PHYSICS 2: EXAM #3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
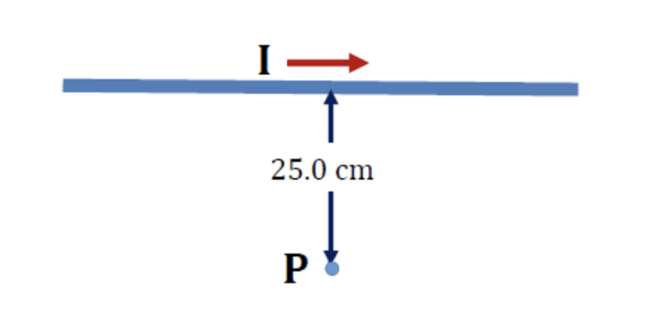
A long, straight wire is carrying a current of 25.0 A in the direction shown in the figure. The point P is 25.0 cm from the wire. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P due to the current in the wire?
B= (μo*I)/2πr
The design requirements of 50-Hz ac generator specify a maximum emf of 6600 V. The generator has a 50-turn coil that has an area per turn of 0.55 m 2. What should be the magnitude of the magnetic field in which the coil rotates?
emf = NABw = 2πfNAB
The coil on the motor of an 18.0 V (DC) cordless drill draws a current of 7.50 A when it first starts up but only 2.50 A when running at full speed. What is the back emf developed at full speed?
R=V/I
I = V-emf back/R
A transformer changes 120 V across the primary to 600 V across the secondary. If the secondary coil has 800 turns, how many turns does the primary coil have?
Np/Ns=Vp/Vs
An electron moving at 1.60×10 3 m/s in a 2.50-T magnetic field experiences a magnetic force of 3.20×10−16 N . What angle does the velocity of the electron make with the magnetic field? There are two answers.
F=qvBsinΘ
A proton is moving in a circular orbit of radius 14 cm in a uniform 0.35-T magnetic field perpendicular to the velocity of the proton. Find the speed of the proton. Mass of proton: mp = 1.67 × 10-27 Kg.
qvB=mpv²/r
A DC power line for a light-rail system carries 1000 A at an angle of 30.0° to the Earth’s 5.00×10−5 -T field. What is the force on a 100-m section of this line?
F=ILBsinΘ
Find the maximum torque on a 100-turn square loop of a wire of 10.0 cm on a side that carries 15.0 A of current in a 2.00-T field.
τ= NIABsinΘ
Find the current in a long straight wire that would produce a magnetic field twice the strength of the Earth’s at a distance of 5.0 cm from the wire. Earth’s field is about 5.0×10−5T.
B= (μo*I)/2πr
The long straight wire carries a current of 3.0 A. A particle has a charge of +6.5x10-6 C and is moving parallel to the wire at a distance of 0.050 m. The speed of the particle is 280 m/s. Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on the particle.
B= (μo*I)/2πr
F=qvB
The magnetic field of a proton is approximately like that of a circular current loop 0.650x10−15 m in radius carrying 1.05x104 A. What is the field at the center of such a loop?
B= (μo*I)/2r
What is the field inside a 2.00-m-long solenoid that has 2000 loops and carries a 1600A
current?
B=μ0nl
Two long parallel wires are separated by 6.0mm. The current in one of the wires is twice the other current. If the magnitude of the force on a 3.0-m length of one of the wires is equal to 8.0 μN, what is the greater of the two currents?
F21
A solenoid 4.0 cm in radius and 4.0 m in length has 8.000 uniformly spaced turns and carries a current of 5.0 A. Consider a plane circular surface (radius = 2.0 cm) located at the center of the solenoid with its axis coincident with the axis of the solenoid. What is the magnetic flux through this surface? (1 Wb = 1 T•m2)
Φ = NBAcosΘ
Φ=BAcosΘ
Suppose a 50.0-turn coil lies in the plane of the page in a uniform magnetic field that is directed into the page. The coil originally has an area of 0.250 m 2 . It is stretched to have no area in 0.100 s. What is the magnitude of the induced emf if the uniform magnetic field has a strength of 1.50 T?
