HISTEC LAB MICROTOMY AND PARAFFIN SECTIONS
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Microtomy
Process by which a processed tissue, most commonly a paraffin embedded tissue, is trimmed and cut into uniformly thin slices or “sections” to facilitate studies under the microscope.
40 deg Celsius
Heat of water bath
5 microns
Size of tissue sections cut
37 degrees Celsius
Temp for drying
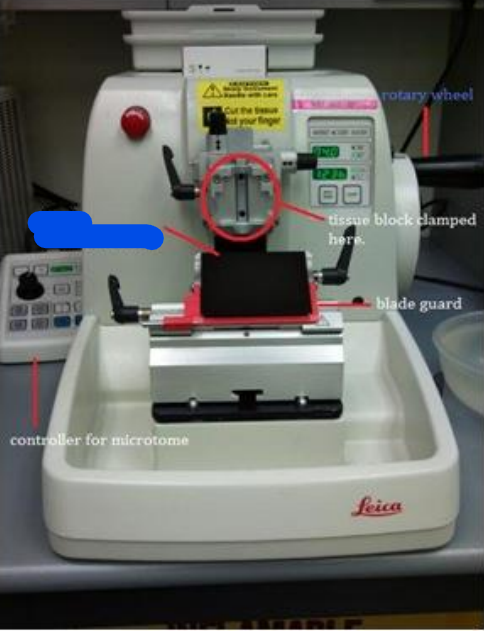
Rotary wheel
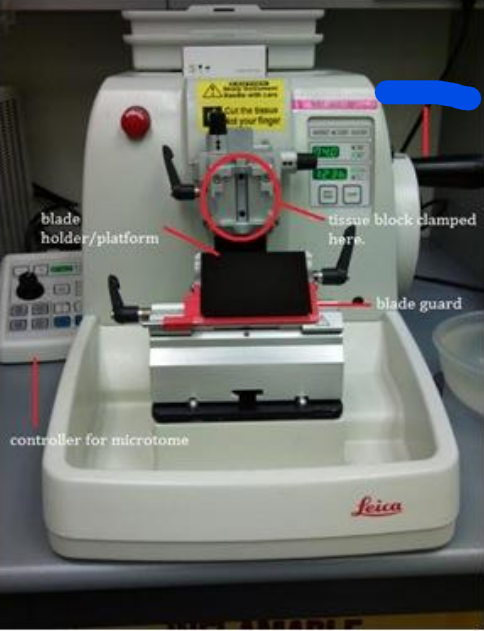

