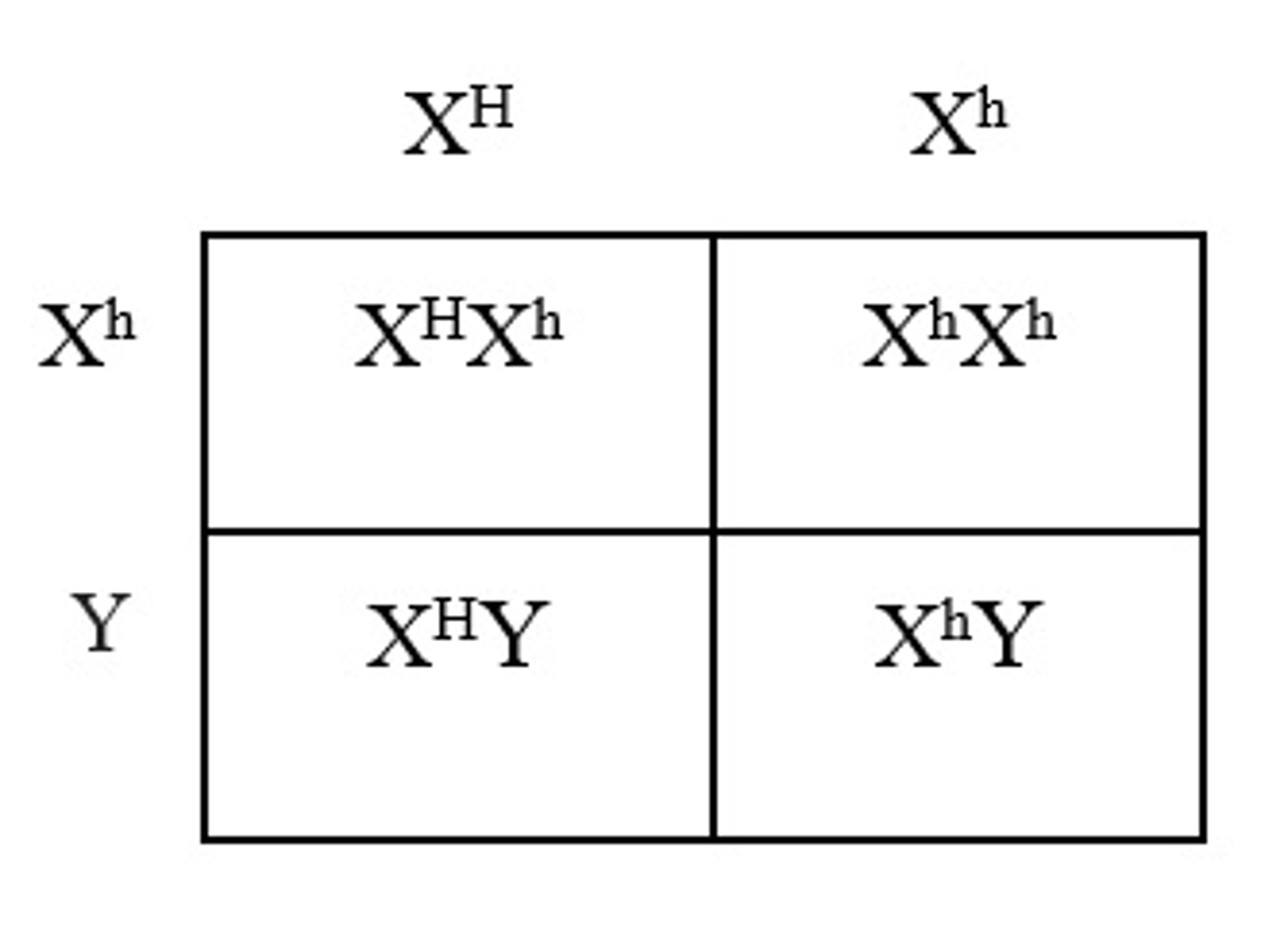
A woman who is a carrier of hemophilia marries a man who has hemophilia. What is the chance of conceiving a daughter who has hemophilia?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
B.25%
Hemophilia is a condition where the ability of the body to form blood clots is severely reduced. A female carrier for hemophilia will have the genotype XHXhand a man with hemophilia will have the genotype XhY. The offspring of these individuals will be 25% XHXh, 25% XhXh, 25% XHY, 25% XhY. Therefore, there is a 25% chance of having a daughter with hemophilia.
