BILD 1 Final COOPER UCSD
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is needed for a recessive X-linked trait to be expressed?
1) female needs 2 copies of the allele (homozygous)
2) male needs 1 copy of the allele (hemizygous) (thus more common in males)
silent mutations
different nucleotide in DNA but same amino acid in protein
Missence Mutation
when a point mutation results in substituting one amino acid for another
nonsense mutation
changes a normal codon into a stop codon
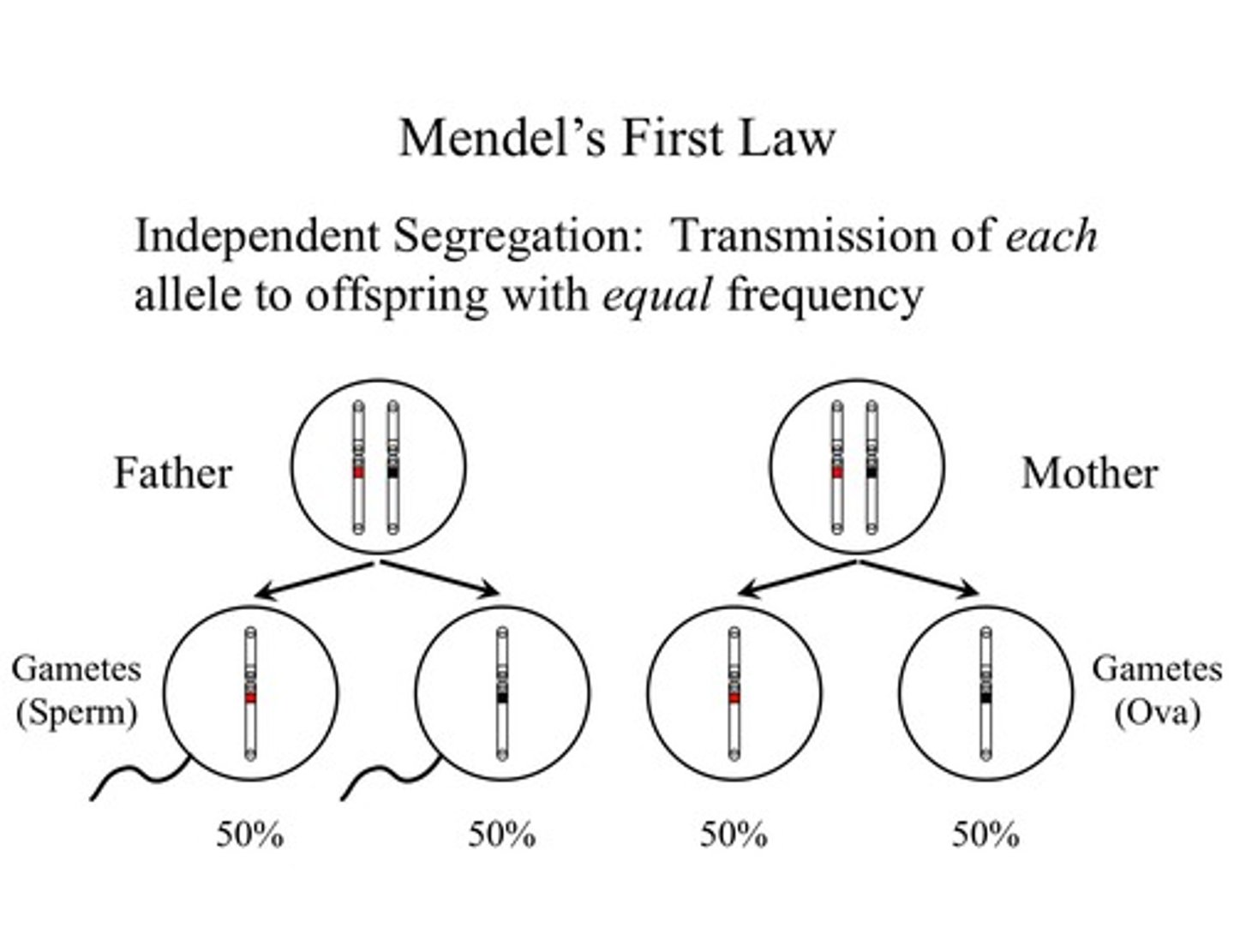
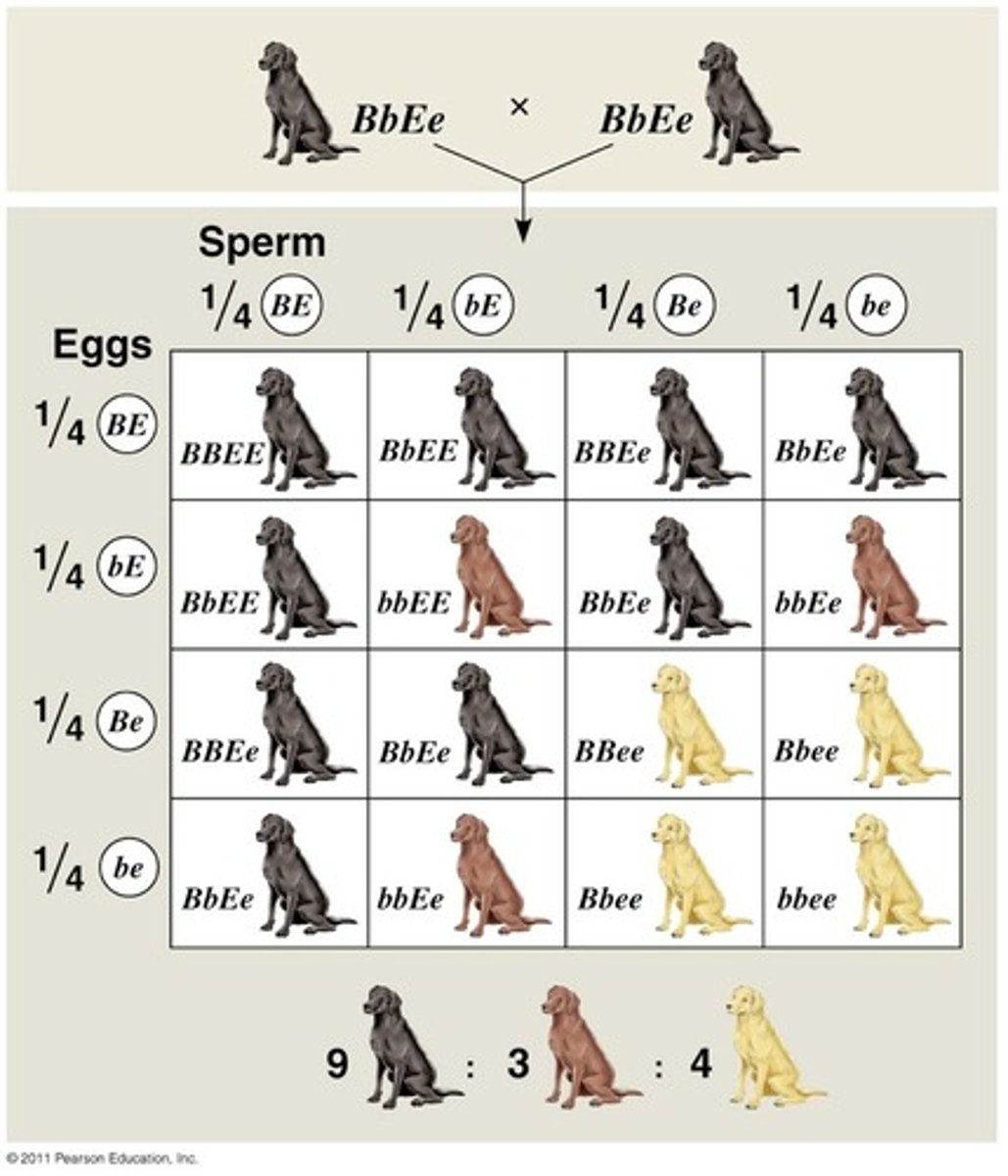
Law of Segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
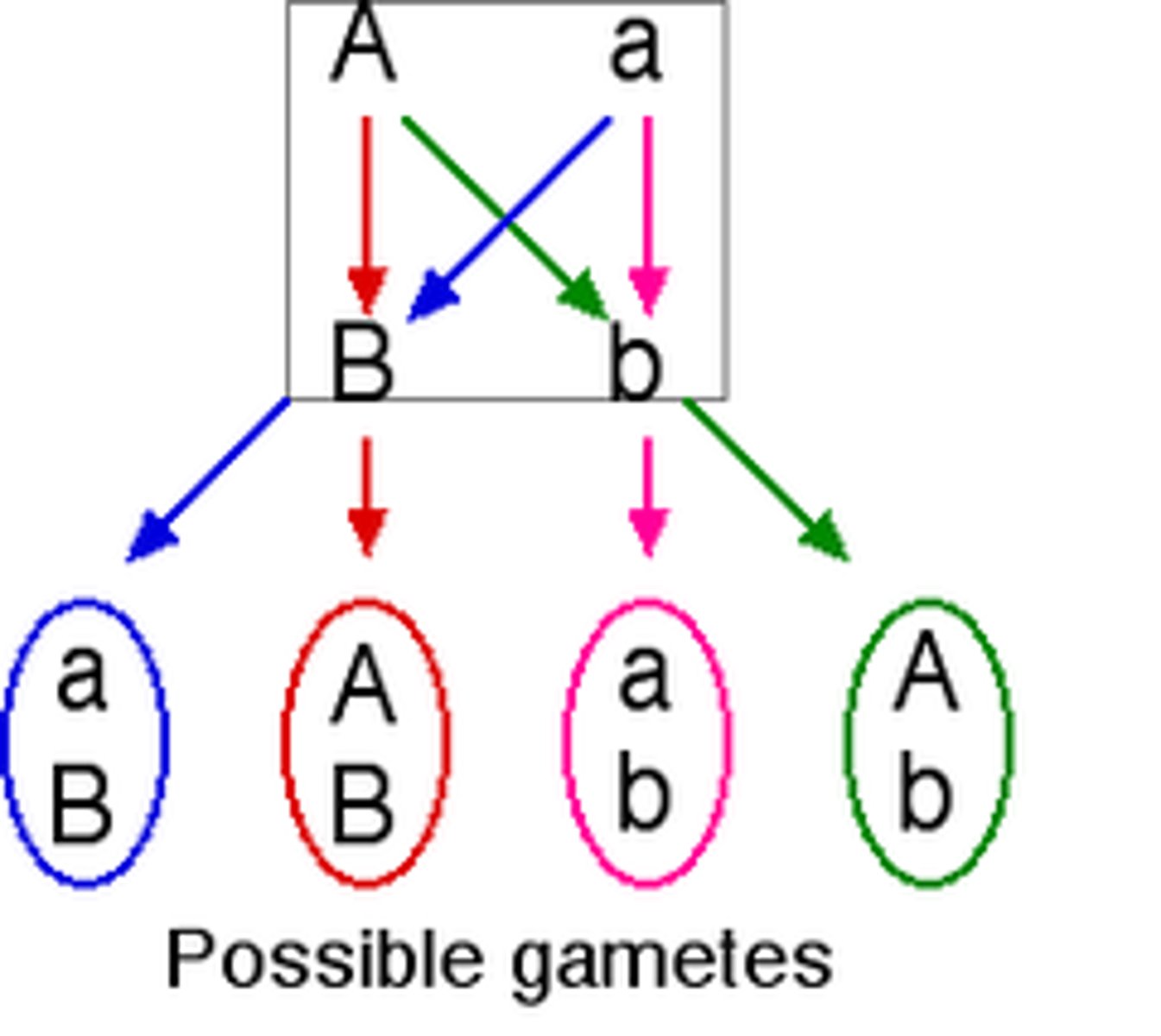
law of independent assortment
Two or more genes assort independently—that is, each pair of alleles segregates independently of any other pair during gamete formation. (only applies to genes on different chromosomes)
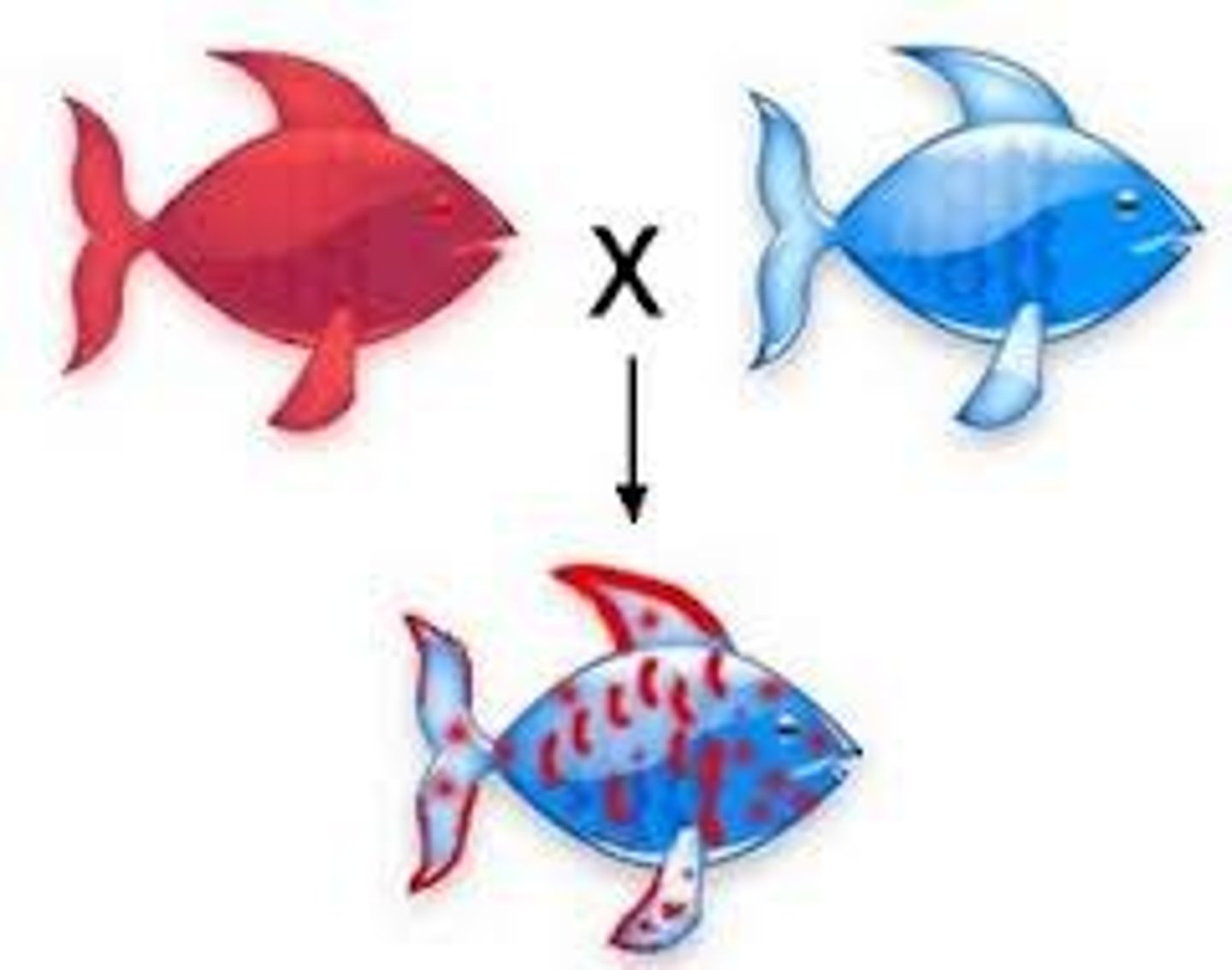
