Neuroscience and Brain Anatomy: Key Structures and Functions
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
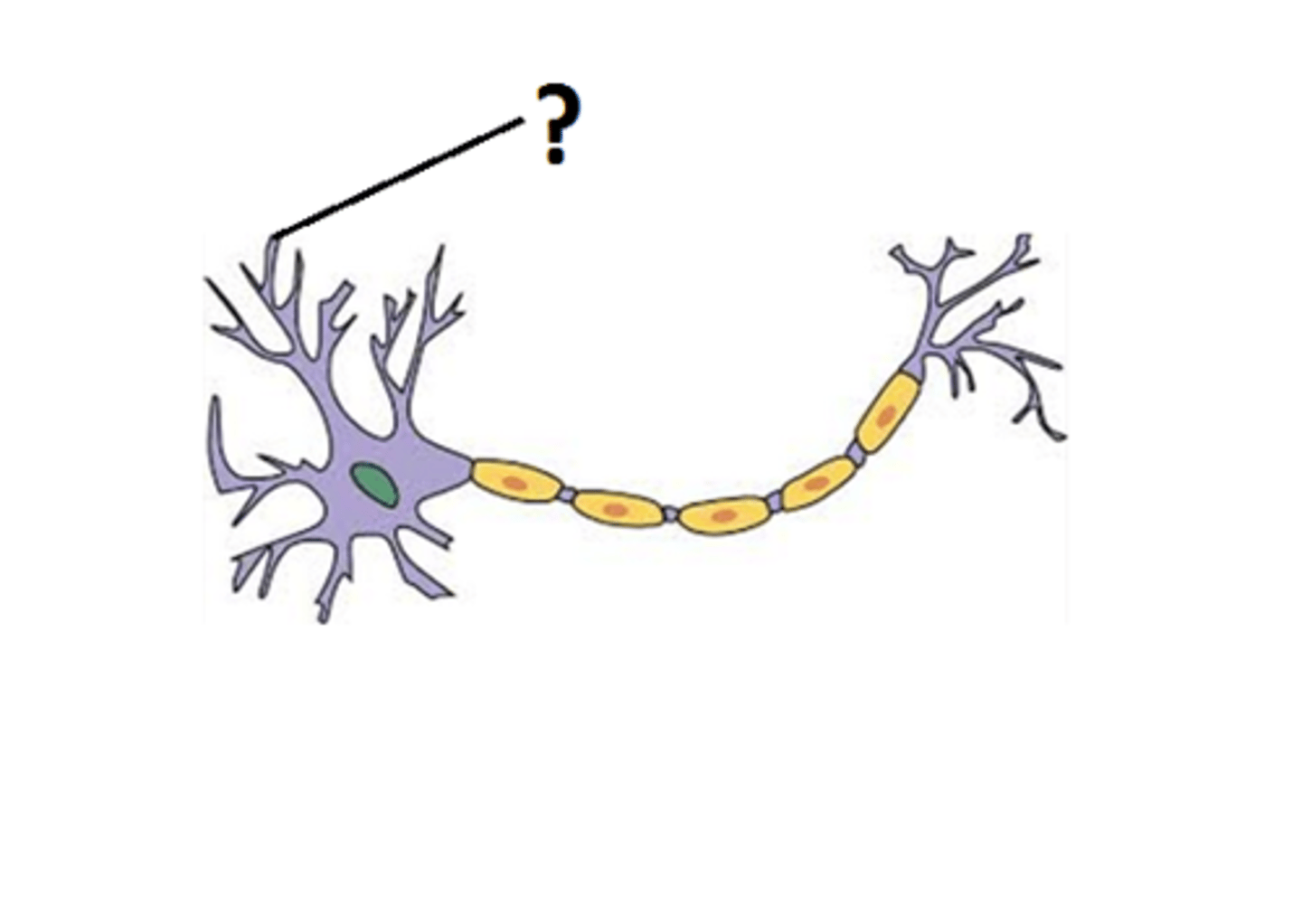
Dendrites
Branch-like structures of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons.
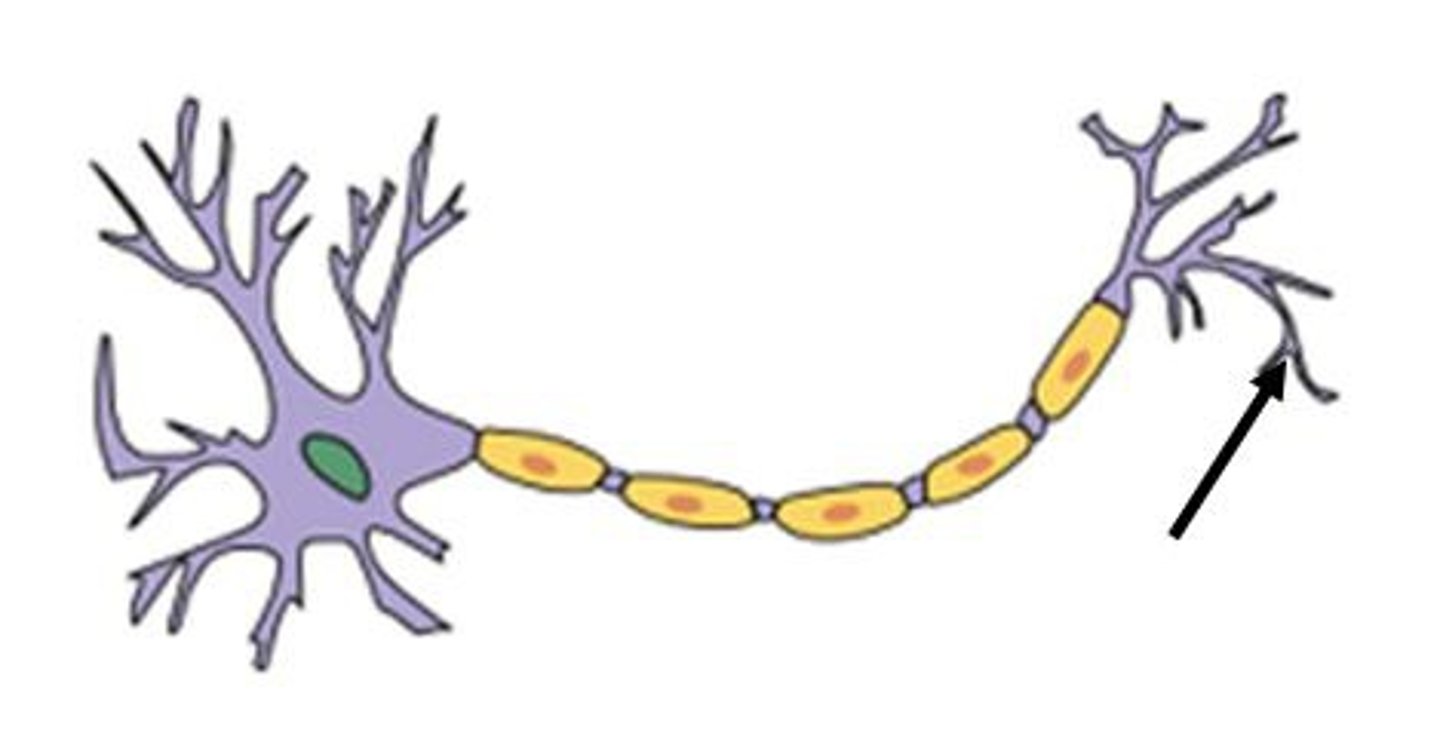
Axon Terminals
The endpoints of an axon where neurotransmitters are released to communicate with other neurons.
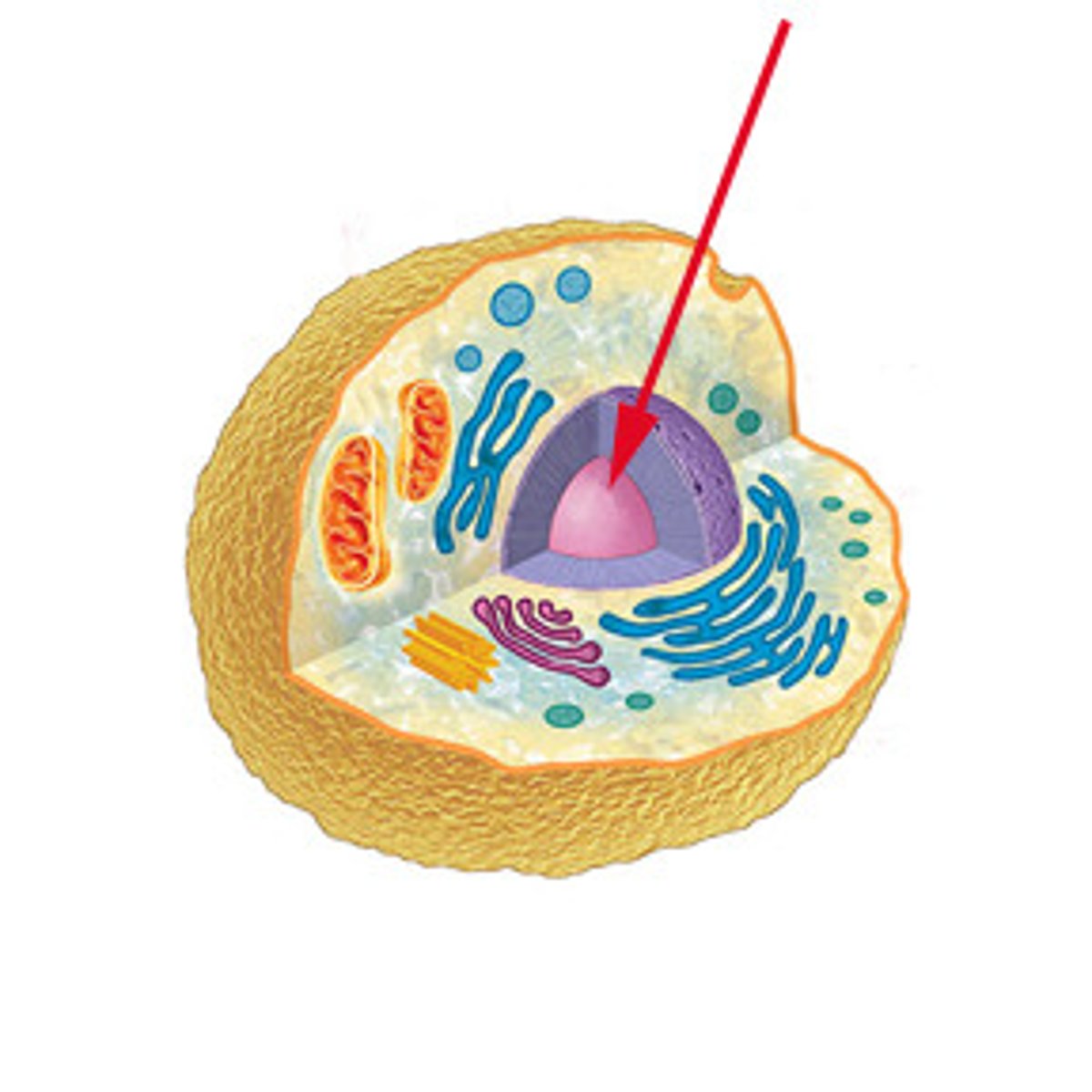
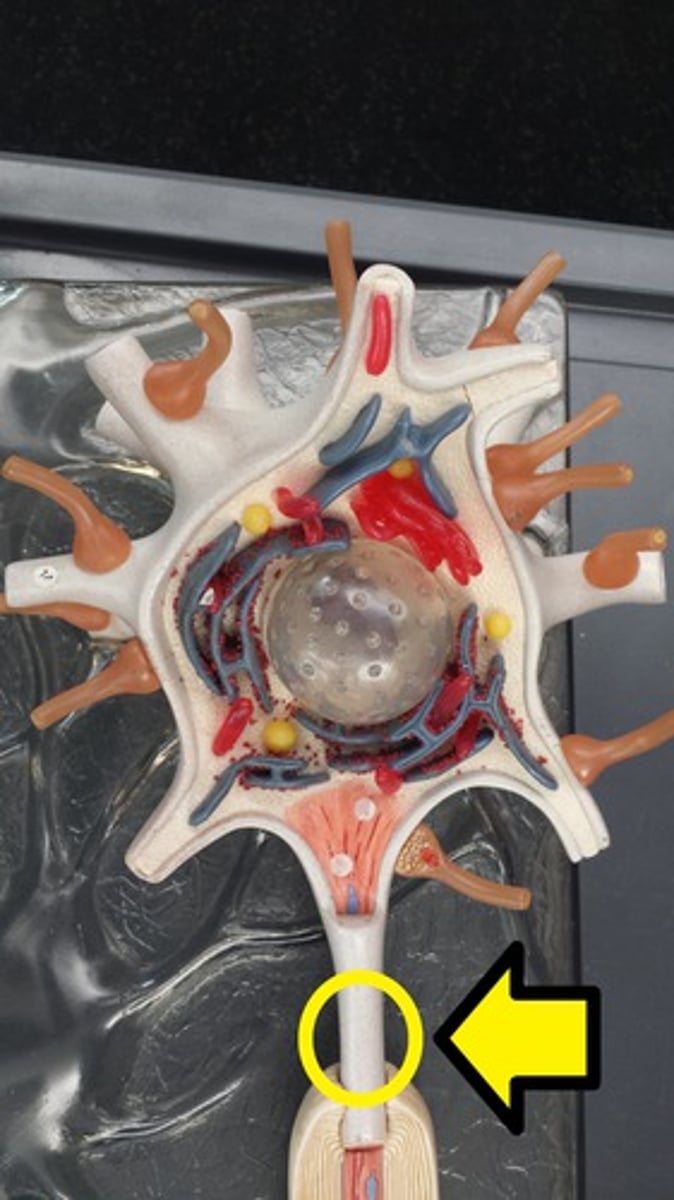
Nucleus
The control center of a cell that contains genetic material.
Axon Hillock
The cone-shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body and where action potentials are initiated.
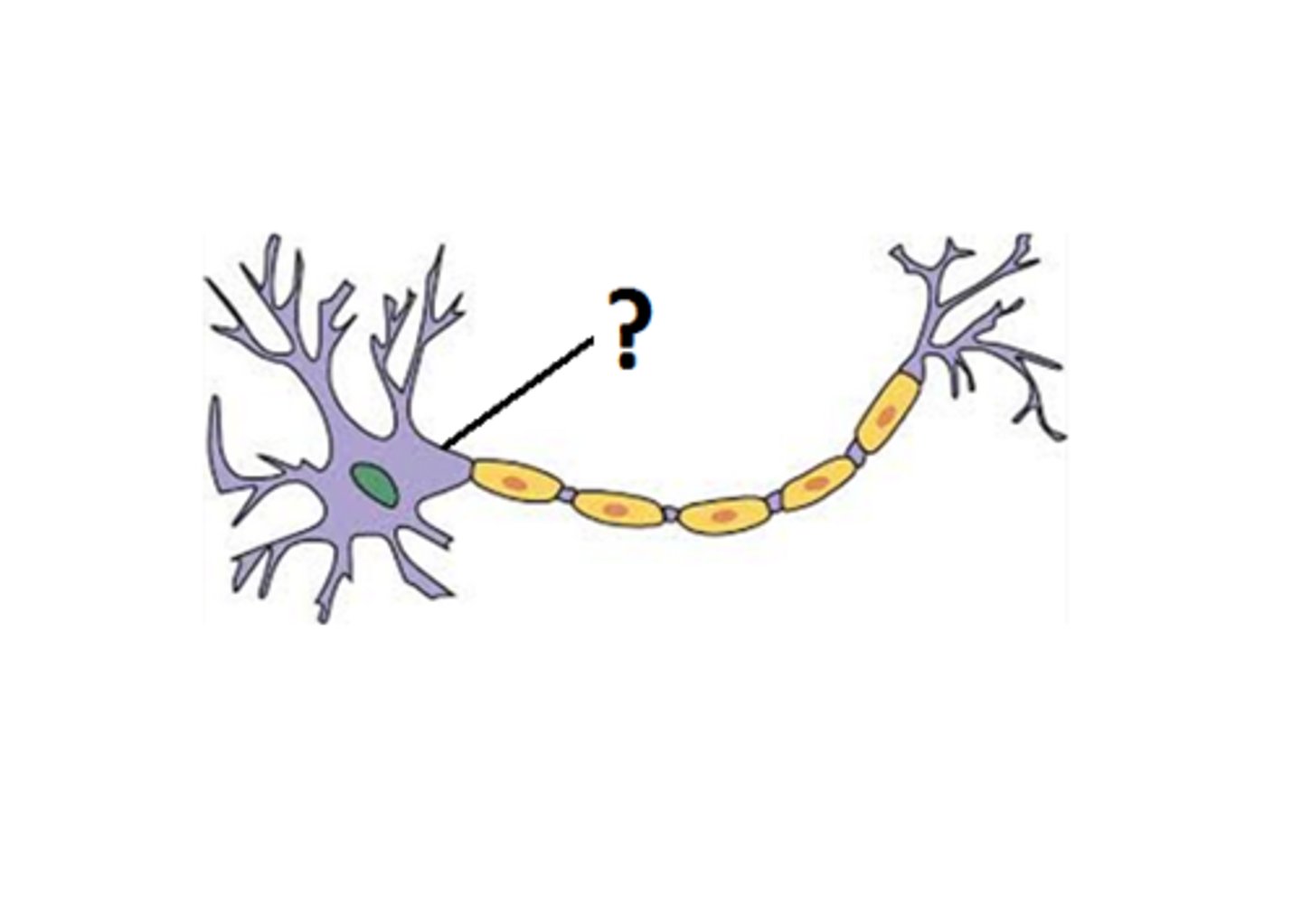
Initial Segment
The part of the axon closest to the axon hillock where the action potential begins.
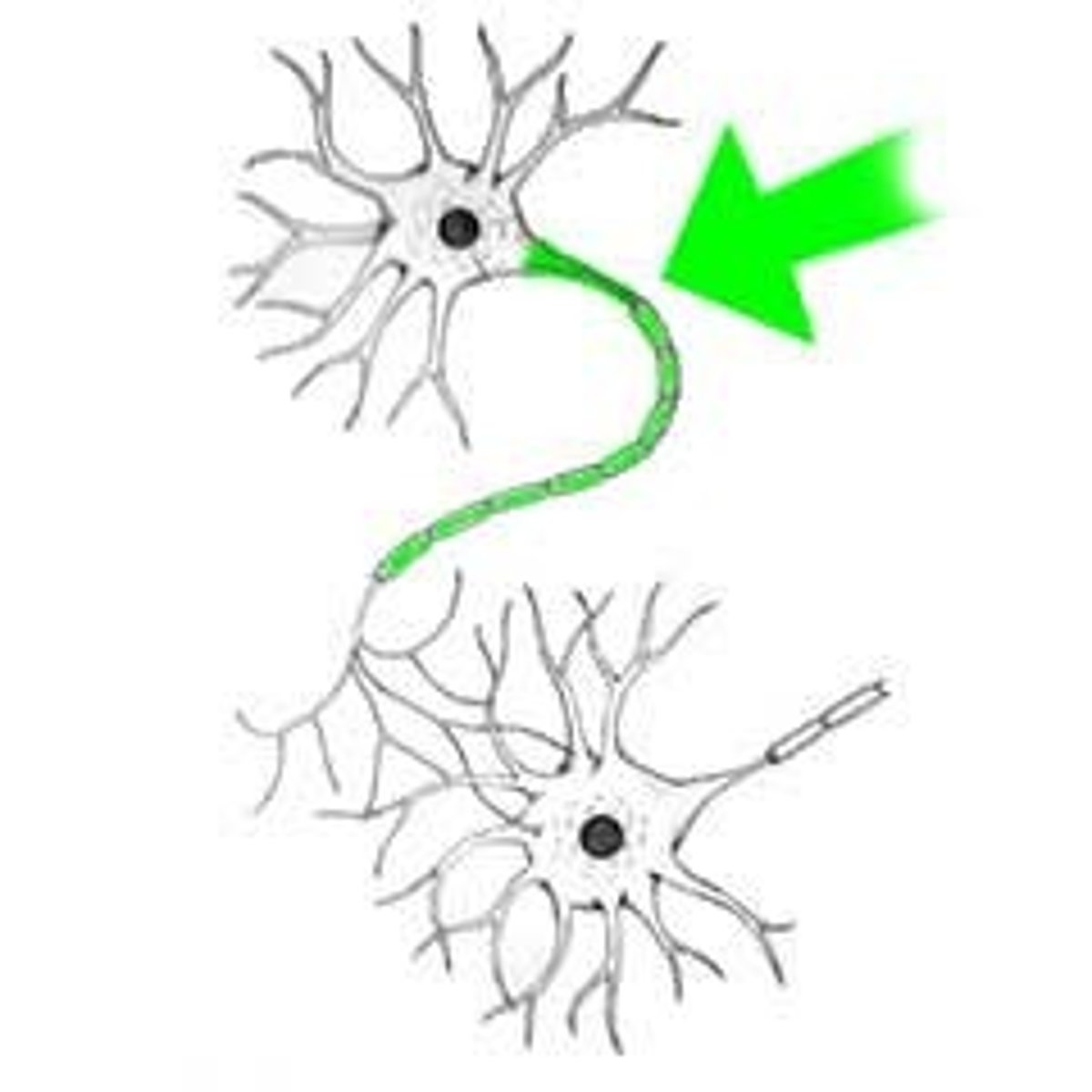
Axon
A long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
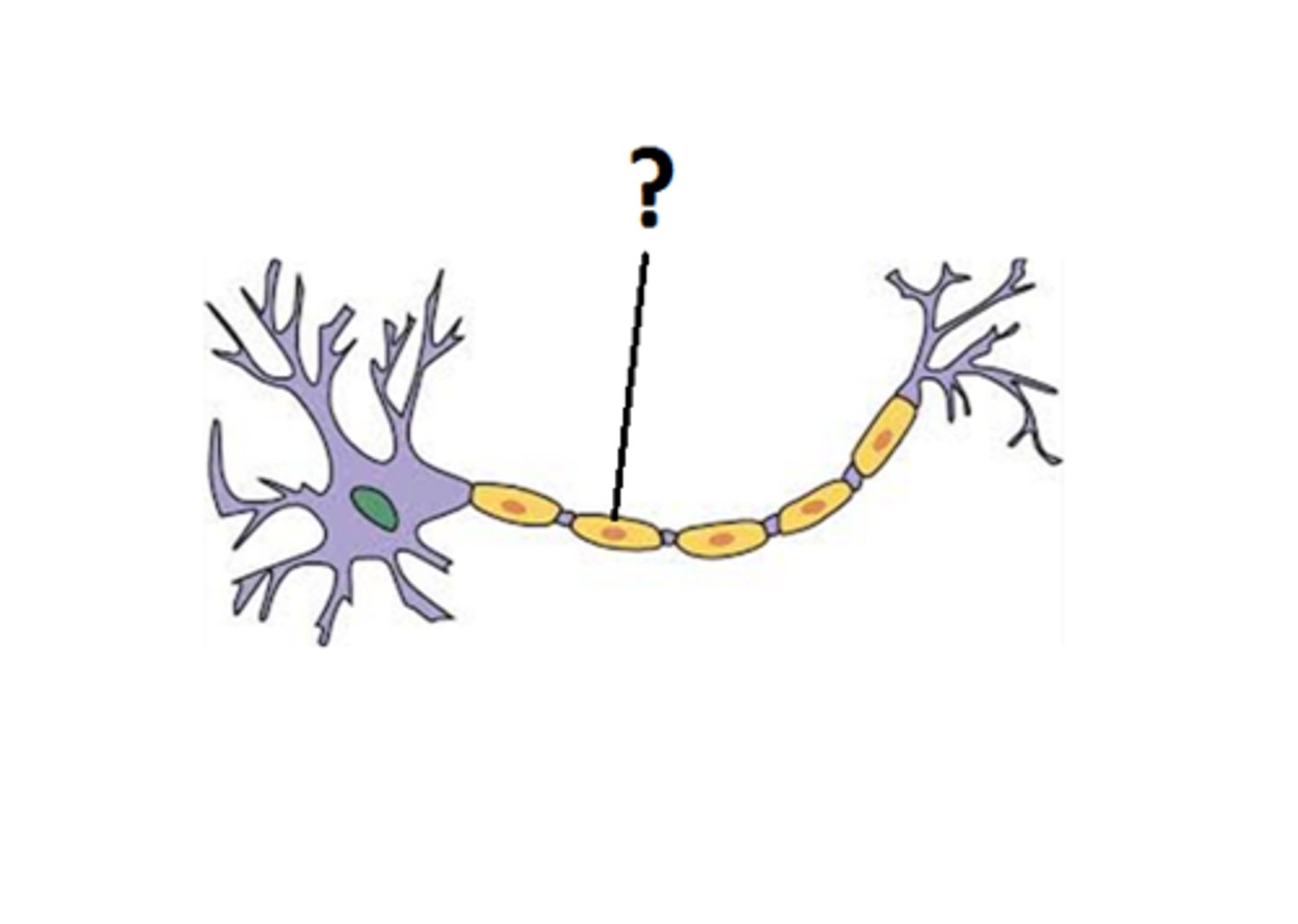
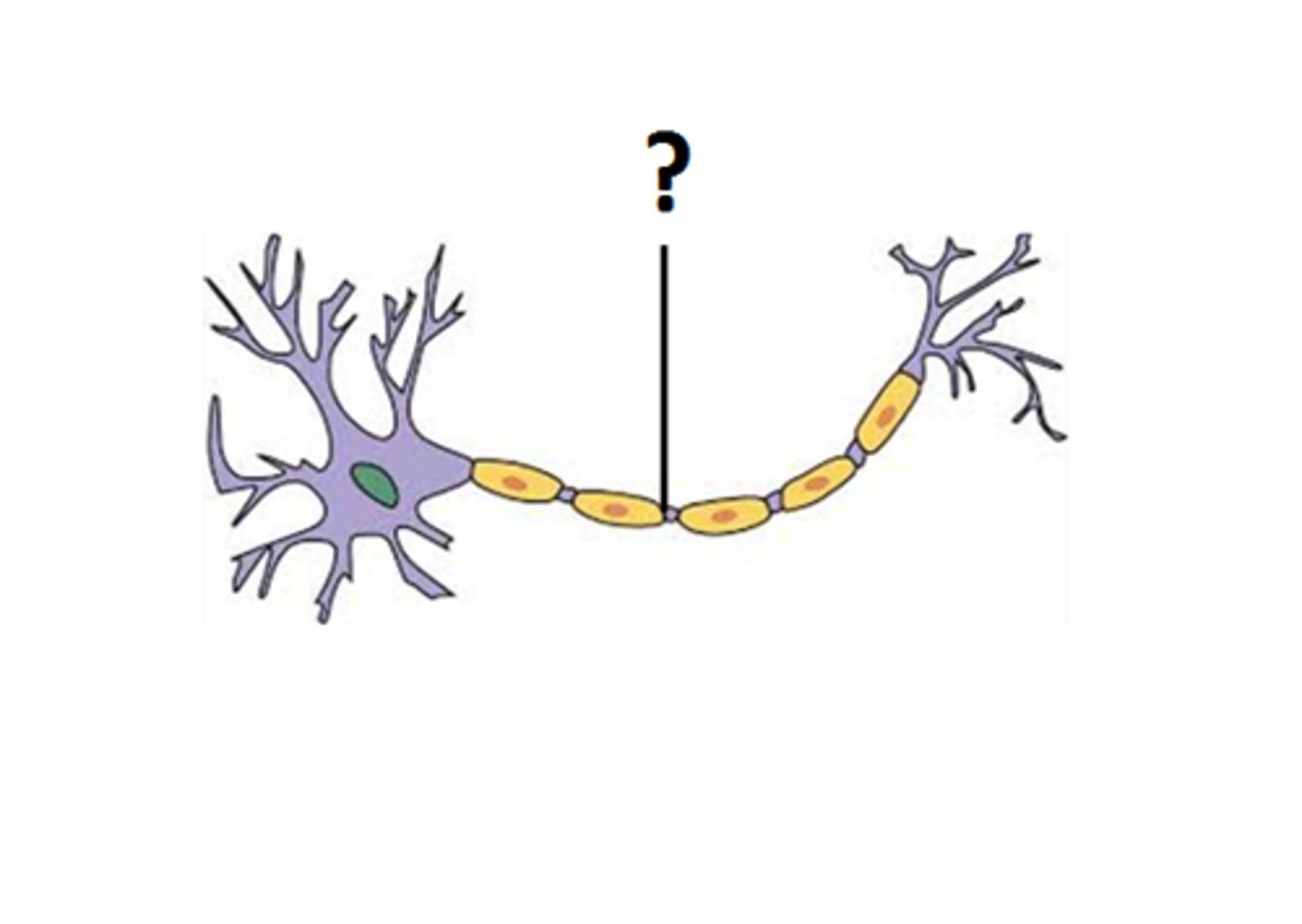
Myelin Sheath
A fatty layer that insulates axons and increases the speed of nerve impulse transmission.
Node of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath that facilitate rapid conduction of nerve impulses.
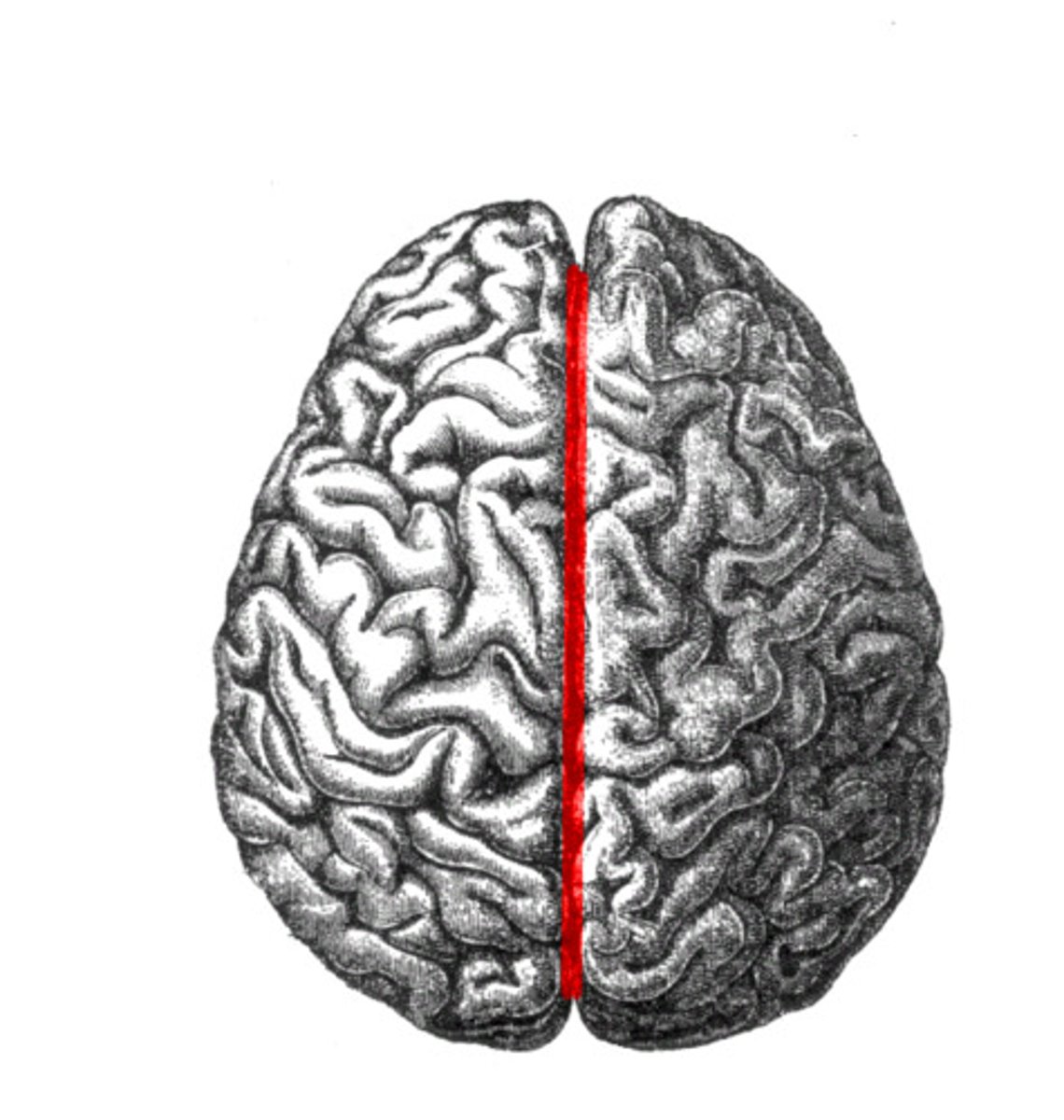
Longitudinal fissure
The deep groove that divides the brain into the left and right hemispheres.
