Week 8 - Anatomy of Articulation and Resonation yeah
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
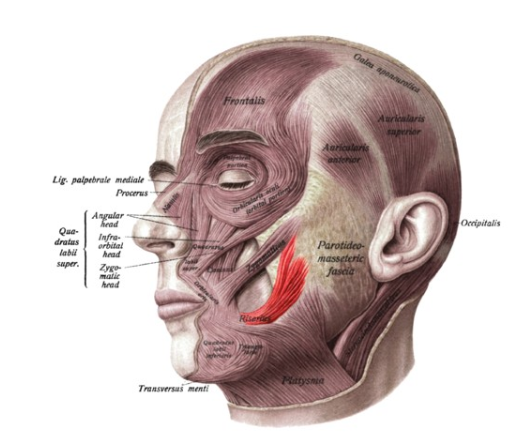
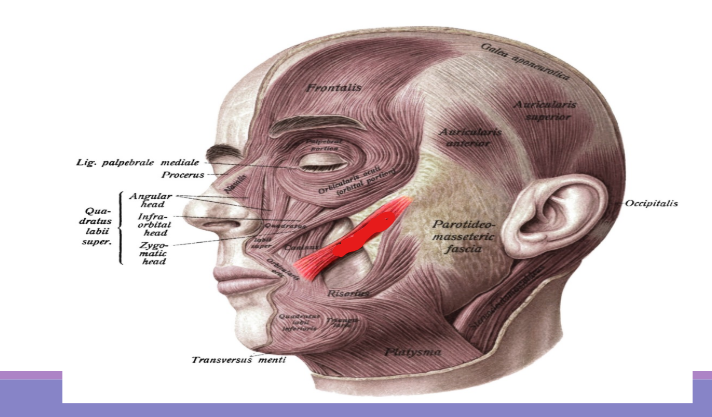
Risorius muscle
Retracts corners of the mouth (e.g., smiling and grinning), also used to move the cheeks while chewing
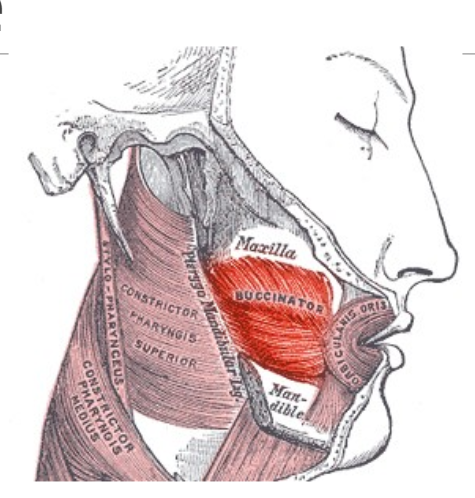
Buccinator Muscle
(Parallel to Risorius, but deep) Primarily used to move the cheeks while chewing
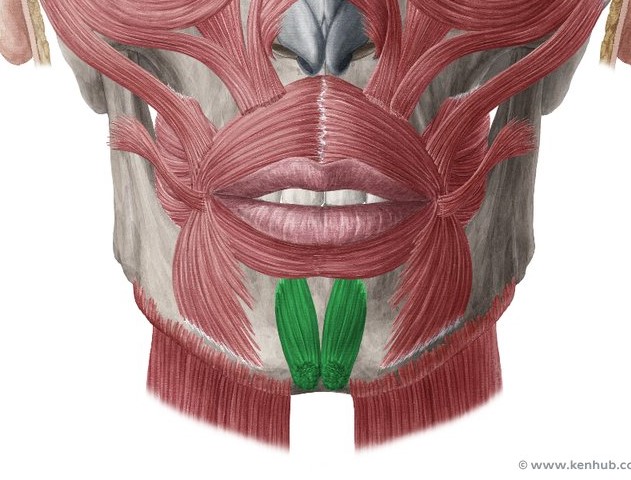
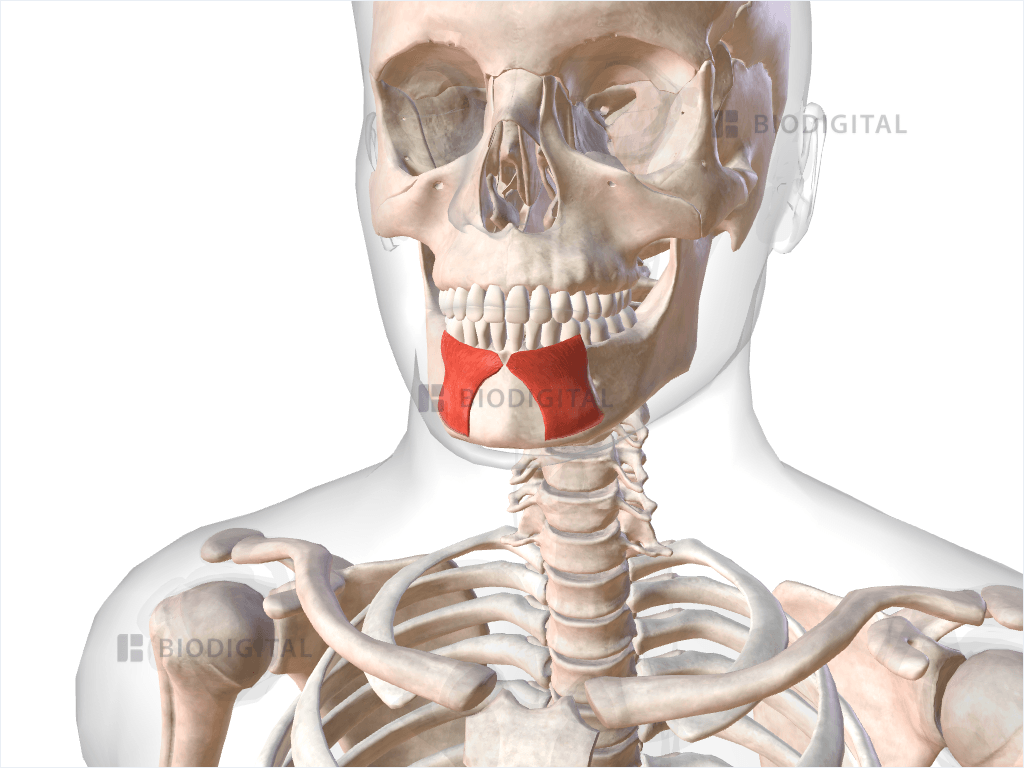
Mentalis
Inserts inferiorly into the skin of the chin, Pulls up on the chin to wrinkle the chin and protrude the lower lip
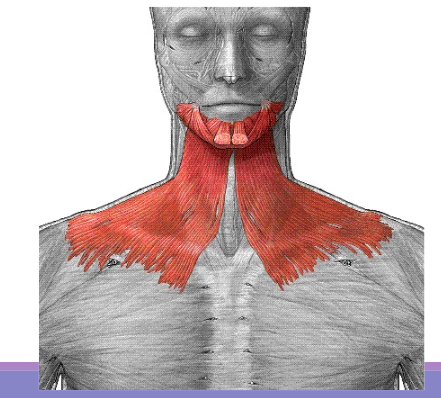
platysma
Pulls the jaw down
3 muscles commonly used together to elevate the lips
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi (origin: frontal process of
