B7 - Non-Communicable Diseases
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Non-Communicable Disease
a disease not capable of being spread from one person to another
Factors of Non-Communicable Diseases
- lifestyle (smoking, diet, alcohol, sleep)
- genes
- substances in the environment (radiation / UV)

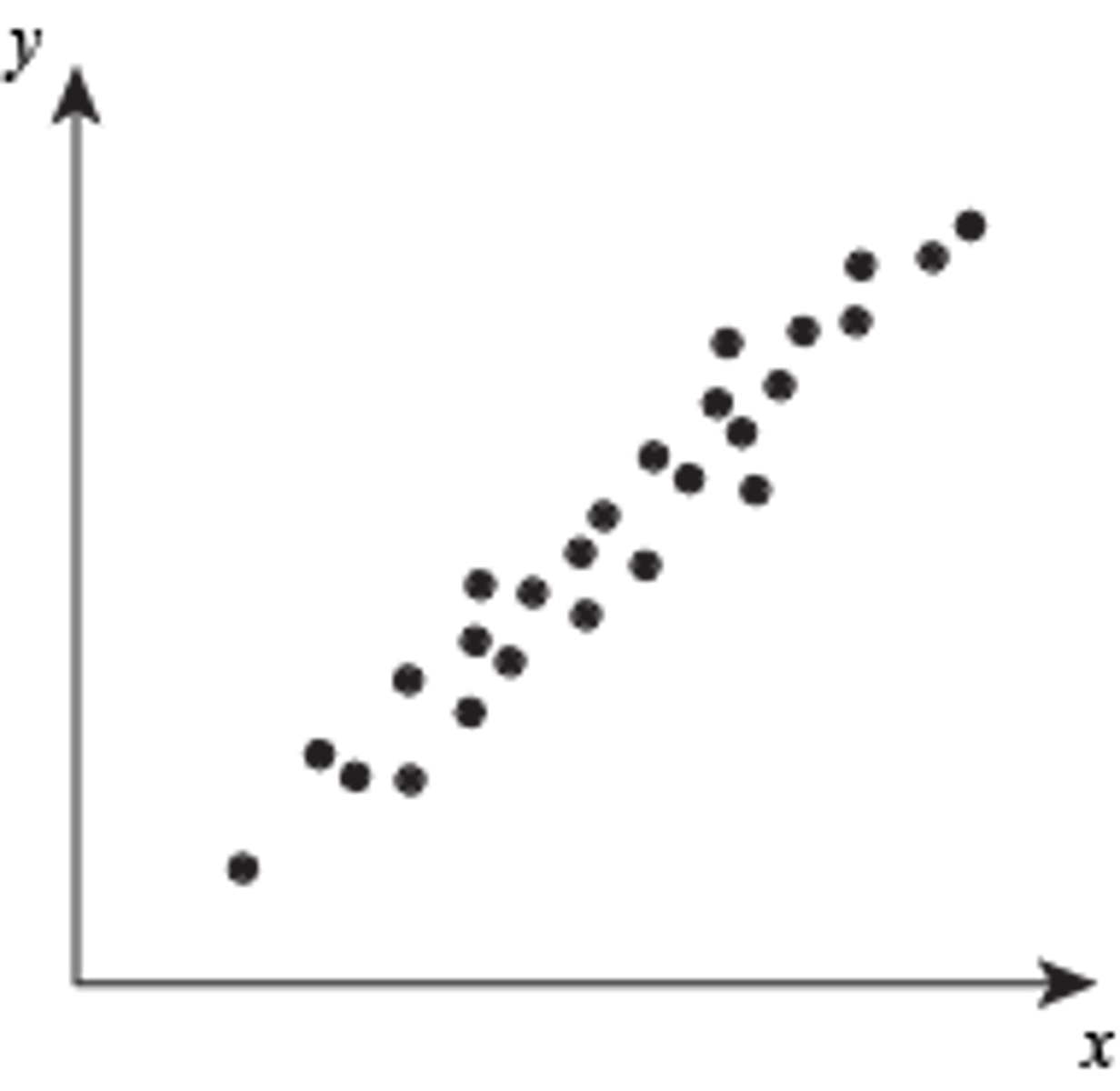
Correlation
a mutual relationship or connection between two or more things
- does not prove cause
Casual Mechanism
something that explains how one factor can influence another