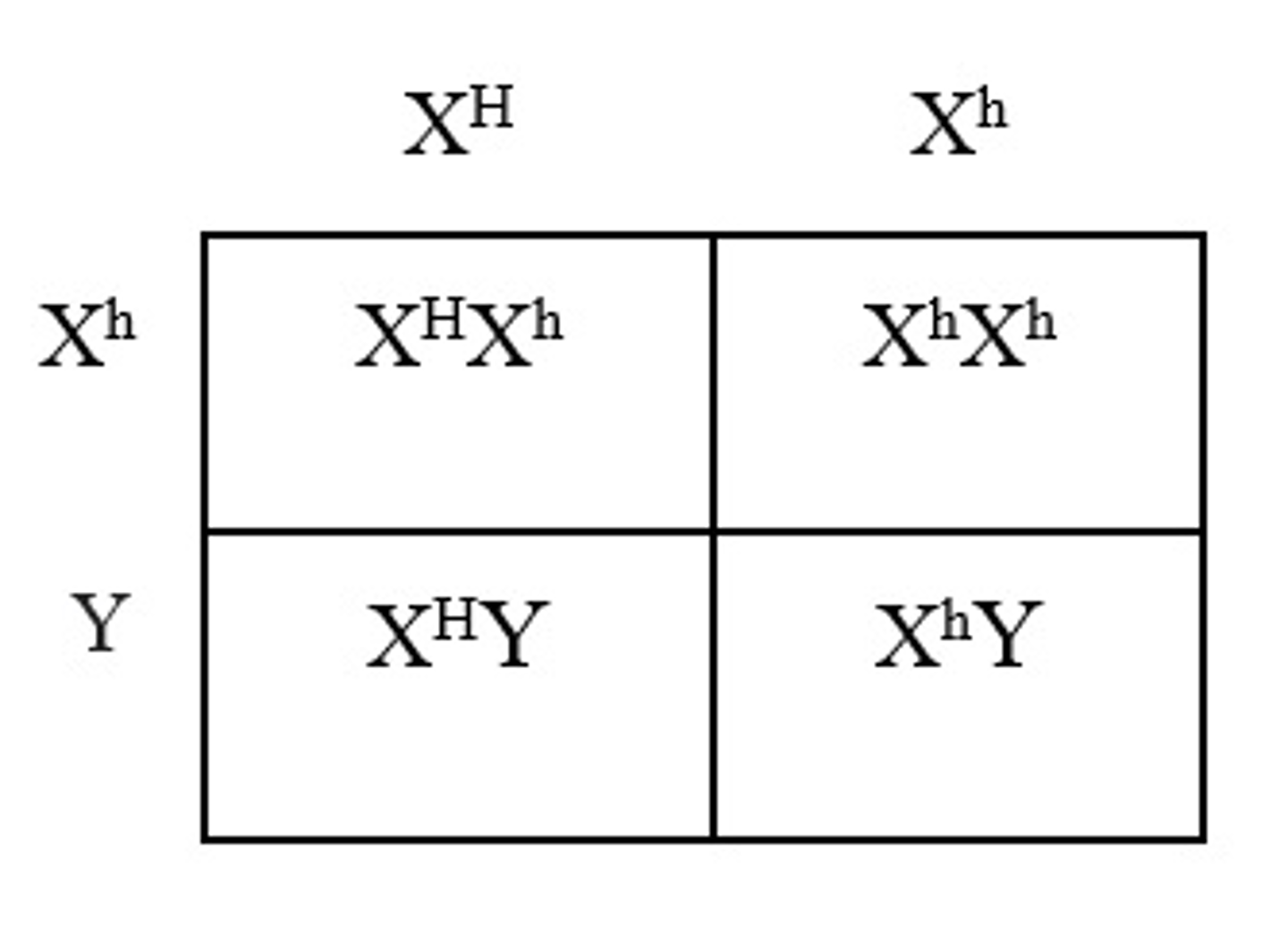
A woman who is a carrier of hemophilia marries a man who has hemophilia. What is the chance of conceiving a daughter and that the daughter is a carrier for hemophilia?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
B.25%
Hemophilia is a condition where the ability of the body to form blood clots is severely reduced. A female carrier for hemophilia will have the genotype XHXhand a man with hemophilia will have the genotype XhY. The offspring of these individuals will be 25% XHXh, 25% XhXh , 25% XHY, 25% XhY. Therefore, there is a 25% chance of having a daughter that is a carrier for hemophilia.