maxilla)
2. Levator labii superioris (origin: infraorbital margin of maxilla)
3. Zygomatic minor (origin: the facial surface of zygomatic bone)
Levator anguli oris
Draws lip up and toward midline
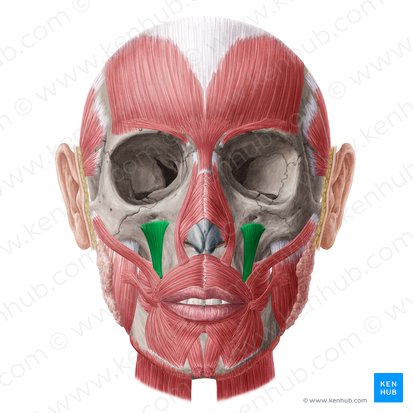
Zygomatic major
Draws corner of lips up and laterally, as in smiling
Depressor labii inferioris
insets into the lower lip medially and pulls the lower lip down and laterally
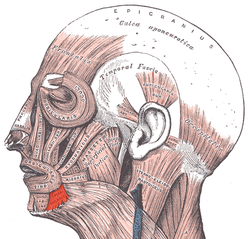
Depressor anguli oris (triangularis)
inserts into the orbicularis and upper lip corner and pulls the corner of the lip down and pulls the upper lip down toward the lower lip
INTRINSIC TONGUE MUSCLES Within the tongue
Superior longitudinal, Inferior longitudinal, Transverse, and Vertical
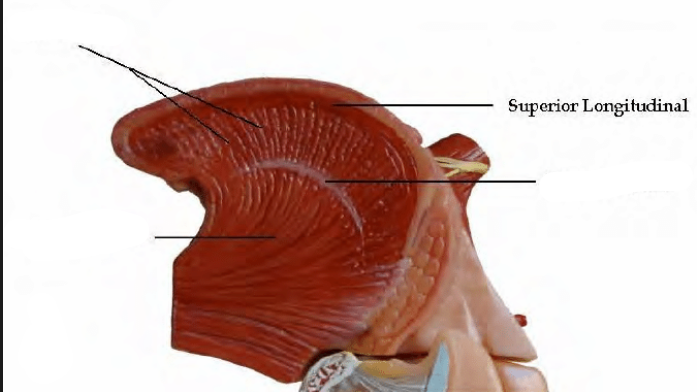