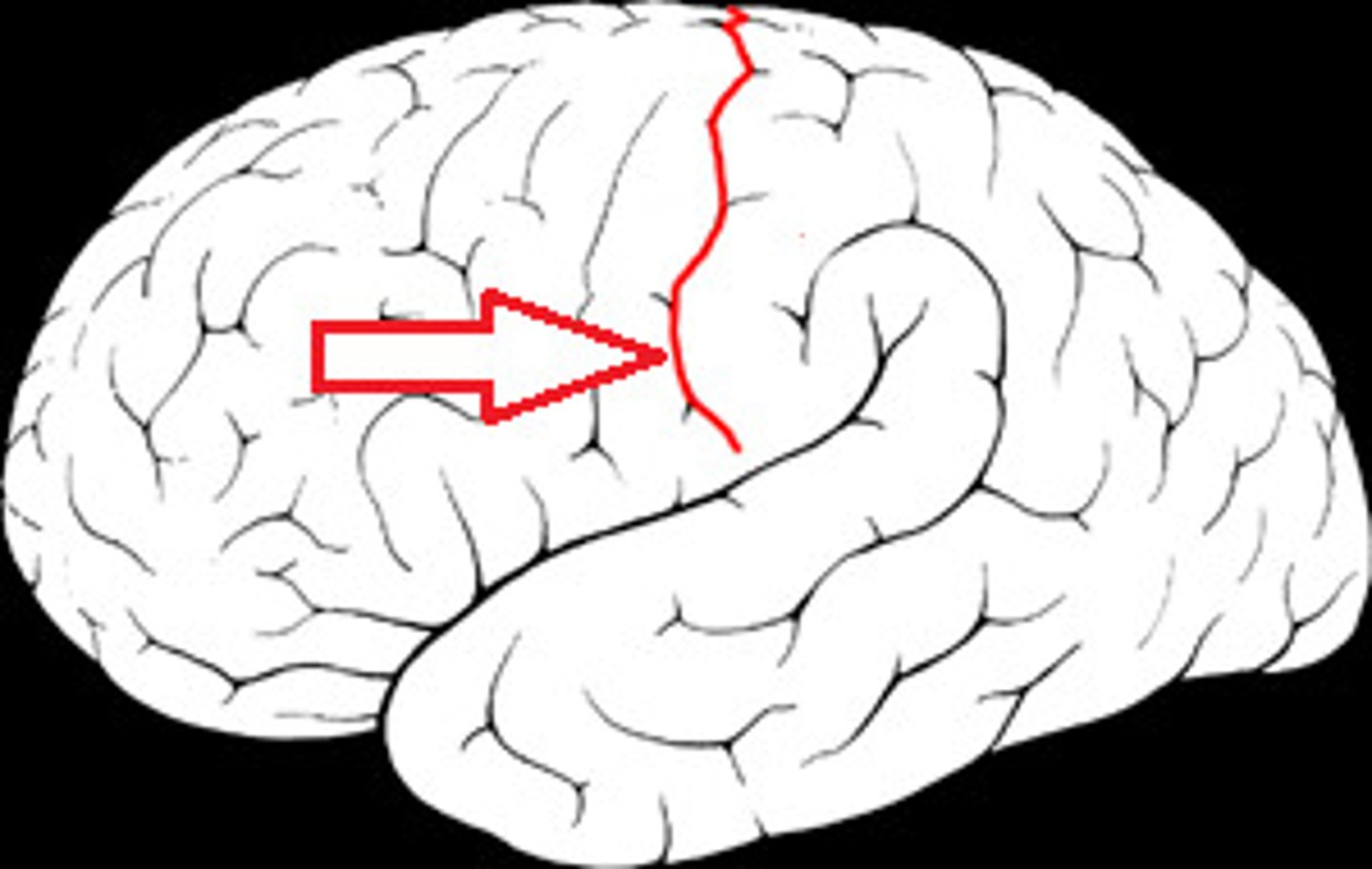
Central sulcus
The groove that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
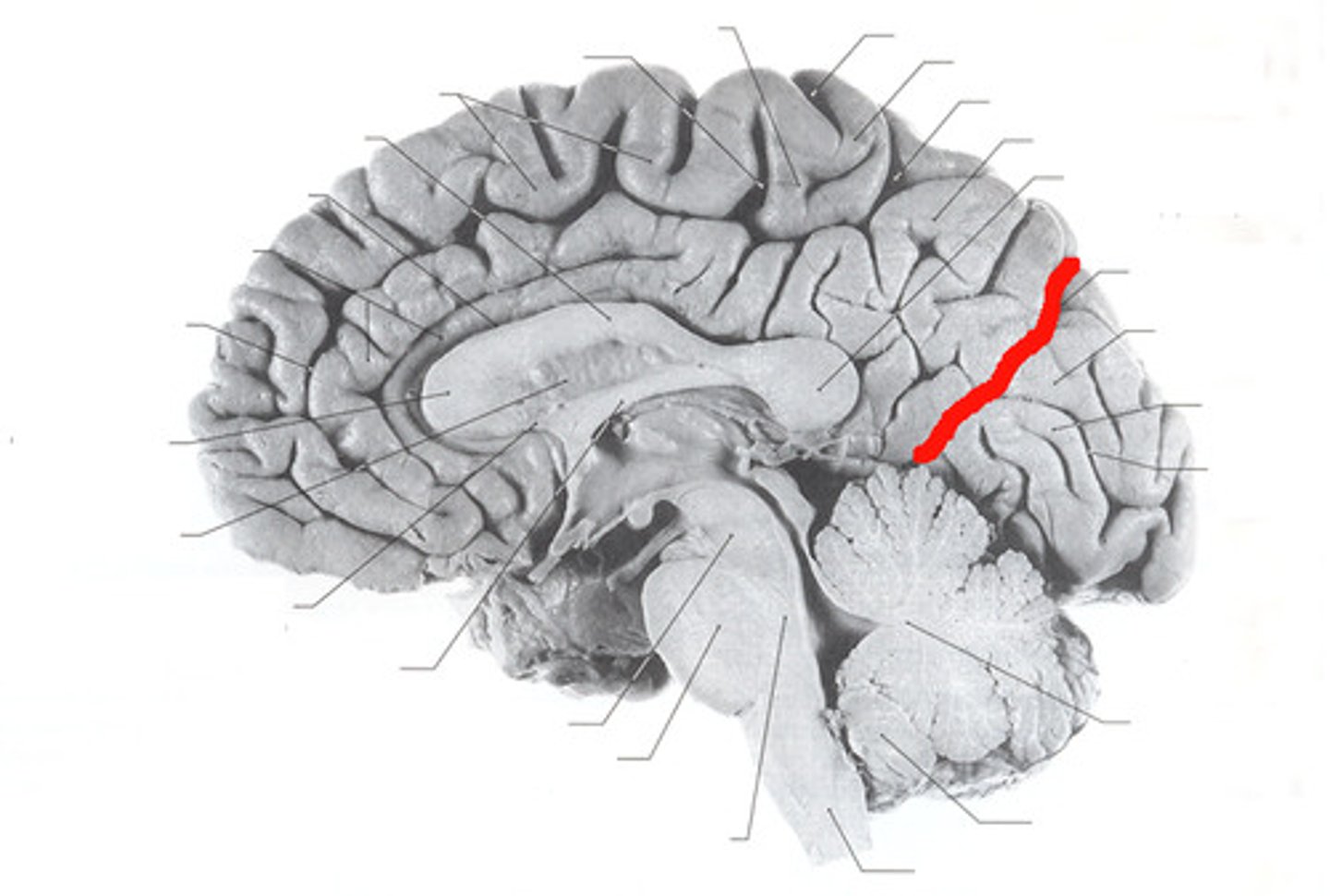
Parieto-occipital sulcus
The groove that separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe.
Lateral sulcus or fissure
The groove that separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes.
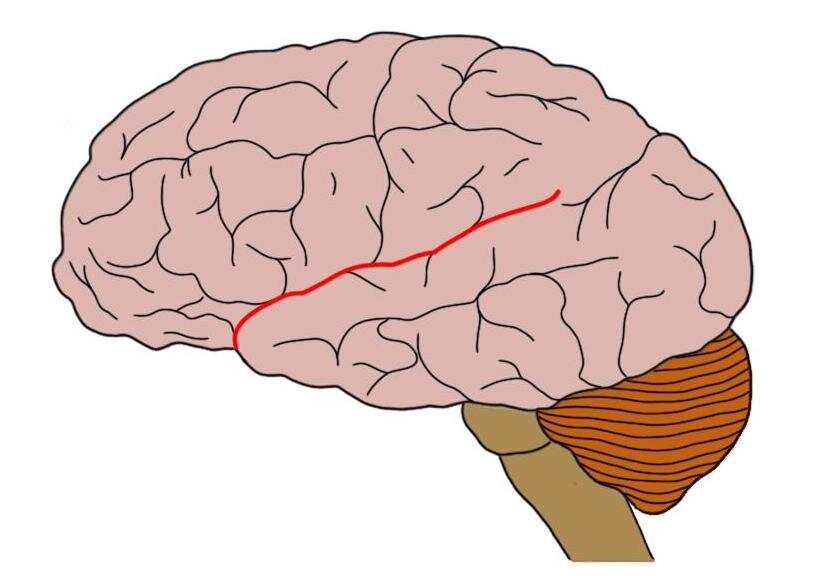
Transverse fissure
The groove that separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum.
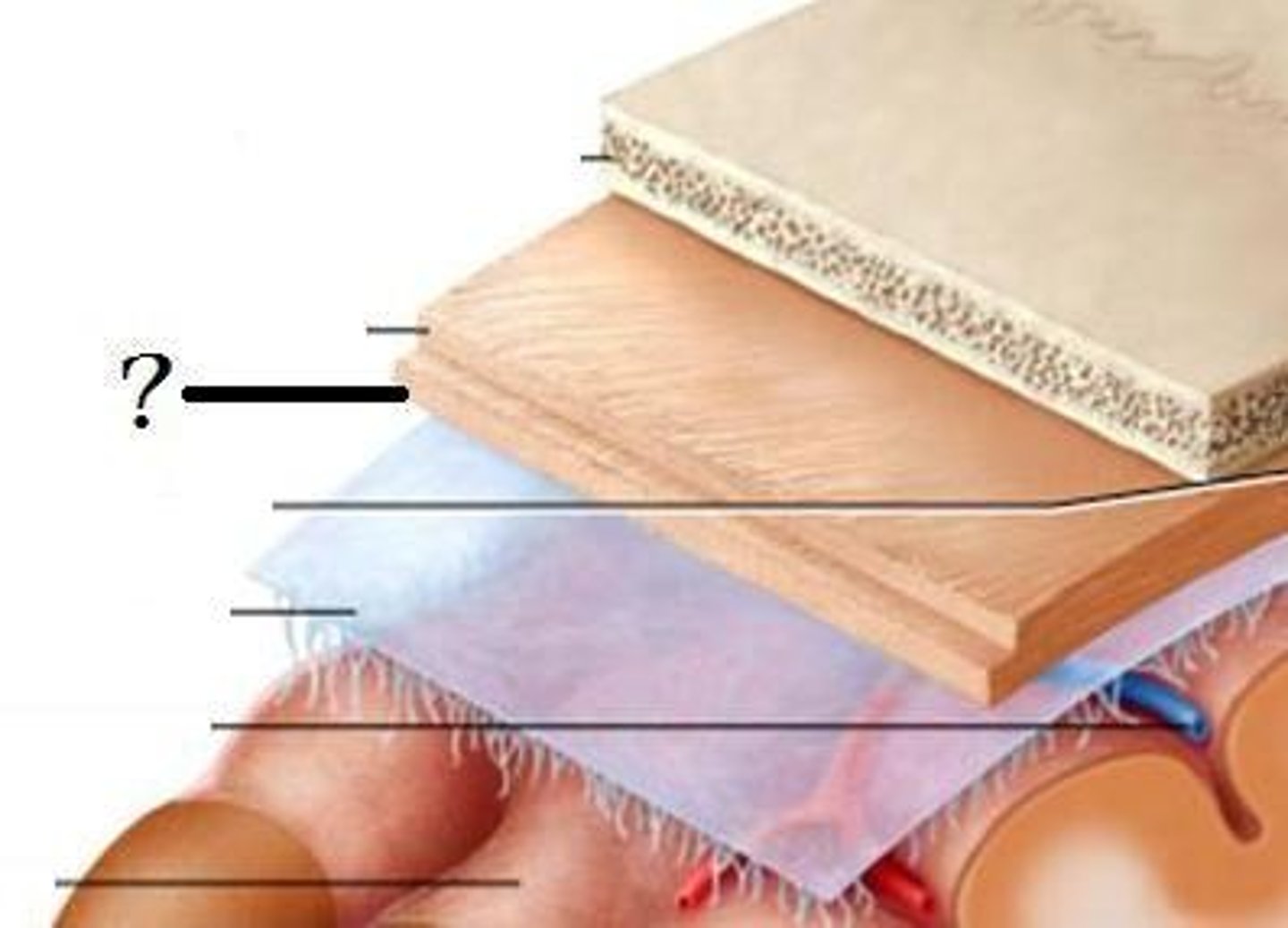
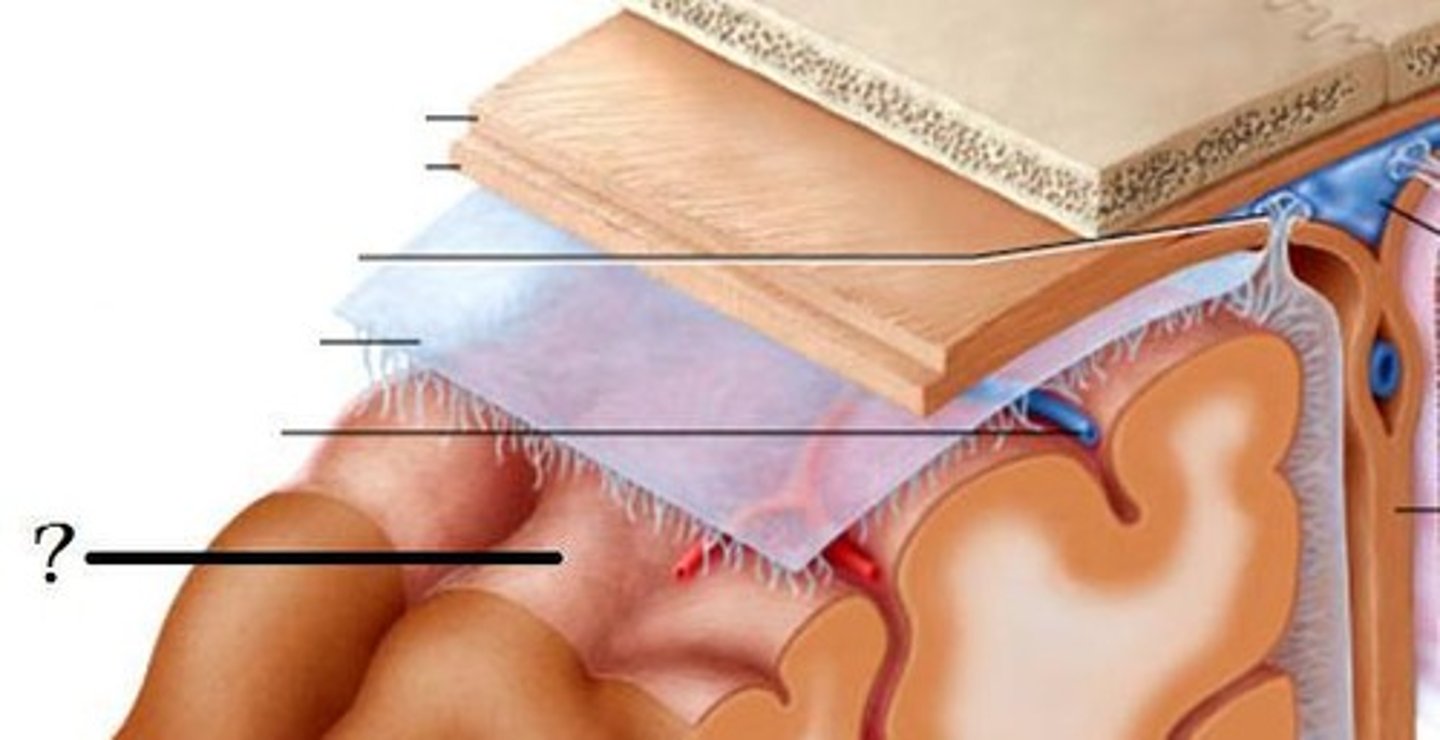
Dura Mater
The tough outermost layer of the meninges that surround the brain and spinal cord.
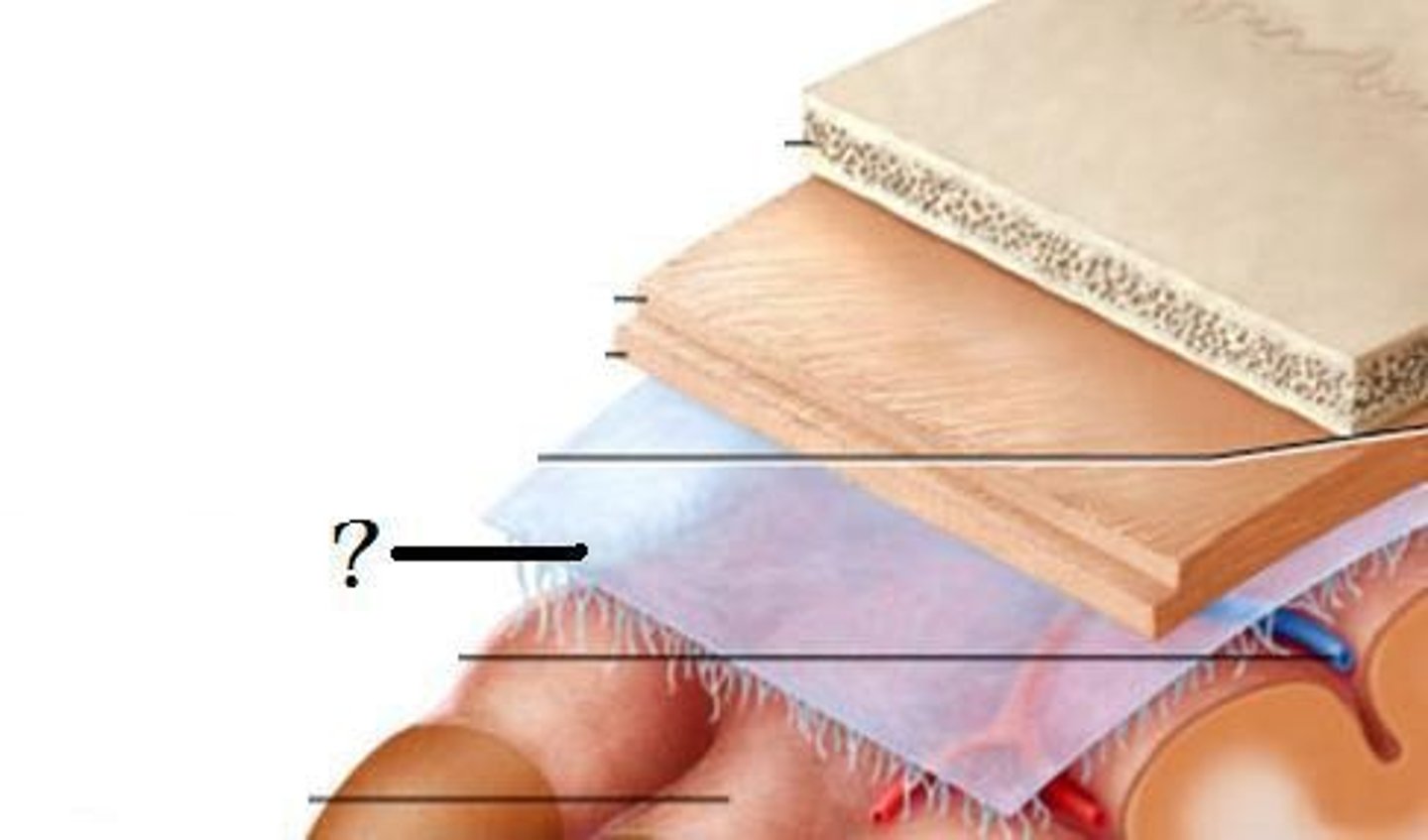
Arachnoid mater
The middle layer of the meninges, which is web-like and contains cerebrospinal fluid.
Pia mater
The delicate innermost layer of the meninges that closely adheres to the surface of the brain and spinal cord.
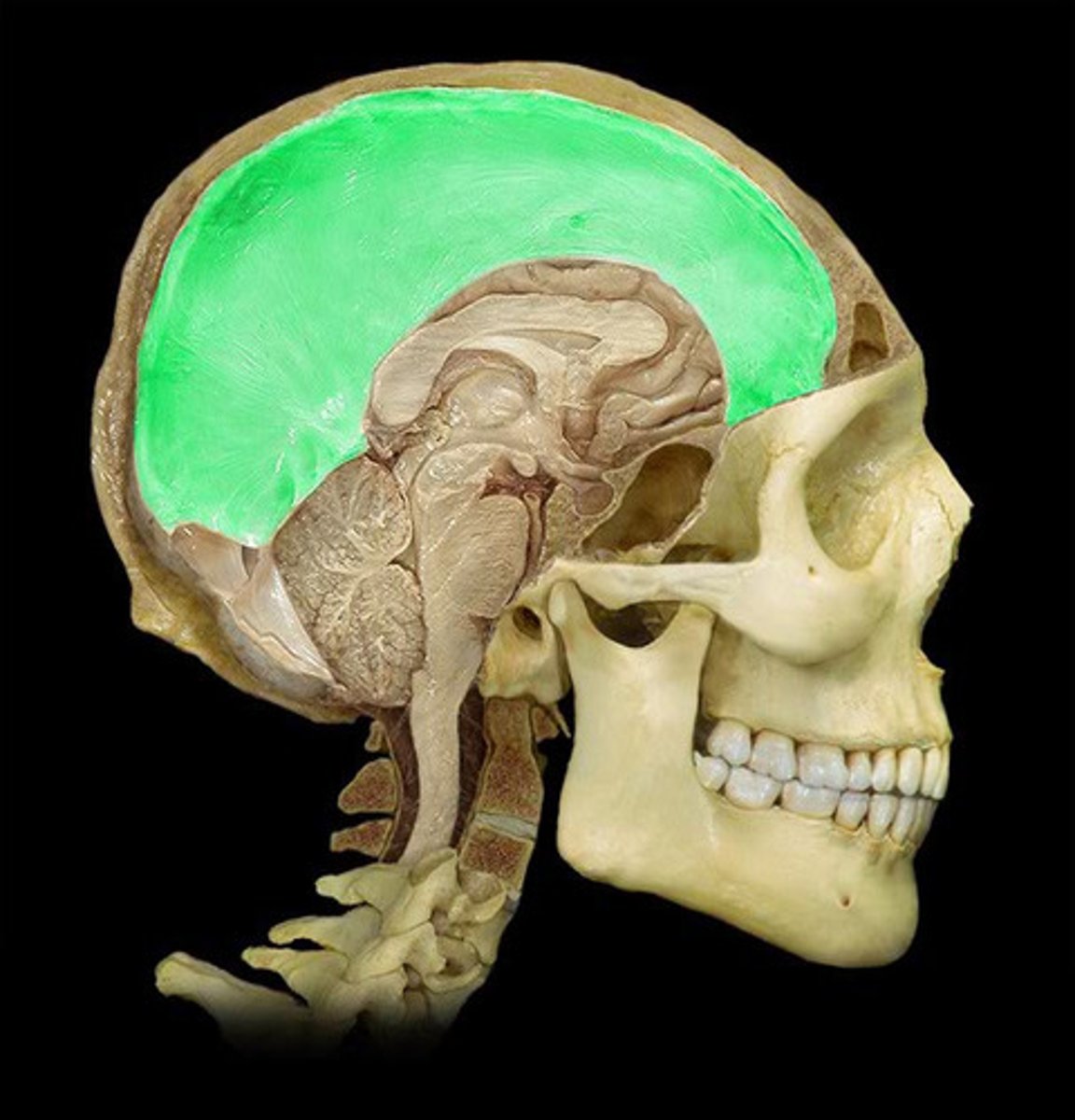
Falx cerebri
A sickle-shaped fold of dura mater that separates the two cerebral hemispheres.
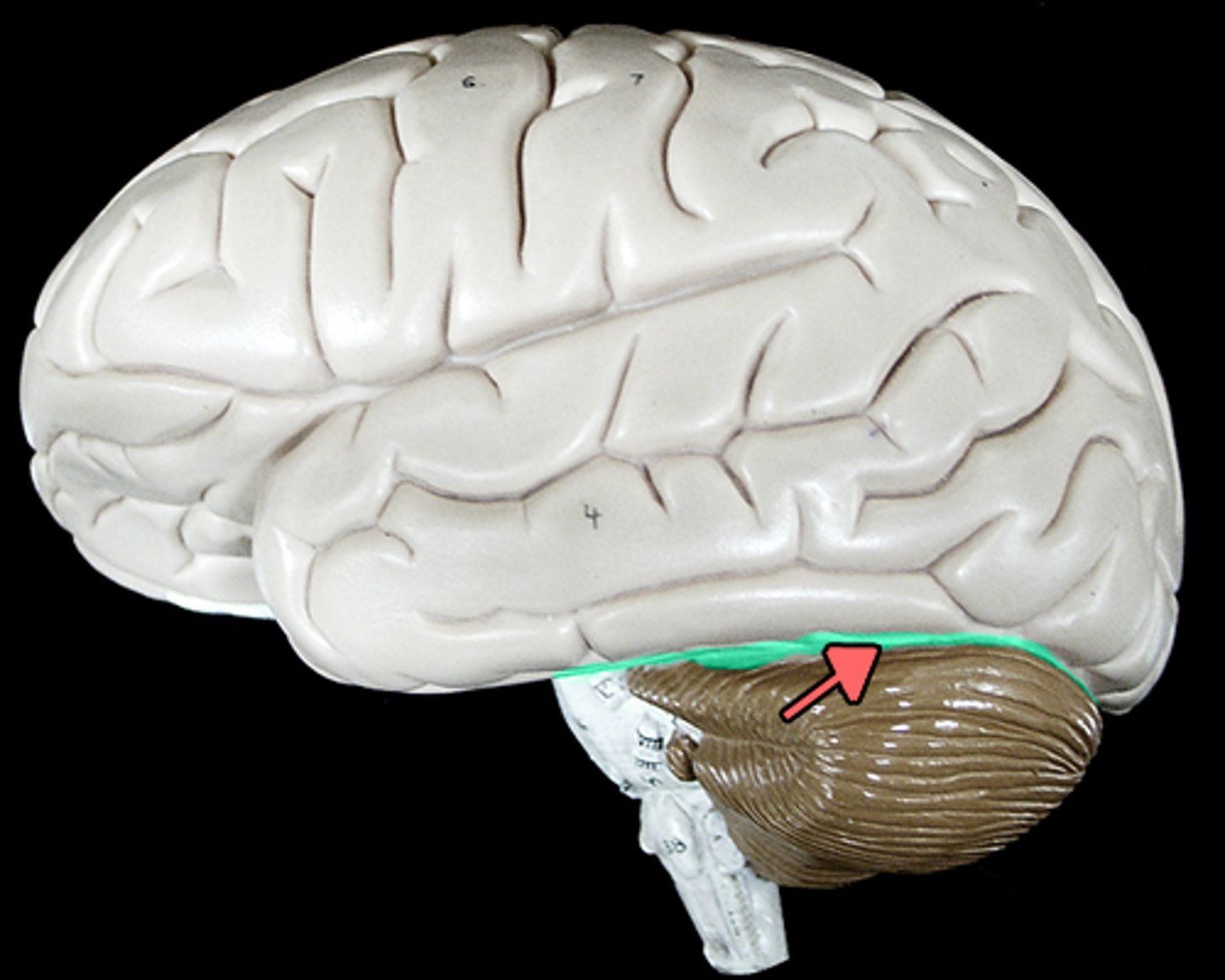
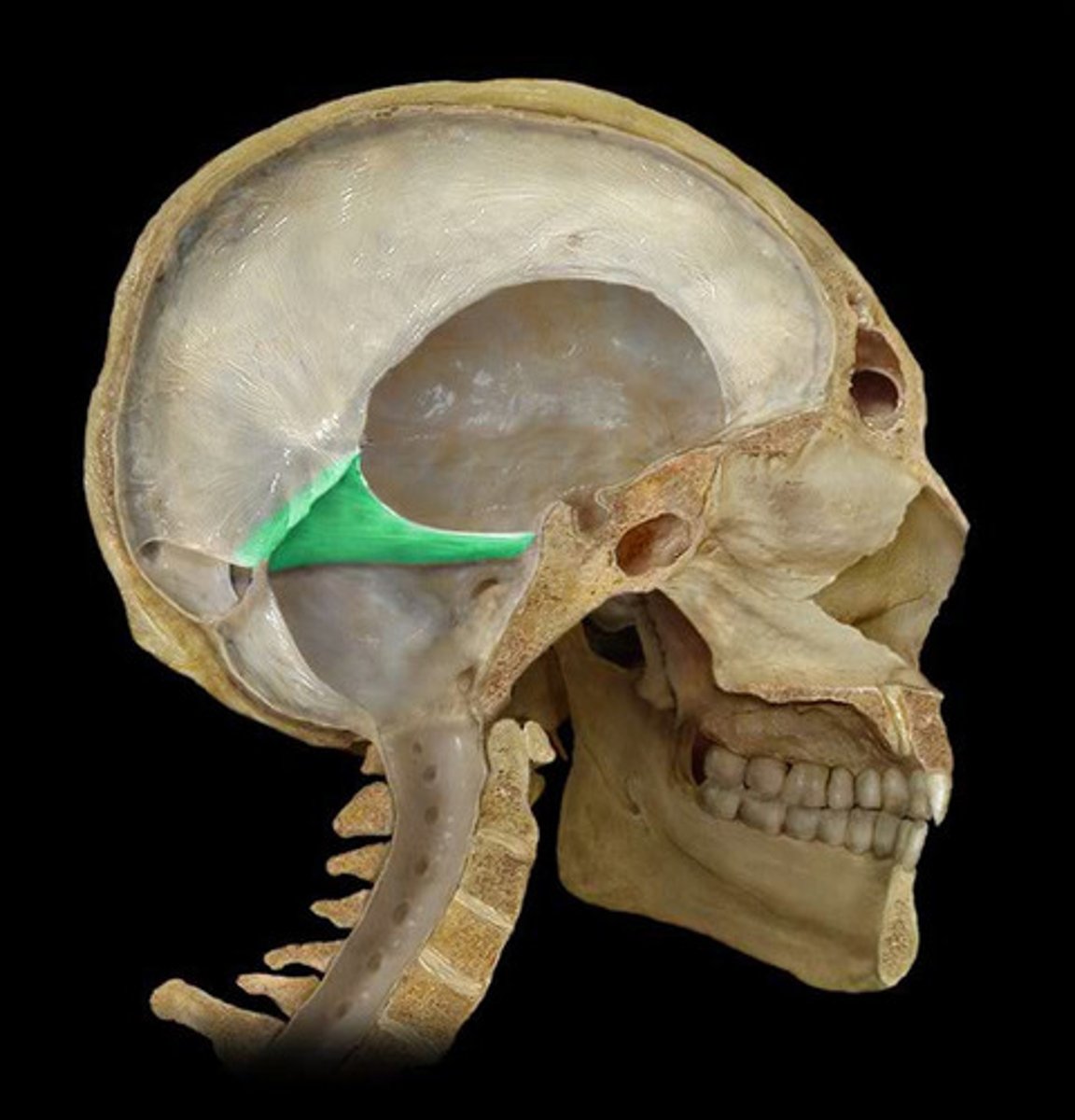
Tentorium cerebelli
A horizontal fold of dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum.
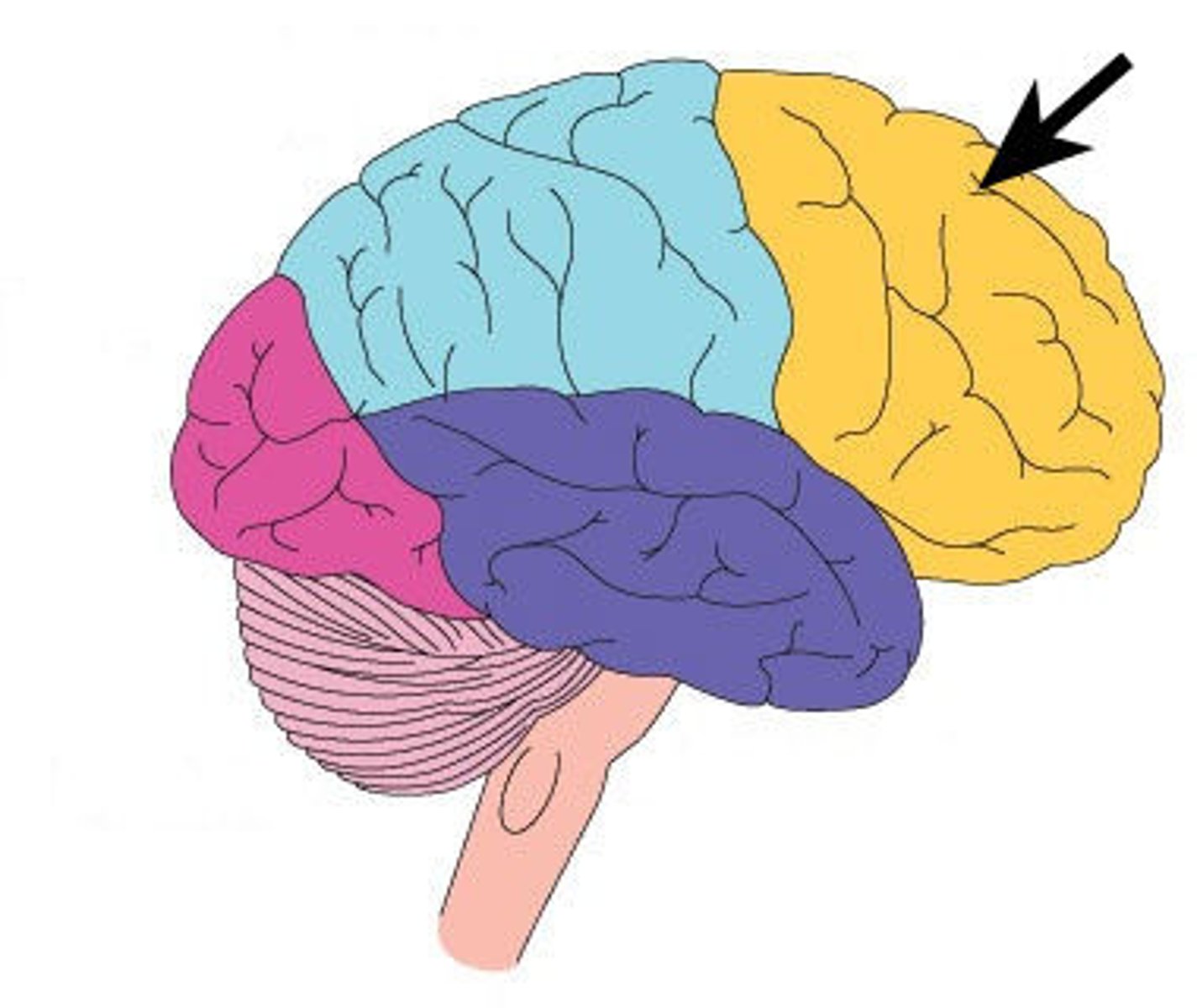
Frontal lobe
The part of the brain associated with reasoning, planning, problem-solving, and emotions.