A woman who is a carrier of hemophilia marries a man who has hemophilia. What is the chance of conceiving a daughter who is a normal noncarrier?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
A.0%
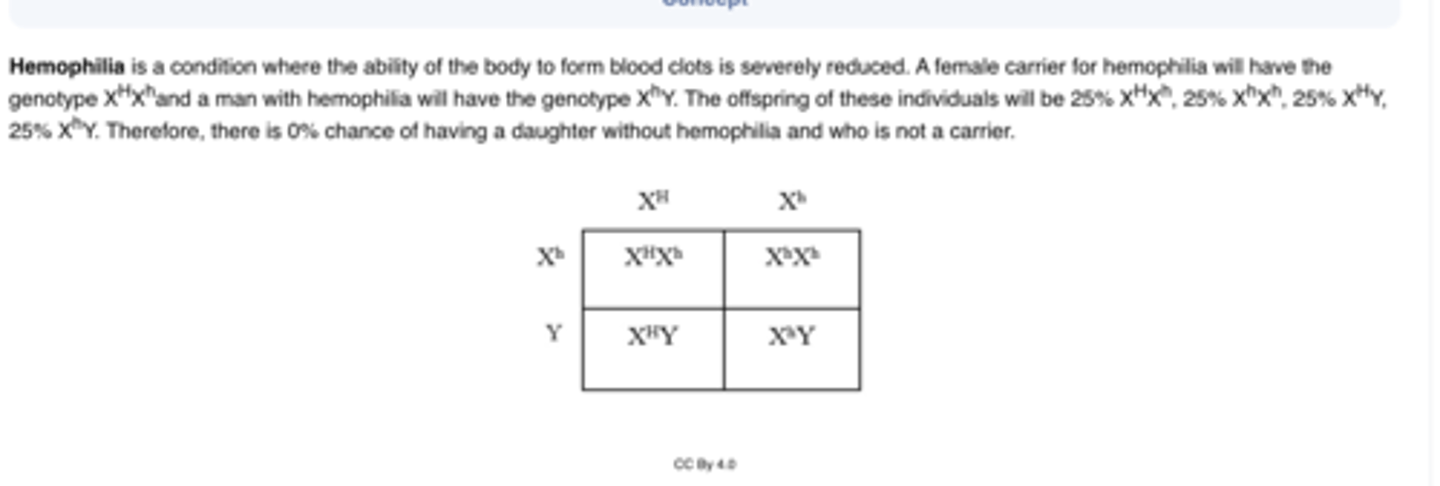
A woman who is a carrier for hemophilia marries a man who has hemophilia. What is the chance of conceiving a normal son?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
B.25%

Color blindness is X-linked recessive. Stefan is a color-blind man and his sister has normal vision. Which of the following is the genotype of his parents, if the color blind gene is "b"?
A.Xb Xb x Xb Y
B.XB XB x XB Y
C.Bb x Bb
D.XB XB x Xb Y
E.Xb XB x XB Y
E.Xb XB x XB Y

Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is caused by the recessive allele "d". If a heterozygous female marries a male with DMD, then what is the chance that their offspring will be a son with DMD?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
B.25%

If a mother with a mitochondrial defect (maternally inherited) and a normal father produce offspring, then what is the percentage of children with normal mitochondria?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
A.0%
Mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA are maternally inherited. If a mother has a mitochondrial defect, the offspring will also have a mitochondrial defect, despite the paternal genotype. Thus, if a mother with a defect marries a normal father, all of the offspring will have a mitochondrial defect, despite the father’s genotype.
Which of the following best describes a hemizygous trait?
A.Only males copy one specific gene
B.Only females copy one specific gene
C.Only one single copy is inherited
D.Only one single copy is silenced
E.Only half a homologous pair is inherited
C.Only one single copy is inherited
The term hemizygous is used to describe an individual who has one inherited copy of a gene. This term is usually used to describe traits that are X linked, and thus can only be present in one copy in male individuals.
The agouti gene (AA) produces a brown fur mouse, the yellow genotype (Aa) produces a yellow fur allele, and genotype aa is lethal. If two yellow fur parents mate, what is the ratio of yellow to brown fur offspring?
A.1:1
B.2:1
C.1:2
D.3:1
E.1:3
B.2:1

A patient takes a blood test and the results show phenylalanine build up. Which condition does the patient have?
A.Tay-Sachs
B.PKU
C.Cystic fibrosis
D.Hemophilia
E.Color blindness
B.PKU
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disorder that causes the amino acid phenylalanine to build up due to the inability to produce the proper enzyme for its breakdown. This causes the degradation product, phenylpyruvic acid, to accumulate and leads to mental retardation.
A patient experiences excessive coughing of thick mucus. Which disease does the patient most likely have?
A.Tay-Sachs
B.Huntington's disease
C.Cystic fibrosis
D.Phenylketonuria
E.Achondroplasia
C.Cystic fibrosis
Cystic Fibrosis is a disorder characterized by the buildup of thick mucus in tracts due to the inability of the body to produce mucus with normal consistency. Due to thick mucus buildup, patients will often present with excessive coughing of thick mucus. Cystic Fibrosis has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance, meaning two copies of the affected gene are required to present with the disorder.
Which of the following is an example of a hemizygous genotype?
A.AB blood type
B.AO blood type
C.BO blood type
D.XX sex chromosomes
E.XY sex chromosomes
E.XY sex chromosomes
The term hemizygous is used to describe an individual who has one inherited copy of a gene. Males have the genotype XY, and thus only have one X chromosome. X-linked genes are considered hemizygous in males because males only have one copy of these genes due to their XY genotype.
Which of the following is the least likely to be passed on from one generation to the next?
A.Autosomal recessive disorders
B.Autosomal dominant disorders
C.Chromosomal disorders
D.X-linked recessive disorders
E.X-linked dominant disorders
C.Chromosomal disorders
Chromosomal disorders are disorders that occur due to abnormal chromosome numbers or abnormal chromosome makeup. Causes of chromosomal disorders include aneuploidy, chromosomal aberrations, and chromosomal breakage. Chromosomal disorders are not inherited but are often caused by errors in cell division.
Which of the following symptoms is mainly associated with hemophilia?