Superior Longitudinal Muscle
Runs the length of the tongue and elevates the tongue tip
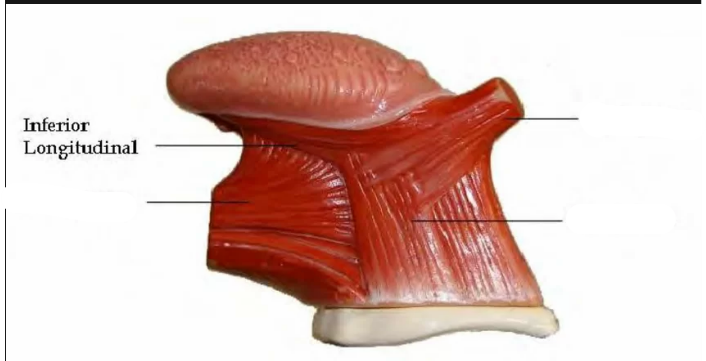
Inferior Longitudinal
Pulls tongue tip (apex) downward; If contracted with the superior longitudinal muscle, retracts the tongue
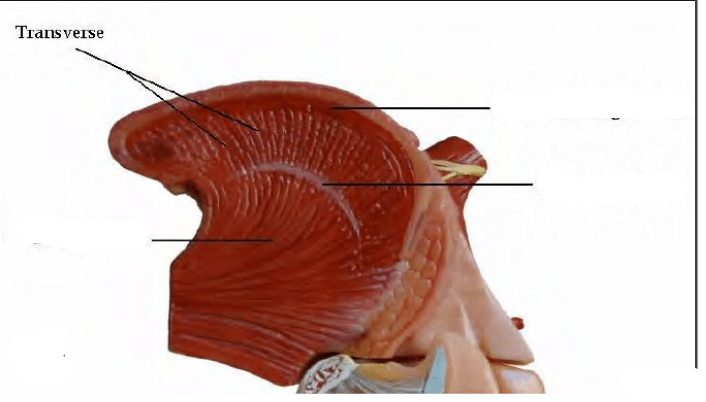
Transverse Muscle
narrows the tongue by pulling tongue edges toward midline
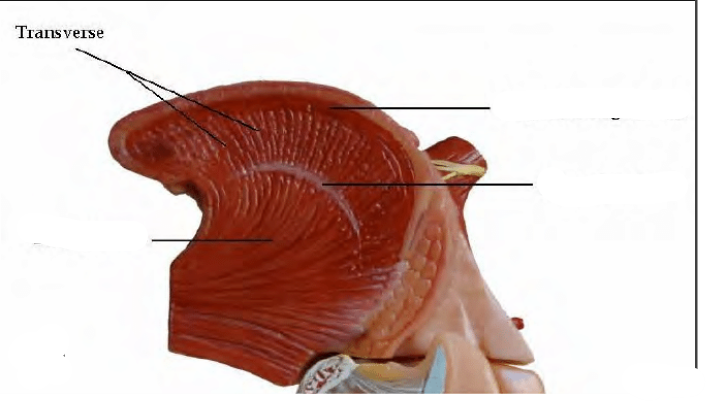
Vertical Muscles
Contraction pulls the tongue down to floor of mouth; Fibers of transverse and vertical muscles of the tongue interweave in the tongue body
Extrinsic tongue muscles that connect to the tongue
1. Genioglossus
2. Hyoglossus
3. Styloglossus
4. Palatoglossus (also a velum muscle)
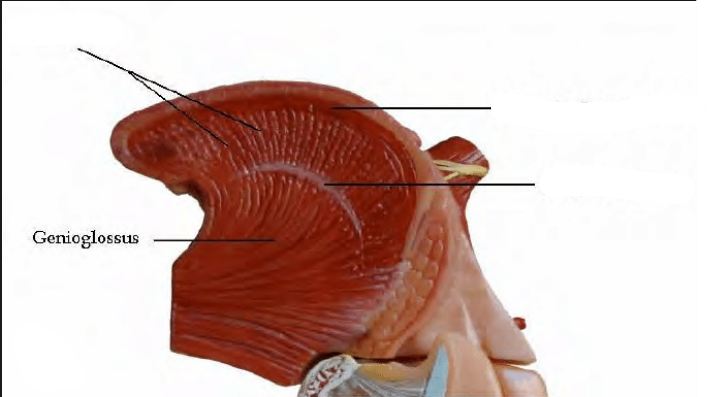
Genioglossus
Anterior fibers: tongue retraction