Blade guard
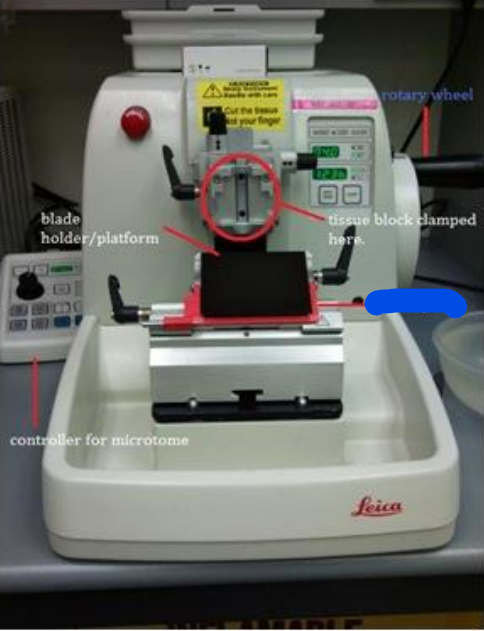

Controller for microtome
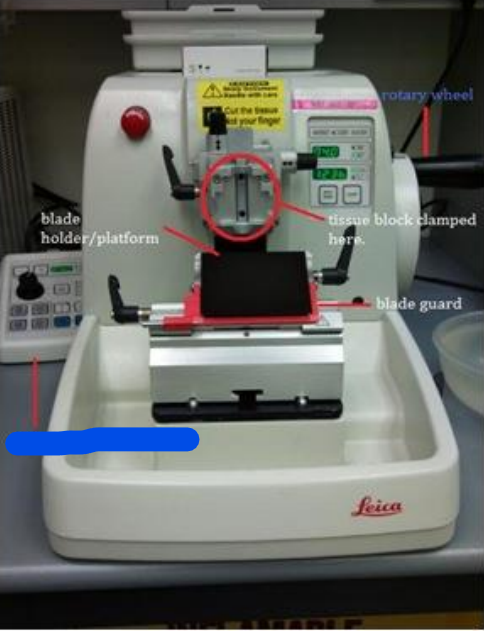

Blade holder/Platform

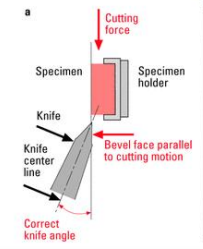
Bevel face parallel to cutting motion
Correct knife angle
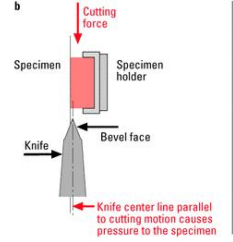
Pressure
Knife center line parallel to cutting motion causes ________ to the specimen
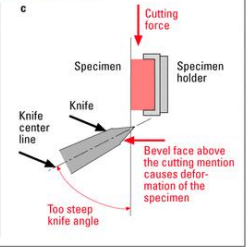
Deterioration
Bevel face above the cutting mention causes __________ of the specimen
Block holder
Knife carrier and knife
Pawl, ratchet feed wheel and adjustment screws
3 essential parts of a microtome (BKP)
Block holder
ESSENTIAL PARTS OF A MICROTOME
Where the tissue is held in position
Knife carrier and knife
ESSENTIAL PARTS OF A MICROTOME
For actual cutting of tissue sections
Pawl, ratchet feed wheel and adjustment screws
ESSENTIAL PARTS OF A MICROTOME
To line up the tissue block in proper position with the knife, adjusting the proper thickness of the tissue for successive sections
Rocking Microtome (Cambridge)
TYPES OF MICROTOME
Simplest and oldest among the different types of microtomes.
Only used to cut small and large blocks of paraffin tissues.
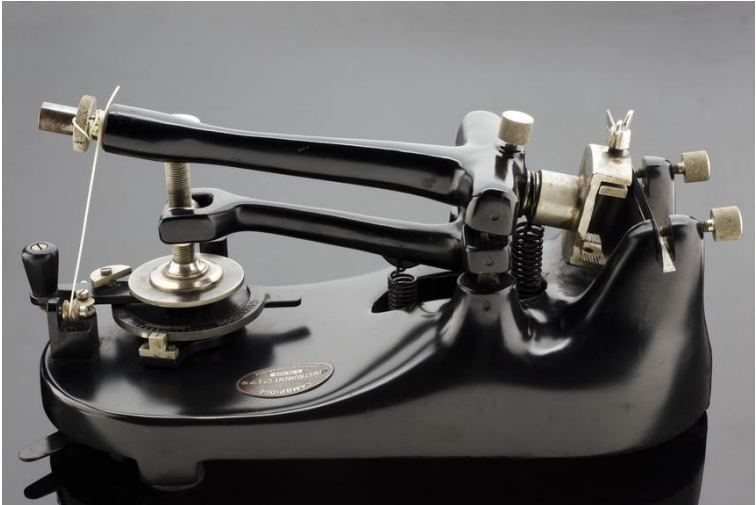