Φ=NBAcosΘ
emf= -ΔΦ/Δt
A coil of wire consists of 20 turns each of which has an area of 0.0015 m2. A magnetic field is perpendicular to the surface. Initially, the magnitude of the magnetic field is 0.050 T and 0.10 s later, it has increased to 0.060 T. Find the average emf induced in the coil during this time.
Φ=NBAcosΘ
emf= - ΔΦ/t

Consider the arrangement shown in figure. Assume that R = 6.00 Ω, ℓ = 1.20m, and a uniform 2.50-T magnetic field is directed into the page. At what speed should the bar be moved to produce a current of 0.500 A in the resistor?
I=BLv/R
The generator coil shown in the figure is rotated through one-fourth of a revolution
(from 𝜃𝜃 = 0° to 𝜃𝜃 = 90° ) in 15.0 ms. The 200-turn circular coil has a 5.00cm radius and is in a uniform 1.25 T magnetic field. What is the average emf induced?
Φ=NBAcosΘ
emf = -ΔΦ/Δt
Area (A)
πr²
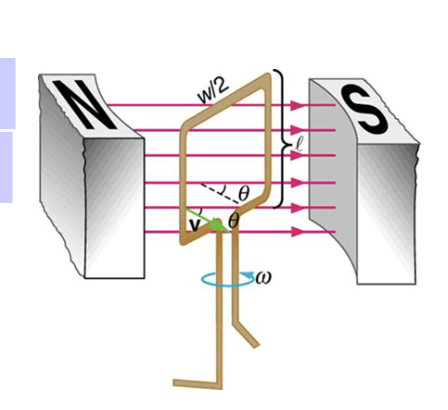
The generator coil shown in the figure is rotated through one-fourth of a revolution
(from 𝜃𝜃 = 0° to 𝜃𝜃 = 90° ) in 15.0 ms. The 200-turn circular coil has a 5.00cm radius and is in a uniform 1.25 T magnetic field. Calculate the maximum emf (emf0) of this generator?
w=ΔΘ/Δt
emf0=NABw
Suppose a motor connected to a 120 V source draws 20.0 A when it first starts.
(a) What is its resistance?
(b) What current does it draw at its normal operating speed when it develops a 100V back emf?
R=V/I0
I=V-emf back/R
A battery charger meant for a series connection of ten nickel-cadmium batteries
(total emf of 12.5 V DC) needs to have a 15.0 V output to charge the batteries. It uses
a step-down transformer with a 200-loop primary and a 120 V input.
(a) How many loops should there be in the secondary coil?
(b) If the charging current is 16.0 A, what is the input current?
Vs/Vp = Ns/Np
Is/Ip = Np/Ns
Consider a solenoid that contains 300 turns, its length is 25.0 cm, and its cross-sectional area is 4.00 cm2.
(a) Calculate the inductance of this solenoid.
(b) Calculate the self-induced emf in the solenoid if the current it carries decreases at
the rate of 50.0 A/s.
L=μoN²A/L
emf = -L(ΔI/Δt)
How much energy is stored in a 0.632 mH inductor when a 30.0A current flows through it?
Eind = ½ (L)(I)²
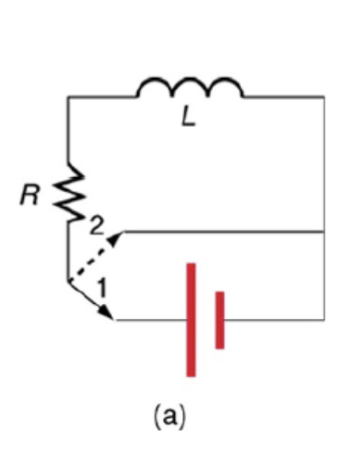
Consider the circuit in figure. Suppose the circuit elements have the
following values: V = 12.0 V, R = 6.00Ω, and L = 30.0 mH.
