Final Business Flashcards
1/313
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
314 Terms
What is the primary focus of Taylor's theory of scientific management?
Studying workers to find the most efficient ways of doing things and teaching those techniques.
What significant finding came from the Hawthorne studies?
Productivity increased regardless of light conditions, indicating a psychological factor at play.
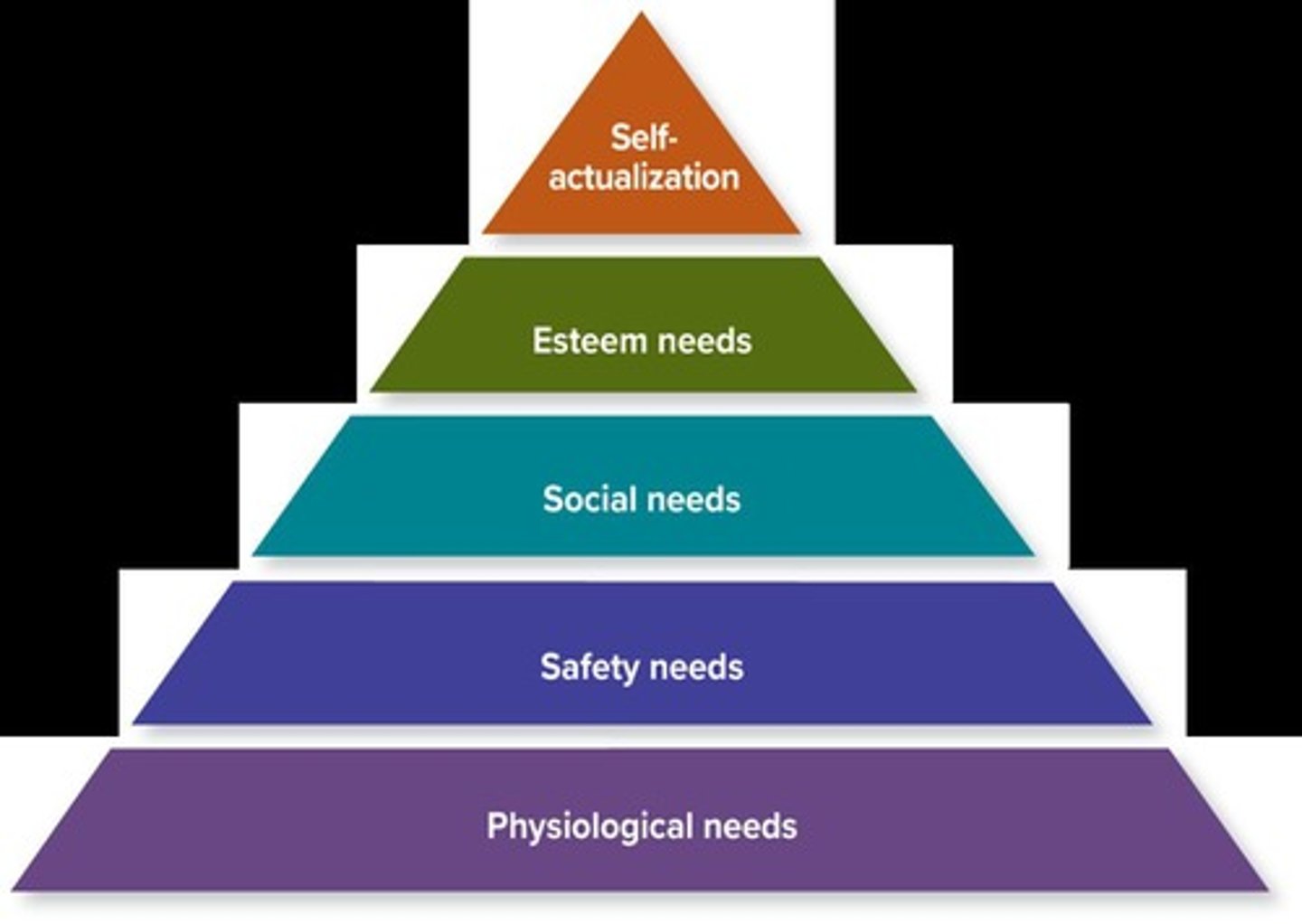
What are the levels of Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
Physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs.