Paldwell Trefall in 1981
Invented Rocking Microtome and what year
Serial section
With the rocking microtome, what type of section is not possible since tissues are cut in slightly curved planes?
Rotary Microtome (Minot)
TYPES OF MICROTOME
Cut paraffin – embedded tissues
Most common type used for both routine and research laboratories
Has adjusting screws to make the tissue block parallel to the knife.
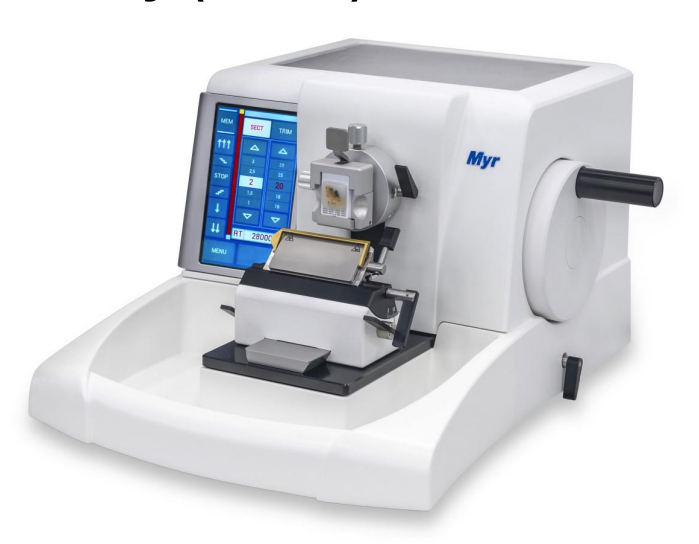

Minot in 1885-1886
Invented Rotary Microtome and what year
Sliding Microtome
Developed by Adams in 1789
2 types
Base-Sledge Microtome
Standard Sliding Microtome
2 types of Sliding microtomes
Base-Sledge Microtome
TYPE OF MICROTOME
Consists of 2 movable pillars holding the adjustable knife clamps, allowing the knife to be set at an angle for cutting celloidin sections
For hard tissue or large blocks that are usually sectioned

Standard Sliding Microtome
TYPE OF MICROTOME
Developed for cutting celloidin – embedded tissue blocks
Recommended for cutting extremely hard and rough tissue blocks
Most dangerous type of microtome due to the movable exposed knife

Freezing Microtome
TYPES OF MICROTOME
Used to cut undehydrated tissues in a frozen state, especially when rapid diagnosis is required
Histological demonstration of fat is needed
Neurological structures are to be studied
Sensitive tissue constituents are easily destroyed or damaged by heat
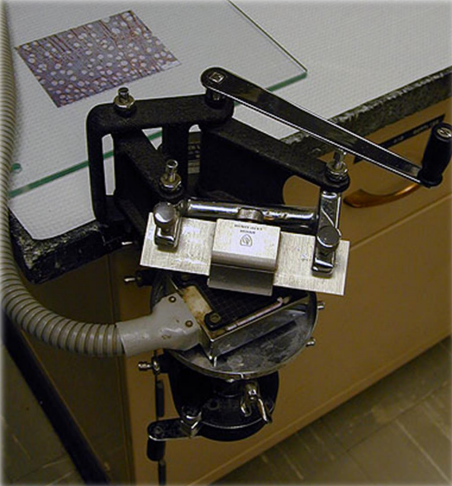

Queckett in 1848
Invented Freezing Microtome and what year
Cryostat
TYPES OF MICROTOME
A refrigerated apparatus used in fresh tissue microtomy for freezing the tissue into the block holder to the correct degree of hardness to facilitate easier and faster sectioning
Rotary microtome + Cold chamber
Fluorescent antibody staining techniques or histochemical enzyme studies
-5 to -30 degrees Celsius (average -20 degrees Celsius)
Cryostat temperature
Ultrathin Microtome
TYPES OF MICROTOME
Used for cutting sections at 0.5 micra
Electron microscopy
Type of microscopy used in Ultrathin Microtome
Osmium tetroxide
Fixative of spx in ultrathin microtome
Plastic
Embedding medium of spx in ultrathin microtome
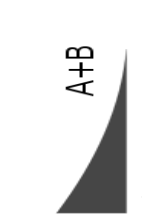
Plane-Concave knife
MICROTOME KNIVES
One side of the knife is flat while the other is concave.
Less concave sides are recommended for cutting celloidin – embedded tissue blocks on a sliding microtome.
More concave sides are used to cut paraffin sections on base – sledge, rotary or rocking microtome
Biconcave
MICROTOME KNIVES
With both sides concave
Recommended for cutting paraffin embedded sections on a rotary microtome

Plane-Wedge Knife
MICROTOME KNIVES
Have both sides straight
Recommended for frozen sections or for cutting extremely hard and tough specimens embedded in paraffin blocks, using a base – sledge type or sliding microtome