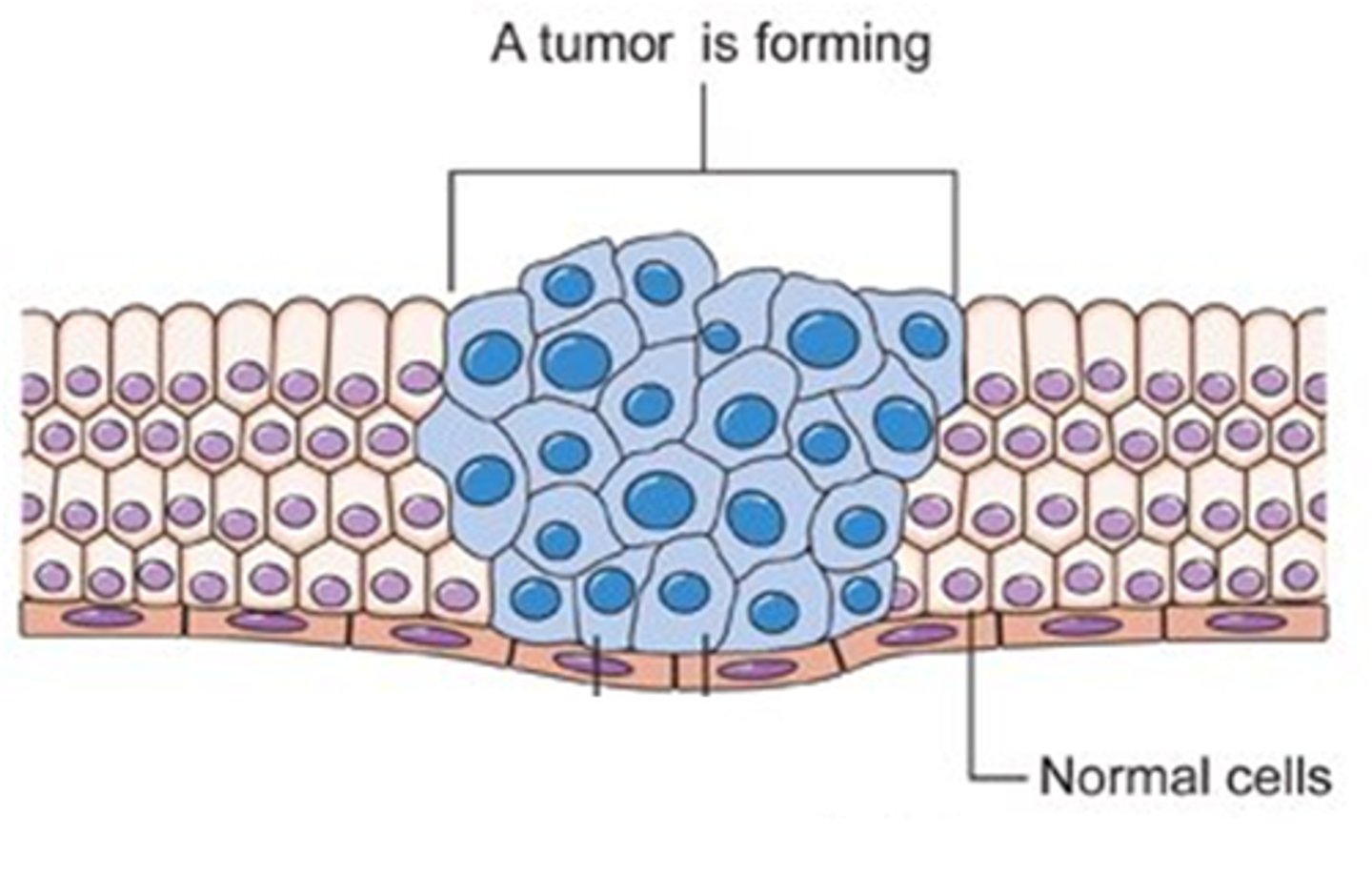
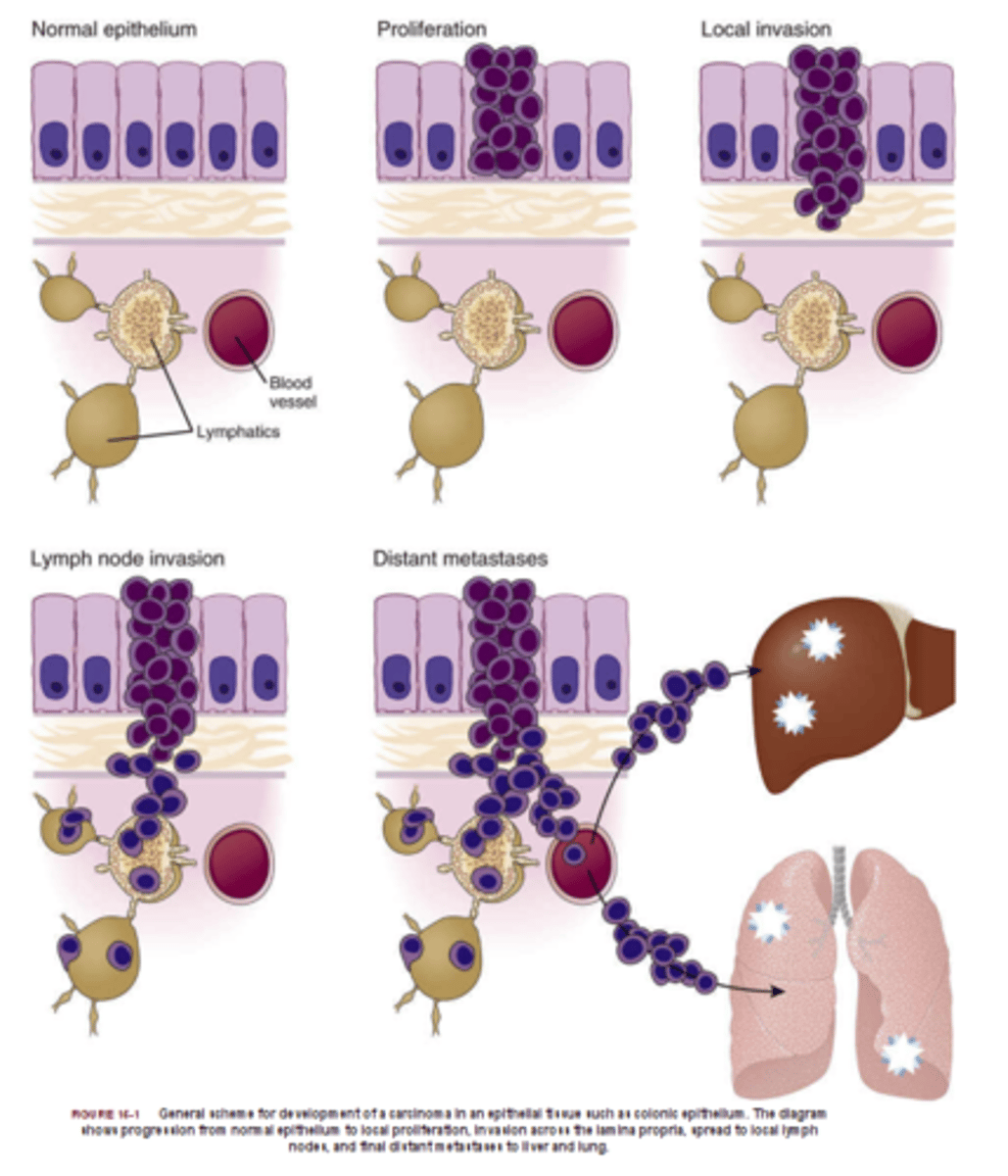
Tumor Cells - Cancer
uncontrollable, rapid and abnormal cell division creating tumours
- the control of the cell division sequence is lost
- very little growth time
Benign Cancer
- does not invade surrounding tissue
- stays in one place
- can grow very large and quickly
- can damage organs: as it causes pressure
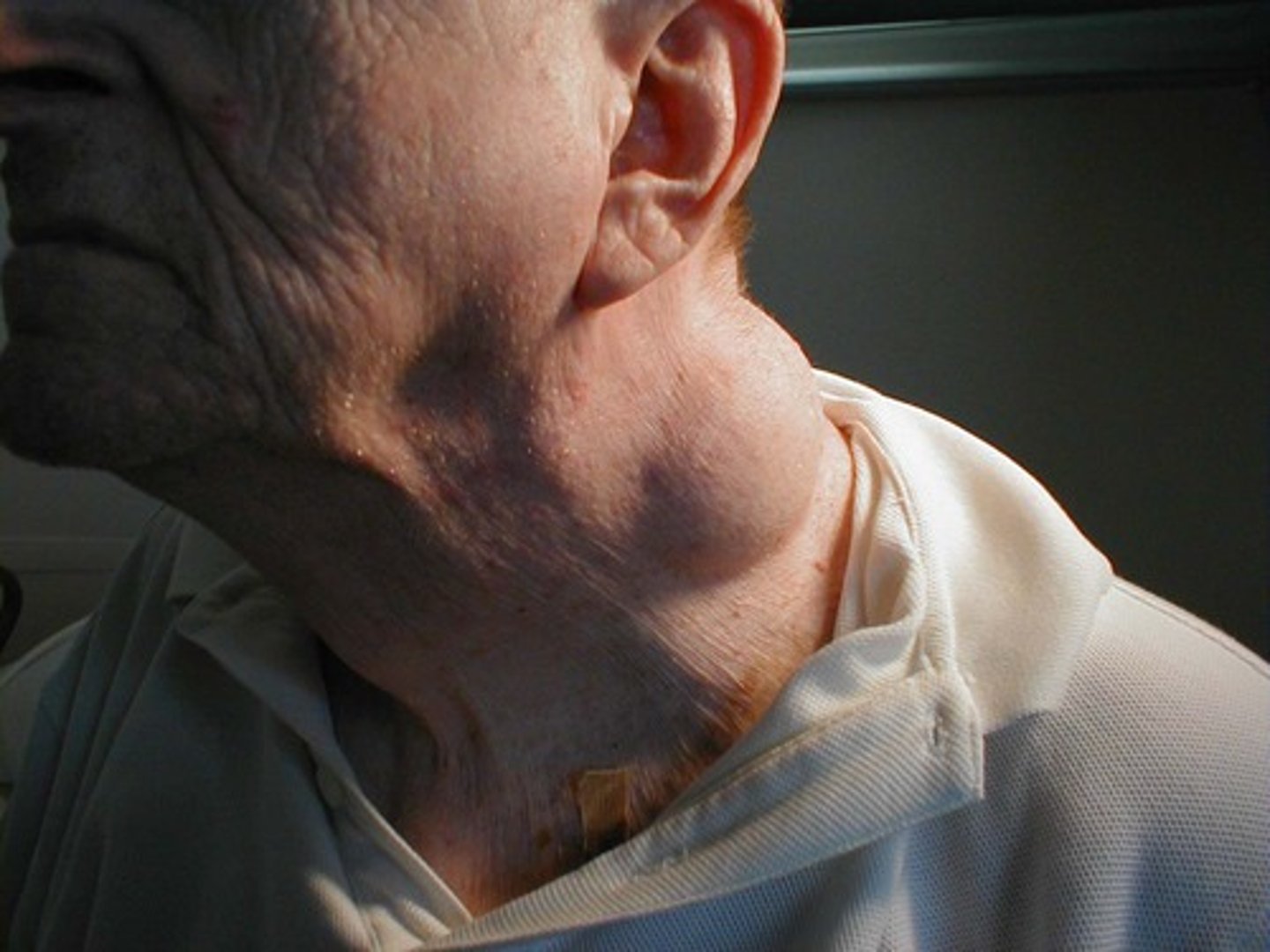
Malignant Cancer
- cancer that can invade
- can split up
- spreads around the body and harm other healthy tissues: lodges
