Unit 3: The Knee is a Claustrophobia (it never ends)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Knee
Largest joint in the body
Does not get hurt as often as the should or ankle, but when it does get hurt, it needs surgery and rehab
Both mobile and stable
What are the chances of losing the leg when the knee is dislocated?
50% chance of losing the leg
50% chance of walking again
Athletes have these percentages higher unless emergency services are available right away
Bone
Below average stability
Ligaments
Average stability
Muscle/Tendon
Above average stability (with potential)
Cartilage
Assist - give bone formation more depth
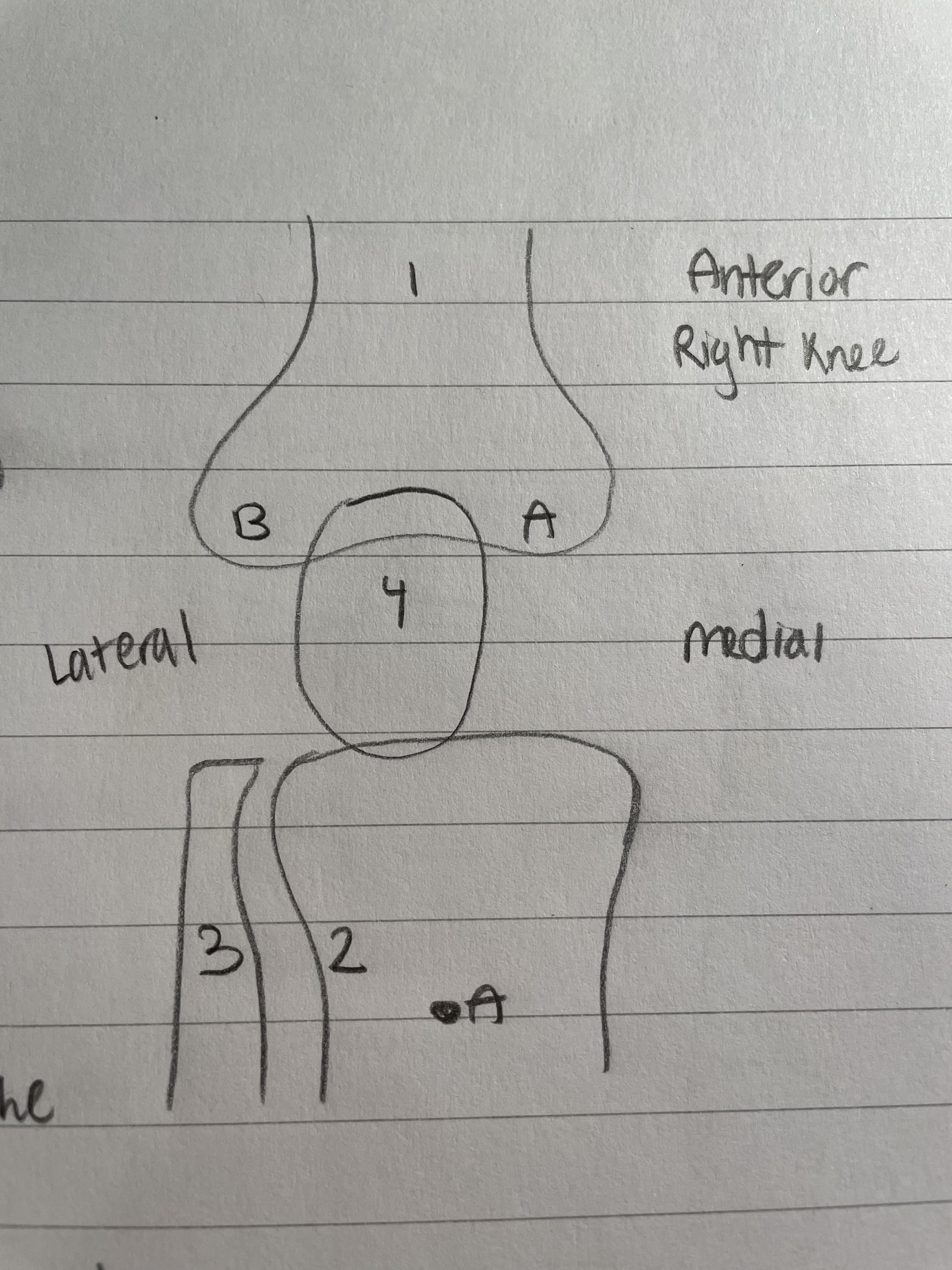
Femur (Knee Bone)
Largest bone in the body
A & B are condyles
A is the medial condyle
B is the Lateral Condyle, which is rounded out/convex
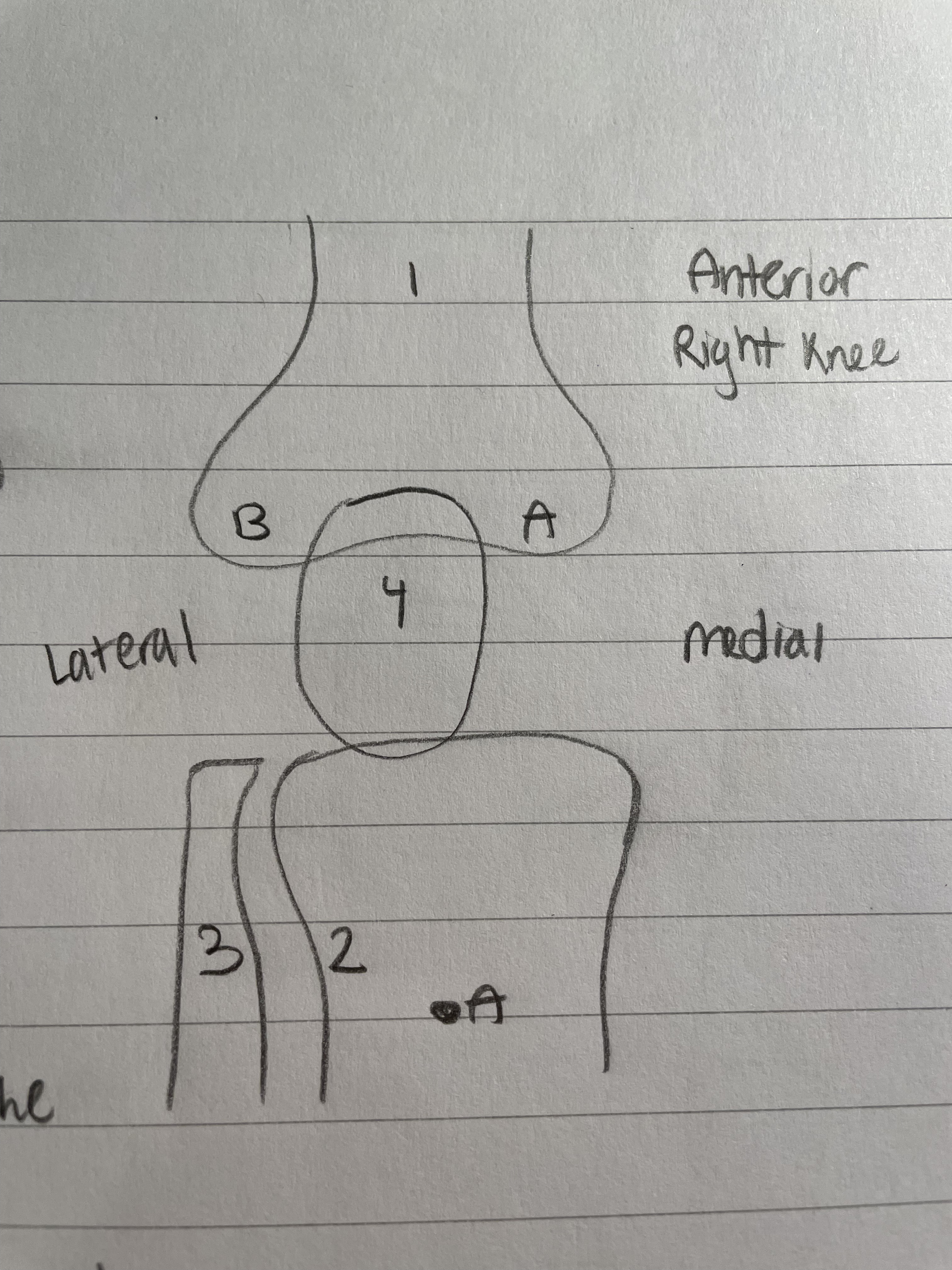
Tibia (Knee Bone)
Medial Bone
Weight bearing bone of the lower leg
A. = Tibial Tuberosity/Tuberocal
4 quad muscles connect here
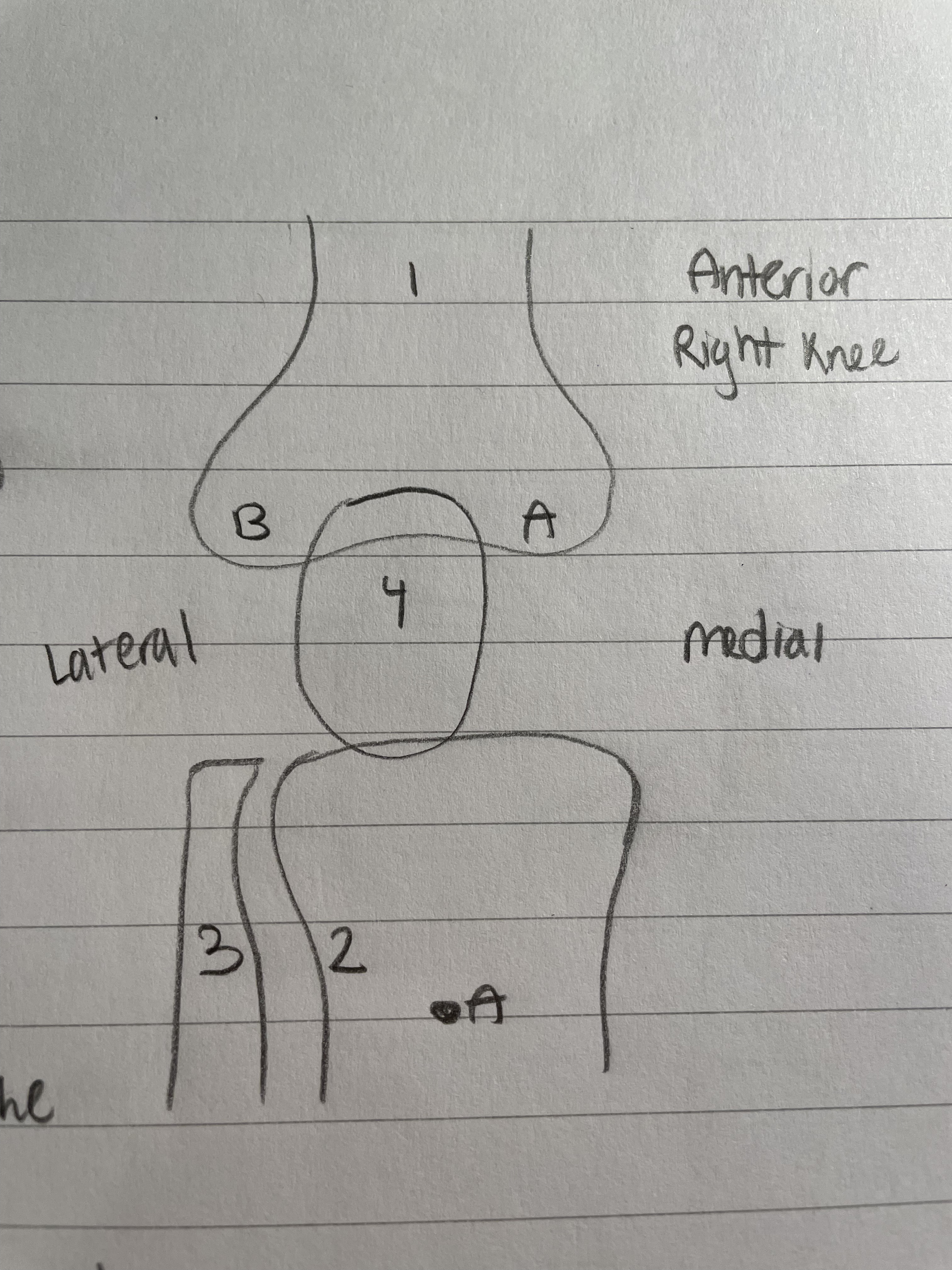
Fibula (Knee Bone)
Lateral Bone
