HKDSE Econ - CH11-13 (Short-run and long-run production, Intergration and expansion of firms)
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MUST ALSO REVISE NOTES
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Production
The process of turning input into output
Variable factors
Factors which quantity changes when output changes
Fixed factors
Factors which quantity remains unchanged when output changes
Total product
Total amount of output produced at a certain level of employment of factors
Average product
Total product / number of variable factor
Marginal product
Change in total product
Law of diminishing marginal returns
When a variable factor is added continuously to a given amount of a fixed factor, the marginal product will eventually diminish, holding technology constant.
Marking scheme to support law of diminishing marginal returns
X is a fixed factor as its quantity remains constant when the output changes
Y is a variabl factor, so it is a short-run production
The MP decreases from A to B when the Cth unit of factor is put to use
Marking scheme to not support law of diminishing marginal returns
The quantity of X and Y both increase when the output changes. There are no fixed factors in the production. It is a short-run production
The MP does not diminish when the output increases
Total cost
Total variable cost + total fixed cost
Marginal cost
Change in TC = Change in TVC
Marginal revenue
Average revenue = Price when constant
Profit maximisation condition
P = MR = MC, where the seller is a price-taker in perfect competition
Effect of profit maximisation when P increases
MR increases → profit maximisation output increases → total revenue increases
Effect of profit maximisation when fixed cost increases
No change in variable cost → no change in MC → profit maximiation output remains unchanged
Total cost increases → total profit decreases
Effect of profit maximisation when variable cost increases
MC increases → profit maximisation output decreases
TC uncertain → profit uncertain
Average fixed cost
Keeps decreasing, but larger than or equal to 0
Average variable cost
Increases initially and eventually decreases
Optimum scale of production
AC / MC minimised
Use of factors minimised
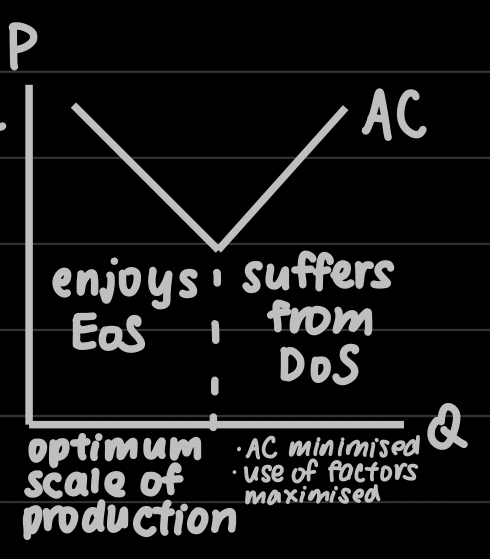
Definition of economies of scale / diseconomies of scale
Firms (blank) from EoS / DoS
Advantages / disadvnatages associated with long-run production that increase / decrease the average long-run cost of production
Enjoy / suffer
How can production scale be expanded?