Posterior fibers: forward tongue movement, assists with apical tongue protrusion
Both anterior & posterior fibers’ contraction: pulls down middle of tongue “cupping of tongue”
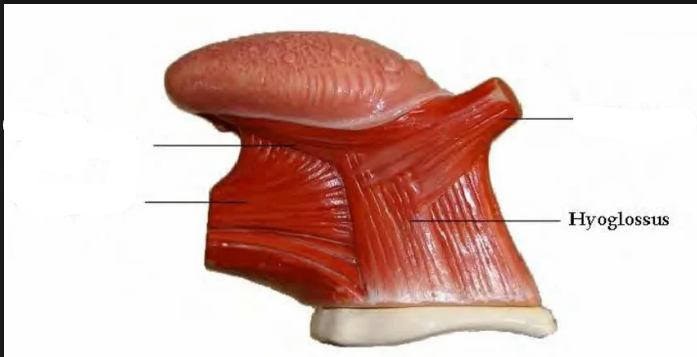
Hyoglossus
pulls down sides of tongue (antagonist muscle to palatoglossus)
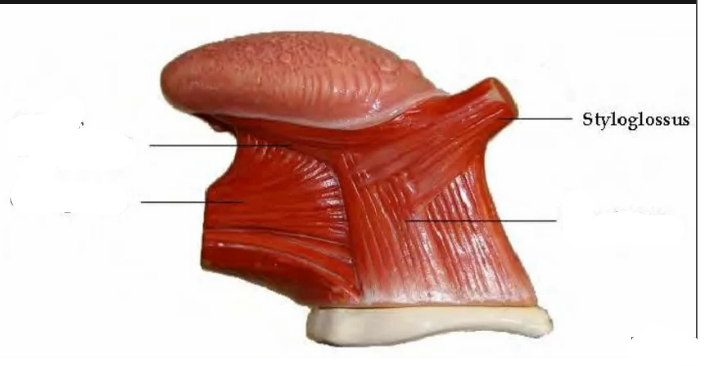
Styloglossus
draws tongue back (retracts) and up (elevates)
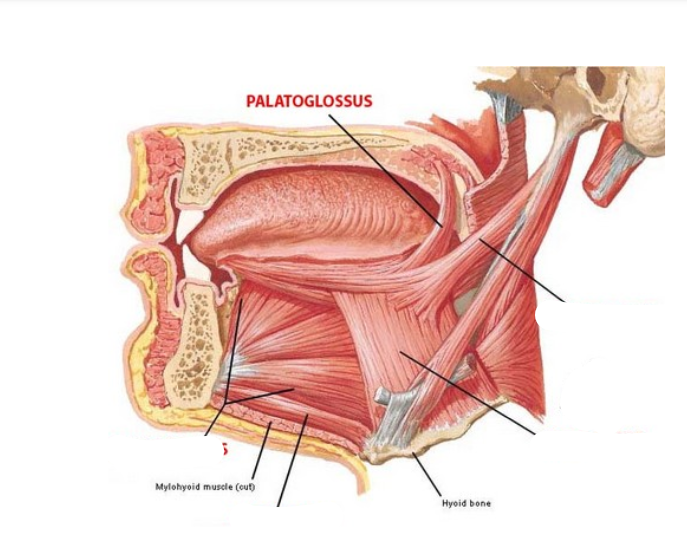
Palatoglossus
Forms the anterior faucial pillar; Elevates tongue and Lowers velum
Levator veli palatini
elevates & retracts soft palate
Musculus uvulae
shortens & lifts soft palate
Tensor veli palatini
dilates auditory tube and tenses & lowers palatal aponeurosis
Palatopharyngeus
lowers soft palate and narrows pharynx
Superior Nasal Concha
A bony structure in the nasal cavity that helps regulate airflow and filter air.