Parietal lobe
The part of the brain that processes sensory information related to touch, temperature, and pain.
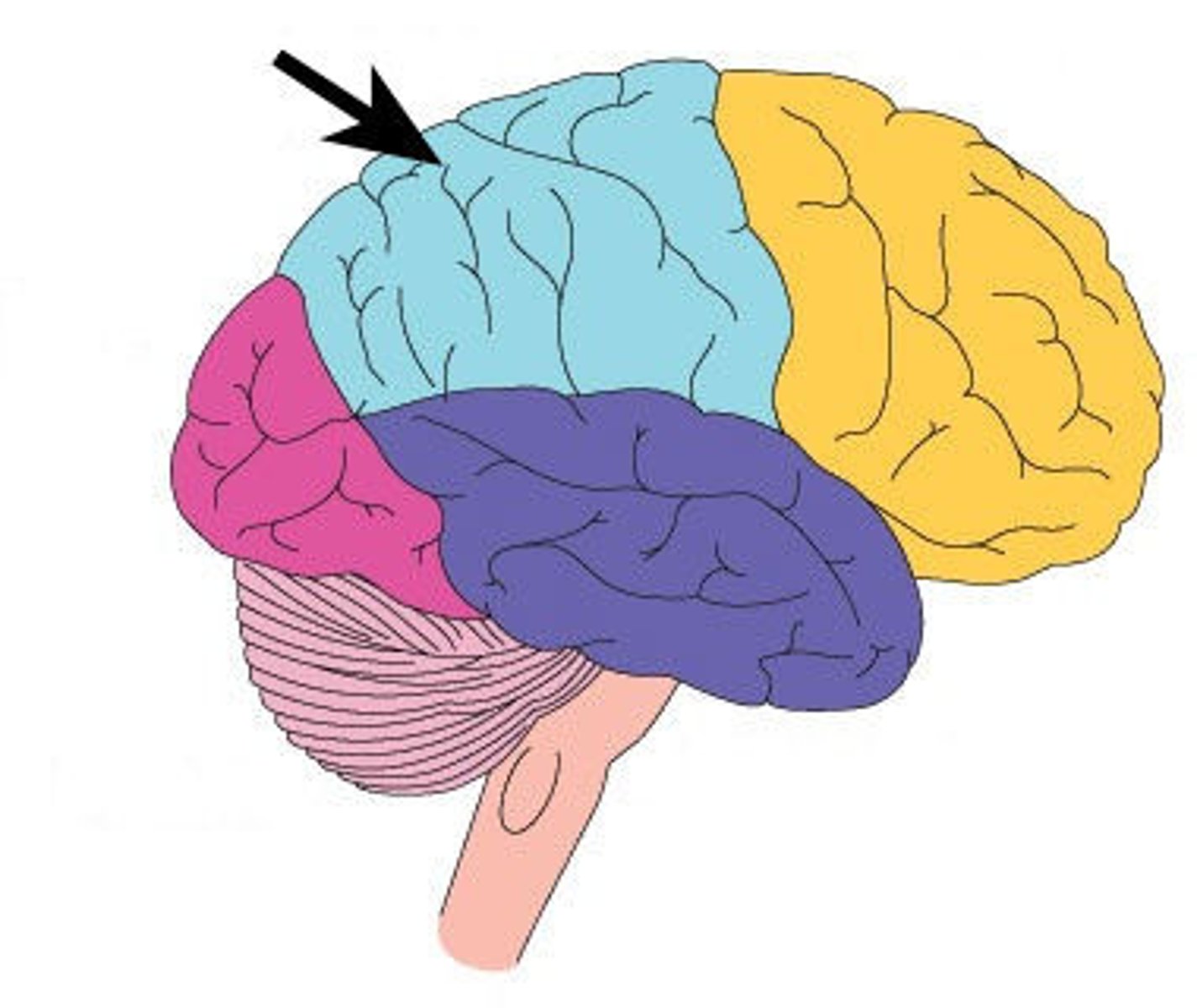
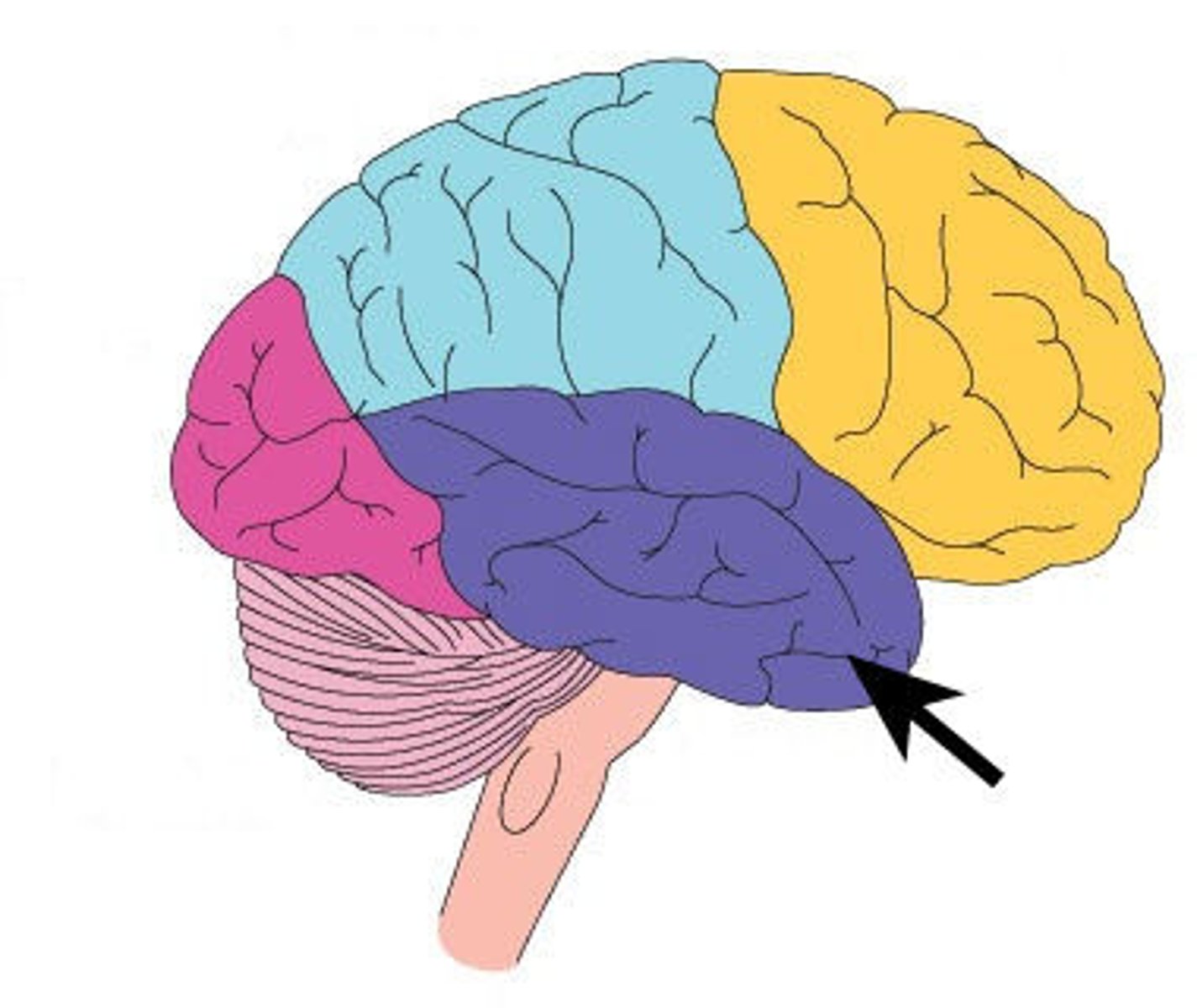
Occipital lobe
The part of the brain that is primarily responsible for vision.
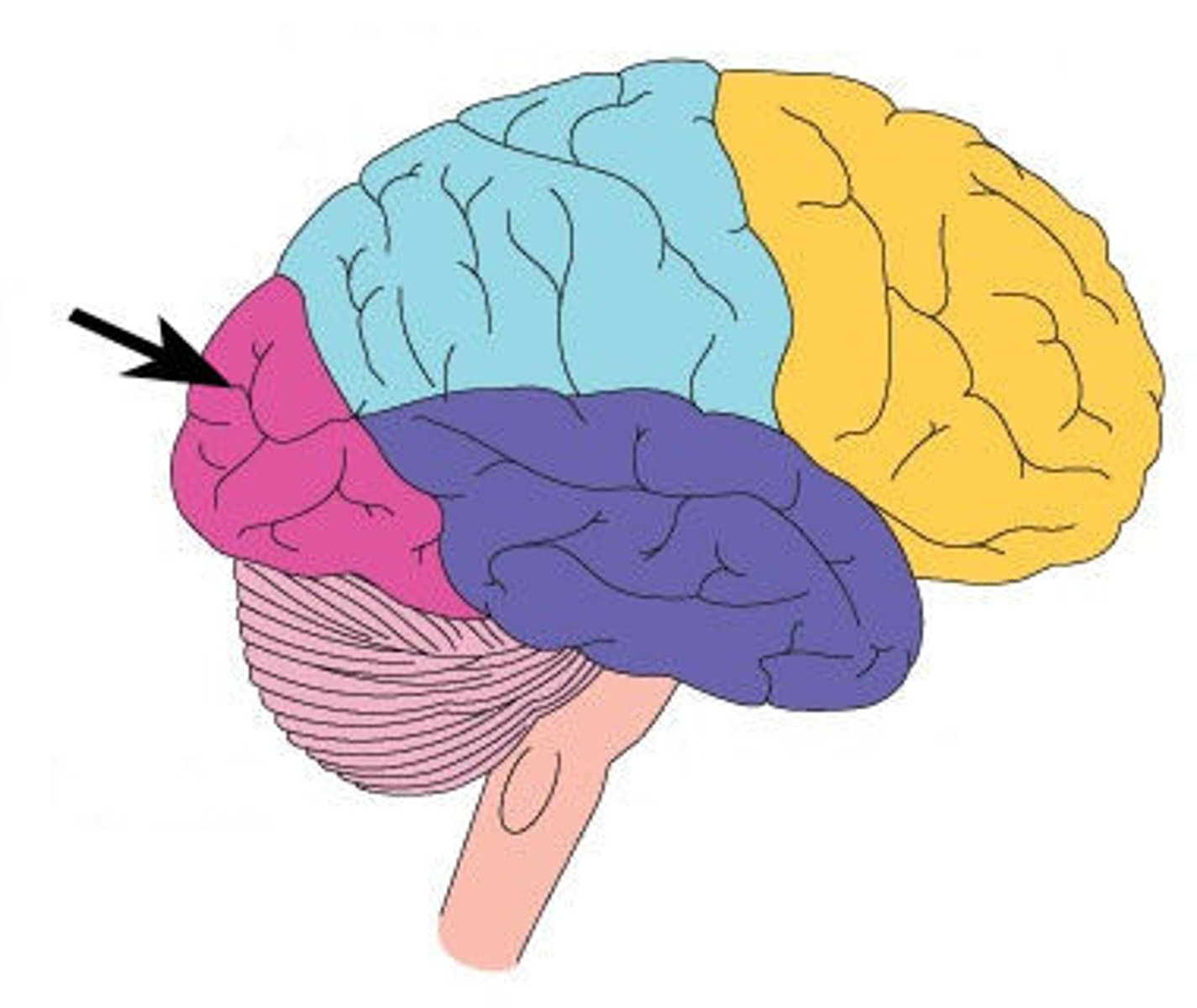
Temporal lobe
The part of the brain involved in processing auditory information and memory.
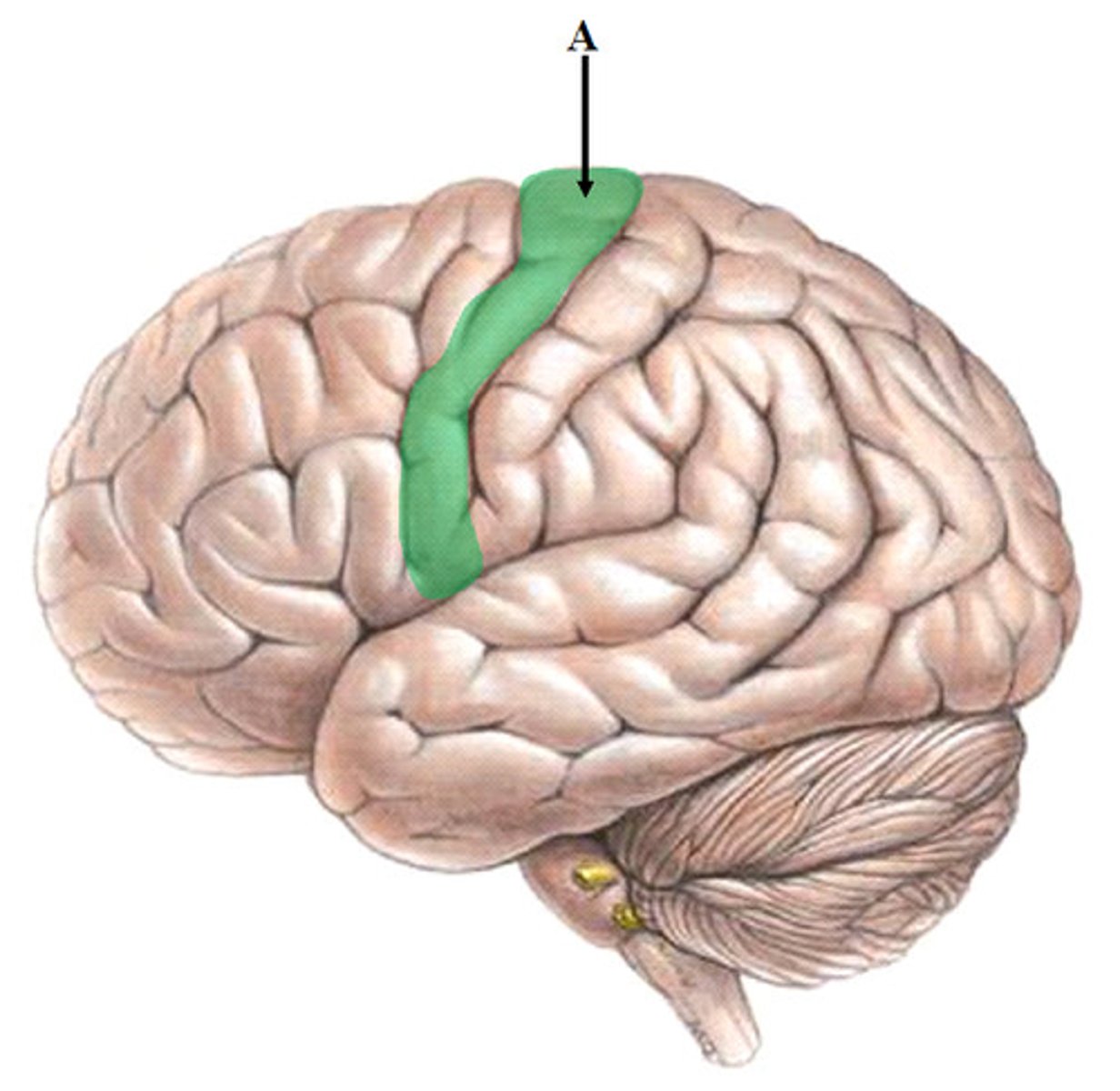
Precentral gyrus
The primary motor cortex located in the frontal lobe, responsible for voluntary movement.
Postcentral gyrus
The primary somatosensory cortex located in the parietal lobe, responsible for processing sensory information.
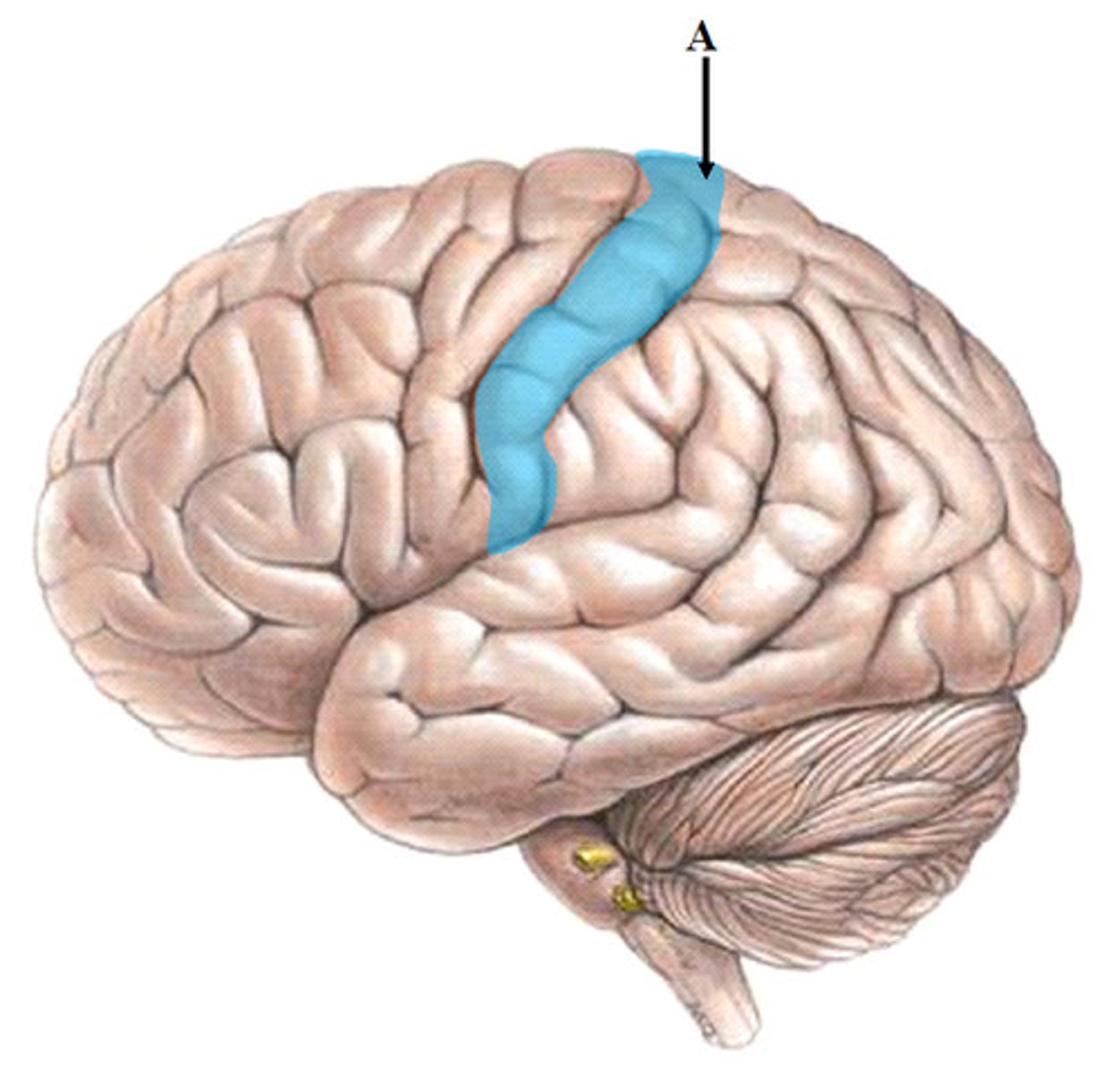
Corpus callosum
A large bundle of nerve fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
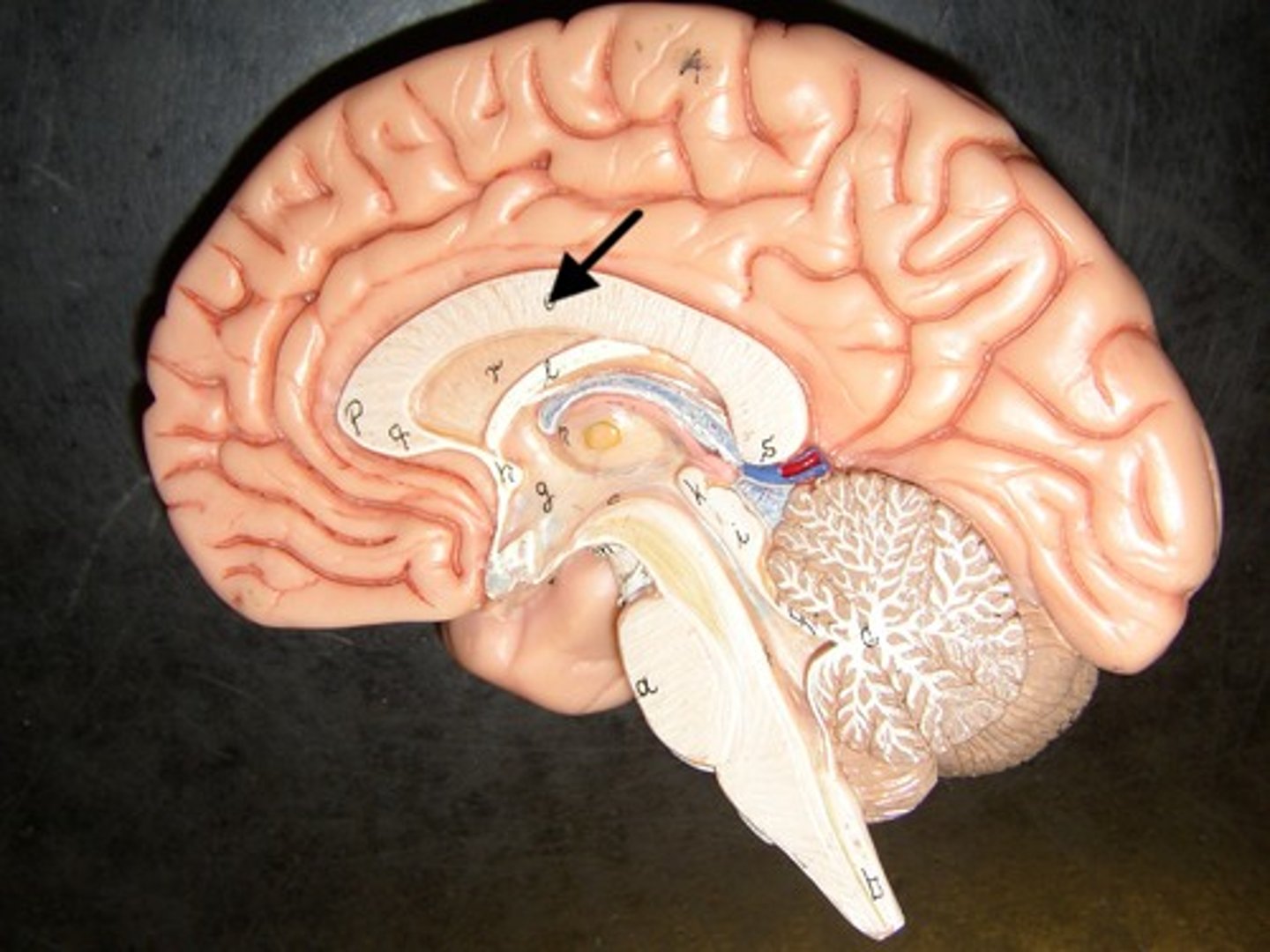
Thalamus
A brain structure that relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex.
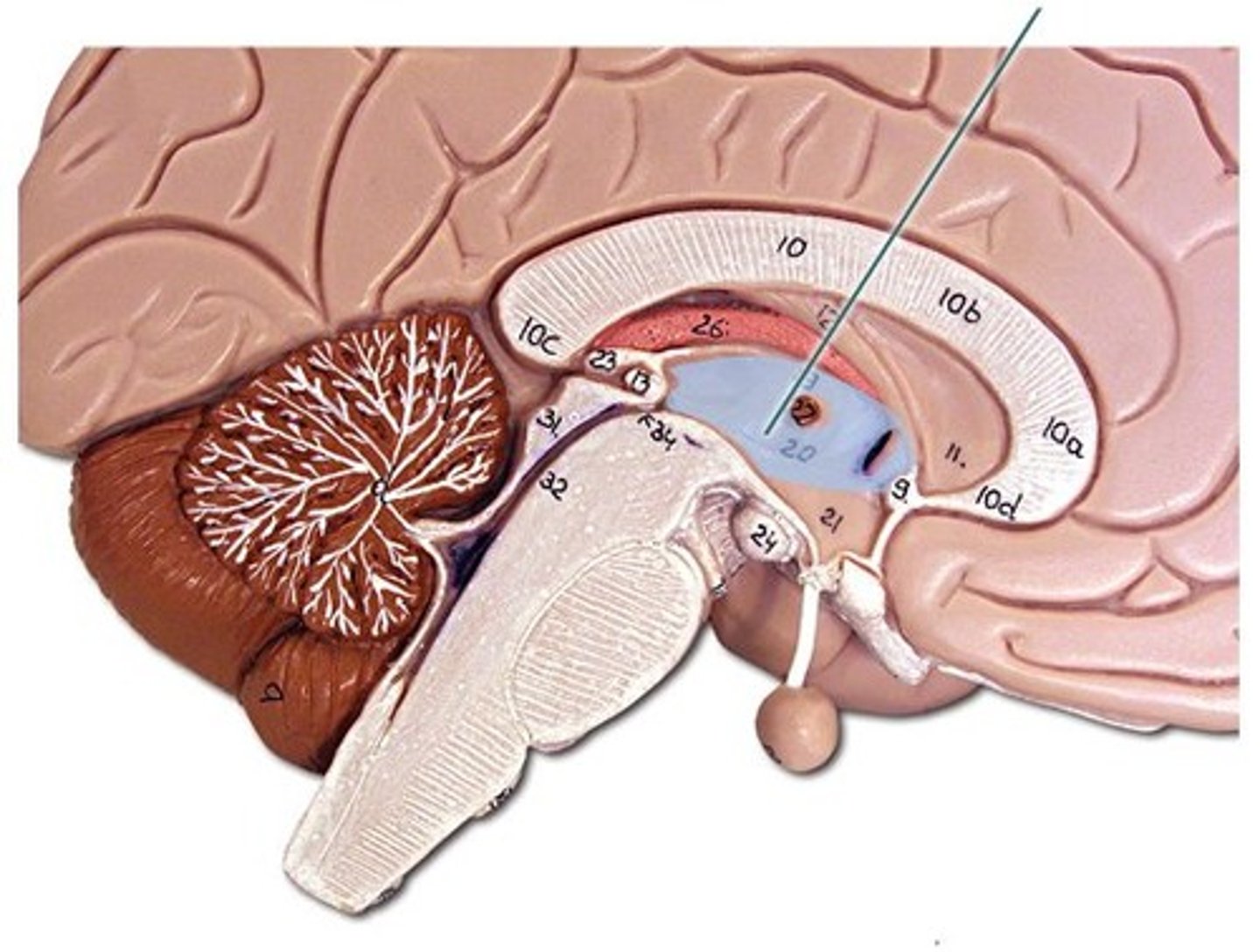
Hypothalamus
A brain region that controls many autonomic functions and regulates homeostasis.
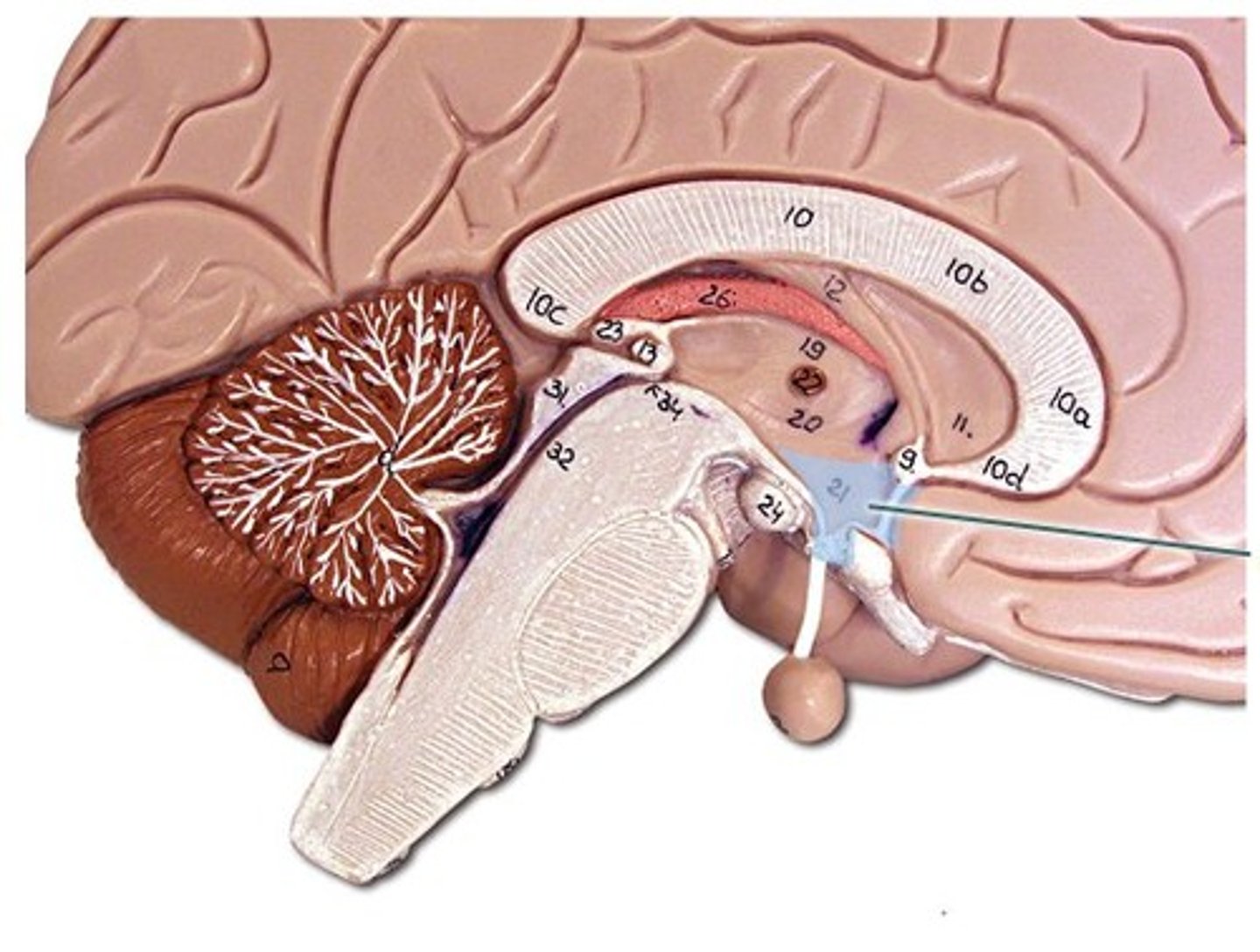
Pituitary gland
An endocrine gland that produces hormones regulating various bodily functions.