What distinguishes motivators from hygiene factors according to Herzberg?
Motivators lead to job satisfaction and productivity, while hygiene factors prevent dissatisfaction but do not motivate.
What is the essence of McGregor's Theory X?
It assumes that employees are inherently lazy and require close supervision.
What does McGregor's Theory Y propose about employees?
It suggests that employees are self-motivated and thrive on responsibility.
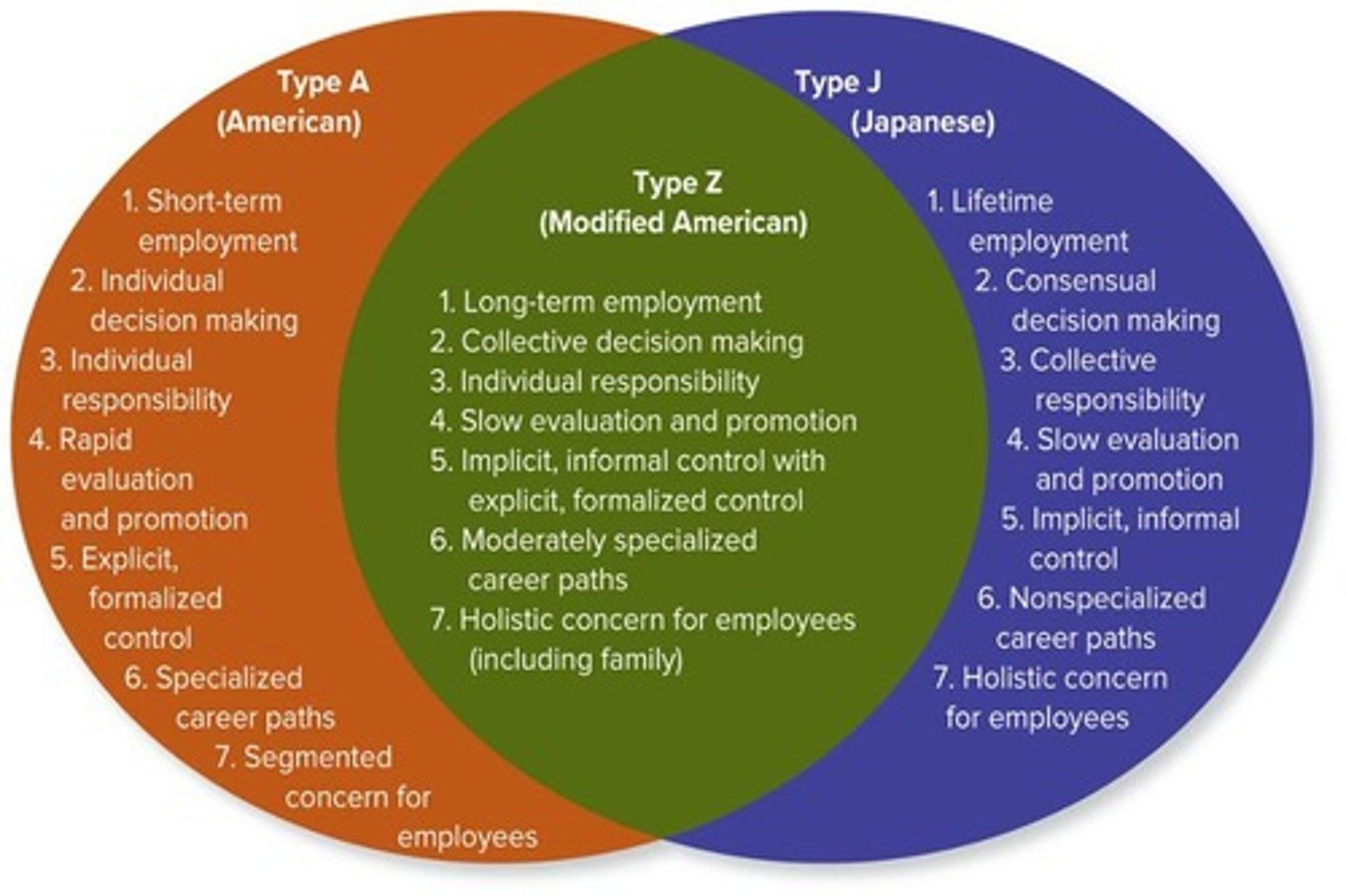
What is Ouchi's Theory Z?
