Human Bio Lab Exam 1
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SU25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Cell (plasma) membrane
Separates the inside of the cell from its outside environment
Nucleus
Houses DNA, called chromatin
Ribosomes
Found in cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER; sites of protein synthesis (makes protein)
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Protein synthesis due to presence of ribosomes; packages proteins into vesicles (has ribosomes on it)
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Lipid synthesis
Golgi apparatus
Modification of products from rough endoplasmic reticulum (packages)
Secretory vesicles
Membrane-bound sacs that house products for secretion from cell (transports)
Mitochondria
Site of ATP production
Fat vacuole
stores fat
Lysosomes
Specialized vesicles containing digestive enzymes for waste removal (digestive)
Centrioles
Control movement of chromosomes during mitosis (aids or helps cell division)
Interphase
looks like a normal cell; most cells you see will be in interphase 90% normal
Prophase 1st
Chromatin begins to condense into chromosomes, which become visible as dark structures in the middle of the cell
Metaphase 2nd
Chromosomes are aligned in center of cell
Anaphase 3rd
Daughter chromosomes are being pulled towards opposite poles
Telophase 4th
The process of cytokinesis is first evident by appearance of a cleavage furrow.
Daughter cells/ Interphase 5th last
The process of cytokinesis is complete; there are now two separate cells.
Epithelial tissues
coverings or linings of hollow organs. This tissue is in contact with either the external environment or the fluids in the internal environment. For example, food touches epithelial tissue in your mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach and intestine. The same is true for urine, blood, etc.
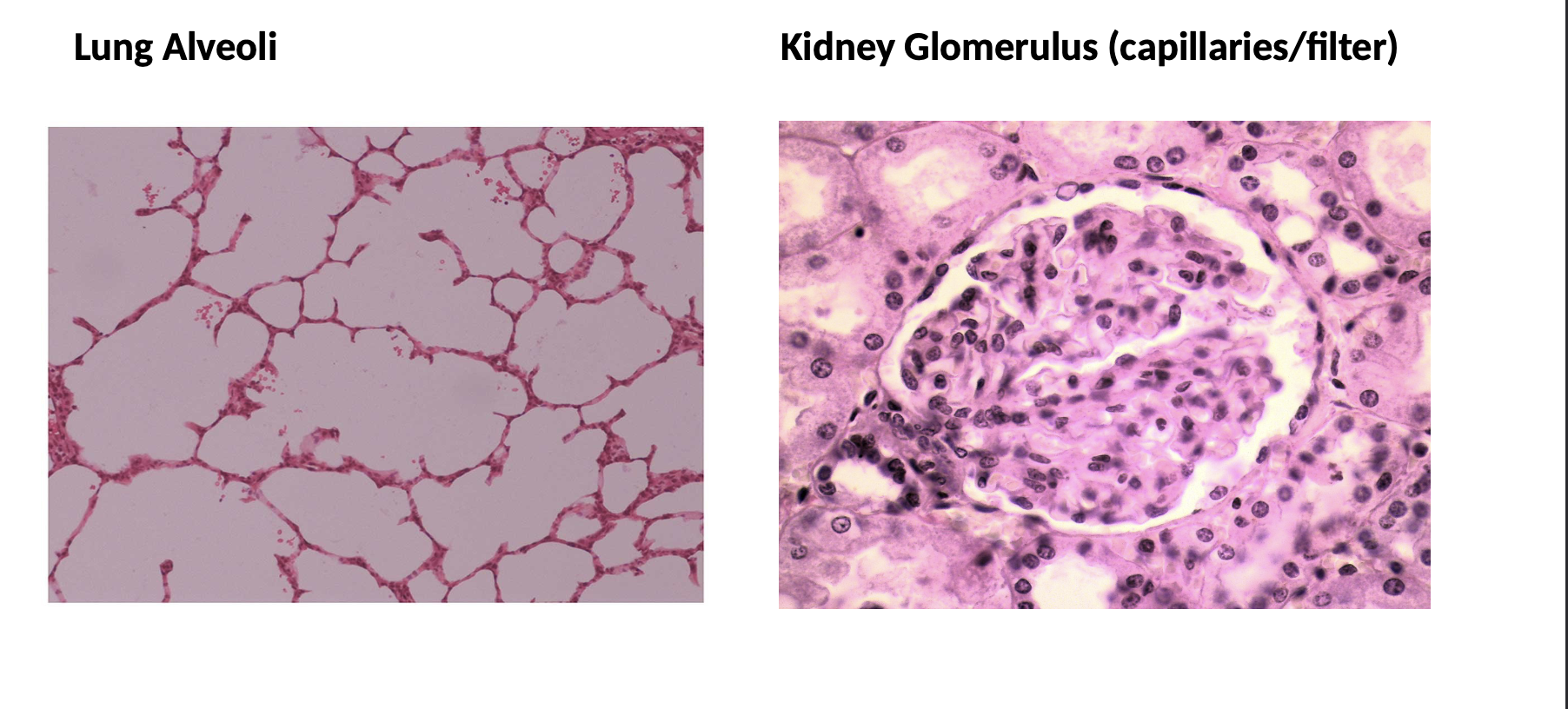
Simple squamous
Look for the cheek (a top down view of individual squamous cells) or lung alveoli (a side view) slide
One layer of flat, thin cells
Function: diffusion and filtration
Locations: lung alveoli, kidney glomerulus, capillary walls
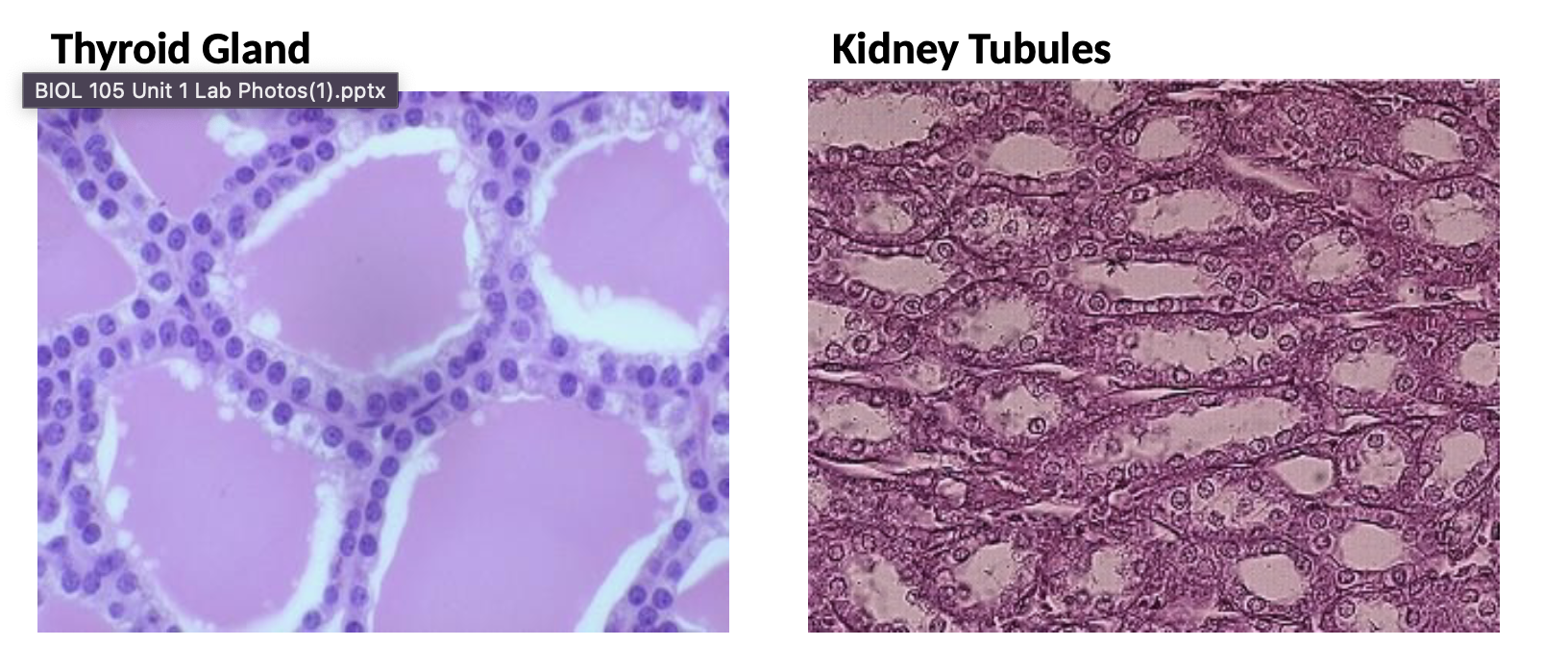
Simple cuboidal
Look for the thyroid or kidney (tubule) slide
One layer of squarish cells
Function: secretion and some absorption
Location: any secretory gland (e.g. sebaceous glands and sweat glands in the skin), kidney tubules and other ducts
Simple columnar
Look for the jejunum slide
One layer of tall, rectangular-like cells
Look for goblet cells that secrete mucus
Function: absorption or secretion
Location: lining of small intestine, vas deferens and other high pressure ducts
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Look for the trachea slide
One layer of mostly rectangular-like cells. But, because the nuclei are at all different heights and not all the cells reach the free surface, this looks like more than one layer of cells.