A.Nervous system degeneration
B.Dwarfism
C.Pattern baldness
D.Abnormal blood clotting
E.Infertility
D.Abnormal blood clotting

Why is color blindness more prominent in men compared to women?
A.There are more men in the world than women
B.The color blindness genes are passed from father to son
C.The color blindness genes are normally damaged in men
D.The color blindness genes are on the X chromosome
E.The colorblindness genes are on the Y chromosome
D.The color blindness genes are on the X chromosome
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait and thus resides on the X chromosome. Males have one copy of the X chromosome which is inherited by their mother. If a male inherits one allele for color blindness, they will be color blind. Therefore, if the maternal genotype consists of one allele, there is automatically a 50% chance of having a son with color blindness. If the mother is color blind, there is a 100% chance of having a son with color blindness. However, females have two X chromosomes, so two copies of the color blindness gene are necessary for females to present with color blindness. Females inherit one X chromosome from their father and one from their mother. Therefore, the father must have the allele for color blindness and must mate with a female that is heterozygous (50% of having a daughter that is color blind) or homozygous recessive (100% chance of having a daughter that is color blind.
Which of the following is the overarching concern with mitochondrial diseases?
A.Cellular inability to breakdown lipids
B.Cellular inability to detect genetic mutations
C.Cellular inability to produce significant energy
D.Cellular ability to epigenetically change in a sporadic manner
E.Cellular ability to stop DNA checkpoints
C.Cellular inability to produce significant energy
One of the main functions of the mitochondria is to produce ATP, the body's main energy source. If there is a mitochondrial disease affecting mitochondrial DNA or mitochondria function, this can affect its ability to produce ATP.
An individual is heterozygous for the mutation that causes cystic fibrosis. Which of the following is true concerning this person?
A.The individual would be a cystic fibrosis patient
B.The individual would be a cystic fibrosis carrier
C.The individual would be completely asymptomatic
D.The individual will not pass cystic fibrosis to their offspring
E.The individual did not have parents with the cystic fibrosis mutation
B.The individual would be a cystic fibrosis carrier
Cystic Fibrosis is a disorder characterized by the buildup of thick mucus in tracts due to the inability of the body to make thin mucus. Cystic Fibrosis has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance, meaning two copies of the affected gene are required to present with the disorder. If an individual is heterozygous for cystic fibrosis, they will be a carrier for the disease.
A man carries one mutated copy of the HTT gene, which is linked to Huntington's disease. Which of the following is true concerning this individual?
A.The man will not pass the mutated gene to his offspring
B.The man will be a Huntington's disease carrier
C.The man will not experience Huntington's disease symptoms
D.The man will not develop Huntington's disease
E.The man will develop Huntington's disease
E.The man will develop Huntington’s disease
Huntington’s disease is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene. Huntington's exhibits complete penetration, meaning that the gene is expressed in all populations who have that gene. Therefore, if a human has just one mutated copy of this HTT gene, the human will develop Huntington's disease.
Both the mother and father are carriers of cystic fibrosis, an autosomal recessive disorder. What is the probability of their child having cystic fibrosis?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
B.25%
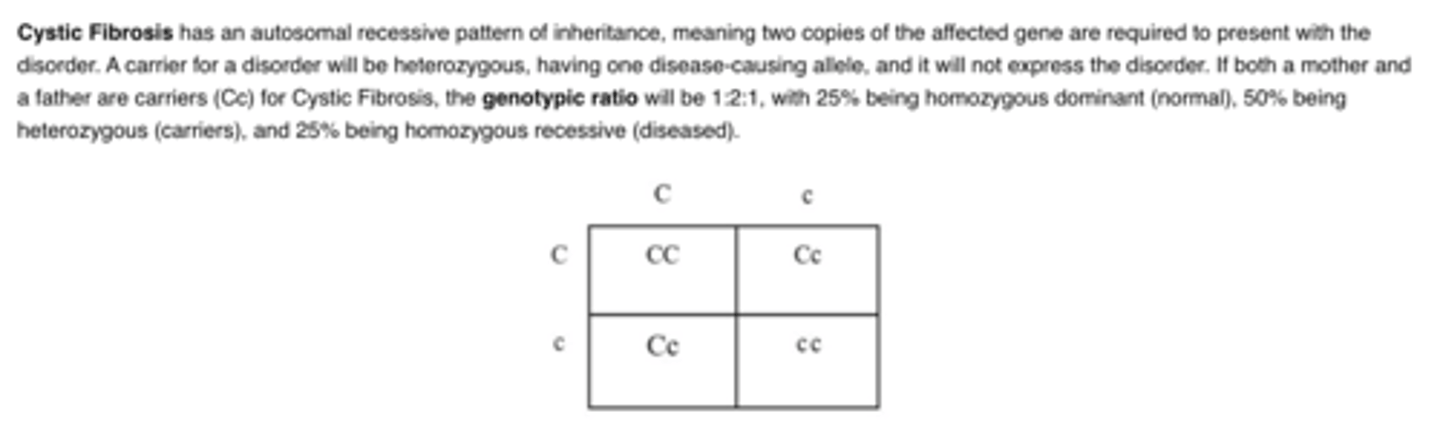
Both parents are carriers of Phenylketonuria, an autosomal recessive disorder. What is the probability that their child is a carrier of Phenylketonuria?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
C.50%

Which of the following is the ratio of unaffected to affected offspring with parents who are carriers for Tay-Sachs, an autosomal recessive condition?
