biotech study guide
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Intron
MRNA (noncoding)
Start in DNA during transcribed into premRNA then removed through RNA splicing not a part of the final mRNA they are degraded
Exons
MRNA (coding)
Transcribed into premRNA some are removed but the remaining join together to form a continuous coding sequence are a part of the final mRNA

B.
Peptide bond
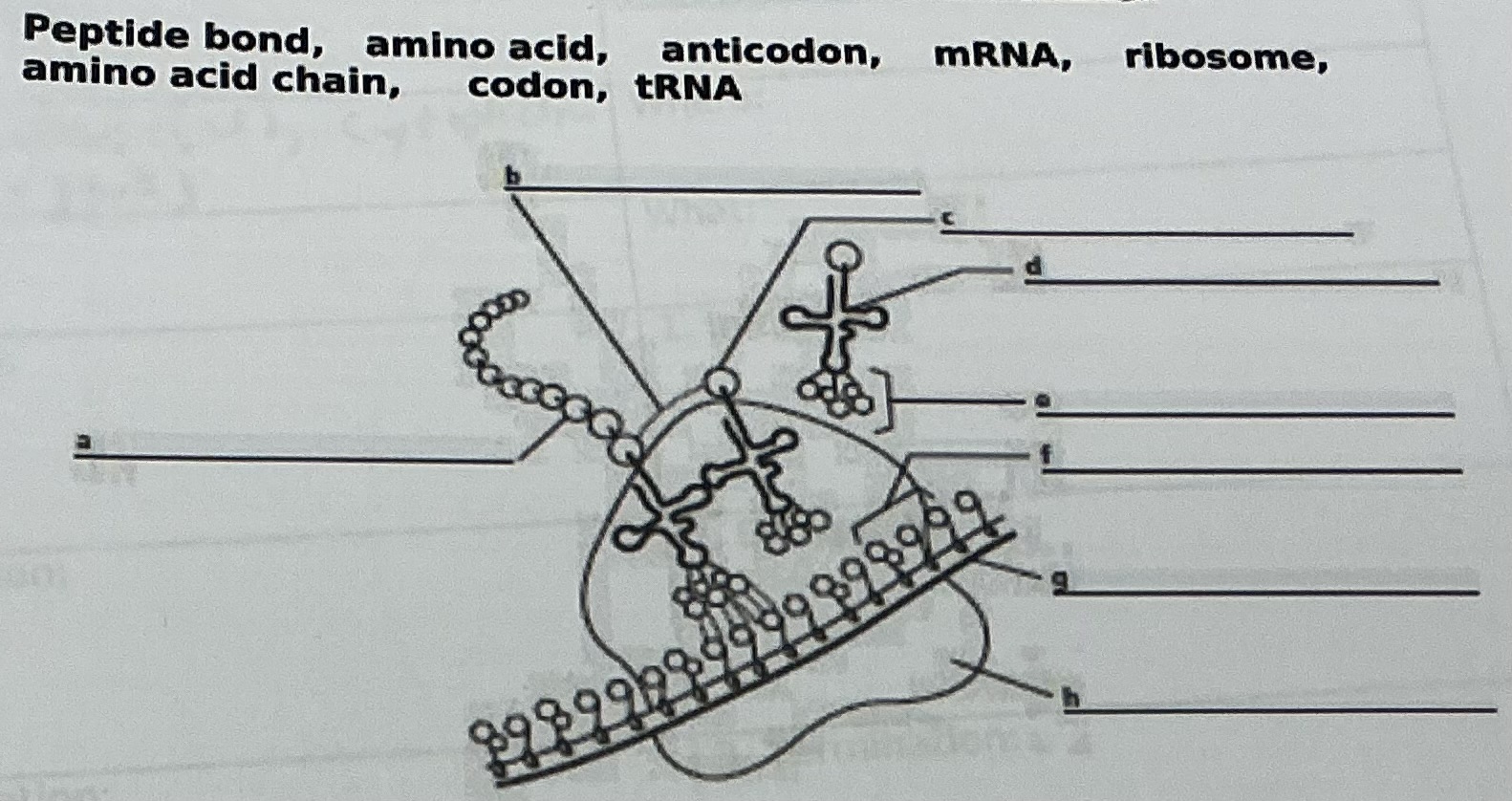
A
Amino acid chain
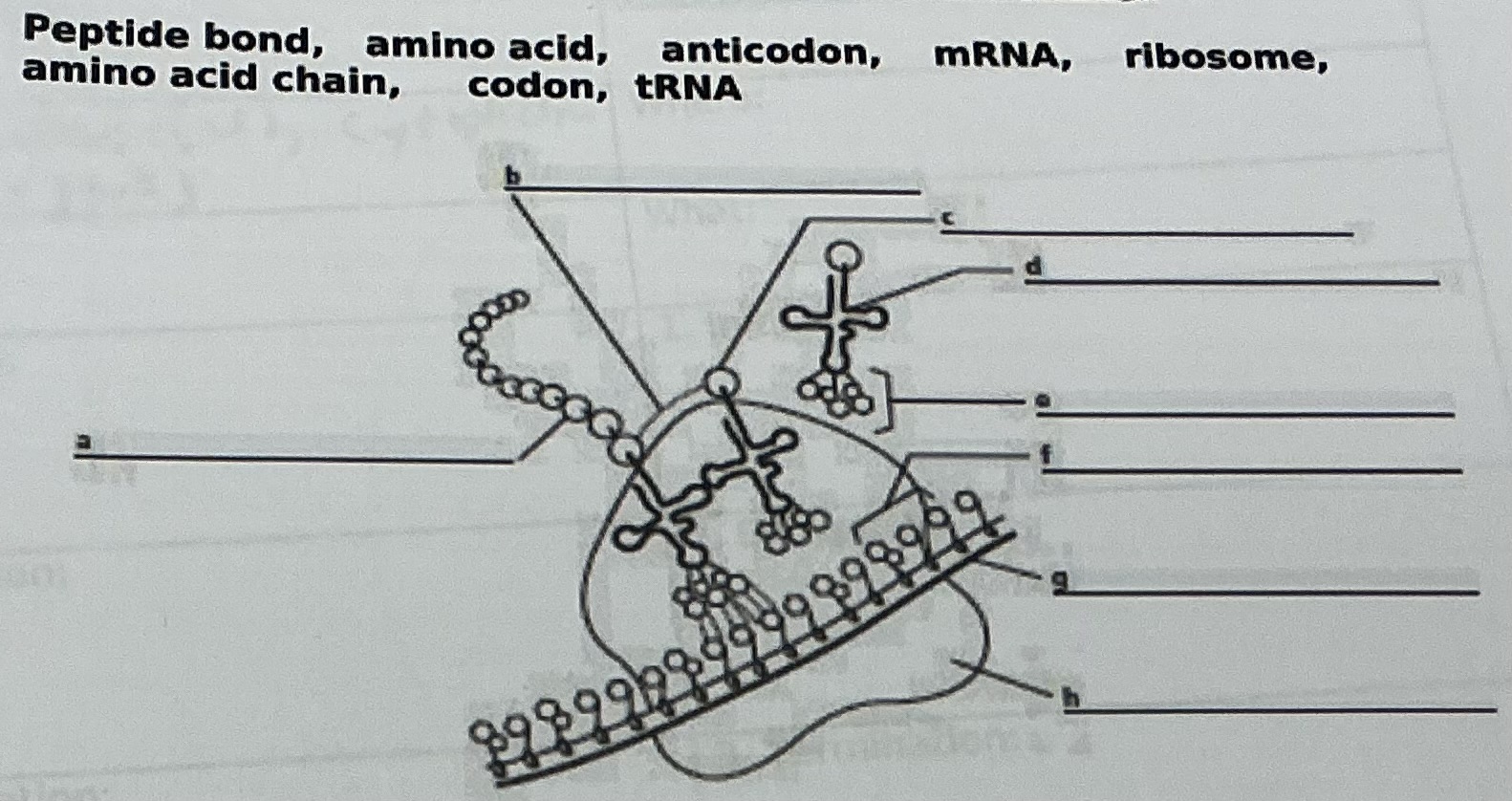
D
tRNA
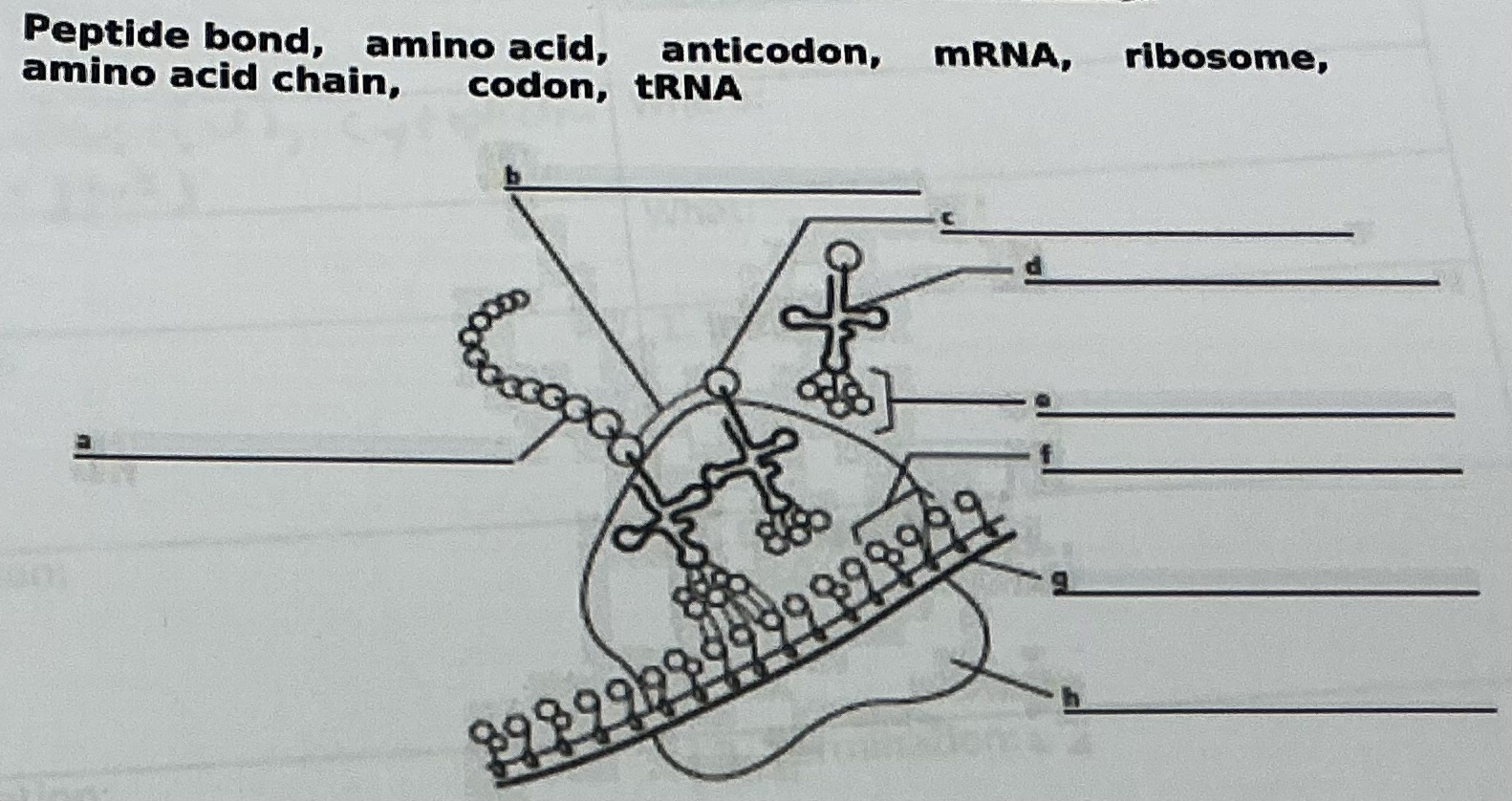
C
Amino acid
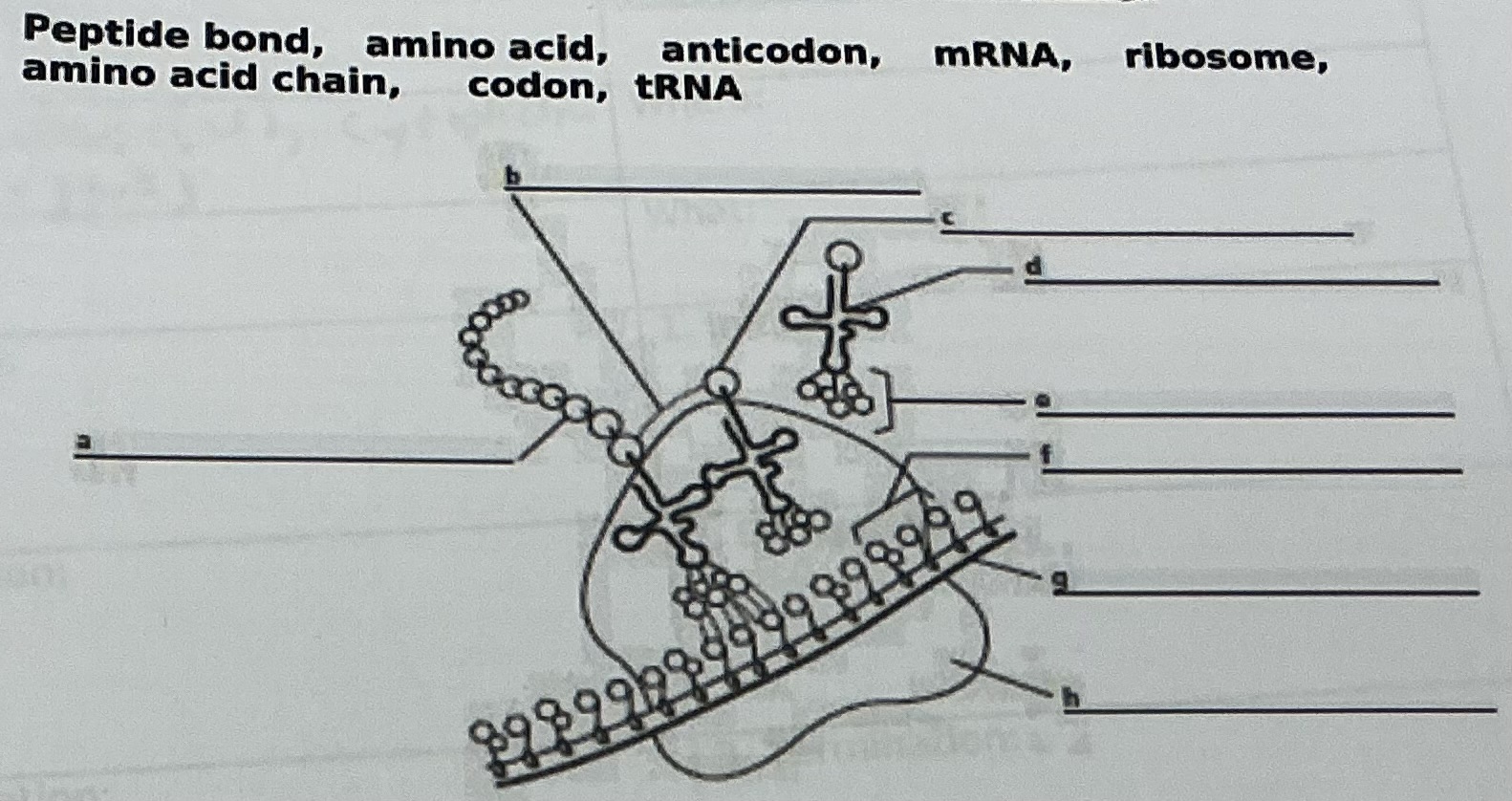
E
Anticodon
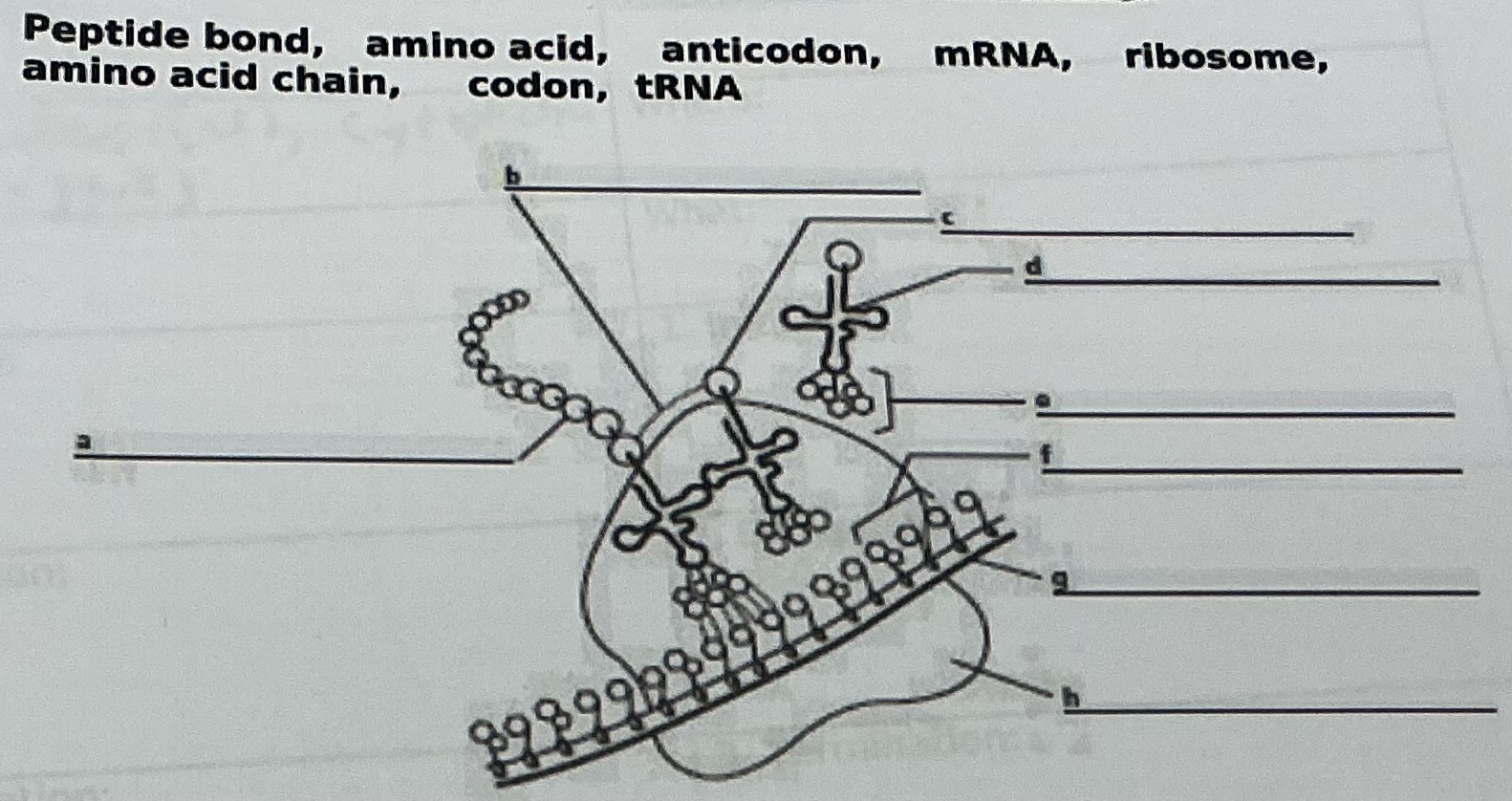
F
Codon
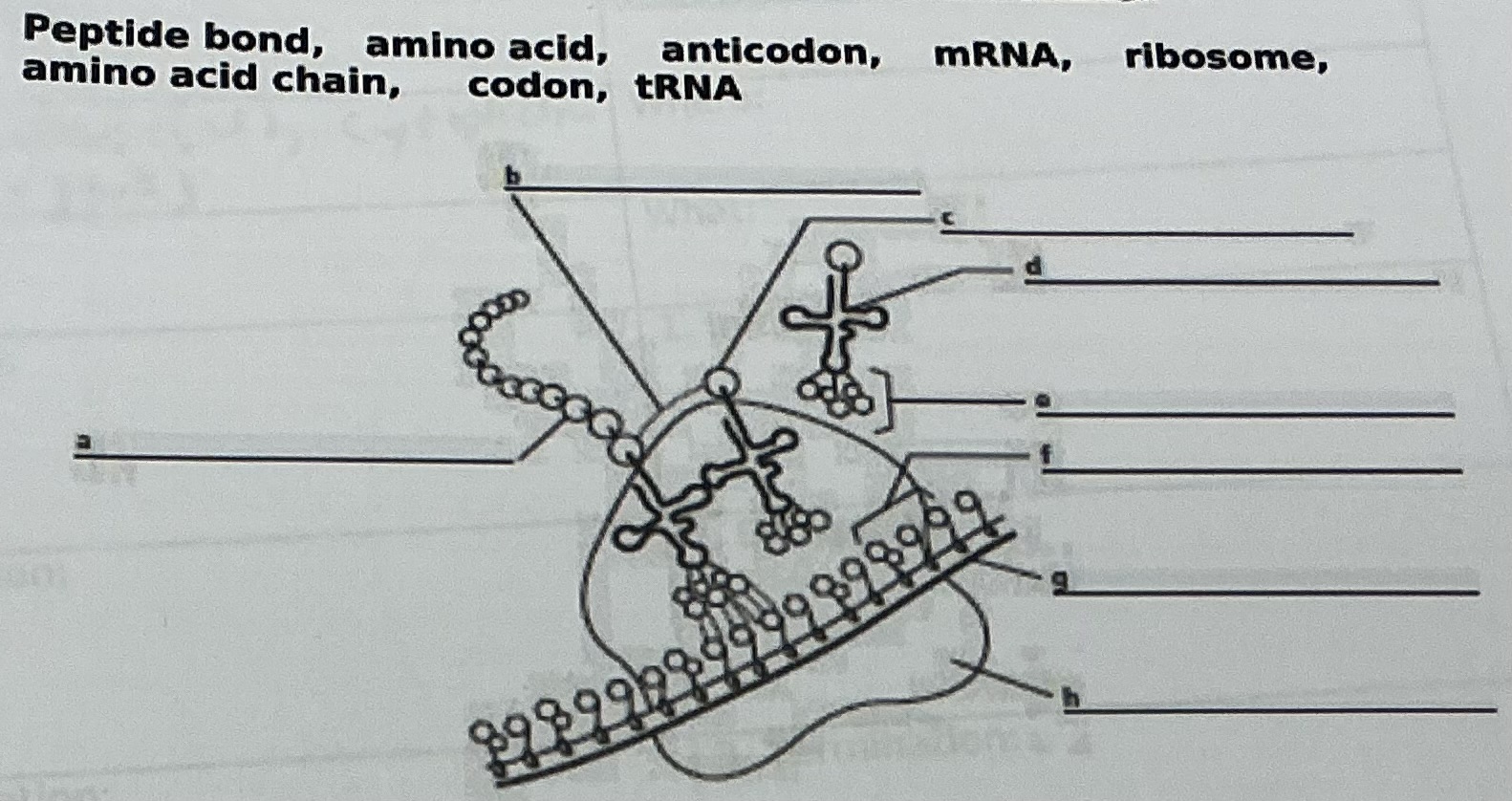
G
mRNA
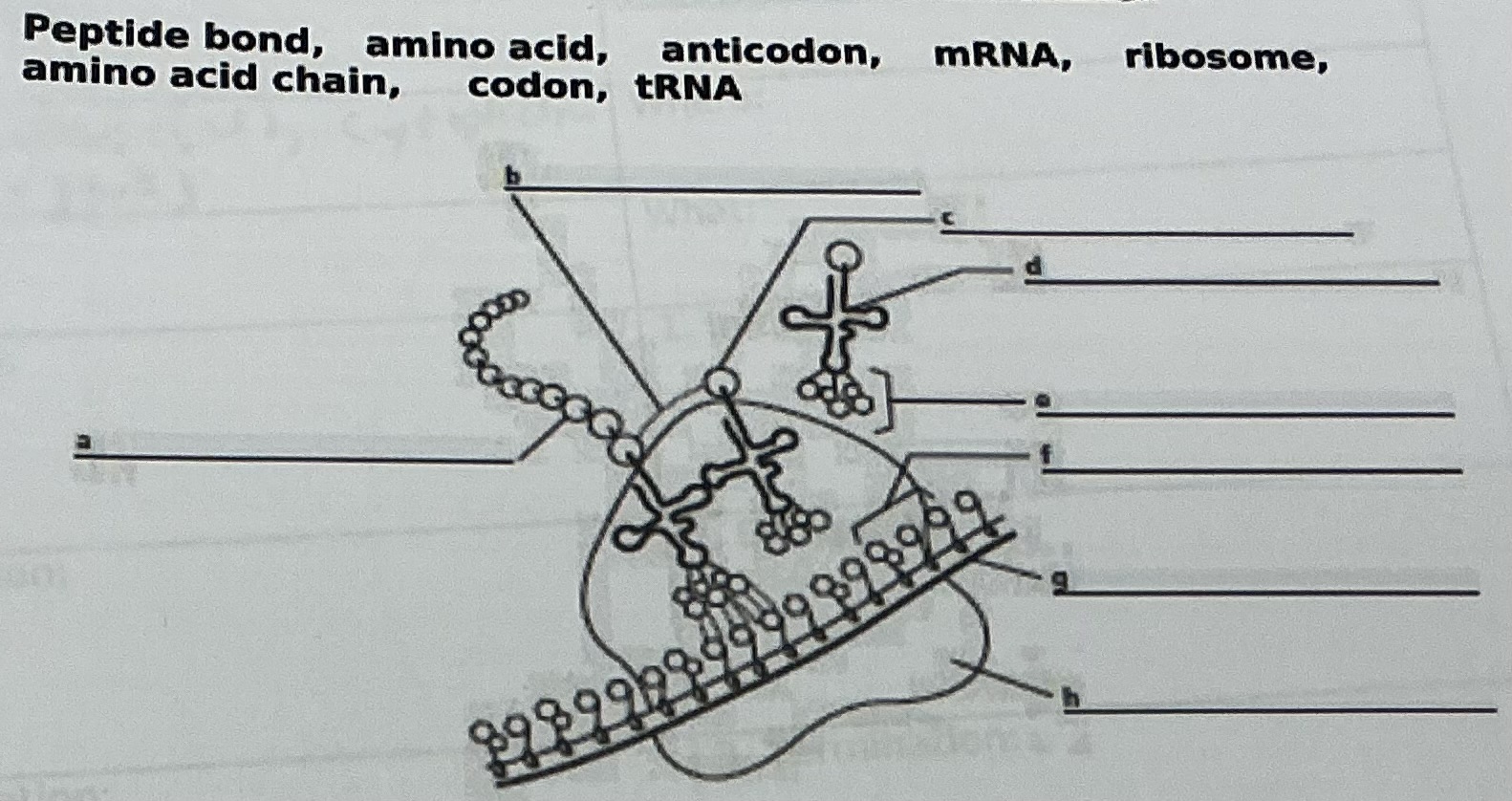
