Musculoskeletal Imaging Introduction and General Bone (done except ask about those 2 flashcards that say to)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What is Wolff’s Law and Utah Paradigm?
A bone grows and remodels as a response to force or demands placed on it
What should you interpretation paradigm be?
Soft tissue changes
Osseous changes (periosteum, cortex, medulla, zone and rate)
Classify as benign or aggressive
Differentials
Why should you radiograph the opposite limb?
For comparison to the other limb
How do you assess the soft tissue?
Are the changes focal, regional, or diffuse
Is there an increase or decrease in volume
Is there an increase or decrease in density
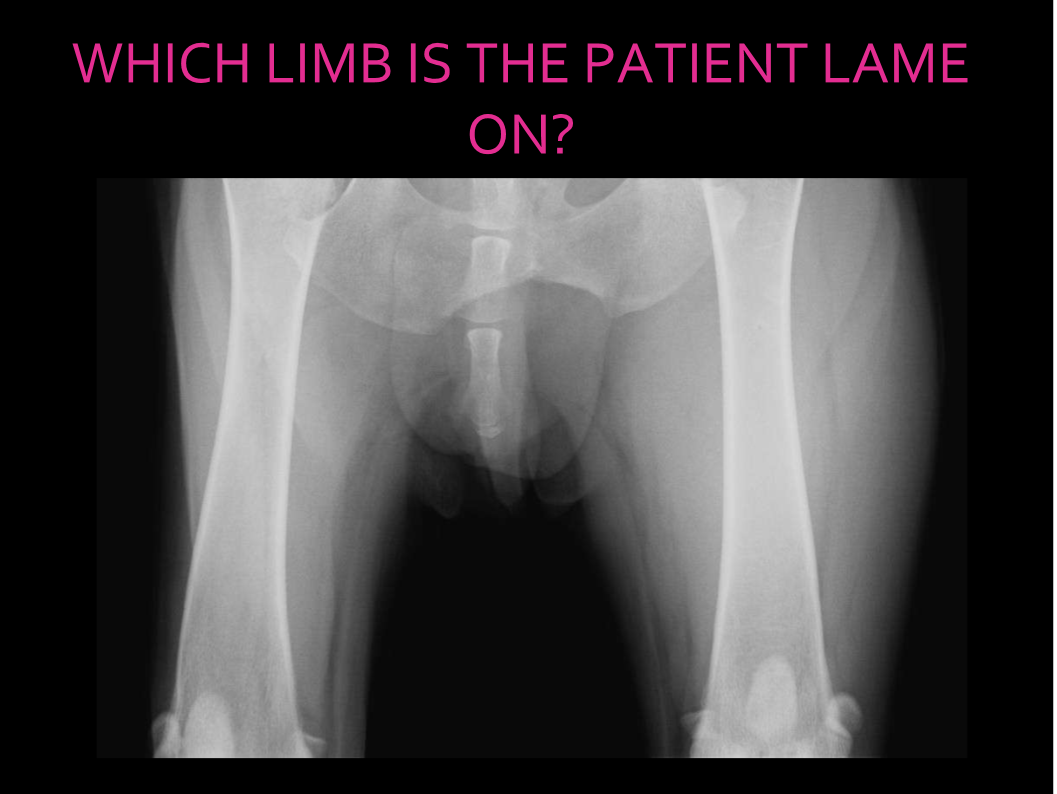
Right, less soft tissue opacity
What is a fascial plane?