- gets into the blood stream
- live longer than other cells
- life threatening
- harm organs
- grows beyond size of benign tumour
Causes of Cancer
- lifestyle (smoking)
- radiation exposure
- viral infections
- genetics
- mutations
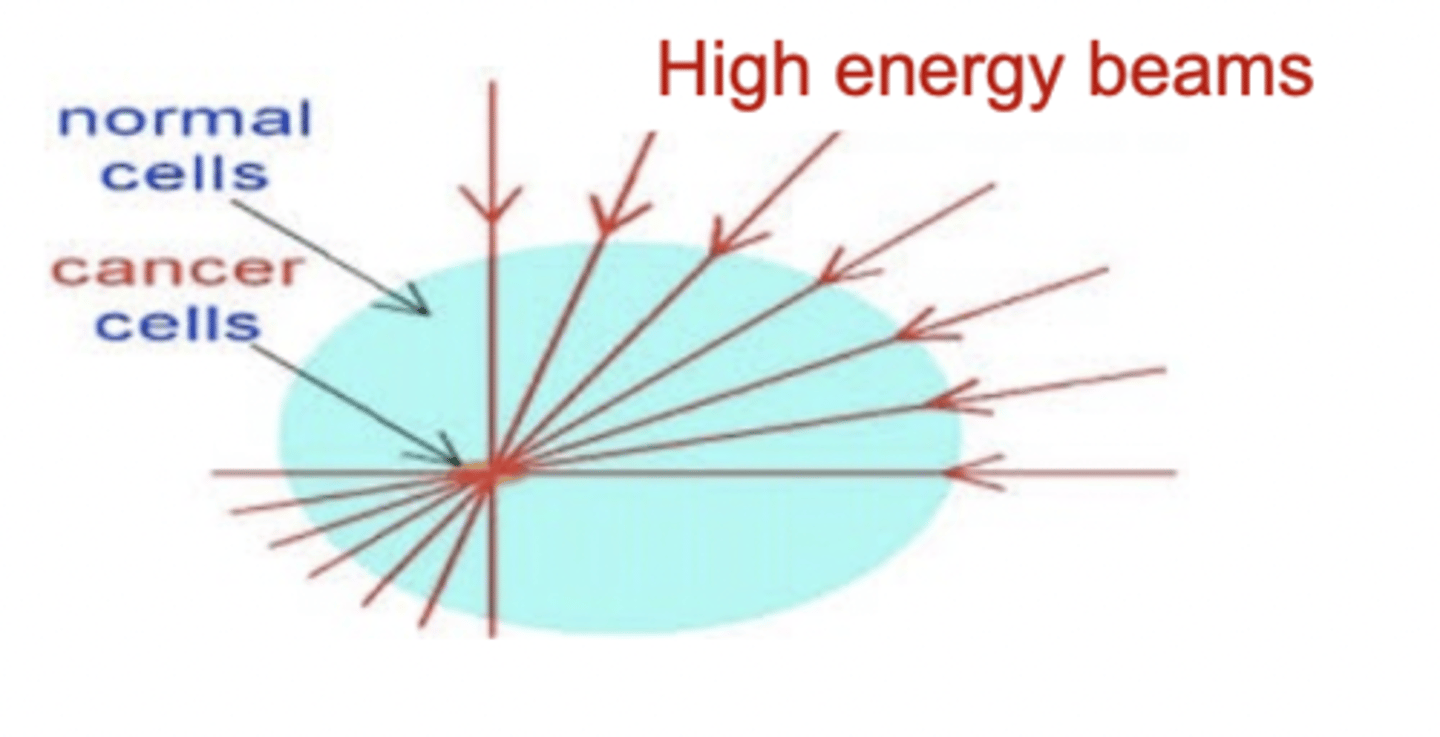
Radiotherapy
treatment with targeted high-dose radiation
- to destroy cancer cells in the body: can stop mitosis
- can also harm healthy ones
Chemotherapy
stopping cells divided
- makes cells self destruct
- drugs
Smoking - Nicotine
- addictive
- moderately harmless
