AP Psych WC-4
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Memory
the persistence of learning over time through the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information
Explicit Memory
retention of facts and experiences from long-term memory that one can consciously know and “declare”
Requires attention and conscious effort
Semantic Memory
Facts and general knowledge (Washington was the first president)
Episodic Memory
Experienced events such as a family trip
Implicit Memory
Retention of learned skills or classically conditioned associations in long-term memory independent of conscious recollection
Automatic Processing
Unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time and frequency, and well-learned info (word meanings)
Procedural Memory
A type of long-term implicit memory for knowing how to perform tasks, actions, and skills
Prospective Memory
the ability to remember to perform a future intention
Parallel Processing
Considering many aspects of a problem simultaneously
Long-Term Potentiation
Strengthening of synapses, an increase in a cell’s firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; a neural basis for learning and memory
Multi-Store Model
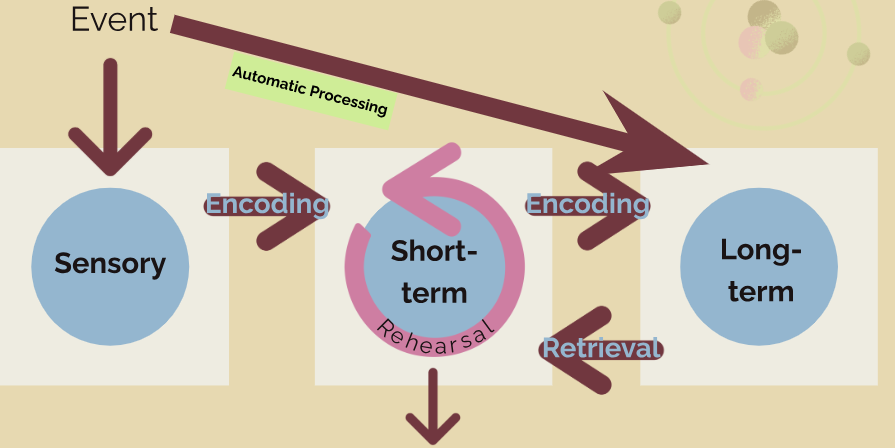
Sensory Memory
The immediate, very brief recording of sensory information (usually a fraction of a second) in the memory system
Long-term memory
relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system
Working Memory Model
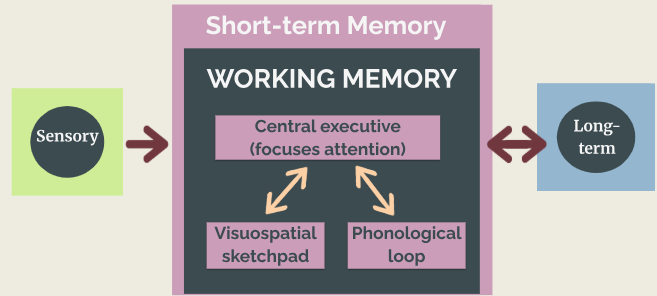
Visuospatial Sketchpad
A component of the working memory model which stores and processes information in a visual or spatial form. (Navigation)
Phonological Loop
A component of the working memory model that deals with spoken and written material
Levels of Processing Model
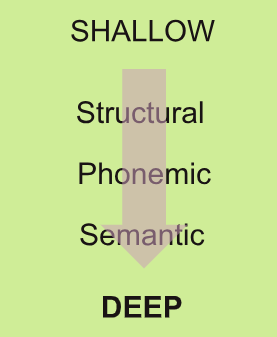
Structural Processing
Encoding based on the physical qualities of something
Phonemic Processing
Processing the sound of something
Semantic Processing
When we encode the meaning of a word and relate it to similar words with similar meaning
Encode
put in the new information
Store
organize the information
Retrieve
pull out the information
Visual Encoding
Involves using visual cues to store information and acoustic means using sound or language to store information
Acoustic Encoding
Involves using auditory cues to store information. Includes linking sound characteristic such as pitch and frequency to the data being stored
Semantic Encoding
Involves using meaning or context to store information. Store meaning along with the term, date or concept to make it more memorable
Elaborative Encoding
Involves connecting new info to prior knowledge to remember it. Contrasted to rote learning where facts are remember in isolation
Tactile Encoding
Refers to using phys. sensations and touch to store info
Organizational Encoding
organizing info into groups or categories
Mnemonic Devices
Processes that aid in encoding info into working and long-term memory
Method of Loci
Using a familiar environment and assigning information to certain locations (encoding), then retrieving the information by “walking” through the location
Chunking
Breaking information into smaller “chunks” in order to recall it easier
Spacing Effect
More information is remembered through distributed practice (1/2 hours over 8 days) rather than massed practice (4 hours on a singular day)
Testing Effect
testing information and then testing your knowledge increases the amount of information retained.