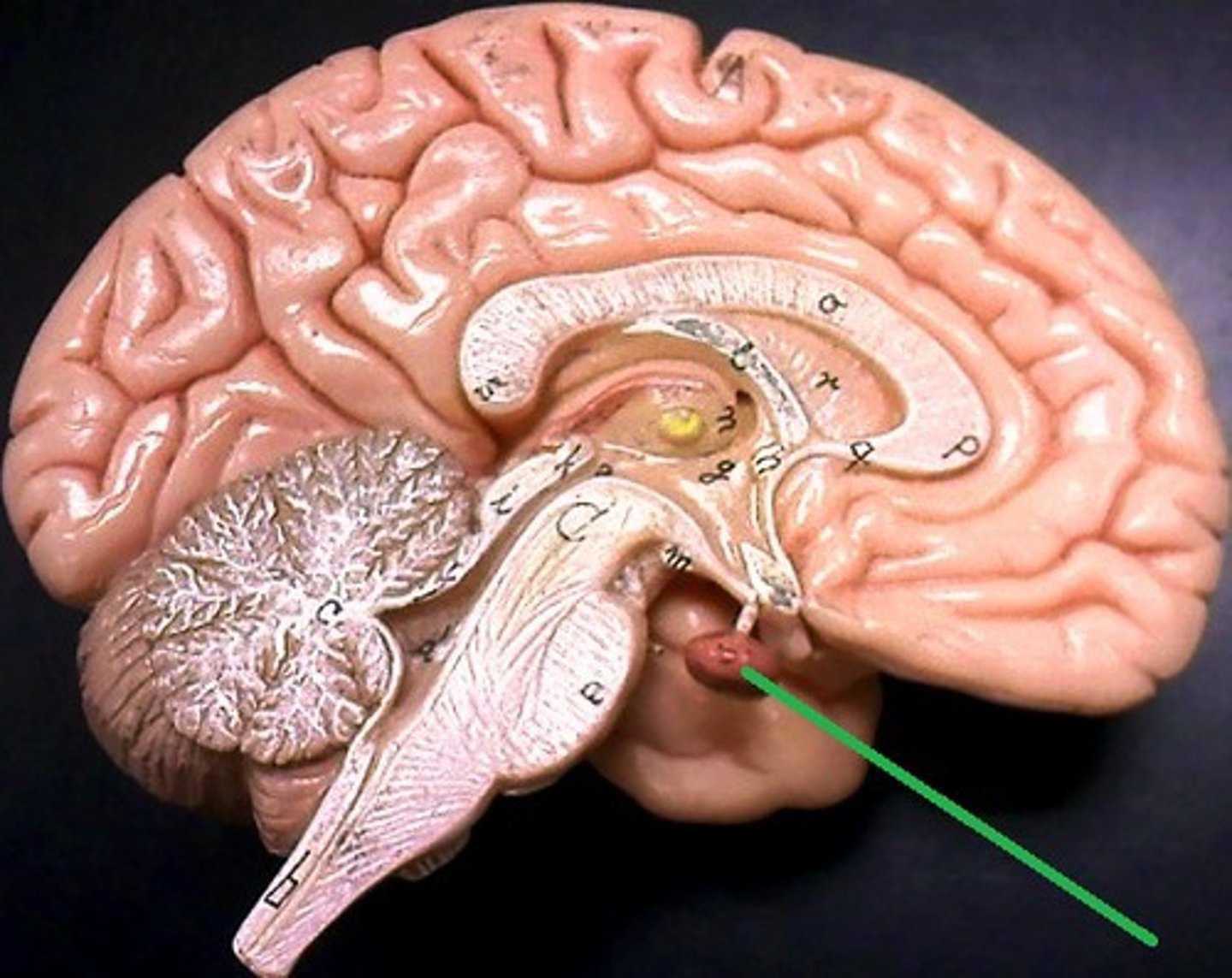
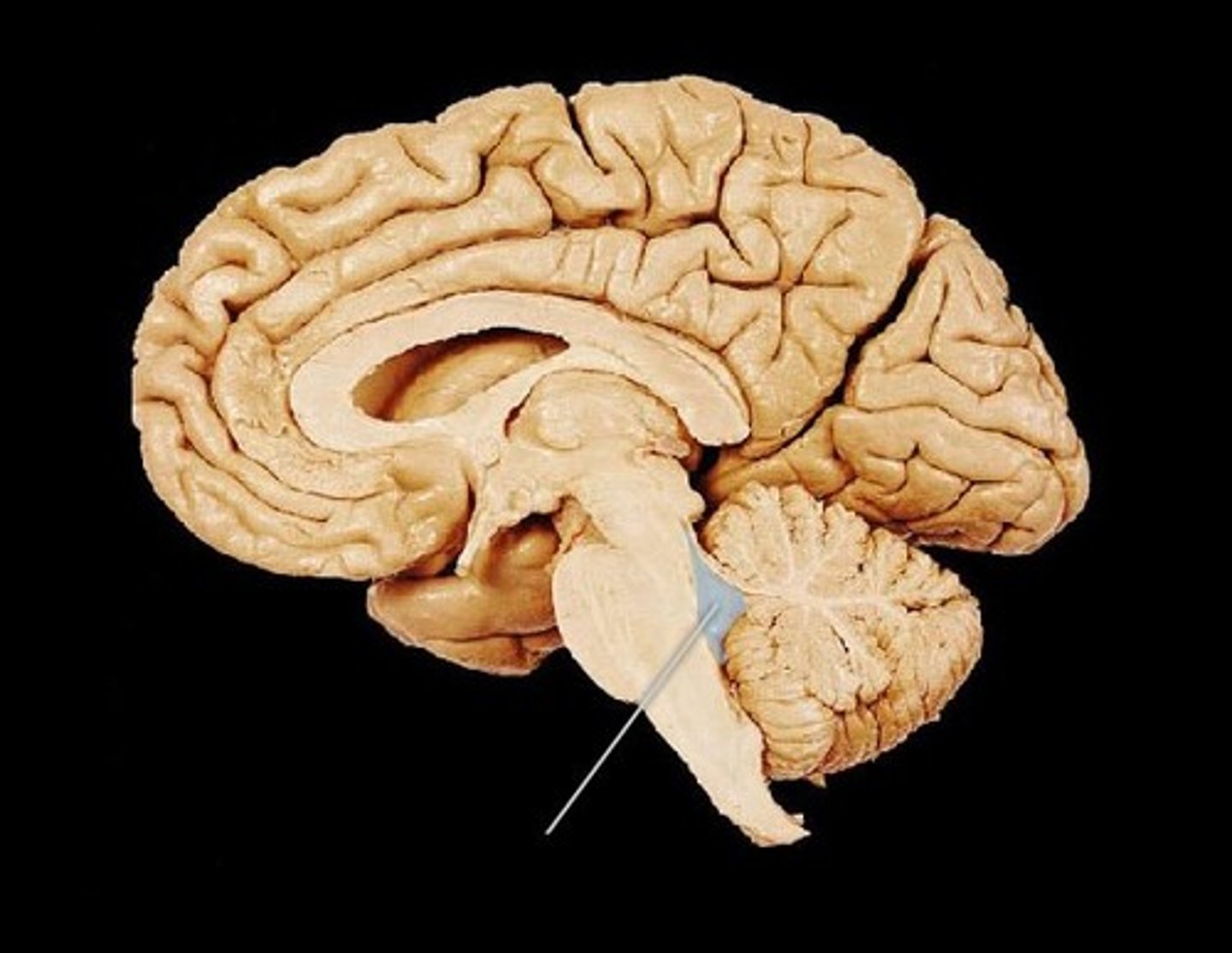
Midbrain
The part of the brainstem that connects the forebrain to the hindbrain.
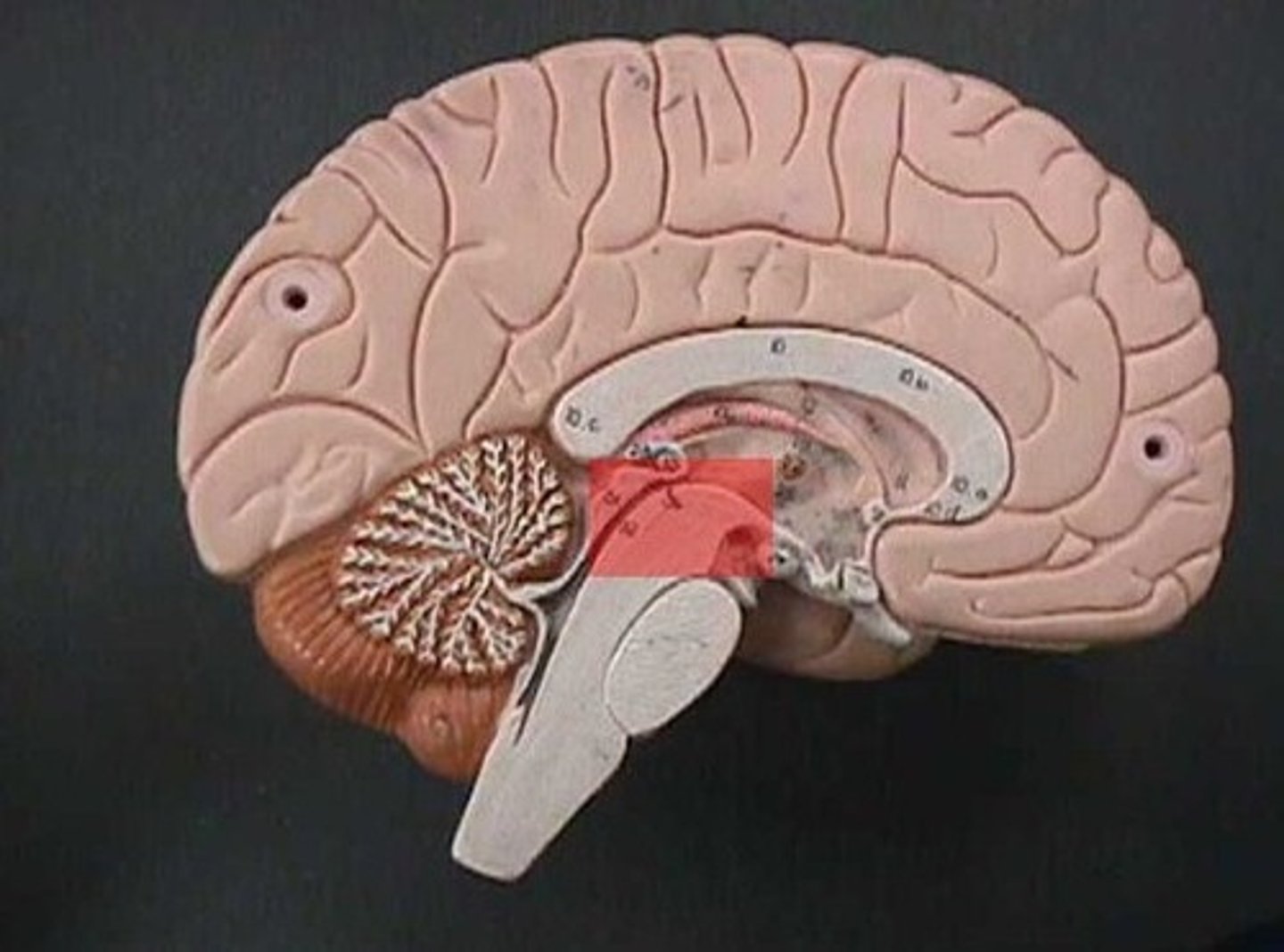
Cerebral Peduncle
A pair of stalks that connect the cerebrum to the brainstem.
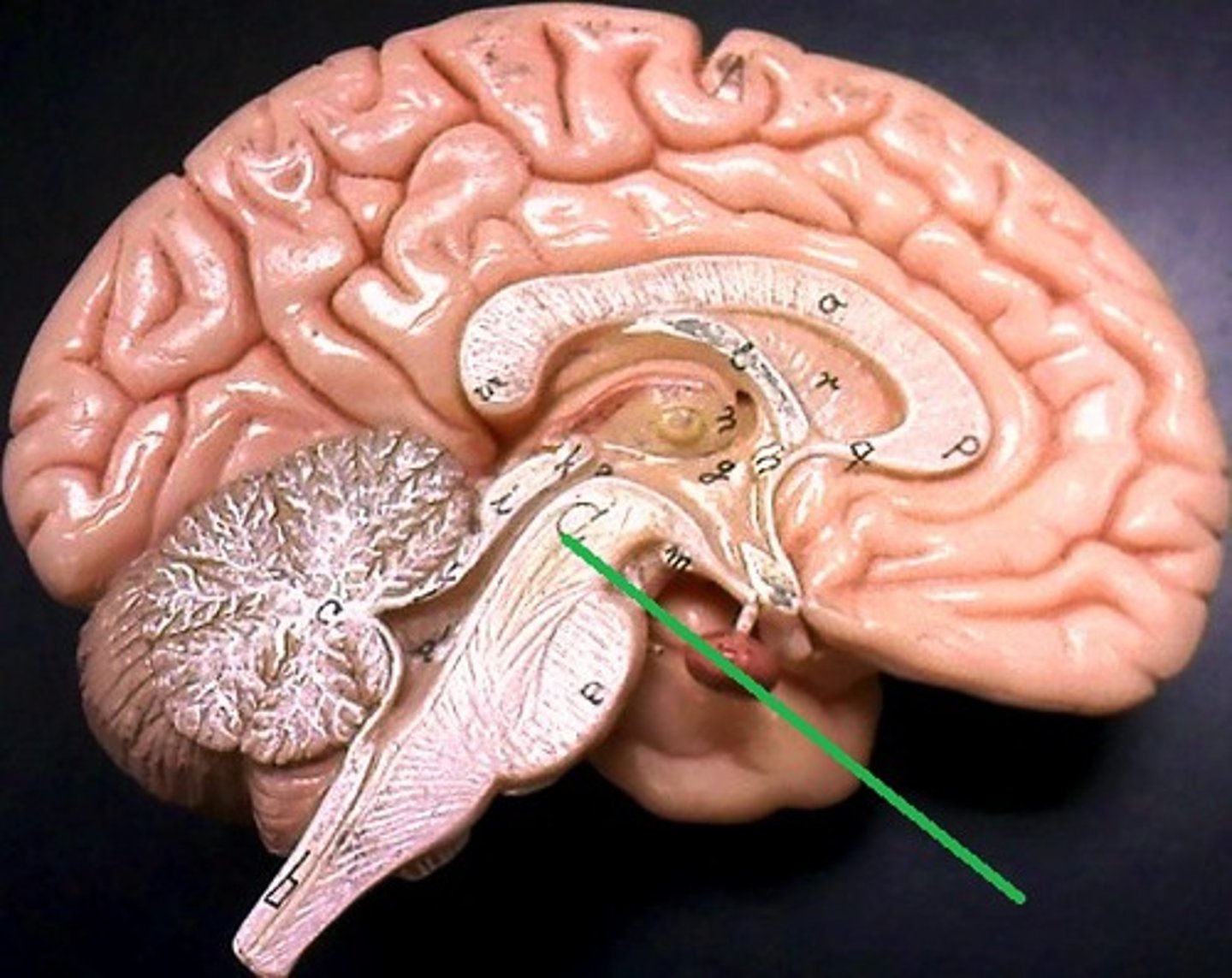
Superior colliculi
Structures in the midbrain involved in visual processing and eye movement.
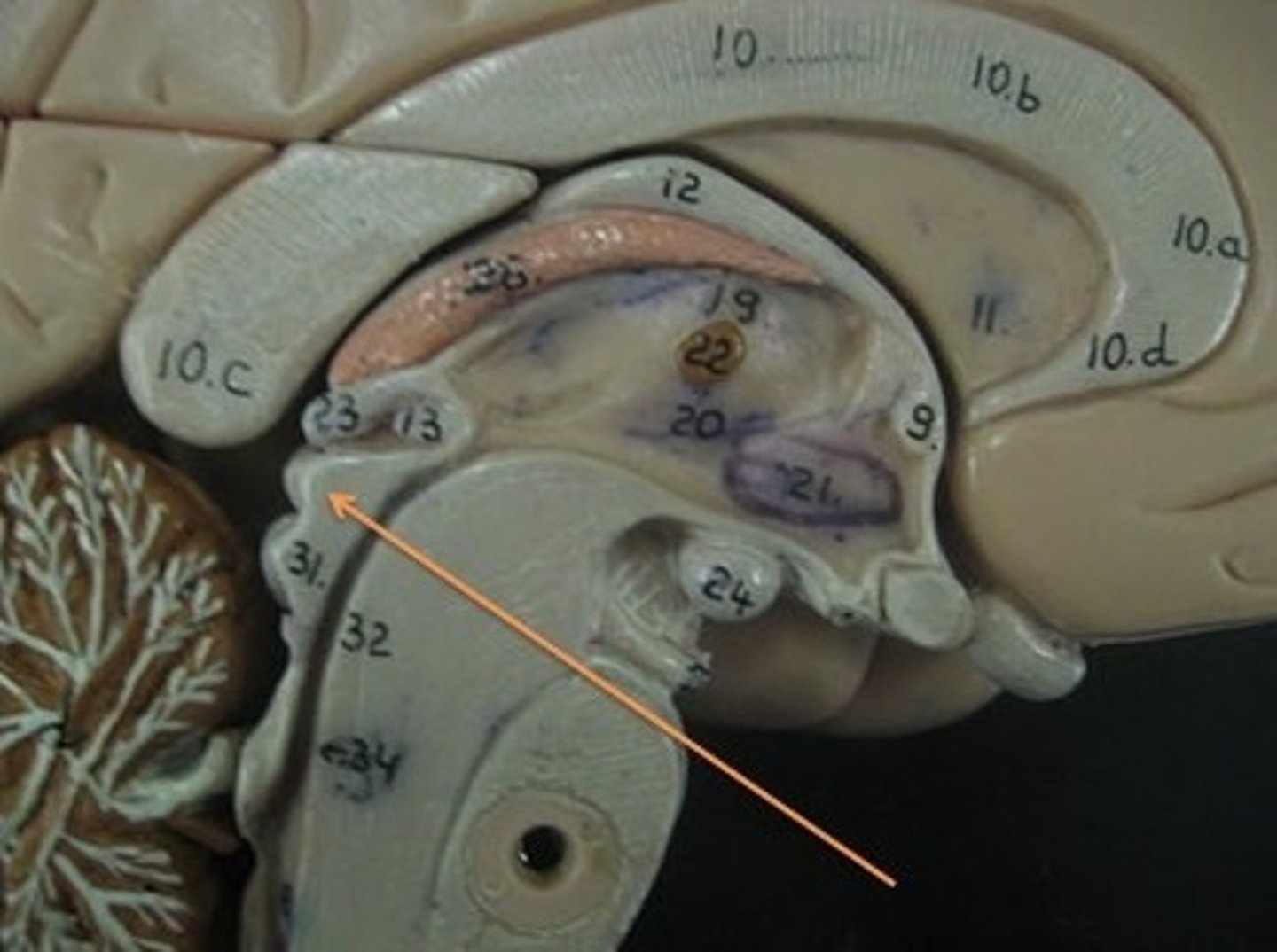
Inferior colliculi
Structures in the midbrain involved in auditory processing.
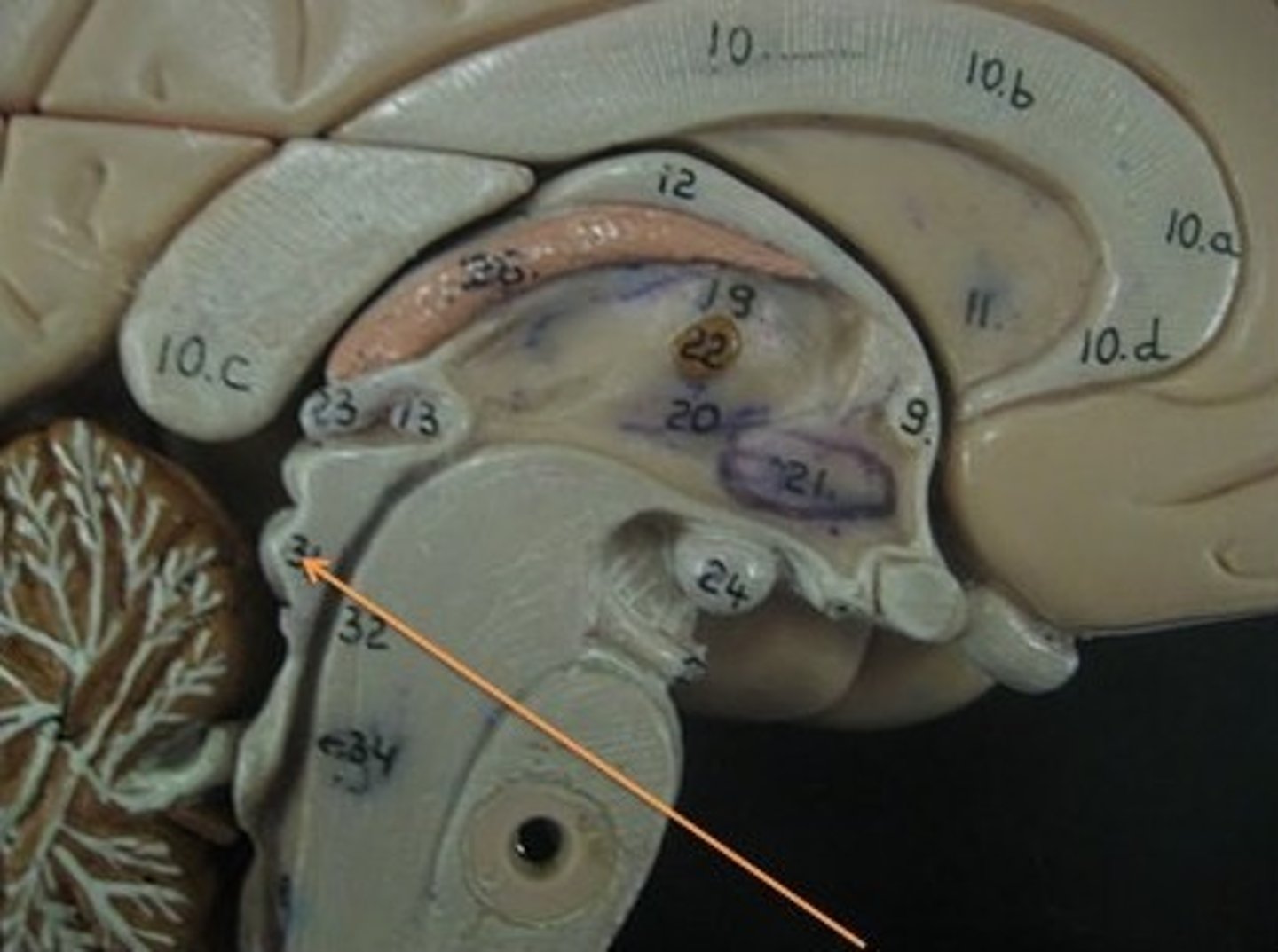
Pons
A part of the brainstem that connects the medulla oblongata and the thalamus.
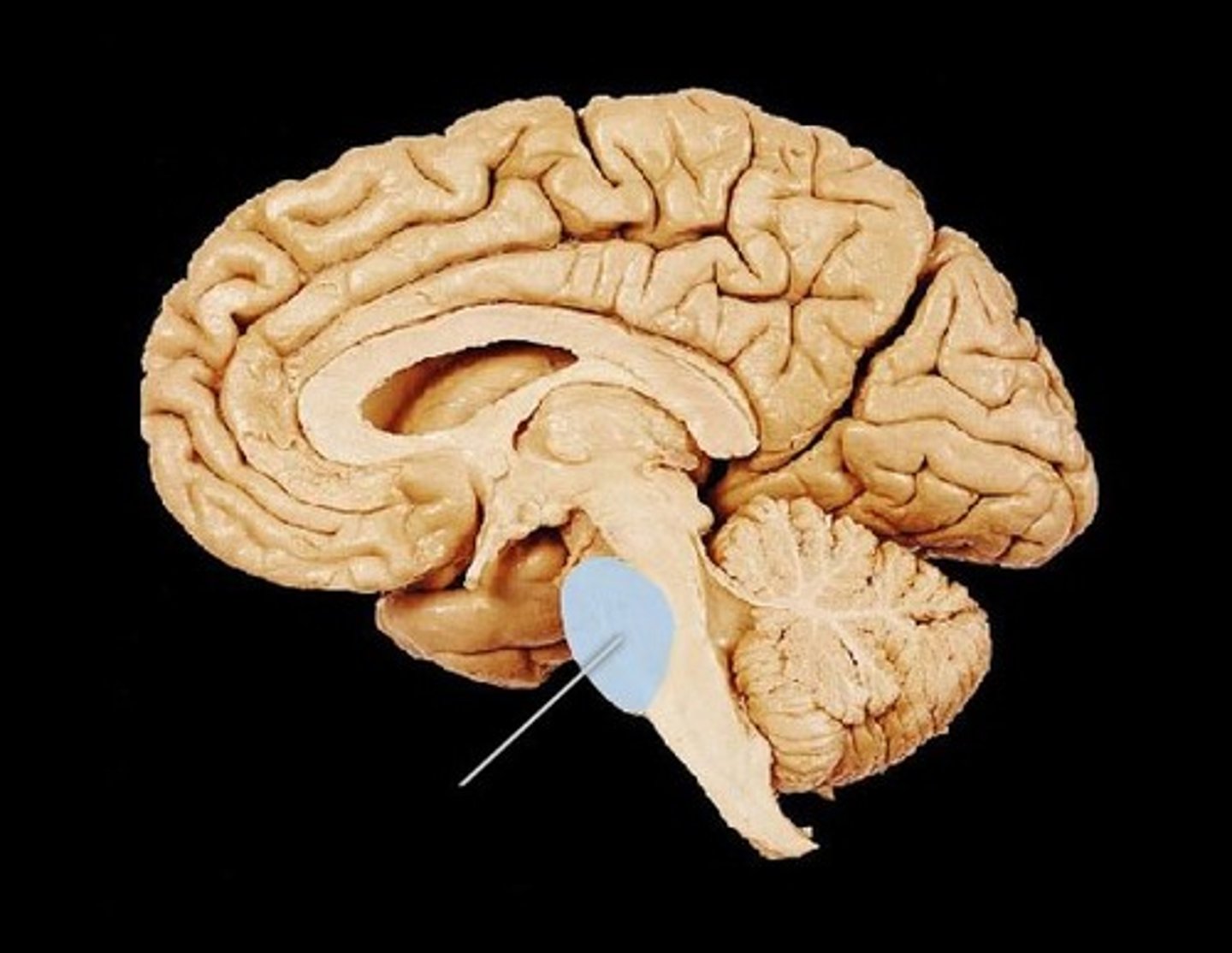
Medulla Oblongata
The part of the brainstem that controls vital functions such as heart rate and breathing.
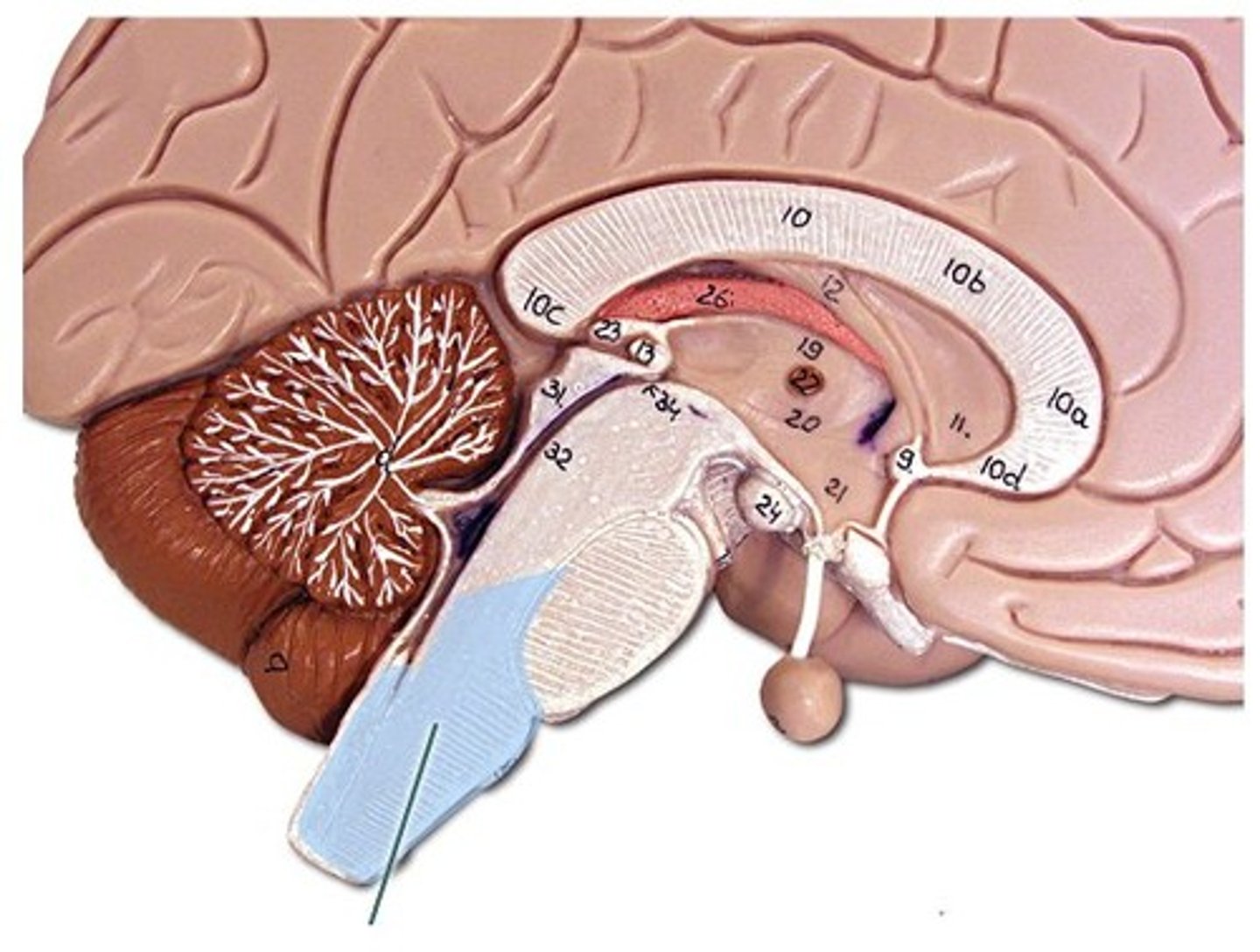
Pyramids
Structures in the medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers.
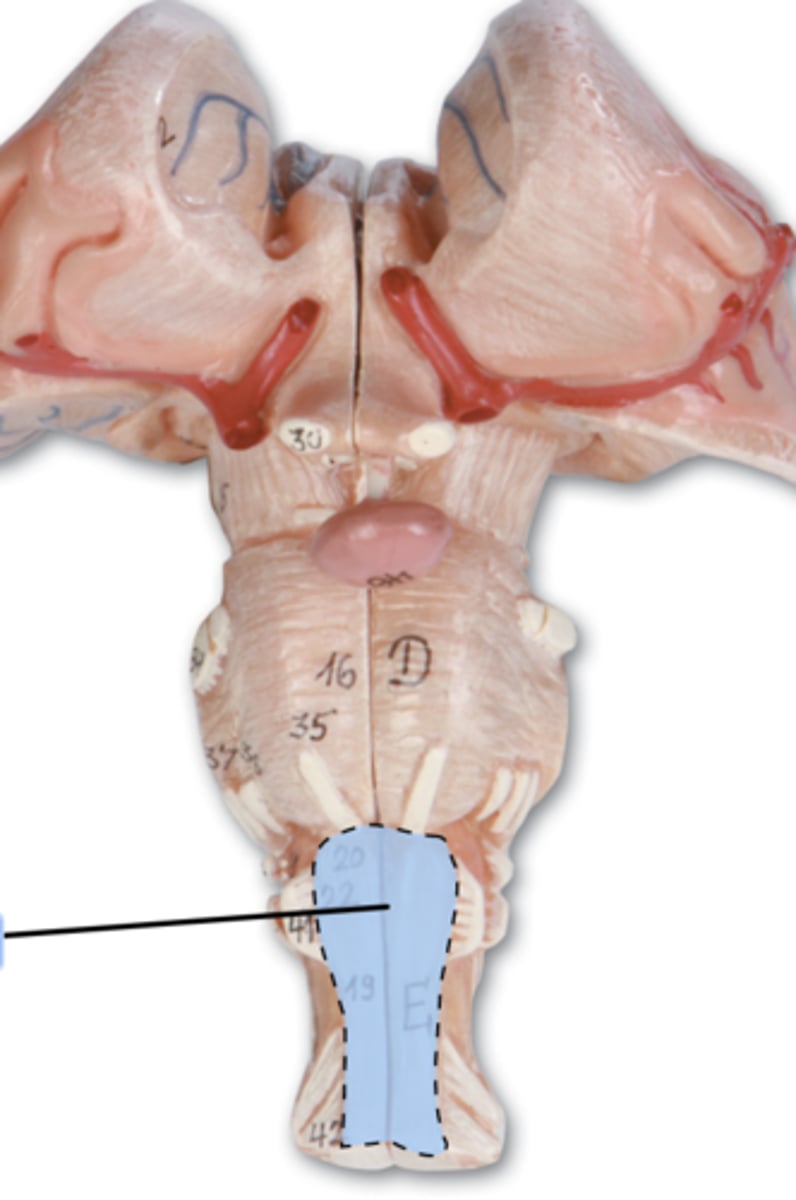
Anterior lobe
The front part of the cerebellum involved in the regulation of voluntary movement.
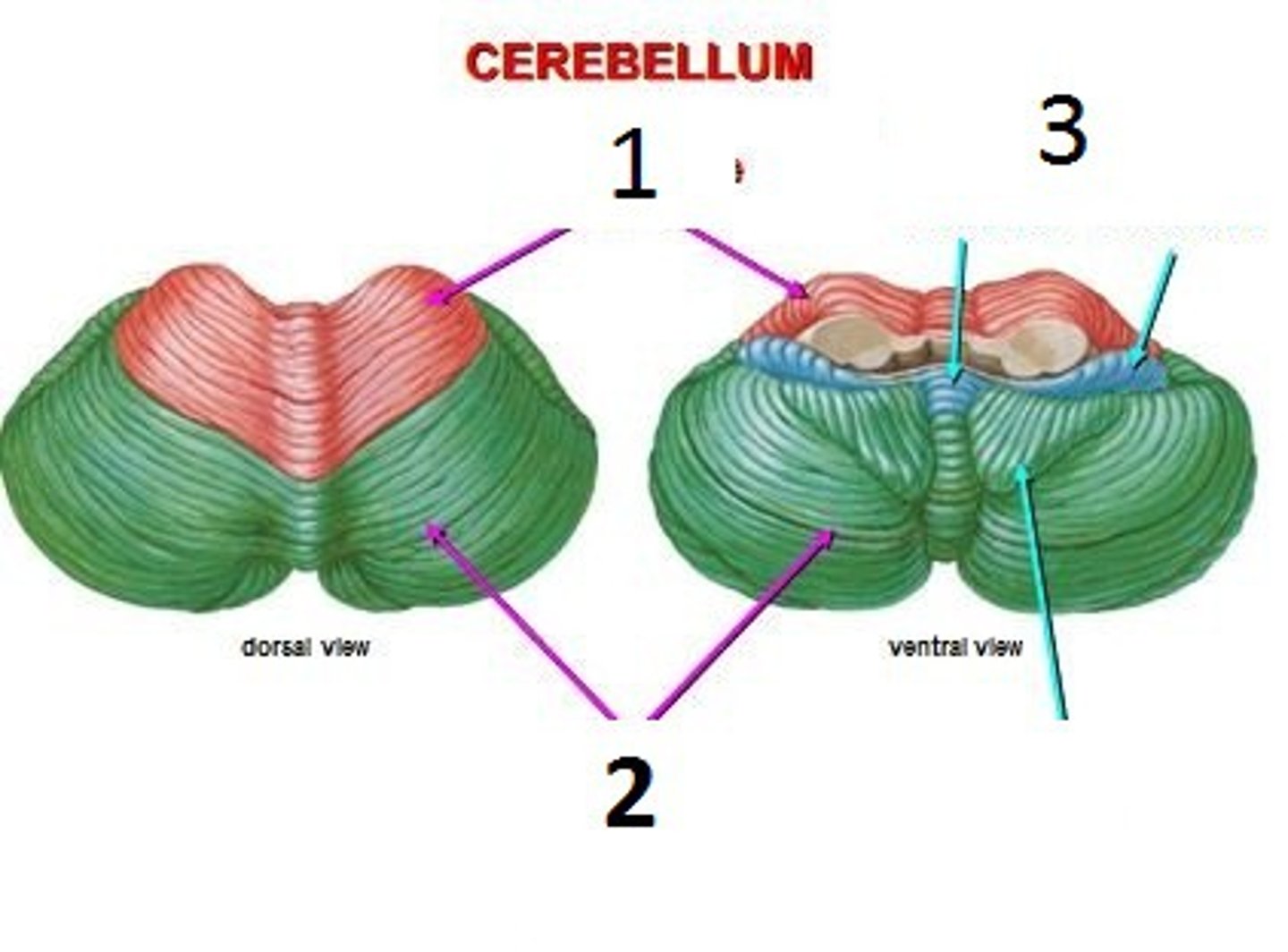
Posterior lobe
The back part of the cerebellum involved in coordination and balance.