- creates a calm, well being sensation
- idealises smoking

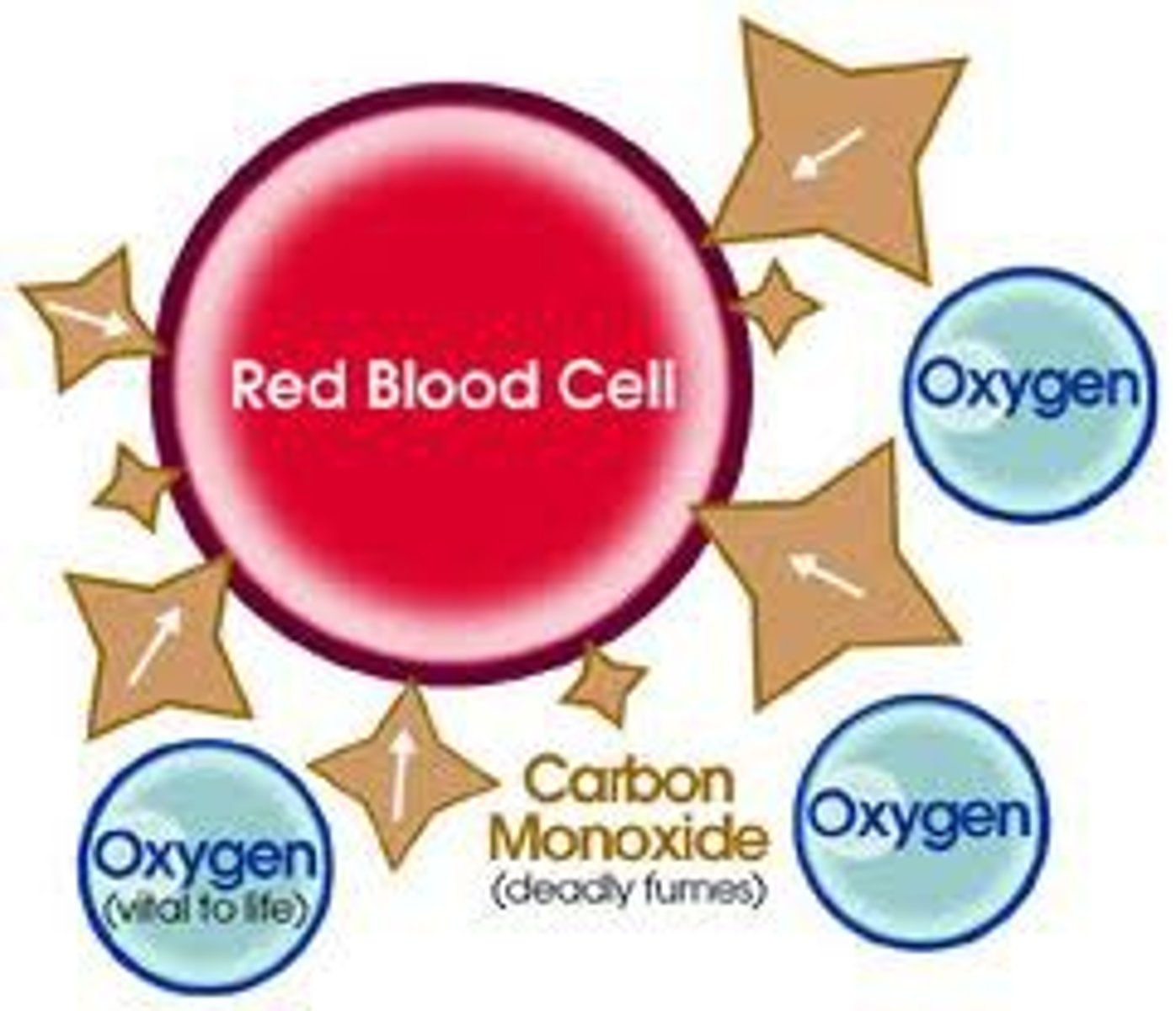
Smoking - Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- poisonous
- blood stream in RBC carries CO instead of oxygen
- narrows blood vessels
- causes a shortage of oxygen
- breathlessness
- destroys cells: not enough aerobic respiration to transfer respiration
Smoking - Fertility
can cause a still birth
- a miscarriage or a mutation in the baby
- foetus does not receive enough oxygen

Smoking - Clia & Alveoli