A management philosophy that emphasizes employee involvement and a strong company culture.
What are intrinsic rewards?
Personal satisfaction and pride in one's performance and achievements.
What are extrinsic rewards?
Recognition given by others, such as pay raises, praise, and promotions.
What is employee engagement?
The level of motivation, passion, and commitment an employee has towards their work.
What is the Hawthorne effect?
The tendency for people to change their behavior when they know they are being observed.
What are the four key principles of Taylor's scientific management?
1) Study how a job is performed; 2) Codify the best method into rules; 3) Choose workers whose skills match the rules; 4) Establish a fair level of performance and pay.
What is the purpose of time-motion studies?
To analyze tasks and the time required to complete them for efficiency.
What is the significance of Herzberg's research?
It identified job content factors as crucial for worker enthusiasm and productivity.
What is the difference between job content factors and job environment factors?
Job content factors motivate employees, while job environment factors maintain satisfaction but do not motivate.
How can managers apply motivation theories in practice?
Through strategies like job enrichment, open communication, and job recognition.
What is the role of employee experience in motivation?
It reflects the level of satisfaction at every step of an employee's journey within a company.
What is the significance of personalizing motivation strategies?
To appeal to diverse employees across different cultures and generations.
What is the impact of happy workers on a business?
Happy workers can lead to happy customers and successful businesses.
What are some strategies to help with workplace stress?
Reaching out for support, consulting a therapist, exercising, eating healthy, and planning regular breaks.
What is the importance of fair treatment in employee motivation?
Fair treatment fosters trust and encourages employee engagement and productivity.
What is the relationship between unmet needs and motivation according to Maslow?
Motivation arises from unmet needs; once a need is satisfied, a higher-level need emerges.
How do intrinsic and extrinsic rewards differ?
Intrinsic rewards are internal feelings of satisfaction, while extrinsic rewards are external recognitions from others.
What did the Hawthorne studies reveal about employee behavior?
Employees behave differently when they feel involved in their work and are being studied.
What is the concept of job enrichment?
Enhancing a job by adding more meaningful tasks to increase employee motivation.
What are the two types of factors in Herzberg's theory?
Motivators and hygiene factors.
What does Herzberg's hygiene factors refer to?
Factors that can cause dissatisfaction but changing them will have little motivational effect.
List some examples of hygiene factors.
Company policy, supervision, working conditions, salary, status, and job security.
What are some examples of motivators according to Herzberg?
Achievement, recognition, responsibility, growth, and advancement.
What is McGregor's Theory X?
Assumes that people are naturally unmotivated, avoid responsibility, and require close supervision.
What is McGregor's Theory Y?
Assumes that people are inherently motivated, capable, and eager to contribute when given the right environment.
What is the primary motivator in Theory X?
Fear and punishment.
What is the primary motivator in Theory Y?
A variety of rewards, including intrinsic motivation.
What are the characteristics of Theory Z?
Focuses on culture, loyalty, and long-term development.
What is Goal-Setting Theory?
The idea that setting ambitious but attainable goals can motivate workers and improve performance.
What are the conditions for effective goal-setting?
Goals must be accepted, accompanied by feedback, and facilitated by organizational conditions.