A.1:1
B.1:2
C.3:1
D.2:1
E.1:3
C.3:1

One parent has two normal genes for cystic fibrosis, an autosomal recessive disorder, whereas the other parent has two faulty cystic fibrosis genes. What is the chance of a non-carrier cystic fibrosis child?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
A.0%
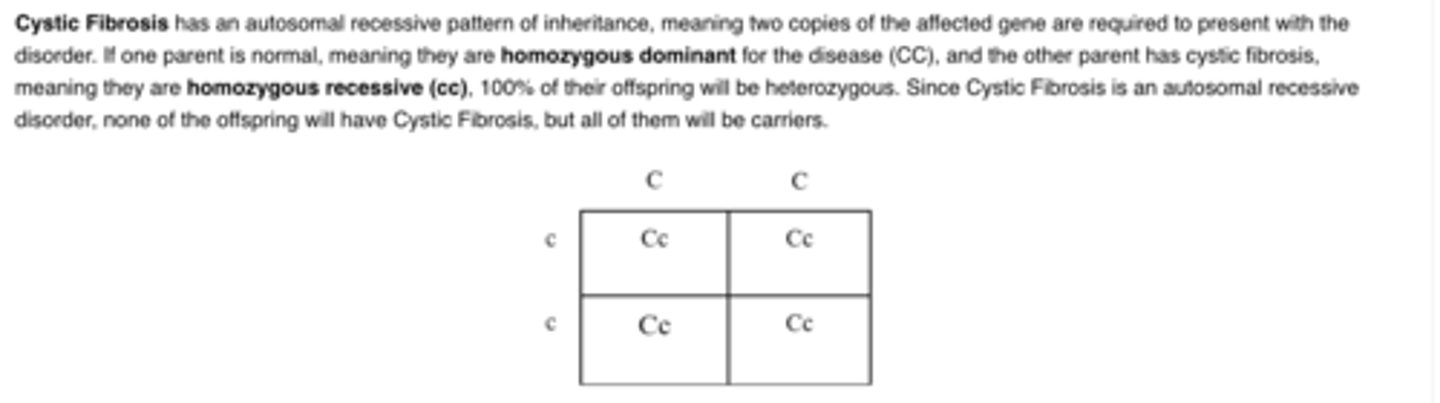
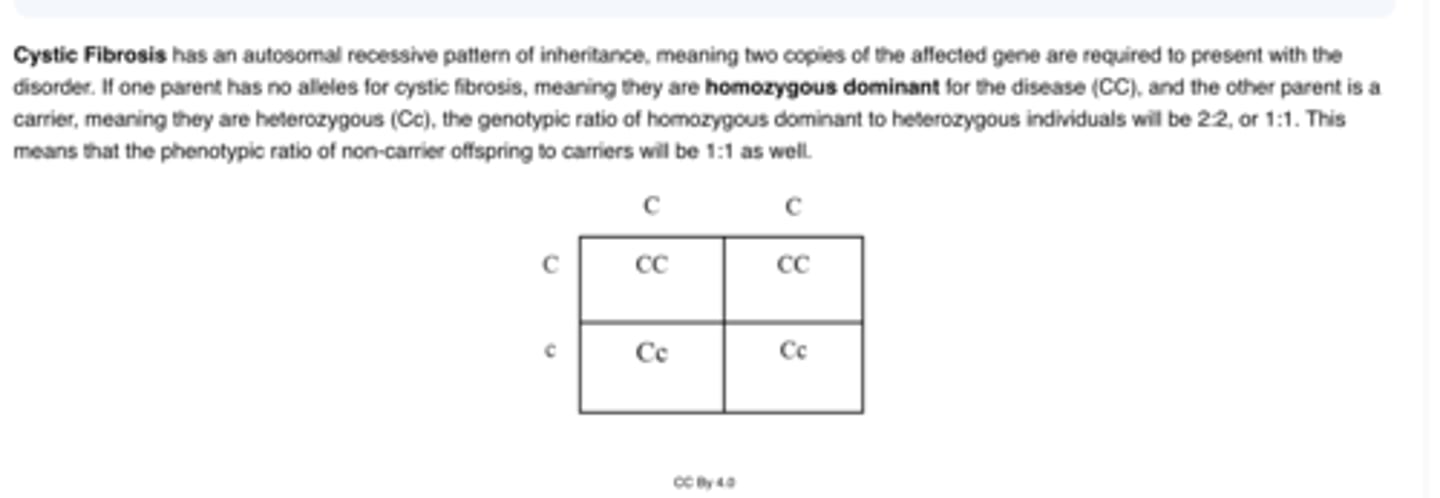
A parent that is a carrier for cystic fibrosis, an autosomal recessive disorder, wants to conceive a child with an individual that does not carry any alleles for cystic fibrosis. What is the ratio of children with no alleles for cystic fibrosis to children that are carriers for cystic fibrosis in their potential offspring?
