3.10 Managing strategic change
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Causes of change
Internal causes
External causes
Types of change
Incremental change
Step change
Disruptive change
Incremental change
Occurs over a period of time in incremental, small changes.
Step change
Significant and occurs rapidly.
Disruptive change
A form of step change that arises from changes in the external environment.
Lewin's Force Field Analysis
Provides an overview of the balance between forces driving change in a business and the forces resisting change.
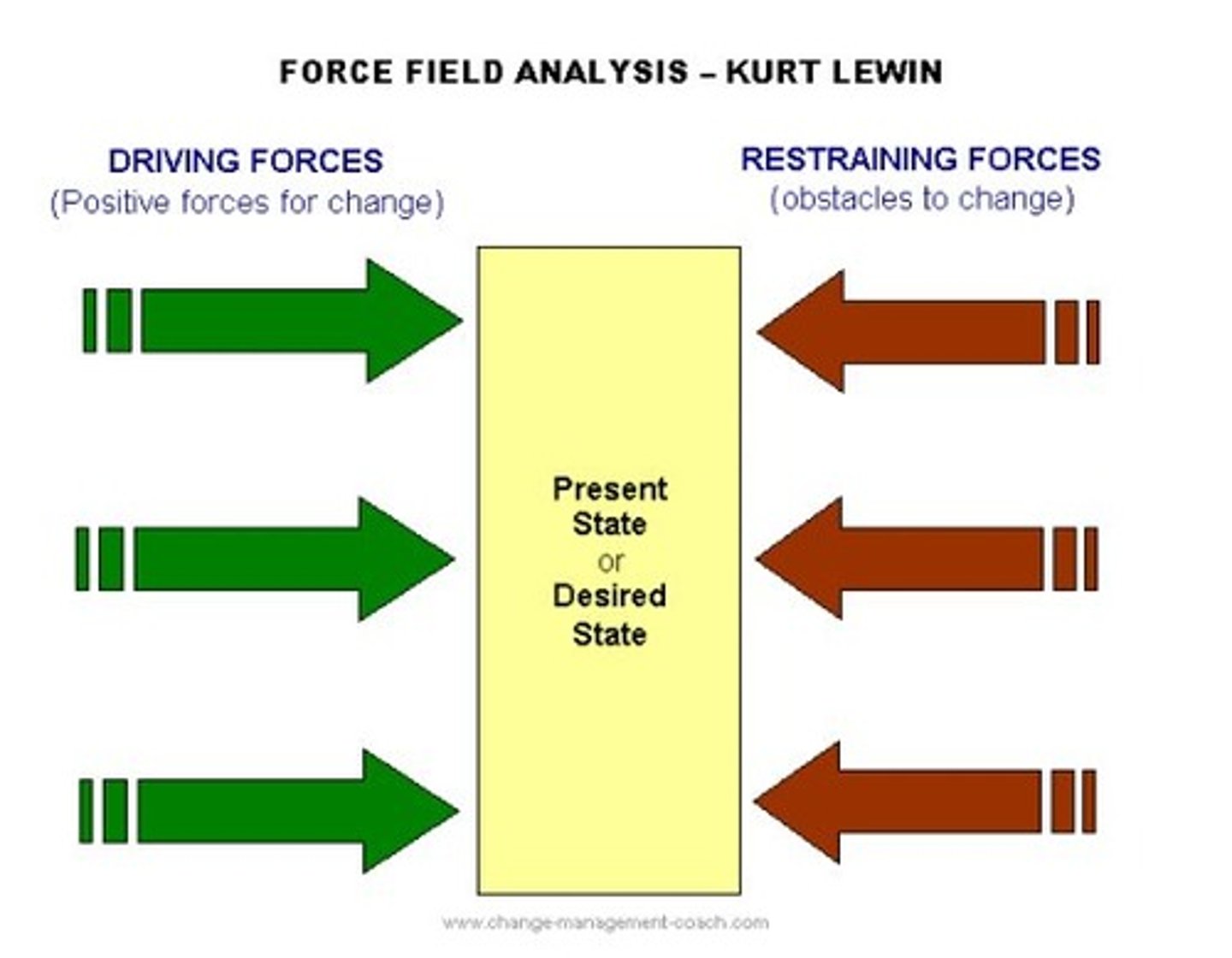
How Lewin's model works
If there is an equilibrium between two sets of forces there will be no change. In addition, for change to happen the driving force must exceed the restraining force.