(a) Find the time constant of the circuit.
(b) The switch is at position 1; calculate the maximum current in the circuit.
τ=L/R
Io=V/R
(a) Calculate the inductive reactance of a 3.00 mH inductor when 60.0 Hz and 10.0
kHz AC voltages are applied.
(b) What is the rms current at each frequency if the applied rms voltage is 120 V?
XL = 2🥧fL
Irms = Vrms/XL
(a) Calculate the capacitive reactance of a 5.00 μF capacitor when 60.0 Hz and 10.0 kHz AC voltages are applied.
(b) What is the rms current at each frequency if the applied rms voltage is 120 V?
Xc= 1/2🥧fC
Irms = Vrms/Xc
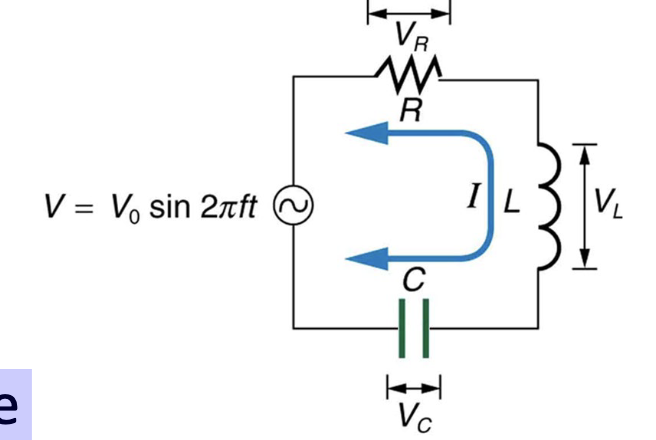
A series RLC circuit has R = 425 Ω, L = 1.25 H, and C = 3.50 μF. It is
connected to an AC source with f = 60.0 Hz and V0 = 150 V. (
a) Find the inductive reactance, the capacitive reactance, and
the impedance of the circuit.
(b) Find the maximum (peak) current in the circuit.
(c) Find the maximum voltage across each element.
XL = 2🥧fL
Io=Vo/Z
VRO = (Io)(R)…

For the same RLC series circuit having a 40.0 Ω resistor, a 3.00 mH inductor,
and a 5.00 μF capacitor:
(a) Find the resonant frequency.
(b) Calculate Irms at resonance if Vrms is 120 V
1/2🥧√LC
Irms = Vrms/R
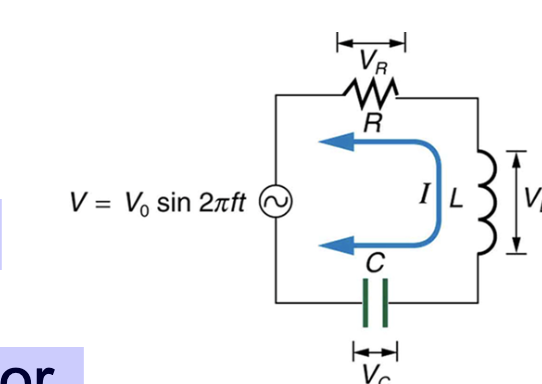
For the same RLC series circuit having a 40.0 Ω resistor, a 3.00 mH inductor, a 5.00 μF capacitor, and a voltage source with a Vrms of 120 V:
(a) Calculate the power factor and phase angle for f = 60.0Hz.
(b) What is the average power at 60.0 Hz?