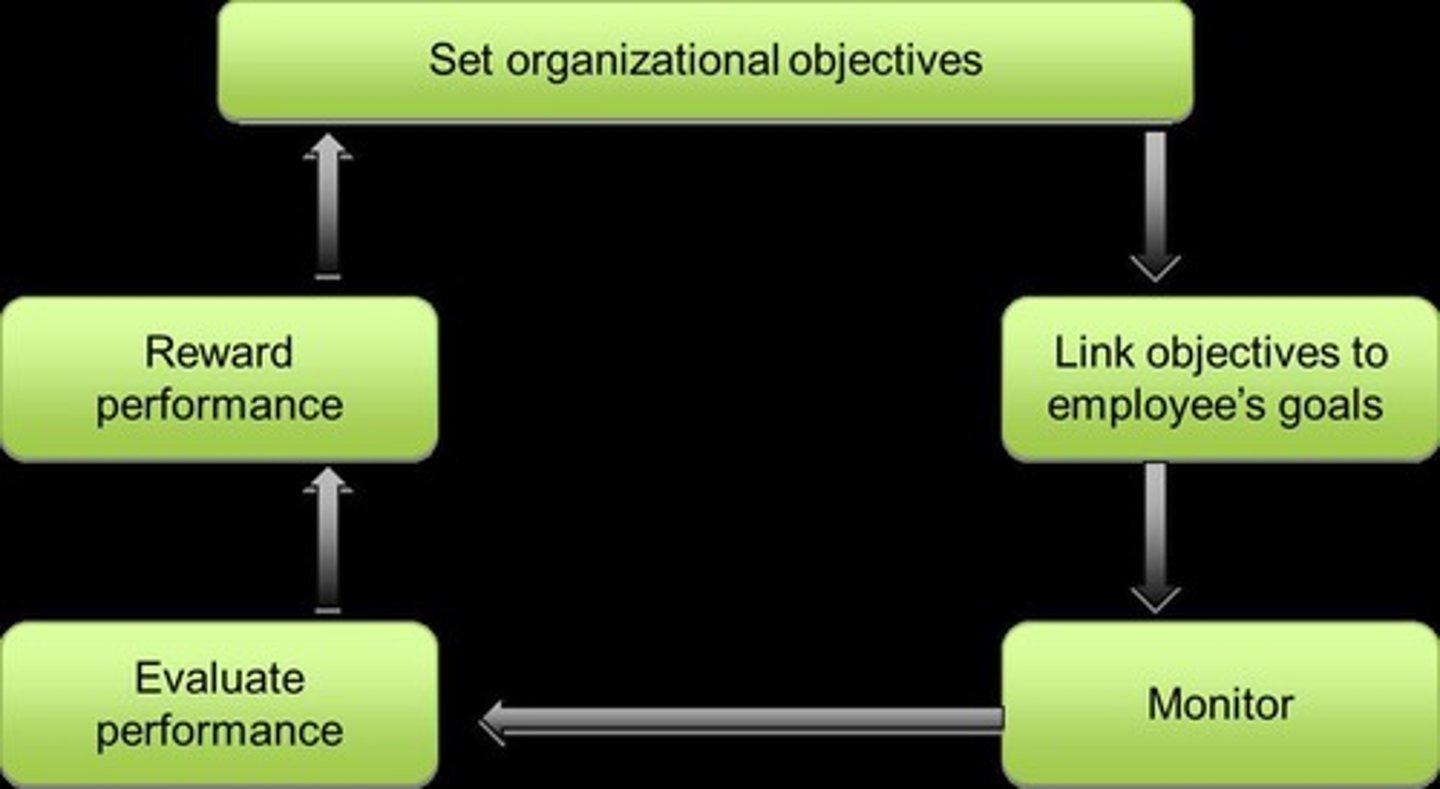
What is Management by Objectives (MBO)?
A cycle of discussion, review, and evaluation of objectives among managers and employees.
What does Expectancy Theory state?
The amount of effort employees exert depends on their expectations of the outcome.
What are the three questions employees ask according to Expectancy Theory?
Can I accomplish the task? What's my reward? Is the reward worth the effort?
What are Nadler and Lawler's Five Steps to Improve Employee Performance?