Not weight bearing
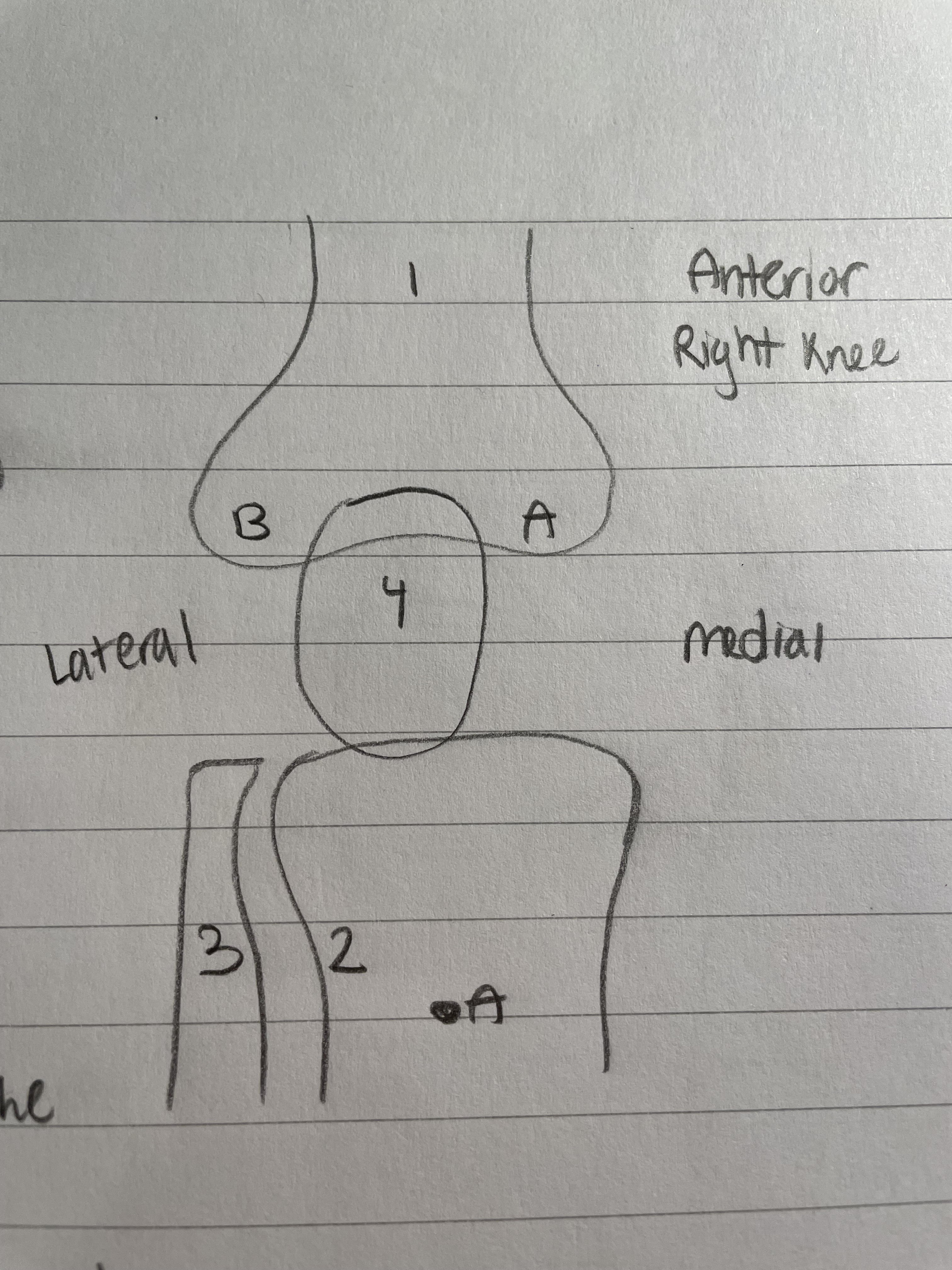
Patella (Knee Bone)
Knee Cap
Sesmoid Bone
Protects the condyles
Dislocates a lot
Sesmoid Bone
Floating bone
Not directly connected to any bone
Patella
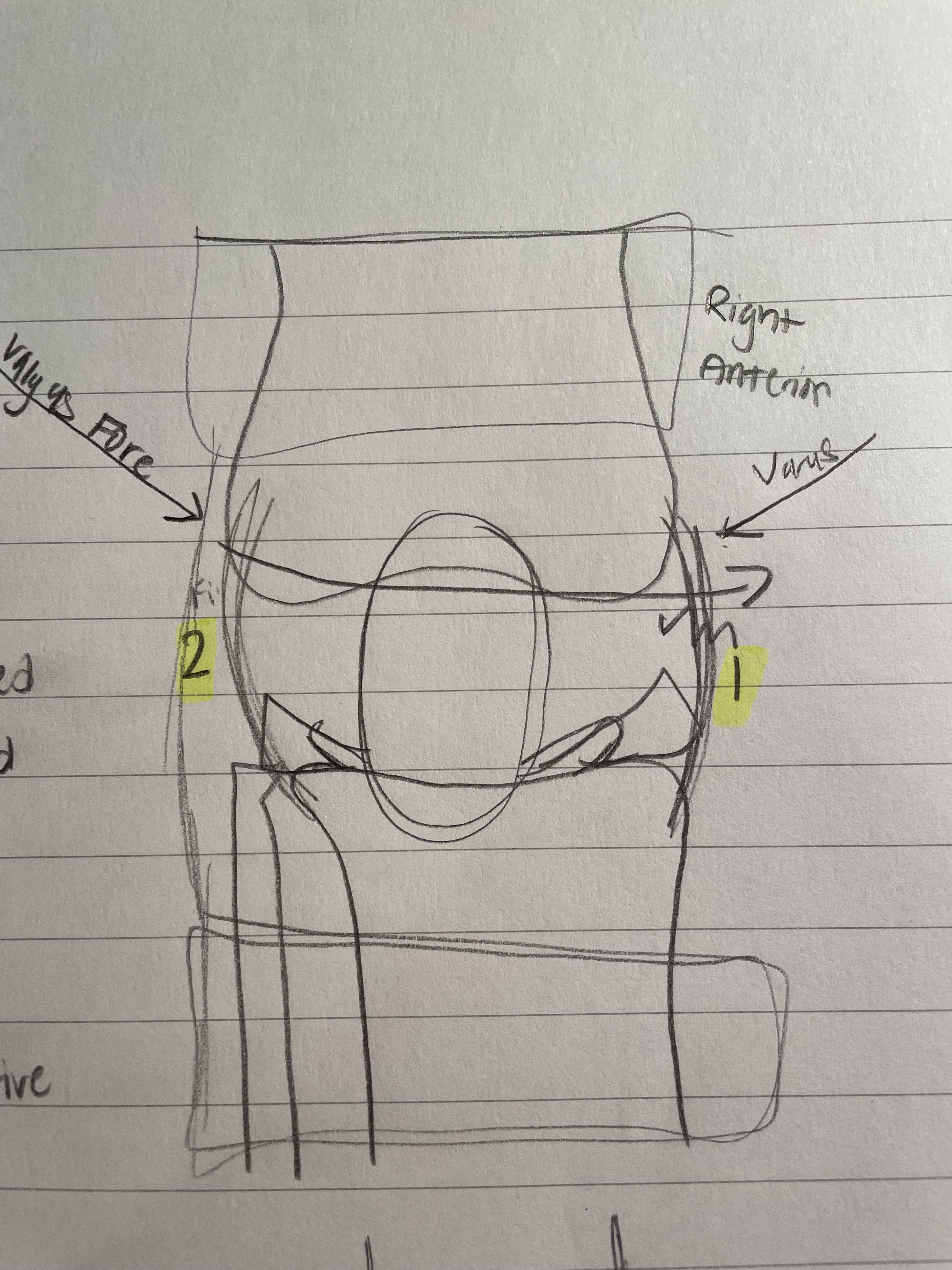
Medial Collateral Ligament
Also known as the Tibial Collateral Ligament
Gets hurt the most and is easiest to hurt
Can live with it being damaged unless cartilage is damaged
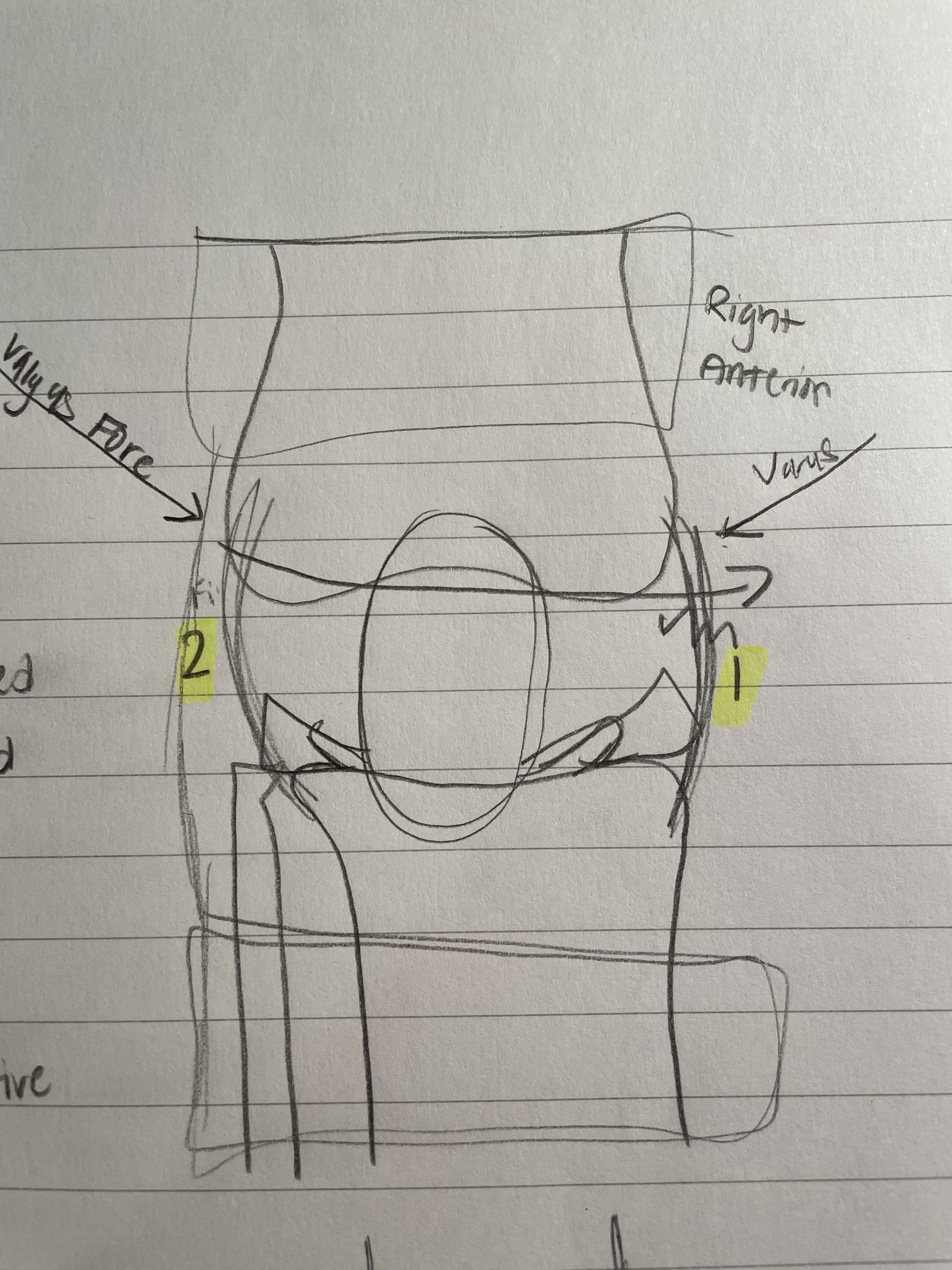
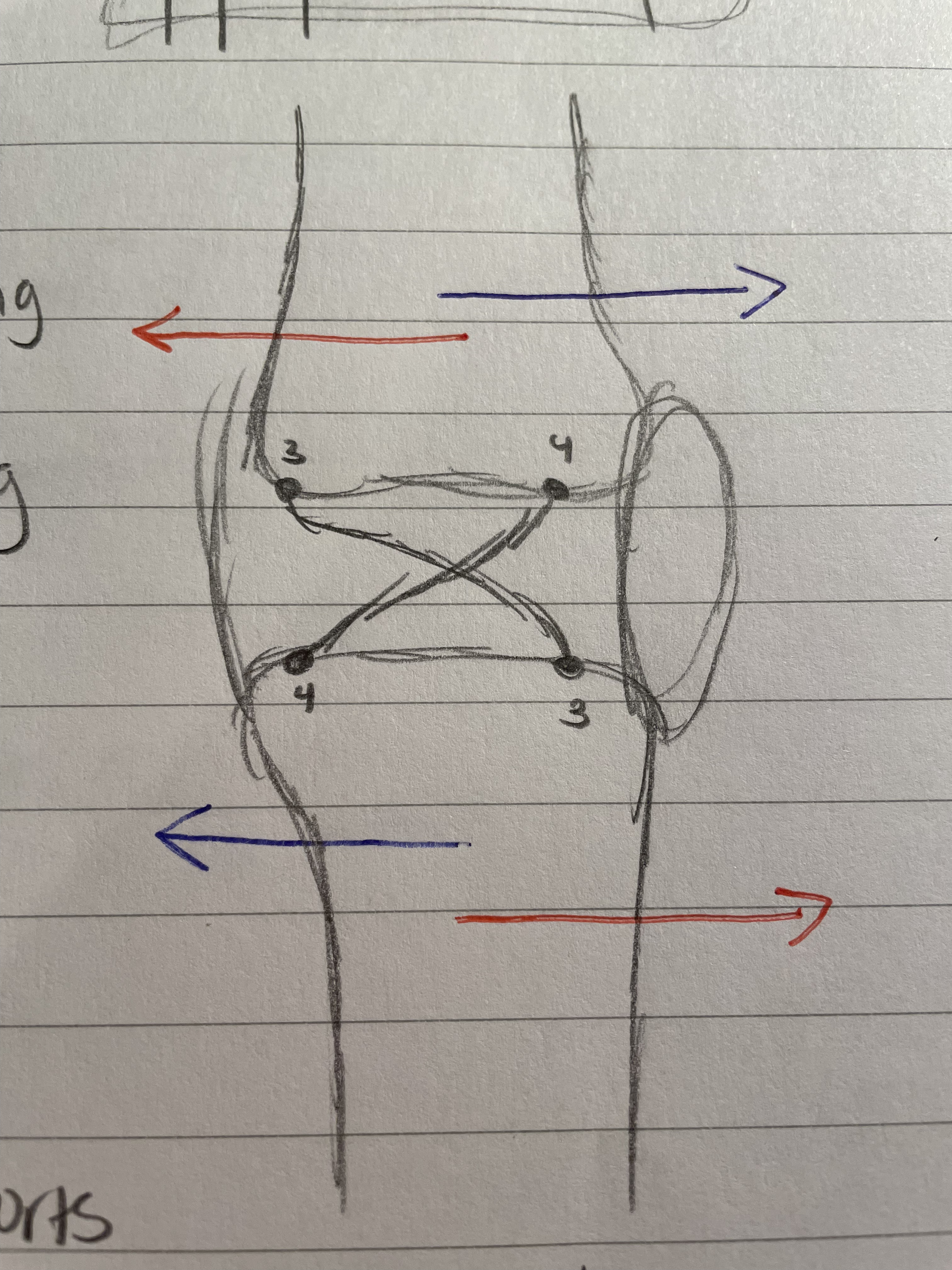
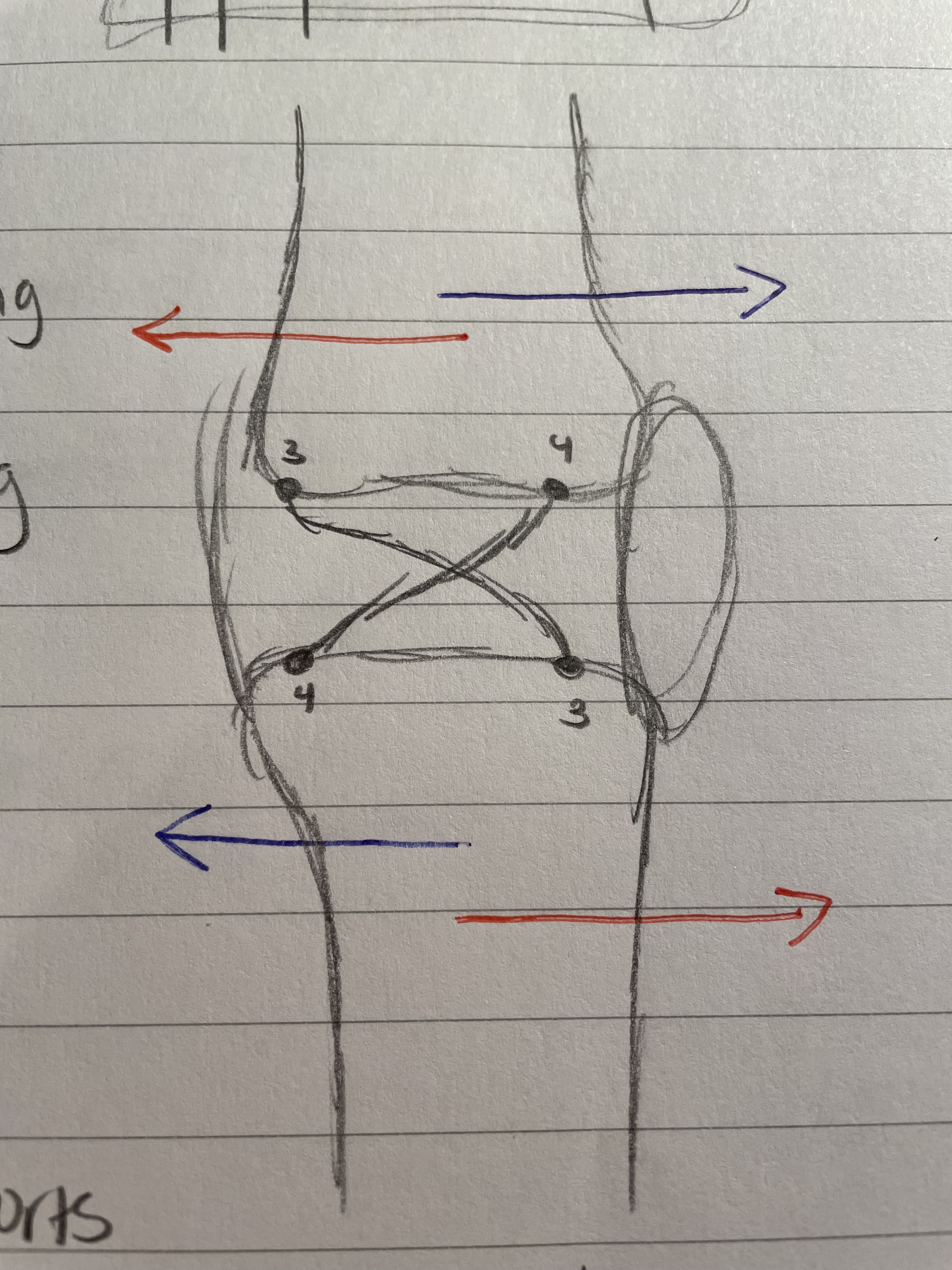