Serial position effect
An items position in a list has on how well it is recalled
Short-Term Memory
memory that holds a few items briefly before the information is stored or forgotten
Working Memory
Builds off of short-term memory but includes our active processing, as our brain makes sense of incoming information and links it with stored memories
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system critical for processing new memories
Structures that build explicit memory and assist in memory consolidation
brain’s process of stabilizing and strengthening recent memory traces into long-term memories
Hippocampus, amygdala, and frontal lobe
Structures that build up implicit memory
Basal ganglia and cerebellum
Basal Ganglia
Responsible for the formation of motor and implicit memory, controlling things like voluntary motor movement , procedural learning, and routine
Because of this, it also believed to be associated with habit-forming such as teeth grinding (bruxism), OCD, and addiction
Cerebellum
Responsible for the timing and execution of learned, skilled motor movements
Flash-bulb memory
A clear, sustained long-term memory of an emotionally significant moment or event.
Hippocampus Damage to the Left
Verbal information recall
Hippocampus Damage to the RightA
visual memory and spatial navigation
Amnesia
Partial or complete loss of memory. Either temporary or permanent, it may be due to physiological factors such as injury or disease
Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to form new memories
Retrograde Amnesia
Inability to retrieve memories of the past
Source Amnesia
Forgetting where/who you acquired a piece of information from
Infantile Amnesia
Inability to remember or early childhood (usually caused by lack of language)
Alzheimer’s Disease
A progressive neurodegenerative illness that destroys memory and other mental functions, primarily causing memory loss, confusion, and general cognitive decline
Connected to lack of ACh
Recall
Retrieving information that is not currently in your conscious awareness but that was learned at an earlier time
FRQ
Recognition
Identifying items previously learned
MCQ
Context Dependent Memory
The phenomenon where recalling info is easier when the surrounding environment or sit. is the same during both the initial encoding and the later retrieval of the memory
Mood Congruent Memory
The tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one’s current good or bad emotional state
State-Dependent Memory
The phenomenon where memory recall is enhanced when an individual is in the same physiological state as when they originally encoded the information
Retrieval Cues
Associate with it other bits of information about your surroundings, mood, seating position
Forgetting Curve
Shows that memory retention decreases rapidly after a learning event, but the rate slows over time
Tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon
We know we know the term, name, etc, we just can’t come up with it
Encoding Failure
Much of what we sense we never notice, and what we fail to encode, we will never remember
Storage Decay
Memory for novel information fades quickly, then levels out
Retrieval Failure
Inability to recall info from long-term memory even though it is stored there
Proactive Interference
Procures the past
If you buy a new combo lock, your old combination may interfere with your retrieval of the new one,
Retroactive Interference
Retroactive remembers recent
Become so used to a new remix of a song that you forget what the original sounds like
Misinformation Effect
Incorporating misleading info into memory
Intelligence
The mental quality encompassing the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
General Intelligence/ g Factor
General intelligence is at the heart of all our intelligent behavior
He noted that those who score high in one area, such as verbal intelligence, typically score higher than average in other areas, such as spatial or reasoning ability
Thurstone
Opponent of Spearman’s “g” who gave 56 different tests to people and mathematically identified seven clusters of primary mental abilities (word fluency, verbal comprehension, spatial ability, perceptual speed, numerical ability, inductive reasoning, and memory). Accidentally proved “g” by showing those who was good in one area were good in others
Multiple Intelligences
Howard Gardner identified eight relatively independent intelligences, including the verbal and mathematical aptitudes assessed by standardizes tests.
