Fields - Magnetic Fields
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
The Law of Magnetic Poles
Opposite magnetic poles attract
Like magnetic poles repel.
Magnetic Force Field
The area around a magnet in which magnetic forces are exerted
The magnetic field at any point is a vector quantity, represented by 𝛽 Ԧ.
Principle of Electromagnetism
Moving electric charges produce a magnetic field
was an accidental discovery
Magnetic Fields Around Bar Magnets
Magnetic field lines are ALWAYS drawn from North Pole → South Pole.
Permanent Magnets
Magnetic field lines always form closed loops – you can never have just a south pole or just a north pole.
the field is the strongest at the poles (the ends)
Domain Theory of Magnetism
tiny magnetically homogeneous regions or “domains” behave based on e- spin
if all e in all the domains spins in the same dir in the structure of a material, the material is magnetic
Earth’s Magnetic Field
The convention is to refer to the south magnetic pole as Earth’s “north magnetic pole.’
Geological studies show that Earth’s magnetic field has completely reversed direction many times during the planet’s history.
right hand rule for solenoids and straight conductors
see notes/watch video
current
charges per time measured in amperes w base units of C/s
current convention
conventional current (flow of positive charges flow from pos to neg) based on orig definition of current b4 scientists det it was the flow of electrons
magnetic field of a current loop
the magnetic field is very strong inside the loop but weak outside.
solenoid
long conductor wound into a coil of many loops that produces a strong magnetic field inside the coil.

electromagnet
a magnet produced from electric current
electromagnets cont’d
Centers of solenoids are often filled with iron to strengthen 𝛽
Adding carbon to iron “locks” domains in place, to create permanent magnets.
Electromagnetics can be turned ON/OFF using electricity.
2D diagrams of currents
dot → going out of page
x → going into page
applications of magn fields
an MRI machine uses magnetic fields that are 60,000x stronger than the Earth’s magnetic field to obtain images of the human body
magn field stren unit
tesla (T)
T = kg / C * s
magn force
non-contact
if a current (moving charges) produces a force on a magnet, then from Newton’s 3rd Law the magnet must produce an equal but opposite force on the current.
act on e and protons and ions
only CHARGED particles moving thru a mag field experiences a mag force
comparing magnetic force w grav force and elec force
Fm is dependent on velocity of the charge, grav and elec are independent of the v of the mass or charge
magn force is non-zero only if
the charge is moving w velocity
when the angle between magn field stren and the v = 90
Fm is a max
when the angle between magn field stren and the v = 0 or 180
Fm = 0 bc the particle is moving in the dir of the magn field
right hand rule for a moving charge in a magn field
If you point your thumb in the direction of the velocity of the charge v, and your straight fingers in the direction of the magnetic field 𝛽, then your palm will point in the direction of the resulting magnetic force Fm.
when q is pos, Fm pts out of palm
when q is neg, Fm pts into palm
motor principle
a magn field can exert a force on a MOVING CHARGE or CURRENT CARRYING CONDUCTOR
this force is known as the lorentz force
magn of Fm depends on
the field stren
I =
current, which is charge over time
I is perpen to field and perpen to force
electric and magn fields can
induce each other
reversing either the current dir or magn field reverses the
direction of the force
a magn field does not
exert a force on a current moving || to the dir of the B
a mass spectrometer is used to
accelerate particles
when launched into a magn field, a moving particle starts undergoing
uniform circ motion
faraday’s iron ring
To improve his results, Faraday built an “iron ring” to increase the magnetic field inside the solenoids
Current still occurred only when current was switched ON/OFF
Law of Electromagnetic Induction
A magnetic field that is moving or changing in intensity in the region around a conductor causes or induces charge to flow in the conductor.
when a current is steady, the magn field is
const; so no current is induced in secondary circuit
the greater the change in magn field,
the larger the induced current.
A constant magnetic field ______ induce a current.
does not; A changing magnetic field induces electric current.
faraday’s principle involves
Moving magnetic field around a conductor
permanent magnet
pnj made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field
how whow to tell when an obj is magnetized
domains are lined up (unmagnetized is when they are not aligned)
how earth’s magnetic field contributes to aurora borealis
energetic electrically charged particles (mostly electrons) accelerate along the magnetic field lines into the upper atmosphere, where they collide with gas atoms, causing the atoms to give off light.
magnetic field lines in a solenoid
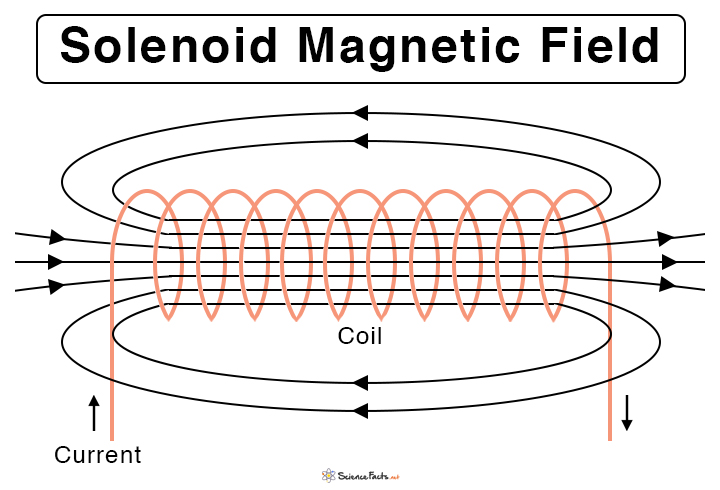
current is measured in
amperes (C/s)
current is a
vector
V increases if
work is done to move a charge against its natural tendency
Ee / q