Labour markets
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
The demand for labour is a
Derived demand
What is Marginal productivity theory
It states that the demand for any factor of production will depend on its marginal revenue product (MRP)
Marginal Revenue Product of labour (MRPl) is
An additional revenue, gained by hiring one more worker
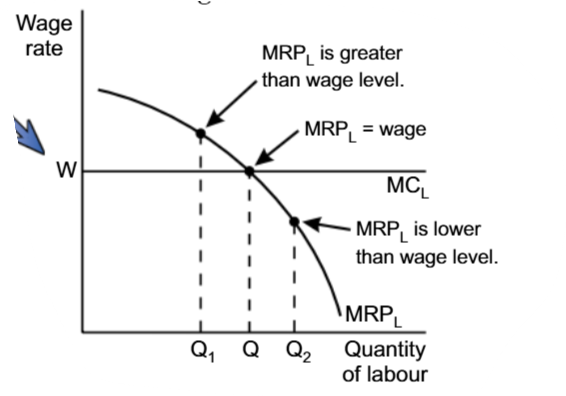
An example of using MRPl

MCl
The Cost of hiring one additional worker is
In the perfectly competitive market, the MCl equals to
the wage, paid to an additional worker

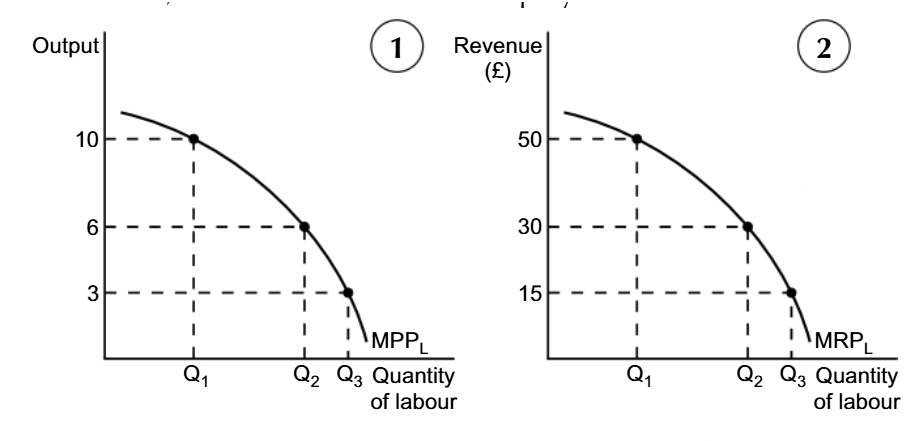
MRPl equals
MPPl*MR
Generally, the demand for labour will decrease as the wages rise, however this depends on
whether the wage increase is accompanied by an increase in productivity
Higher levels of productivity reduce the
unit labour costs
What are the unit labour costs
labour costs per unit of output

this means that the unit cost for labour stays the same, and then the demand for labour is unaffected
An example of unit cost of labour staying the same, which means the demand for labour stays untouched as well
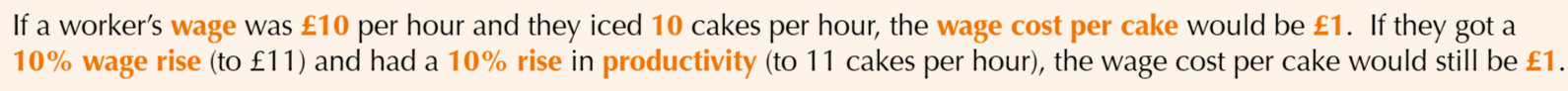
What could high unit labour costs do to the country entirely?
Reduce its international competitiveness
In case of the unit labour costs reduction is also experienced in other firms, then
the international competitiveness will stay unchanged (since other countries’ productivity increased too)
International competition may mean the unit labour cost in a particular industry is too high in some countries for them to be
competitive and production in that industry will stop
MRPl curve is also the demand curve for
labour
The decreased demand for labour would cause the MRPl to
shift to the left
Factors, affecting the labour productivity
imposition of new technology or training increases the productivity of labour, this would increase the demand for labour and make the MRPl curve shift to the right
If any other costs of labour (besides on the wages) increased, then
The MRPl curve would shift to the left
Elasticity of demand for labour is
A measure of how much the quantity of labour demanded changes in accordance with changes in wages
Factors, influencing the Labour demand Elasticity (LDE)

Individuals labour supply is
The total number of hours that they would like to work at a given wage rate
For an occupation, the labour supply is
the total number of workers willing to work at a given wage
The labour supply may be influenced by
job satisfaction
The net advantage of a job could be divided into to groups

Other factors that impact labour supply to a particular job or industry

The quantity of labour supplied depends on
The elasticity of labour supply
The main determinant of elasticity of labour supply is
the level of skills and qualifications needed for a job
Low skilled jobs