A potential space around muscles
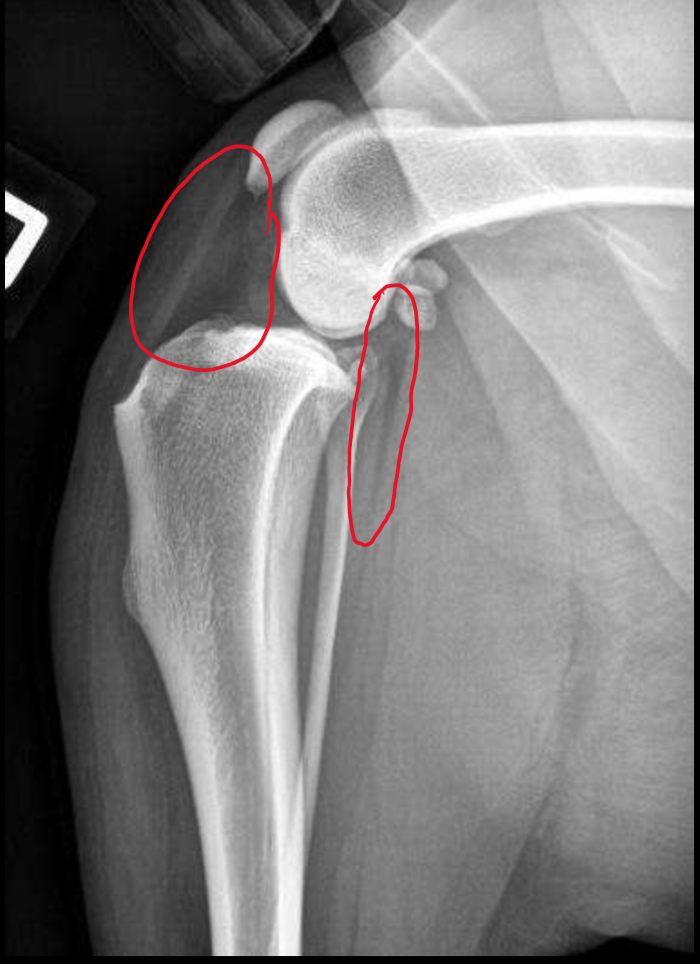
Fascial plane. Cranial is infrapatellar fat pad. Caudal fascial plane
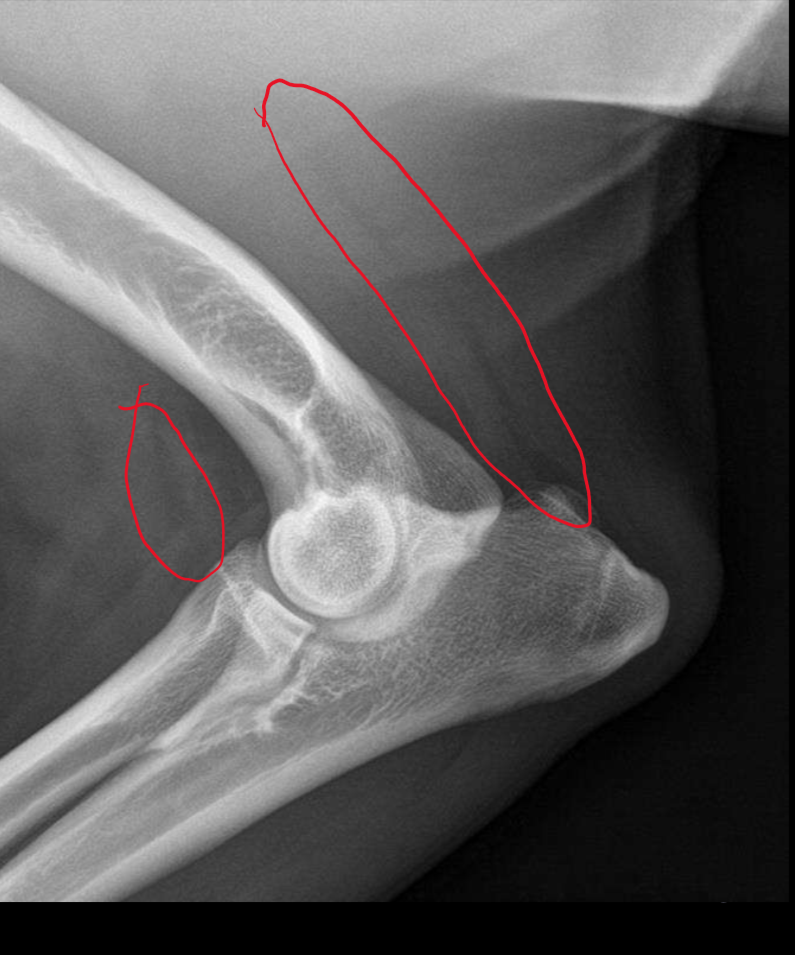
Fascial planes
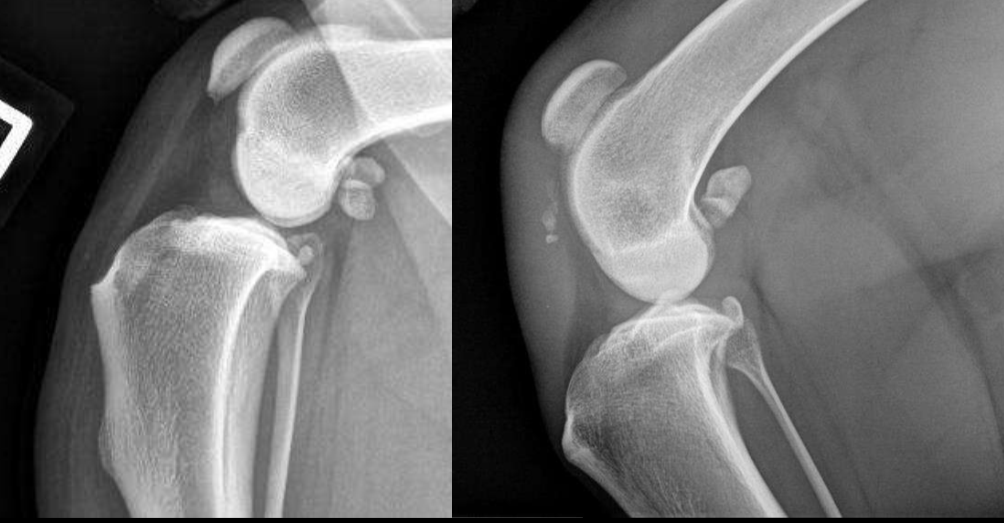
Which is abnormal and why?