Facet angle
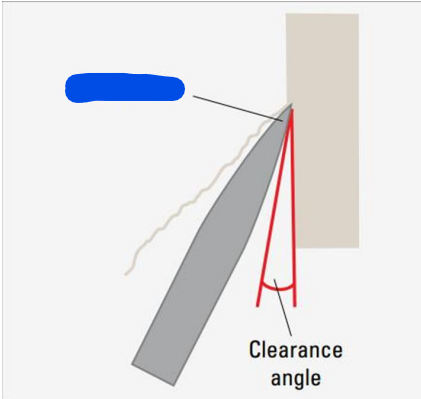
Clearance angle
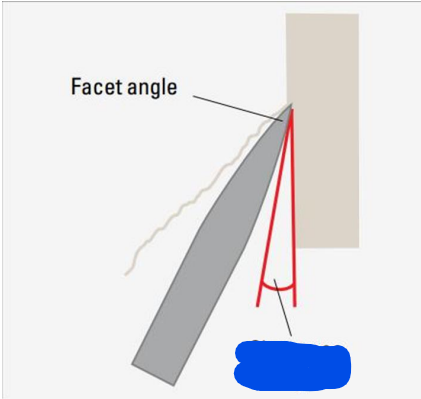
Bevel Angle
Angle formed between the cutting edges
27-32 degrees
Normal bevel angle (range)
2-3 microns
A good cutting edge should be made of good quality steel and be able to cut good sections from a paraffin wax block about________ microns thick, without any serrations noted on examination
15 degrees
The perfect and optimum cutting angle is obtained when the sides of the wedge knife are inclined at an angle of about ______ causing maximum penetration of the tissues and minimizing distortion.
Jagged edges
Produce tears or striae in tissue sections
Mineral and Clove oil
Xylene
Liquid paraffin
Soapy water
Before honing, surface of the hone must be wiped clean.
Then cover the surface with a thin film of any of the following for lubrication (4) (MXLS)
Honing
Involves the removal of gross nicks on the knife edge
Coarse honing
HONING
to remove blemishes and then grinding the cutting edge of the knife on a stone
Honing proper
HONING
to acquire an even edge
Honing
removal of fine nicks
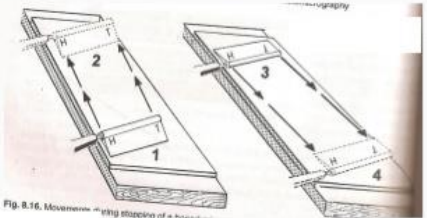
Heel to toe
Honing motion
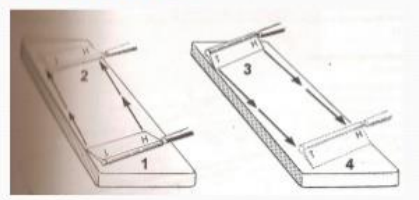
Stropping
sharpen knife which is free of nicks
on leather strop
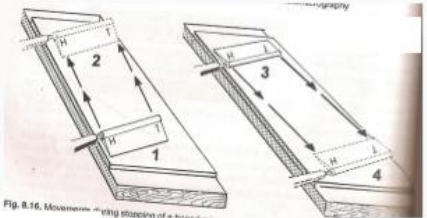
Toe to heel
Stropping motion
Carborundum
Hard grinding surface used in honing
Belgium Yellow
HONING GRINDING SURFACES
For manual sharpening when cutting edge has been rendered blunt or nicked. This type usually gives the best result.

Arkansas
HONING GRINDING SURFACES
Gives more polishing effect than the Belgium Yellow

Fine Carborundum
HONING GRINDING SURFACES
Much courser than the first two types and is used only for badly nicked knives followed by either one of the first two knife sharpeners