Function: protection, removal of foreign material
Location: nasal cavities & sinuses, pharynx, trachea, & bronchi of lungs
Look for goblet cells here too
Look for cilia on the free surface. These are "hair-like" projections that sweep mucus and dirt along these cells.
Stratified squamous
Look for the thick skin slide, esophagus slide, or anus slide
Many layers of flat, thin cells stacked on top of each other
Function: protection against abrasion
Location: epidermis, oropharynx (throat), anal canal
Connective tissues
this group of tissues is probably the most diverse group, but there is one main unifying feature: the presence of a matrix. The matrix is material that separates the cells from each other. Unlike epithelial tissues where the cells are put together like a brick wall or path, connective tissue cells are unevenly spaced and have matrix in between.
In this way, the connective tissues are more like a stone path where grass (matrix) grows in between the stones (cells). The matrix can be solid (e.g. bone), semi-solid (e.g. cartilage) or liquid (e.g. blood).
Areolar connective tissue (collagen)
Function: attach one tissue/organ to another, separates muscles
Location: under skin, surrounding vessels, glands, muscles & nerves
Adipose (fat)
Function: this is fat-it is for energy storage and insulation under skin and cushioning around organs (padding)
Location: under skin, around heart, kidneys, eyes, hips, breast
Dense regular connective tissue (White Fibrous c.t. slide)
Parallel rows of collagen fibers with very small fibroblasts