Right because infrapatellar fat pad is indented and caudal fascial plane is obstructed
What is a term for gas within the soft tissue?
Emphysema
What can cause soft tissue emphysea?
Penetrating trauma wounds
Iatrogenic from an injection
Gas producing bacteria
What are the types of mineralization?
Dystrophic
Metastatic
What causes increased soft tissue opacity?
Mineralization
What is dystrophic mineralization?
A tissue is injured and metaplasias into mineral
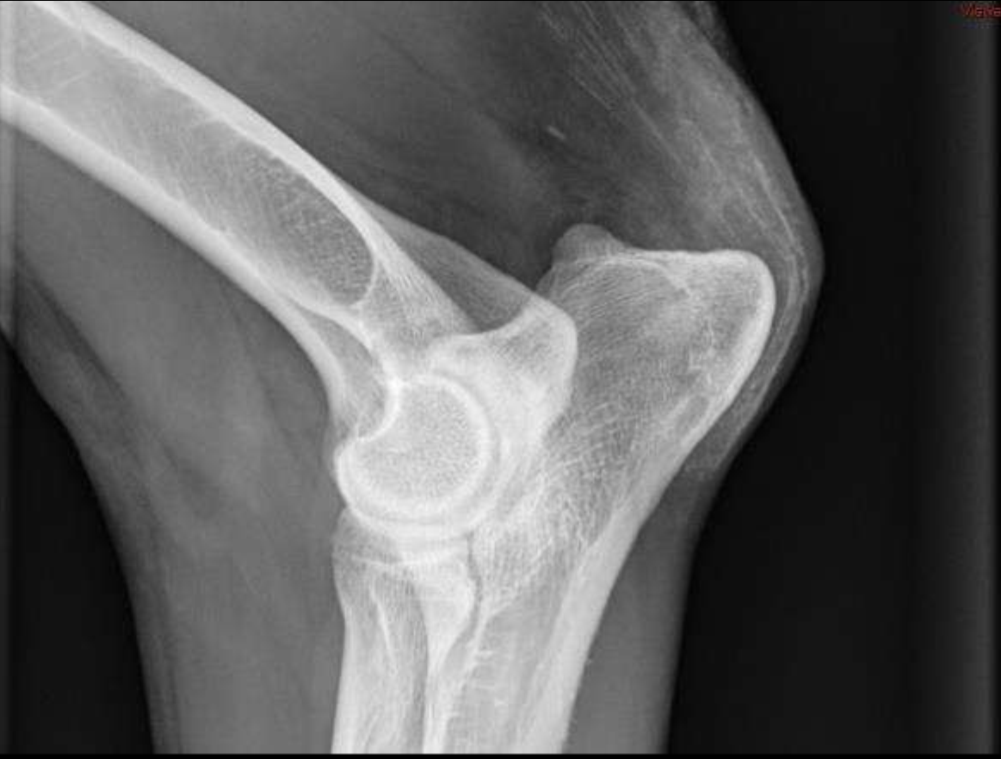
Soft tissue mineralization of the triceps at its insertion on the tuber olecrani
dystrophic
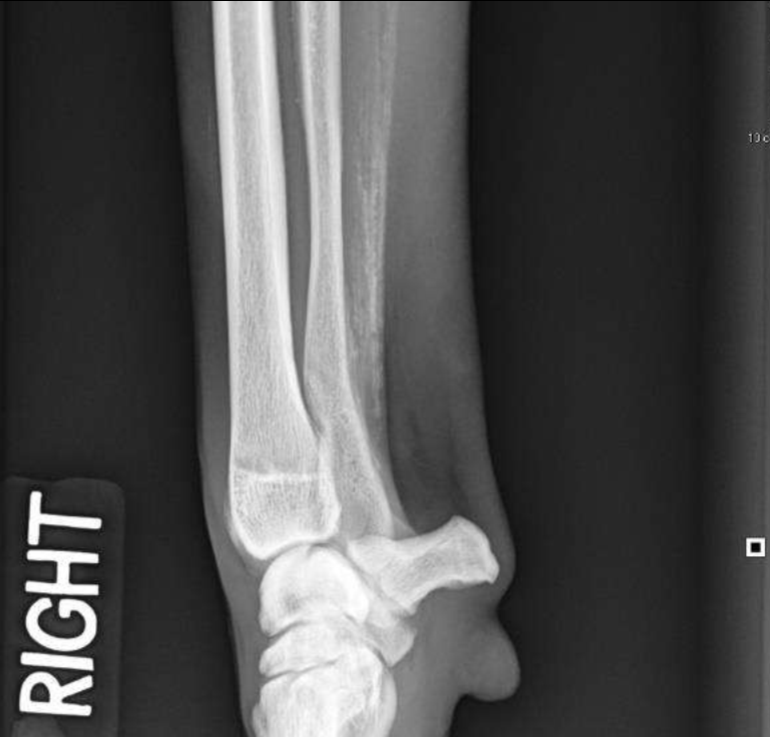
Soft tissue mineralization caudal to the ulna
Dystrophic
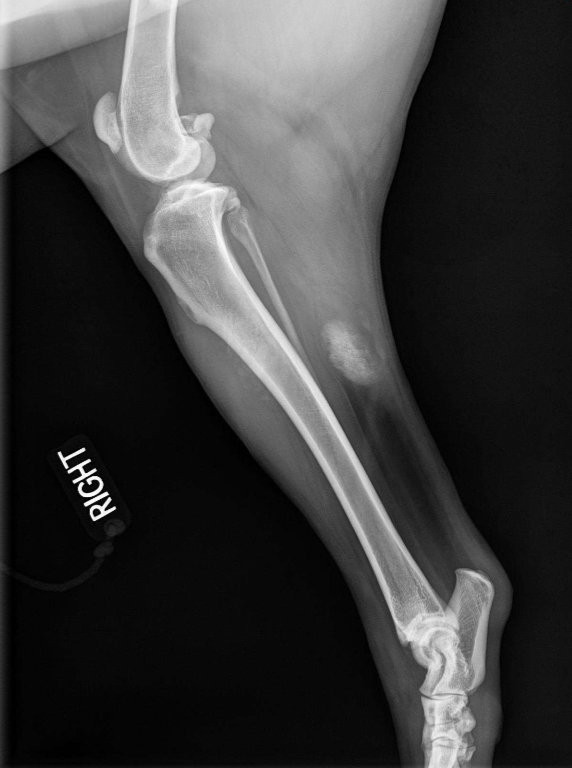
Soft tissue mineralization at the area of the gastrocnemius