Examples of forces driving change
Internal forces
Need for higher profits
Poor efficiency
Lack of innovation
Need to change culture
Change of leadership
External forces
Customer demand
Competition
PESTLE
Why change is resisted
Self interest
Misunderstanding
Low tolerance of change
Different assessment of the situation
Organisational structure
Shows how people and management are organised in a business.
Flexible organisation
One that is able to adapt and respond relatively quickly to changes in its external environment in order to gain advantage and sustain its competitive position.
Organic structures
Informal, Flexible and fluid communication which favours verbal communication. Usually associated with decentralised decision making with change being easier to handle.
Mechanistic structures
Formal, Bureaucratic with formal communication associated with centralised decision making and supervision and favours standardised policies and procedures, little perceived need for change.
Characteristics of a flexible organisation
Use flexible working
Flat hierarchies
Culture embraces change
Quick decision making
Hierarchy
The number of layers of management or supervision in the organisation structure.
Delayering
Removing layers of management from the hierarchy of an organisation.
Benefits of Delayering
Lower labour costs
Faster decision making
Shorter communication paths
Stimulating employee innovation
Drawbacks of Delayering
Often significant one-off costs of making managers redundant
Increased workloads for managers who remain
Impact of redundancies on organisational morale
Loss of expertise
Flexible working
Employees have options in terms of working time, working location and pattern of working.
Gig economy
Self employed work such as food delivery, with high labour flexibility for firms and employees.
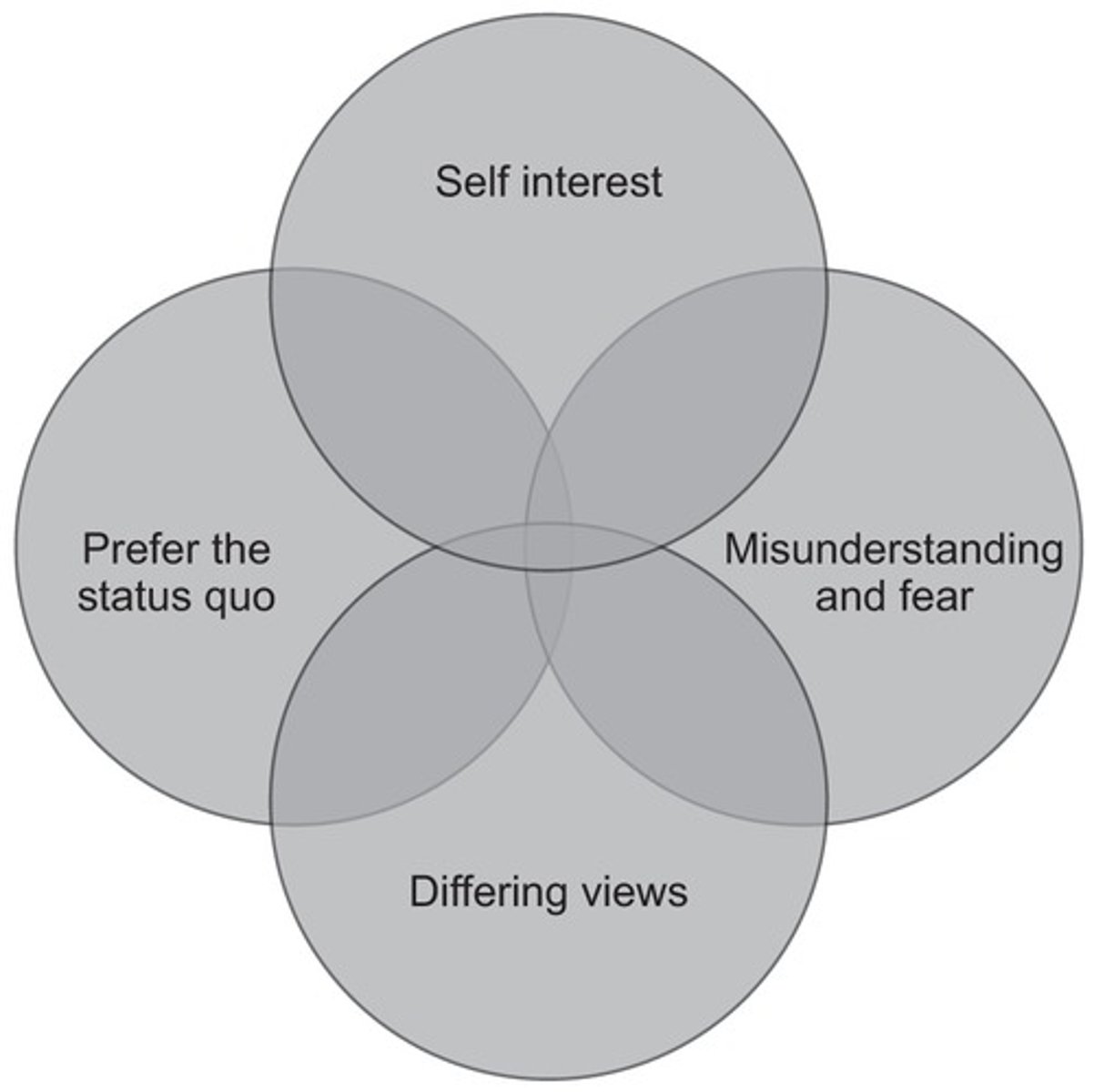
Kotter and Schlesinger's Reasons for resistance to change
Self interest
Perceived threat employees feels such as job security, status and financial position.
Prefer the status quo
Rather keep things as what they are - bad experience of change
Differing views
Disagreement of what to change and the need of change
Misunderstanding and fear
Misinformed about the position of business
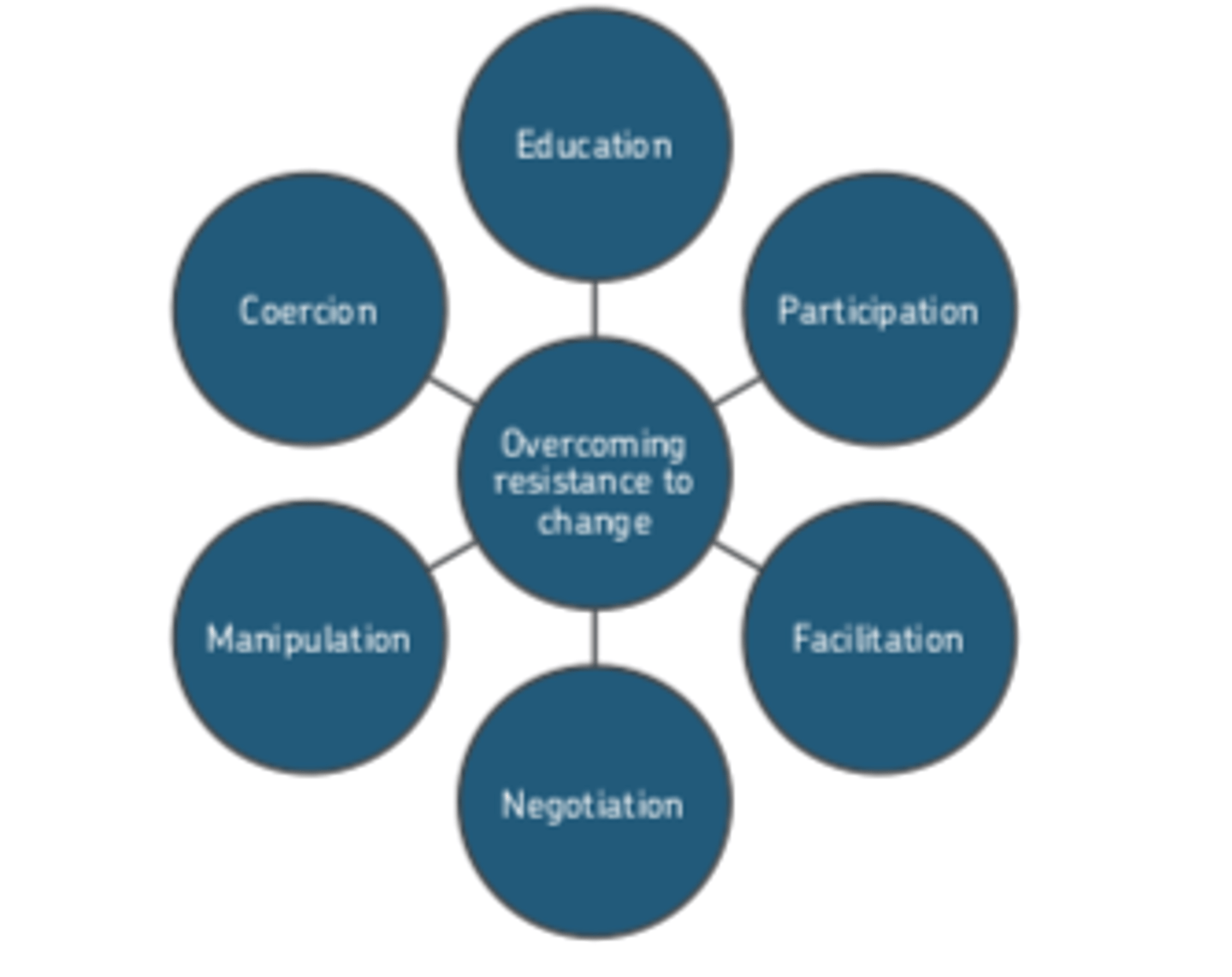
Kotter and Schlesinger's Model of overcoming resistance to change
Education
Participation
Facilitation
Negotiation
Manipulation
Coercion
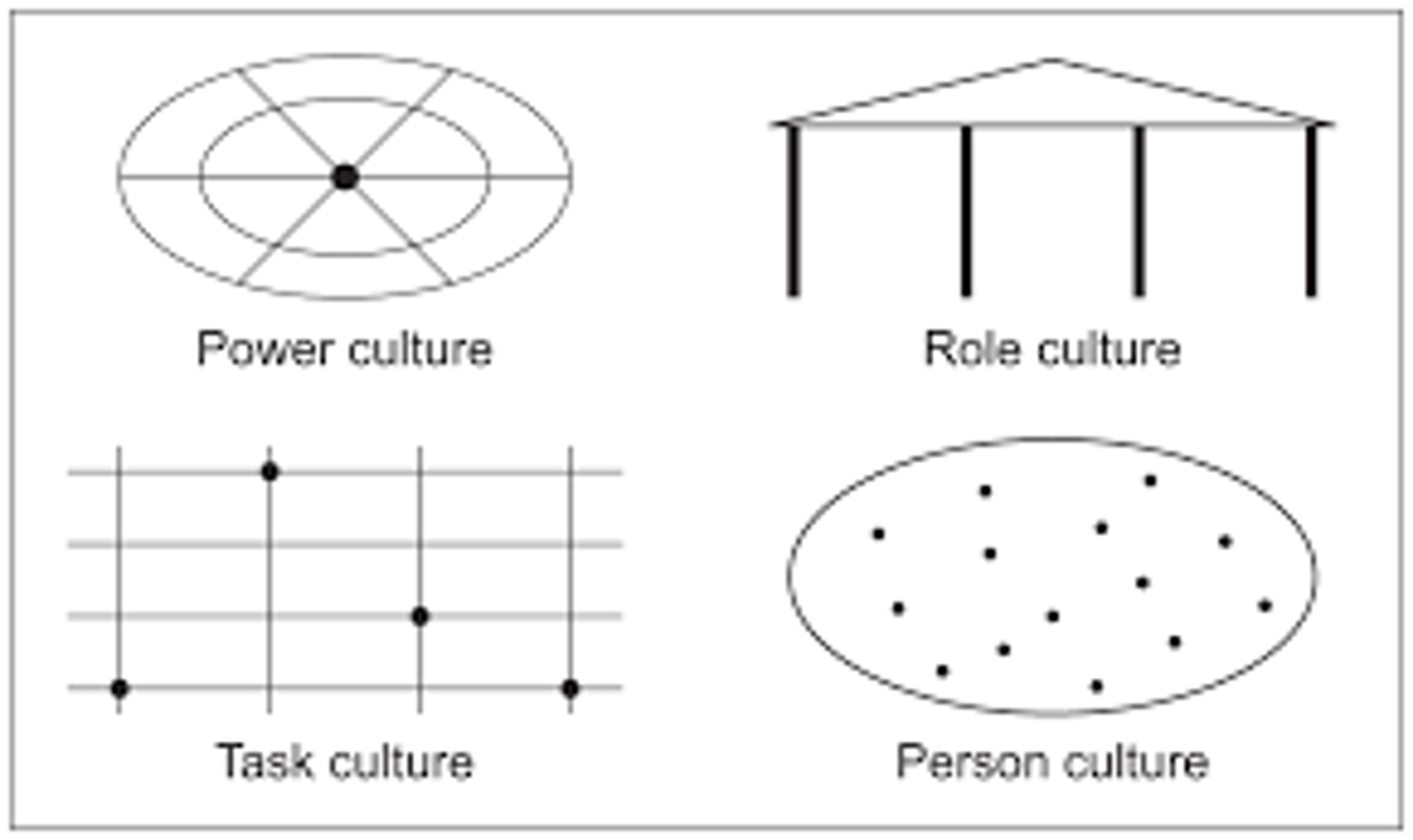
Handy's four types of culture