- mucus & bacteria build up in bloodstream
- carcinogens build up
- blocks bloodstream
- prevents oxygen circulating
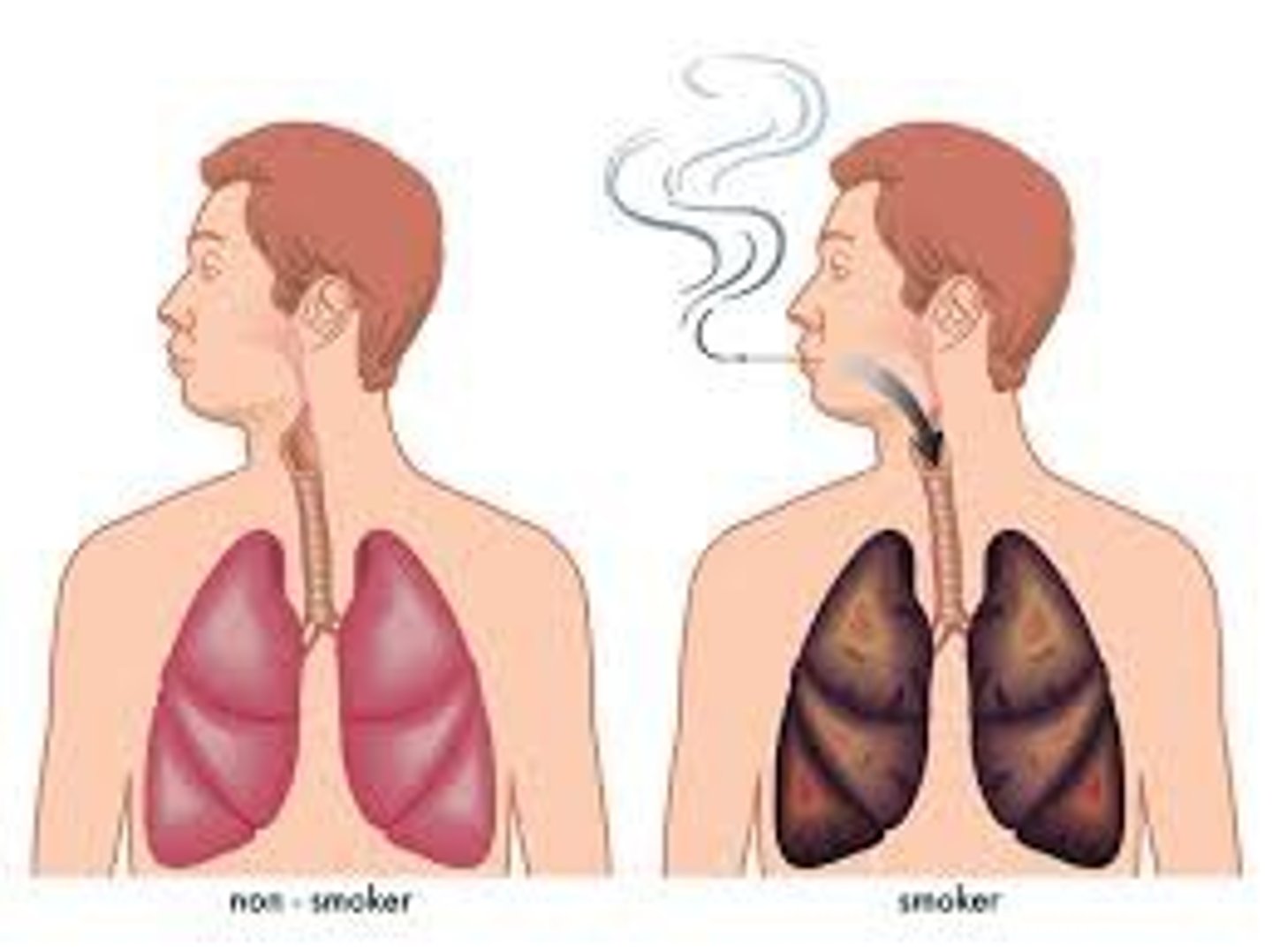
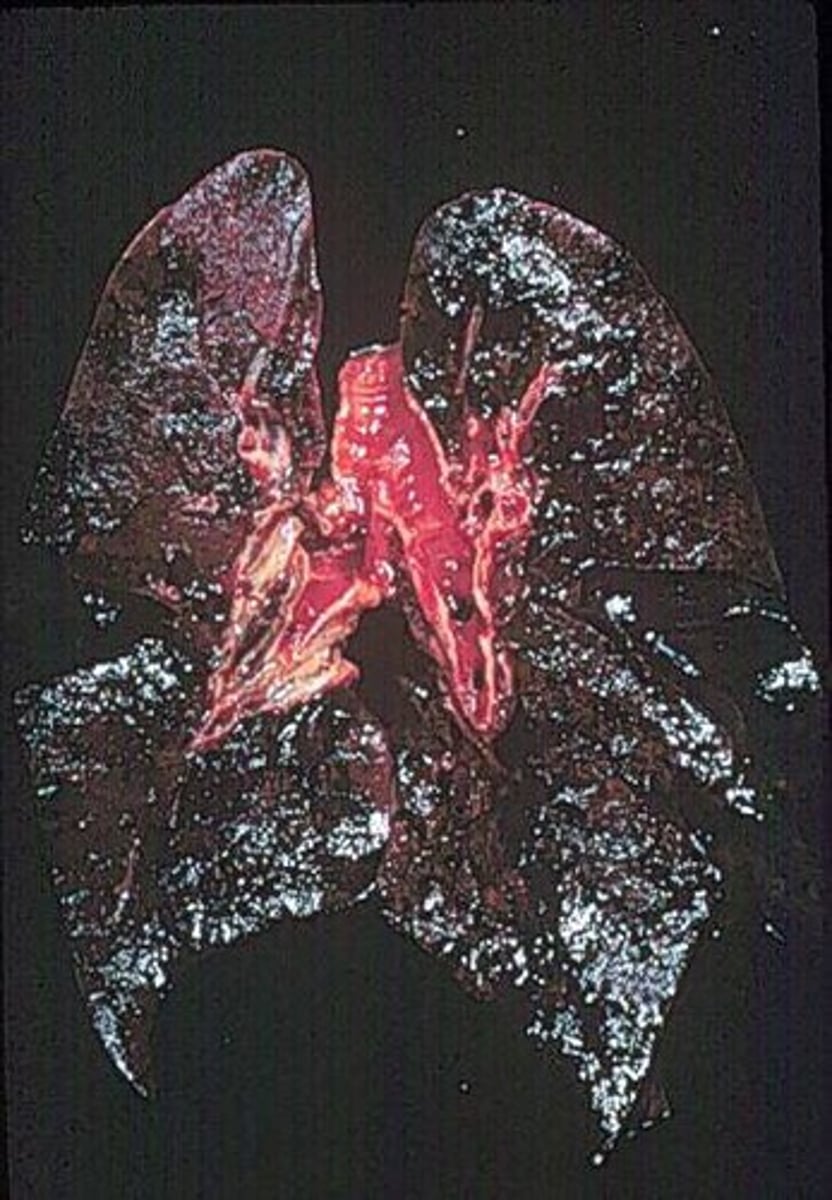
Smoking - Tar
a thick, sticky, dark fluid produced when tobacco burns
- a carcinogen
- turns lungs black
- can develop Bronchitis
- breaks down alveoli structures
- causes breathlessness: lung cancer
Dangers of smoking
- heart attack
- brittler bones
- lung cancer
- stained teeth & lungs
- constricts arteries
- asthma
- breathlessness
- eye disease
- CVD