Valgus Force
Mechanism of Injury
Shown in the diagram, valgus force comes in from the right (for the right knee) and tears the Medial Collateral Ligament
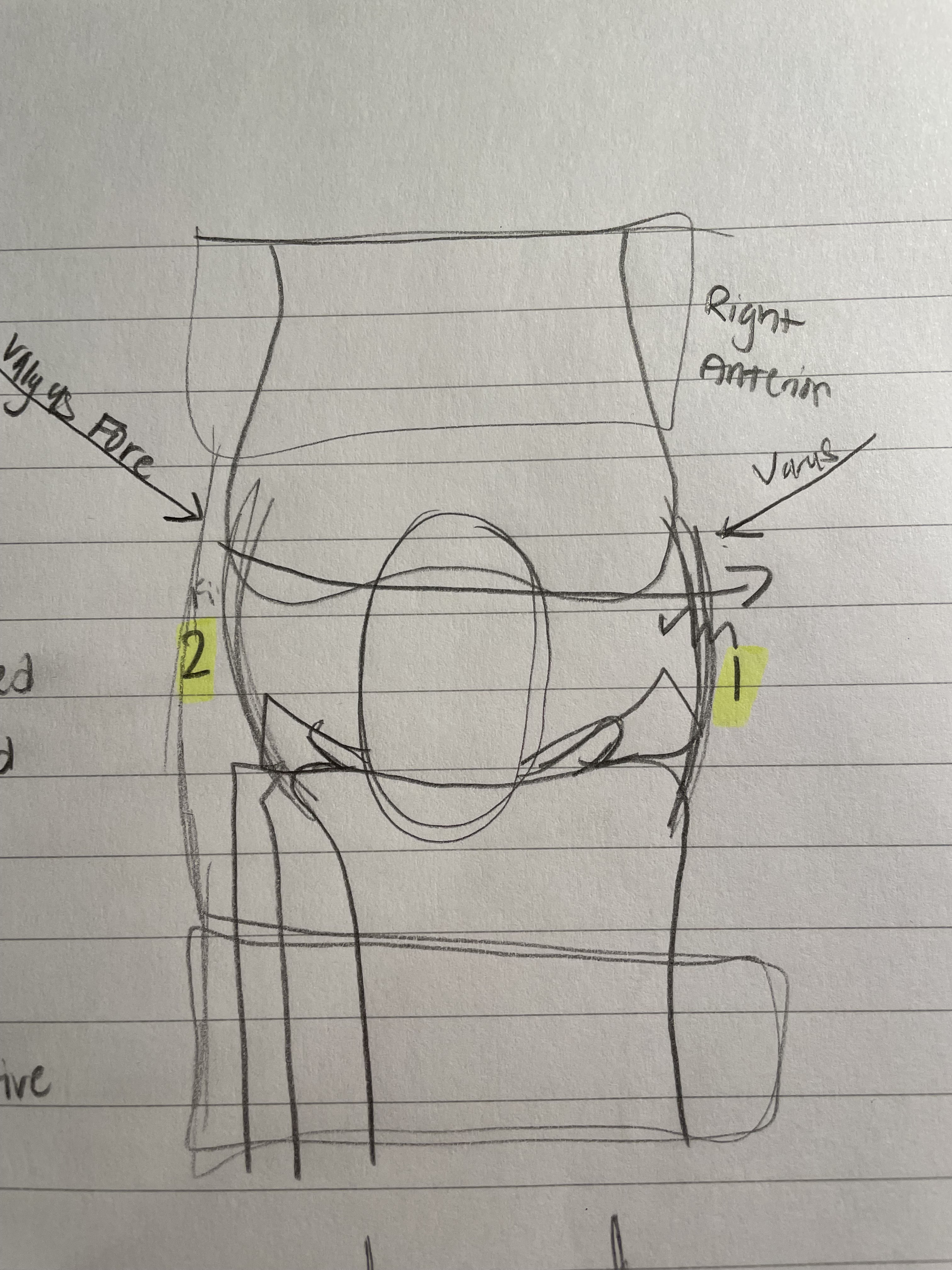
Lateral Collateral Ligament
Also known as the Fibial Collateral Ligament
Braces are super effective here
Keep feet moving to avoid injury
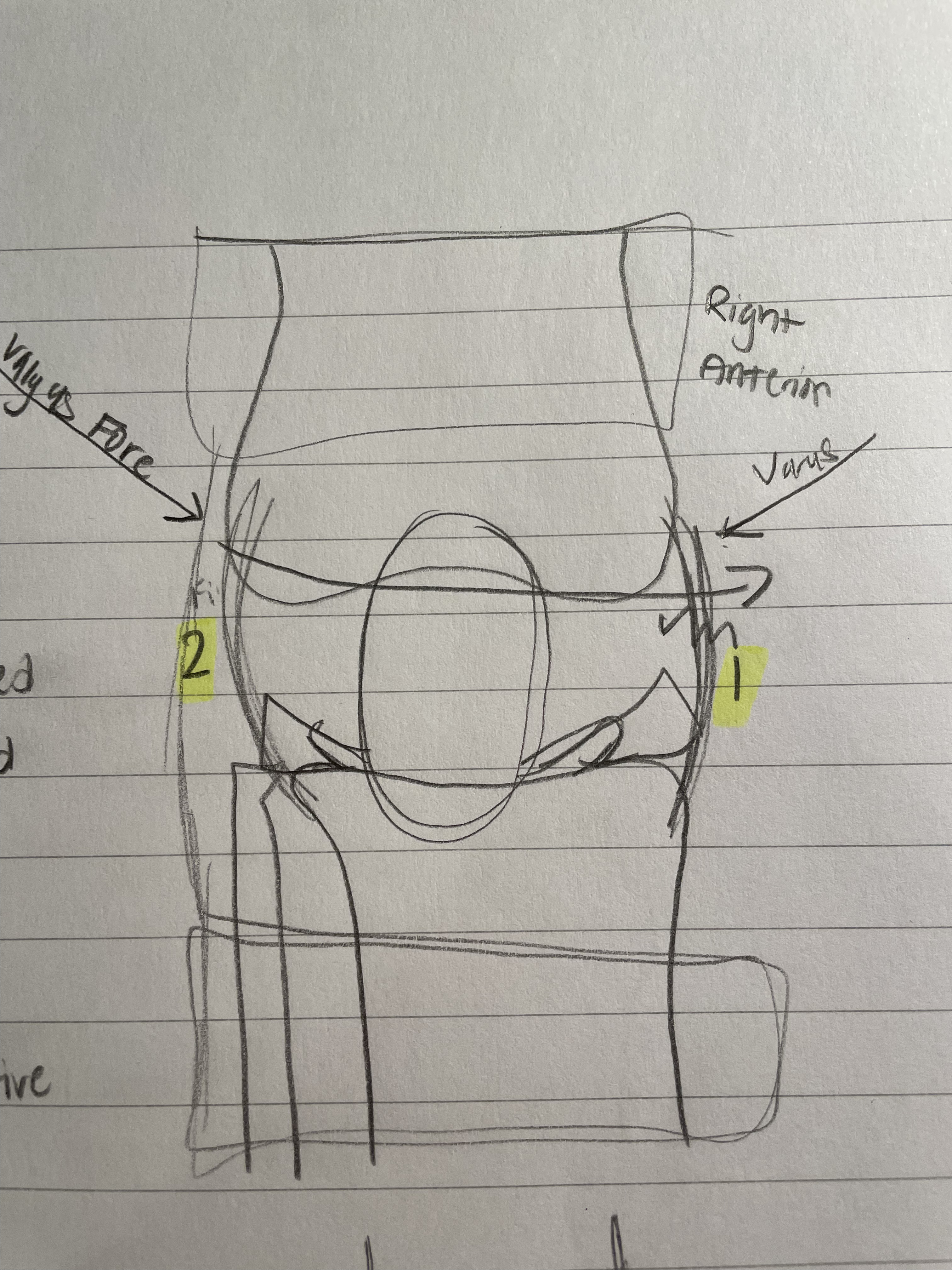
Varus Force
Mechanism of Injury
As shown in the diagram, varus force comes from the left side (of the right knee) and tears the lateral collateral lig.