Incomplete Dominance
Phenotype of heterozygous is intermediate between the homozygous dominant and recessive (blended)
Codominance
Phenotype is affected by two different alleles in separate and distinguishable ways
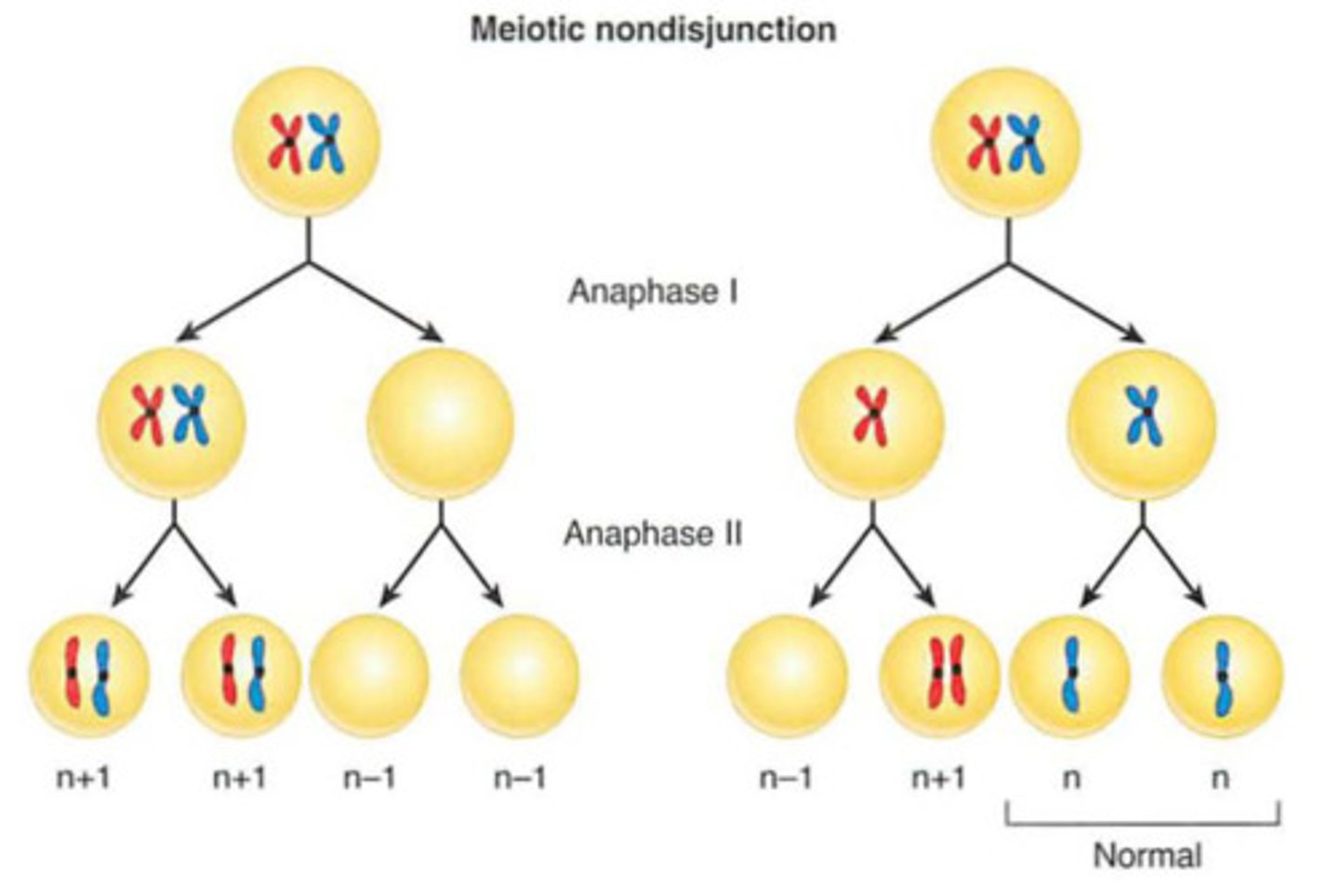
Nondisjunction (and result)
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
Result: 1 gamete receives 2 of the same type of chromosome and the other receives no copy
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.
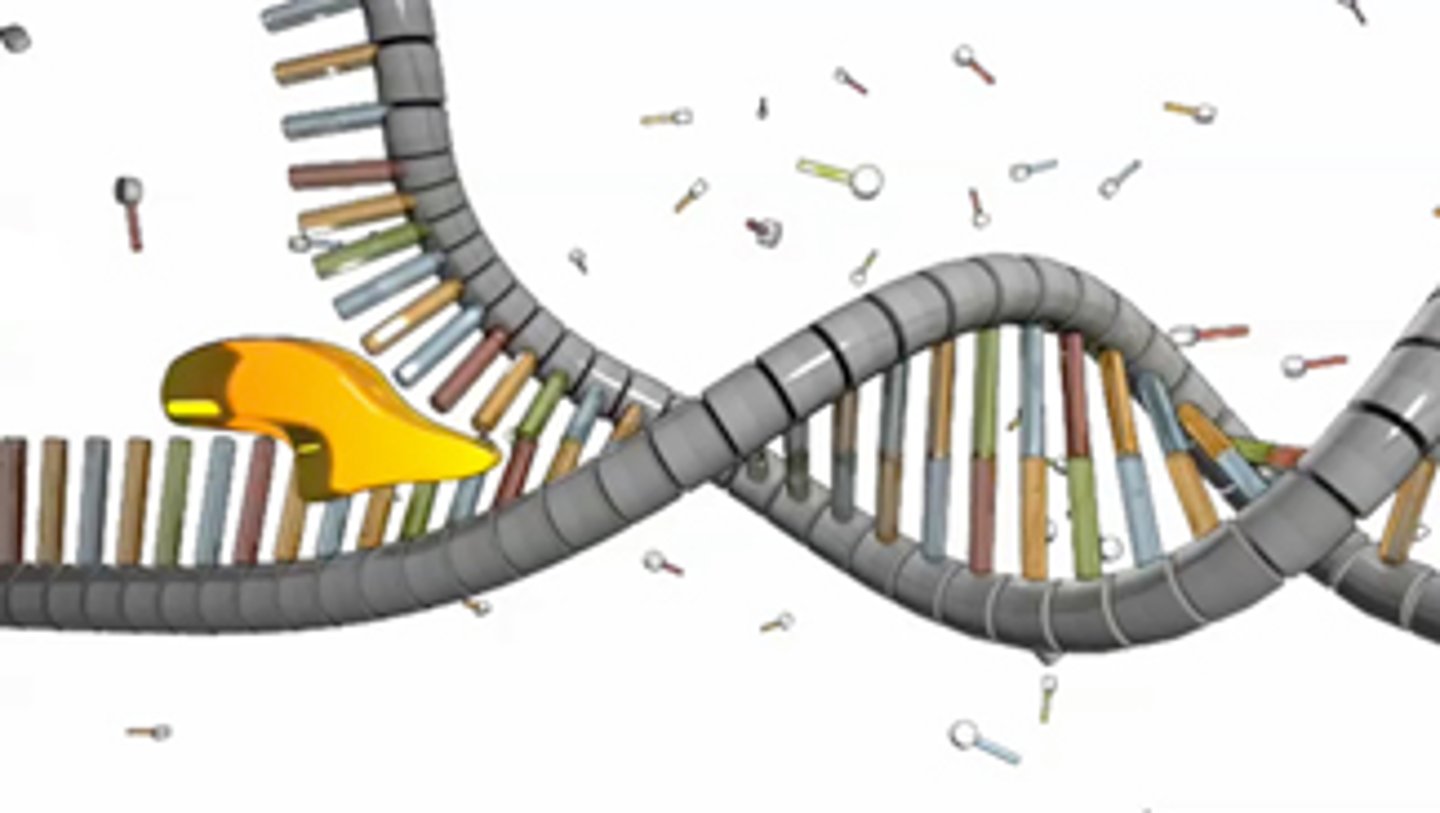
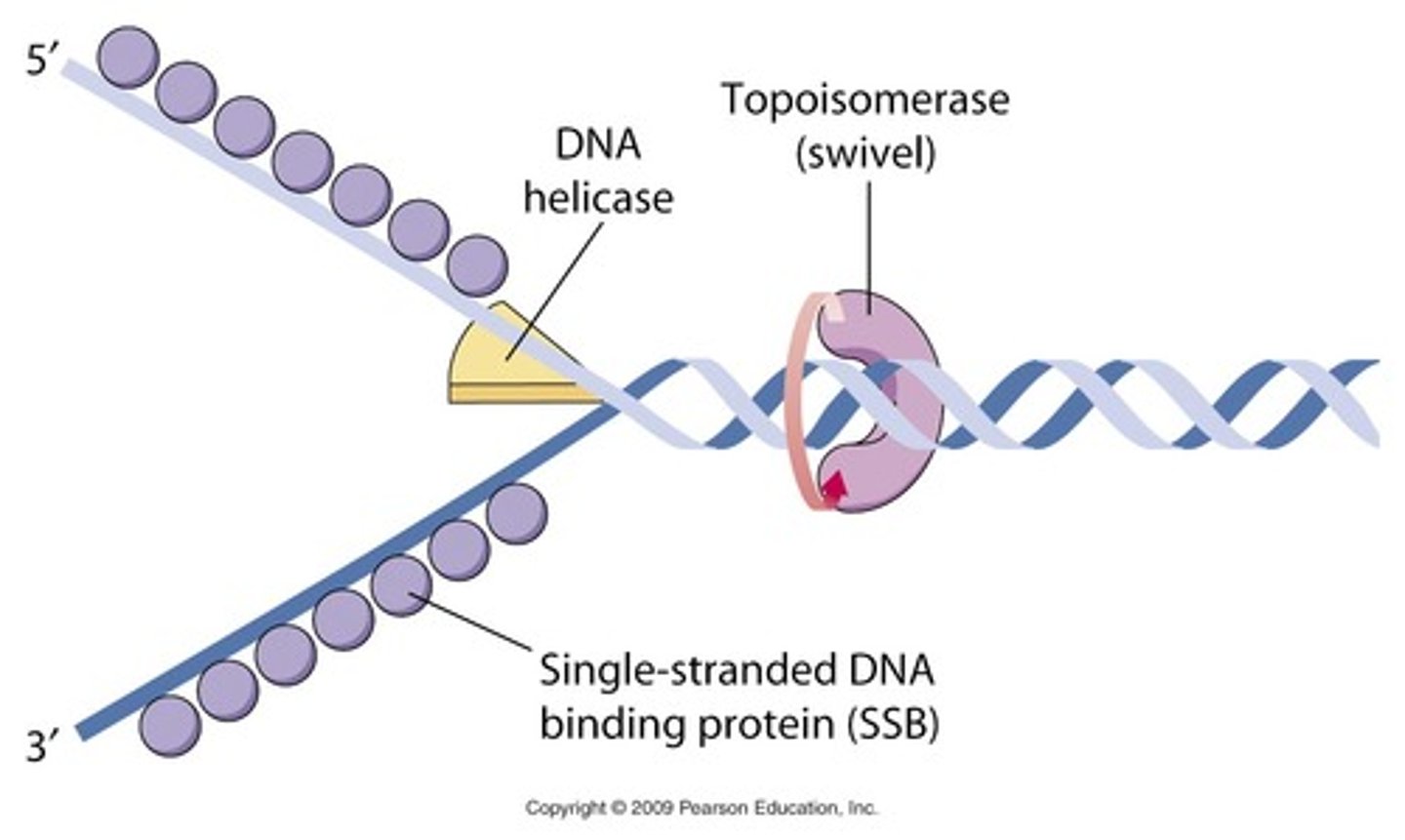
Helicase
Enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks
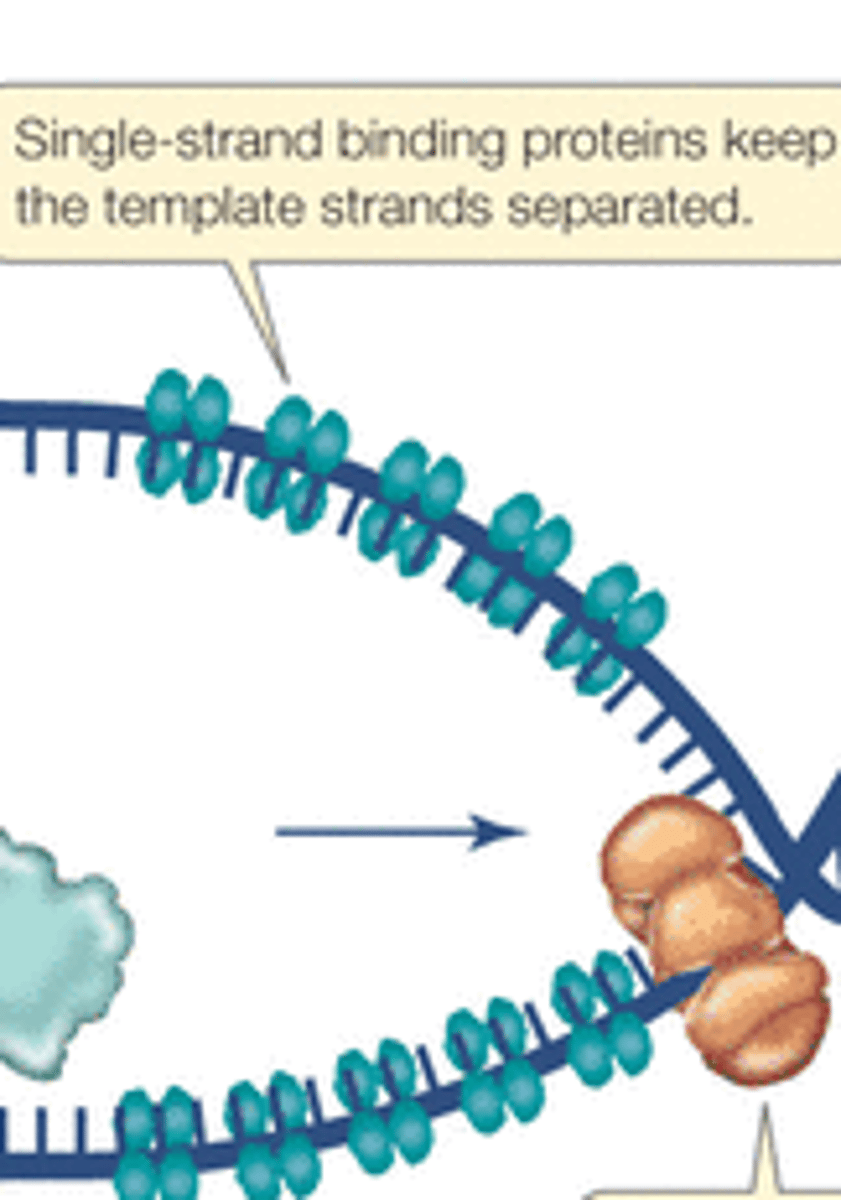
Single strand binding proteins
hold DNA strands apart
Semi conservative replication
Each half of an original DNA molecule serves as a template for a new strand, and the two new DNA molecules each have one old and one new strand.