Power culture - Centralised culture which focuses on key decision makers, most effective in smaller businesses.
Role culture - Formalised culture with jobs having clear rules and procedures, appropriate for medium to large businesses but may cause a 'silo' mentality where employees do not communicate information.
Task culture - Focus on specific tasks and procedures, usually occur in design and advertising agencies.
Person culture - Individuals have freedom to act independently, may occur in legal or medical practices where individuals have a high level of expertise.
Influences on the organisational culture of a business
Founder
Business size
Rewards
Industry/market
Organisation structure
Work environment
Reasons for changing organisational culture
Business performance
New leadership/strategy
Change in External Environment
To support change management
Critical path analysis (CPA)
A project analysis and planning method that allows a project to be completed in the shortest possible time.
Information needed for CPA
A list of all ACTIVITIES required to complete the project
The time (DURATION) that each activity will take to completion
The DEPENDENCIES between the activities (e.g. activity D cannot be completed until activity B & C done)
CPA Network Diagram Calculates
The longest path of planned activities (Critical path)
Earliest start time (EST) and Latest start time (LFT) that each activity can start and finish without making the project longer.
Four Golden rules of a CPA diagram
1. EST - Calculate first and always work from left to right
2. EST- Where two or more activities meet, EST is always the highest calculated figure.
3. LFT - Calculate after EST and always work from Right to Left
4. LFT - Where two or more activities meet, LFT is always the lowest calculated figure
Float
The duration an activity can be extended or delayed so that the project still finishes within the minimum time.
Calculated as LFT - Duration - EST
Identifying the critical path
Activities with a float of 0 (zero) cannot be delayed without delaying the entire project this is the critical path
On the critical path, activities have an equal EST and LFT
Planned strategy
The intended strategy influenced by specific corporate objectives. Based on formal strategic planning. (e.g. SWOT analysis, PESTLE, Porter's five forces)
Emergent strategy
The strategy that actually happens, strategy that responds to events as they arise often involves strategical and tactical changes.
Strategic drift
When the strategy of a business is no longer relevant to the external environment facing it.
