C3.1 Integration of body systems
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What does interdependence of body systems mean?
Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems have to be organized and need to be able to communicate with one another. The individual parts do not function by themselves, only when they are all put together
What are the subsystems of an organism?
Cell → tissue → organ → organ system
Name all 11 organ systems
Digestive
Urinary
Skeletal
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Muscular
Lymphatic (part of immune system that produces lymphocytes, so white blood cells)
Integumentary (outer layer, skin, hair, nails etc.)
Endocrine
Nervous
Reproductive
What are emergent properties?
Characteristics or behaviours that arive from the interaction between different body parts or organ systems
Give an example of emergent properties
A cheetah relies on skeletal and muscular organ systems to run fast, and the respiratory system to supply a lot of oxygen to muscular system
What is the nervous system?
It is an organ system that is responsible for transmitting electrical impulses. It consists of the peripheral nervous system - nerves and neurons - and the central nervous system - brain and spinal cord
What is the endocrine system?
It is an organ system of glands that releases hormones in the form of chemicals into the blood stream to target specific organs.
What is the difference between the nervous system and the endocrine system?

What is a system that transports substances?
Blood. It transports:
Oxygen from lungs to heart
Carbon dioxide from heart to lungs
Hormones secreted from glands
Antibodies produced by white blood cells or other immune defenses
Nutrients such as glucose
What is the function of the brain?
It receives information from sense receptors throughout the body. It is the central information organ.
What are the components of the brain and what do they do?
And the pituitary gland below the hypothalamus - producing and releasing hormones
The hypothalamus also controls homeostasis
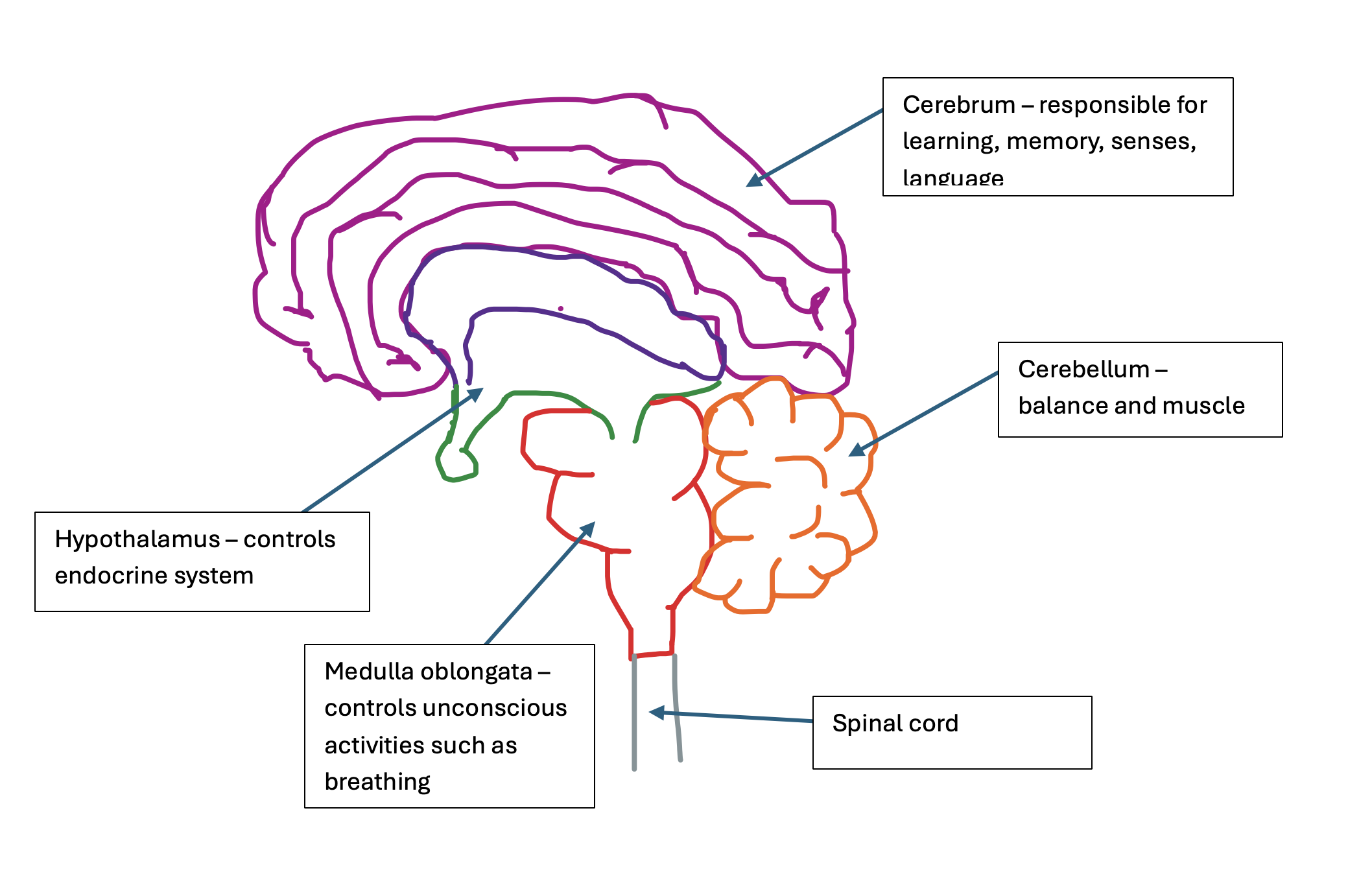
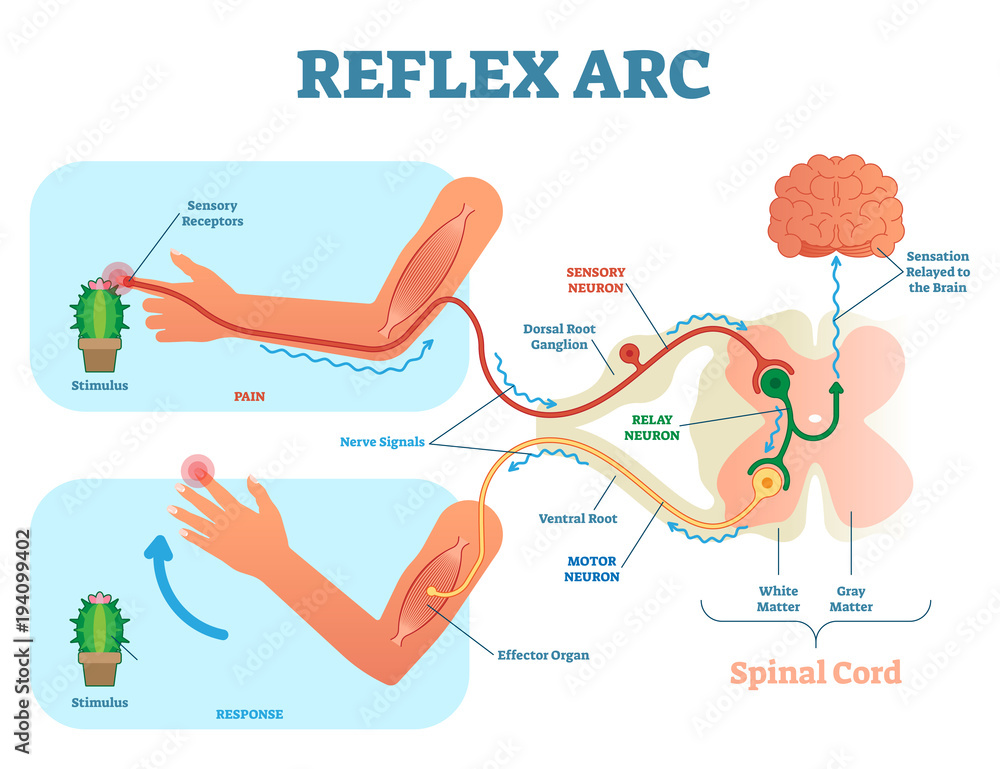
What is the spinal cord responsible for?
It is the pathway of communication between the brain and the rest of the body. It is responsible for unconscious processes such as the pain reflex arc
What does a conscious process mean?
These are mental activities that an individual is aware of. They are performed when an individual is awake, such as writing
What does an unconscious process mean?
These are mental activities that occur without awareness. They are involuntary, such as a heartbeat or digestion
What are sensory, motor and interneurons?
Sensory neurons → convey messages from sense receptors to the spinal cord
Motor neurons → convey messages from spinal cord to effector muscles or glands
Interneurons → convey messages between sensory and motor neurons, conveying messages up spinal cord to the brain
What are nerves?
Bundles of neurons. They can be myelinated (covered by myeline sheath) or unmyelinated
What do myelinated neurons do?
They can transmit quicker and stronger impulses, as they are insulated
What is the reflex arc?