Not as common, as the left side of the right knee is on the inside.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
Prevents the Tibia from going to far forward
Prevent Knee from dislocation
Once damaged, a new one is needed
Happens in open field collisions
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
Rarely needs surgery
Only happens in skating sports
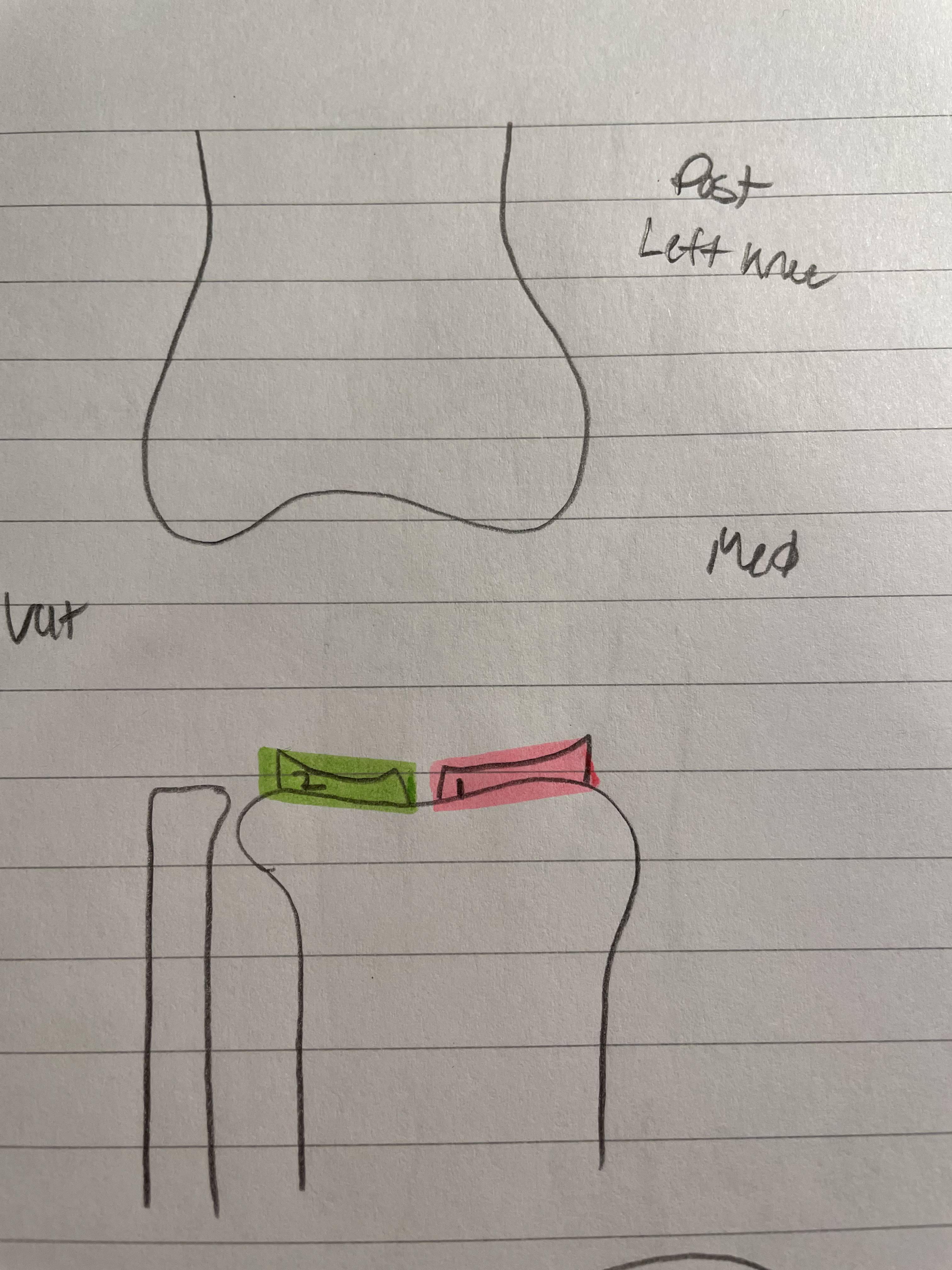
Medial Meniscus
Works as a pad
Keeps condyles in place
Release synovial fluid
Keeps Femur in place
Gets injured more
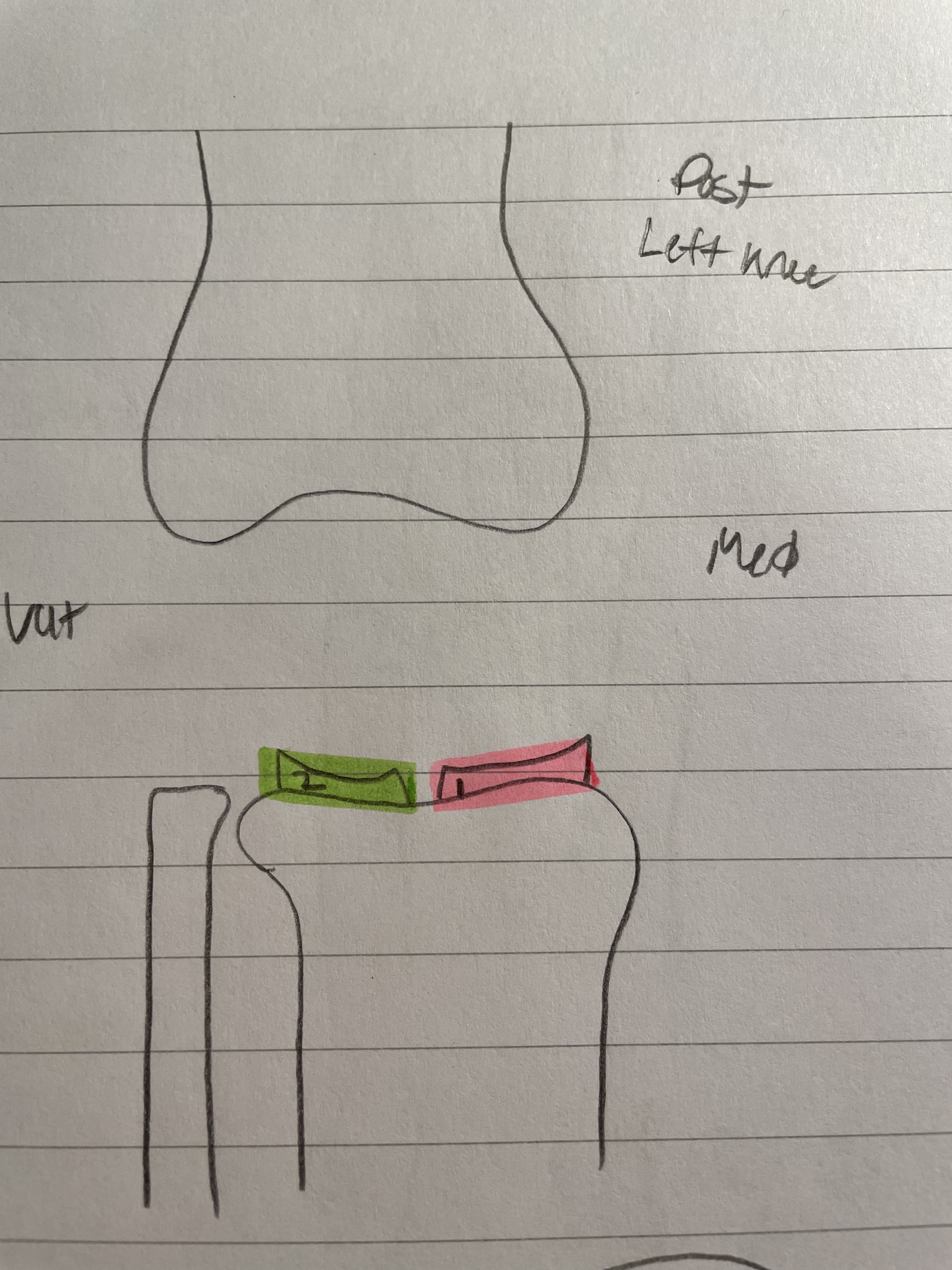
Lateral Meniscus
Works as a pad
Keeps condyles in place
Release synovial fluid
Keeps Femur in place
Menisectomy
Take out the tear
Can lead to tendinitis wayyyyy faster
Meniscal Repair
Suture the tear
Chemicals stimulate healing
Might not heal though
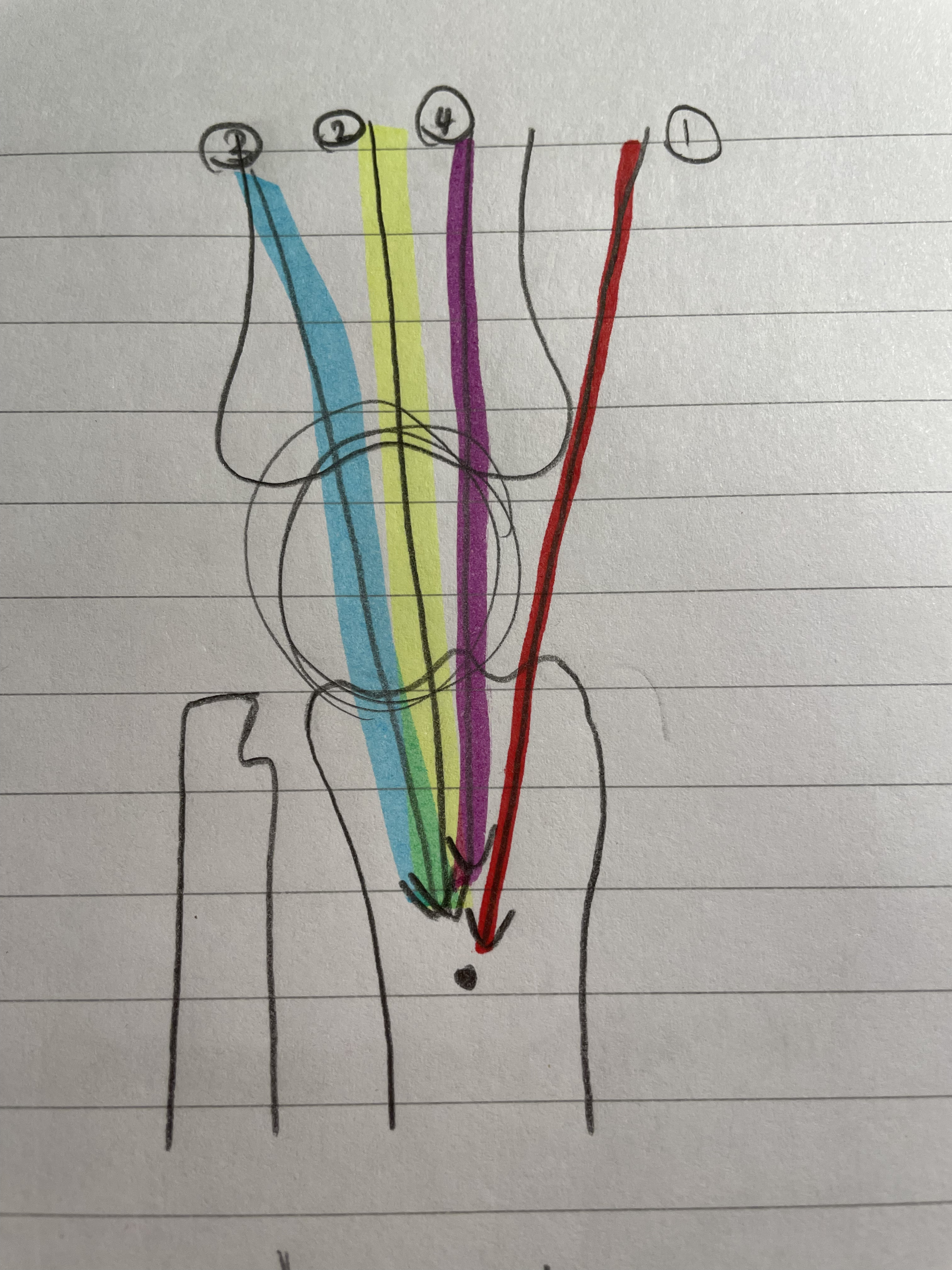
