Lab #6 - Equine Management + Milk Quality
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
normal respiratory rate for an adult horse
10-24 bpm
normal heart rate/pulse for an adult horse
24-44 bpm
normal mucous membrane color
pink-normal
red → infection
white → abnormal + anemic
blue → low oxygen
normal capillary refill time (CRT)
< 2 seconds
normal temperature range
99-101 F
name the blood vessels at the two locations where you can feel a horse’s pulse
transverse facial artery
facial artery
transverse facial artery
right by the eye
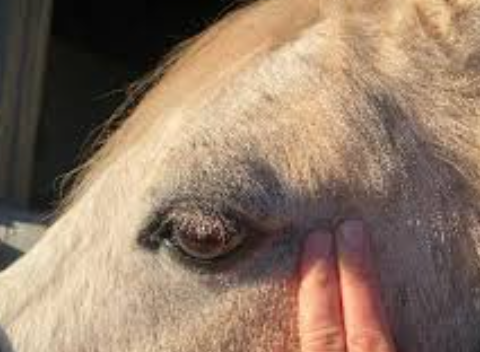
facial artery
in the submandibular region
under the jaw

where to feel for the digital pulse on the leg
above and below the fetlock
lateral → outside of leg
medial → inside of leg
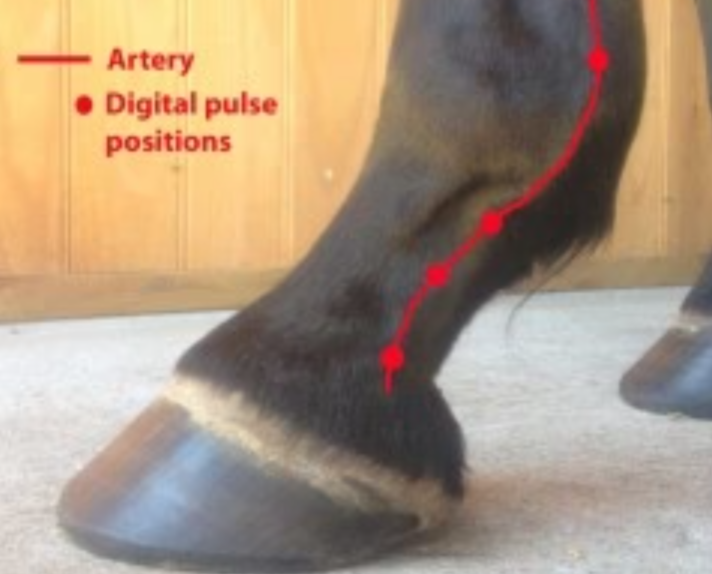
what is the significance of a bounding digital pulse?
indicates infection/inflammation in the hoof
ex. laminitis
where should you place a stethoscope to auscult (listen to) the heart
just below the elbow (nestle it in)

where should you place a stethoscope to auscult (listen to) the cecum
flank area right side
1-3 gut sounds per minute

where to auscult for breath rate
lung area
list 4 factors that may increase a horse’s temperature, pulse and/or respiratory rate
1) increased activity
2) stress
3) body conditioning score
4) illness/pain
5) weather
foals → everything is higher
list 6 areas that you should evaluate when assigning a body conditioning score to a horse
1) withers
2) crest of neck
3) ribs
4) shoulders
5) loin/back
6) tailhead/dock
scale: 1-9
ideal: 4-5
what is the definition and purpose of the stay apparatus and reciprocal mechanism?
composed of ligaments, tendons, and muscles that allow a horse to support its body weight while standing with 3 legs straight and 1 hind leg relaxed without using significant energy and muscle activity
→ can rest standing up with minimal energy
what is clinical mastitis?
the visible infection/inflammation of the mammary gland or milk
what is subclinical mastitis?
the infection/inflammation of the mammary gland/milk that IS NOT VISIBLE
4 methods of identifying mastitis in dairy cows… clinical, subclinical or both?
California Mastitis Test (CMT)
both clinical and subclinical
Observing mammary gland
clinical
Observing milk quality
clinical
Culture milk for bacteria
both
what is milk made up of?
87% water + water soluble vitamins
4-6% milk fat
7-9% skim solid → proteins, carbohydrates
how is clinical mastitis usually treated on dairy farms?
intramammary antibiotics
what is the role of a farrier for horses?
a specialist in horse hoof care who trims and balances hooves and places shoes if needed
how often should an average horse’s hooves be evaluated and/or trimmed?
every 6-8 weeks to keep them even and prevent damage
what is the rate of hoof growth for adult horses?
0.24-0.4 inches per month
list 3 different reasons for shoeing a horse
1) basic hoof protection
2) traction + support
sports, work, athletic endeavors
3) treatment of medical conditions