Ethical hacking
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Define Information Security
A state of wellbeing information and infrastructure in which the possibility of theft ,tampering, and disruption of information and services is low or tolerable.
Name the elements of information security
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
Authenticity
Non-Repudation
What are some Motives behind information security attacks
Disrupting business continuity
Stealing information and manipulating data
Causing financial loss to the target
Demanding ransom
Achieving a state’s military objectives
What makes an attack?
Motive (Goal) + Method + Vulnerability
Define Motive
notion that the target system stores or processes something valuable, and this leads to the threat of an attack on the system
Define Attack
trying various tools and attack techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in a computer system or its security policy and controls to fulfil their motives
Name 5 types of Classification Attacks
Passive Attacks
Active Attacks
Close-in Attacks
Insider Attacks
Distribution Attacks
Information Warfare
to the use of information and communication technologies to gain competitive advantages over an opponent
Defensive Information Warfare
To all strategies and actions desgined to defend against attacks on ICT assets
Offensive Information Warfare
To information warfare that involves attacks against the ICT assets of an opponent
Define Cyber Kill Chain Methodology
Is a component of intelligence-driven defense for the identification and prevention of malicious intrusion activities
Define Tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs)
refers to the patterns of activities and methods associated with specific threat actors or group of threat actors
What is tactics?
A way an attacker performs the attack from start to end
What is techniques?
Technical methods used by an attacker to achieve intermediate results during the attack
What is procedures?
are organizational approaches that threat actors follow to launch an attack
What is MITRE ATT&CK?
Its a globally accessible knowledge base adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations
What is ATT&CK?
its a knowledge base used as a foundation for the development of specific threat models and methodologies in the private sector, government, and the cybersecurity product and service comumnity
Name the 2 PRE-ATT&CK
Recon and Weaponize
Name the 5 types of Enterprise ATT&CK
Deliver
Exploit
Control
Execute
Maintain
Explain what is the Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis?
It offers framework for identifying the clusters of events that are correlated on any of the systems in an organization
name the 4 meta-features of the Diamond Model and define each
Adversary : Who was behind the attack
Victim: Where the attack was preformed
Capability: how the attack was performed
Infrastructure: What the adversary used to reach the victim
What is hacking?
Refers to exploiting system vulnerabilities and compromising security controls to gain unauthorized access or inappropriate access to system’s resources
Who is a hacker?
intelligent individual with excellent computer skills and for some hackers hacking is a hobby or to probe and do illegal things
name 4 different hacker classes
Black hats: individuals with extraordinary skills
White hats: individuals who use their professed hacking skills for defensive purposes
Gray Hats- who work both offensively and defensively
Suicide hackers, who aim to bring down critical infrastructure and not worry about facing jail terms or any other punishment
part 2 Name the 4 types of hacker classes
Script kiddies are unskilled hacker who compromises a system by running scripts , tools , etc
Cyber terrorists are individuals with wide range of skills who are motivated by religious or political beliefs
State-Sponsored Hackers- individuals employed by the government to penetrate and gain top secret information
Hactivists- individuals who promote a political agenda by hacking
What is ethical hacking?
It involves the use of hacking tools, tricks, and techniques to identify vulnerabilities and ensure system security and focuses on simulating the techniques used by attackers to verify the existence of exploitable vulnerabilities in a system’s security.
Why Ethical Hacking is Necessary?
as it allows for attacks against malicious hackers through anticipating the methods used to break into the system
Name me 3 reasons why organizations recruit ethical hackers
1) To prevent hackers from gaining access to the organization’s information systems
2) To help help safeguard customer data
3) To uncover vulnerabilities in systems and explore their potential as a security risk
What is the scope of ethical hacking?
Ethical hacking is crucial component of risk assessment, auditing, counter fraud, and information systems best practices
Name 3 Technical Skills
1) A computer expert adept at technical domains
2) In-depth knowledge of major operating environments such as Windows, Unix, Linux, and Macintosh
3) Knowledgeable about security areas on related issues
Name 3 Non-technical Skills
1) the ability to learn and adopt new technologies quickly
2) Strong work ethics and good problem-solving and communication skills
3) an awareness of local standards and laws
What is information assurance?
IA refers to the assurance that the integrity, availability, confidentiality, and authenticity of information and information systems is protected during the usage, processing, storage, and transmission of information
What are the four security approaches?
1) Protect: Defense-in-depth Security Strategy
2) Detect: continuous threat monitoring
3) Respond: Incident Response
4) Predict: Risk and Vulnerability Assessment, Attack Surface Analysis, Threat intelligence
Define Defense-in-Depth
Its a security strategy in which several protection layers are placed throughout
an information system .