High skilled jobs

Another factor, affecting the labour supply
The mobility of labour
Another aspect, which can increase the supply of labour
Net migration of labour
The wages tend to be high, if
The demand for labour is high and inelastic, supply is low and inelastic
The wages tend to low, if
The demand is low and elastic, the supply is high and elastic
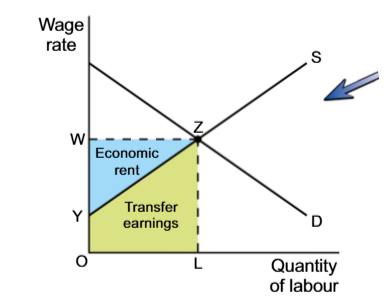
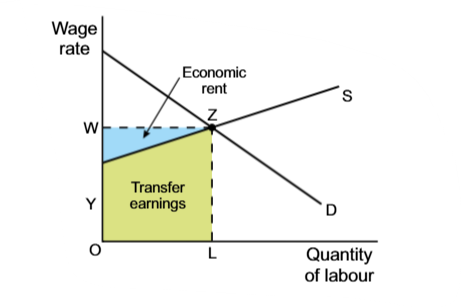
Transfer earning
The wage to keep the labour force functioning
Economic rent
Money, paid besides on the transfer earnings


In perfectly competitive Labour markets, firms are
Price takers

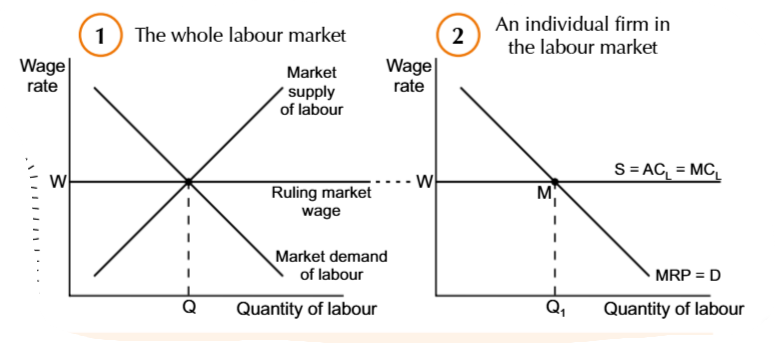
Monopsony market means
A market with only one buyer
In a monopsony labour market, there is only one
employer to work for
A monopsonist employer can pay the wage
Lower than the worker’s MRP

Trade unions increase the
bargaining power of the workers
Productivity bargains

Trade union wage negotiations might result in
Unemployment
Trade unions can cause labour market failure by forcing the wages up
to the rates higher than the market equilibrium wages, causing a surplus of labour
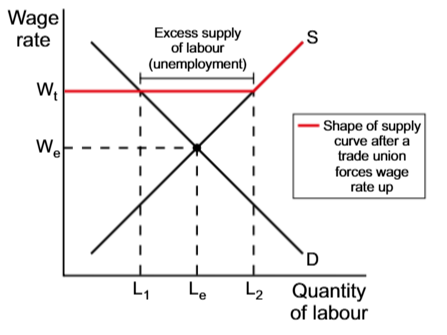

Pay rises, negotiated by trade unions may
Not lead to unemployment
How can trade unions, negotiating for the pay rises, not end up fostering excess labour supply
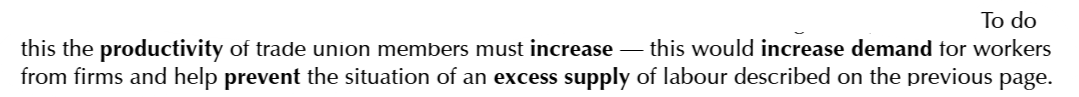
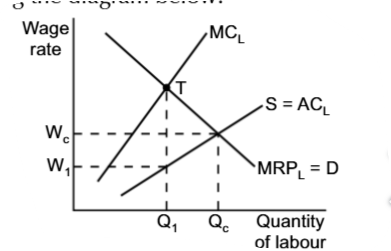
In monopsonistic labour markets, trade unions can
increase the wages and jobs
Since, in a monopsonistic market, the wages, paid to the workers, are lower than their MRP; with trade union,
the wages could be increased up to the Equilibrium ones
A monopsony with a present trade union is labelled as a
bilateral monopoly, because it has a single buyer and a single seller
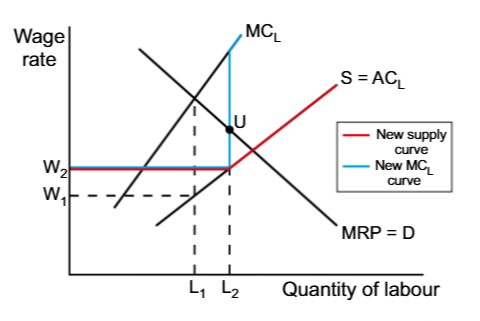