Function: connection of two structures together, for example tendons and ligaments (Strong connections)
Location: tendons, ligaments,Hyaline cartilage
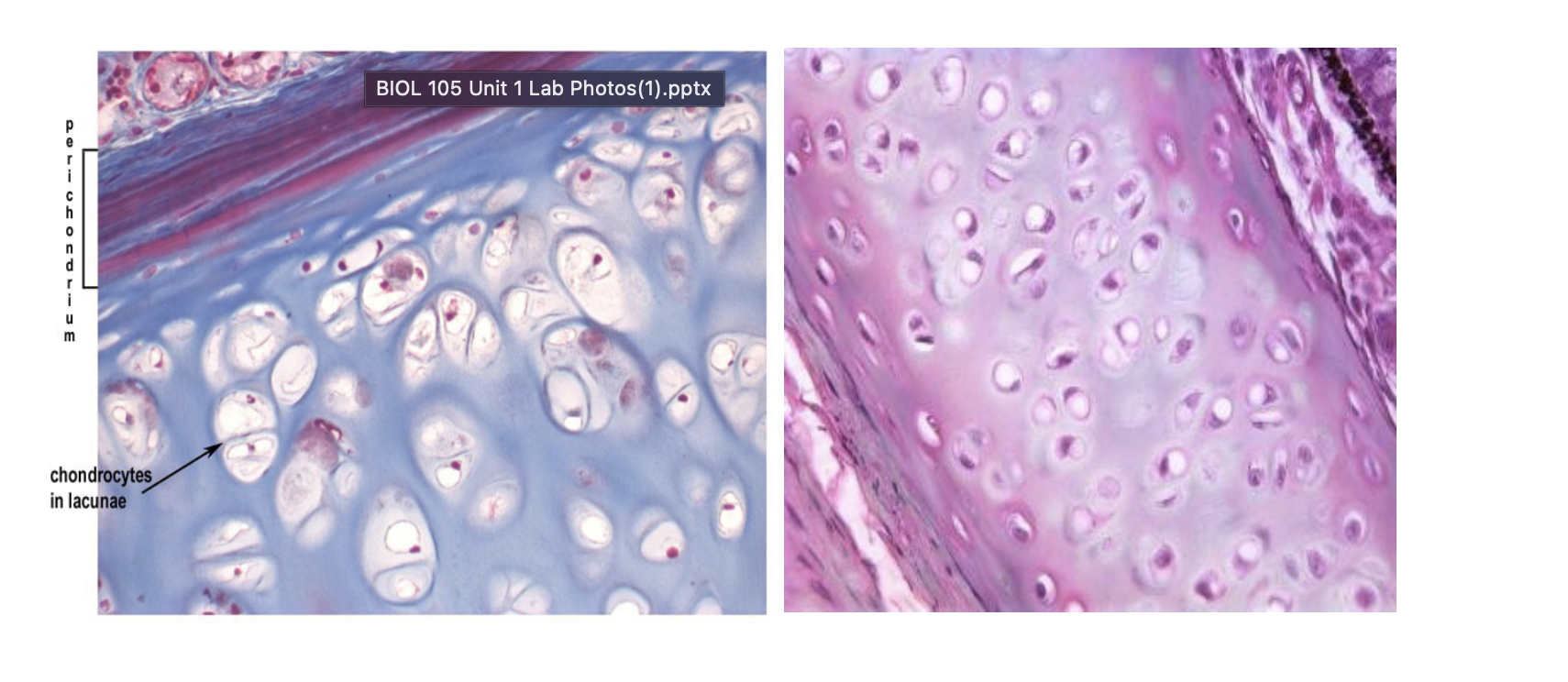
Hyaline cartilage
All cartilages have the same basic appearance. The differentiation is with subtle variations in the matrix, size of cell spaces (lacunae).
Hyaline cartilage has the matrix most homogenous in appearance and midsized lacunae
Function: support
Location: costal (rib) cartilage, end of nose
Elastic cartilage
____ cartilage has very obvious dark staining elastic fibers in the matrix, large lacunae
Function: provide flexible support
Location: outer ear, epiglottis in larynx
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage has the smallest lacunae that are widely spaced apart.
Function: support, (padding, protection)
Location: intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis,
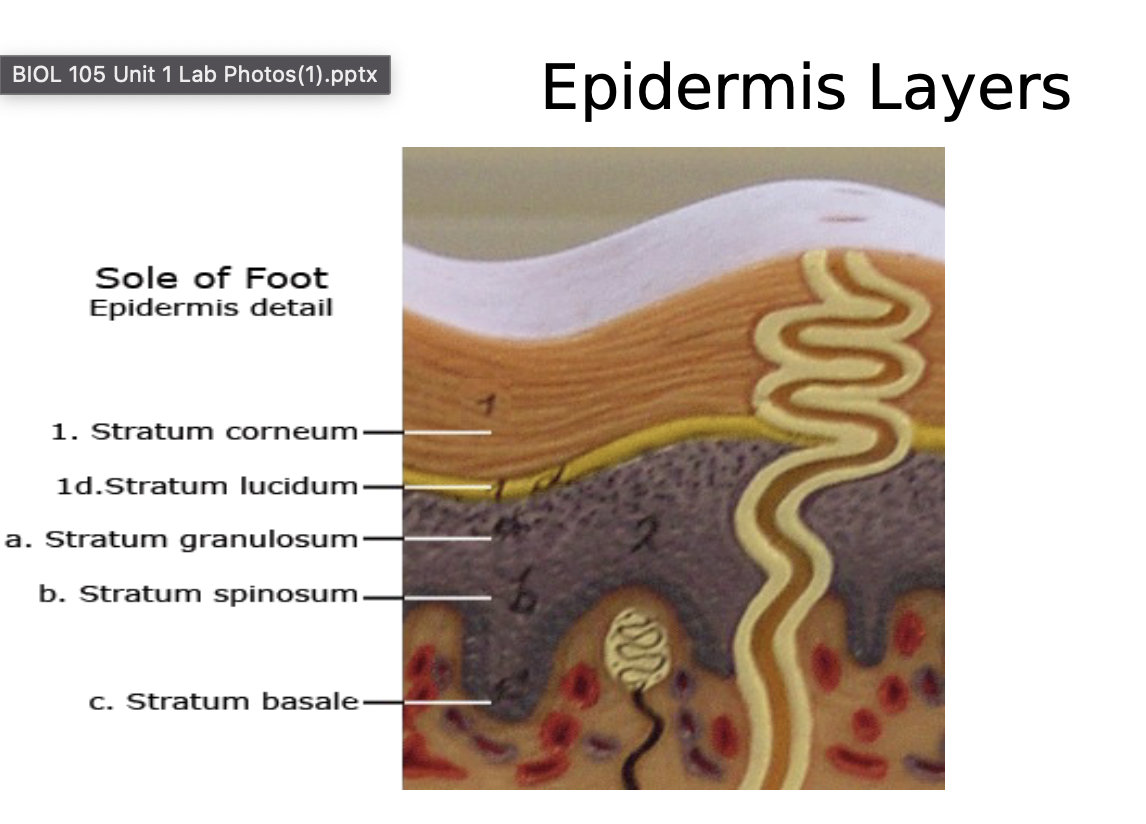
Skin Model
is the first organ system of the body we will study. It is an organ system because there is more than one organ type present. Several of the specialized skin structures you'll study are organs because there is more than one tissue type present. For example, some of the touch receptors we look at have both connective and nervous tissue, which qualifies it as an organ. We will also look at two types of skin: thin (scalp) and thick (sole of foot, or palm). The significance is that, in each case, the outermost layer (the epidermis) is stratified squamous epithelial, but individual layers of stratified squamous cells are only visible in the thick skin.