Topoisomerase
A protein that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork by twisting and rejoining DNA strands
What aspects of genomes and cell structure makes DNA replication more complicated in eukaryotes than prokaryotes?
- circular vs. linear DNA
- prokaryotes don't have a nucleus
- prokaryotes have 1 chromosome; humans have 46
RNA primer
short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication
DNA polymerase require a primer to which they can add nucleotides
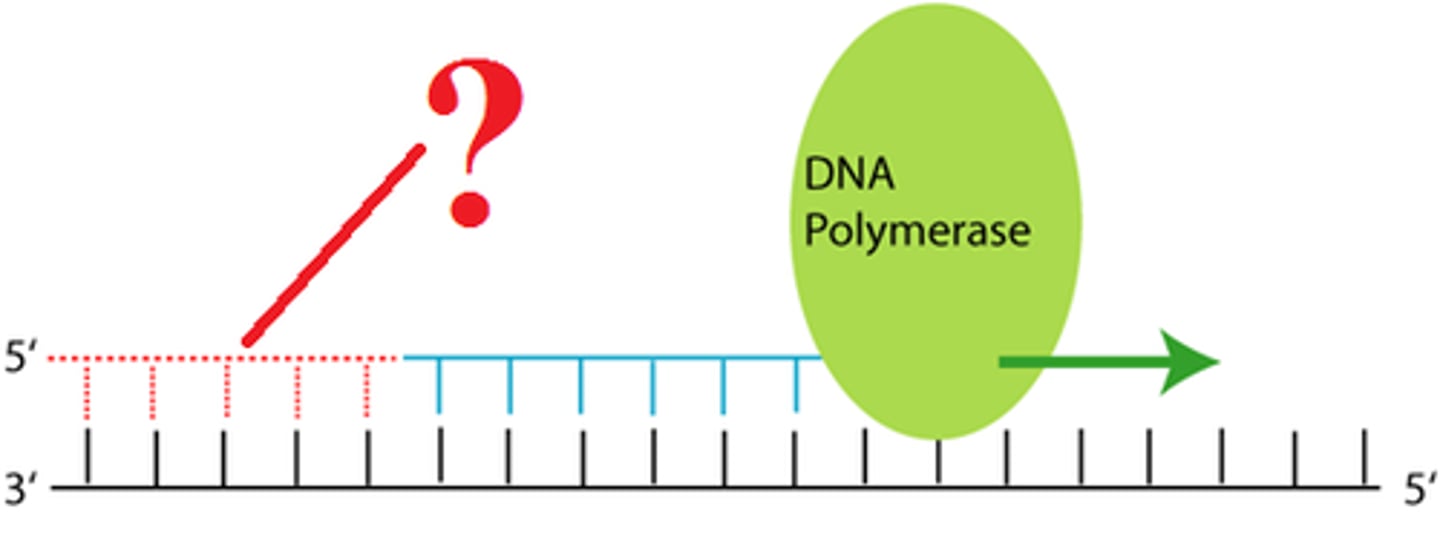
Primase
makes a short RNA molecule (~10 base pairs) that creates a small double stranded section
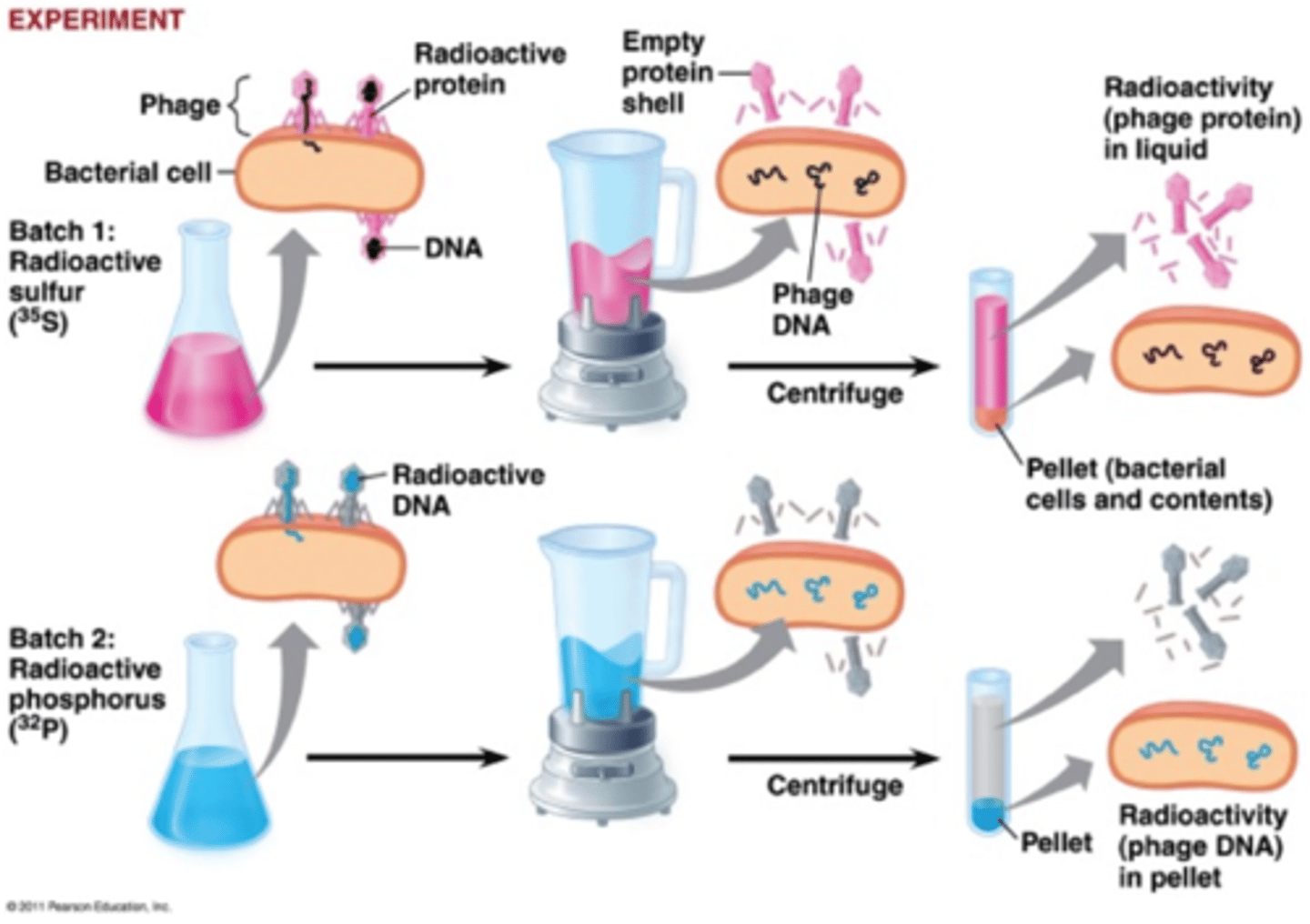
Hershey-Chase Experiment
determined that DNA is the genetic material
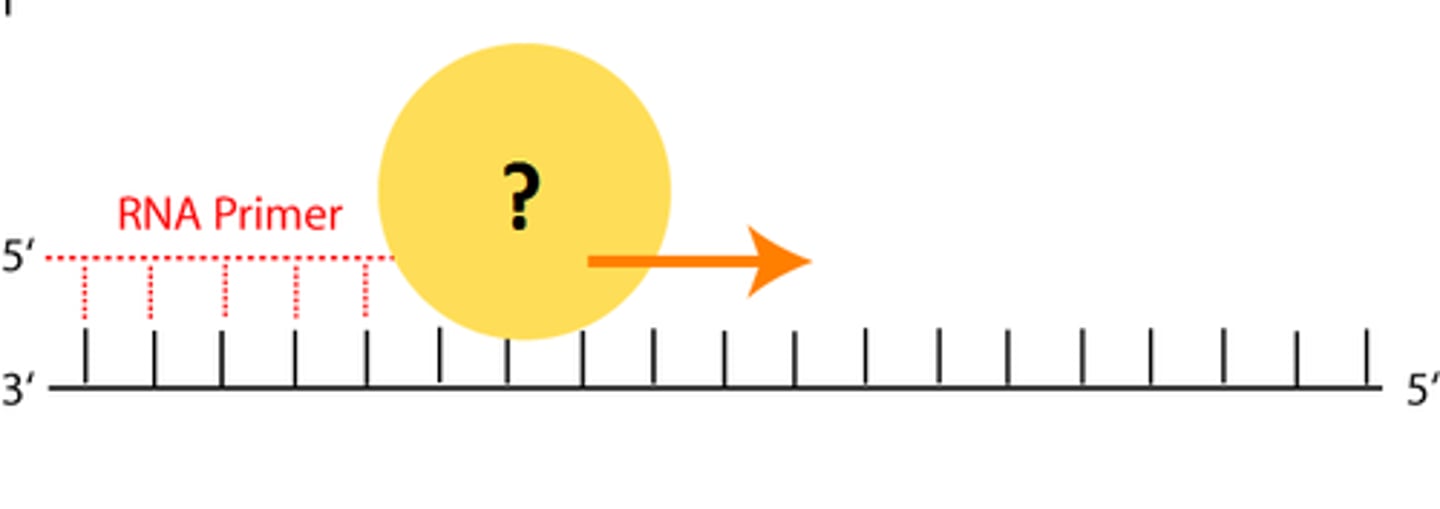
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA at replication fork
DNA ligase
Joins DNA together to make one continuous strand

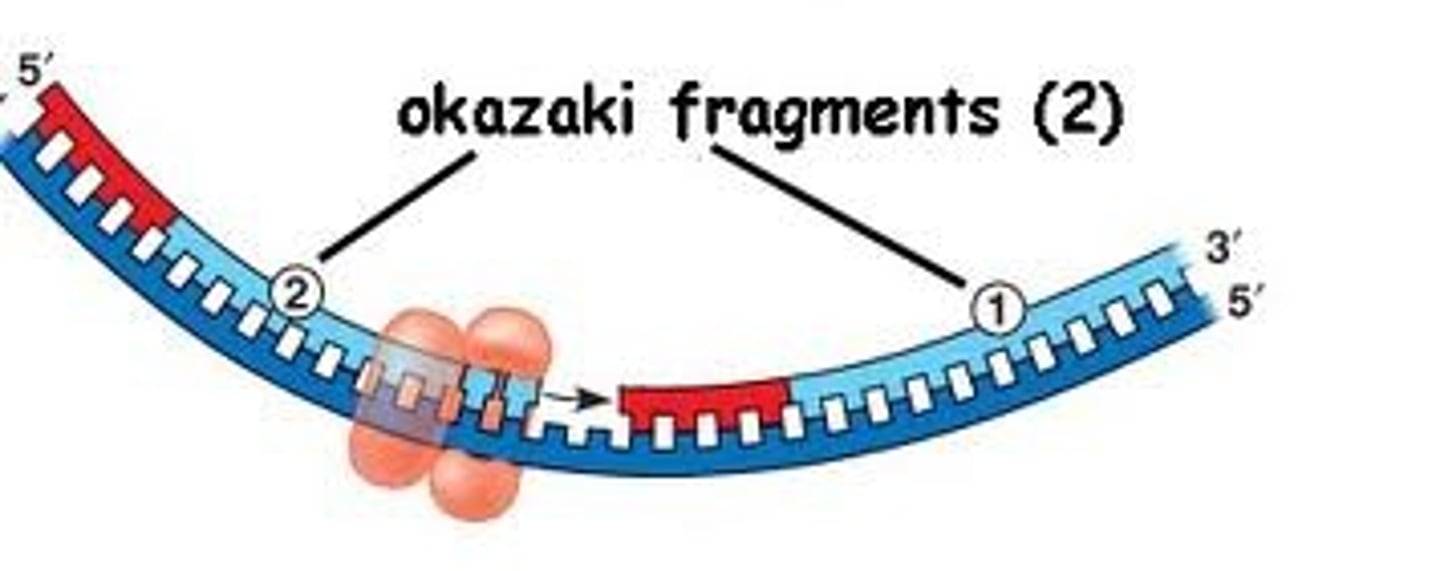
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
DNA polymerase I
replaces RNA primer with DNA
DNA polymerase III
makes new DNA strand by adding nucleotides one at a time to the 3' end
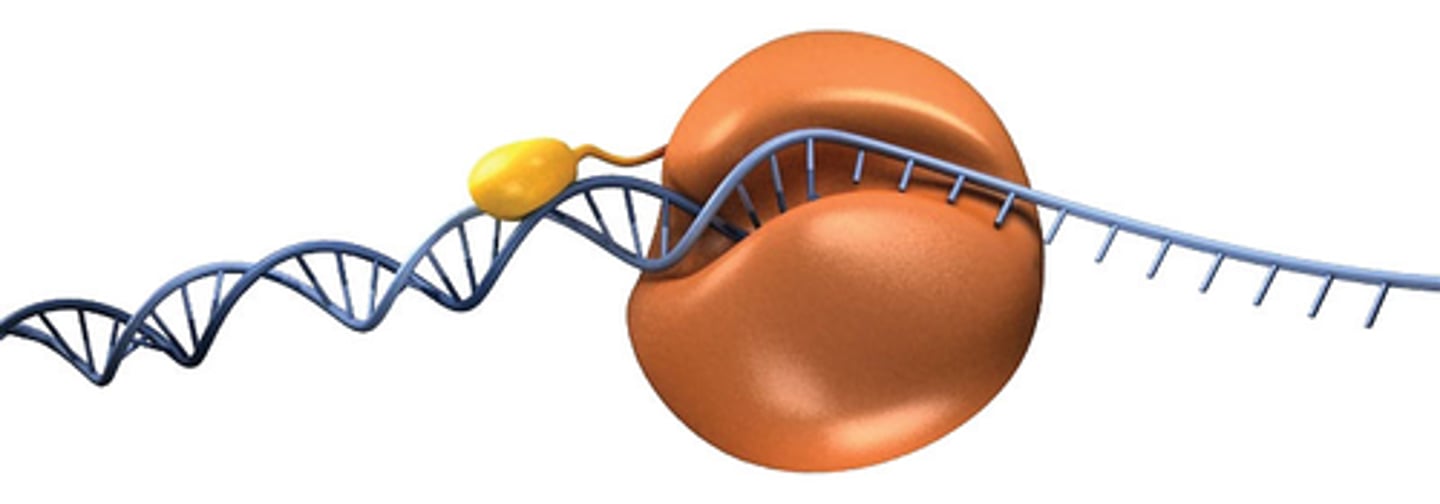
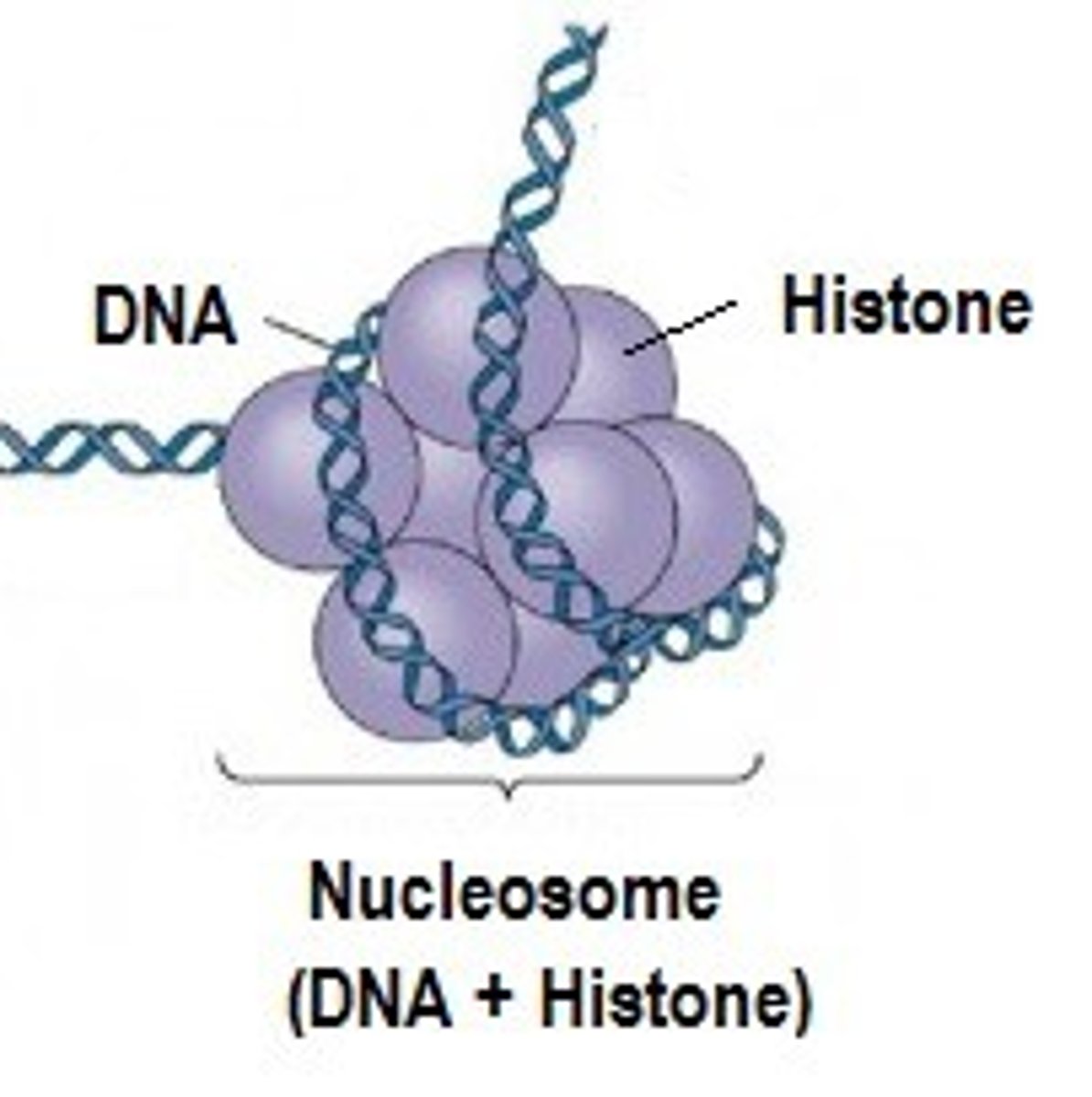
Histones
Responsible for the first level of DNA packing in chromatin
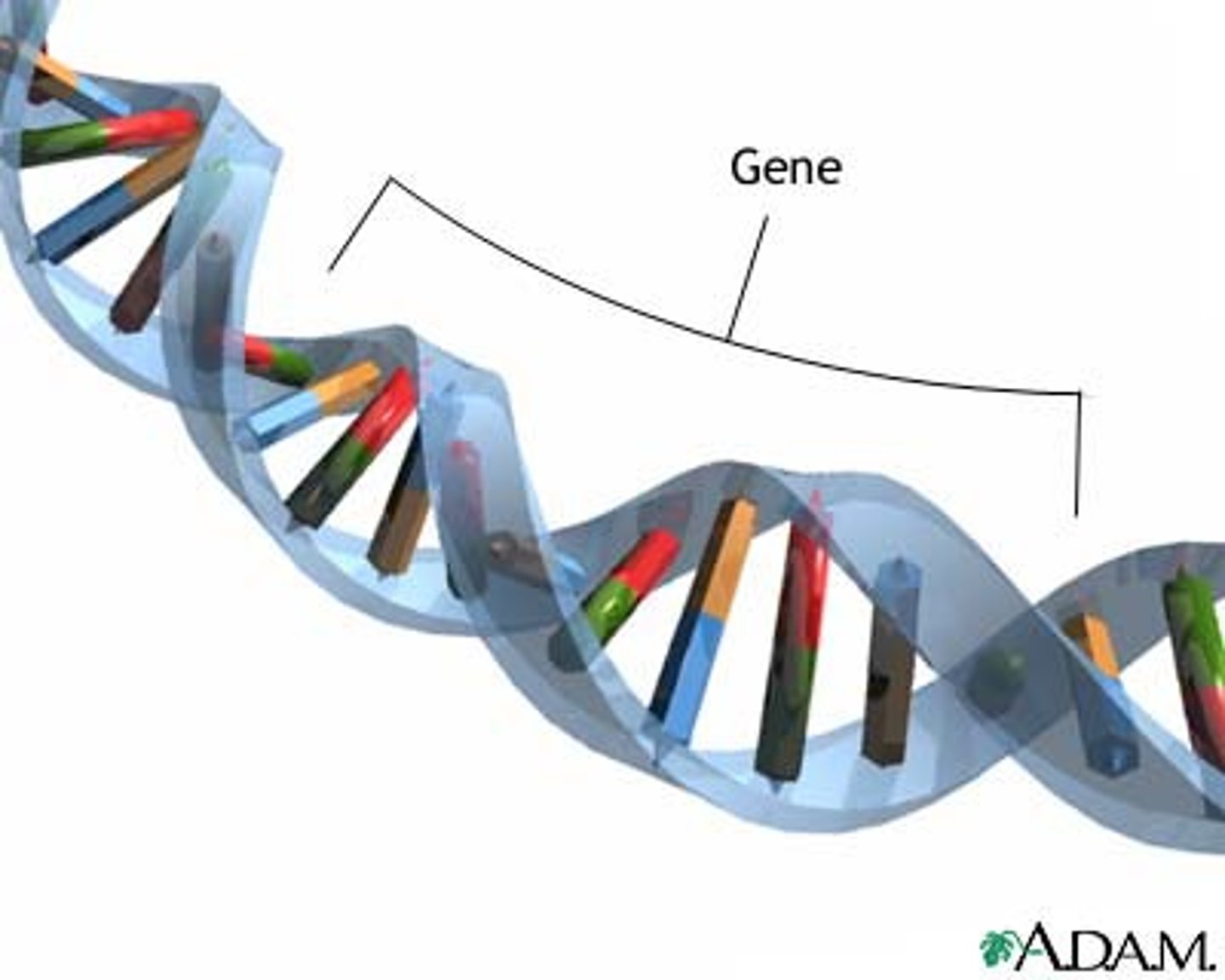