XL = 2🥧fL
Xc = 1/2🥧fc
cosΦ = R/Z
Pavg = (Irms)(Vrms)(cosΦ)

What is the direction of the magnetic force on a positive charge that moves as shown?
left (west)

What is the direction of the magnetic force on a positive charge that moves as shown?
up (North)
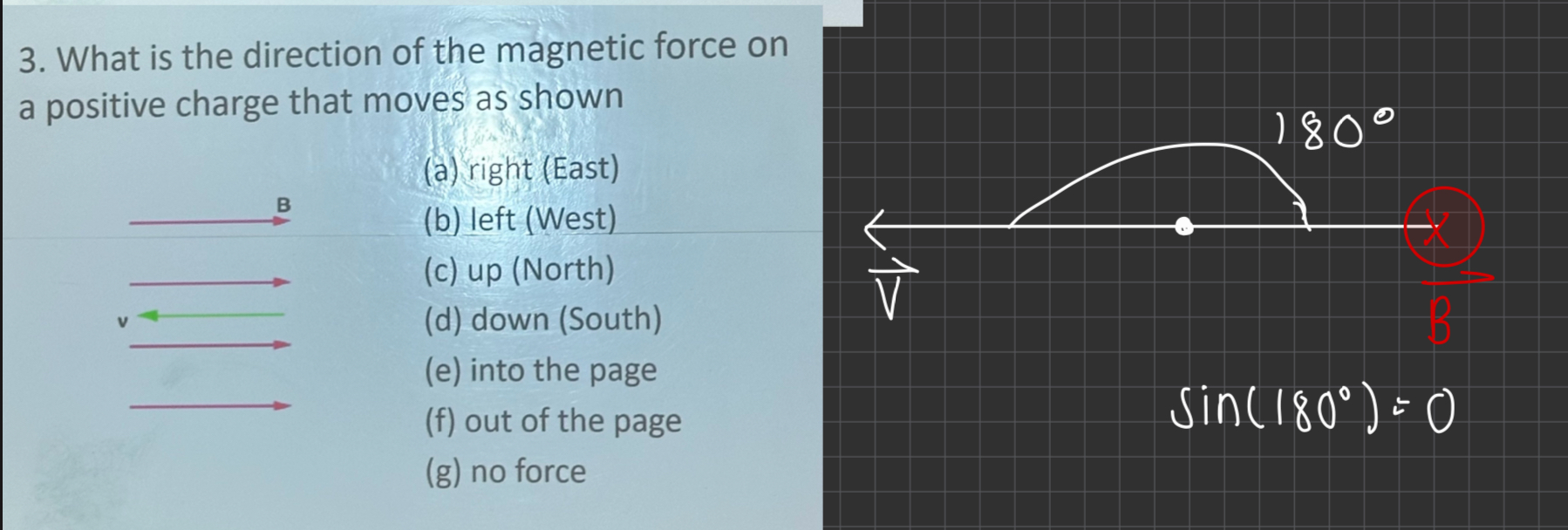
What is the direction of the magnetic force on a positive charge that moves as shown?
no force
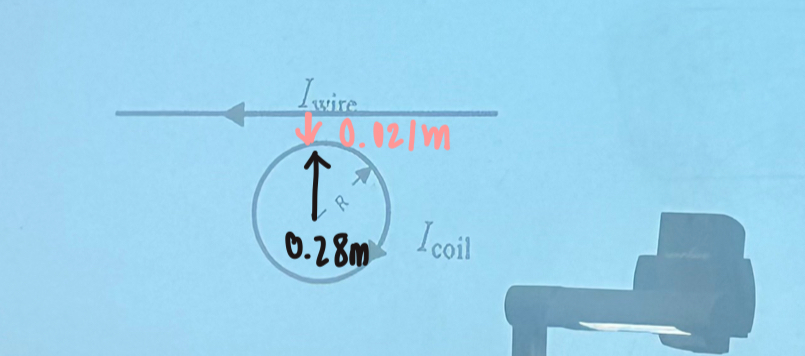
The radius of a coil of wire with N turns is R = 0.28m. A clockwise current of Icoil = 1A flows in the coil as shown. A long straight wire carrying a current Iwire = 29A toward the left is located 0.04m from the edge of the coil. The magnetic field at the center of the coil is zero tesla. Determine N, the number of turns.