H
Ribosome
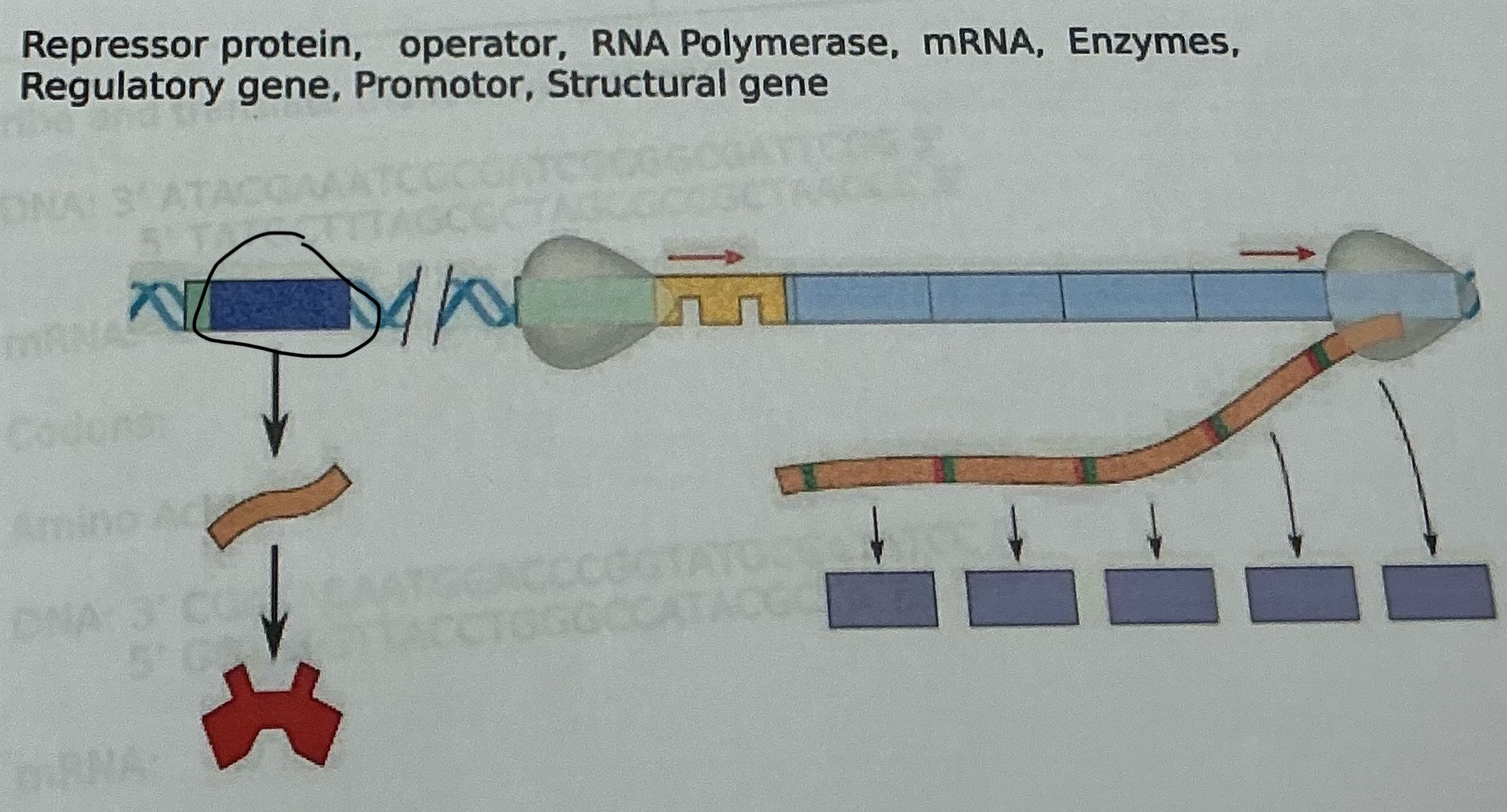
What is this
Regulatory gene
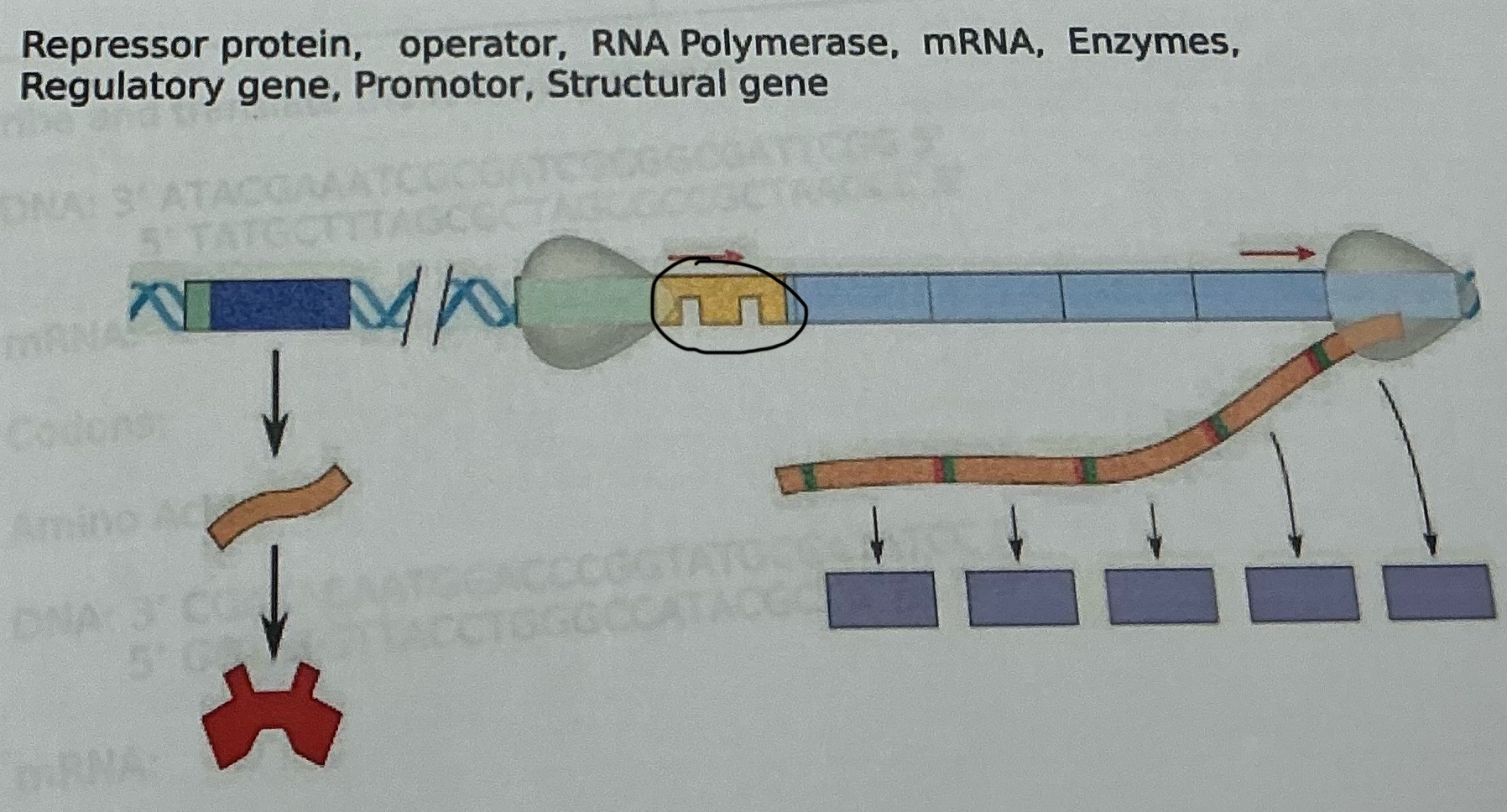
What is this
Operator
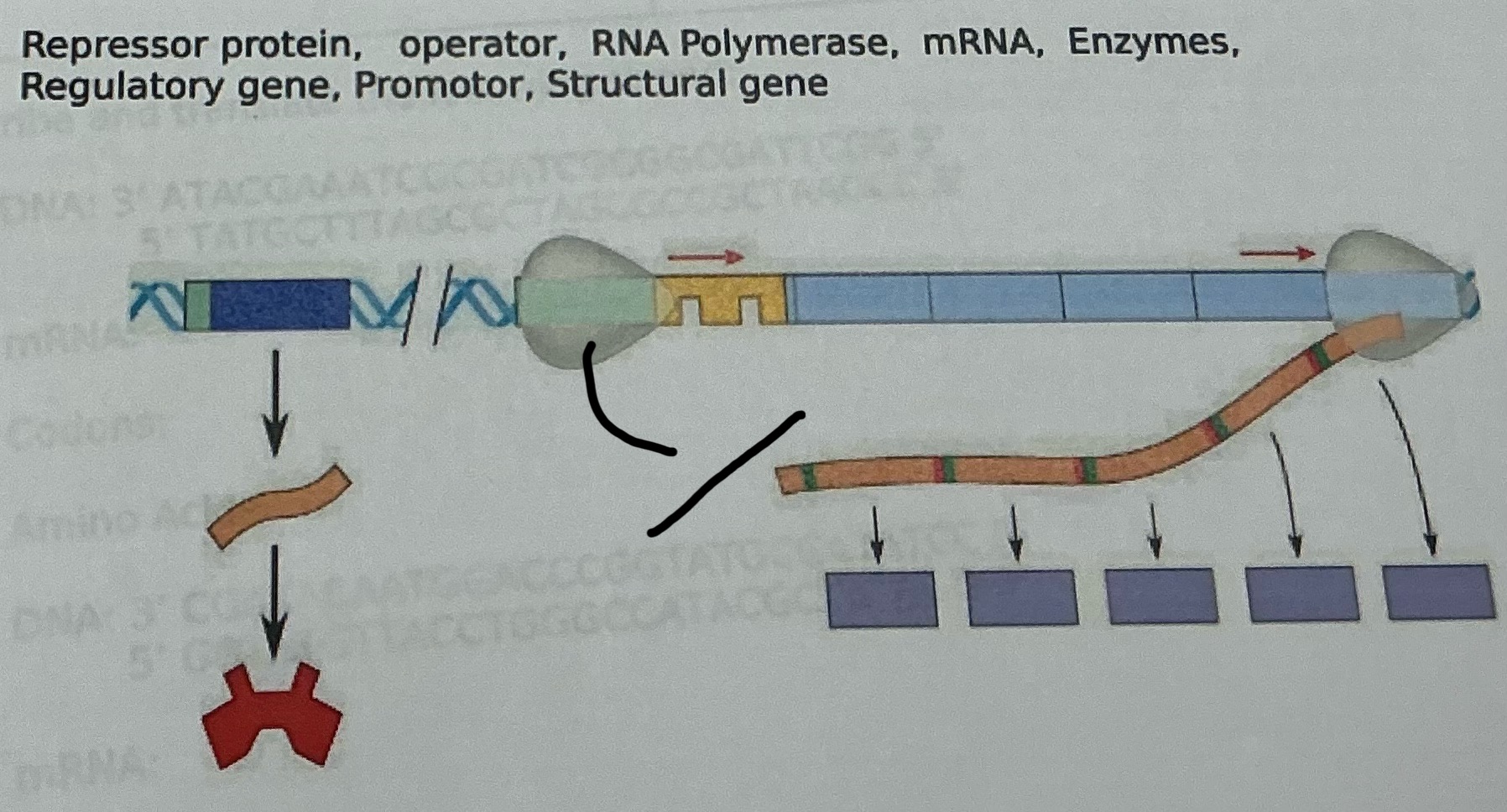
What is this
RNA polymerase
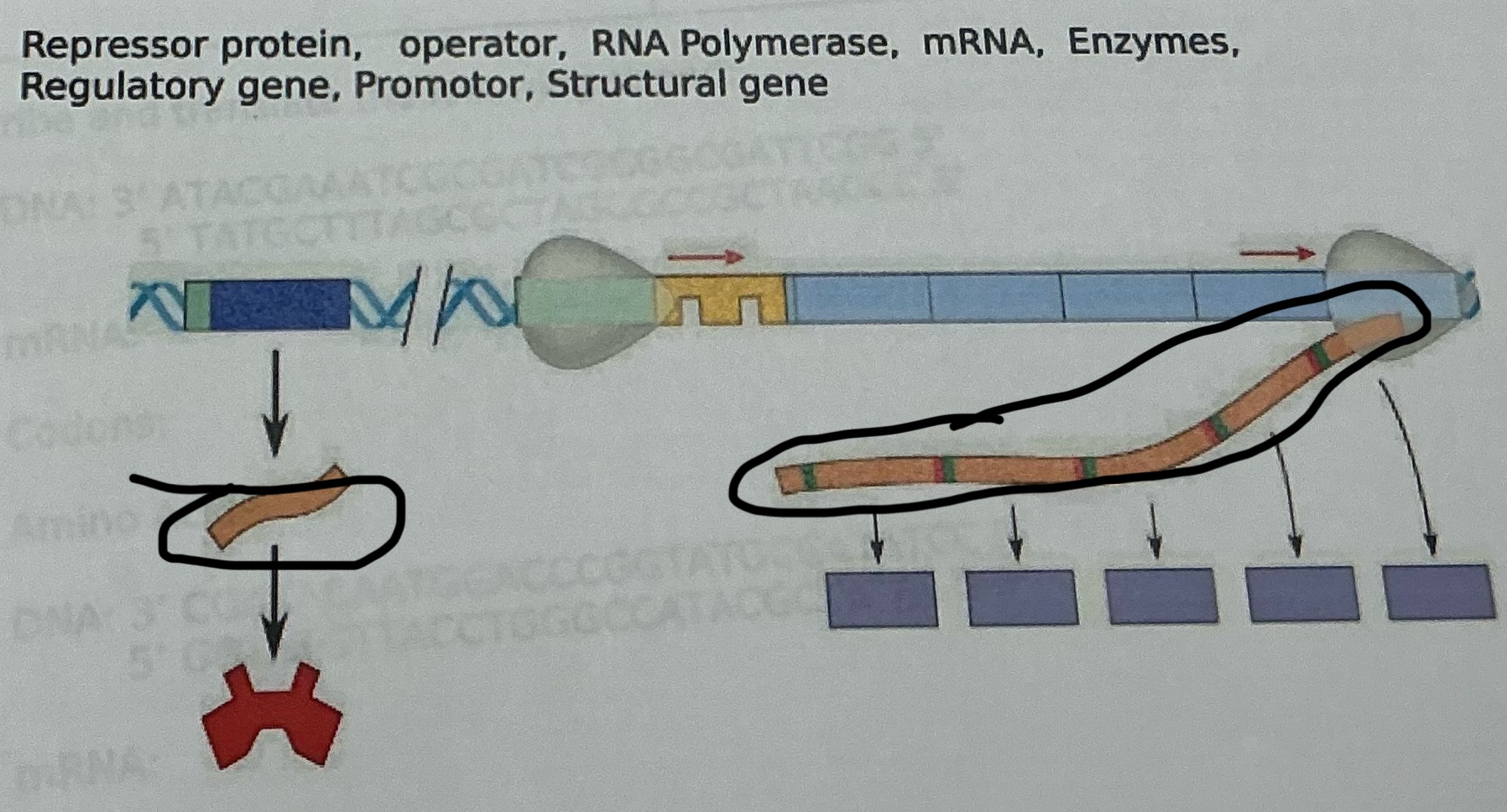
What is this
mRNA
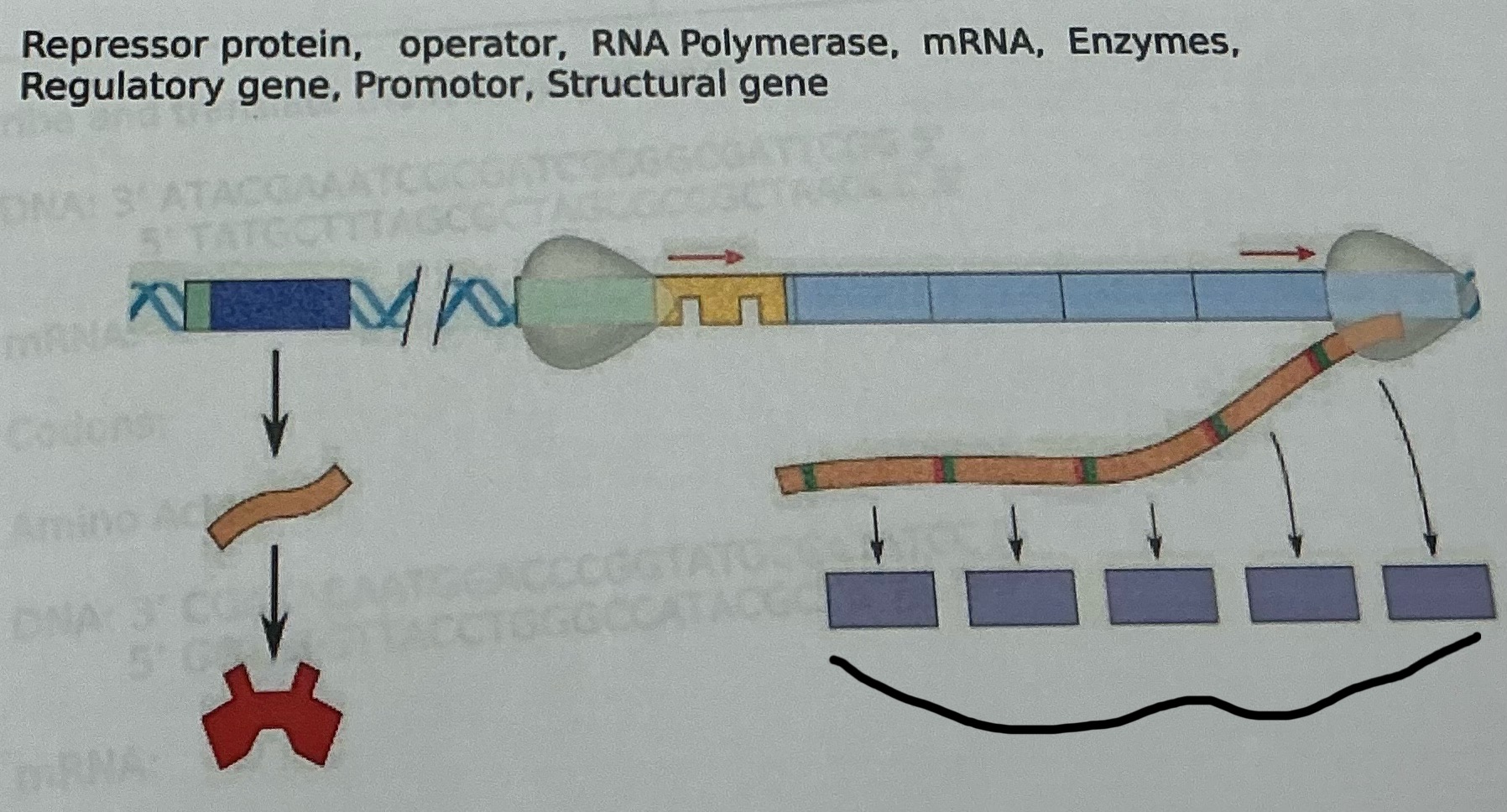
What is this
Enzymes
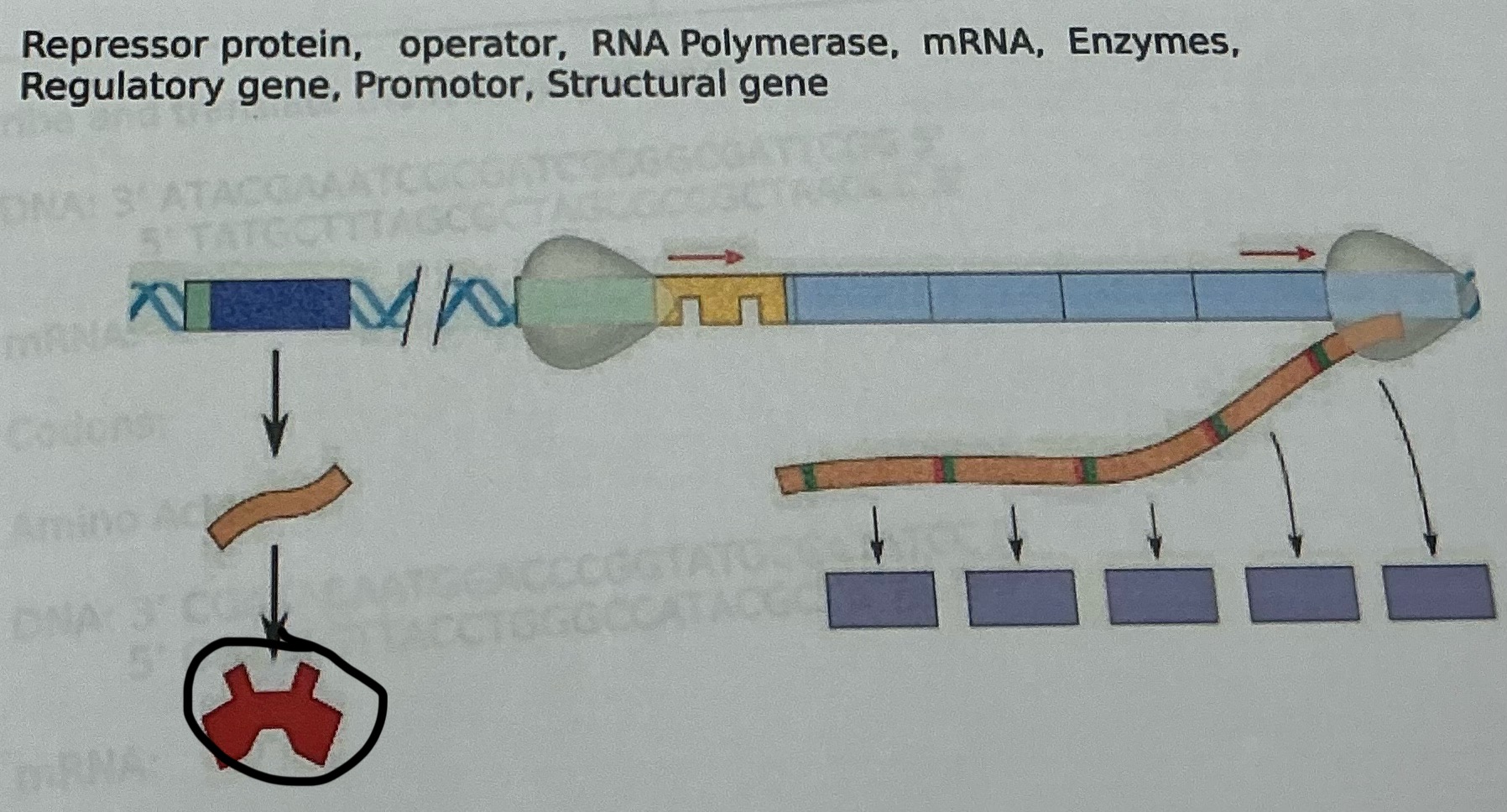
What is this
Repressor proten
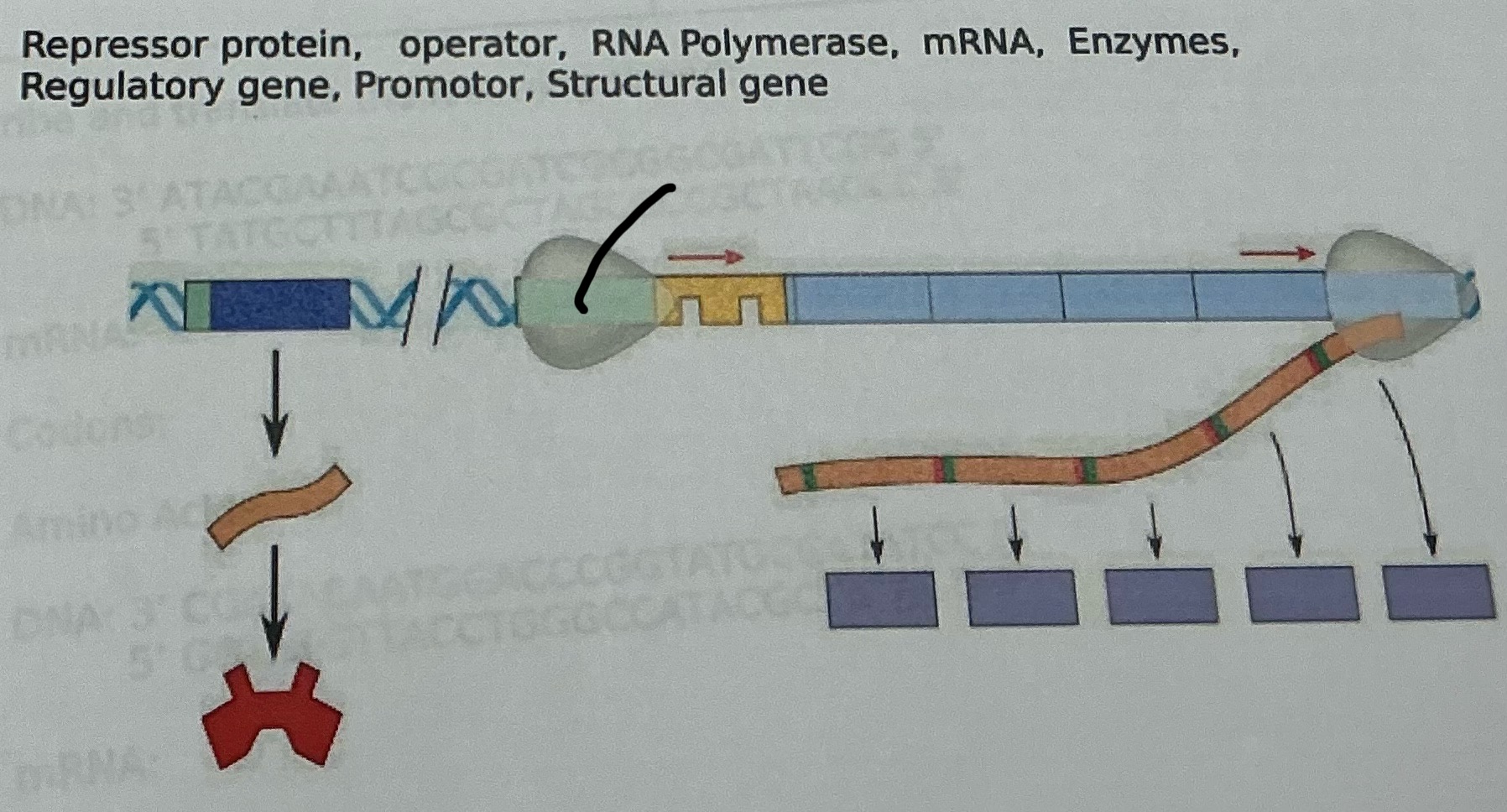
What is this
Promoter
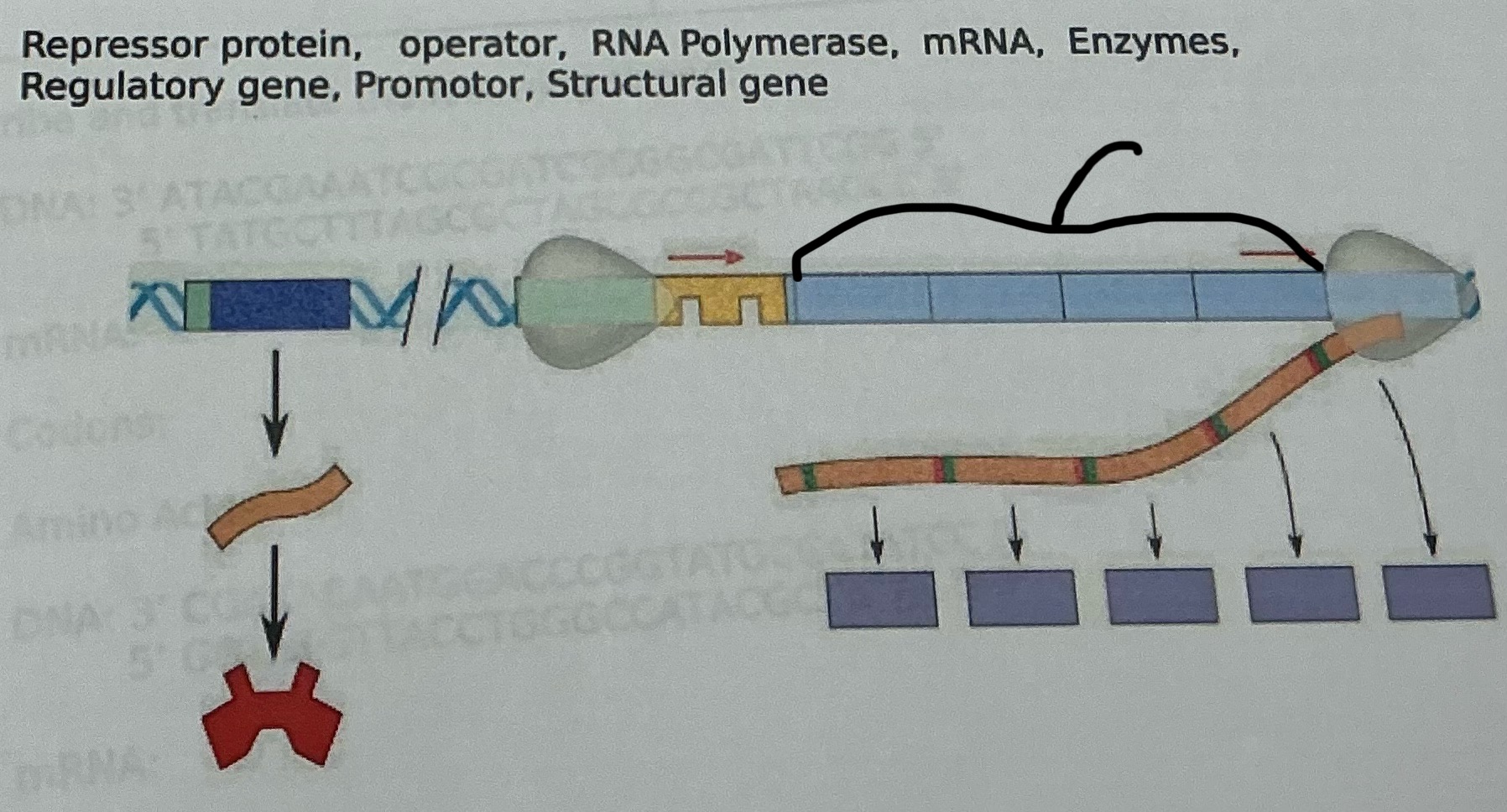
What is this
Structural gene
DNA
Promoter, structural gene, terminator, represor protein(regulatory gene), operon(prokaryotes),gene, RNA poly(DNA RNA where transcription stops)
RNA
Amino acid(tRNA), mRNA: intron, exon,RNA poly(DNA RNA where transcription stops)
