Biology Learning Goals - Cell Structure
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Define Eukaryotic cell
Cells with a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
Define ultrastructure
Those features which can be seen by using an electron microscope
Draw and label diagrams of typical plant and animal cells
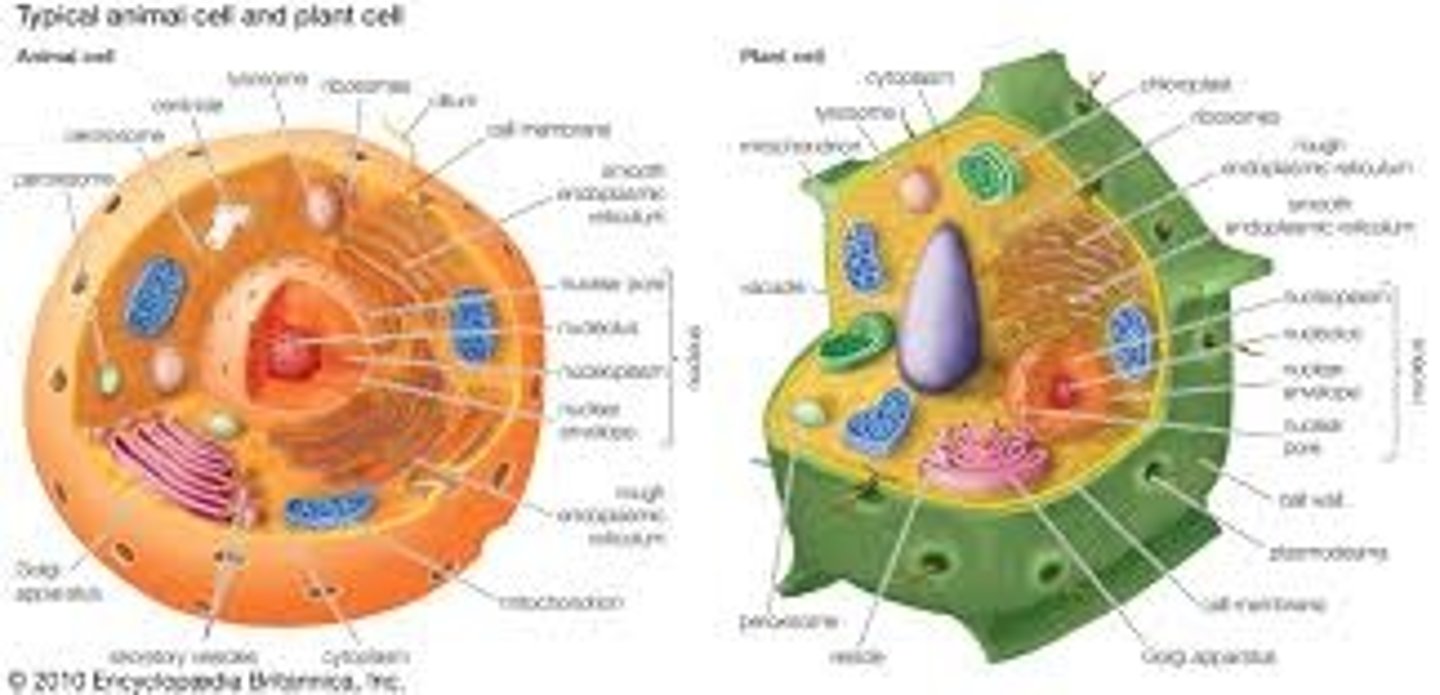
Nucleus
Contains coded genetic information in the form of DNA. Directs protein synthesis - controls metabolic activities of the cell
Nucleolus
Area within the nucleus responsible for producing ribosomes. Composed of proteins and RNA
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane surrounding nucleus protects it from damage. Has nuclear pores allowing molecules to move in and out of the nucleus
R.E.R.
Ribosomes bound to surface. Responsible for synthesis + transport of proteins
S.E.R.