Epidermis layers
skin models show an enhanced view of the individual layers of the epidermis
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
Dermis layer
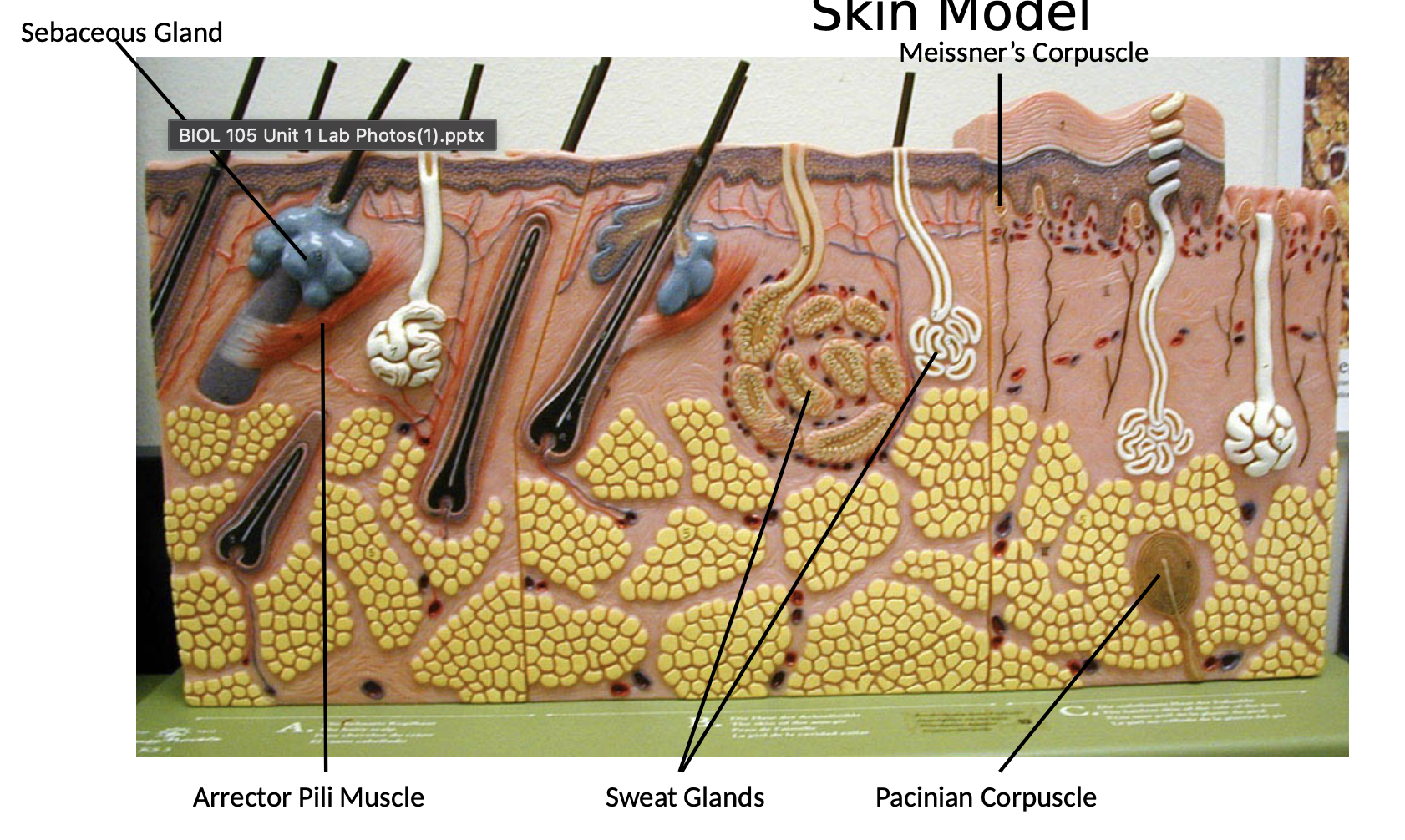
Pacinian/pressure corpuscle