Vastus Medialis Oblique
VMO
Weakest
Tear drop shape
Knee Extension
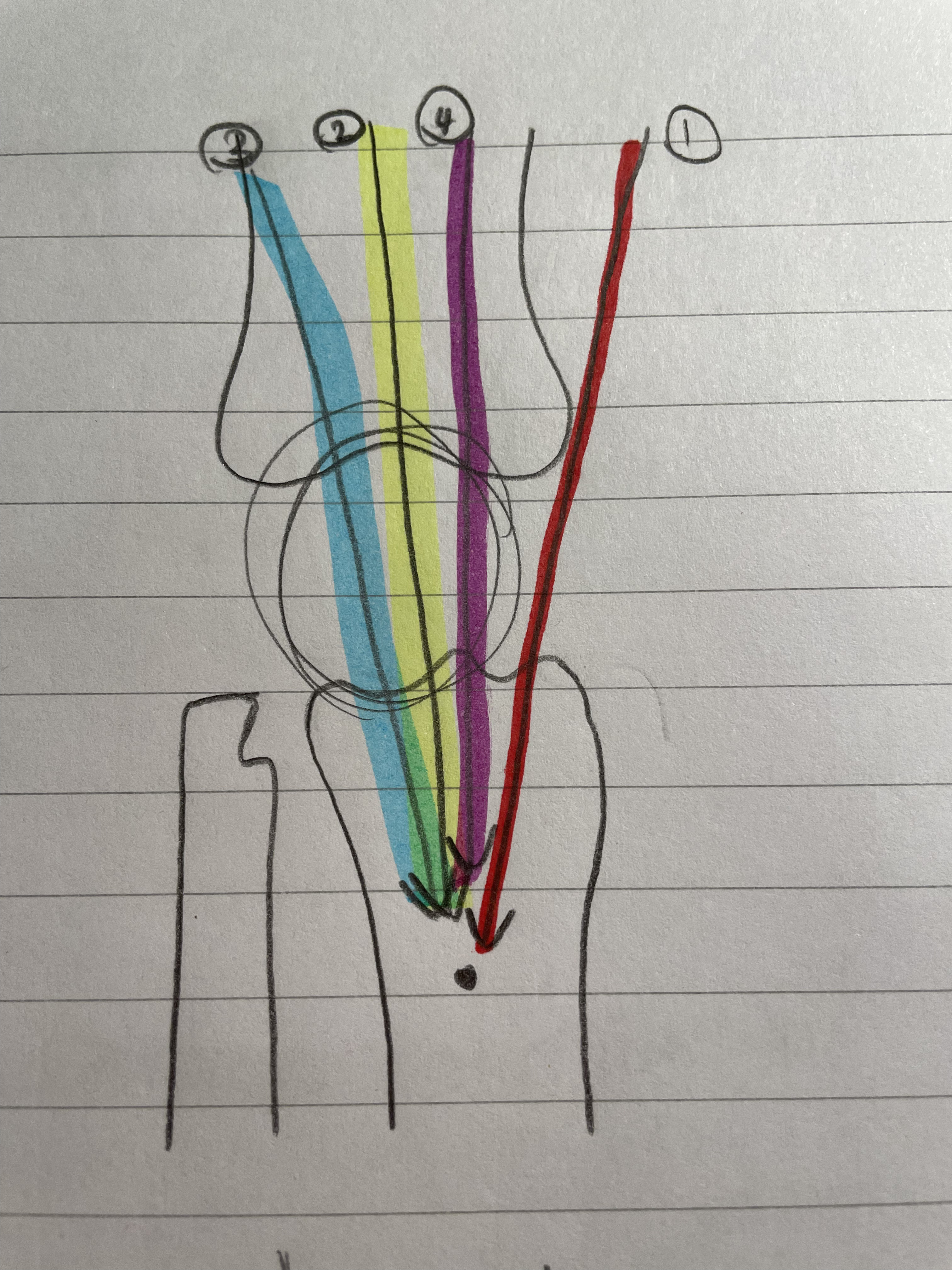
Vastus Intermedialis
Knee Extension
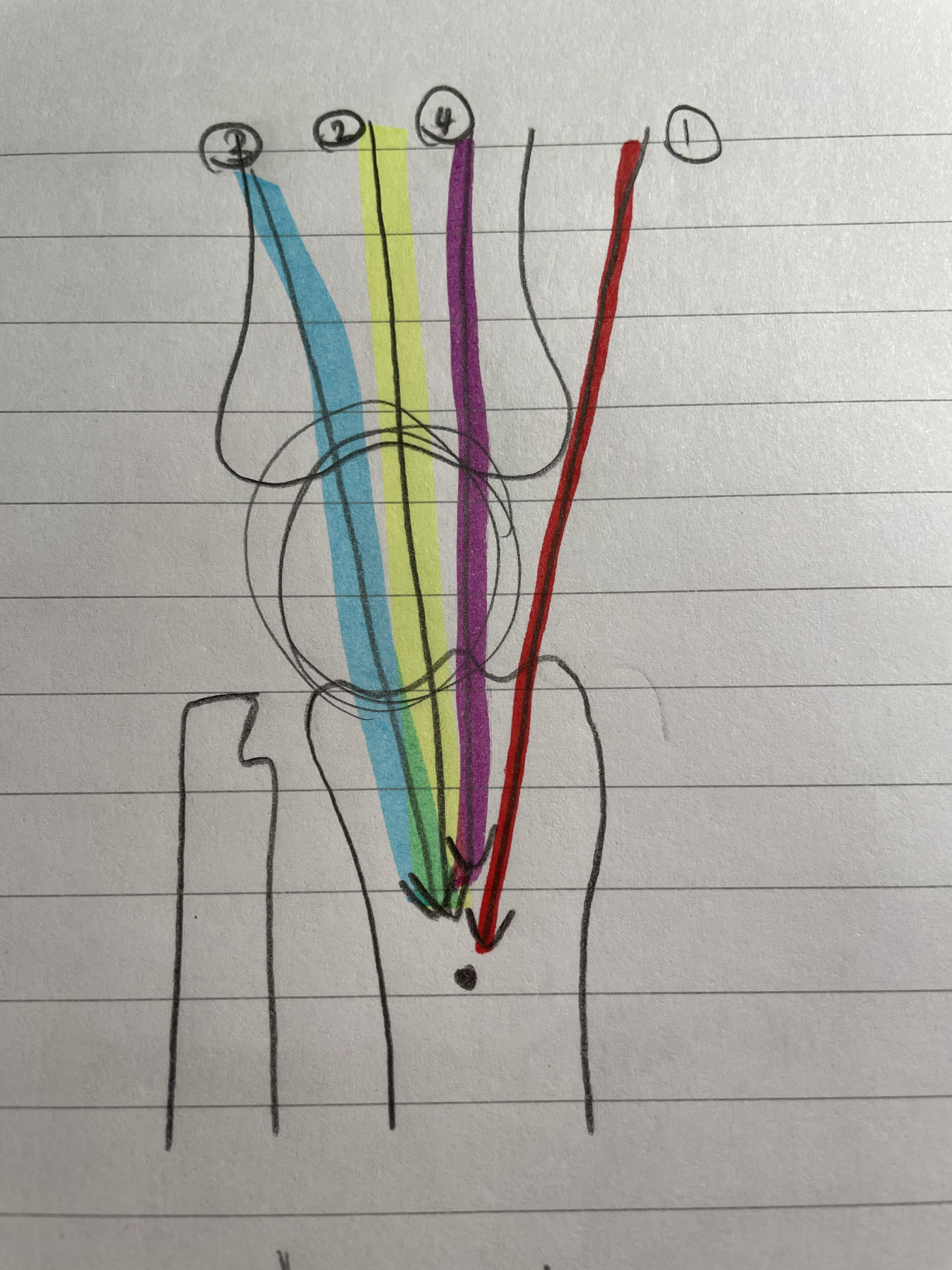
Vastus Laterilis
Strongest
Knee Extension
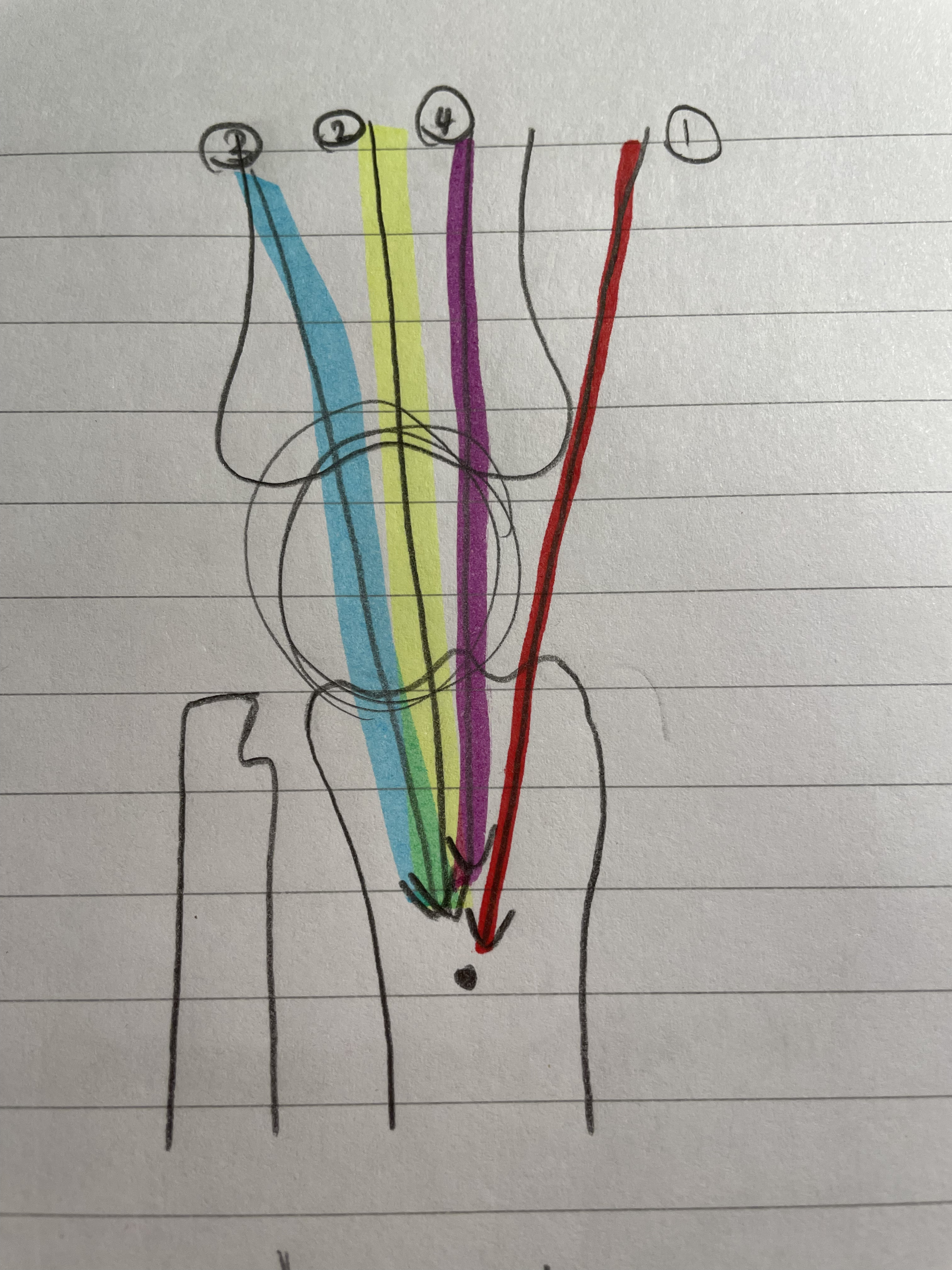
Rectus Femoris
Hip and Knee
Extends knee and flexes hip
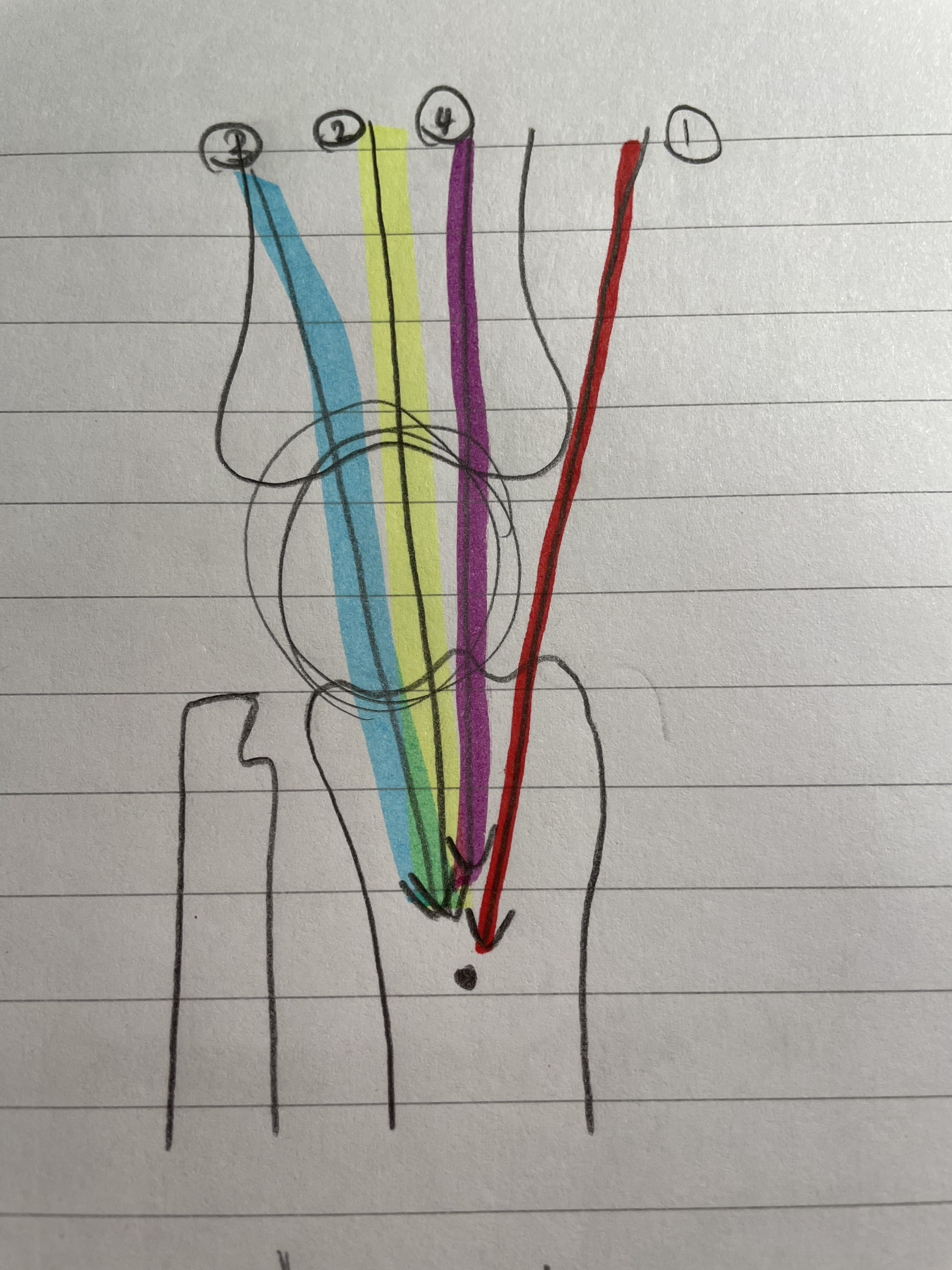
The Vastus Medialis Oblique, Vastus Intermedialis, Vastus Laterilis, and Rectus Femoris categorize as…
Quadriceps
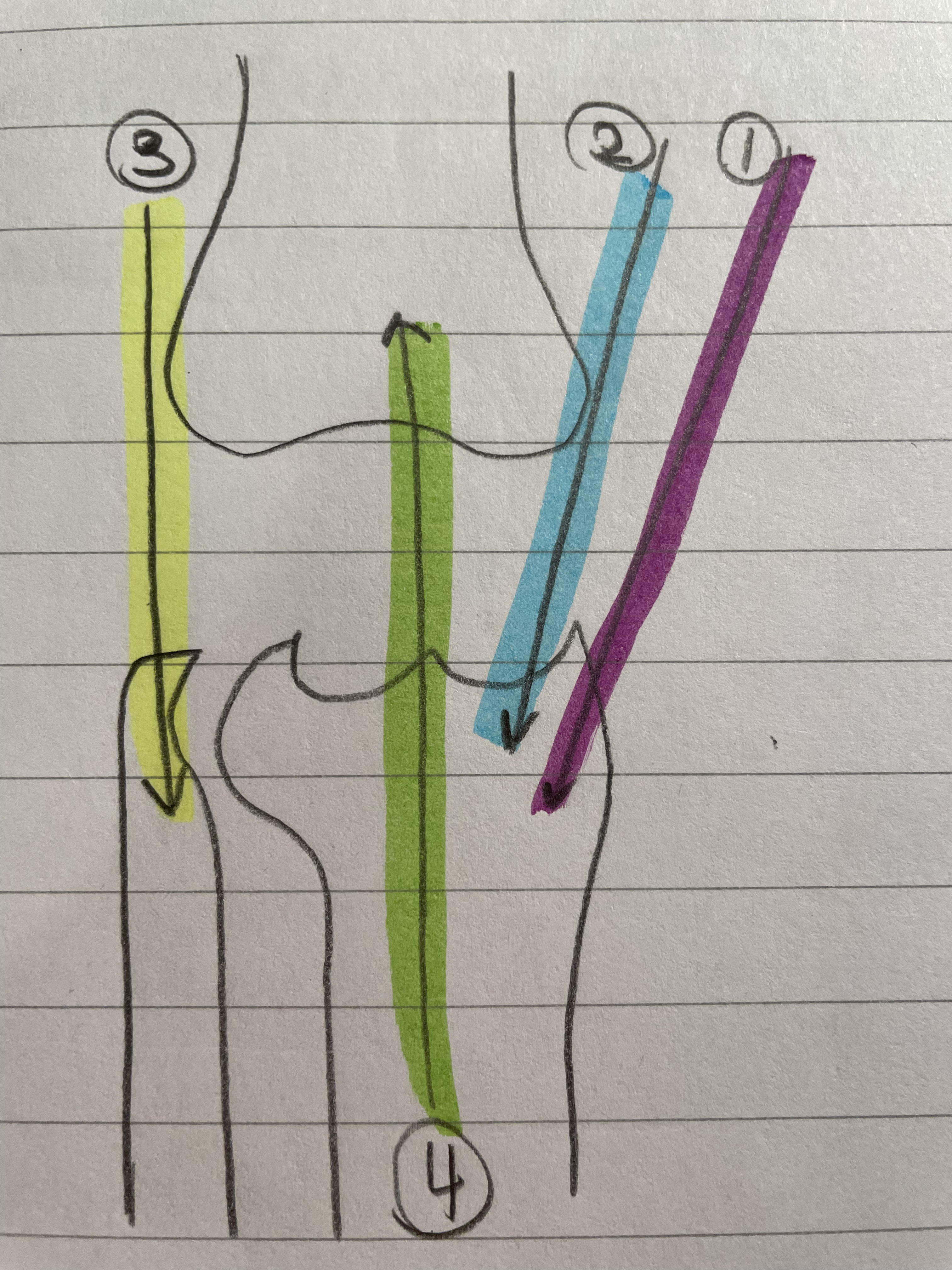
Semi-membrinosus
Two Joint Muscle
Knee and Hip
Natural ACL brace
Ham string
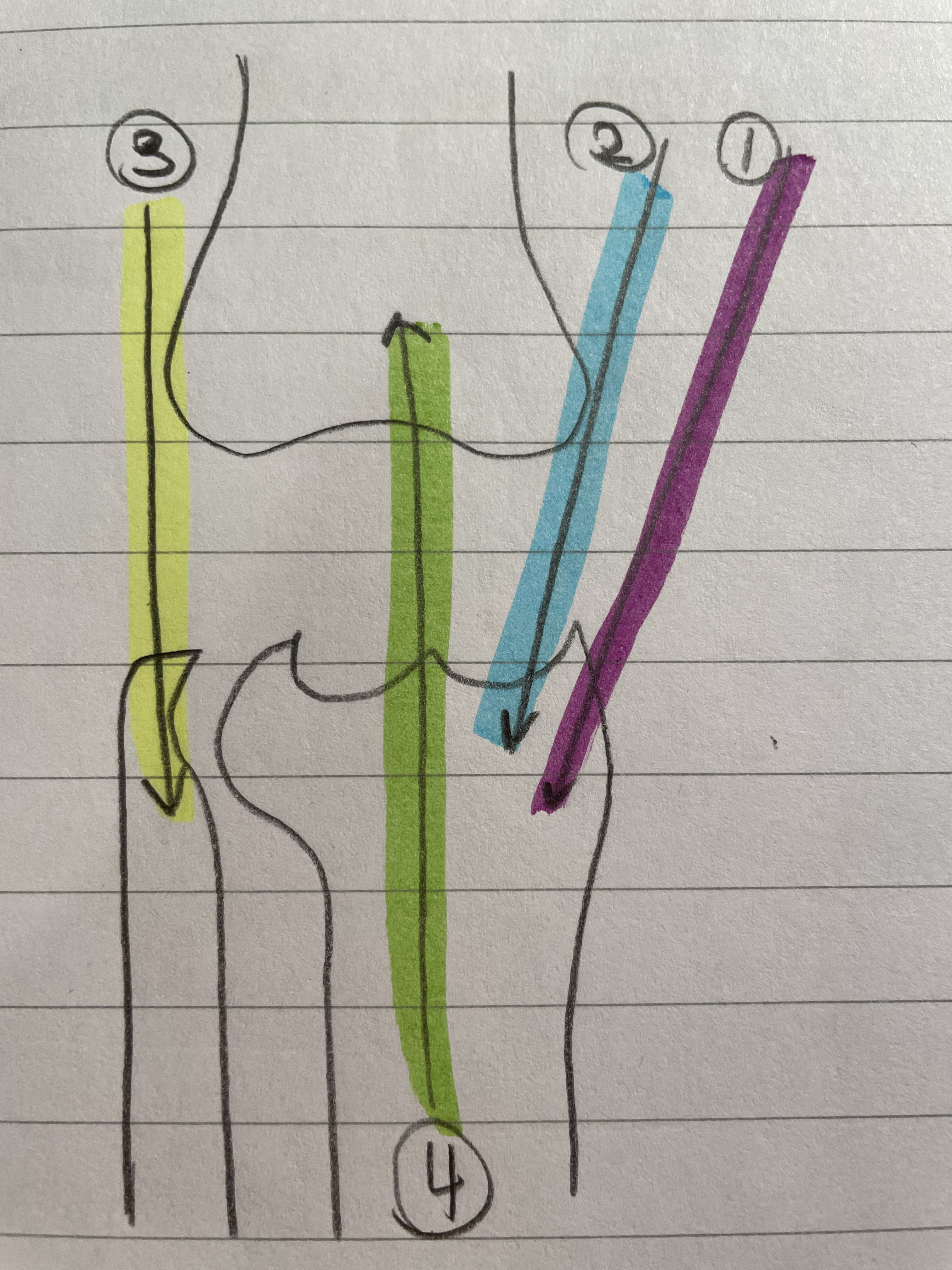
Bicep Femoris
Two Joint Muscle
Knee and Hip
Natural ACL brace
Ham string
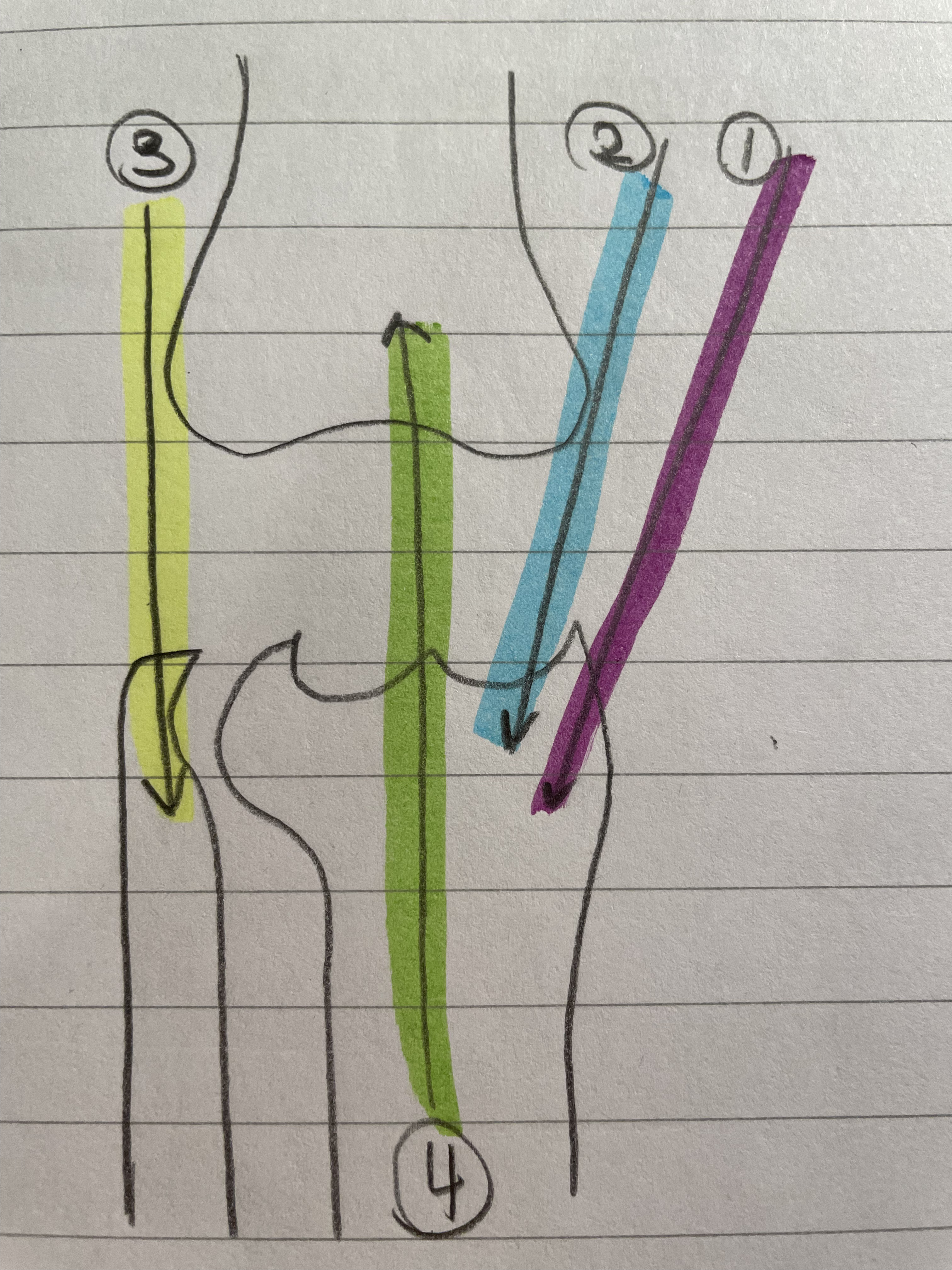
Semitedinosus
Two Joint Muscle
Knee and Hip
Natural ACL brace
Ham string
Gastrocnemius
Calf muscle