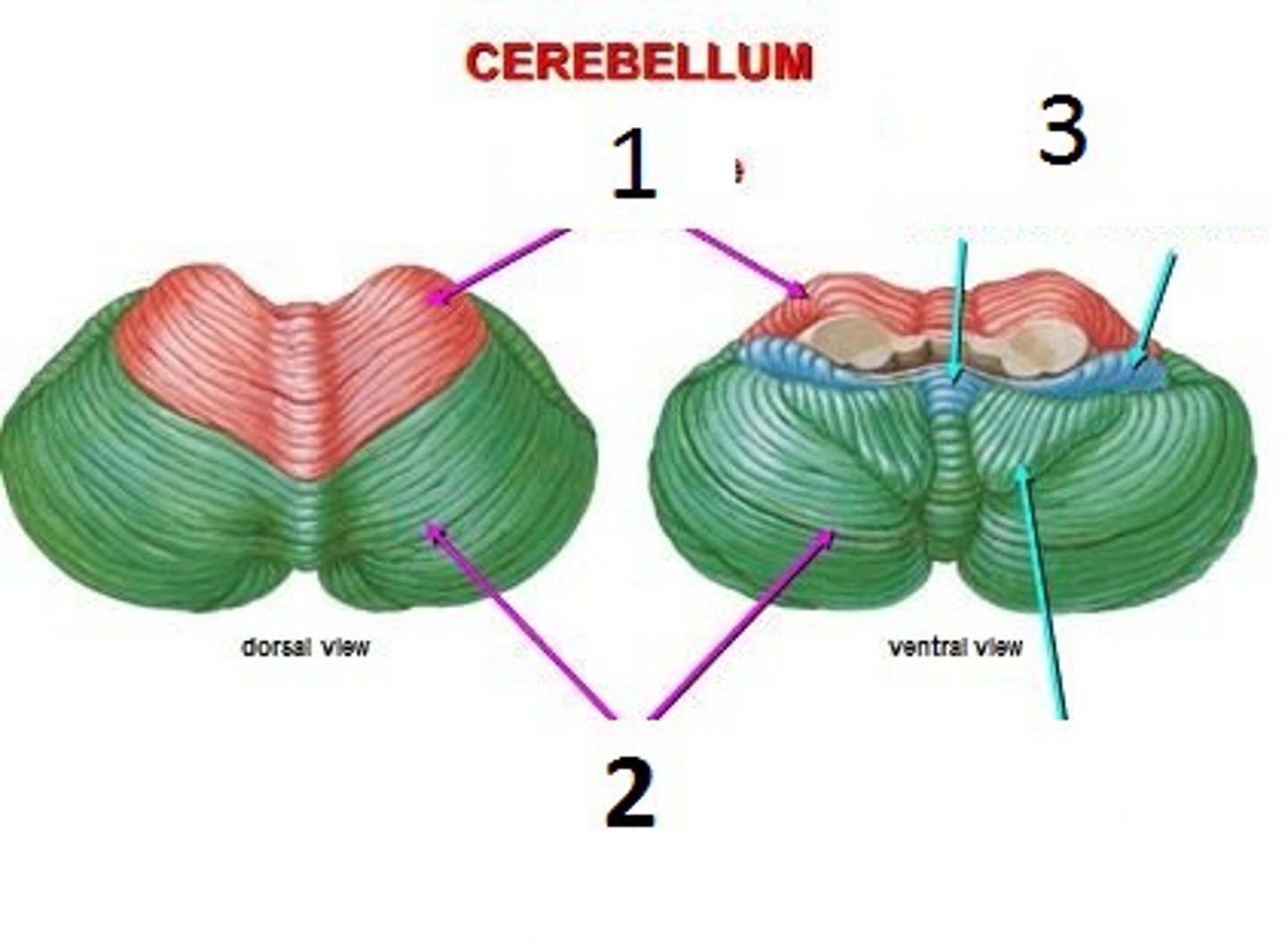
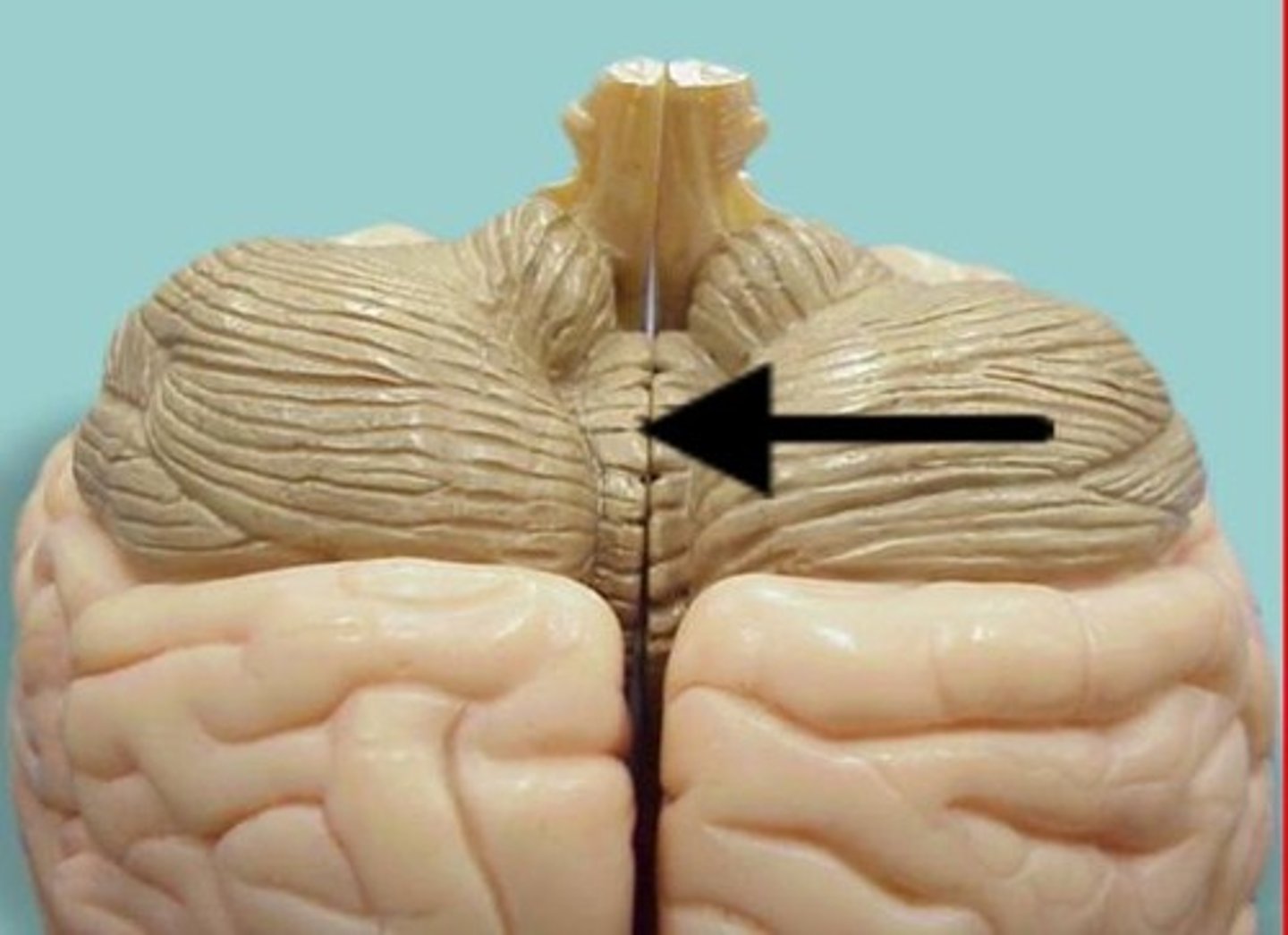
Vermis
The narrow, central part of the cerebellum that connects the two hemispheres.
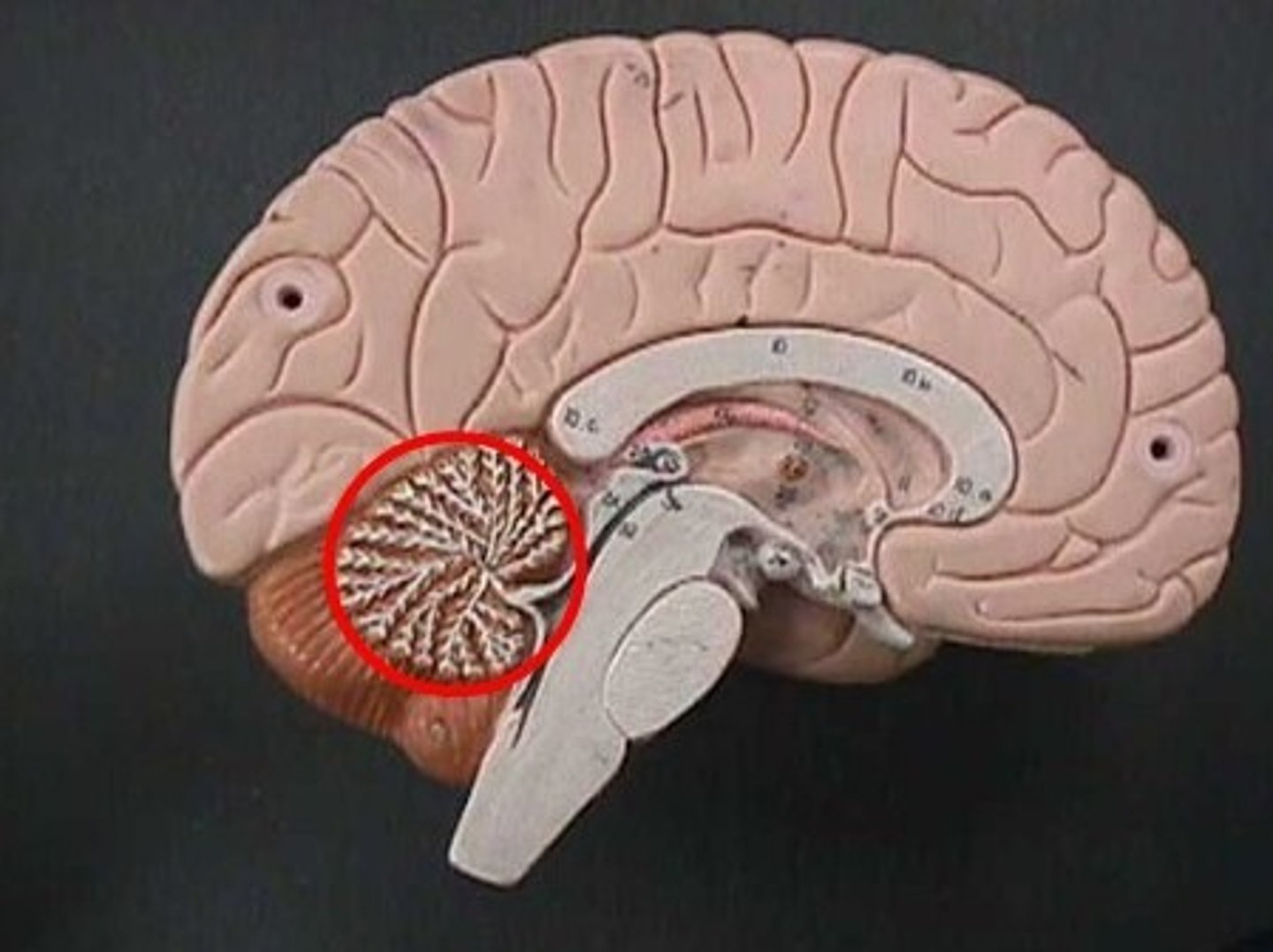
Arbor vitae
The tree-like structure of white matter in the cerebellum.
Flocculondular lobe
A small lobe of the cerebellum involved in balance and eye movements.
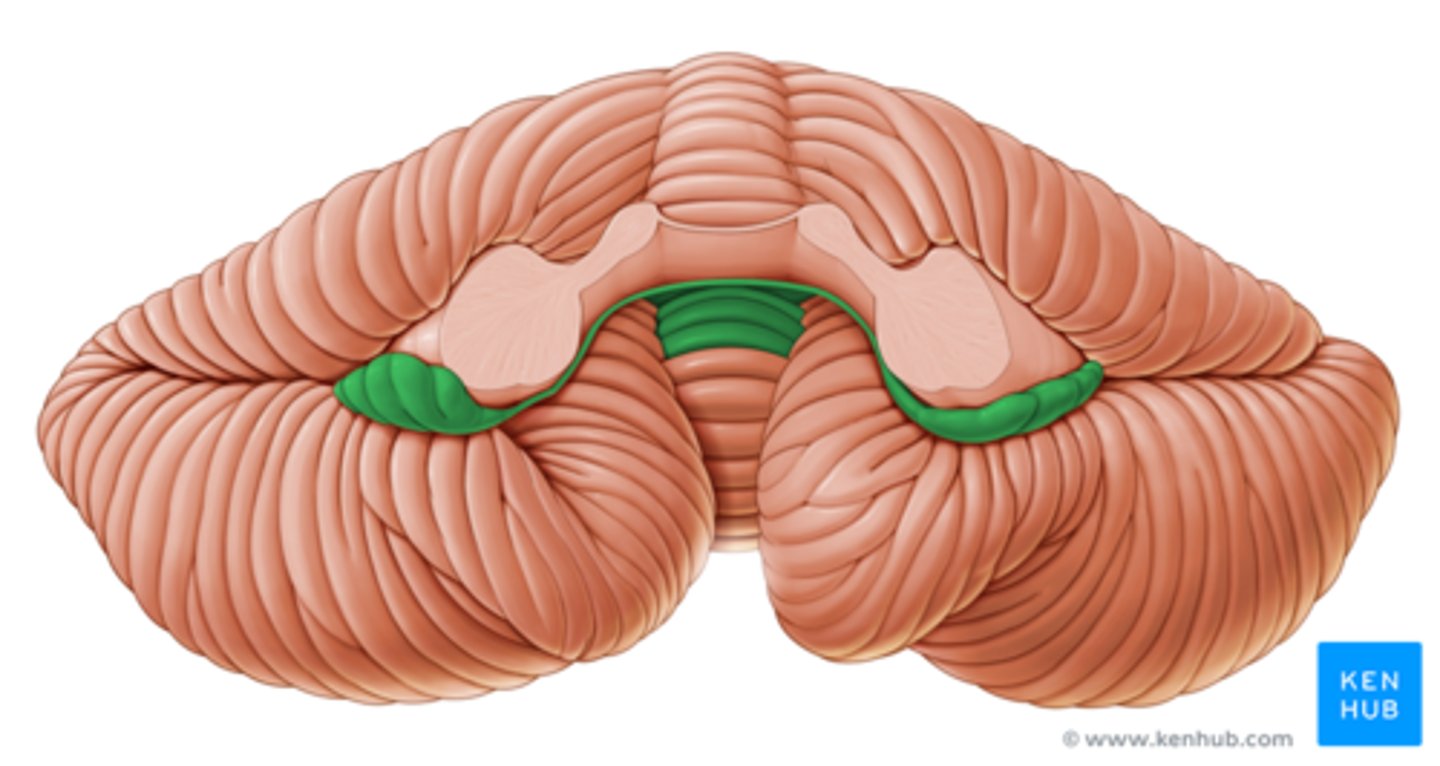
Lateral Ventricles
The largest ventricles in the brain, located in each hemisphere.
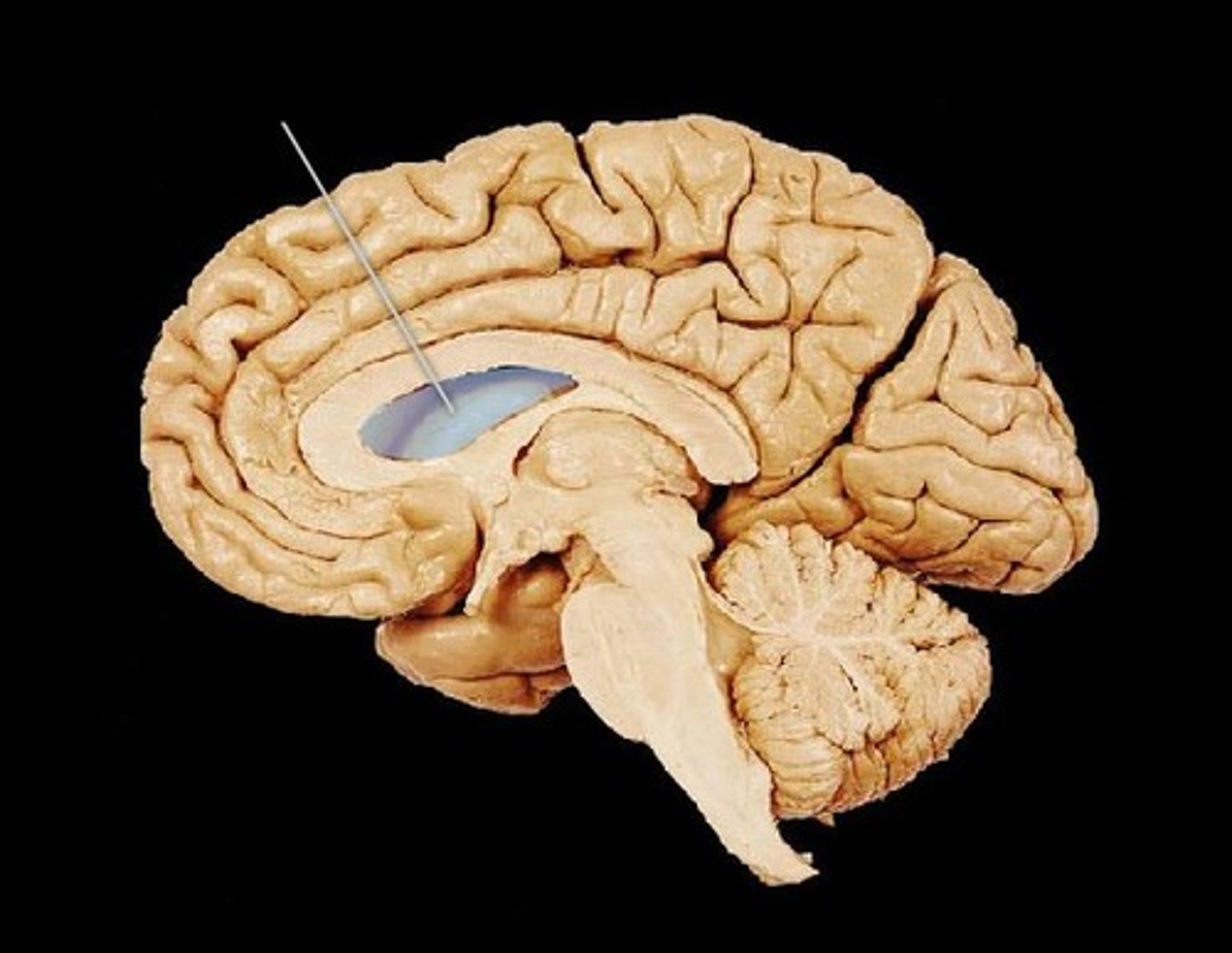
Third ventricle
A narrow cavity located between the two halves of the thalamus.
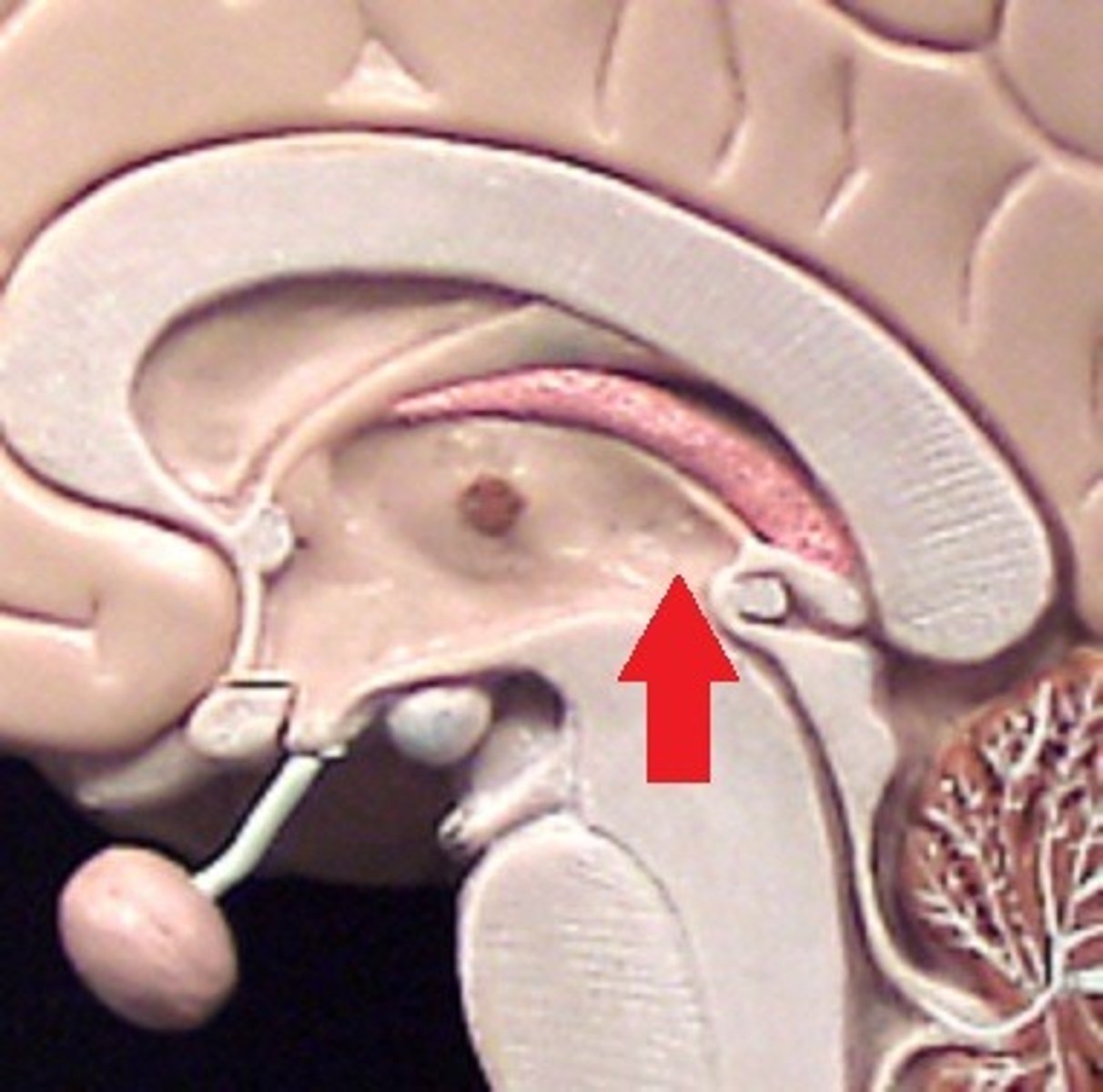
Cerebral aqueduct
A narrow channel that connects the third and fourth ventricles.
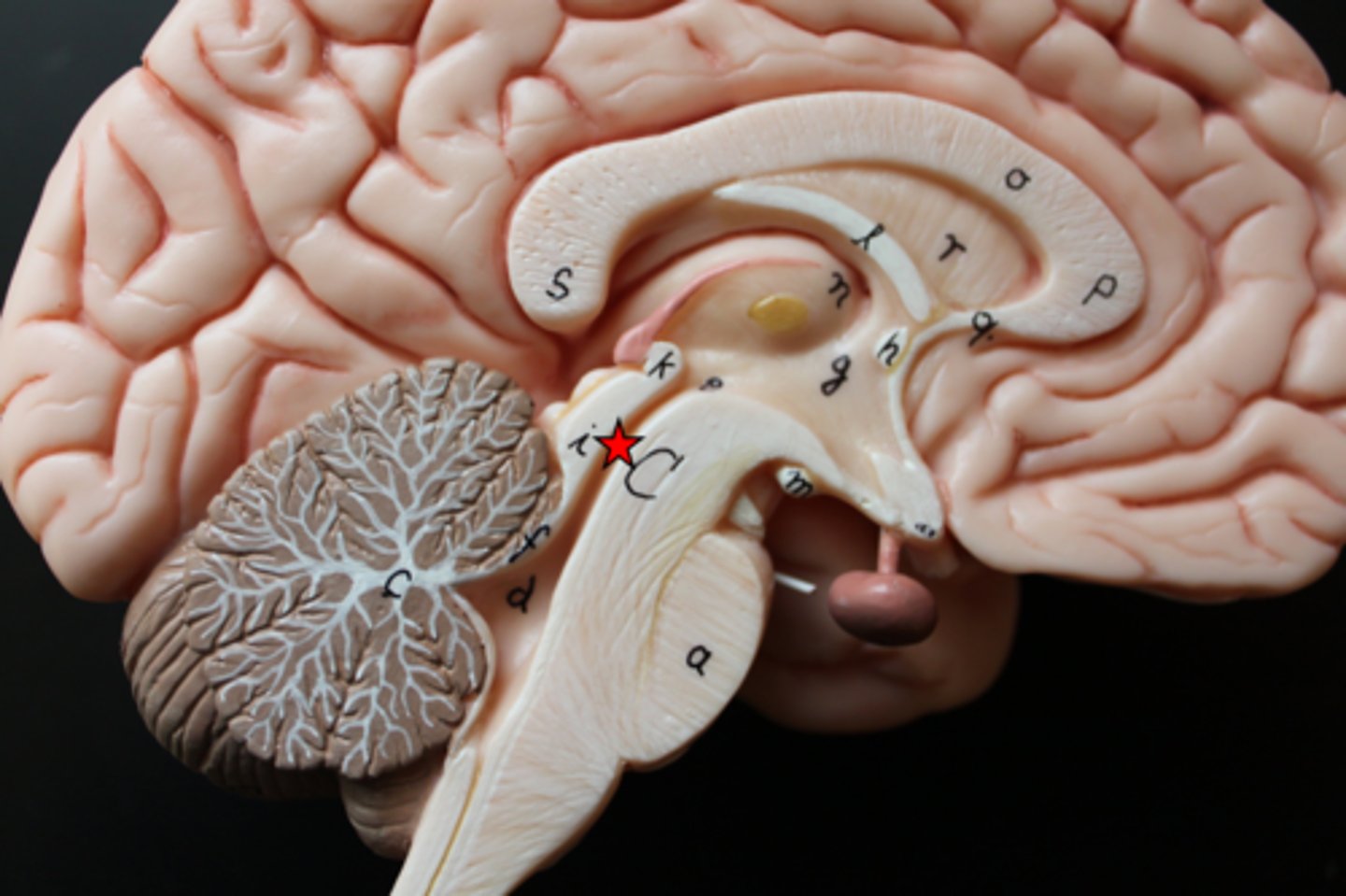
Fourth ventricle
A cavity located between the brainstem and the cerebellum.
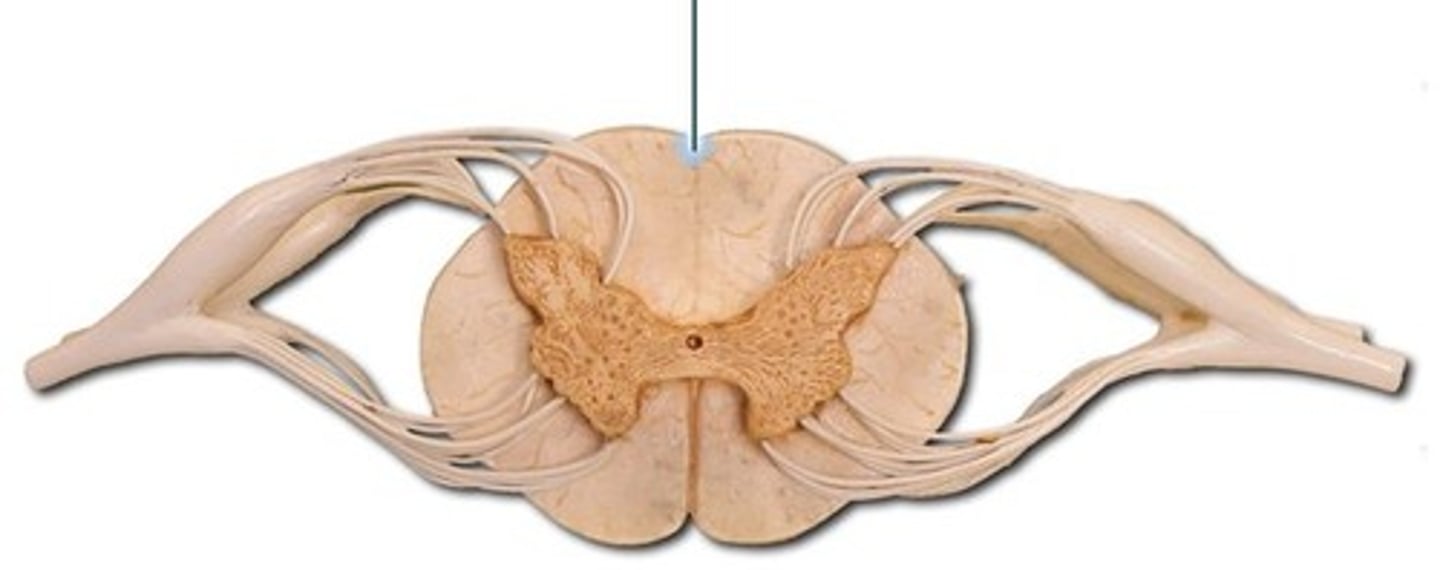
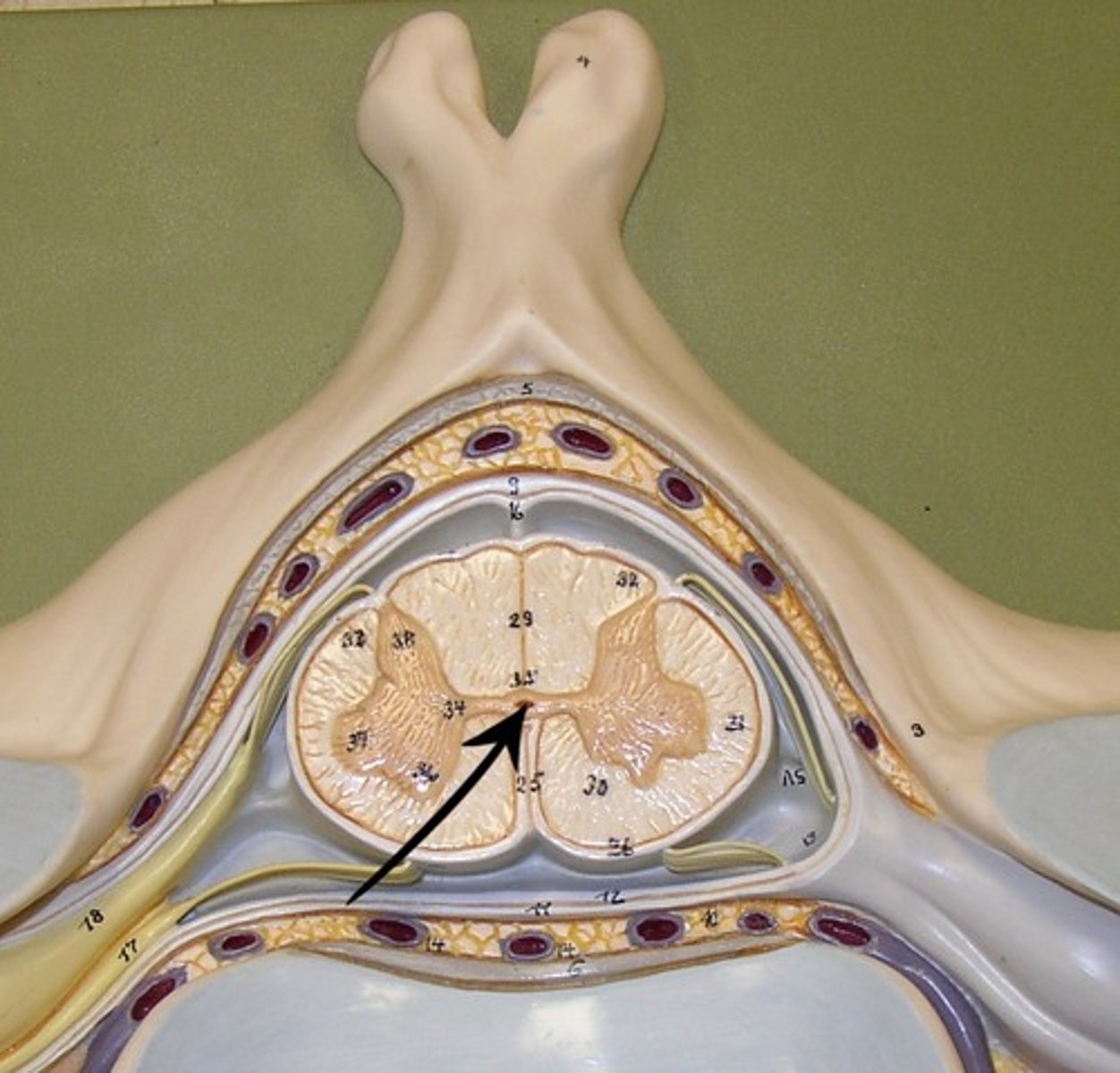
Anterior Median fissure
A groove along the midline of the spinal cord.