By increasing production output
Internal economies: increase in production scale of the firm
External economies: increase in production scale of other firms / entire industry
Internal EoS
Financial economies: lower borrowing costs / less collaterals
Marketing economies: advertising costs / extra services provided to customers spread over a larger output
Managerial economies: wider scope of specialisation → improves managerial efficiency and productivity
Research and development economies: research expenses spread over a larger output → develop technologies to decrease cost
Technical economies: more output → capital goods / machinery can be utilised more fully and efficiently
Purchasing economies: purchase raw materials in bulk → obtain discounts
Risk diversitifcation economies: diversify products / markets to reduce risk
External EoS
Managerial economies: more talented workers are attracted to the industry and trained
Marketing economies: Firms may benefit from the advertisement of other firms promoting similar products → create trends to attract customers
More supporting services: transport and communication networks are better developed
Technical economies: lower prices for backup services
Purchasing economies: larger industries have more bargaining power to purchase materials earlier than smaller industries
Internal DoS
Financial economies: large outstanding loans → increase in borrowing costs
Banks face higher risk when a large sum of money is borrowed again and again → increase interest rate to compensate for higher risk
Marketing economies: market becomes saturated → marketing costs increase
Managerial economies: too large in scale
External DoS
Purchasing economies: excessive expansion in production output bids up prices of raw materials / inputs
Increase in transport costs: over-concentration of business activities leads to traffic congestion
Technical economies: firms providing backup services also suffer from DoS → increase price
Internal integration vs external integration / expansion
Internal: within a firm’s own capacity → opening more branches / introducing more products
External: combine with another firm
General motives of integration
Make use of established brand’s goodwill to decrease advertising costs
Enjoy economies of scale to reduce average cost
Better use / reduce duplicates of faciltiies and resources (synergy effect)
Vertical forward integration
Expand to a business in the later stage of prodcution / that provides market outlets for produts
Obtain market information through market outlets
Ensure steady supply of market outlet of products
Reduce transaction cost
Develop relationship with customers
Vertical backward integration
Expand to a business in the preceding stage of production / that provides inputs or raw materials for production
Ensure steady supply of inputs to prevent risk of disruption to production due to inadequate supply of input
Horizontal integration
Expand to a business selling similar / the same produts
Increase market share / market power by influencing market price
Reduce competition, eg avoiding price wars
Lateral integration
Expand to a business selling similar but not competitive products
Reduce risk through diversification (use profits of one business to cover the loss of the other)
Conglomerate integration
Expand to a business in a completely unrelated industry
Reduce risk through diversification (use profits of one business to cover the loss of the other)
Perfect vs imperfect competiiton
Buyer / sellers have perfect / imperfect information on the market
Market
A set of arrangements that allow a transaction to take place
Buyer
Seller
Product
Price
P competition (eg. discounts)
Non-P competition (eg. gifts / advertisements / improve product quality)
Price-taker
Firms lose all customers when they set price different from other sellers
No influence on market price
Price-searcher
Buyers / sellers are not fully informed on every aspect of the market
Market information involves cost to obtain
Characteristics of perfect competition
Many sellers
Free entry
Homogenous product
Perfect market information
Price-taker
Behaviour of sellers in perfect competition
No non-P comp (sellers can sell whatever Q they want at the same P)
P comp (not expected to do so)
P changes when D / S change
MC same for all individual sellers (profit maximisation: MC=MR=R)
Characteristics of monopolistic competition
Many sellers
Free entry
Heterogenous products
Imperfect market information
Price-searchers (seller can determine price on their own)
Behaviour of sellers in monopolistic competition
P competition and non-P competition
Characteristics of oligopoly
Many sellers but with several dominant sellers
Free or restricted entry
Homogenous or heterogenous products
Imperfect market information
Price searcher:
Sell heterogenous products
Customers favour certain brands
Hold significant market share
Behaviour of sellers in oligopoly
P competition and non-P competition
Interdependent / price leadership
Consider the reaction of competitors when making business decisions (will follow competitors if they lower P) → keep lowering prices → leads to price wars (lowering P below the cost of production to increase market share)
Price tends to be rigid (agree on same / similar P) → non-P competition
Characteristic of monopolistic competition
One seller (no close substitutes)
Restricted entry
Heterogenous (eg electricity) or homogenous (eg 1st class in MTR) products
Imperfect market information
Price-searcher (set P to maximise profit)
Behaviour of sellers in monopoly
Face P copmetition and non-P competition from
Sellers of substitutes
Producers using similar production process / resources
Competition to be the only seller (eg. licenses)
Business risk from inefficient operation
Sources of monopoly power
Natural monpooly (high set-up costs → EoS decrease AC → no room for second producer)
Government provision of strategic goods
Ownership of patent / copyright (right of an inventor to buy / sell / produce their product)
Ownership of essential technologies (eg. possession of superior raw materials)
Sole ownership of franchise (license to operate in a particular trade / business)
Collusion / integration with firms (collaborating with firms to increase joint profits eg. cartels)