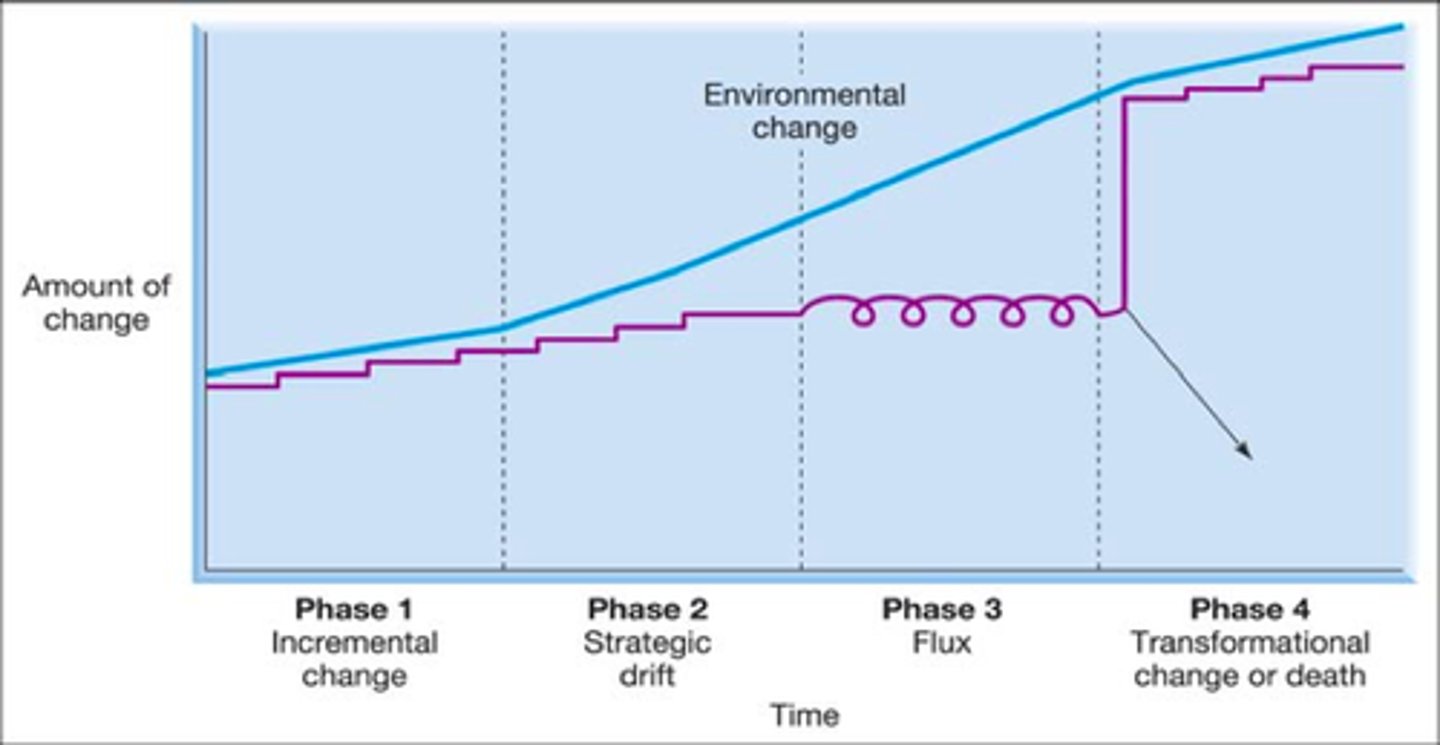
Four phases of strategic drift
Phase 1 - Incremental change, Strategy falls behind from the environment
Phase 2 - Strategic drift, Growing mismatch between strategy and the environment
Phase 3 - Flux, Sudden major strategic change to correct the mismatch
Phase 4 - Transformational change or demise
Corporate Governance
Is the system in which companies are directed and controlled focusing on the needs of their shareholders, managers, employees and other stakeholders.
Contingency planning
The process of preparing alternative courses of action to ensure a business can respond effectively to unexpected events or crises.
Crisis management
The process of dealing with sudden, unexpected events that threaten a business, aiming to reduce harm and restore normal operations quickly.