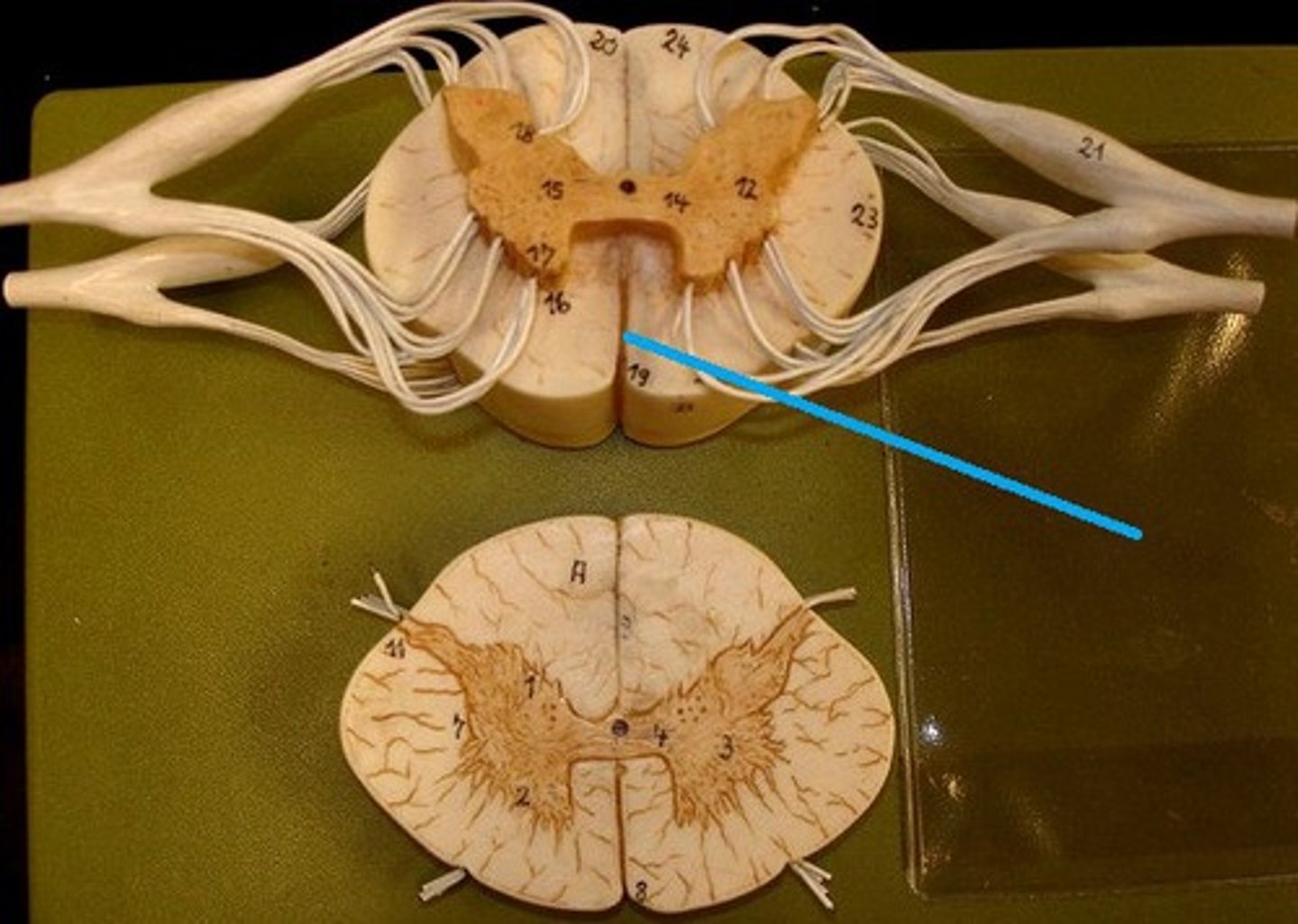
Posterior Median sulcus
A groove along the back of the spinal cord.
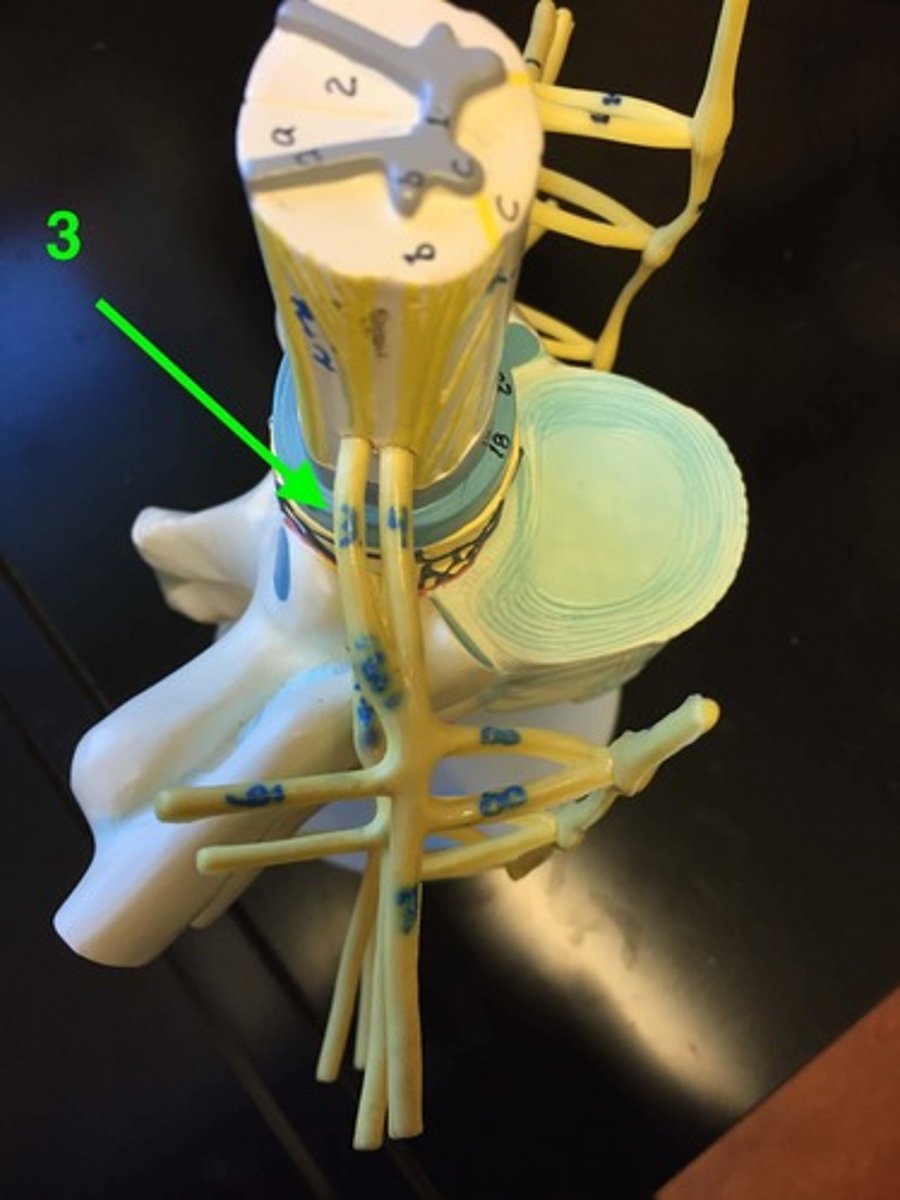
Dorsal roots
Nerve roots that carry sensory information into the spinal cord.
Dorsal root ganglion
A cluster of sensory neuron cell bodies located in the dorsal root.
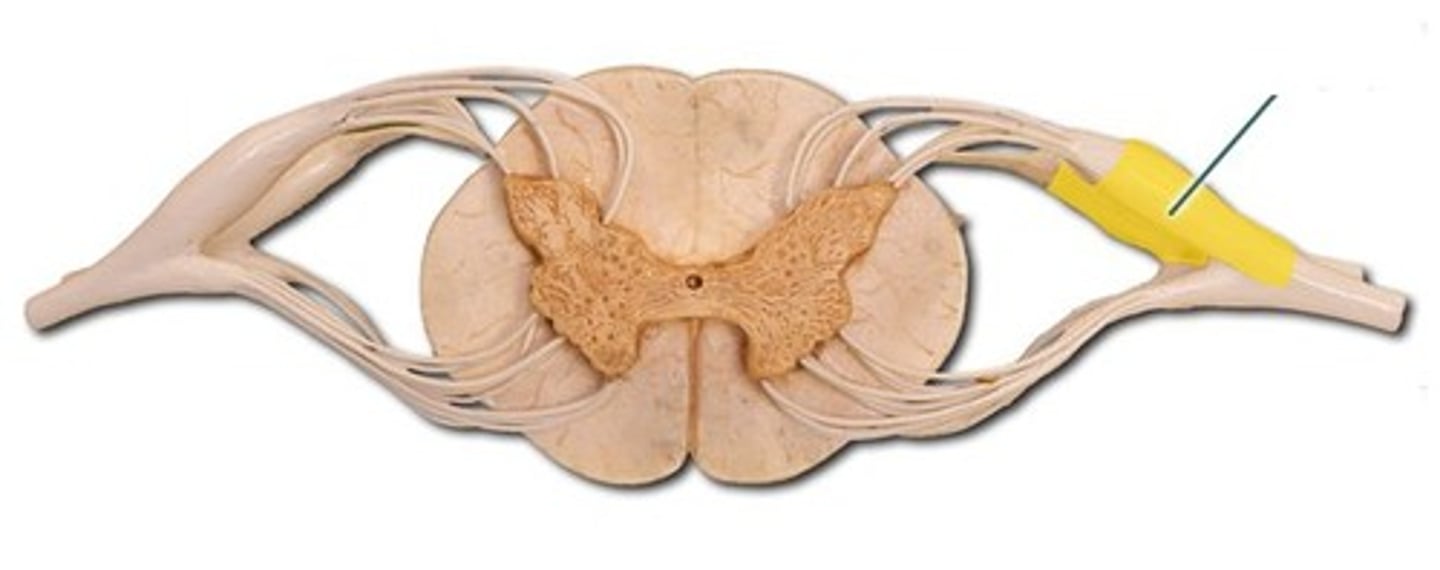
Ventral roots
Nerve roots that carry motor information away from the spinal cord.
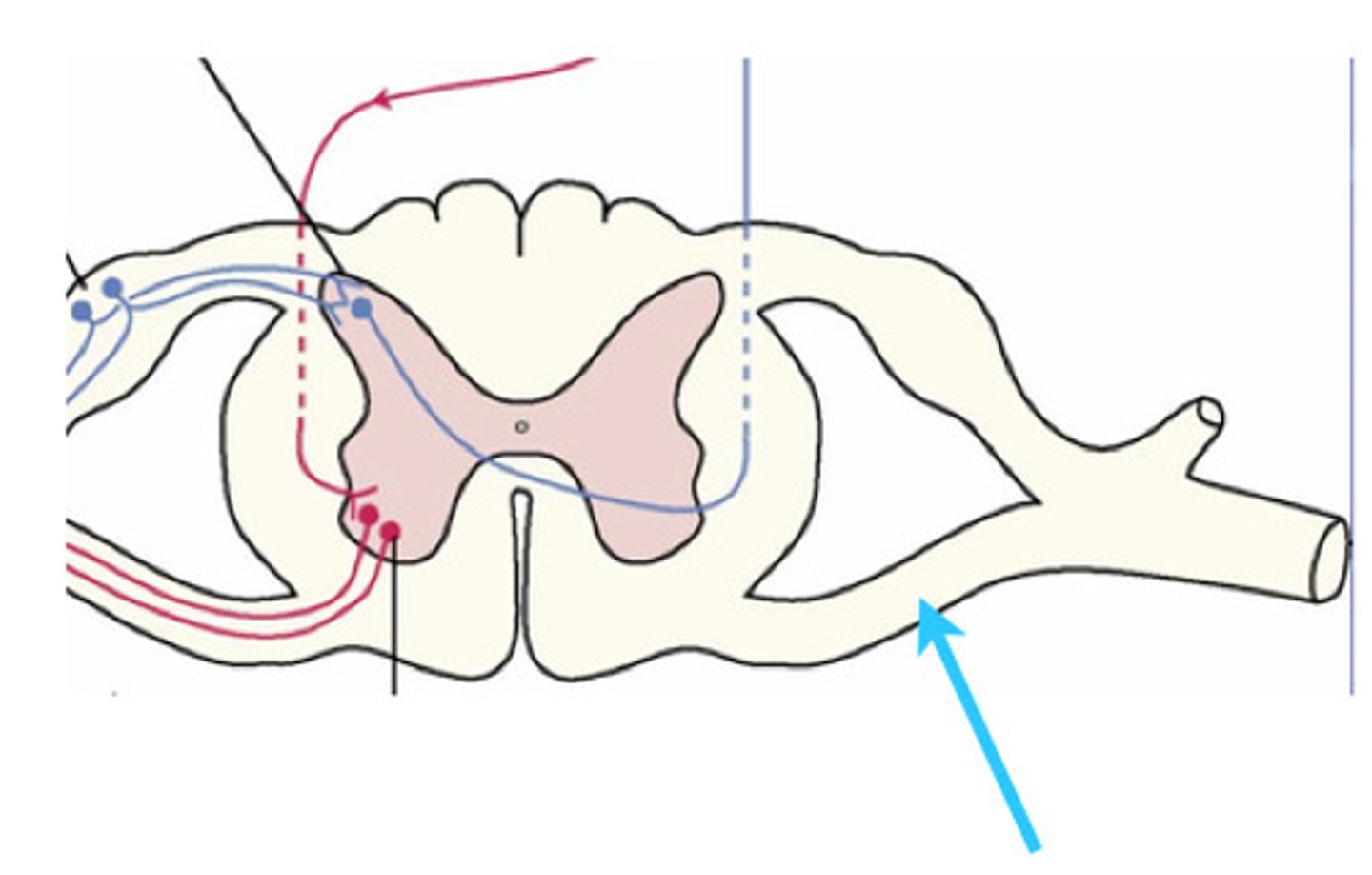
The posterior grey horns
contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei
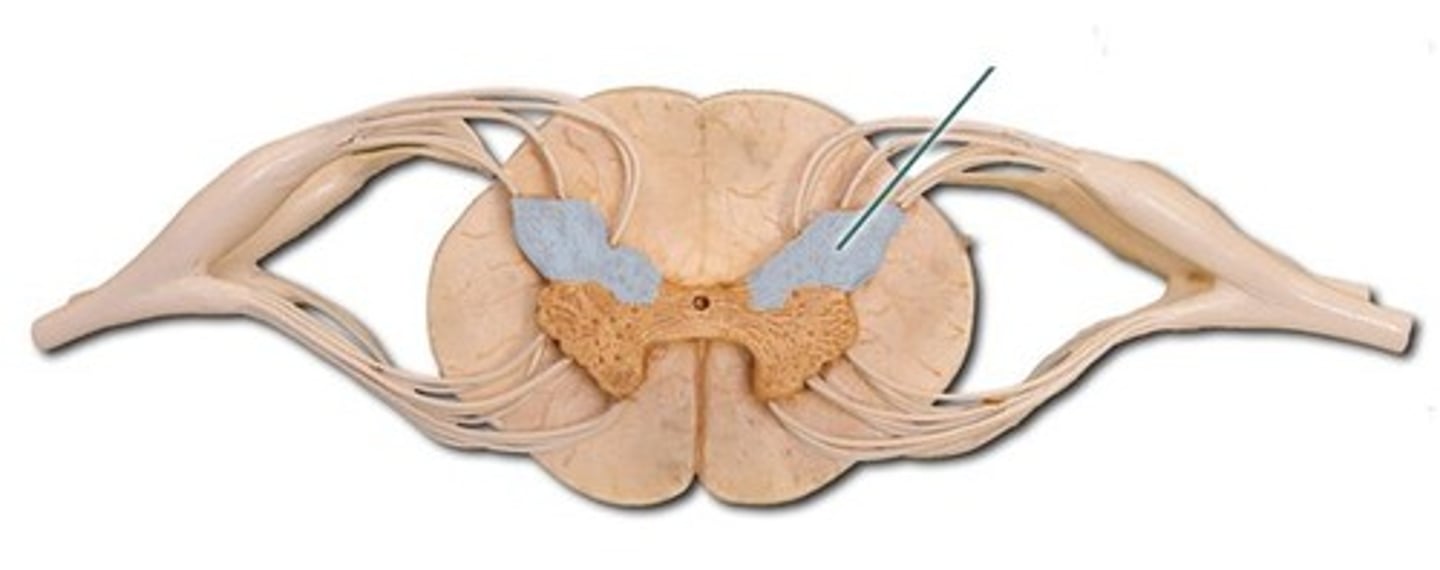
Lateral Grey Horn
visceral motor nuclei
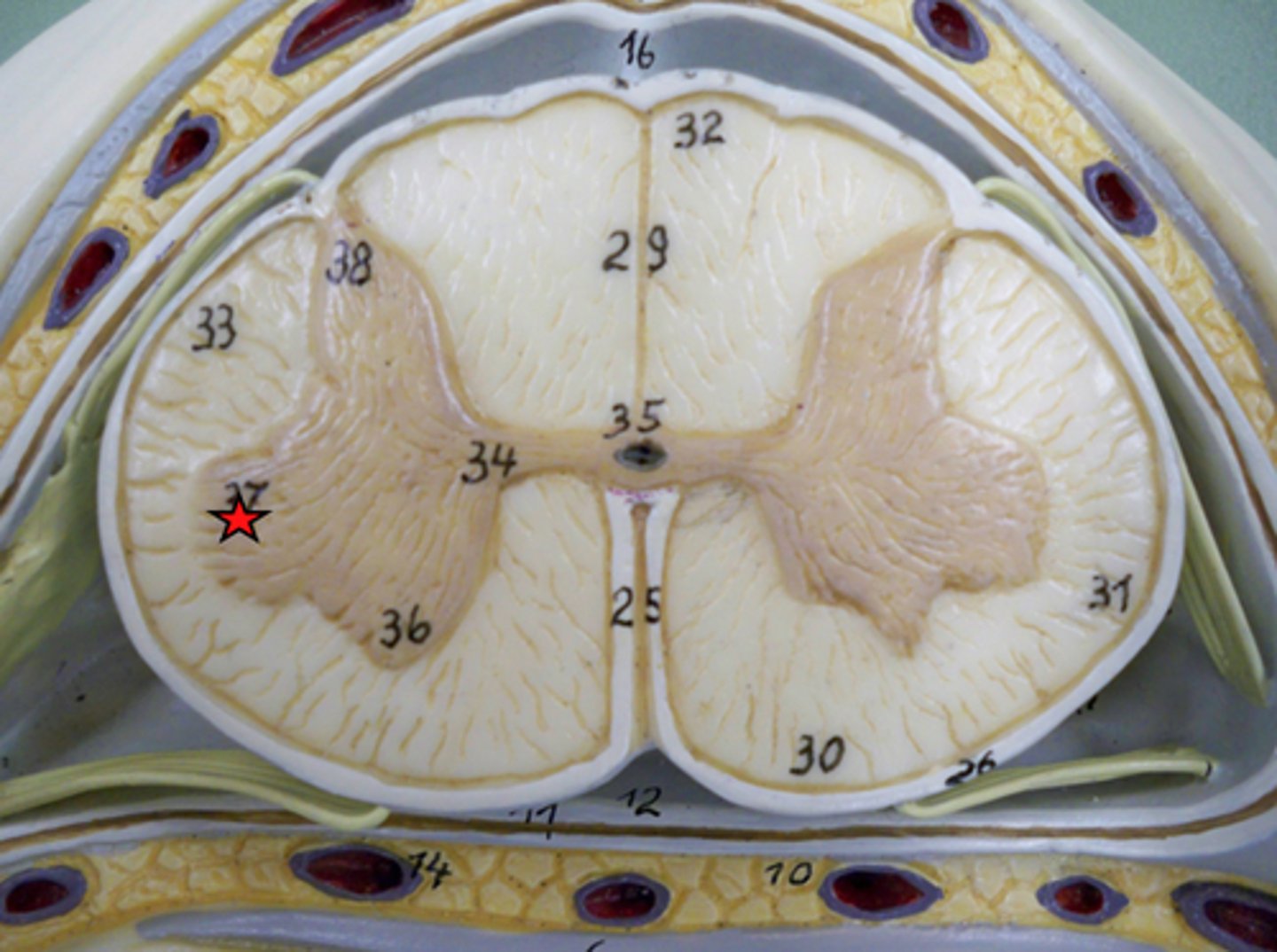
Anterior Grey Horn
somatic motor nuclei
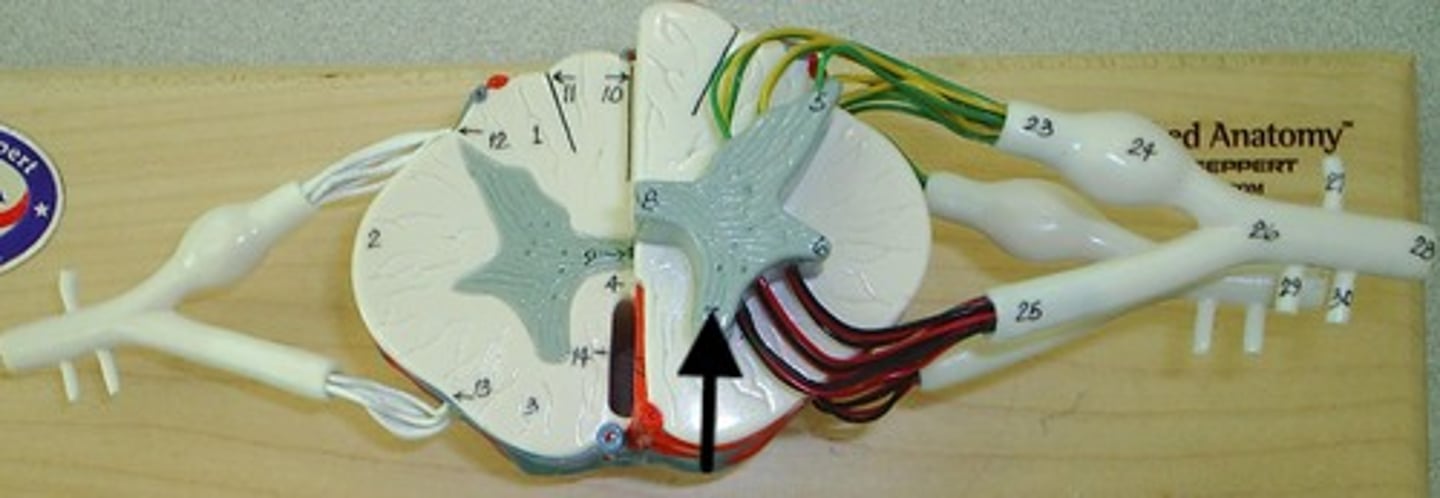
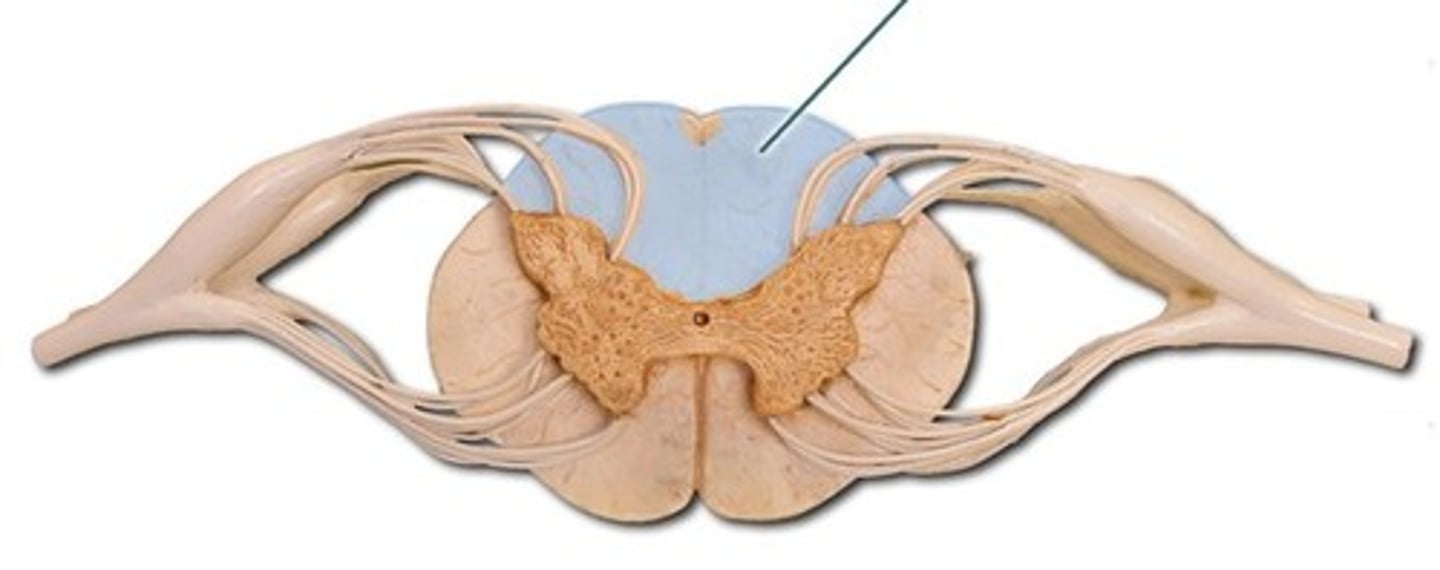
The posterior white columns
lie between posterior gray horns and posterior median sulcus
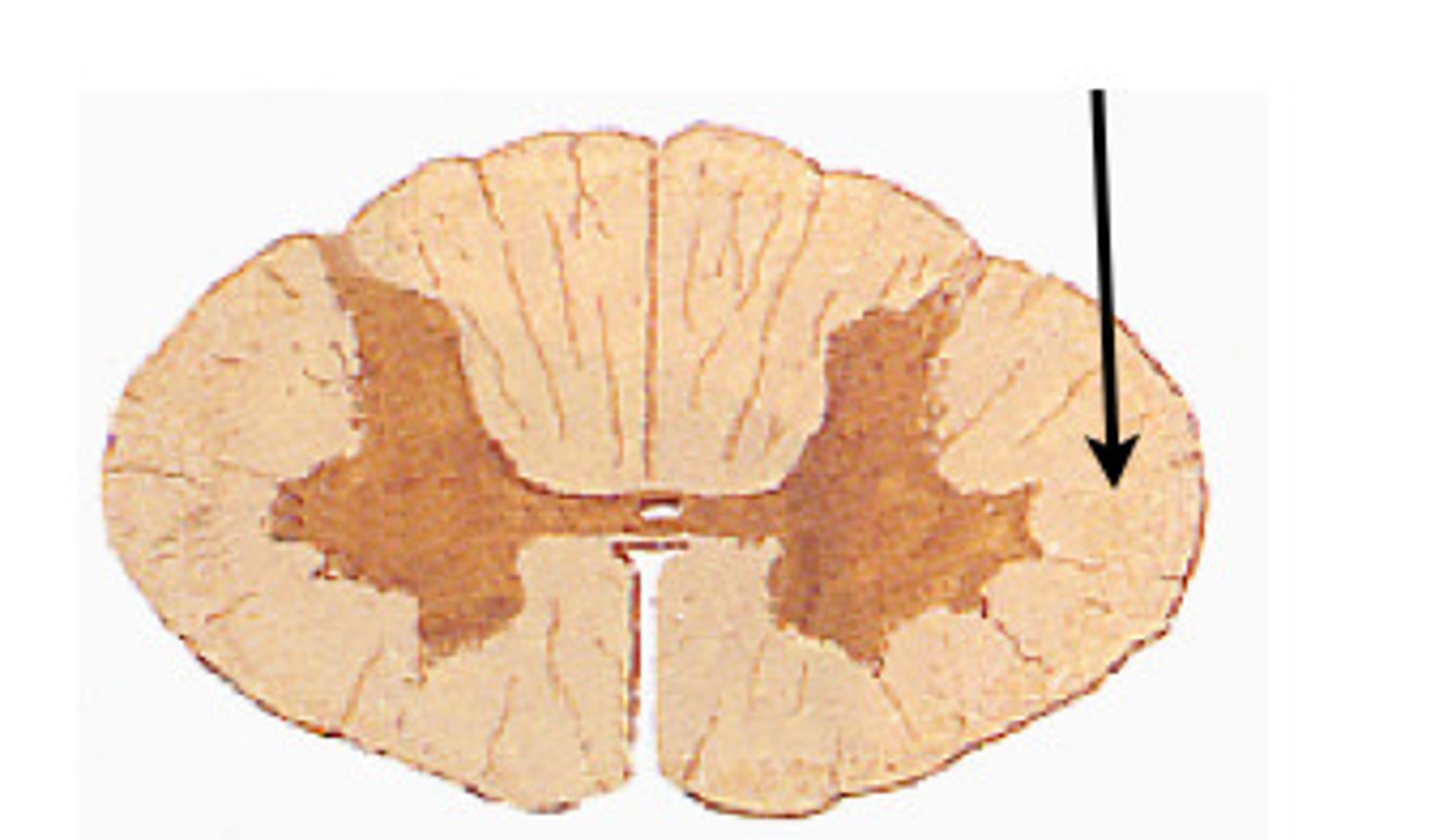
Lateral White columns
located on each side of spinal cord between anterior and posterior columns
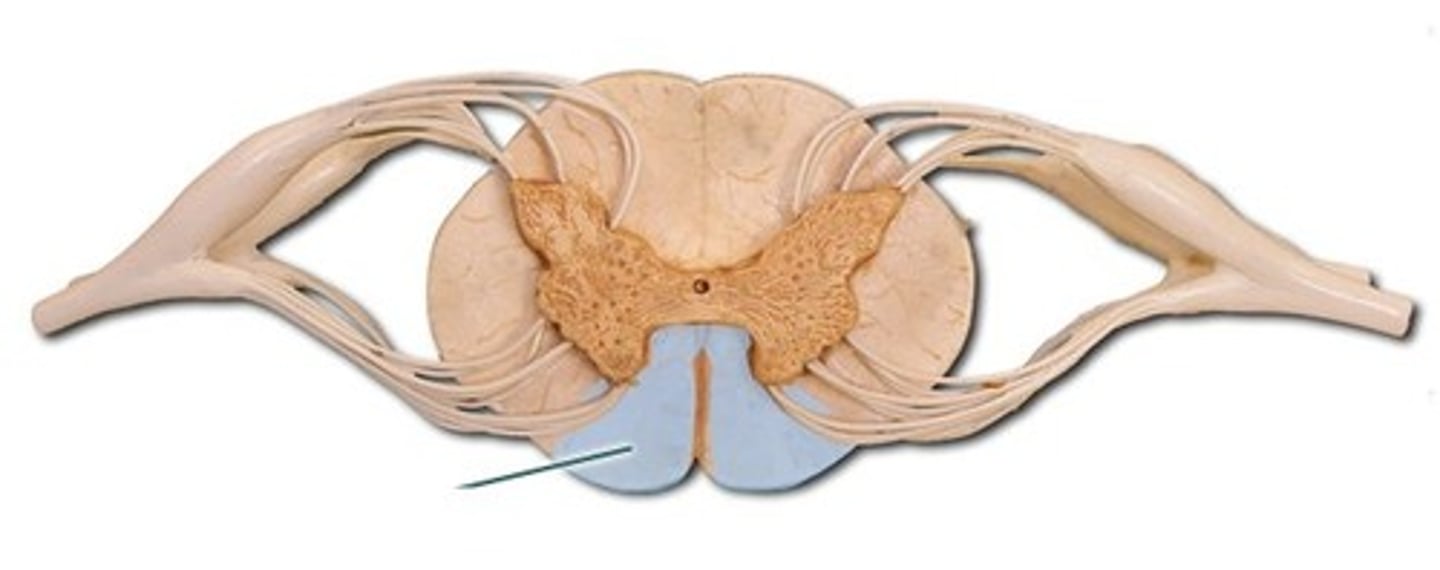
Anterior White column
lies between the anterior gray horns and the anterior median fissure
Central canal
A small channel in the center of the spinal cord that contains cerebrospinal fluid.
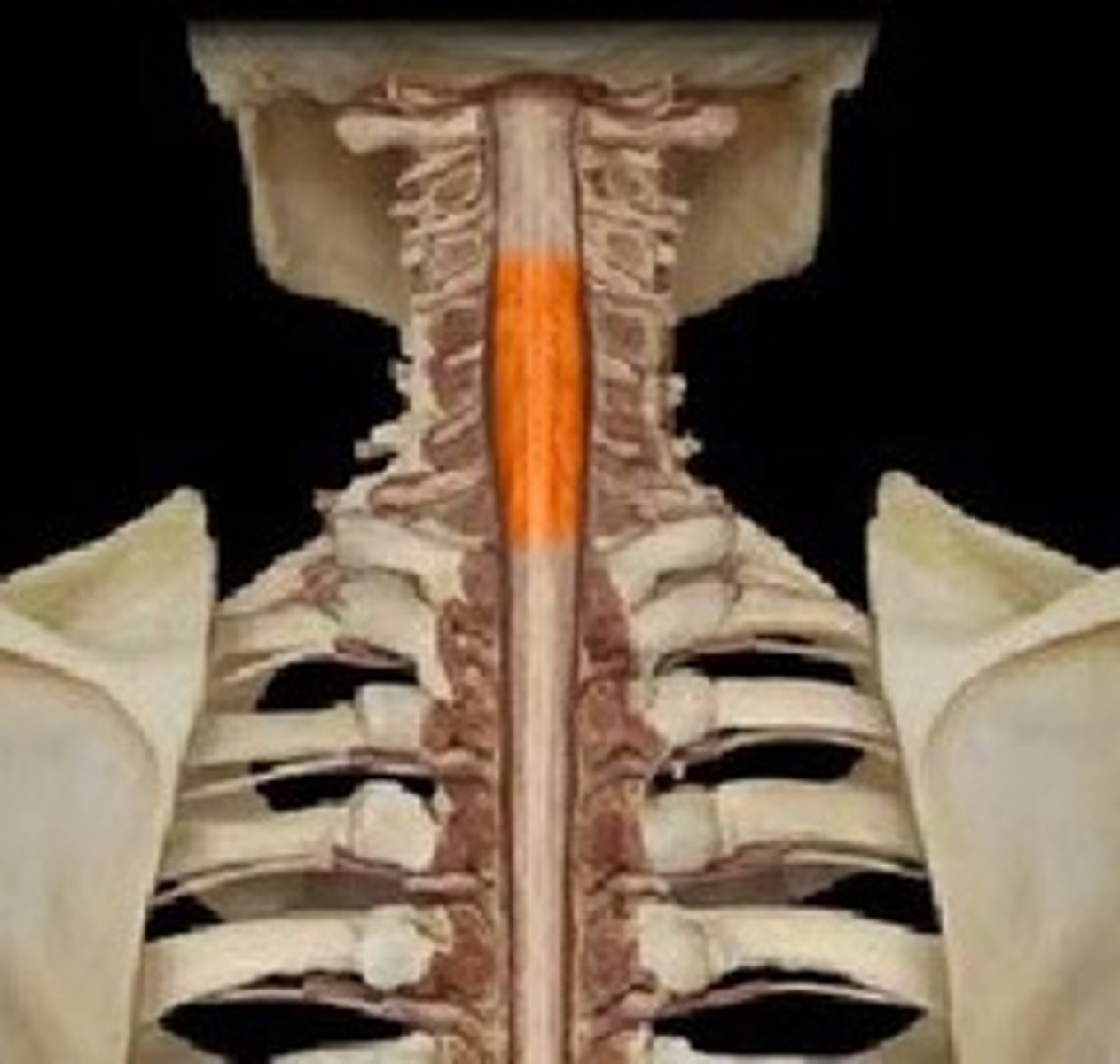
Cervical enlargement
The enlargement of the spinal cord in the cervical region that supplies nerves to the upper limbs.