Could be healing from a wound, or a lymph node. Maybe dystrophic?
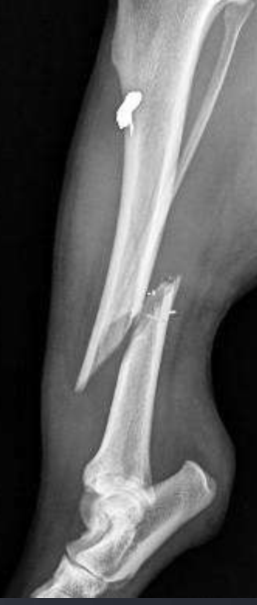
metal opacity from a ballistic
What are causes of metal opacity in soft tissue?
Ballistics
Implants
Microchip
How can lesions in a bone be distributed?
Monostotic
Polyostotic
Focal
Generalized
Symmetrical
Asymmetrical
What does monostotic mean?
Only effects one bone
What does polyostotic mean?
Effects multiple bones
What are predilection sites?
IDK i couldnt understand her
How can bone respond to disease?
Take away bone
Add more bone
T/F bone can be taken away and added at the same time?
True
What is osteosclerosis?
Radiographic term for increased bone opacity/density
What is osteopenia?
Radiographic term for decreased bone opacity/density
What are the 2 types of osteopenia?
Osteoporosis
Osteomalacia
What is osteoporosis?