Meissner's/touch corpuscle
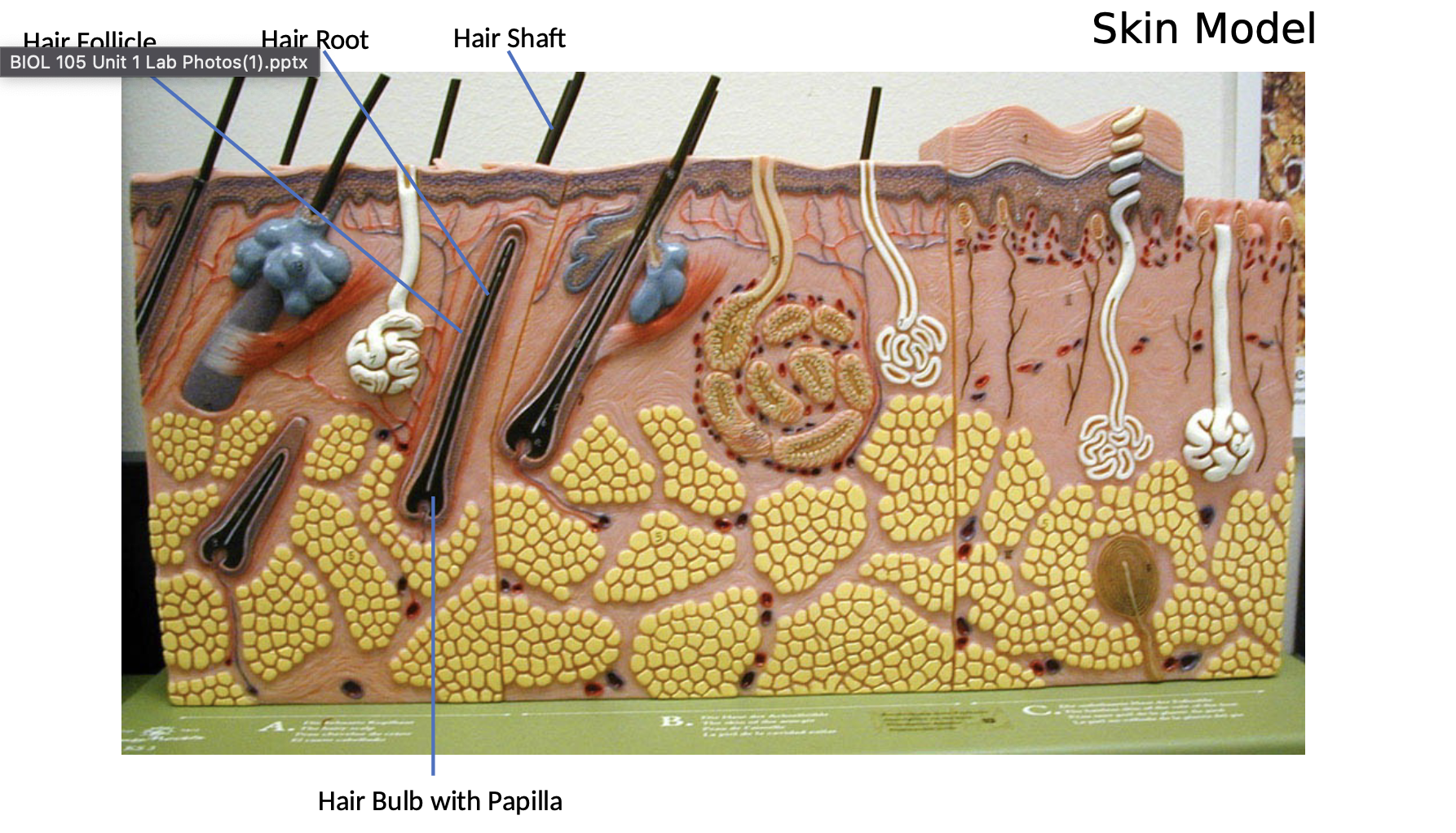
Hair follicle
hair shaft o hair root
o hair bulb containing hair papilla
Arrector pili muscle
Sweat gland (both types)
Sebaceous gland
Hypodermis (subcutaneous) layer
adipose tissue