1. Determine what rewards employees value. 2. Learn each employee's performance standard. 3. Ensure performance standards are attainable. 4. Guarantee rewards tied to performance. 5. Ensure rewards are considered adequate.
What is Equity Theory?
The idea that employees try to maintain equity between inputs and outputs compared to others in similar positions.
What can perceived inequities lead to?
Lower productivity, reduced quality, increased absenteeism, and even resignation.
What is the impact of employee involvement in Theory Z?
It is key to increased productivity.
How do Theory X managers view their employees?
As individuals who dislike work and need to be controlled.
How do Theory Y managers view their employees?
As individuals who view work as a natural part of life and seek responsibility.
What is the role of feedback in Goal-Setting Theory?
Feedback is essential for motivating workers and improving performance.
What is the significance of employee control in Theory Z?
Control is implied and informal, fostering trust and cooperation.
What is the effect of a non-intimidating work environment according to Theory Y?
Employees perform better in such environments.
What does Herzberg's theory suggest about job satisfaction?
Job satisfaction is influenced by motivators, while dissatisfaction is influenced by hygiene factors.
What is the relationship between motivation and performance in Expectancy Theory?
Motivation is linked to the belief that effort will lead to desired performance and rewards.
What can perceived inequities lead to in the workplace?
Lower productivity, reduced quality, increased absenteeism, and even resignation.
Briefly describe Theory X.
Theory X assumes that employees are inherently lazy and require strict supervision.
Briefly describe Theory Y.
Theory Y posits that employees are self-motivated and thrive on responsibility.
Briefly describe Theory Z.
Theory Z emphasizes a holistic approach to management, focusing on employee involvement and long-term employment.
What does goal-setting theory emphasize?
The importance of setting specific and challenging goals to enhance motivation and performance.
What is expectancy theory?
A theory that suggests individuals are motivated to act based on the expected outcomes of their efforts.

What are the principles of equity theory?
Equity theory states that employees are motivated by fairness in the workplace, comparing their input-output ratio to others.
What is job enrichment?
A motivational strategy that emphasizes motivating the worker through the job itself, based on Herzberg's motivators.
Name one of the five characteristics of work that affect motivation.
Skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, or feedback.
What is job enlargement?
A job enrichment strategy that involves combining a series of tasks into one challenging and interesting assignment.
What is job rotation?
A job enrichment strategy that involves moving employees from one job to another.
How can open communication motivate employees?
By creating an organizational culture that rewards listening and encourages effective communication.
What are some ways to recognize a job well done?
Advancement opportunities, challenging work, public recognition, paid time off, and flexible schedules.
How can AI be used to improve employee engagement?
AI can monitor employee-manager interactions to evaluate conversations and identify issues before they lead to employee turnover.
What challenges do global managers face in motivating employees?
Cultural differences that affect worker motivation, requiring flexibility and cultural awareness.
What are the characteristics of Baby Boomers in the workplace?
They experienced economic prosperity and job security, leading to optimism about their future.
What defines Generation X in the workplace?
They prioritize career security over job security and are effective at collaboration and feedback.
What traits are associated with Millennials in the workplace?
They are tech-savvy, value work-life balance, and seek fun and stimulation in their jobs.
What defines Generation Z's approach to work?
They are cautious, security-minded, tech-savvy, and want to improve the world through their work.
What communication preferences do Baby Boomers have?
They prefer meetings and conference calls.
What communication style do Millennials prefer?
They prefer using technology, particularly social media, for communication.
What is a key principle for managers when communicating across generations?
Understanding that different generations have varying communication preferences.
What are some steps firms can take to increase internal communications?
Communicate often, acknowledge team milestones, and be flexible with scheduling.
Why is it important to adjust motivational styles to individual employees?
To effectively meet the diverse needs and preferences of employees for better engagement.
What are the four functions of management?
Planning, Organizing, Leading, Controlling.
What is the primary role of managers today?
To be collaborative and emphasize team building.
What does planning in management involve?
Setting organizational goals, developing strategies, determining resources, and setting standards.