Plate Glass Honing
HONING GRINDING SURFACES
A flat circular glass plate with finely powdered aluminum oxide made into paste with water (used as an abrasive)
Diamantine
Used as final polishing for plate glass honing
Automatic hone
Fast becoming indispensable in histopath laboratories
Time saving and fairly easy to manipulate
Consists of glass disc or wheel driver by an electric motor
The knife is pressed together against the flat side of the rotating glass wheel
8 × 3 inches
PRECAUTIONS DURING HONING
The hone should be long enough to allow the whole length of the knife edge to be sharpened. What size?
Warm soapy water or fine oil
PRECAUTIONS DURING HONING
The hone should be lubricated with __________ or __________ before using
20-30 times
PRECAUTIONS DURING HONING
The amount of strokes should be how many times in each direction?
Before, during, and after use
PRECAUTIONS DURING HONING
The hone should be cleaned __________, __________and _________use
Nailbrush
PRECAUTIONS DURING HONING
A black film that develops in the hone usually is imparted by the knife that is being sharpened and should be brushed out with a good _________ in running water.
Stropping
The process whereby the “burr” formed during the honing is removed and the cutting edge of the knife is polished
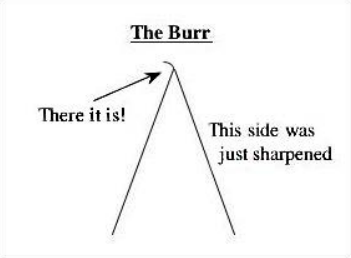
Delicate work
STROPPING
For ___________, knife should be stropped before every object is sectioned
Sagging
STROPPING
A paddle strop made up of the best quality horse leather, firmly attached to a solid back, in order to prevent __________ is preferred
Xylene
PRECAUTIONS OBSERVED IN STROPPING
The knife should be flushed with ________
Disposable blades
Sharp cutting edge that can cut 2-4µ thick sections with ease
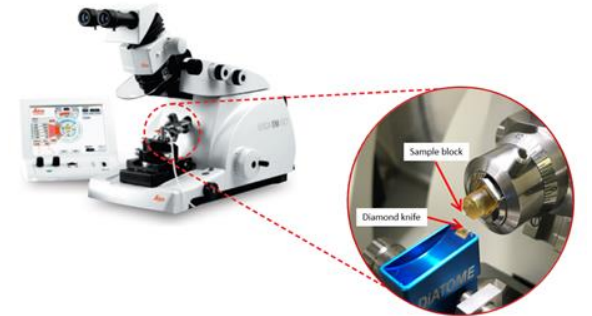
Glass Knives
Knife generally used for trimming and semi – thin sectioning of tissue blocks for Electron Microscopy
Diamond Knives
Used to cut any type of resin block for EM
Brittle and expensive, but very durable and the cutting edge must be kept clean to make it cut longer and to avoid damage during sectioning
Sectioning
is a process whereby tissues are cut into uniformly thin slices or “sections” with the aid of a machine, to facilitate the studies under the microscope.
Course and fine trimming
2 types of trimming
15mm
Fine trimming is set at what thickness?
4-6 microns
Routine section thickness
Discard
What to do with incomplete sections?
Camel hair brush
Pair of forceps
Fingers
Complete sections are picked up using? (3) (CPF)
Exhaling
Tissue that tend to crumble or do not form a smooth flat surface can be sectioned with ease, by ___________ gently into the block surface while the section is being cut slowly to reduce the effects of static electricity
45-50 degrees Celsius, 6-10 decrees Celsius lower than melting point of wax
Temperature of water bath after sectioning
30 seconds
Maximum time for sections to be left on water to avoid undue expansion and distortion of tissue
Floating out bath
The circular, thermostatically controlled bath, 10 to 12 inches in diameter and 3-4 inches in depth is widely used
The inside surface is black and this enables the sections to be easily seen in the bath