Quantity of bone is decreased but existent bone is of normal composition
What is osteomalacia?
Quality of bone is decreased. Increased % of non-calcified osteoid or insufficient mineralization of osteoid matrix
What are the causes of generalized osteopenia?
Metabolic
Nutritional
ASK WHAAT OTHER 2 ARE
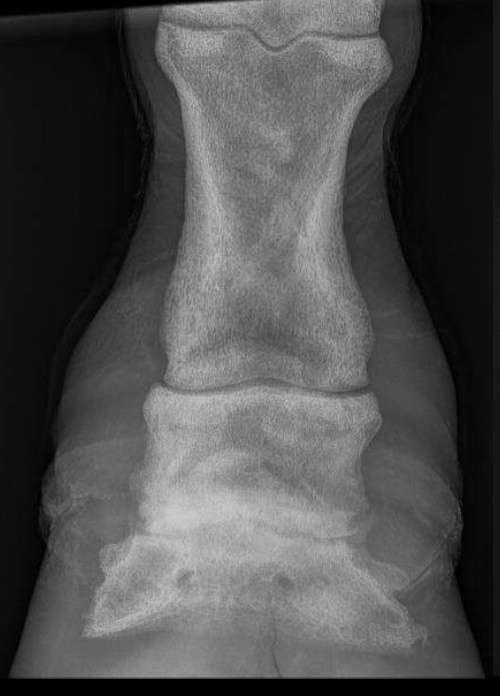
Osteopenia (decreased overall density, more trabeculae)
What is a pathological fractures?
No trauma but getting a fracture
How long does it take for lytic changes to appear radiographically?
5-7 days
How long does it take for productive/blastic changes to appear radiographically?
10-14 days
What causes osteoblastic change?
Periosteal reactions
Callus (fracture)
Osteophytes and enthesophytes (joint)
What are the patterns of osteolytic change?
Geographic lysis
Moth eaten lysis
Permeative lysis
What is the periosoteum?
Outer layer of the bone
What is the structure of the periosteum?
Inner cambium layer
Outer fibrous layer
Attached to bone by Sharpey’s fibers
T/F the periosteum is invisible until pathology arises?
True
What is a periosteal reaction?
Caused by when periosteum is damaged or elevated from underlying bone. It heals by new bone being laid down from the inner cambium layer
What can you use to determine between non-aggressive and aggressive bone lesions?
Location and number
Pattern of lysis
Pattern of new bone production
Cortical changes
Transition zone to normal bone
Change in lesion over time
T/F the radiographic appearance of an aggressive lesion will change rapidly compared to non-aggressive lesions?
True
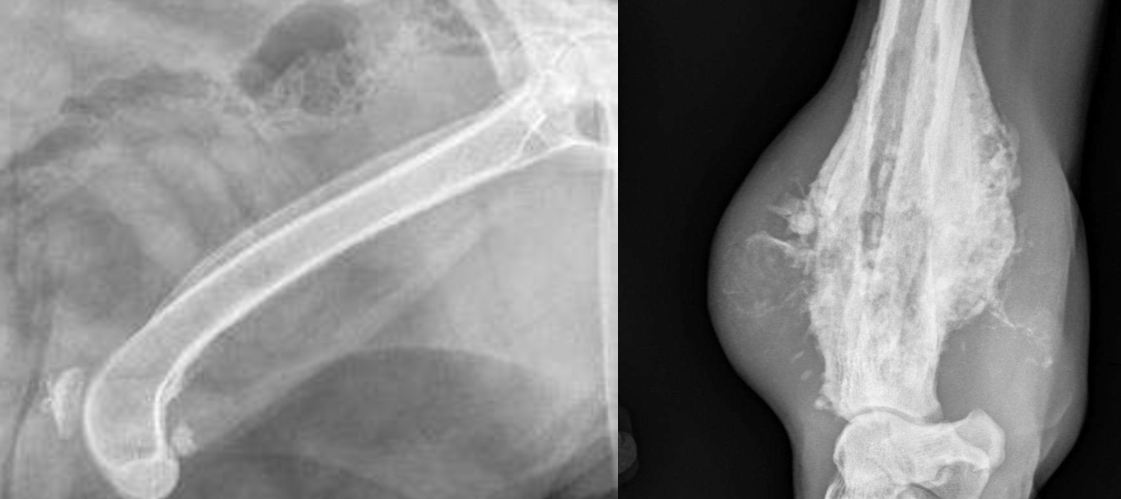
Which is more aggressive?