A.1:1
B.1:3
C.1:2
D.4:0
E.3:1
A.1:1
A type B man and type O mother produce a child with type O blood. What is the probability their next child will be type O as well?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
C.50%

Sickle cell anemia (ss) is an autosomal recessive condition that affects the shape of red blood cells. If two parents produce one child with sickle cell anemia and three children with normal healthy red cells, what must be the phenotype of the parents?
A.Both parents are ss
B.Both parents are Ss
C.Both parents are SS
D.One parent is SS and the other is Ss
E.One parent is Ss and the other is ss
B.Both parents are Ss

If a red flower and a blue flower are crossed to produce a flower with both red and blue petals, which of the following is true?
A.The alleles that produce red and blue are codominant
B.The red-producing allele is incompletely dominant over the blue allele
C.The blue-producing allele is dominant over the red allele
D.The red-producing allele is dominant over the blue allele
E.The red-producing allele is homozygous recessive
A.The alleles that produce red and blue are codominant
Codominance is when both inherited alleles are completely expressed. If an offspring produced from a cross were to express both the dominant and recessive traits, then the trait is codominant. Since the parental traits are blue and red, and the offspring expresses both of these traits, the alleles for red and blue colors are codominant.
If a male is homozygous dominant for a mutated Huntington's disease HTT gene and marries a normal woman, then what is the chance their offspring will develop Huntington's disease?
A.0%
B.25%
C.50%
D.75%
E.100%
E.100%
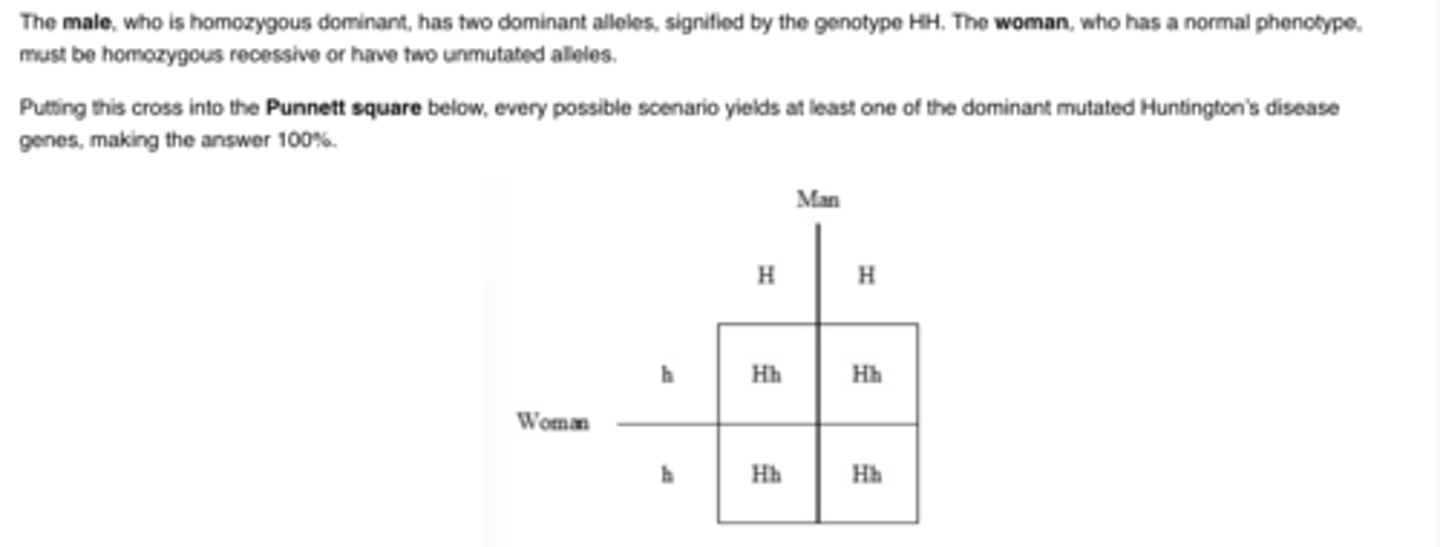
Wavy hair (W) is an autosomal dominant trait and straight hair (w) is recessive. If a male and female, both of who are heterozygous for wavy hair, mate and produce three children with wavy hair, then which of the following is true?