Bw=Bc
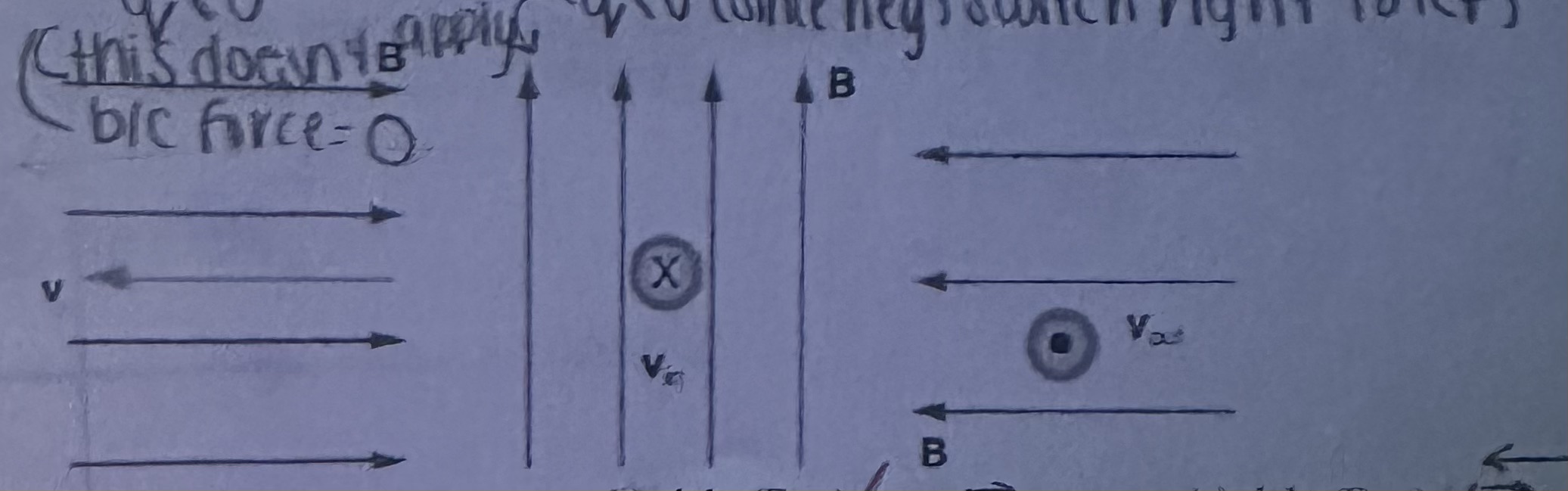
What is the direction of the magnetic force on a negative charge that moves as shown in each of the cases below?
no force
left
up
A charged particle is launched with a velocty of 5×10^4 m/s at an angle of 35 with respect of 0.0045T magnetic field. If the magnetic field exerts a force of 0.0026N on the particle determine the magnitude of the charge on the particle.
F=qvBsinΘ
A 0.750m long section of cable is carrying current to a car starter motor makes an angle of 30 with the Earth’s 5.50×10^-5 T field. What is the current when the wire experiences a force of 7.00×10^-3N?
F=ILBsinΘ
The figure shows two long straight horizontal wires that are parallel and a distance 2a (a=10cm). If both wires carry current I=5A in the same direction, what are the direction (out or into the page) and magnitude of the magnetic field at point (a) P1 and (b) P2
Current acts on BOTH P1 and P2
B1 and B2 are in opposite directions, so Bnet=0
Bnet=B1=B2
B1=μoI/2🥧r
The radius of the (single turn) loop of wire is 12cm and the distance fro the long straight wire to the center of the loop is 24cm. The current in the long straight wire is 15A flowing down the page. The net magnetic field at the center of the loop is zero. What is the current in the loop?
Bwire=μoI/2🥧r
Bcoil=μoI/2🥧r
Bw=Bc