Simple Squamous: Other Locations
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Adipose (connective) Tissue
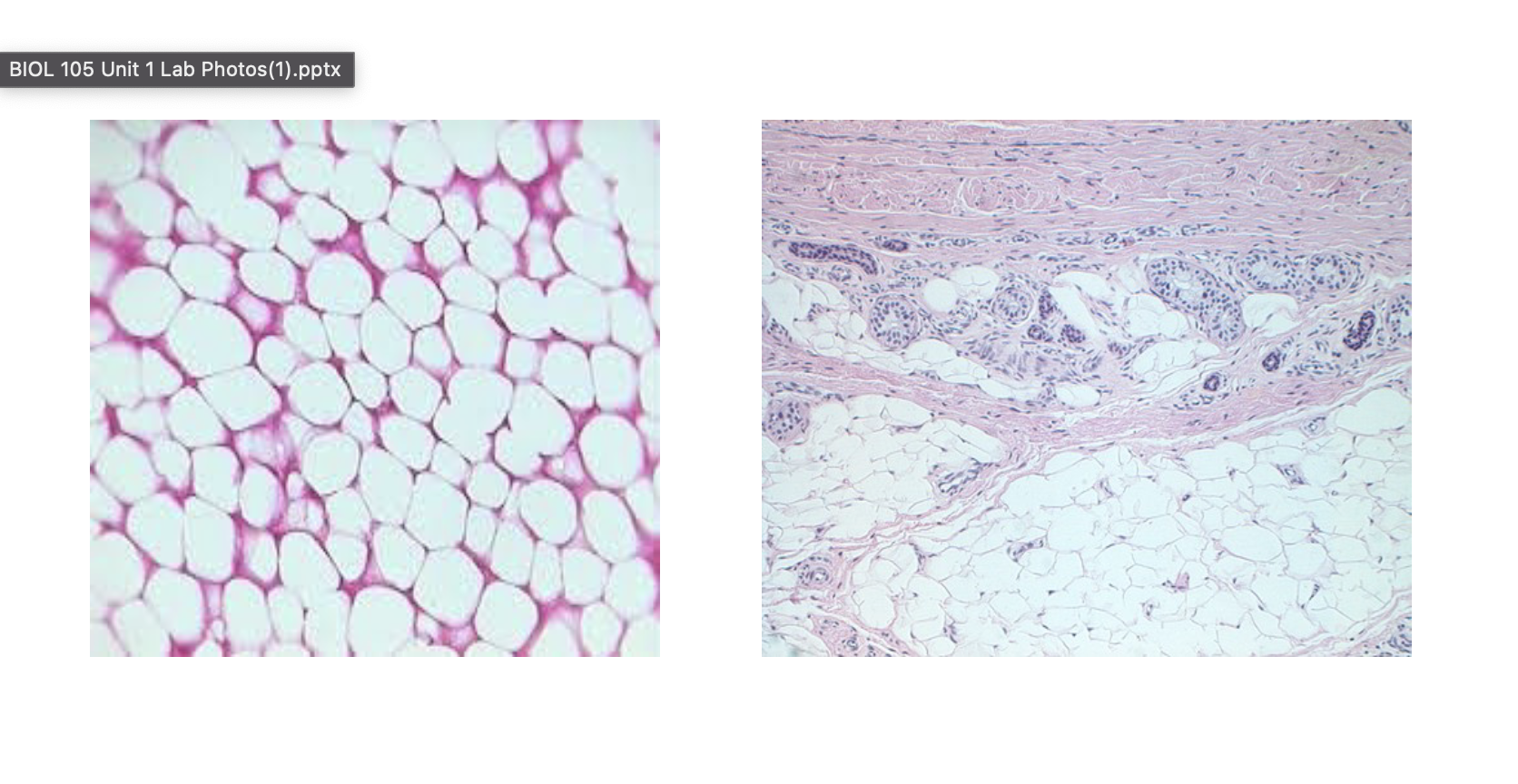
Dense Regular Connective Tissue

Hyaline Cartilage
memorize
memorize
memorize