Right
What are the types of continuous periosteal reactions?
Solid
Lamellar
Lamellated
What are the types of periosteal reactions?
Continuous and interrupted
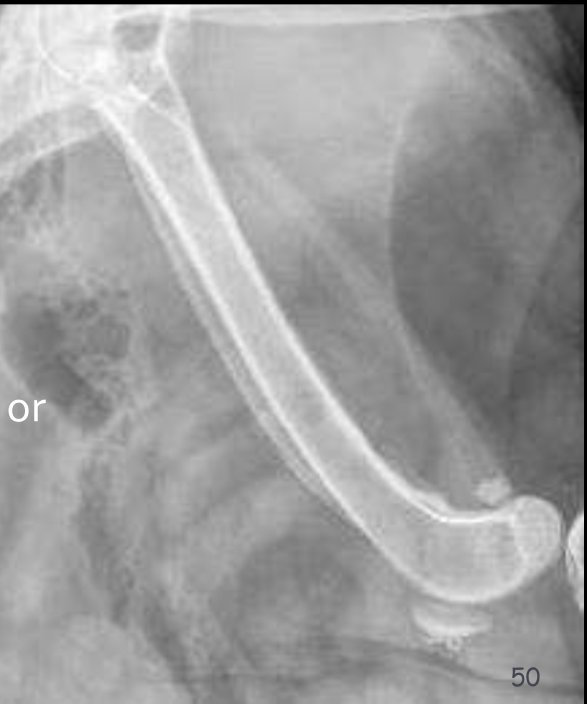
What type periosteal reaction?
Solid
Describe a solid periosteal reaction?
bone completely fills the area under the reaction
More chronic, the more solid/mineralized
Surface can be smooth or undulating
Non-aggressive
Callus
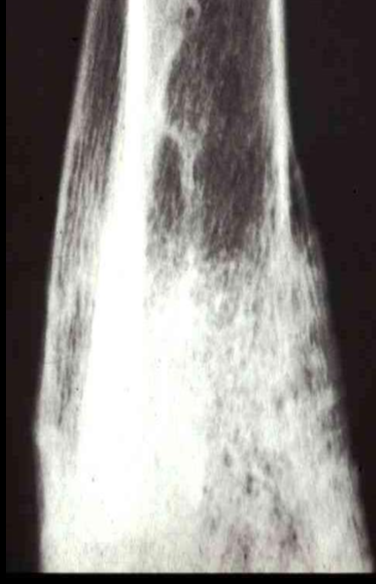
What type of periosteal reaction?
Lamellated periosteal reaction
Describe a lamellated periosteal reaction
Layered or onion skin appearance
Indicates a cyclic or intermittent process
More aggressive than solid, smooth bone usually associated with a benign process
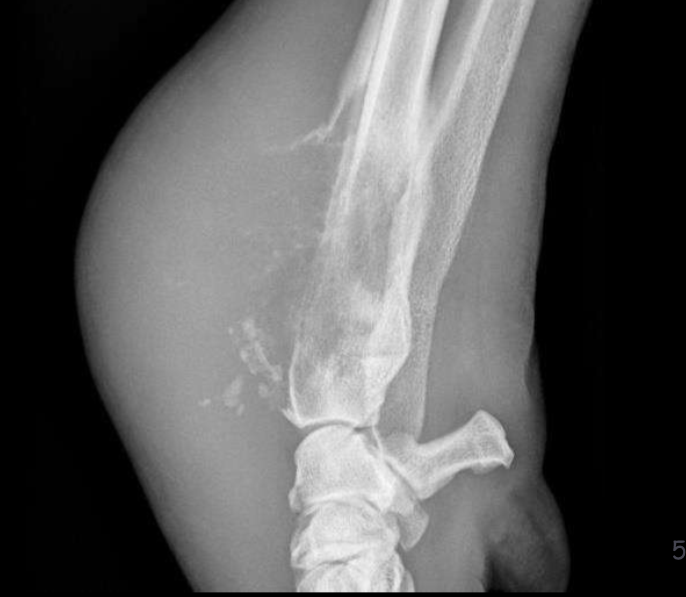
What type of periosteal reaction
Amorphous periosteal reaciton
What is the most aggressive periosteal reaction?
Amorphous
What are the patterns of bone lysis in order of aggressiveness?