Wage discrimination can result in
lower wage costs for firm
The wage discrimination takes place when firms with monopsony power pay
different wage rates, depending on workers’ willingness to supply labour

Labour market discrimination
Workers being discriminated, based on their race, gender etc
Disadvantages of wage discrimination
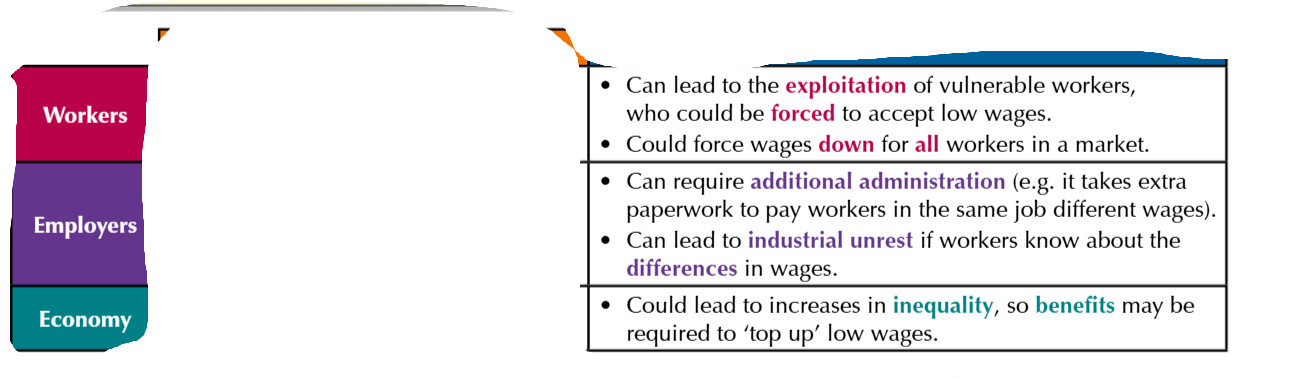
Advantages of wage discrimination

A lot of employers believe that
the MRP of employees, that they discriminate, tends to be lower
By discriminating against workers, based on such a concept, employers
miss out on a lot of qualified and efficient workers, who in fact have a much higher MRP. This entirely leads to lower efficiency of the firm and higher costs, lower wages(as the MRP curve shifts to the left)
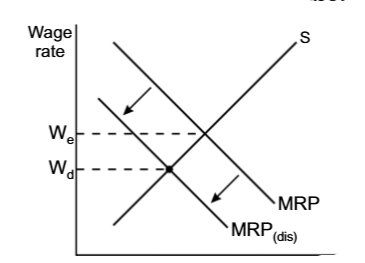

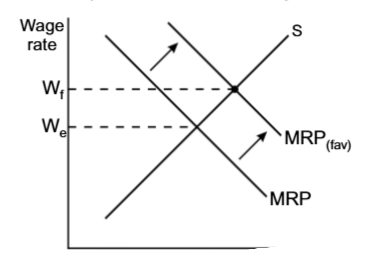

Employers, that do not discriminate,
have larger supply, their supply curve shifts to the right, which makes the discriminated workers’ wages even lower
Discrimination, generally, leads to
increased costs for both government, and the economy
The costs of discrimination include
Necessity to pay benefits to unemployed individuals, absence of allocative and productive efficiency in some industries (decreased international competitiveness), absence of taxes that could have been paid by discriminated employees
Skill shortages in some labour markets lead to
Increased costs for the firms
Incentives might be given out,
in order to motivate people to work
It is widely argued that, imposing
the National Minimum Wage (NMW), leads to unemployment
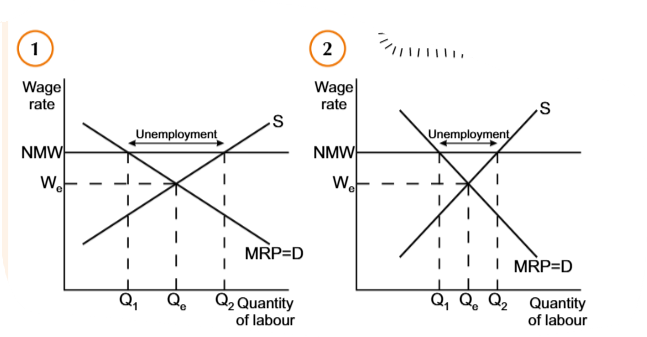

Advantages of introducing the NMW

Disadvantages of introducing the NMW

The living wage covers
the basic cost of living