How do managers empower employees?
By giving them independence to make informed decisions.
What is the difference between leaders and managers?
Leaders inspire and motivate, while managers focus on organizing and controlling tasks.
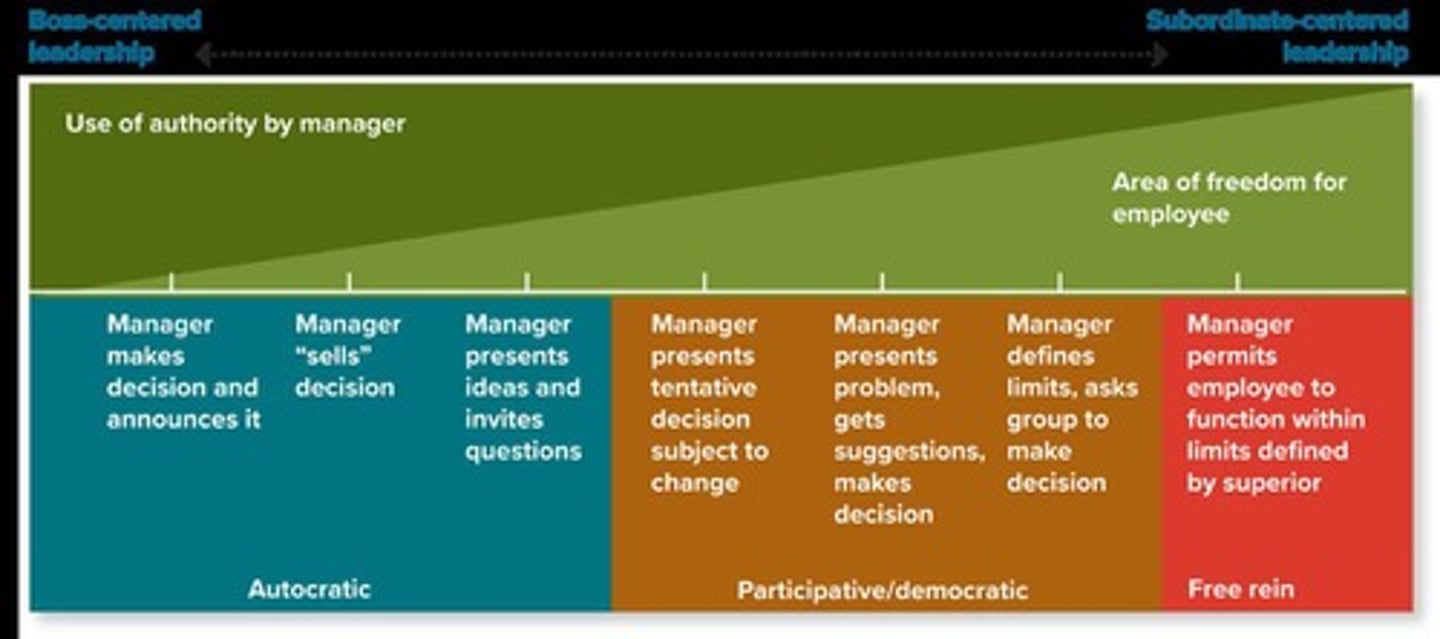
What is a mission statement?
An outline of an organization's fundamental purposes, including self-concept, philosophy, and customer needs.
What is the purpose of a SWOT analysis?
To analyze an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
What is the significance of a vision in planning?
It explains why the organization exists and where it aims to go.
What are objectives in the context of management?
Specific, short-term statements detailing how to achieve the organization's goals.
What does the organizing function of management include?
Allocating resources, assigning tasks, and establishing procedures.
