Chapter 2.1-2.2-2.3 - Dissolving & Solubility & Chromatography - Year 8 2023
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a solute?
A solid, smaller part that dissolves.
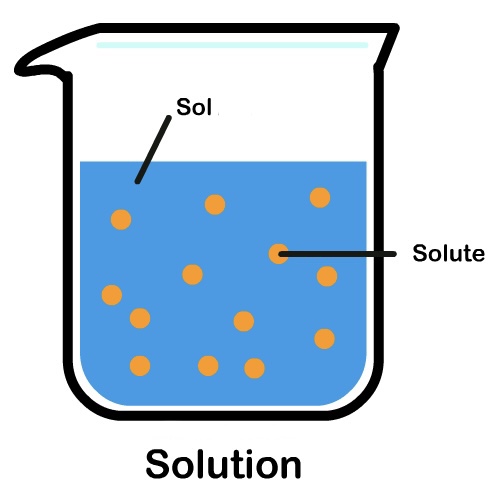
What is a solvent?
A liquid, which is the bigger part, and does the dissolving.
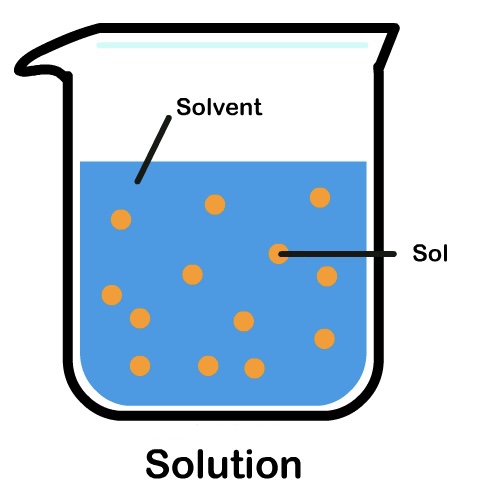
What is the universal solvent?
Water

What is a solution?
A colourless or transparent homogenous mixture made from a solute and a solvent.

Solubility
The ability of a solute to dissolve in a solvent.

Transparent
You can see through something.

Opaque
You can’t see through something.

Melting
1 substance
Change of state
Change of energy

Dissolving
2 or more substances
Creates solution or mixture
Particles evenly distributed

Law of Conservation
Mass of solution = mass of solute + mass of solvent
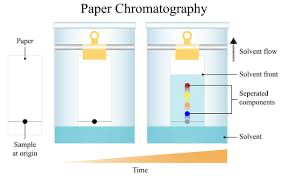
What is chromatography?
technique used to separate mixtures into component’s molecules

Why do molecules move up the paper at different rates?
→ solubility
→ molecular mass
→hydrogen bond with paper

What does pure mean?
When only 1 spot is produced on the chromatograph.

What does impure mean?
When 2 or more spots are produced on the chromatograph.

What is a chromatograph?
Machine that helps scientist separate and analyse different substances to see if it’s a mixture or a pure substance.
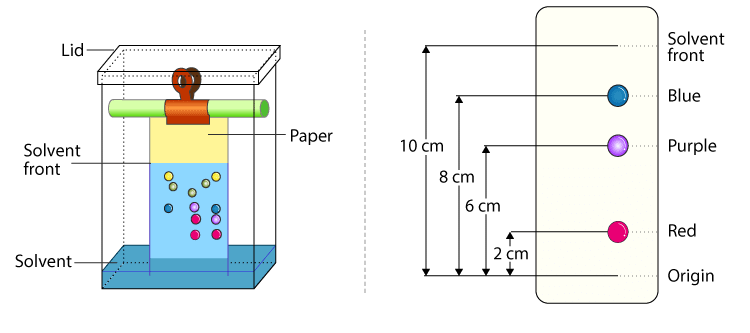
What is a chromatogram?
It’s a colourful graph showing the end result of an analysis which shows all the substances which make up a mixture.
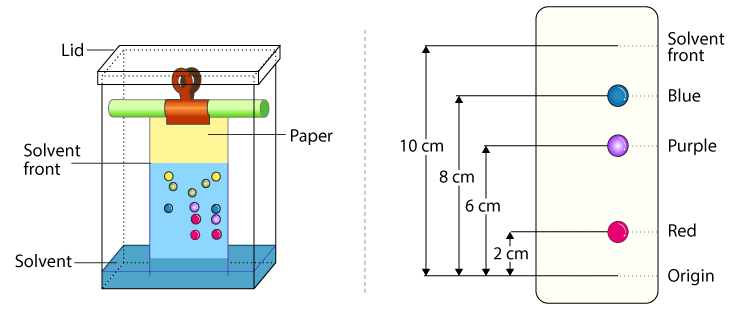
What is the stationary phase in chromatography?
When there’s just paper in the jar.

What is a mobile phase?
When there is water in the jar where your doing paper chromatography.
What is a solvent front?
The furthest point where the solvent in its mobile phase has traveled.