Geographic
Moth-eaten
Permeative

Geographic bone lysis
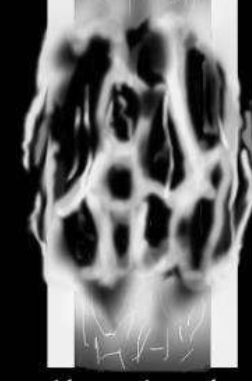
Moth-eaten bone lysis
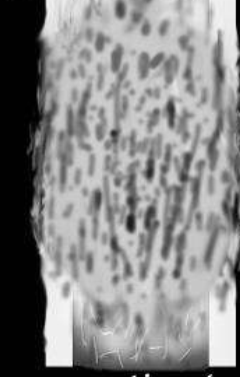
Permeative bone lysis
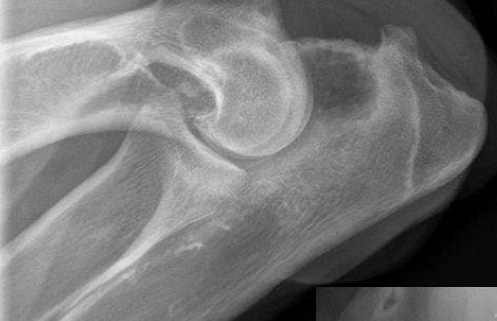
Geographic bone lysis
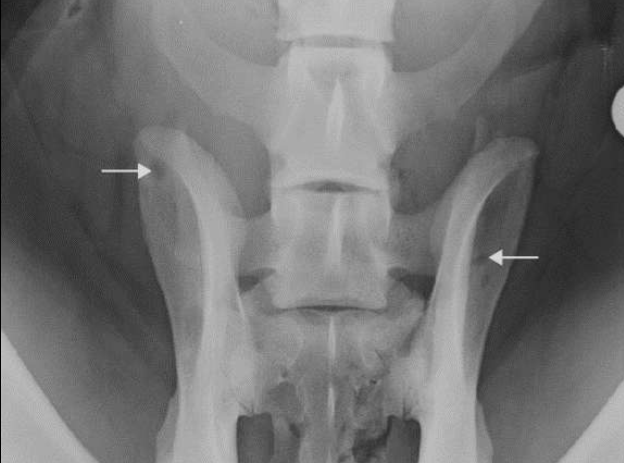
Geographic bone lysis (multiple myeloma identified by the “punch” wound in the bone)
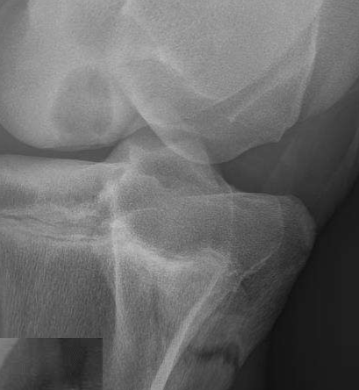
Geographic bone lysis
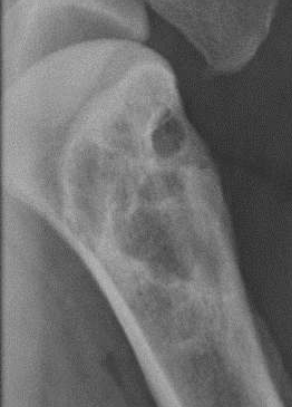
Moth eaten lysis
Moth eaten lysis
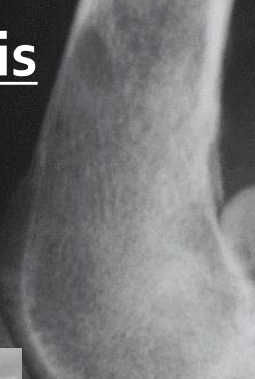
Moth eaten lysis
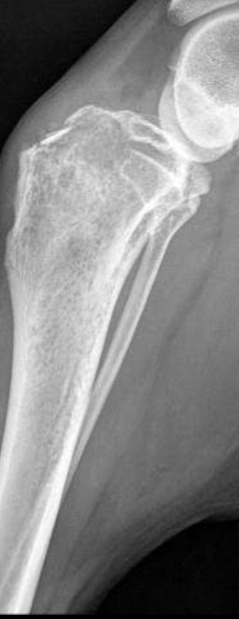
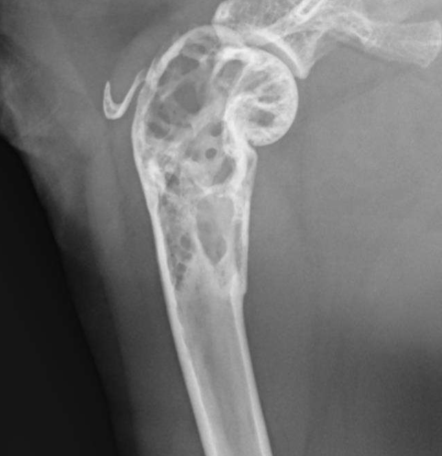
Permeative lysis
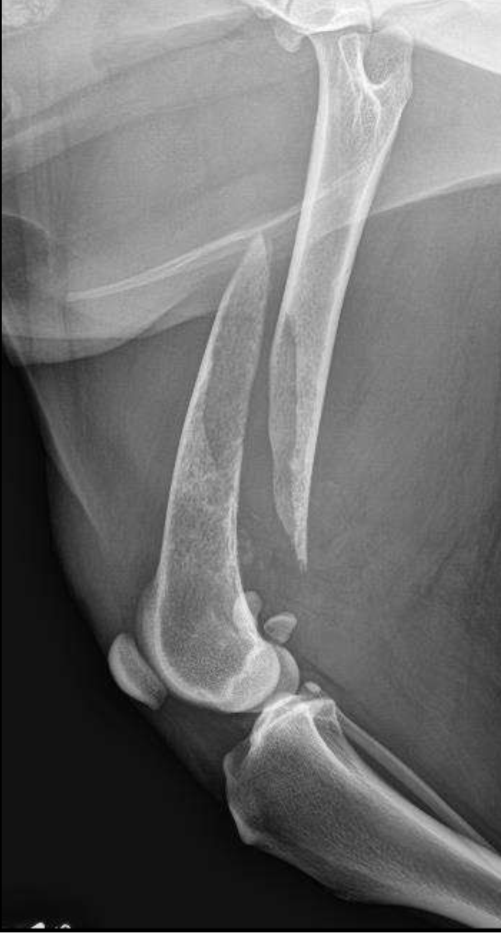
Permeative lysis and a fracture
How should you characterize a lesion?
Based on the most aggressive feature
T/F skeletal changes fall along a continuum?
True
What can cause a solid periosteal reaction?
Callus, benign
What can cause a lamellated periosteal reaction?
Low grade osteomyelitis