Articulators
The parts of the vocal system that come together to produce speech sounds, including mobile (e.g., tongue) and immobile (e.g., alveolar ridge) articulators.
Articulatory system
The system comprised of articulators that shape speech sounds by joining and moving to create different sounds for communication.
Vocal tract
The part of the articulatory system that filters or shapes the sound source to produce different speech sounds based on the positioning of the tongue, lips, and other parts of the vocal tract.
Filter
The aspect of the source filter theory that refers to the shaping or modification of the sound source by the vocal tract to create specific speech sounds.
Phonation
The process of vocal folds vibrating to create a buzzing sound, which is essential for speech production but needs to be shaped by articulators to form distinct sounds for communication.
Pharynx
The part of the vocal tract located behind the oral cavity and nasal cavity, playing a role in speech production and swallowing.
Oral Cavity
The part of the vocal tract inside the mouth, including structures like the lips, teeth, palate, and tongue, crucial for articulating speech sounds.
Nasal Cavity
The part of the vocal tract located behind the nose, contributing to the resonance of speech sounds.
Alveolar Ridge
The bony ridge behind the upper front teeth, important for producing sounds like /t/ and /d/.
Glottis
The space between the vocal folds in the larynx, crucial for phonation and sound production.
Resonant Frequency
The specific frequency at which a cavity vibrates most effectively, influencing the quality of sound produced during speech.
Articulators
Organs or structures in the vocal tract that are involved in shaping sounds during speech production.
Mobile/Active Articulators
Articulators that can move, such as the tongue and lips, used to produce different sounds in speech.
Tongue
The largest articulator in the vocal tract, with different parts like the tip, back, and dorsum used to create various sounds in English.
Mandible
The jaw bone, important for speech production and movement of the lower part of the face.
A movable articulator that can be raised or lowered to control airflow for nasal or oral sounds.
Soft Palate
Lips and Cheeks
Articulators used to shape sounds, like rounding the lips for the sound "wa."
Alveolar Ridge
A bony ridge in the roof of the mouth where the tongue can make contact to produce certain sounds.
Cranium Bones
The bones of the skull that protect the brain and house structures important for speech production.