Undertrained
Ankle and Knee
All hamstring muscles are undertrained at…
The hip; most injuries occur here
Patellar Dislocations
Happen on a hard floor
Hit straight on in a bent position
Goes to the strongest muscle (Vastus Lateralis)
Relocated easily by AT
Athletes have stronger quads, so does not happen as often to them
What happens if the patella is dislocated for too long?
The tissues around it stretch out
Patella Dislocation Rehab
Strengthen the Vastus Medialis Oblique
Prevent it from happening again
Brace does not address VMO
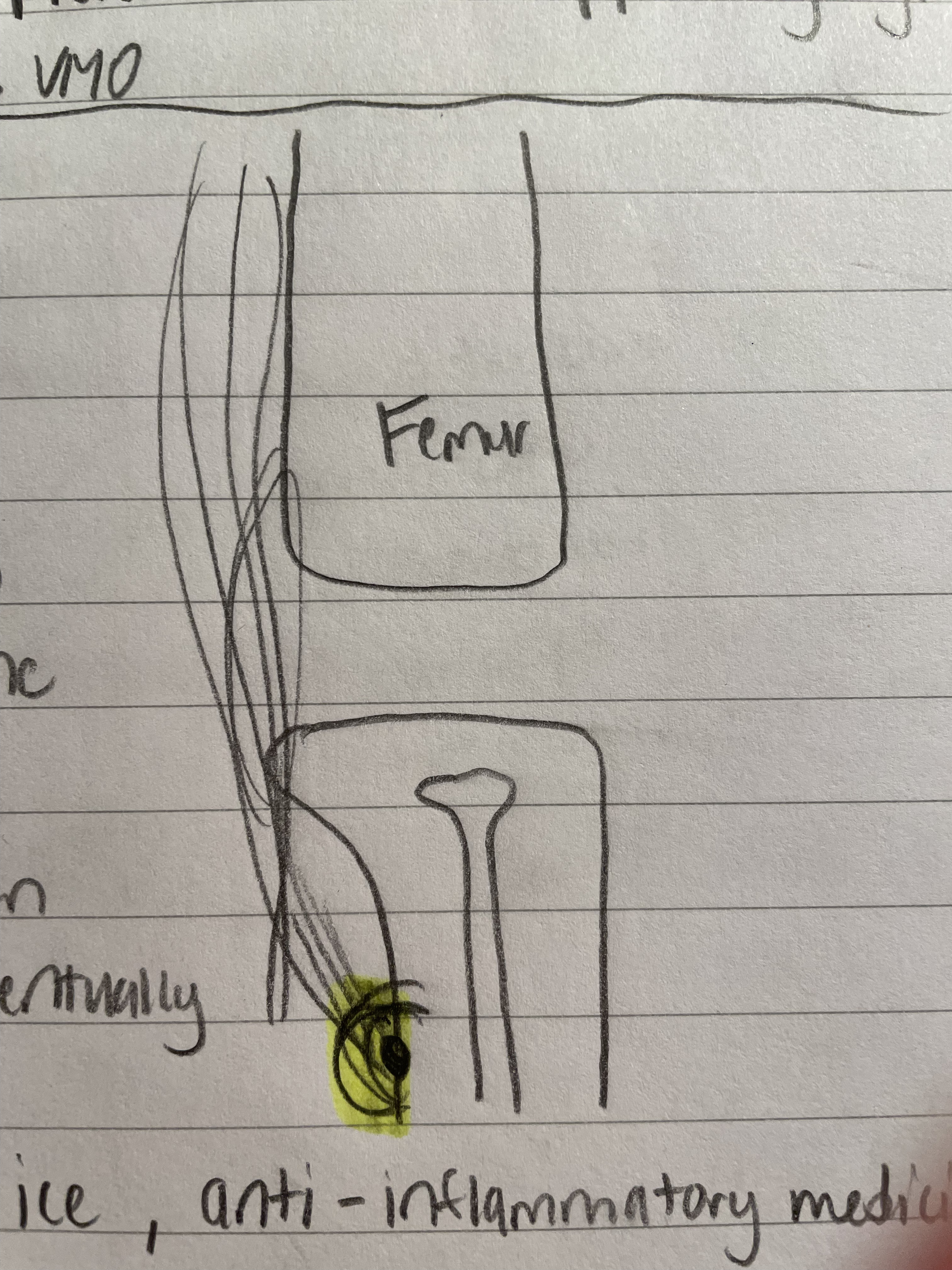
Osgood Schlatters
Happens when the femur rapidly grows and the muscles can’t keep up
Because the bone grows so fast, calcium is grown at Tibial Tuberosity
Pain, tenderness, soreness, swollen
Technically will go away itself, but ATs cheat the system with stretching, ice, and anti-inflammatory drugs
ACL Surgery
Autograft or Allograft
Reconstruction surgery
Autograft
Getting the graft from somewhere else in the body
Semi-Tendinosus (Hamstring)
Patellar Tendon (1/3 of it - most common)
Lowest retear rate, but a lot of tendinitis
Quadriceps Tendon
Can retear, less tendinitis
Allograft
Getting the graft from someone else
From cadaver: Achilles Tendon
Don’t need to make something else weaker
Rejection Risks: May not work with the body
Tend to retear at a higher rate
Propioception
Important to Rehab
Minimize the chances of ACL Tear
McMurray’s Test
Medial Meniscus Test
Tends to have a lot of false positives
FP caused by chondromalacia
Lachmens
ACL Test
Most Popular
Anterior Drawer
ACL Test
Easier for hamstrings to cheat, false negatives
Pivot Shift
ACL Test
Literally pop the knee out (super painful)
Orthopedic doctors