- increased heart rate
BMI - Body Mass Index
a measure of body weight relative to height
Mass in KG / Height in M ^2
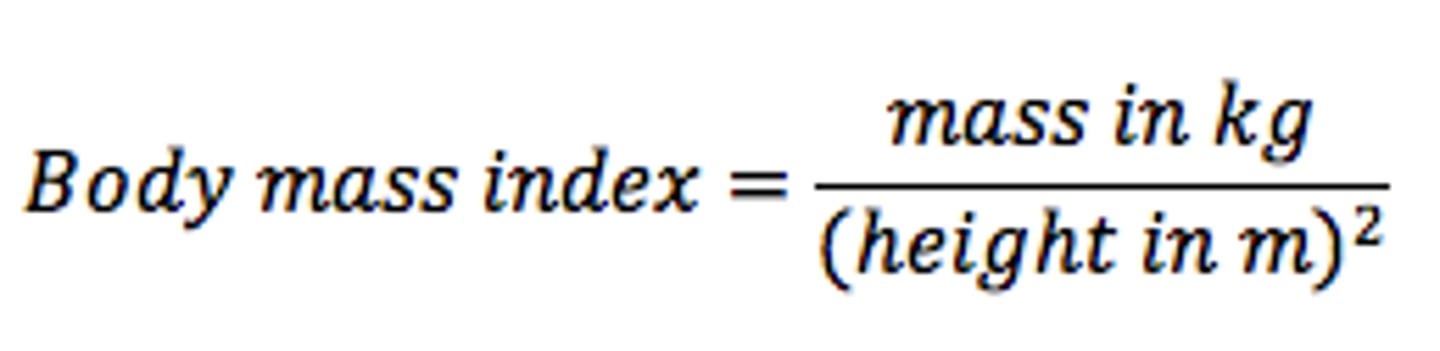
Obesity
having an excess amount of body fat
- taking more energy in than needed
- excess energy stored as fat
- causes diabetes
- causes clots: not enough oxygen supplied which can cause a heart attack
- some fat is essential to cushion organs and insulate

Insulin
regulation of glucose levels in the blood.
- a protein hormone
- made in the pancreas
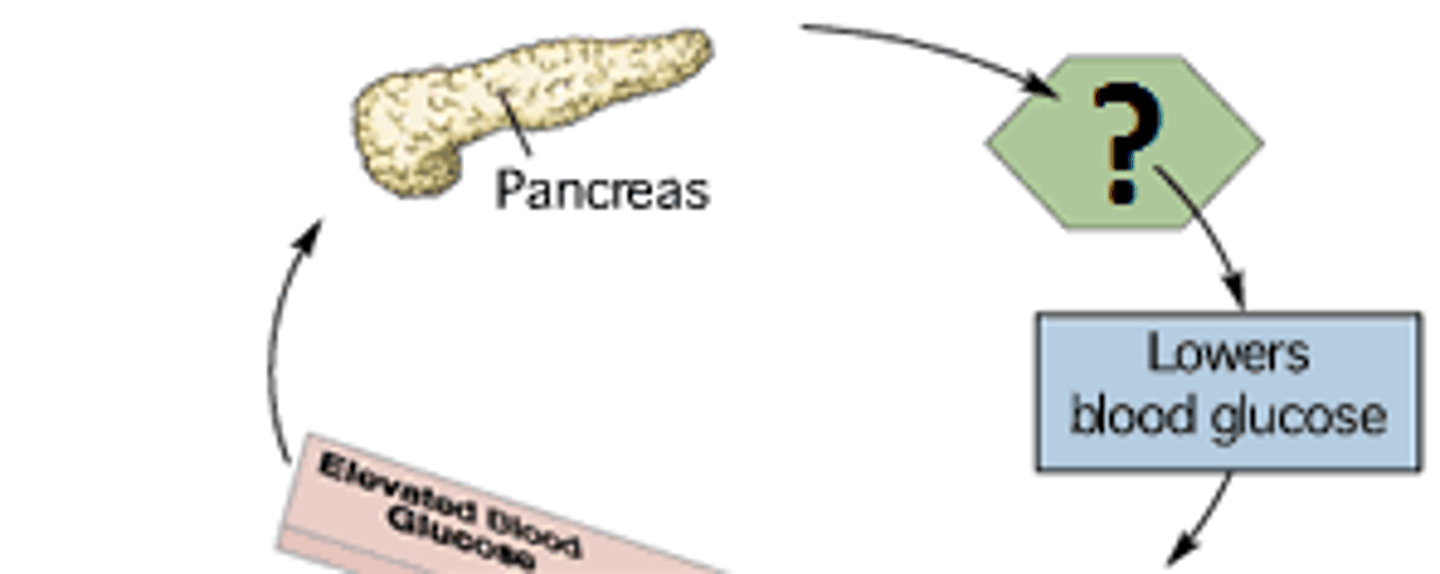