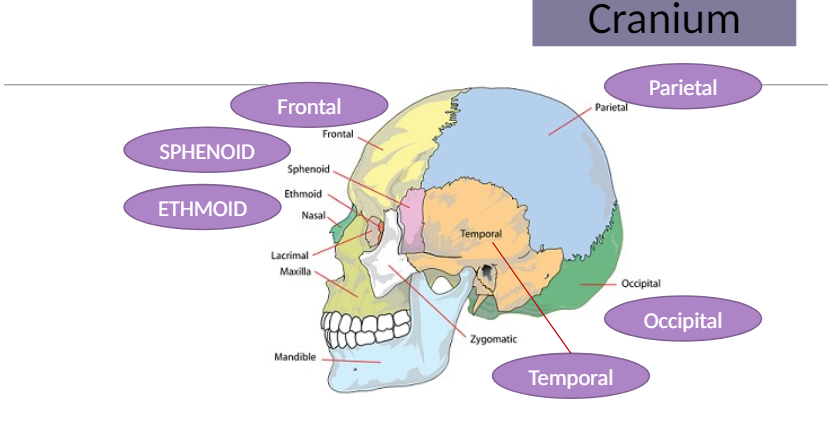
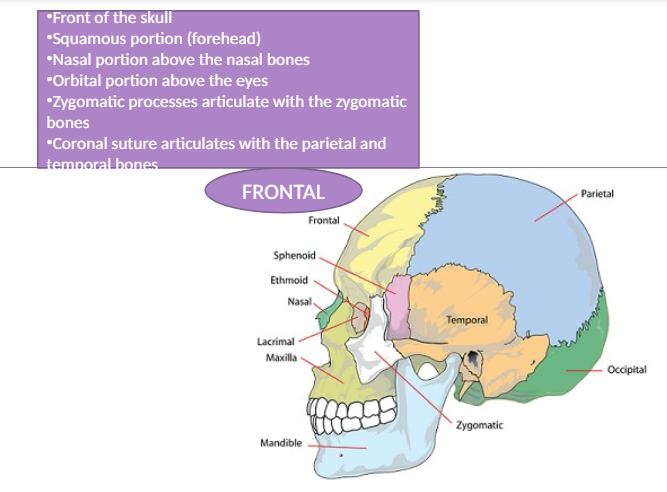
Frontal Bone
The bone at the front of the skull that covers the frontal lobe of the brain and articulates with other bones like the parietal and temporal bones.
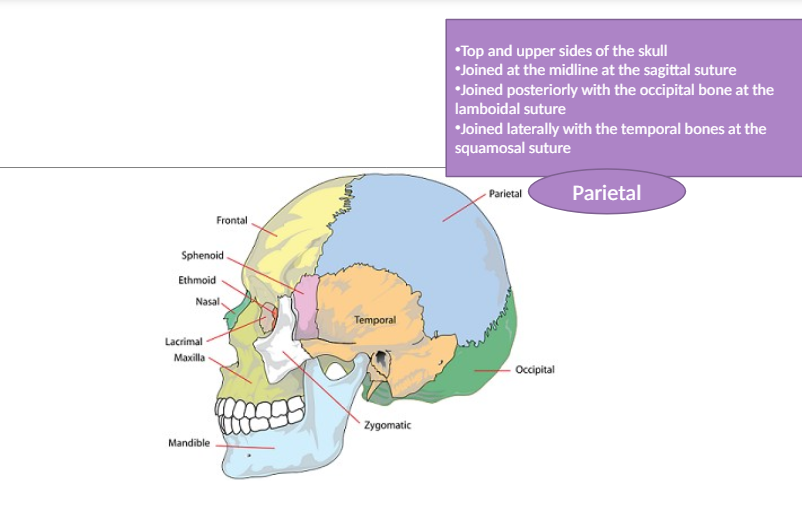
Parietal Bone
The bone at the top and sides of the skull that joins with other bones through sutures and protects the brain.
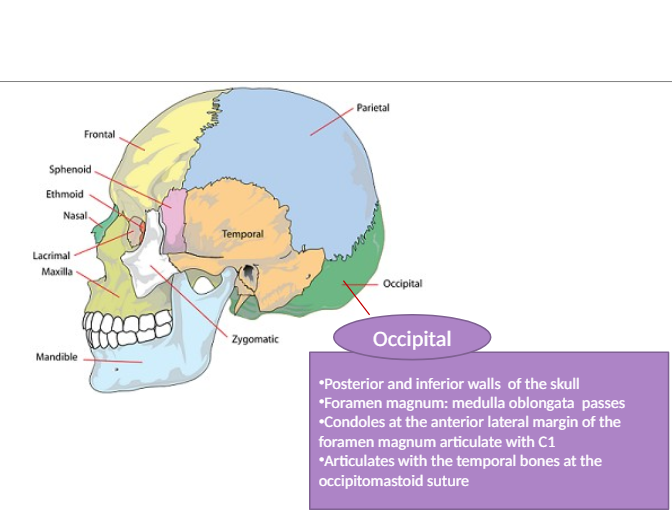
Occipital Bone
The bone at the back of the skull that contains the foramen magnum and articulates with other bones like the temporal bone.
Temporal Bone
The bone at the inferior sides of the skull with parts like squamous, mastoid, tympanic, and petrous portions.