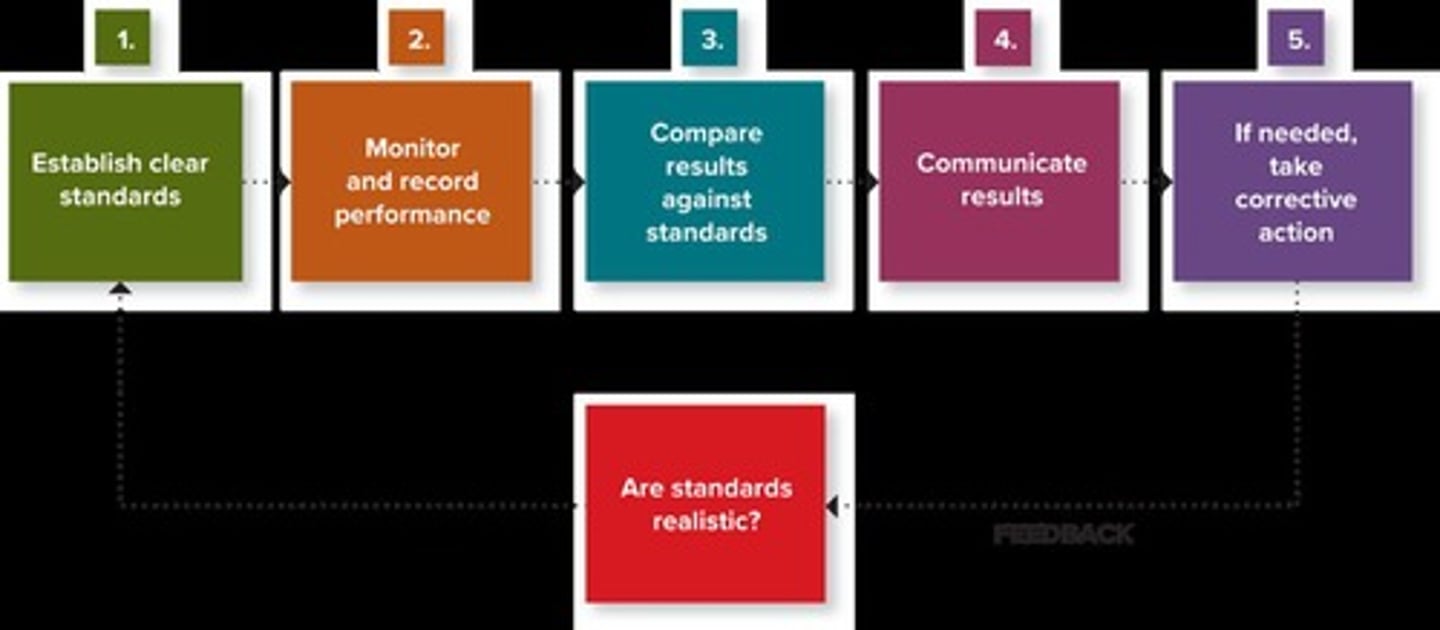
What are the five steps of the control function of management?
Measuring results, monitoring performance, rewarding performance, taking corrective action, and ensuring standards are met.
What is the role of a CEO in an organization?
To provide leadership and ensure the organization meets its goals.
What skills do modern managers need?
Skilled communication, teamwork, and global preparedness.
What is the importance of team building in management?
It fosters collaboration and improves overall organizational effectiveness.
What does controlling in management ensure?
That the organization is meeting its objectives and standards.
What should managers do to guide employees effectively?
Provide clear assignments, explain routines, and give feedback on performance.
What is the role of a manager in decision making?
To set the organization's vision and make strategic decisions to achieve goals.
How do managers respond to changes in the business environment?
By adapting their planning and operational strategies accordingly.
What is the significance of leadership styles in management?
Different styles can influence employee motivation and organizational culture.
What is the importance of recruiting and training in organizing?
To ensure employees are placed effectively and are equipped to meet organizational goals.
What are core competencies in management?
Key strengths that give an organization a competitive advantage.