Chornic/repeated
What can cause a columnar (palisading periosteal reaction)?
Hypertrophic osteopathy
Bacterial osteomyelitis
What can cause a spiculated periosteal reaciton?
Neoplasia or osteomyelitis
What can cause an amorphous periosteal reaction?
Amorphous
Rank the periosteal reactions from least to most aggressive
Solid, smooth bone
Lamellated
Columnar
Spiculated
Amorphous
What are the interrupted periosteal reactions?
Thick brush-like
Thin brush-like
Sunburst
Amorphous bone production
What is a spiculated periosteal reaction?
Periosteal reaction perpendicular to the cortex along the Sharpey’s fibers
What does spiculated periosteal reaction appear as?
Columns of bone or radiating like a sun burst
When is columnar spiculated periosteal reaction seean?
Diseases like hypertrophic osteopathy
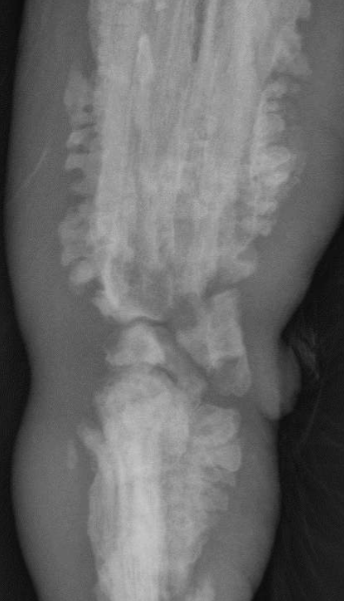
What periosteal reaction
Palisading periosteal reaction
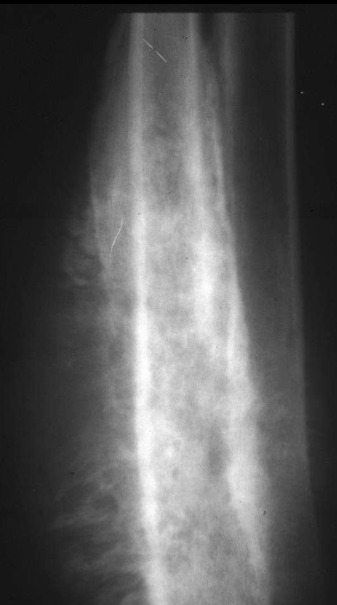
What periosteal reaction?
Sun burst