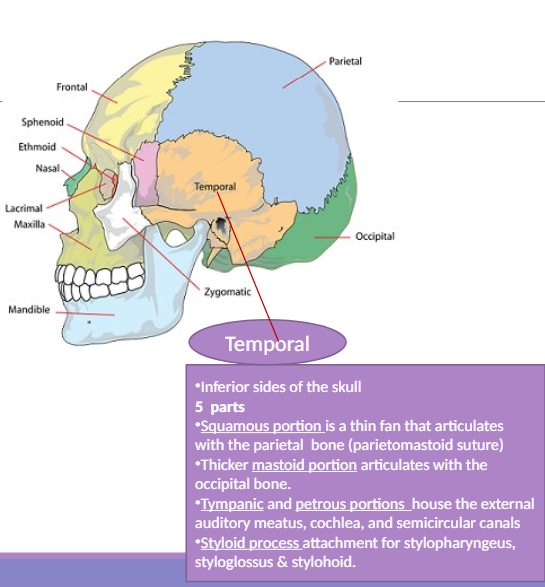
Tympanic portion
Part of the temporal bone that houses the external auditory meatus.
Petrous portion
Part of the temporal bone that houses the cochlea and semicircular canals.
External auditory meatus
The ear hole where sound enters the ear.
Semicircular canals
Parts of the ear that help with balance.
Styloid process
An attachment point for various muscles on the temporal bone.
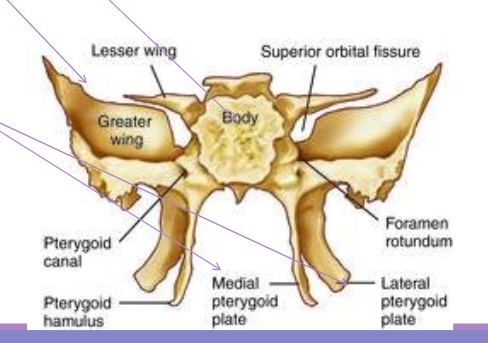
Sphenoid bone
Bone located at the center of the head, containing sinuses and channels for optic nerves. includes corpus, greater wings, rostrum, and pterygoid plates.
Ethmoid bone
Upper part of the nasal septum important for warming air for respiration.
what makes up the upper portion of the nasal septum?
Perpendicular plate
what makes up the upper wall of the nasal cavity?
Cribiform plate
Orbital plate
lateral, articulating with the frontal bone and maxilla
Mandible
U-shaped bone housing teeth and used for chewing and speech.
Maxilla
Paired bones forming the upper jaw and part of the hard palate.
Nasal bone
Bone forming the bridge of the nose.
Inferior nasal concha
Small, scroll-shaped bone in the nasal cavity that helps humidify and filter air as it passes through the nose.
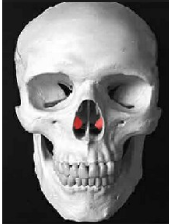
Vomer
Makes up the inferior and posterior part of the nasal septum; Midline bone that divides the nasal cavity into two halves
Cleft Lip
A congenital split or gap in the upper lip.
Cleft Palate
A congenital split or gap in the roof of the mouth.
Glottal Stop
A sound made by briefly stopping the airflow in the vocal tract.
Bones of the Nasal Cavity
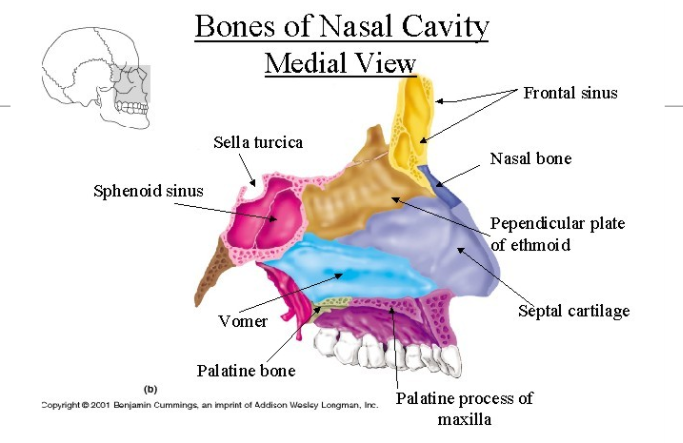
Hard Palate
The bony structure that forms the roof of the mouth.