Responsible for lipid + carbohydrate synthesis and storage
Golgi apparatus
Compact structure formed of cisternae, no ribosomes. Modifies + packages proteins into vesicles
Ribosomes
Free floating or on R.E.R., not surrounded by membrane. Constructed of RNA. Site of protein synthesis
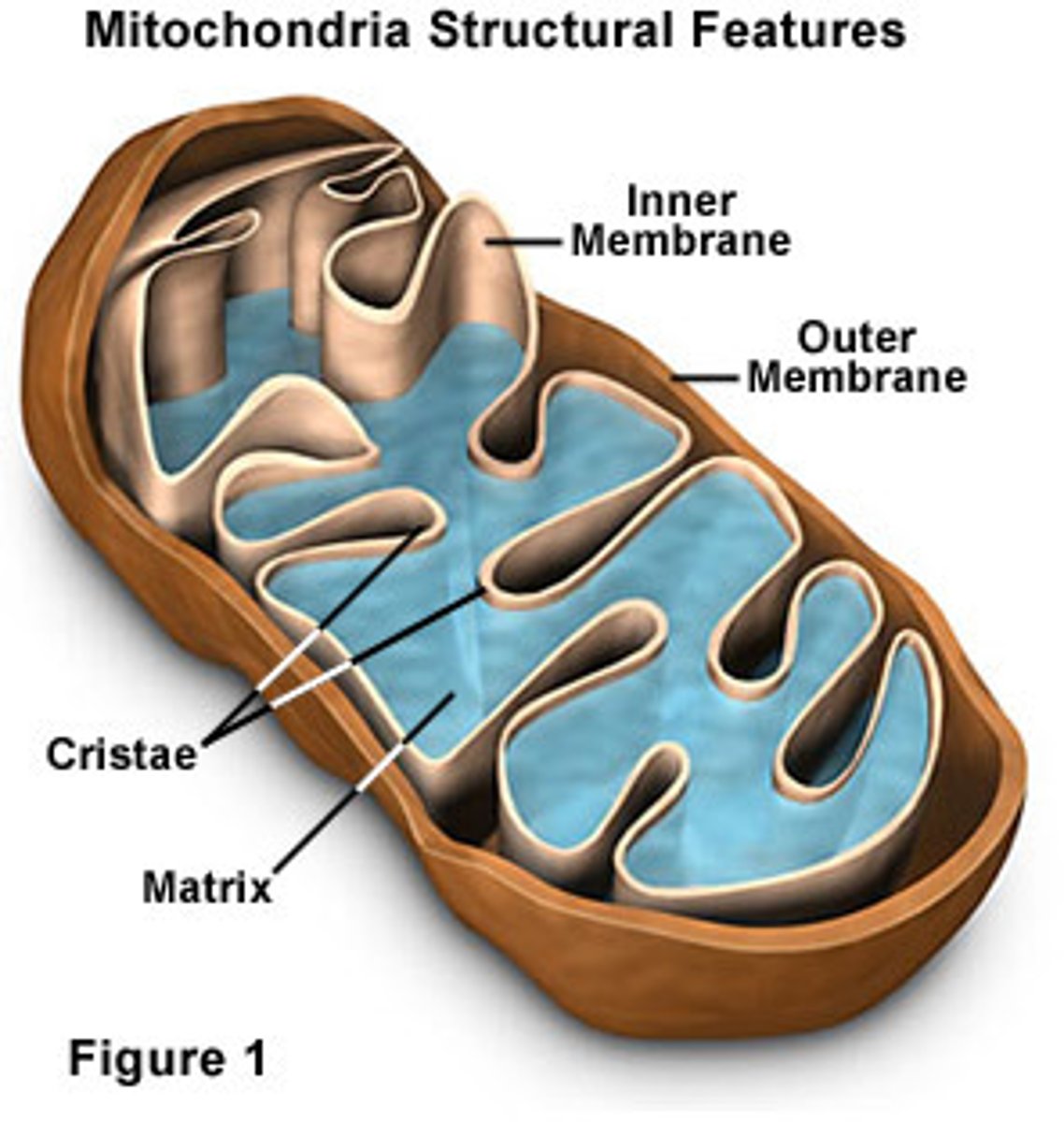
Mitochondria
Site of final stages of respiration producing ATP.