Bath should be filled with water to within ½-1 cm from the top
Emptied and thoroughly wiped clean after use
False, must not be floated out simultaneously to avoid cross-contamination
Sections from 2 different blocks can be floated out simultaneously. (T/F)
Protein
Adhesive mixtures are all _______ solutions
Adhesive mixture
Reduce the surface tension thereby producing closer capillary adhesion of the sections to the slides
Thymol
Adding this in adhesive mixtures prevents bacterial contamination
Mayer’s egg albumin glycerol
Adhesive mixture for coating slides
Most popular adhesive mixture
Composed of 50mL of white fresh egg and 50mL of glycerol which are mixed and then filtered through several layers of gauze
Thymol is added as the preservative
Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APES)
Adhesive mixture for coating slides
BEST SECTION ADHESIVE!!
Clean slides are dipped in 2% APES in acetone and drained two times and finally dipped in distilled water
2-5 degrees Celsius above melting point of paraffin used
The mounted section is then placed in a paraffin oven to dry.
Maintained at a temperature of?
Hot plates
___________ are NOT recommended because they can cause overheating and there is a risk of dust falling onto the section during the drying period
25
Amount of slide divisions of a metal rack
5 minutes
How long to dry mounted sections in heated oven
Collagen
Overheating should be avoided because it will distort the tissue and melt some of the structures like?
Celloidin sections
Sections are usually cut by a sliding microtome
Both the sections and the block are being kept moist with 70% alcohol during alcohol (wet method) to avoid dehydration and shrinkage
Sections do not come off in ribbons and have to be collected into 70% alcohol immediately
Stored in the same solutions in jars with tightly fitting lids and finally mounted on to slides after they have been stained
Section too thick
First section in ribbon chosen
Sectioning at too great a speed
Poor processing
Microtome needs recalibration
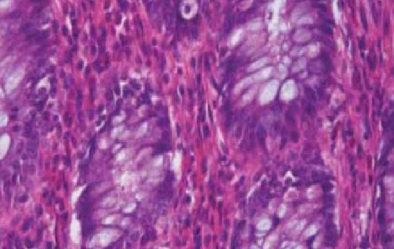
Holes from rough trimming
Block trimmed too quickly
Block surface not polished by cutting some thin sections after roughing
Inappropriate section thickness used when trimming
Block brittle or too cold when trimmed
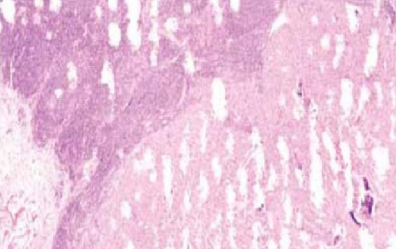
Knife lines
Damaged knife or blade used
Poor processing
Hard material such as calcium in block
Debris in unfiltered in wax
Buffer salts precipitated in specimens
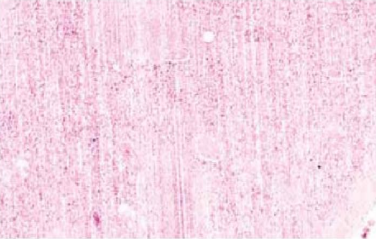
Disruption
Rough handling of specimen during grossing
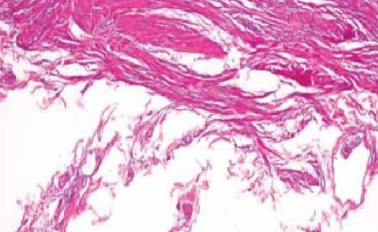
Fine cracks or micro-chatter
Tissue over-processed
Block too cold
Cutting too fast
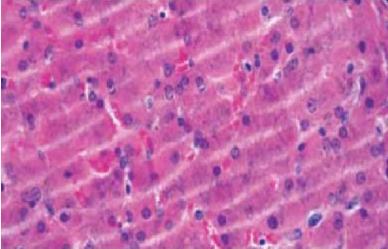
Coarse chatter
Clamping mechanism not securely locked
Very large or hard specimen
Worn microtome
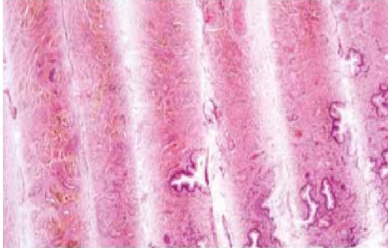
Folds
Poor flotation technique
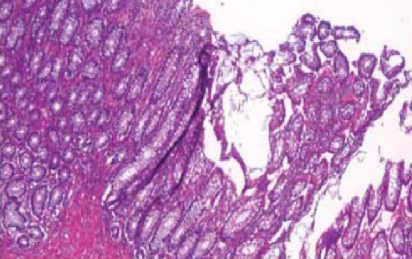
Excessive compression
Poor processing (insufficient support)
Bubbles under the section
Bubbles adhering to base and sides of flotation bath