Type 2 Diabetes
when excess blood sugar levels mean cells become less responsive to insulin
- stored as fat
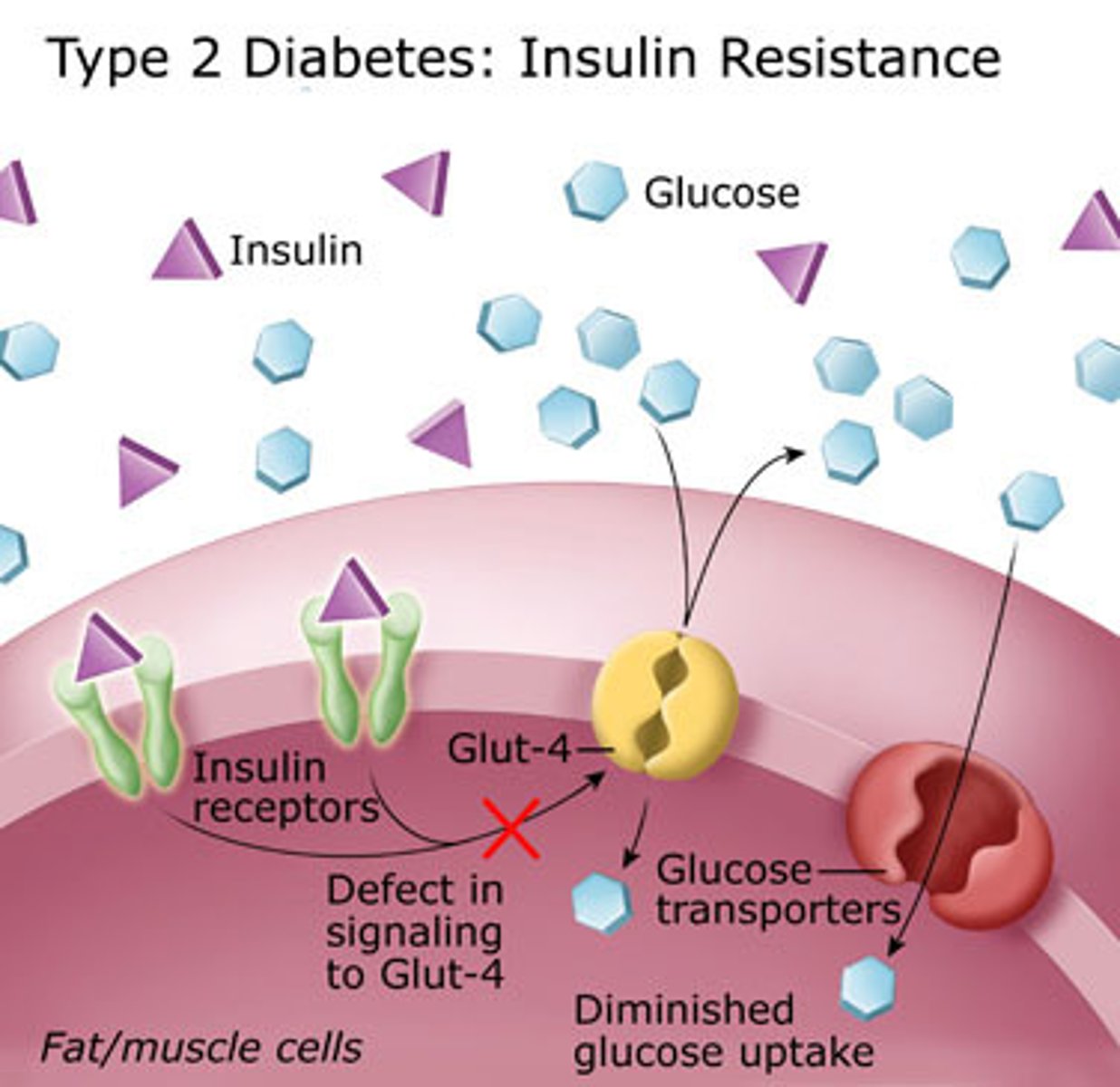
Effects of Type 2 Diabetes
not enough oxygen get's around the body
- heart disease
- asthma
- arthertis
- high cholesterol levels
How Exercise Improves Health
- increases heart rate and pumps more oxygen
- strengthens bones
- relieves stress by releasing endorphins
- increases muscle to fat ratio
- a higher metabolic weight
- lowers cholesterol
- increases heart & lung capacity
Carcinogen
substance that causes a cellular mutation in living tissue DNA
- causes cancer

Short Term Effects of Alcohol
changes to the brain :
- immediate slow down of central nervous system
- bad decision making
changes to the liver
- converts alcohol to water, energy & CO2
- causes intoxication

Long Term Effects of Alcohol
- sleep disturbances
- brain damage (turns softer & plumper)
- high blood pressure
- heart disease
- cirrhosis
- addiction
- fertility problems
Ionisaing Radiation
- ultraviolet lights
- X-rays
- granite
- nuclear blasts