A stimulus is detected by a receptor cell → this electrical impulse is transmitted along sensory neuron → travels to interneuron which sends signal to brain → interneuron carries signal from brain to motor neuron → effector cell which can be either a muscle or gland creates a response to stimulus
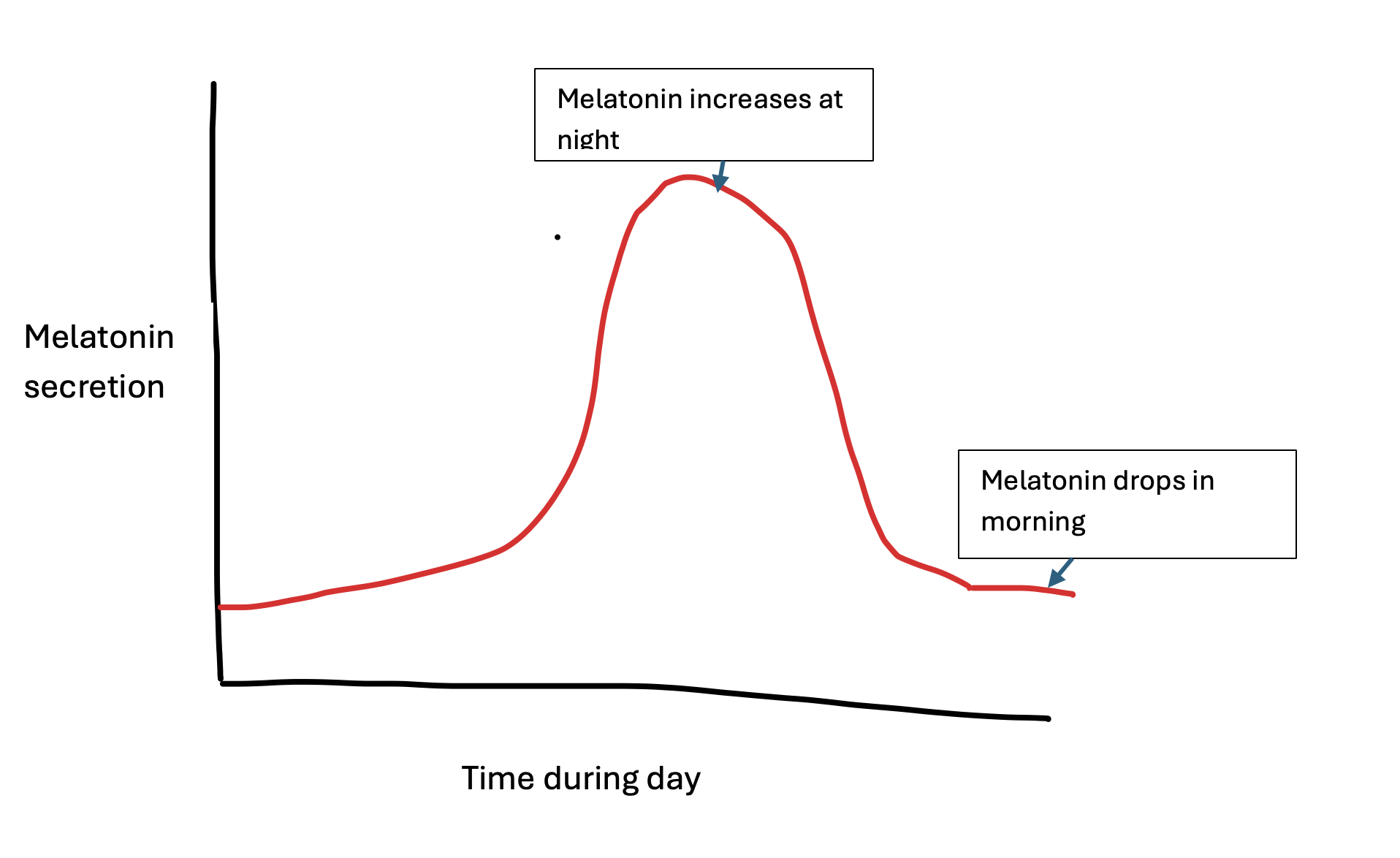
What are circadian rhythms?
They are physical, mental and behavioural changes that follow a 24 hour cycle in response to light and dark. It is like an internal clock
What is the function of melatonin?
It assists in the circadian rhythm, as it is a hormone to help wake up during the day and sleep during the night.
What is epinephrine/adrenaline?
It is a hormone secreted from the adrenal glands, which prepares the body for action: fight or flight.
How does adrenaline prepare the body for activity?
Widens bronchioles so more oxygen gets in lungs and in bloodstream - to provide muscles with more oxygen
More glucose is released in bloodstream for energy
Heart pumps harder and faster to provide muscles with oxygen and glucose
pupils dilate to improve vision
What controls the endocrine system?
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain working together. The hypothalamus either secretes release factors to the pituitary gland to release hormones, or produces its own hormones to store in the pituitary gland
What are baroreceptors and chemoreceptors?
Baroreceptors monitor blood pressure, as they are stretch-sensitive.
Chemoreceptors monitor blood contents, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and pH
These are located near the heart and send signals to the medulla oblongata in the brain (which controls unconscious activity)
What do the baroreceptors do if there is low or high blood pressure?
Low blood pressure → increase heart rate
High blood pressure → decrease heart rate
What do the chemoreceptors do if there is low or high contents in the blood?
Low contents (e.g., oxygen, pH) → increase in HR
High contents → decrease in HR
What happens with blood pH during physical activity?
The blood pH decreases, as respiration increases, which leads to more carbon dioxide in blood. Chemoreceptors monitor this change, and sends signals to the medulla oblongata. This then increases the ventilation rate to get pH levels back to normal
What is the autonomic nervous system, and its branch?
It is responsible for the control of bodily functions which are not under conscious control, such as breathing or heartbeat. A branch of this system is the enteric, which controls the unconscious process of food moving along the digestive system by peristalsis
What is peristalsis?
It is the involuntary movement of food through the digestive system by the contraction and relaxation of muscles