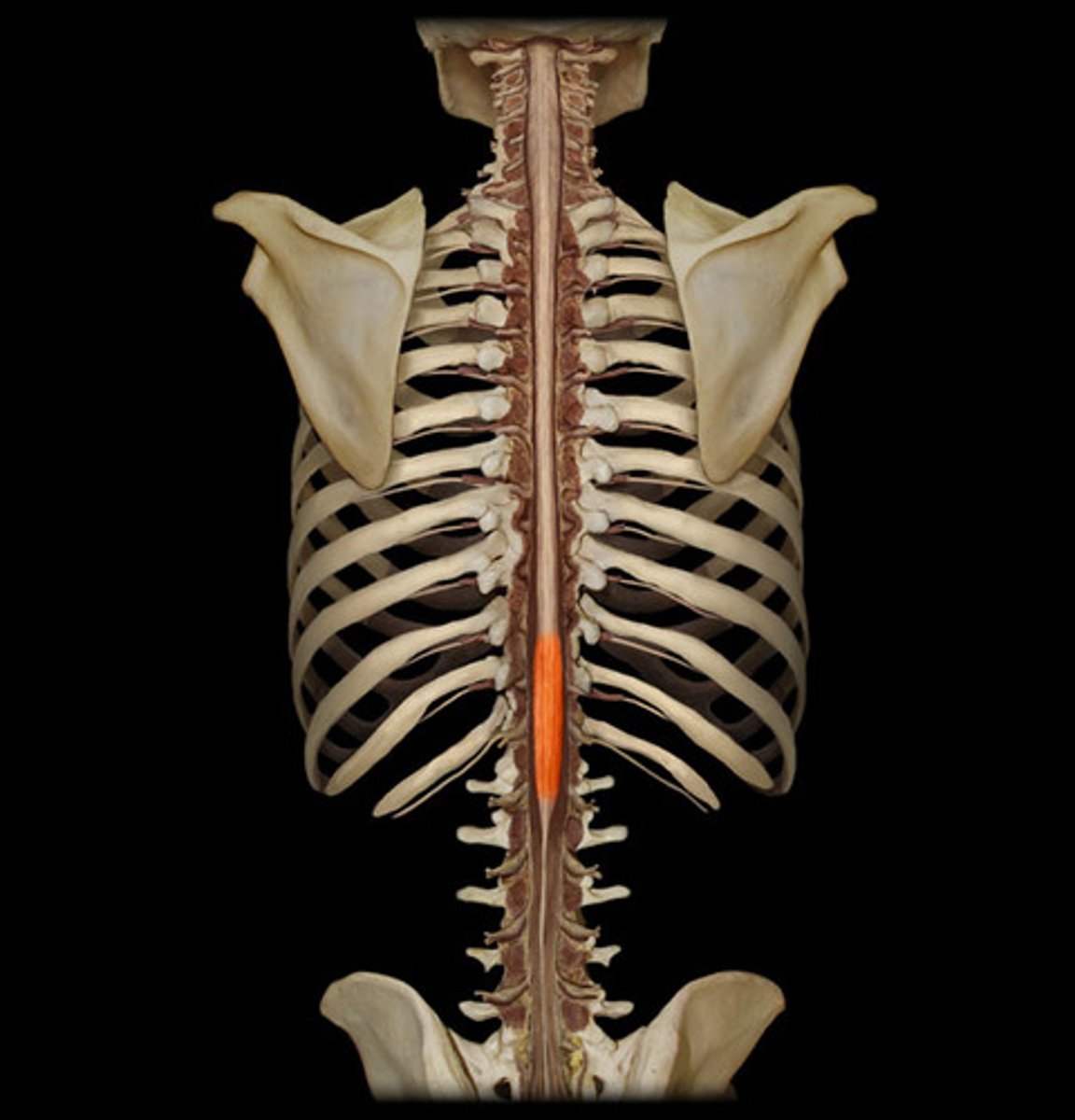
Lumbosacral enlargement
The enlargement of the spinal cord in the lumbar region that supplies nerves to the lower limbs.
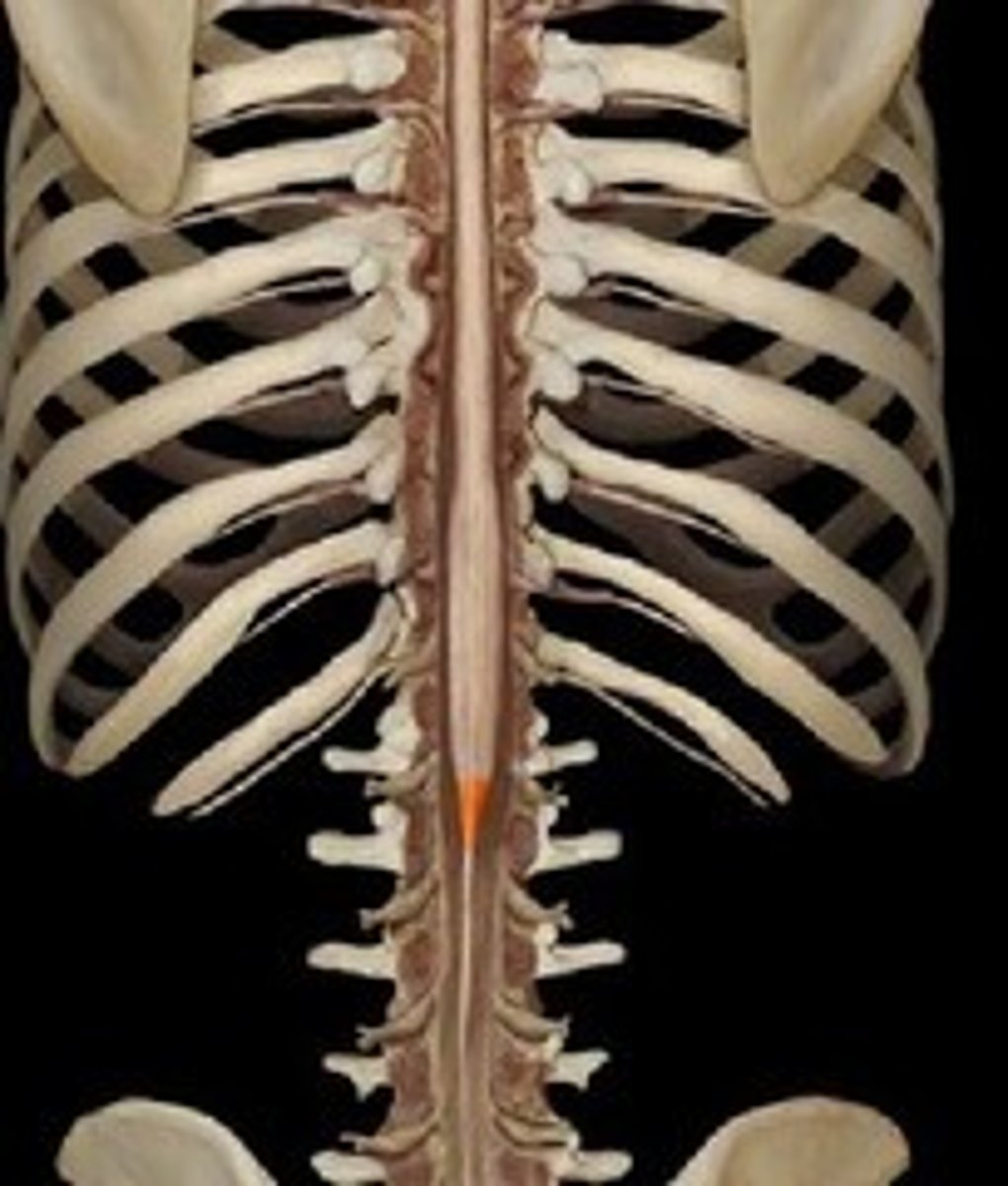
Conus medullaris
The tapered end of the spinal cord.
Cauda equina
A bundle of spinal nerves and nerve roots located below the conus medullaris.
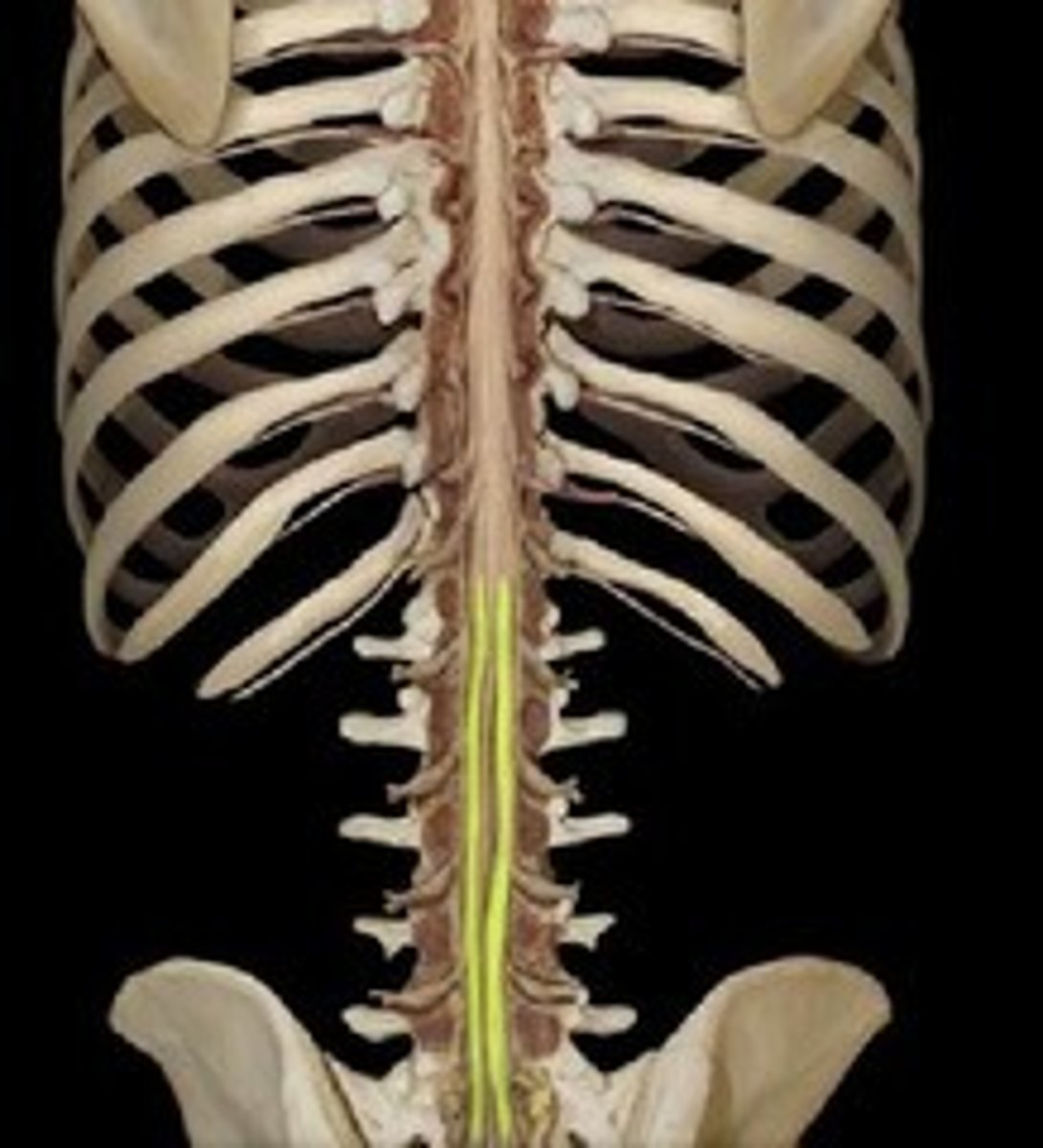
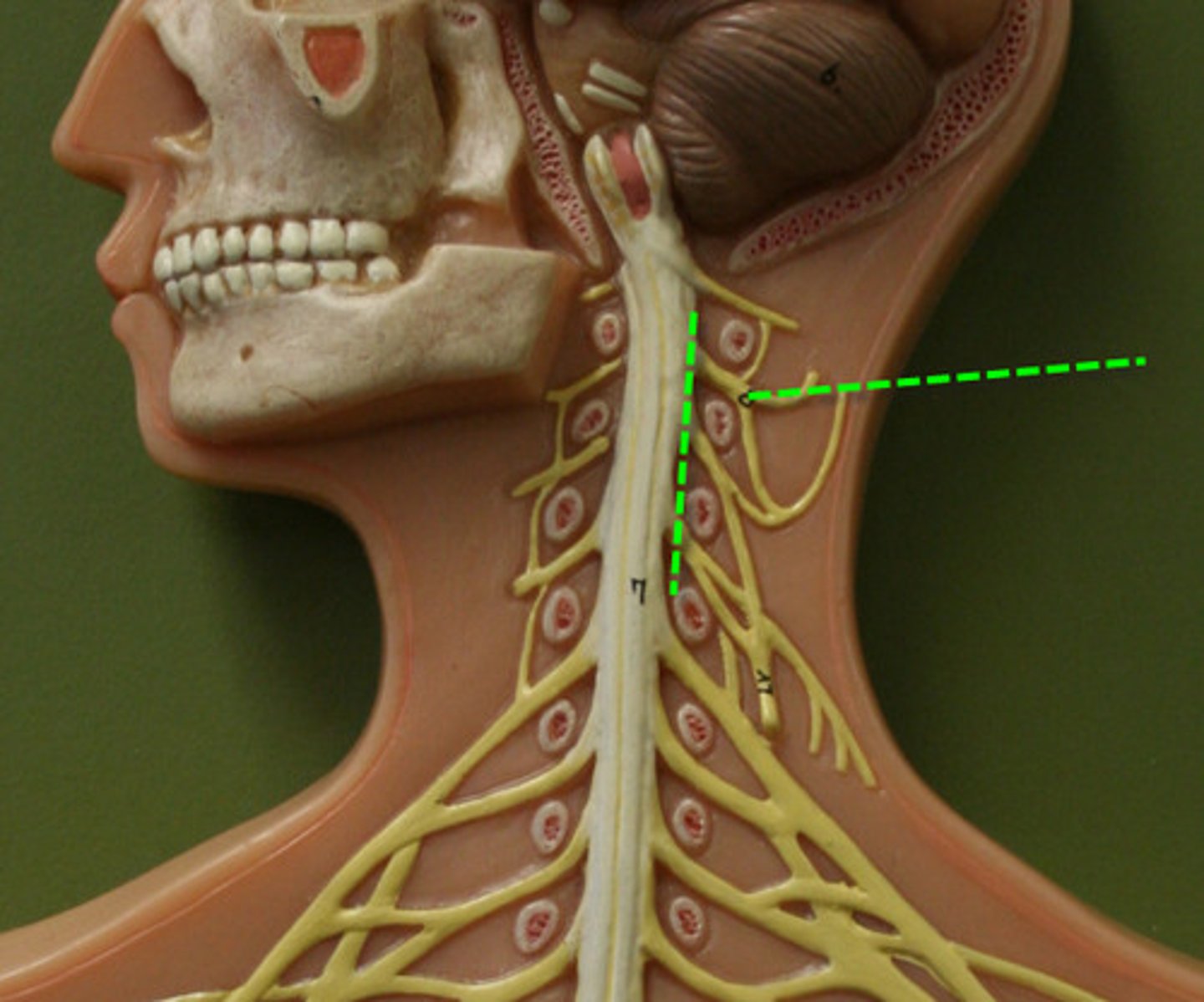
Cervical plexus and phrenic nerve
A network of nerves in the neck that supplies the diaphragm.
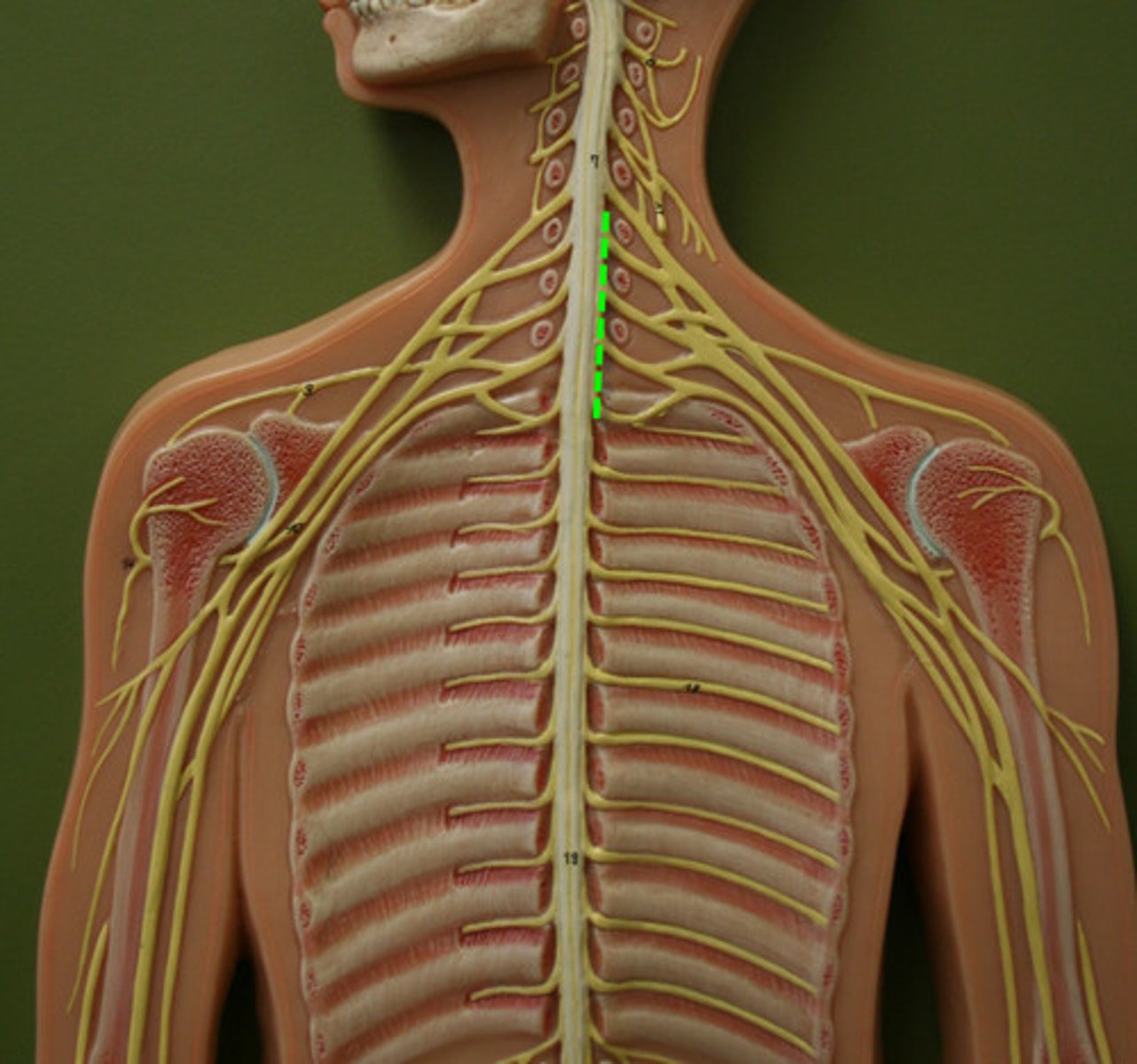
Brachial plexus
A network of nerves that innervates the upper limb.
Lumbar plexus
L1-L4
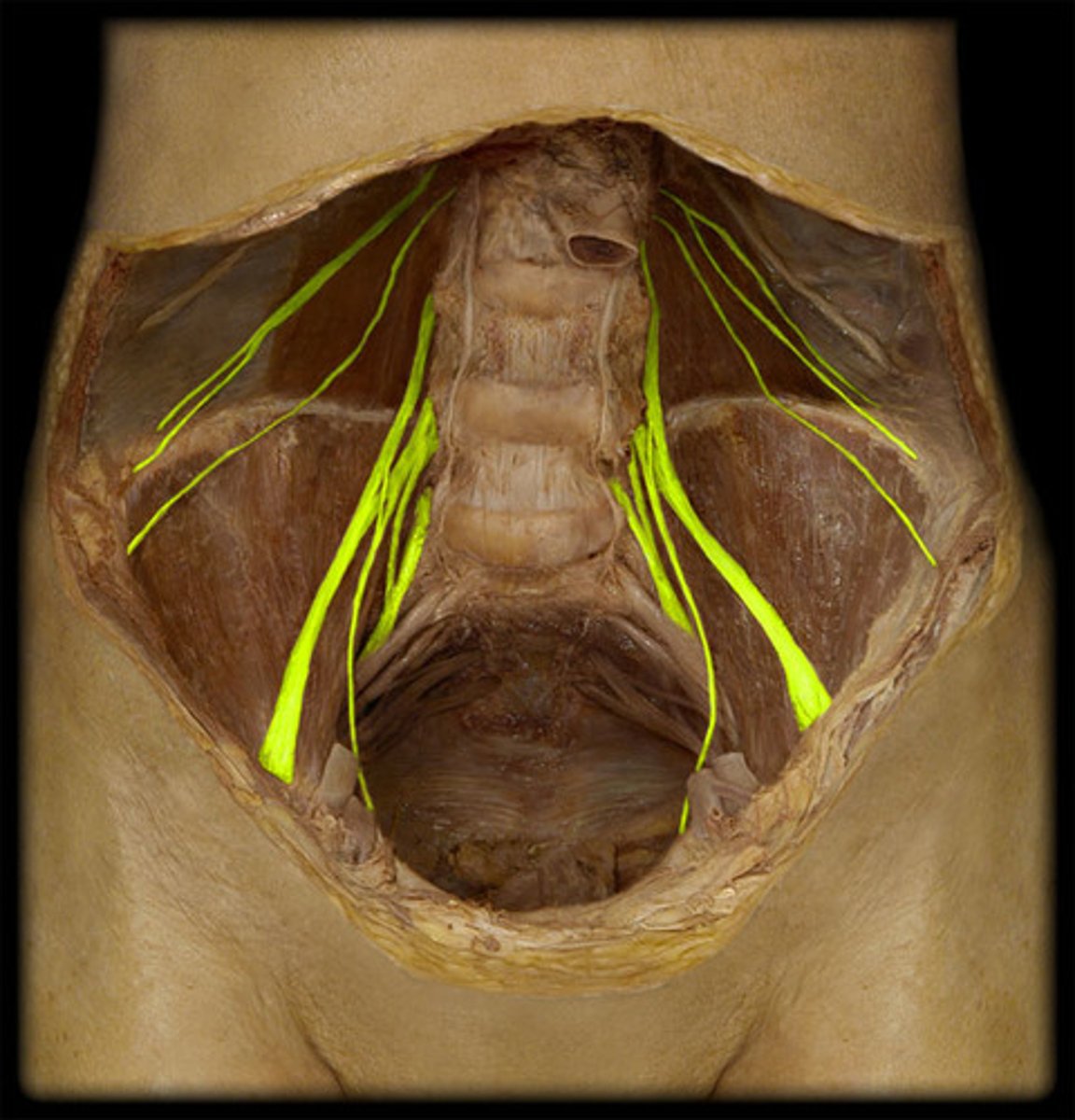
Sacral plexus
L4-S4
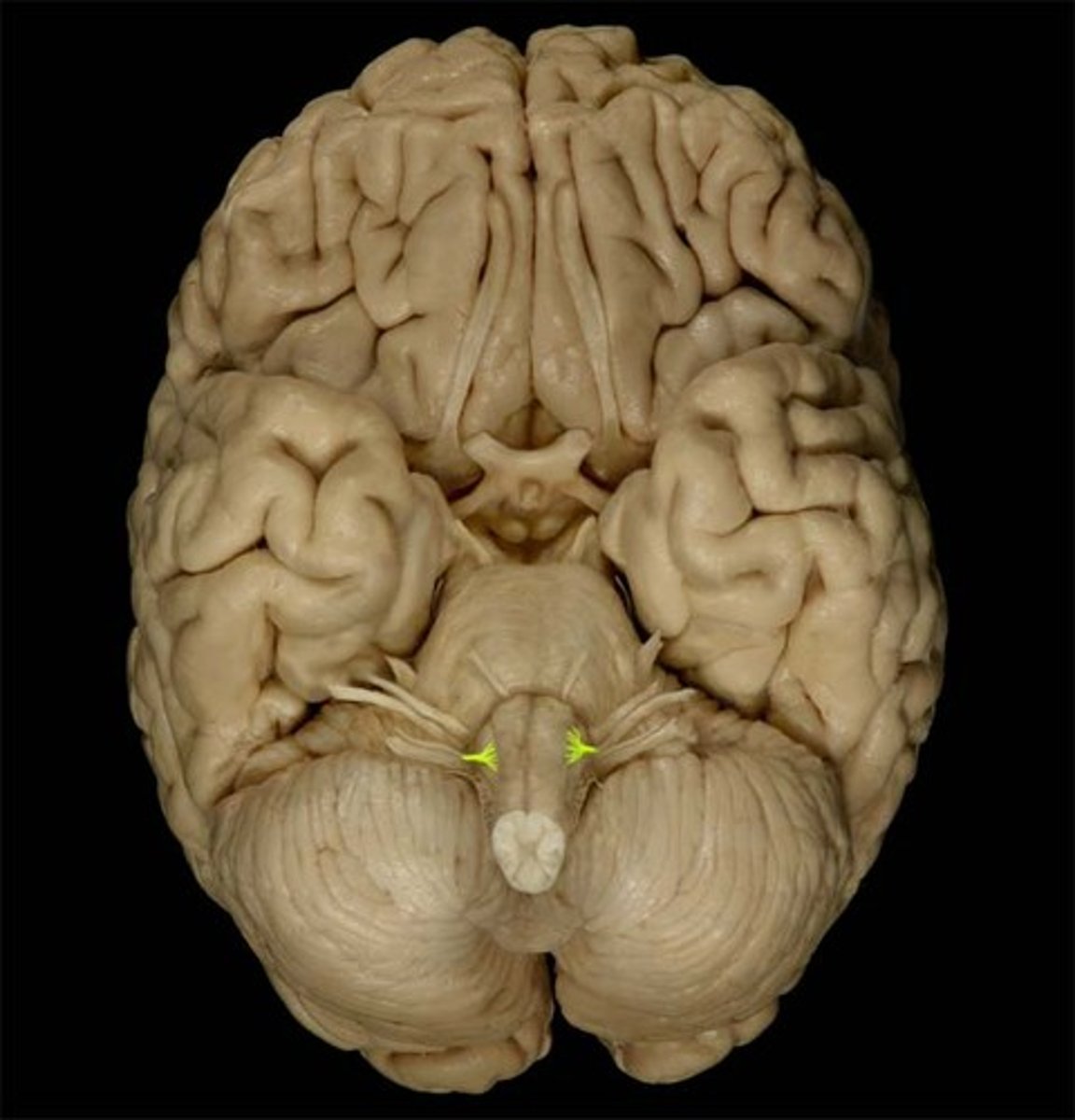
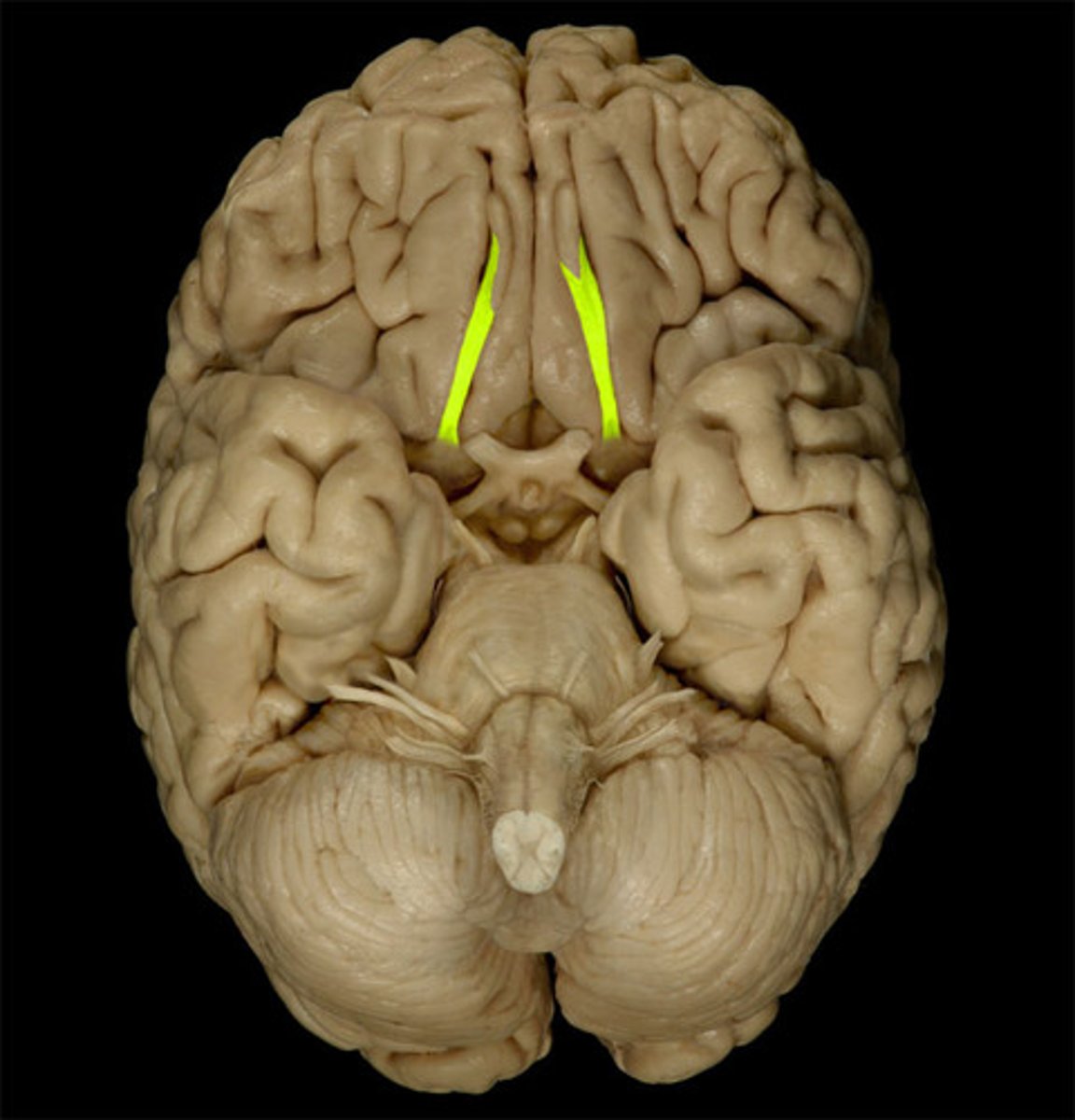
Olfactory
The cranial nerve responsible for the sense of smell.
Optic
The cranial nerve responsible for vision.
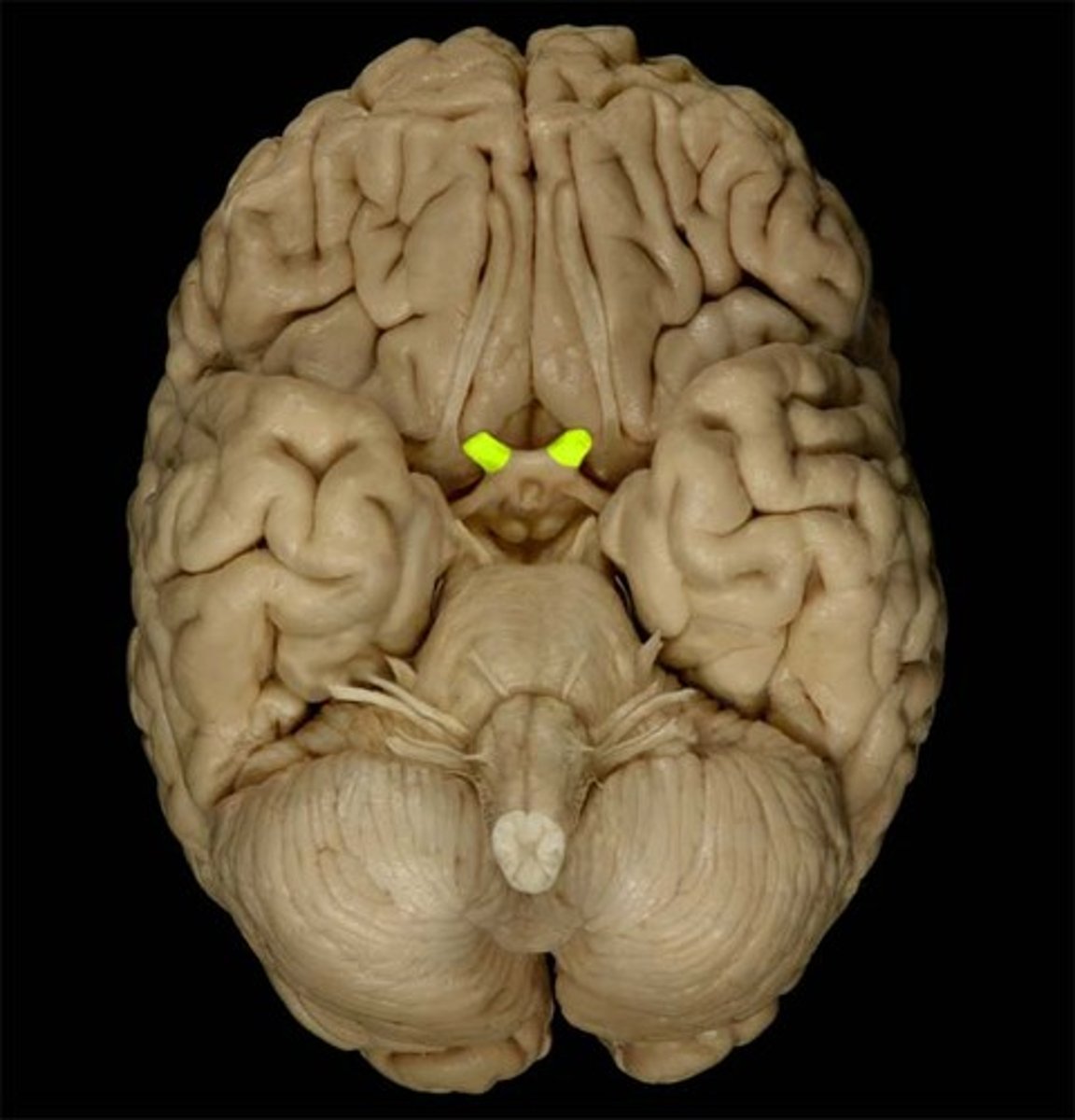
Oculomotor
The cranial nerve responsible for eye movement and pupil constriction.