Nasal Concha
Spongy bones that extend horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity.
Palatine Bone
Bones contributing to the hard palate and lateral nasal cavity walls
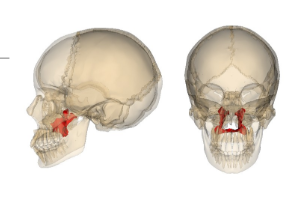
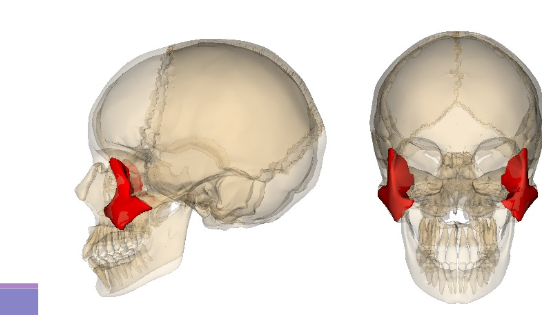
Zygomatic bone
Also known as the cheekbone, it forms the prominence of the cheek and articulates with the temporal, frontal, and maxillary bones.
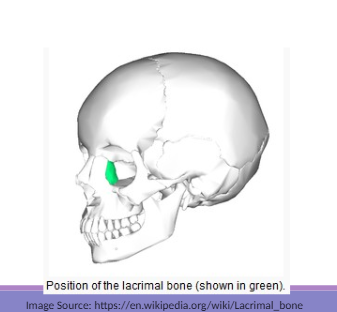
Lacrimal Bones
The smallest facial bones that articulate with frontal, ethmoid, maxilla, & inferior nasal concha
Incisors
The sharp-edged teeth at the front of the mouth used for cutting food.
Cuspids
The pointed teeth next to the incisors, also known as canines, used for tearing food.
Bicuspids
The premolar teeth located between the cuspids and molars, used for crushing and grinding food.
Molars
The flat-surfaced teeth at the back of the mouth used for grinding and chewing food.
Crown
The visible part of the tooth above the gum line.
Pulp
The soft tissue inside the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels.
The part of the tooth that can cause pain when irritated, usually associated with toothaches.
Nerve
Mesial Surface
The side of the tooth closer to the midline of the mouth.
Lingual Surface
The surface of the tooth facing the tongue.
Buccal Surface
The surface of the tooth facing the cheek.
Occlusal Surface
The chewing surface of the tooth where upper and lower teeth meet.
Quadrants
The division of the mouth into four parts for dental purposes.
Lateral Incisors
The teeth next to the central incisors.
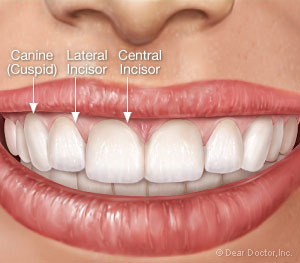
Malocclusion
Misalignment of the teeth when the upper and lower teeth do not fit together properly.
Overbite
A malocclusion where the upper teeth protrude over the lower teeth.
Occlusion
The way the upper and lower teeth come together when the mouth is closed.
Malocclusion
Misalignment of the teeth, specifically when the lower teeth are significantly in front of the front teeth, causing difficulties in speech production and chewing.
Micronathia
Condition where the jaw is smaller than it should be.
Macranathia/Meganathia
Condition where the jaw is larger than it should be.
Class One Malocclusion
Molars are correctly aligned, but other teeth are misaligned or twisted.
Oral Cavity
The cavity in the mouth, extending from the lips to the posterior fascial pillars.
Nasal Cavity
The cavity in the nose, from the nostrils to the nasopharynx.
Nasopharynx
The upper part of the pharynx, located closer to the nose, containing the eustachian tubes and adenoids.
Oropharynx
The part of the pharynx situated behind the oral cavity, extending from the base of the tongue to the pharynx wall.
Laryngopharynx
The lower part of the pharynx, positioned above the esophagus and below the oropharynx.
Levator labii superioris, levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, zygomatic minor
Muscles working together to elevate the upper lip.
Lingual frenulum
A thin band of tissue under the tongue, aiding in tongue movement and sometimes associated with conditions like tongue tie.