Central Dogma
DNA to RNA to PRoteins
What is the central dogma of molecular biology for prokaryotes?
DNA → mRNA → Protein (no nucleus, no RNA processing).
What is the central dogma of molecular biology for eukaryotes?
DNA → pre-mRNA → mRNA → Protein (has nucleus, RNA processing).
What is transcription?
Synthesis of RNA using DNA as a template.
Where does transcription occur in prokaryotes?
Cytoplasm.
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotes?
Nucleus.
What are the requirements for transcription?
DNA template, RNA nucleotides, RNA polymerase, enzymes/proteins.
What is the first step of transcription?
Initiation: RNA polymerase binds promoter (TATA box); transcription factors help binding.
What happens during the elongation phase of transcription?
RNA polymerase moves 3'→5' on DNA, building RNA 5'→3'.
What is the termination sequence in eukaryotes?
AAUAAA.
What is RNA processing in eukaryotes?
Adding a 5' G-cap and a 3' poly-A tail, splicing out introns and keeping exons.
What role does snRNA play in RNA processing?
snRNA performs splicing.
How does transcription differ from DNA replication?
Uses RNA polymerase, only one DNA strand as a template, shorter segments, and makes RNA instead of DNA.
What is translation?
Assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide using mRNA instructions, occurring in the cytoplasm at the ribosome.
What are the main players in translation?