What is risk?
refers to the degree of uncertainty or expectation that an adverse event may cause damage to the system .And categorized into different levels according to their estimated impact on the system.
What does risk management do?
It’s the process of reducing and maintaining risk at an acceptable level by means of well-defined and actively employed security program
Name 5 different types of Risk management phases
1) Risk identification
2) Risk Assessment
3) Risk Treatment
4) Risk Tracking
5) Risk Review
Define Cyber Threat Intelligence
the collection and analysis of information about threats and adversaries and drawing of patterns
Name + Define the 3 types of Threat Intelligence
Strategic: High-level information on changing risks
Tactical: Information on attackers’ TTPs
Operational: Information on a specific incoming attack
Name 5 different types of Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
1) Planning and Direction
2) Collection
3) processing and Exploitation
4) Analysis and Production
5) Dissemination and Integration
Define Threat Modeling
a risk assessment approach for analyzing the security of an application by capturing, organizing, and analyzing all the information that affects the security of an application
Explain the 5 steps of Threat Modeling Process
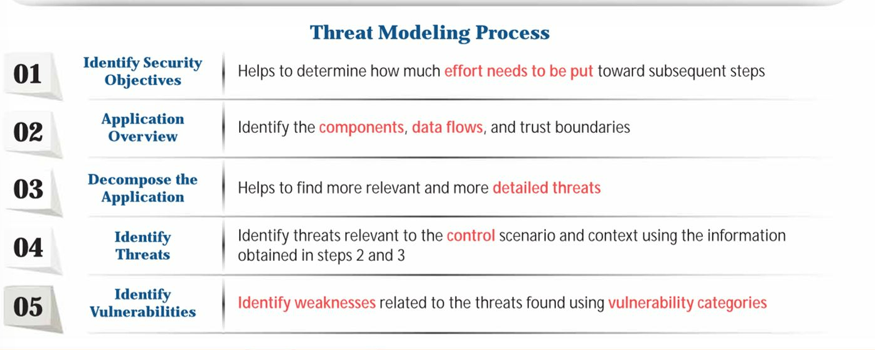
Define Incident Management
is a set of defined processes to identify, analyze, prioritize, and resolve security incidents to restore normal service operations as quickly as possible and prevent future recurrence of the incident
Define Incident Handling an Response
the process of taking organized and careful steps when reacting to a security incident or cyberattack
Role of Ai and Ml in cybersecurity
Refer to the slide
Define Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
its a proprietary information security standard for organizations
ISO/IEC
specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system
General Data Protection Regulation
most stringent privacy and security laws globally and those who violate its privacy and security standards with penalties reaching tens of millions of euro
What is Footprinting?
Footprinting is the first step of any attack on information systems in which an attacker collects information about the target to identify various ways to intrude into the system
Types of Footprinting
Passive Footprinting and Active Footprinting
Define Passive Footprinting
Gathering information about the target without direct interaction
Define Active Footprinting.
Gathering information about the target without direct interaction
What is the information Obtained in Footprinting?
Organization information, Network information, System information.
Examples of Organization information:
Employee details.
Telephone numbers.
Branch and location details.
Background of the organization.
Web technologies.
New articles, press releases, and related documents.
Examples of Network information
Domains and sub-domains.
Network blocks.
Network topology, trusted routers, and firewalls
IP addresses of the reachable systems
Whois records
DNS records
Examples of System information:
Web server OS
Location of web servers
Publicly available email addresses
Usernames and passwords
How can attackers perform footprinting through search engines?
Attackers use search engines to extract information about a target.
What is the Google Hacking Database?
The Google Hacking Database (GHDB) is an authoritative source for querying the ever-widening reach of Google search engine.
What are social networking services?
Social networking services, such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn, provide useful information about the individual that helps the attacker in performing social engineering and other attacks
What is ‘people search’?
The people search can provide critical information about a person or an organization, including location, emails, websites, blogs, contact information, important dates, etc.
How can attackers gather information using LinkedIn?
Attackers use theHarvester tool to perform enumeration on LinkedIn and find employees of the target company along with their job titles.
What is ‘Harvesting Email Lists'?
Gathering email addresses related to target organizations acts as an important attack vector during the later phases of hacking.
What do attackers use to harvest emails?
Attackers use tools such as theHarvester and Email spider to collect publicly available email addresses of the target organization, that helps them perform social engineering and brute-force attacks
How can attackers perform Footprinting through job sites?
Attackers use the technical information obtained through job sites, such as Dice, LinkedIn, and simply Hired, to detect underlying vulnerabilities in the target IT infrastructure.
Define ‘Deep web’.