gene
A DNA sequence that is expressed to form a functional product: either RNA or polypeptide
Leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
Lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments (joined together by DNA ligase), each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
Gene expression
The process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation
Transcription +product
Synthesis of RNA using information in DNA
Produces mRNA
Translation +site
Synthesis of a polypeptide using the information in the mRNA
Ribosomes are the site (ribosomes found on rough ER and in the cytoplasm)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jnP8_1eIfgo
What separates transcription and translation in eukaryotic cells?
The nuclear envelope
Primary transcript
The initial RNA transcript from any gene prior to processing
Central dogma
Concept that cells are governed by a cellular chain of command:
DNA → RNA → Protein
Template strand
Provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript
will be 3' to 5'
Codon
mRNA base triplets that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid (position on polypeptide)
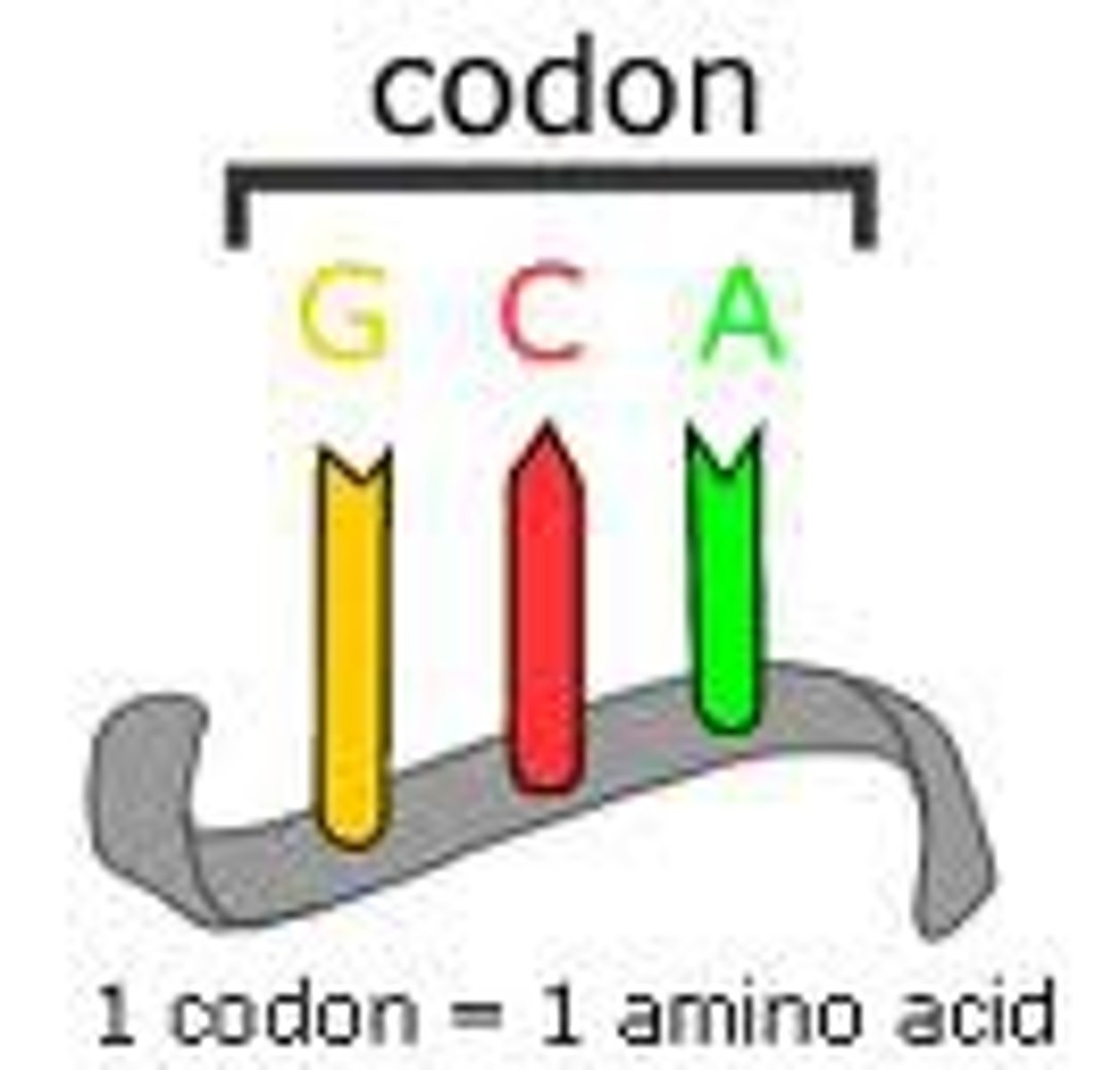
How many condons are there?
64
61 for amino acids and 3 are stop signals to end translation
What are the 3 stages of transcription?