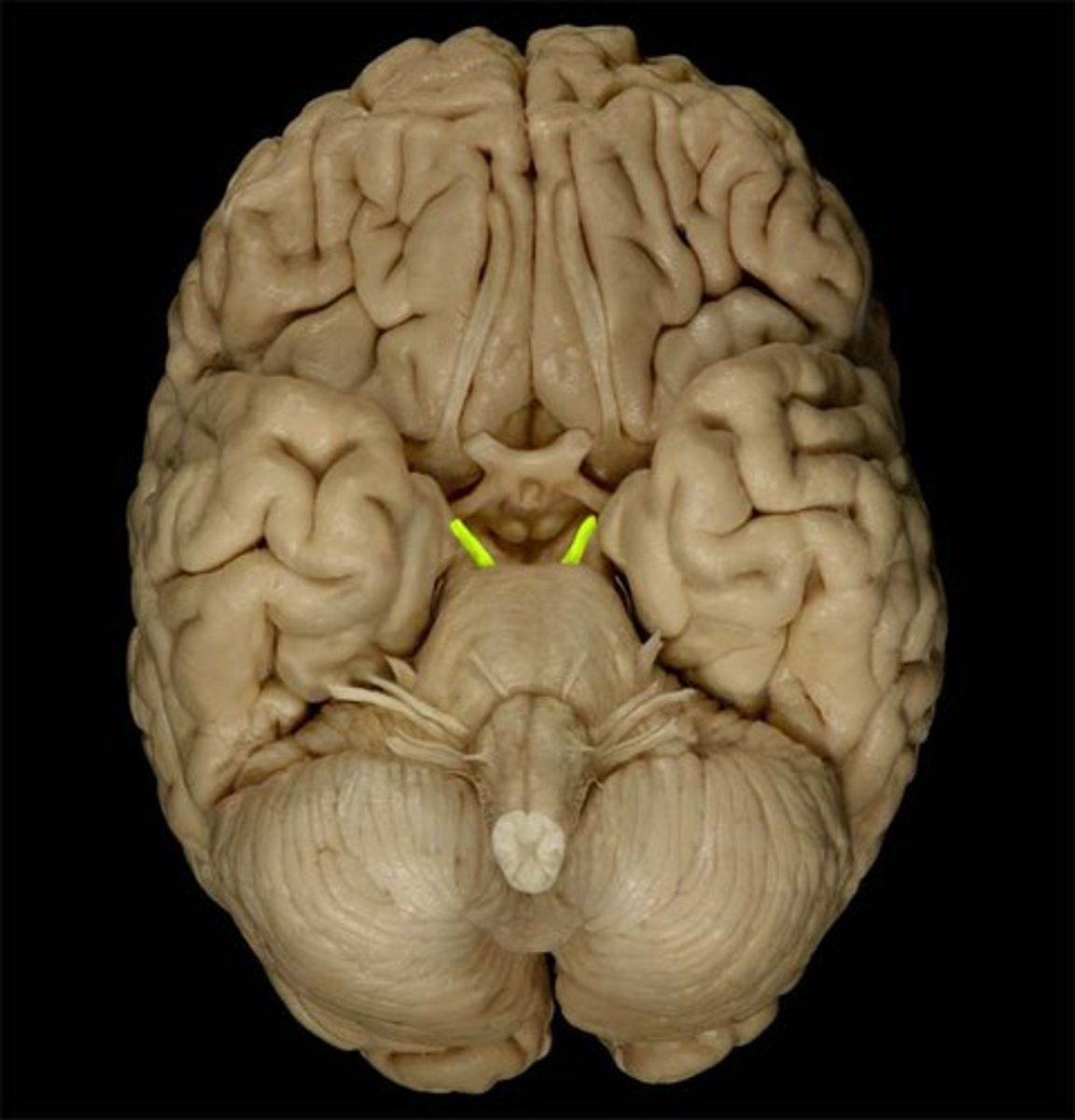
Trochlear
The cranial nerve that innervates the superior oblique muscle of the eye.
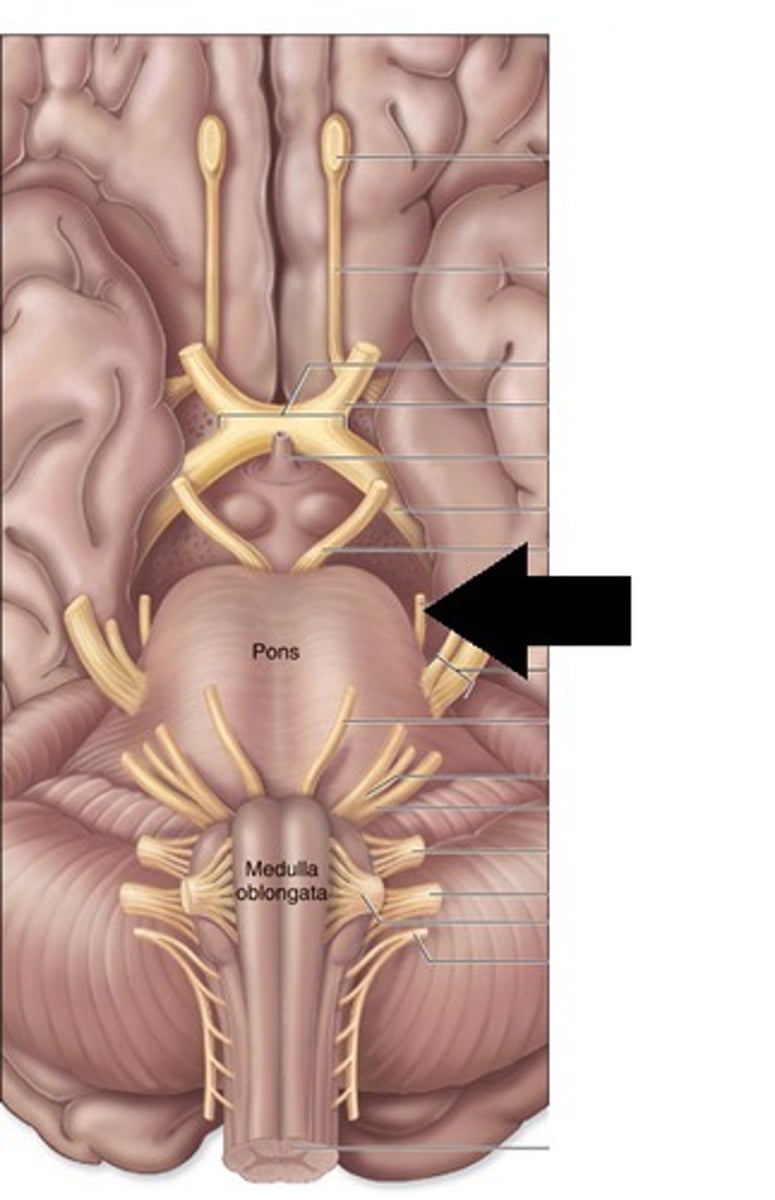
Trigeminal
The cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing.
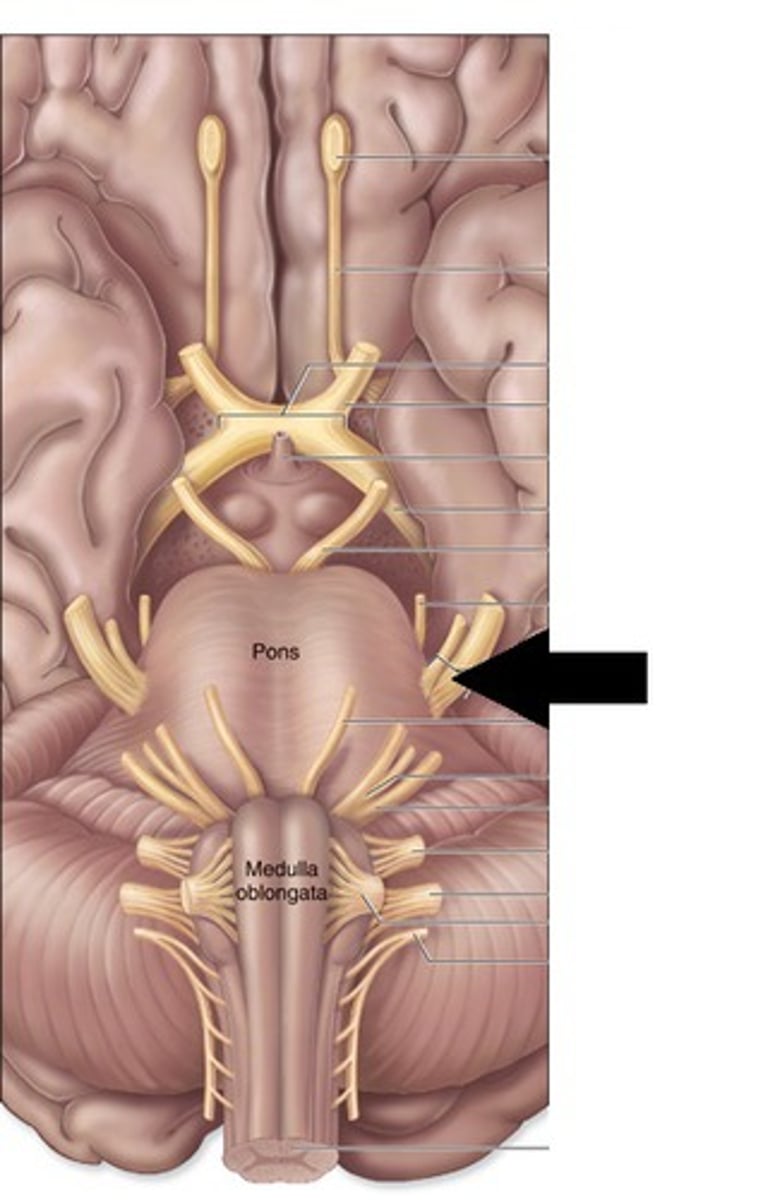
Abducens
The cranial nerve that controls the lateral rectus muscle of the eye.
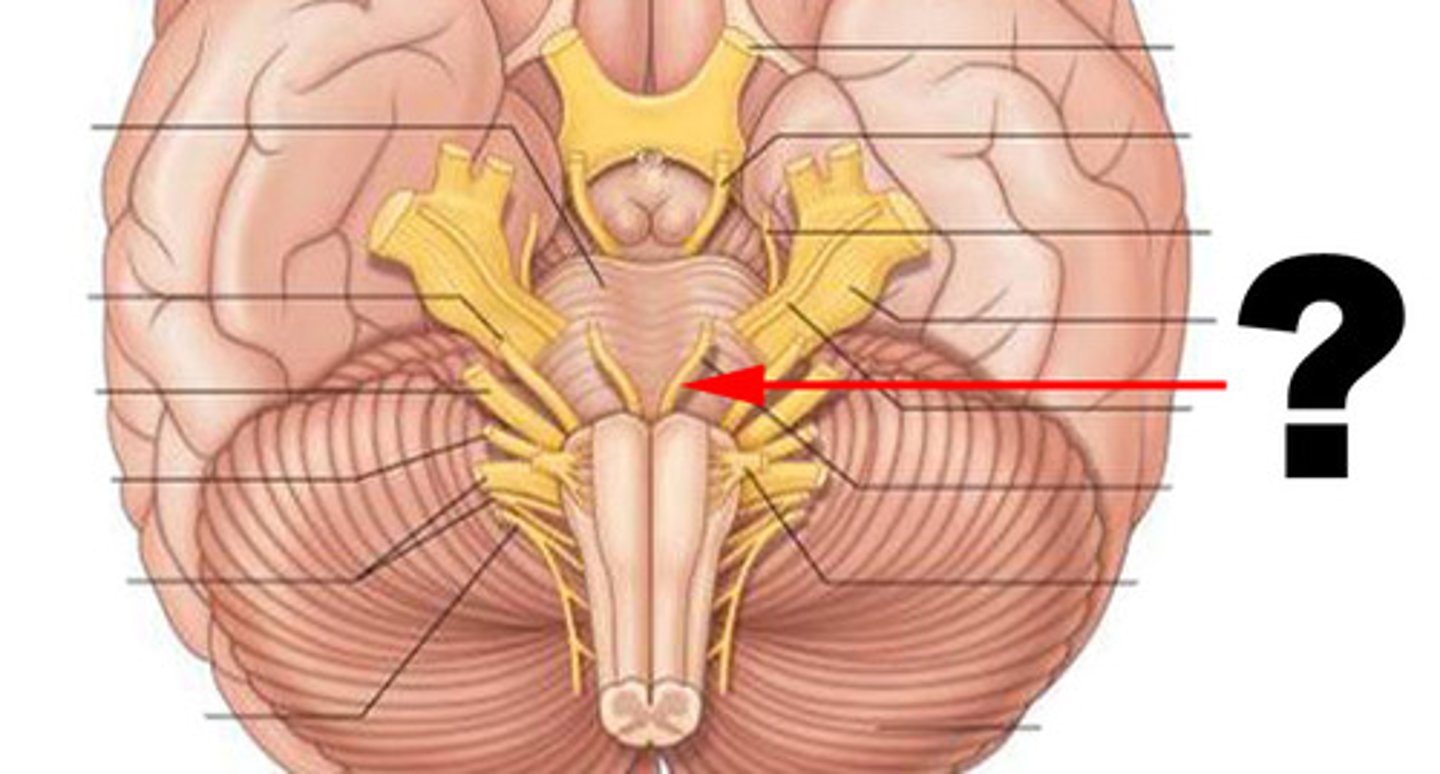
Facial
The cranial nerve responsible for facial expressions and taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
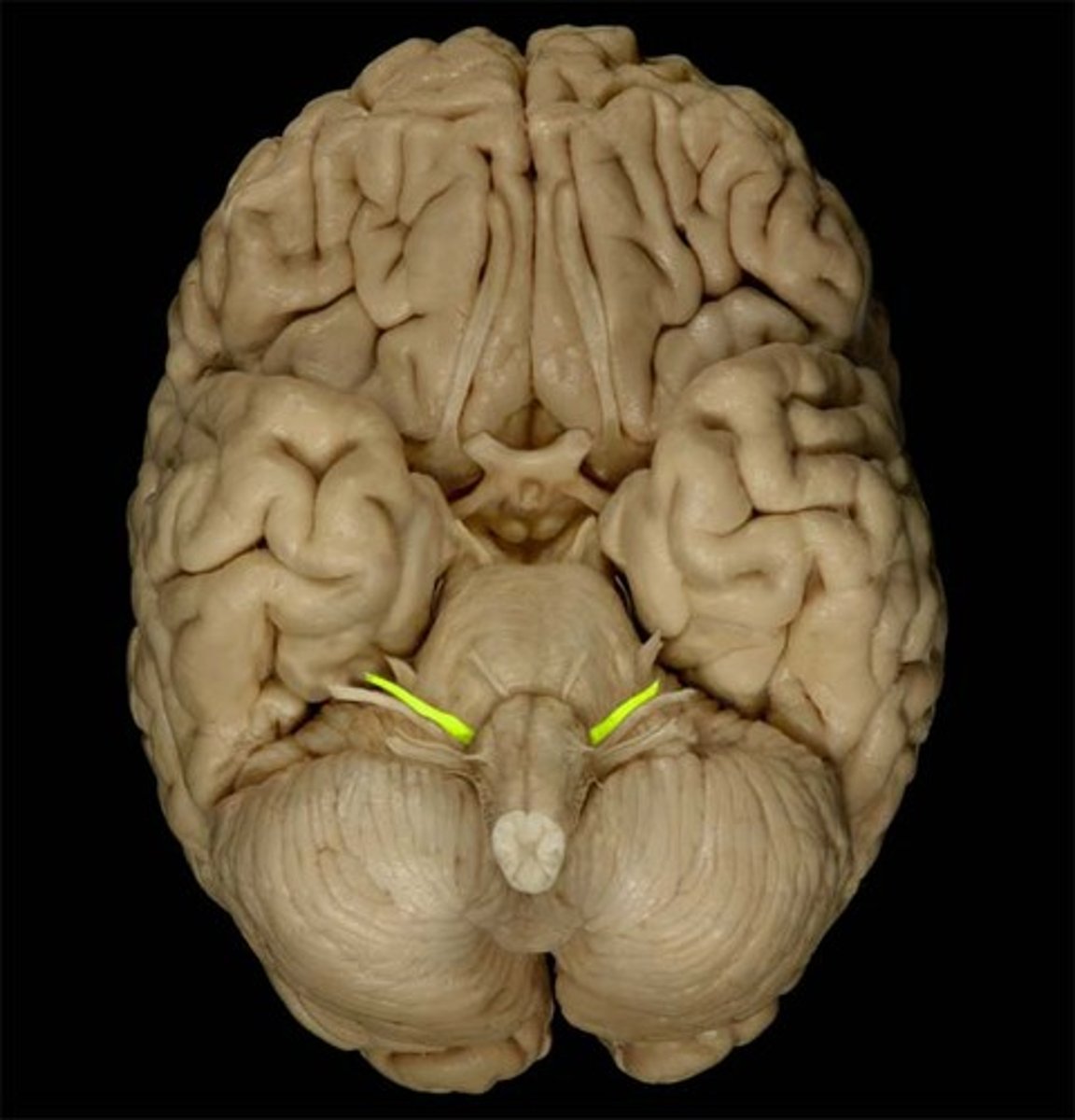
Vestibulocochlear
The cranial nerve responsible for hearing and balance.
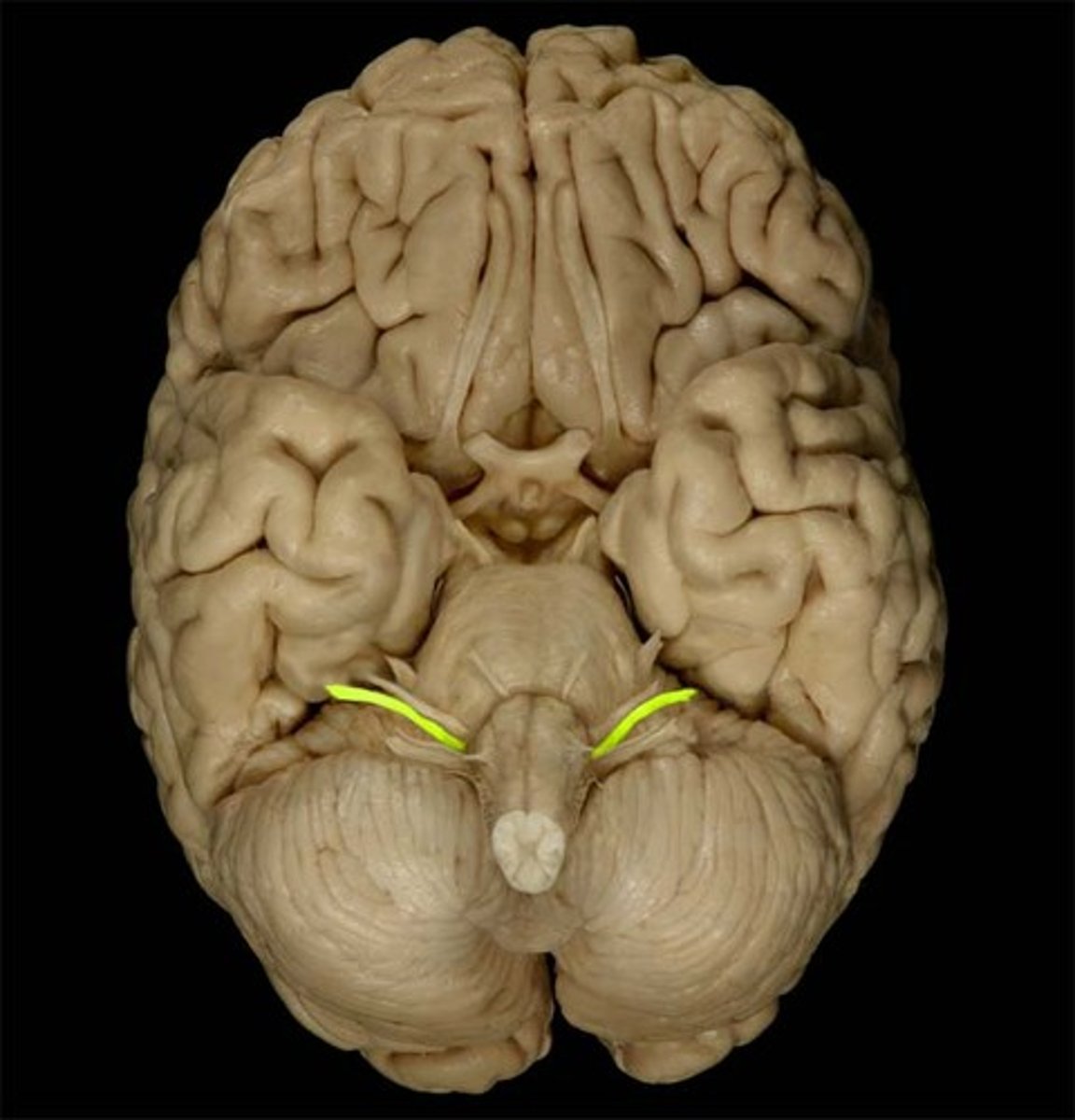
Glossopharyngeal
The cranial nerve responsible for taste and swallowing.
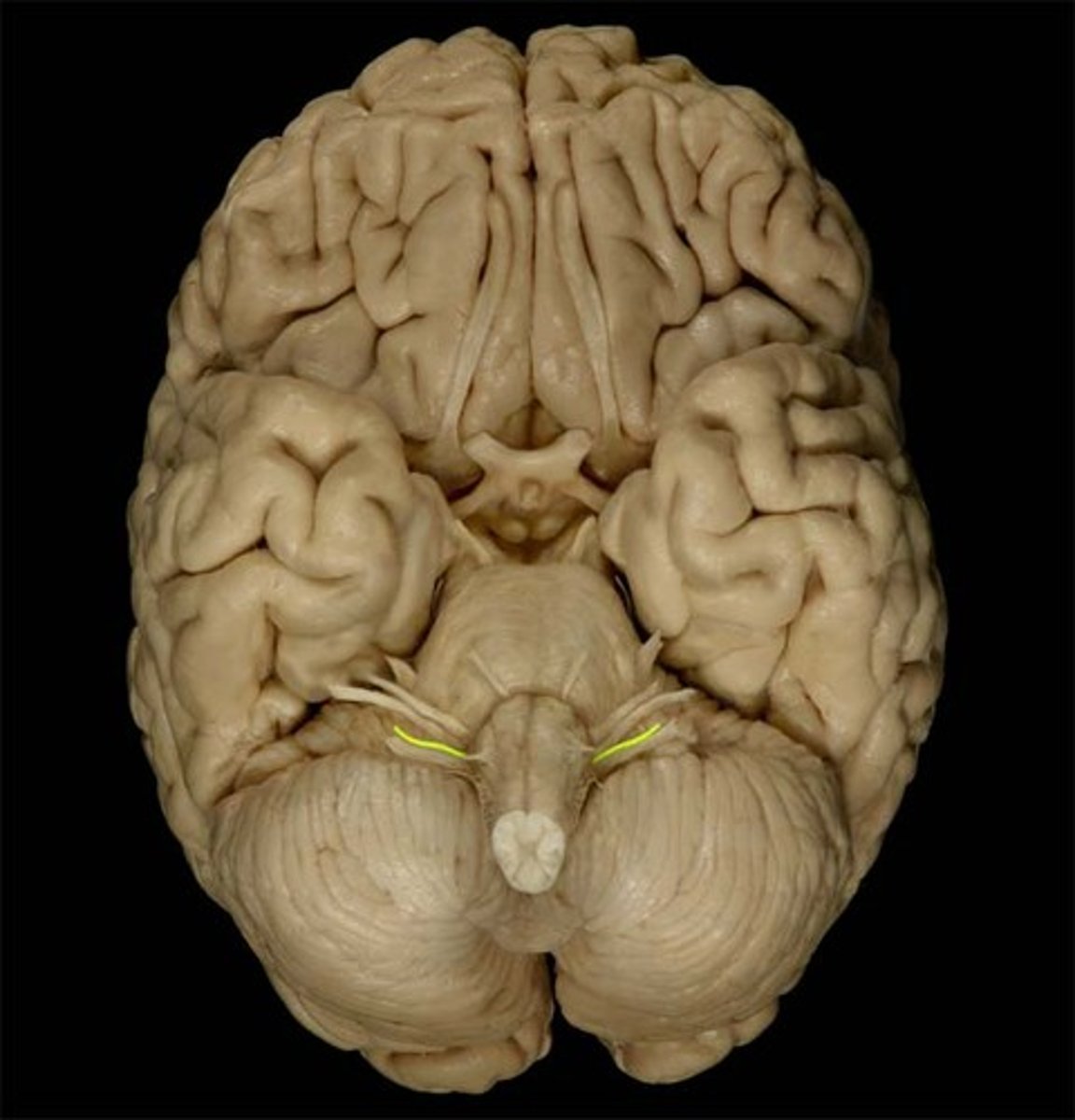
Vagus
The cranial nerve that innervates organs in the thorax and abdomen.
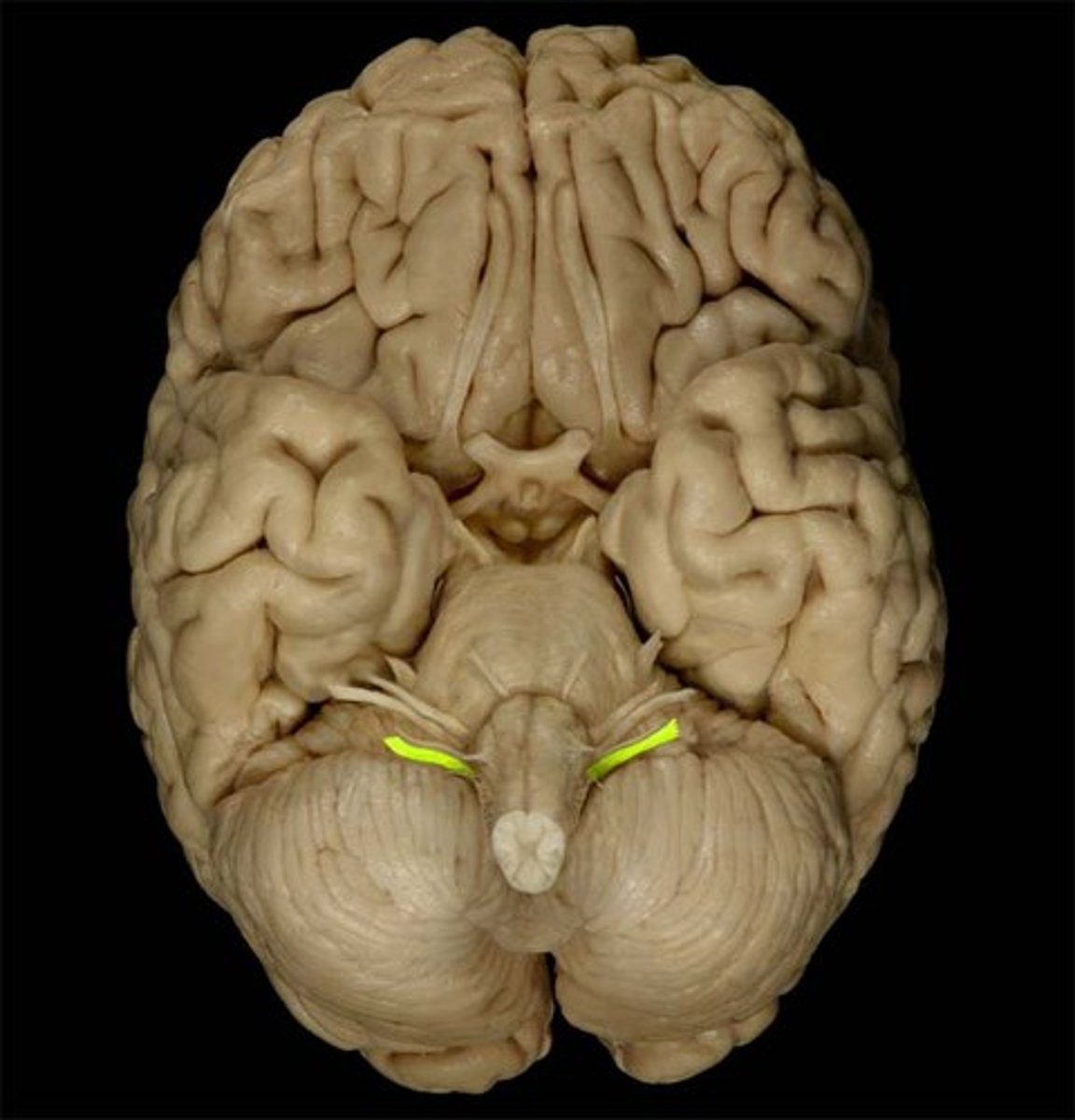
Accessory
The cranial nerve that controls neck and shoulder movements.
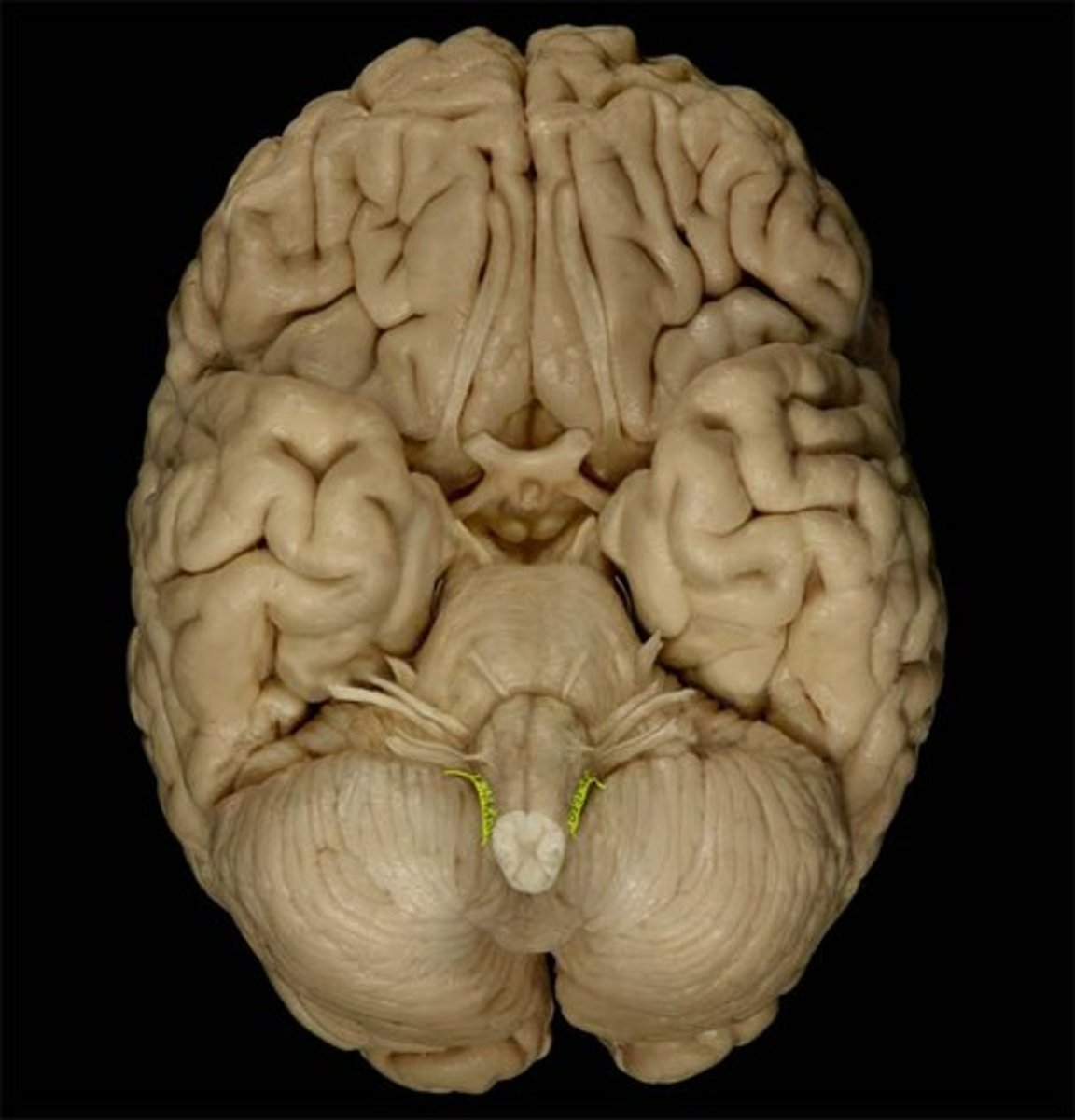
Hypoglossal
The cranial nerve that controls tongue movements.