Deep web consists of web pages and contents that are hidden and unindexed and cannot be located using traditional web browsers and search engines
Define ‘Dark web’.
Dark web is a subset of the deep web that enables anyone to navigate anonymously without being traced.
Define ‘TOR Browser’.
is used to access the deep and dark web where it acts as a default VPn for the user and bounces the network IP address through several servers before interacting with the web.
Why do attackers use Deep and Dark web?
Attackers use deep and dark web searching tools such as Tor browser and ExoneraTor, to Gather confidential information about the target, including credit card details, medical records, social media accounts, Social Security Numbers (SSNs), etc.
Define ‘SHODAN’.
SHODAN search engine lets you find connected devices (routers, servers, IoT, etc) using a variety of filters.
Define ‘Censys’.
search engine provides a full view of every server and device exposed to the internet.
Define ‘Competitive Intelligence Gathering’.
is the process of identifying, gathering, analyzing, verifying, and using information about your competitors from resources such as the internet.
List the 10 sources of competitive intelligence:
Company websites and employments ads
Search, internet, and online database
Press releases and annual reports
Trade journals, conferences, and newspapers
Patent and trademarks
Social engineering employees
Product catalogs and retail outlets
Analyst and regulatory reports
Customer and vendor interviews
Agent, distributors, and suppliers
How do attackers collect information through Social engineering on Social Networking sites?
Attackers use social engineering tricks to gather sensitive information from social networking websites.
How do attackers do use General resources for locate information from social media sites?
Attackers track social media sites using BuzzSumo, Google Tend.etc.. to discover most shared content using hashtag or keywords. Using these information attackers perform phishing, social engineering and other types of attacks
Define ‘Website Footprinting’?
Monitoring and analysis of the target organizations website for information
Explain Website Footprinting using Web spiders:
perform automated searches on the target website and collect specified information, such as employee names and email addresses
What do extract website information from https://archive.org do?
It allows one to visit archived versions of websites
Define ‘Mirroring entire website’.
Define ‘Mirroring entire website’
Mirroring an entire website onto a local system enables an attacker to browse website offline; it also assist in finding directory structure and other valuable information from mirrored copy without sending multiple requests to web server
How do attackers Track email communications?
Attackers track email to gather information about a target recipient, such as IP address, geolocation, browser and OS details, to build a hacking strategy and perform social engineering and other attacks
What does Email Tracking Tools do?
Allows attackers to track an email and extract information , such as sender identity, mail server, sender’s IP address, and location
Define ‘Email tracking’
Email tracking is used to monitor the delivery of emails to an intended recipient.
Define ‘Whois Lookup’.
Whois databases are maintained by Regional Internet Registries and contain personal information of domain owners
Whois Lookup table

Finding IP Geolocation Information
help identify information , such as country, region/state, city, ZIP/postal code, time zone, connection speed, and helps collect ip geolocation information about the target which in turn helps attackers launching social engineering attacks
How do attackers extract DNS information?
Attackers can gather DNS information to determine key hosts in the network and can perform social engineering attacks.
Why do attackers perform Reverse DNS lookup?
Attackers perform a reverse DNS lookup on IP ranges in an attempt to locate a DNS PTR record for those IP addresses
Define how to Locate the Network range.
assists in creating a map of the target network and one can find the range of IP addresses using ARIN whois database search tool
Define ‘Traceroute’
Traceroute programs work on the concepts of ICMP protocol and use the TTl field in header of ICMP packets to discover the router on path to a target host
How does an attacker use traceroute analysis?
Attackers execute traceroute to find the IP address of intermediate devices such as routers and firewalls present between a source and its destination
Define ‘Social Engineering’.
an art exploiting human behavior to extract confidential information.
Name the different types of collecting information:
Eavesdropping , shoulder surfing , Dumpster Diving, and Impersonation
What are the two Footprinting Tools?
Maltego: used to determine the relationship and real world links , Recon-ng: a web reconnaissance framework
Define footprinting tool ; OSINT framework:
an open source intelligence gathering framework that is focused on gathering information from free tools or resources
Footprinting Countermeasures

Define Network Scanning
a set of procedures used for identifying hosts, ports, and services in a network
Name the 6 different TCP communication Flags
URG - FIN — RST- PSH- ACK- SYN
Define Scanning tool: Nmap and how the attackers use it
inventorying a network, managing service upgrade schedules, and host or service uptime. And attackers use nmap to extract information such as live hosts on the network, open ports, services, types of packet filters, etc..
Define Hping3
Ccommand line network scanning and packet craftng tool for TCP/IP protocol
How does host discovery techniques work?
used to identify the active/live systems in the network