1) Initiation
2) Elongation
3) Termination
Transcription factors
Mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription
Promoter
Region of DNA just before the part that will be made into the mRNA
situates RNA polymerase
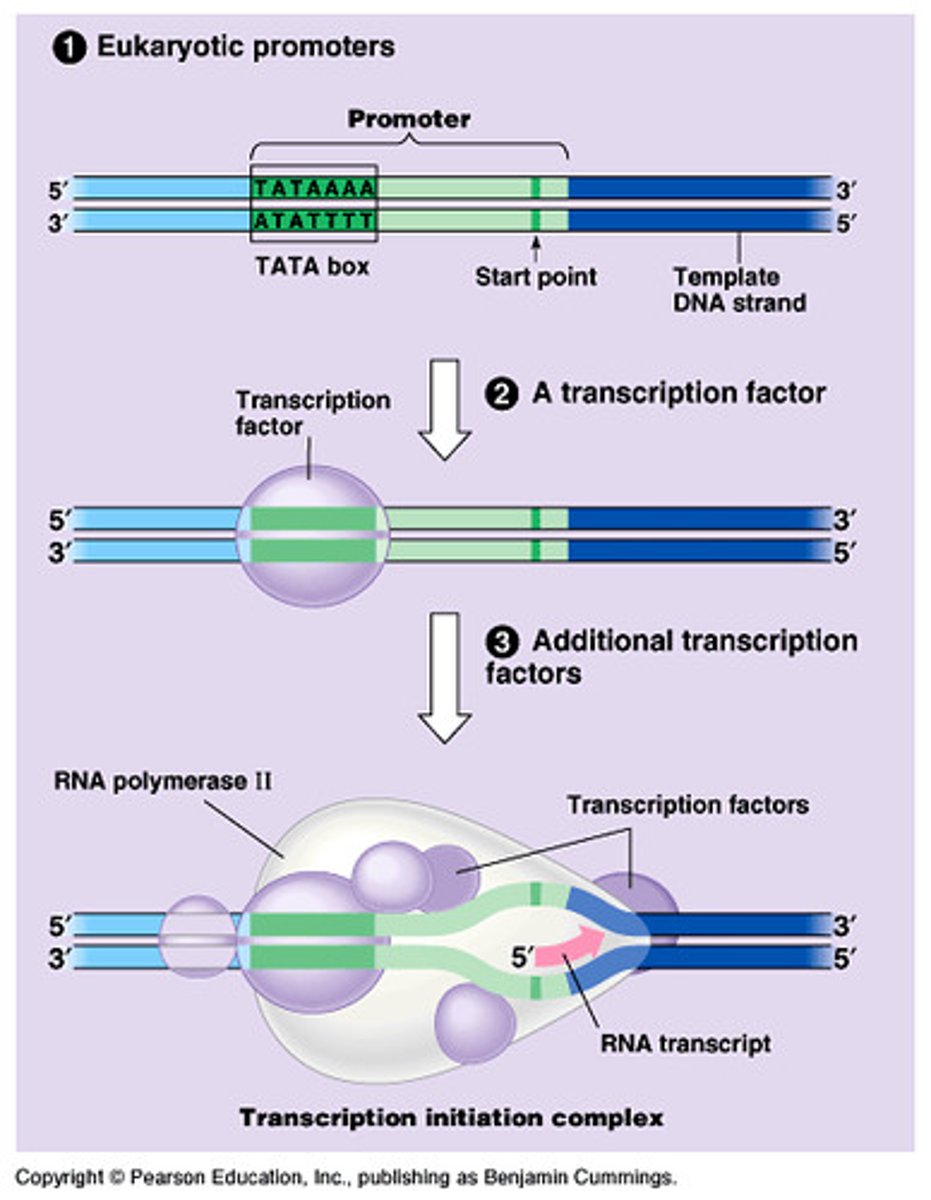
TATA box
A promoter crucial in forming the initiation complex in eukaryotes
Pre-mRNA processing
(only in eukaryotes)
1. 5' cap & Poly-A tail
2. Splicing
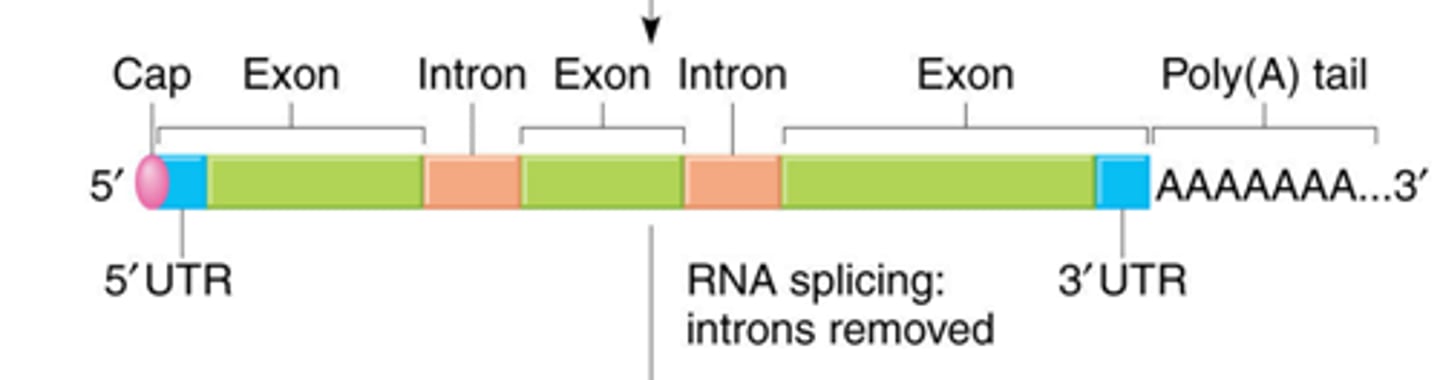
5' cap & Poly-A tail
Prevent mRNA from being broken down in the cytoplasm
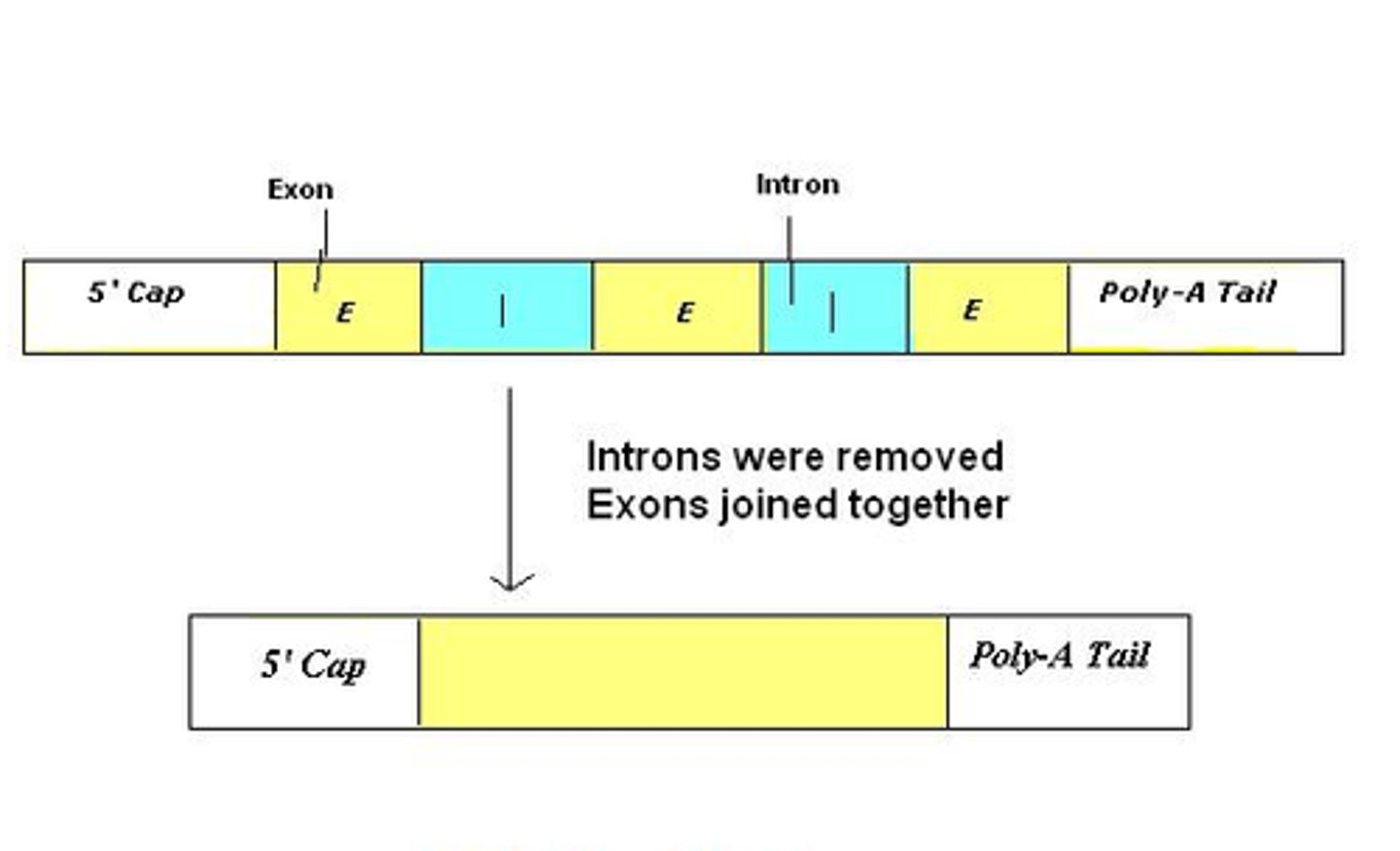
Splicing
removal of introns (RNA sequences that do not get translated into proteins)
Termination of transcription, prokaryotic vs eukaryotic
Prokaryotic: polymerase stops transcription at the end of the terminator and the mRNA can be translated without further modification
Eukaryotic: RNA polymerase II transcribes the polyadenylation signal sequence; the RNA transcript is released, 10-35 nucleotides past this polyadenylation sequence
Introns
Noncoding segments of DNA that lie in between coding regions
Can have sequences that regulate gene expression