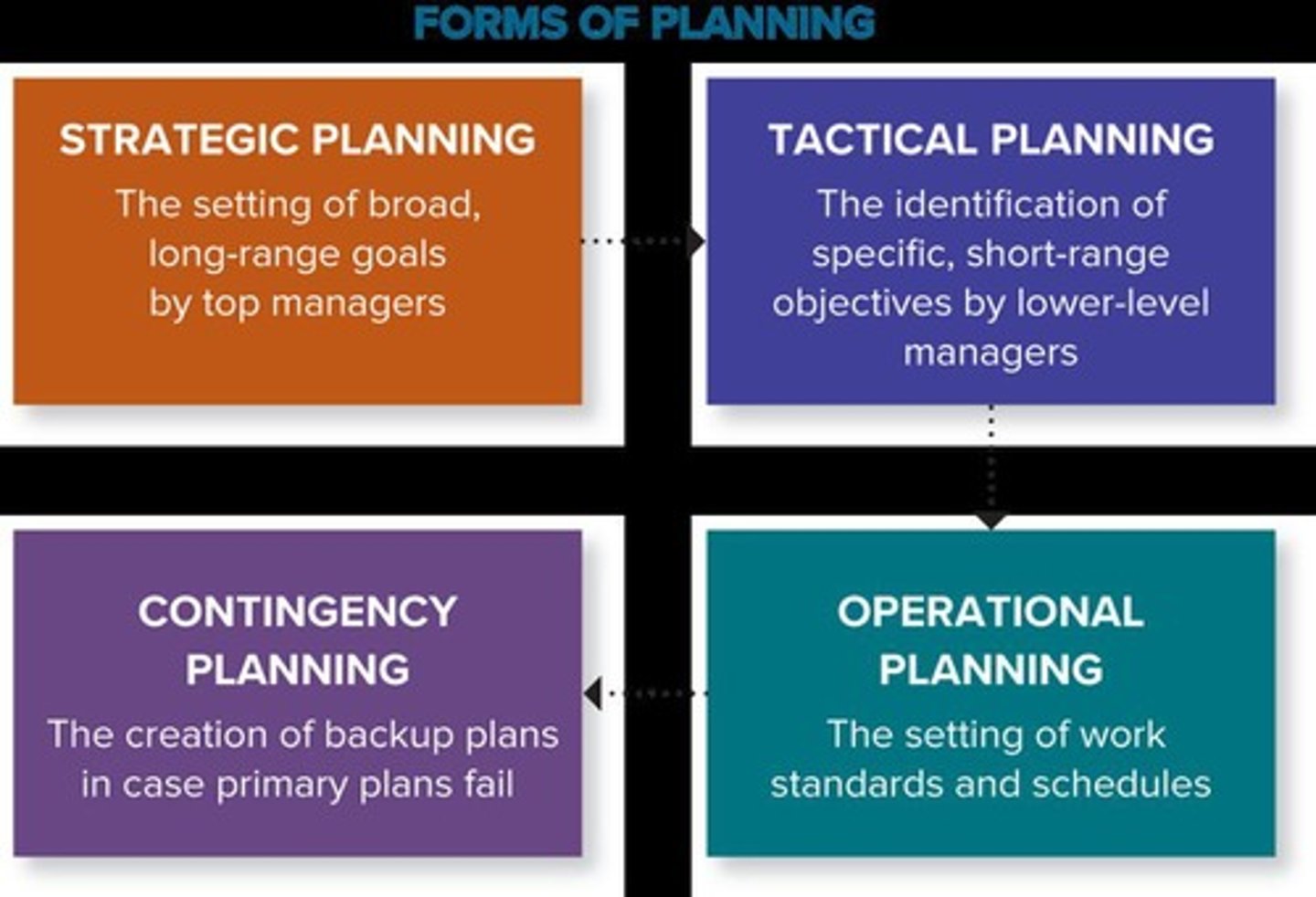
What does strategic planning involve?
Long-term planning to achieve major organizational goals.
What is tactical planning?
Short-term planning that outlines specific actions to achieve strategic goals.
What is operational planning?
Day-to-day planning that focuses on the execution of tactical plans.
What is contingency planning?
Preparing alternative plans to address potential future scenarios.
What is strategic planning?
Determining the major goals of the organization and the policies and strategies for obtaining and using resources to achieve those goals.