Triarchic Theory
Robert Sternberg agreed with Gardner that there is more to success than traditional intelligence and that we have multiple intelligences. But Sternberg’s triarchic theory proposes three, not eight or nine, intelligences
Analytical
Creative
Practical
Crystalized Intelligence
Our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age
Increases with age
Fluid Intelligence
Our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease with age, especially during late adulthood
Decreases with age
Fixed Mindset
The belief that intelligence and abilities are innate- you’re either born with them or you’re not
Growth Mindset
The belief that intelligence and abilities can be developed through effort and learning
Stereotype Threat
Decreases performance due to fear of conforming a negative stereotype
Stereotype Lift
Increases performance by allowing individuals to feel superior to members of negatively stereotyped groups
Intelligence Quotient
(Mental Age/ Chronological age) *100
Historical use was to assess school children
Still used for many educational services
Binet-Simon Scale
The og. IQ test, designed for school children
Stanford-Binet
Built off of original Binet test, focused on children/adolescents, provides a general score
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
Specifically for adults (ages 16-90), provides more detailed subscores
Psychometric Principles
Standardization
Uniformity
Reliability
Consistency
Validity
Accuracy
Socio-cultural Responsiveness
Freedom from bias
Standardization
Procedures must be uniform
Environment: Controlled and consistent
Pretested standardization sample acts as control
Instructions everyone takes the test the same way
Questions: Same types of question
Scoring: fair scoring procedures
Test Retest
Same test on two occasions
Measures stability over time by correlating scores from the same test given to the same group at two different times
Split-Half
Two equal halves
Measures internal consistency by correlating two randomly selected halves of a single test given at one time
Content Validity
The degree to which a test or measurement covers all the important aspects of a specific domain or construct
Construct Validity
The extent to which a test measures the underlying theoretical concept (the “construct”) it is supposed to measure
Criterion Validity
The extent to which a test’s scores correlate with a known, concrete outcome or “criterion” that the test is meant to measure
Predictive Validity
A specific type of criterion validity that assesses how well a measure can predict a future outcome or behavior
Flynn Effect
IQ scores across much of the world have generally increased over time
Education, health care, nutrition, technology
Discrepancies in IQ
Differences within groups, interpretation bias, poverty, discrimination, inequalities
Achievement
Current measure of understanding
Aptitude
Future performance
When Amy was seven years of age, she had a babysitter from France. During this time Amy learned to speak a little French. Years later, when Amy got to college, she signed up for a beginning French class. Amy learned the material in her French class much more quickly than her classmates did. Amy’s rapid learning was most likely due to
Implicit Memory
Shallow processing involves which of the following?
Encoding information based on its structure or appearance
The moment you look up a phone number and immediately dial it, the number is held in which temporary storage system?
Working Memory
Which of the following scenarios best demonstrates the role of context effects in memory?
Amy studied for a vocabulary test in the same classroom and at the same time of day as the normal class, and she performed better on the test than students who studied in different classrooms under different conditions.
A corporation created what they referred to as an “intelligence assessment” to give to people who are applying for jobs with their company, which sells medical equipment. The assessment asked questions about popular culture, sports, and historical events that occurred in the United States. Which of the following might explain why the assessment results did not give the company a diverse pool of final candidates?
The assessment lacked validity by only asking about United States cultural and historic topics.
The hypothesis that intelligence is in part inherited is best supported by the fact that the IQ correlation for
pairs of identical twins is greater than for pairs of fraternal twins
Research on intelligence tests must be especially mindful of ethical principles related to confidentiality of data. A major reason for this is best described by which of the following?
Intelligence test scores have been used to determine access to opportunities such as jobs and education.
Henry took an intelligence test and scored lower than he thought he should. He kept retaking the test, but he kept getting about the same score each time. This series of events indicates that the test was
reliable