Exons
Eventually expressed, usually translated into amino acid sequences
What are the 3 properties RNA that enable it to function as an enzyme?
It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself
Some bases in RNA contain functional groups that may participate in catalysis
RNA may hydrogen-bond with other nucleic acid molecules
Do prokaryotes have introns? +why
No, because they have transcription coupled to translation. They don't have time/space for that, since intron splicing will stop the coupling
Do eukaryotes have introns? + why
Yes, they evolved the nucleus, where splicing can be done
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
helps decode a mRNA sequence into a protein
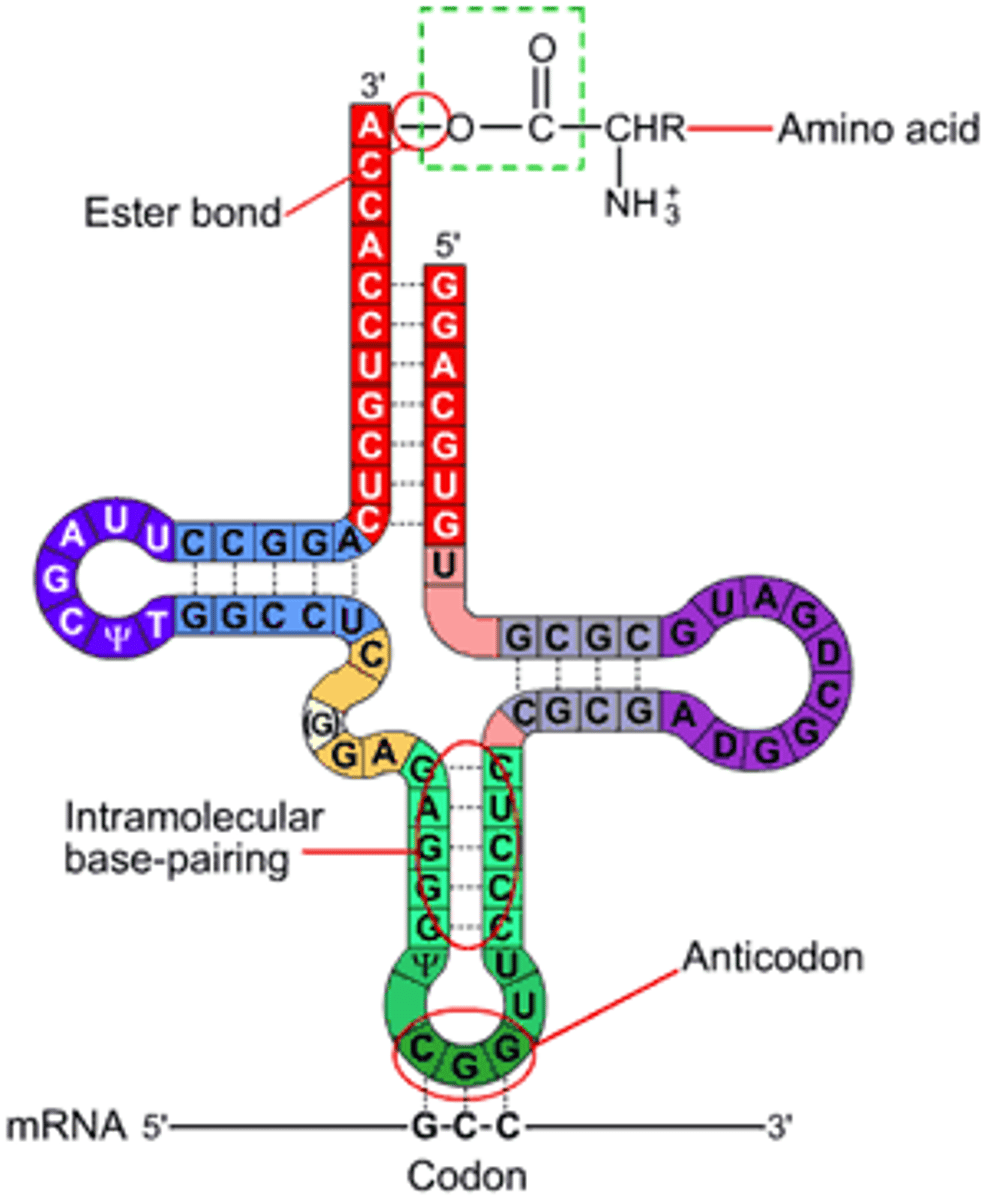
Initiation
- Small subunit of RNA is holding a tRNA; slides down the RNA until it finds the "AUG"
- Large subunit comes (uses GTP)
Elongation
Chain broken of P-site tRNA, goes to A-site tRNA, everything slides down one, once in E-site gets kicked out
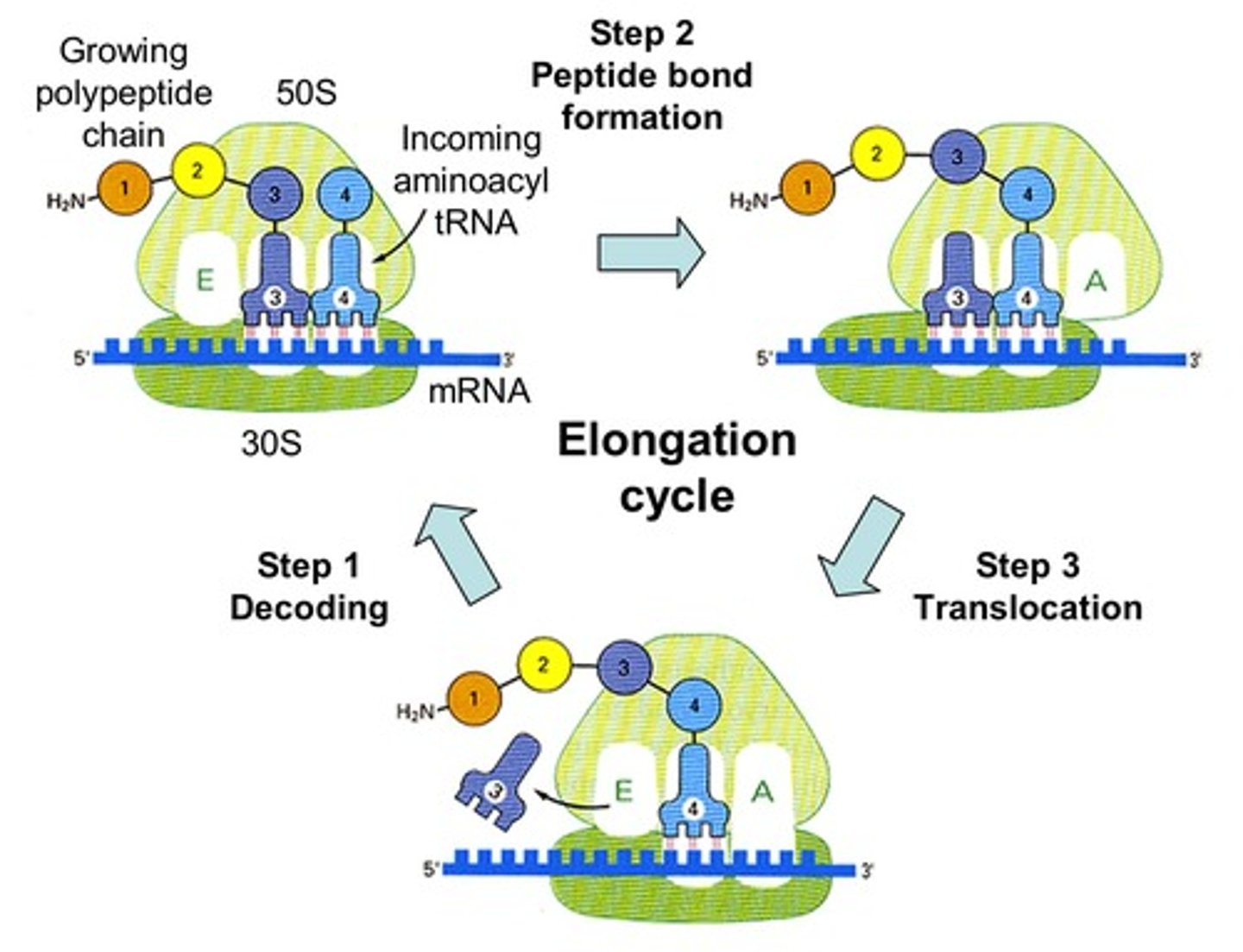
Termination
- Ribosome reaches stop codon
- Release factor
3 Binding sites for tRNA
EPA
eating
pink