mRNA (message from DNA), tRNA (carries amino acids), and rRNA (makes up ribosome).
What are the steps of translation?
- Initiation: Small ribosomal subunit binds mRNA, finds AUG, tRNA brings methionine, large subunit binds. 2. Elongation: tRNA adds amino acids; peptide bonds form. 3. Termination: Stop codon triggers release of polypeptide and detachment of ribosome.
What are the ribosome sites and their functions?
A site: tRNA entry, P site: peptide bond formation, E site: exit of empty tRNA.
What is the structure of an amino acid?
Amino group (NH₂), carboxyl group (COOH), central carbon, hydrogen, and R-group (side chain).
How many amino acids are there?
20 amino acids, all sharing a backbone but differing in R-groups.
What are the categories of amino acids?
Nonpolar (hydrophobic), Polar (hydrophilic), Acidic, Basic.
What are the levels of protein structure?
- Primary: Amino acid sequence. 2. Secondary: α-helix/β-sheet. 3. Tertiary: 3D folding. 4. Quaternary: Multiple polypeptides combine.
How is protein function determined?
By its shape, which is determined by the amino acid order, which is in turn determined by the DNA sequence.
What is gene expression?
The process of turning genes on/off to make RNA/protein.
What is an operon?
A group of genes in prokaryotes that are regulated together, consisting of a promoter, operator, structural genes, and a regulatory gene.
What is the Lac Operon?
An inducible operon that is off by default but turns on when lactose is present.
What is the Trp Operon?