A.Their next child will also have wavy hair
B.Their next child will have straight hair
C.Their next son will have wavy hair
D.Their next child has a 50% chance of having wavy hair
E.Their next child has a 25% chance of having straight hair
E.Their next child has a 25% chance of having straight hair
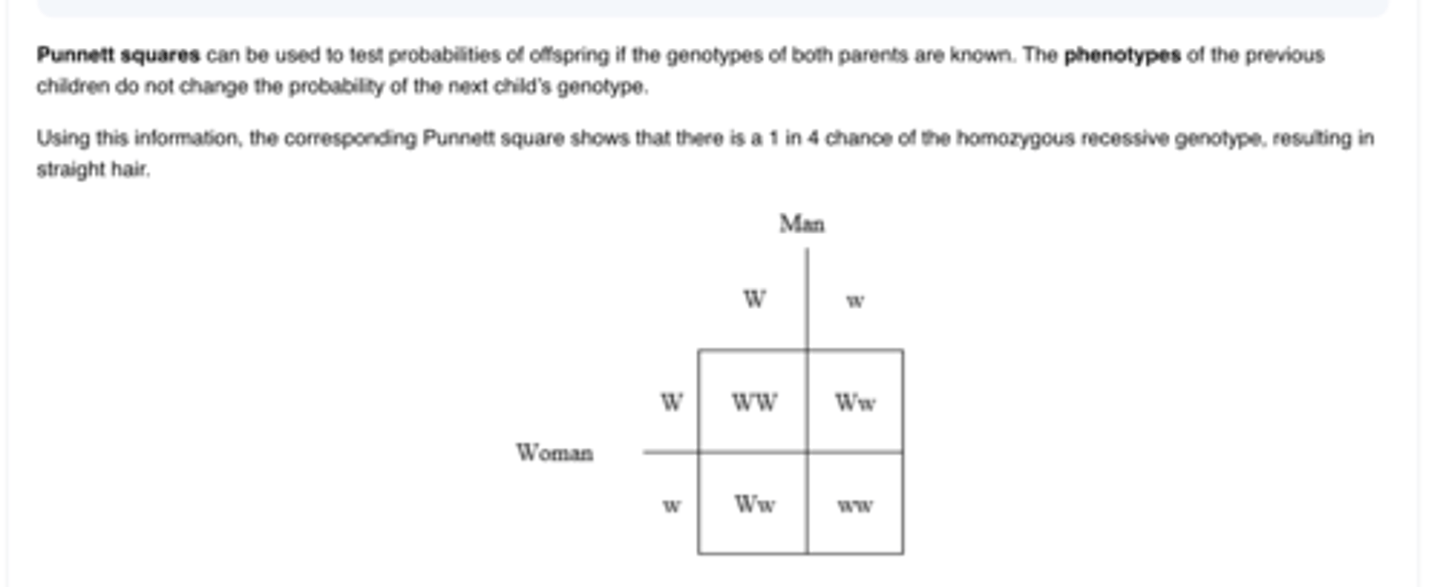
A pure red flower and a pure white flower are crossbred, producing a pink flower. Which of the following is true concerning the relationship between the two-color alleles?
A.The red color-producing allele is dominant over the white-producing allele
B.The white color-producing allele is dominant over the red-producing allele
C.The red-producing allele is completely dominant over the white-producing allele
D.The red-producing allele is incompletely dominant over the white-producing allele
E.The color-producing allele skips generations
D.The red-producing allele is incompletely dominant over the white-producing allele
Incomplete dominance is a unique heterozygous phenotype that blends the expression of the two alleles rather than having one dominant over the other. Codominance is another unique heterozygous expression where both alleles are fully expressed. In this case, the heterozygous flowers would be both red and white, not pink.
Complete dominance results in only the expression of the dominant allele in heterozygous organisms.
Which of the following is the correct phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross between pea plants that are heterozygous for round, yellow peas (RrYy)?
A.1:2:2:1
B.4:4:4:4
C.9:3:3:1
D.9:4:2:1
E.16:4:2:1
C.9:3:3:1
A dihybrid cross shows the genotypic possibilities of a cross involving two genes on different chromosomes. However, it is easier to recognize that the 9:3:3:1 ratio is a classic dihybrid cross.
If a tall (T) stalk in plants is autosomal dominant and a short (t) stalk is recessive. What is the phenotype of the F1 generation if two true-breeding tall and short plants are crossed?