apples
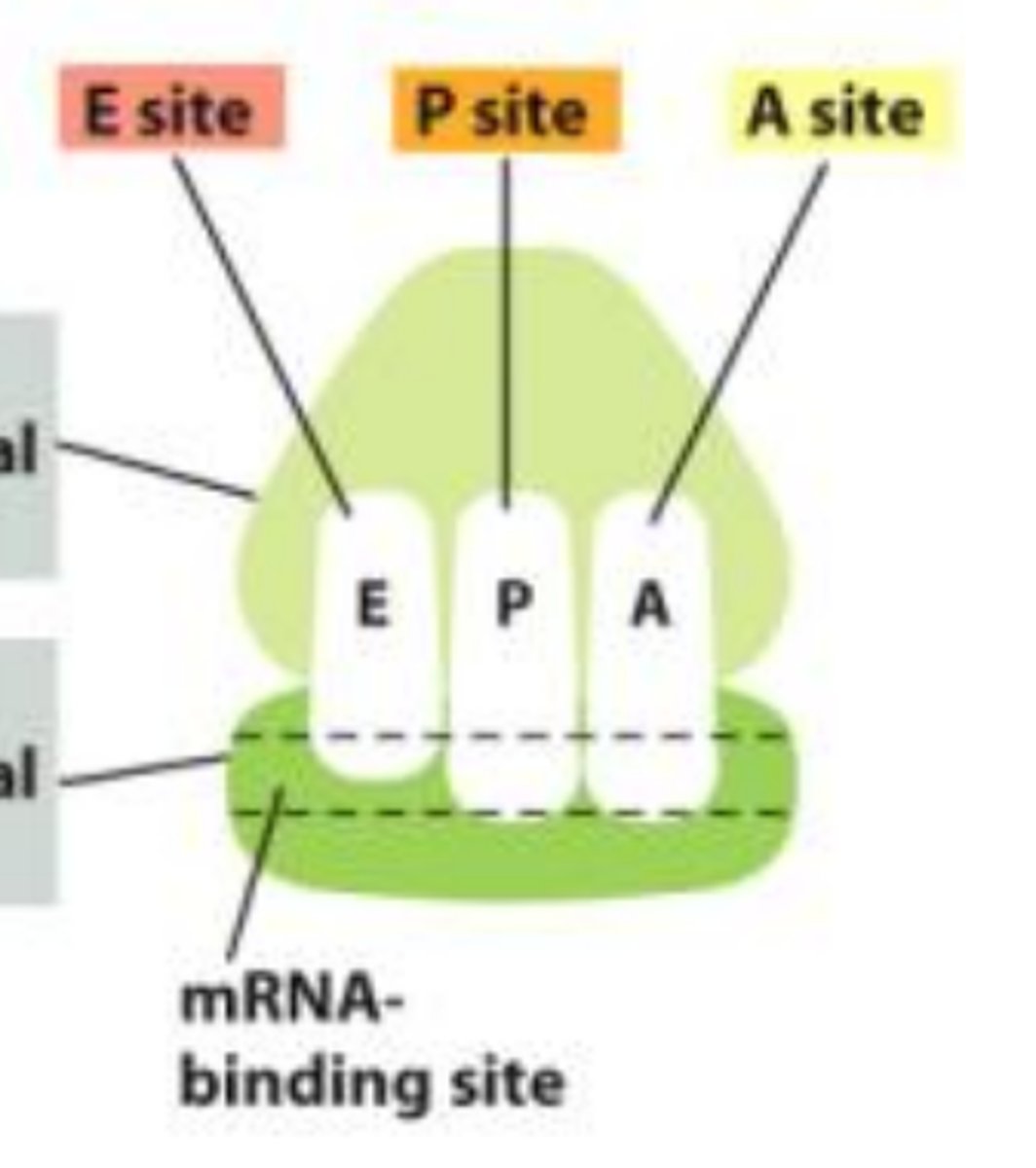
P site
Holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain
A site
Holds the tRNA that carries the next amino acid to be added to the chain
E site
Discharged tRNAs leave the ribosome E for exit
What signals the start of translation?
The start codon AUG
Operon
a unit made up of linked genes which is thought to regulate other genes responsible for protein synthesis
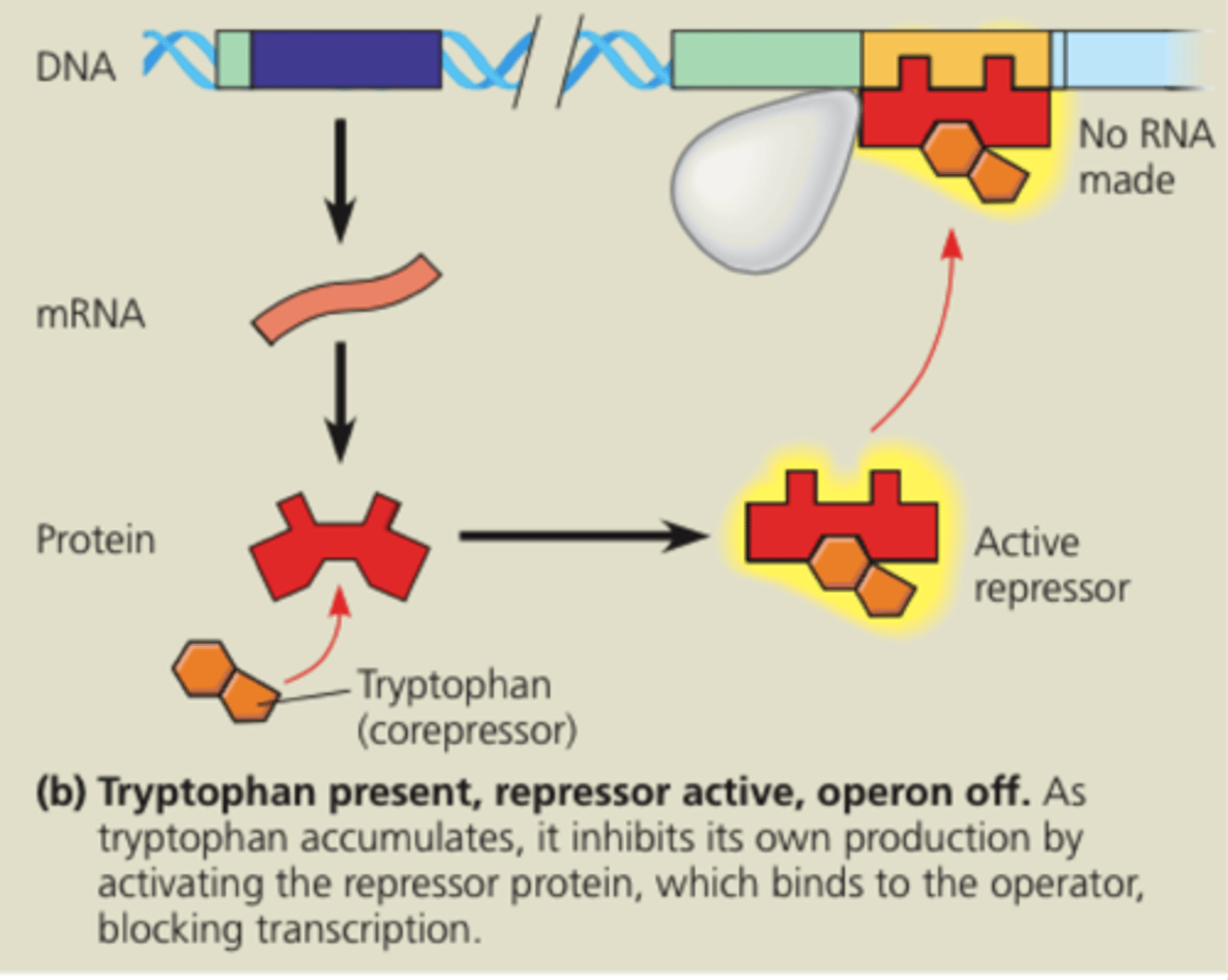
Repressible operon
transcription is usually on, but can be inhibited (repressed) when a specific small molecule binds allosterically to a regulatory protein (example tryptophan)
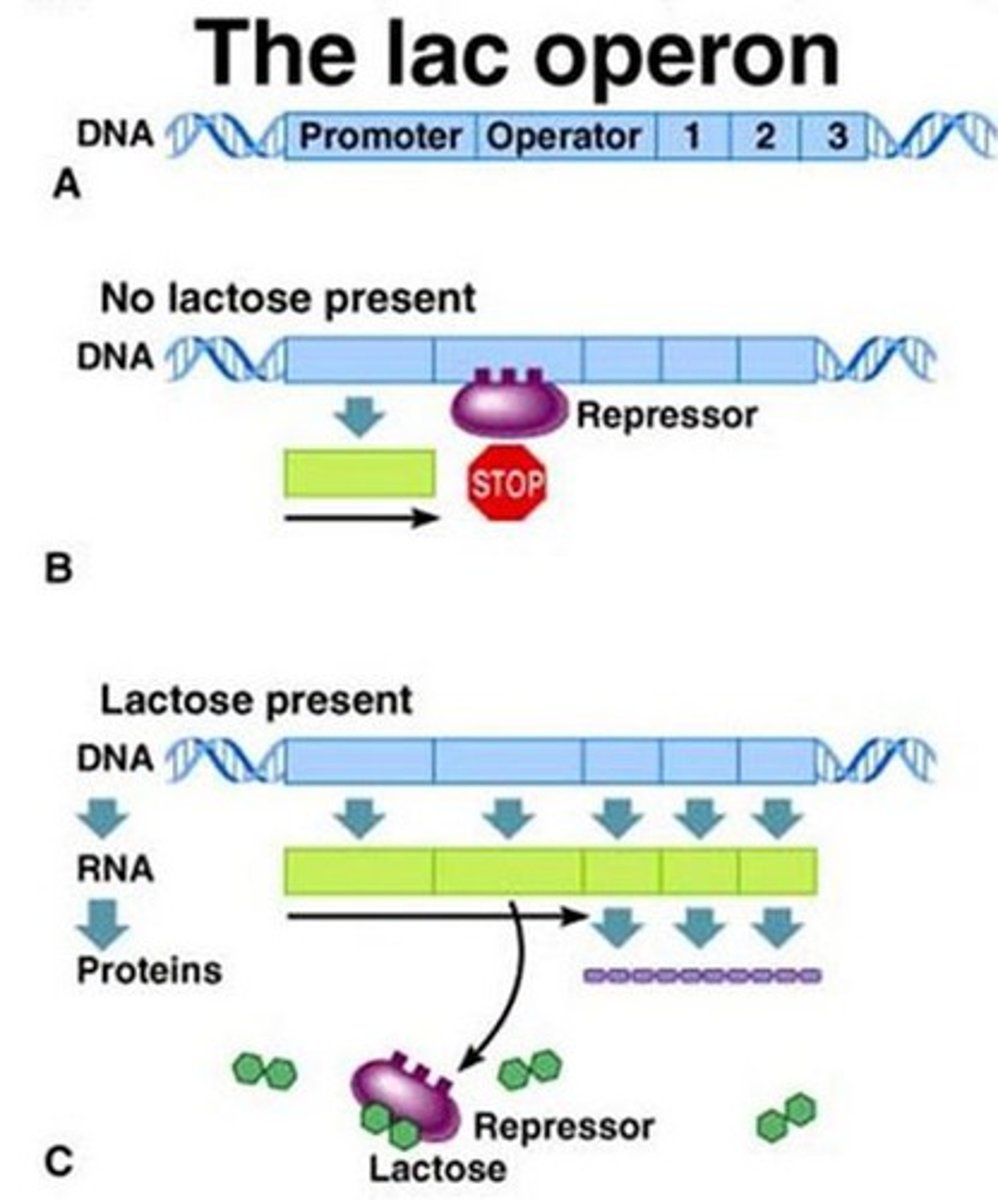
Inducible operon
usually off, but can be stimulated (induced) when a specific small molecule interacts with a regulatory protein (example lac operon)
corepressor
a small molecule that cooperates with a repressor protein to switch an operon off
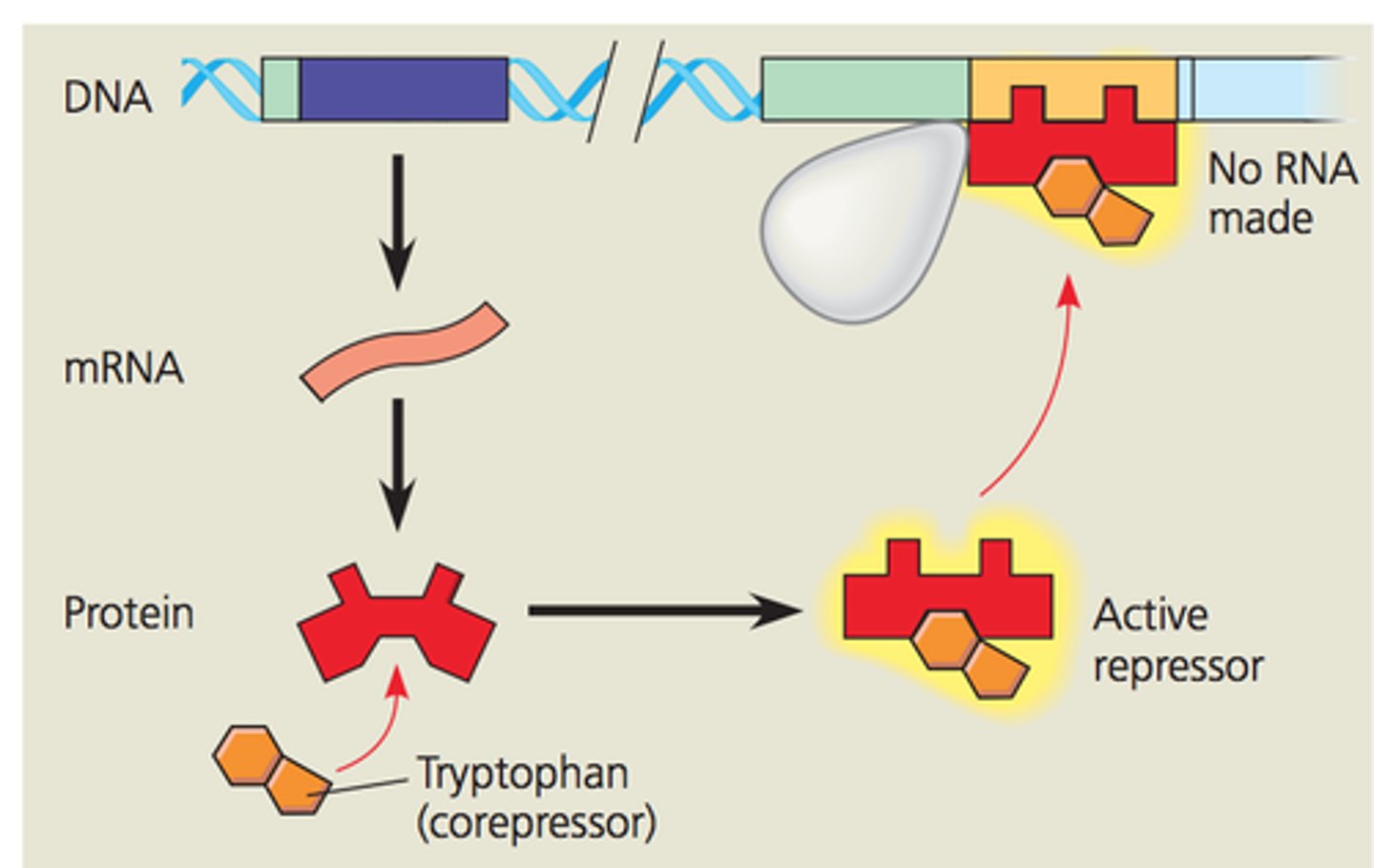
inducer
A specific small molecule that inactivates the repressor in an operon (turns operon on)
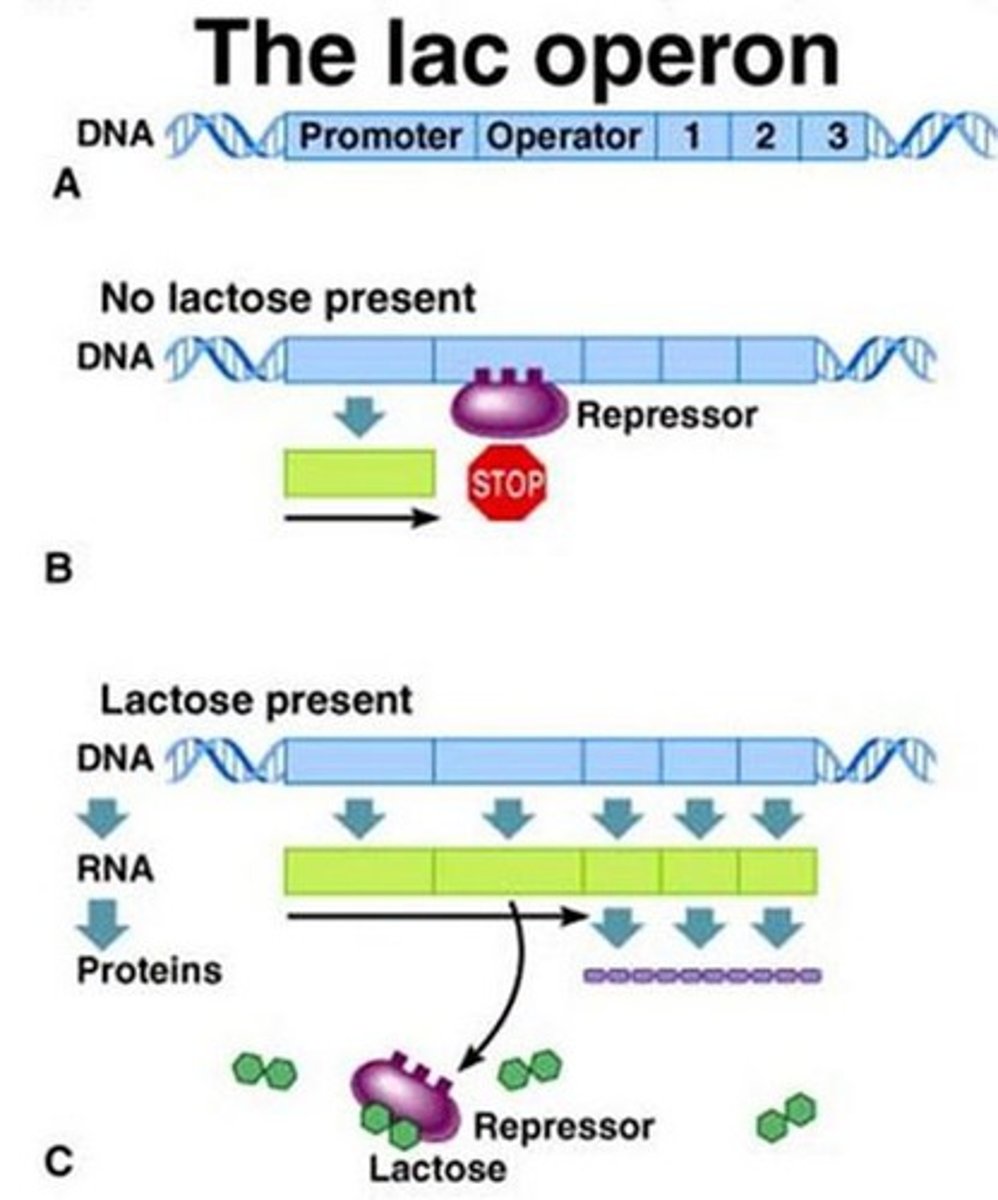
Regulatory gene