A repressible operon that is on by default but turns off when tryptophan is present.
What is euchromatin?
Loose chromatin that is transcriptionally active.
What is heterochromatin?
Condensed chromatin that is transcriptionally inactive.
What are epigenetic tags?
Chemical modifications to DNA that affect gene expression, such as acetylation (activating) and methylation (silencing).
What is RNA interference (RNAi)?
A process that destroys faulty mRNA or blocks ribosomes to silence genes.
What is a codon?
A 3-nucleotide mRNA sequence that codes for an amino acid.
What is an anticodon?
A complementary 3-base sequence on tRNA that pairs with the codon.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA has deoxyribose sugar, thymine base, and is double-stranded; RNA has ribose sugar, uracil base, and is single-stranded.
What are silent mutations?
Mutations that do not change the amino acid due to redundancy in the genetic code.
What is the structure of a virus?
Composed of a genome (DNA or RNA), a capsid (protein coat), and optionally an envelope (lipid membrane).
What are the two life cycles of viruses?
Lytic cycle (virus replicates and bursts the cell) and lysogenic cycle (viral DNA integrates into host genome).
What is a retrovirus?
A virus that uses reverse transcriptase to convert RNA into DNA and integrate it into the host genome.
What is the purpose of vaccines?
To introduce a harmless virus or viral piece to stimulate the immune system to build memory.