A.100% short stalk
B.100% tall stalk
C.50% short stalk
D.50% tall stalk
E.25% tall stalk
B.100% tall stalk
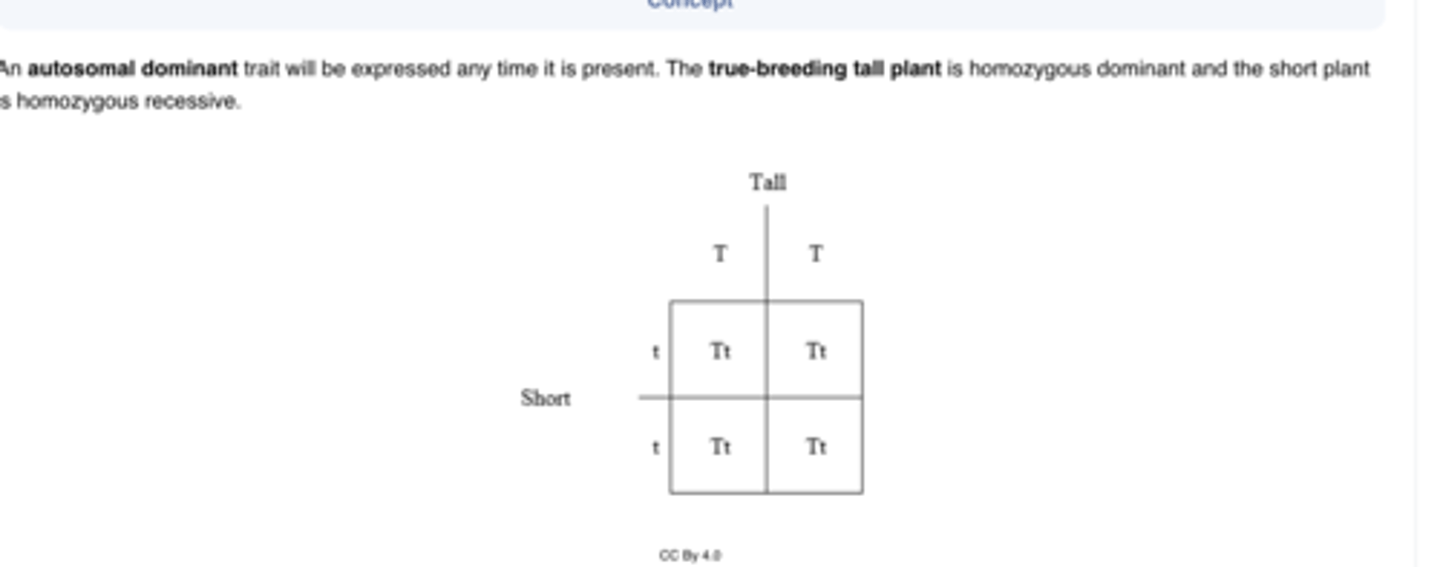
In which of the following situations will the dihybrid cross of heterozygous traits produce a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1?
A.The gene pairs are linked
B.The gene pairs are codominant
C.The gene pairs independently assort during recombination
D.The gene pairs are recessive-producing traits
E.The gene pairs involve a nutation
C.The gene pairs independently assort during recombination
The 9:3:3:1 ratio is a typical phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross. This is dependent on the law of independent assortment, which states that alleles are sorted independently during gamete formation.
Linked genes are too close together on chromosomes to independently sort, changing phenotypic ratios when crossed.
Which of the following best defines the notations within the four squares that make up a Punnett square?
A.Maternal allele
B.Paternal allele
C.Offspring allele
D.Offspring phenotype
E.Parental phenotype
C.Offspring allele
A Punnett square is used to determine probabilities of genotypes of offspring given the genotypes of the parents. The parental genes are placed outside the square, with the notations within the squares representing possible offspring alleles.
If an individual has a genotype AABbCCDdEeFf, then how many possible gamete combinations can be produced?
A.4
B.8
C.16
D.32
E.64
E.64

If the recombination rate of two genes is 0.001%, then which of the following statements is true?
A.The genes are on different chromosomes
B.The genes are on the sex chromosomes
C.The genes are spatially very close
D.The genes are not inheritable
E.The genes are bacterial
C.The genes are spatially very close
Recombination rates represent how likely two genes on the same chromosomes will be separated. The lower the recombination rate, the less likely the two genes will be separated and the closer they will be with respect to each other on the chromosome.
Since the recombination rate is close to 0%, the probability that the two genes will be separated is very unlikely which means they are spatially very close together.
Each of the following are true concerning Down's syndrome EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
A.Frequency increases with maternal age
B.Frequency increases with mitotic division
C.Produced due to an increased number of chromosome 21
D.Generally does not run in families
E.Known as a chromosomal disorder
B.Frequency increases with mitotic division
"Frequency increases with mitotic division" is a false statement because the most common cause of Down syndrome is nondisjunction during meiosis, which occurs during gamete formation. This produces full Trisomy 21, whereby each cell of an individual with Down syndrome will have an extra copy of chromosome #21. While nondisjunction can also occur in mitosis, this does not contribute to the frequency of full Trisomy 21.
A pedigree diagram shows only females passing a disease to all offspring despite their sex. Affected males do not pass the disease to their offspring. The trait is most likely ___________.
A.Autosomal recessive
B.Autosomal dominant
C.Sex-linked dominant
D.Mitochondrial
E.Random
D.Mitochondrial
Mitochondrial diseases are inherited from the mother due to the fact that mitochondria are maternally inherited. This is because the zygote’s mitochondria are the mitochondria of the oocyte which means that sperm mitochondria do not contribute to the zygote’s pool of mitochondria.
An affected mother will pass on this disease to all offspring, but an affected father will not pass on the disease at all.
Which of the following best describes how an x-linked dominant trait appears on a pedigree?
A.The trait only affects females
B.The trait only affects males
C.The female offspring of affected males have the dominant trait
D.The male affected offspring do not have affected mothers
E.The trait skips generations
C.The female offspring of affected males have the dominant trait
Affected males only have one X chromosome and it has the mutated copy of the gene. Therefore, all female offspring of this male will be affected since the male can only pass the X chromosome down to the female offspring.