a gene that produces a repressor substance that inhibits an operator gene
DNA Methylation
The addition of methyl groups to bases of DNA after DNA synthesis; may serve as a long-term control of gene expression.
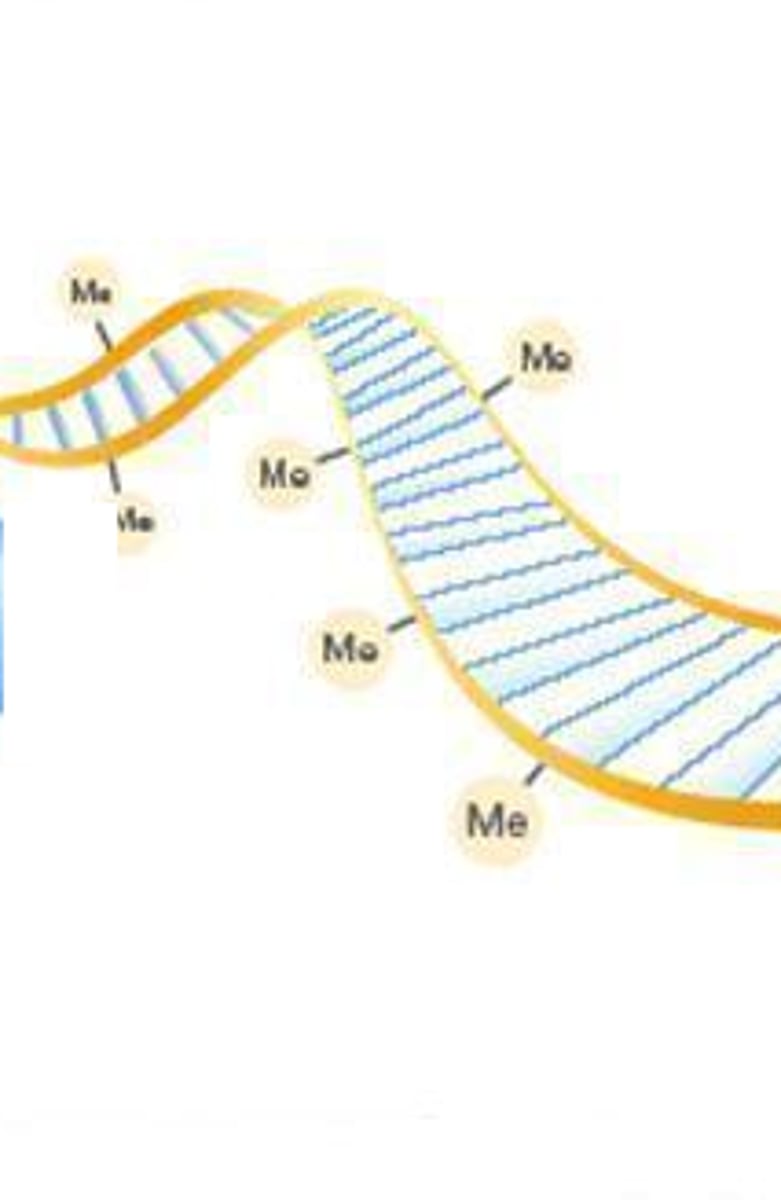
Chromatin structure
More dense DNA is not used as frequently
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
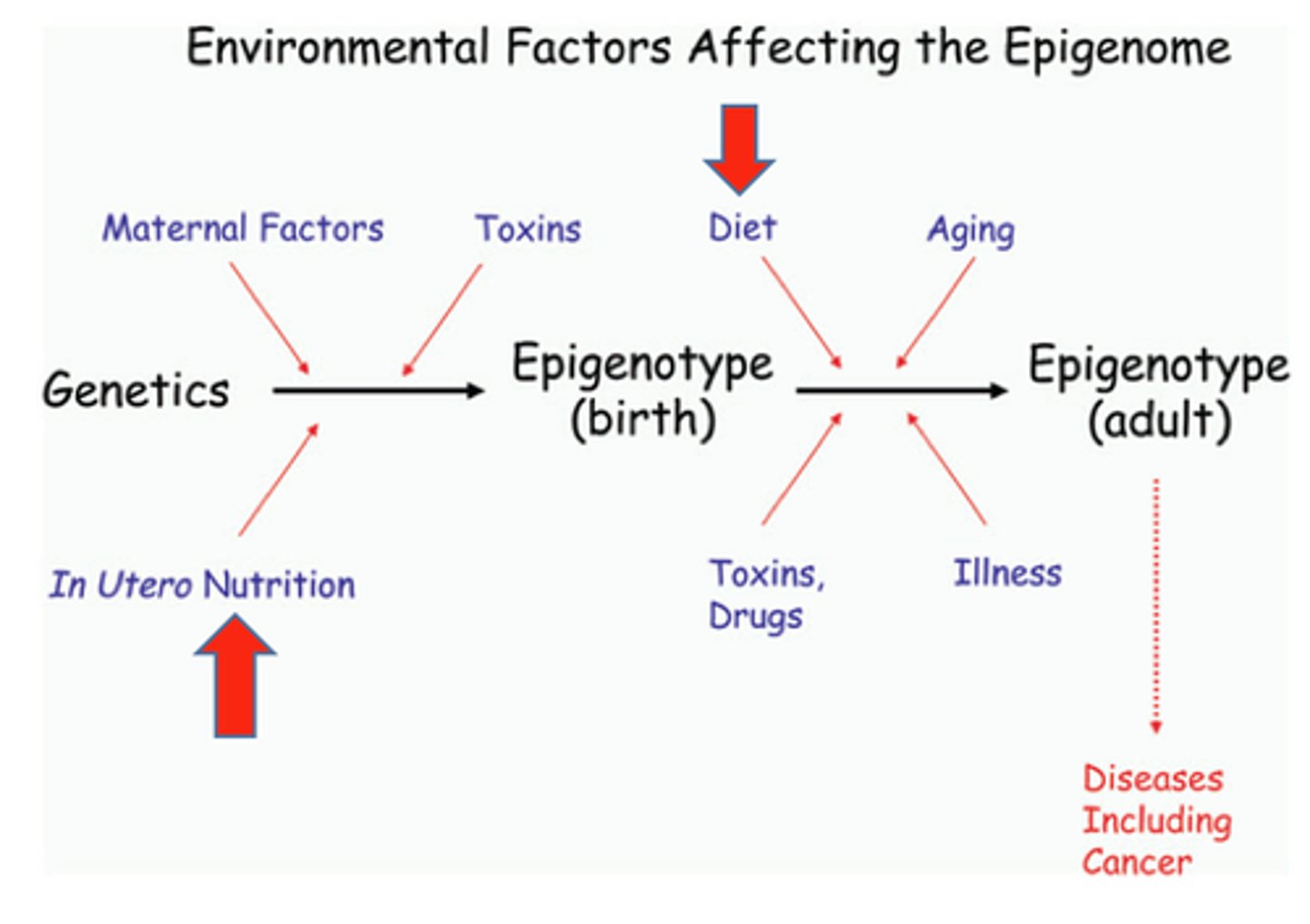
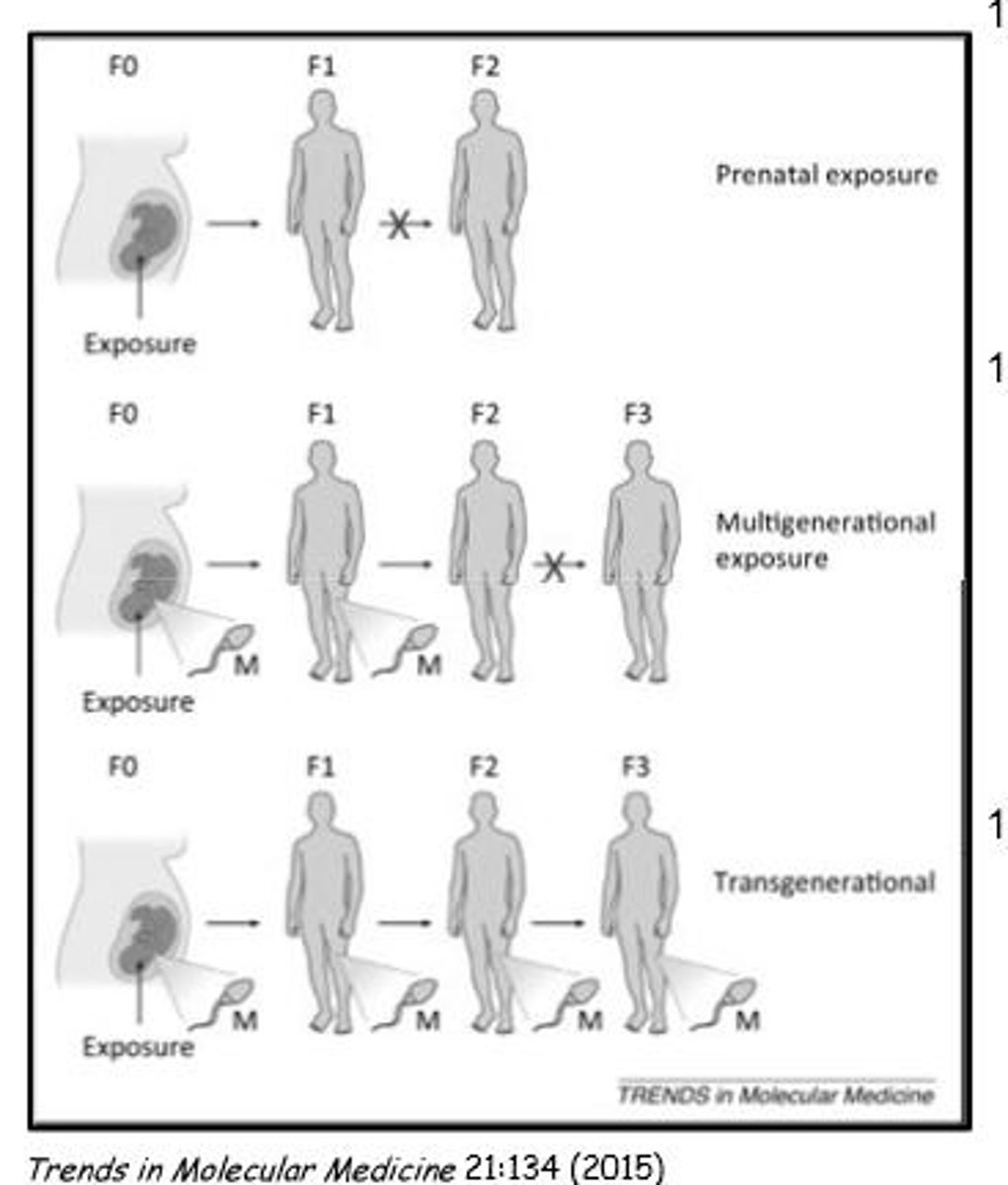
Transgenerational Exposure
Generations out: effects of exposure on gene expression/epigenetic markers
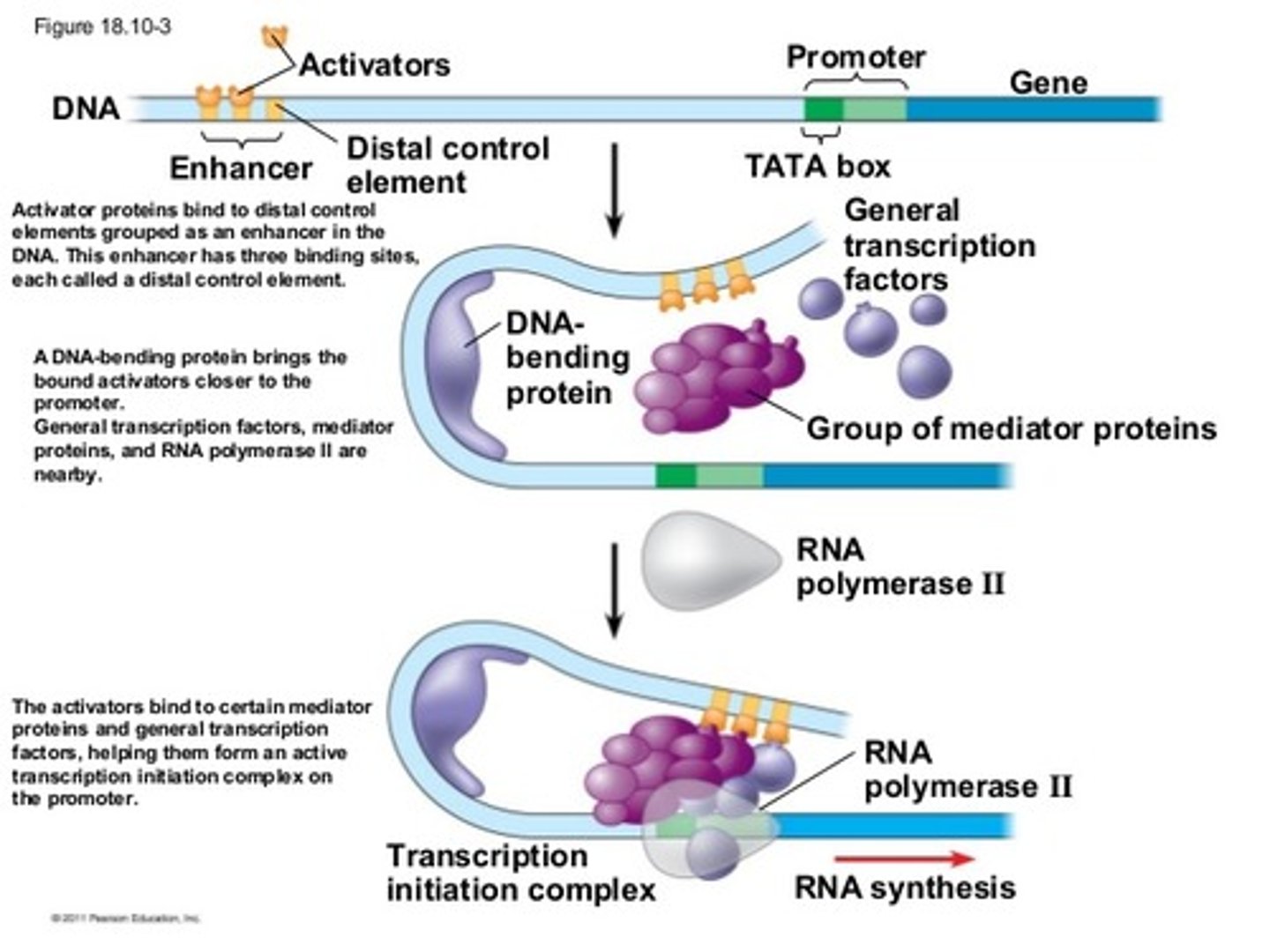
transcription factors
Bind to promoter; situate RNA polymerase
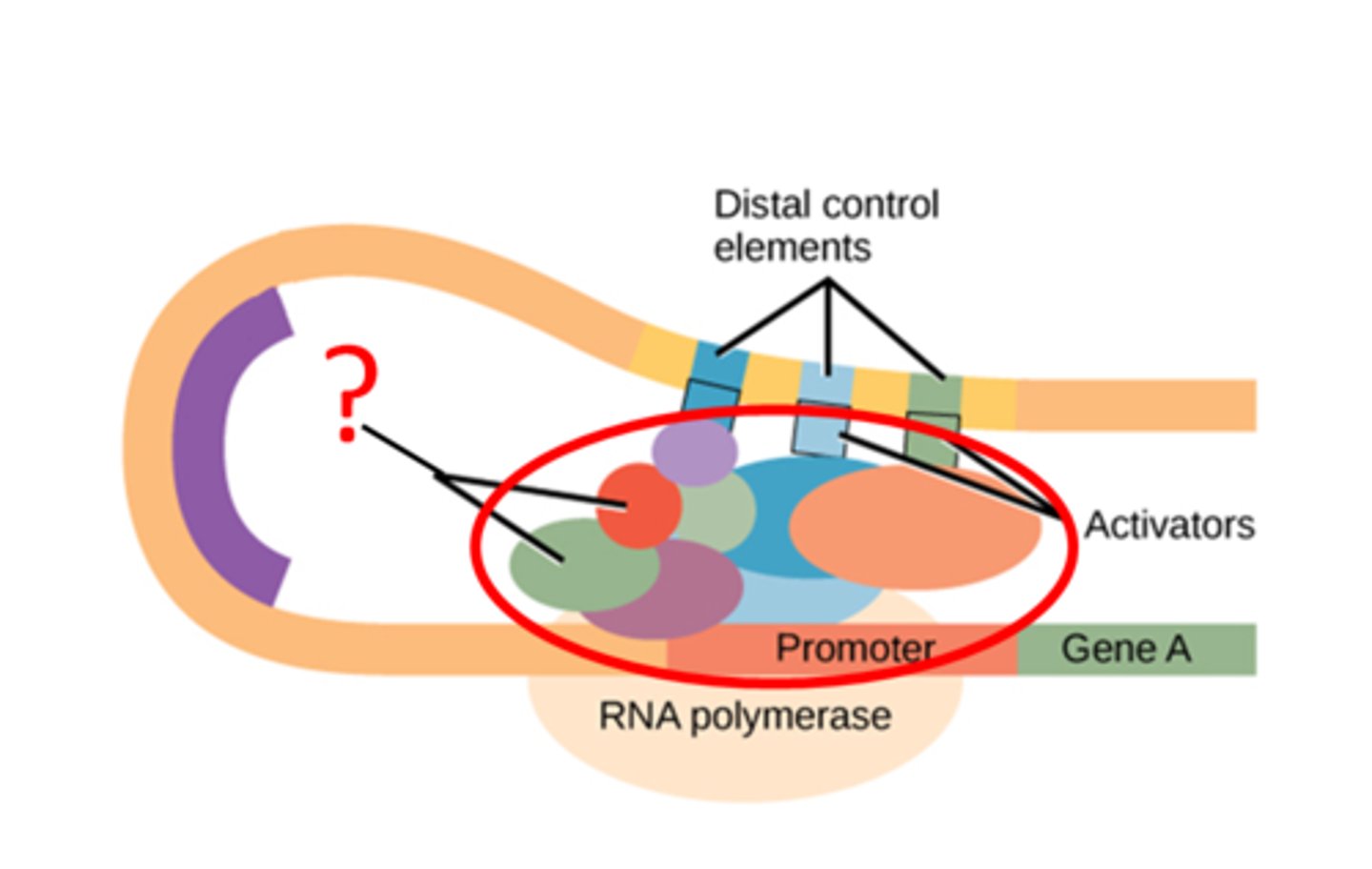
Enhancers and Activators
(similar to transcription factors) Small bits of DNA (further away in DNA); stabilize RNA polymerase
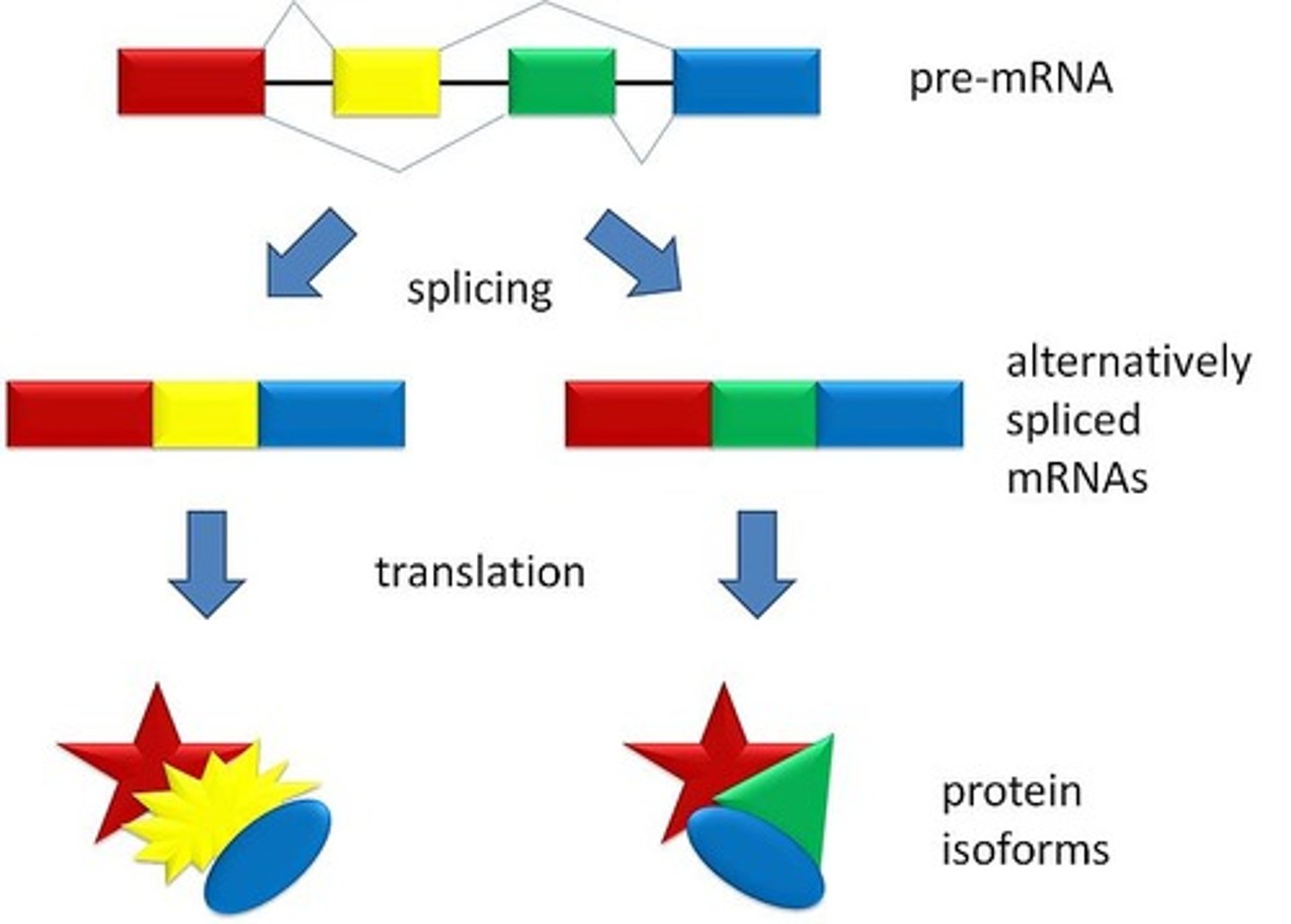
Alternative splicing
Post-translational RNA modification process in which some exons are removed
Mutually-exclusive exons get cut out
3 + 4 = mutually exclusive
1235
1245
x inactivation
one of two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated and remains coiled as a Barr body