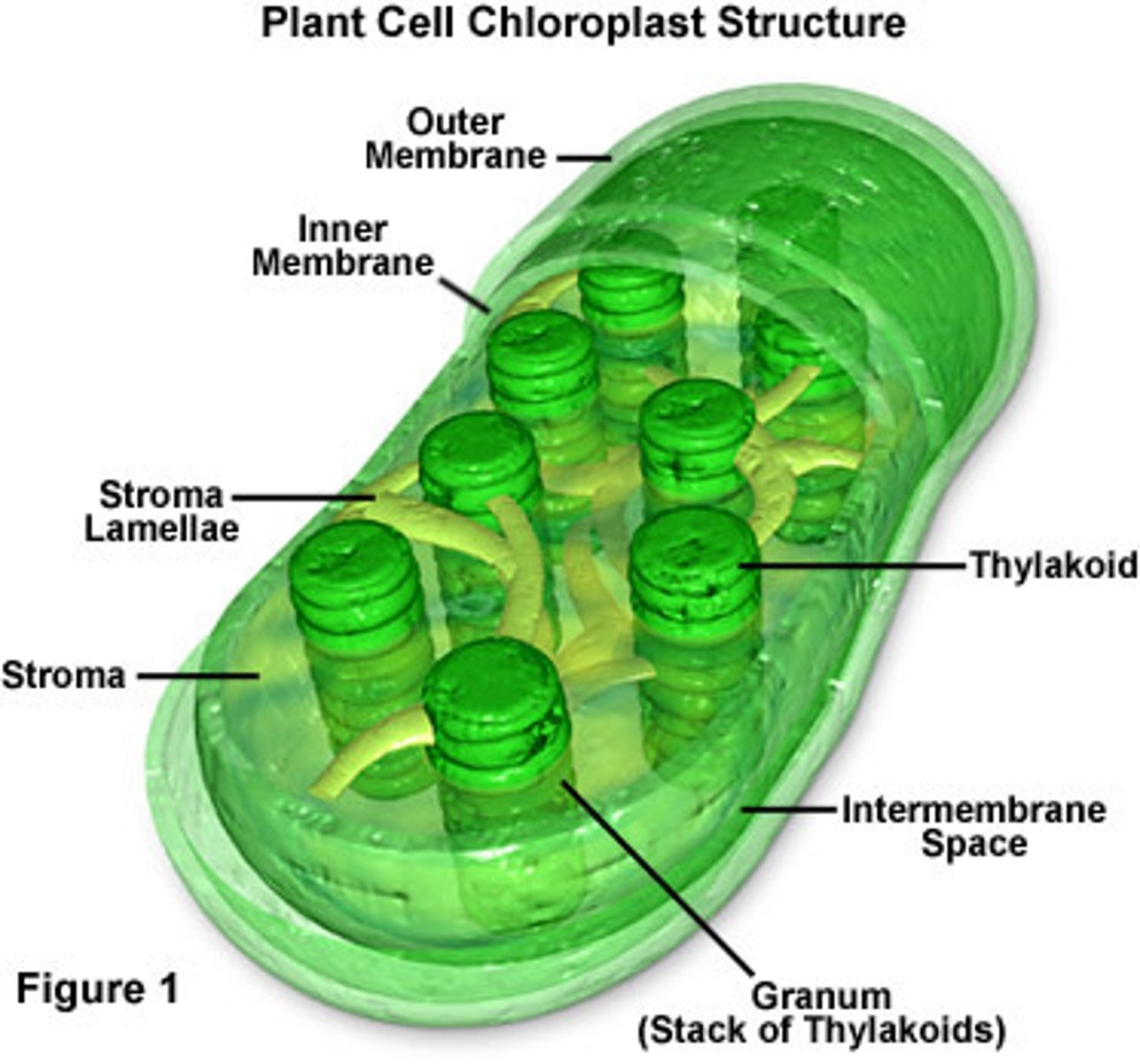
Chloroplasts
Responsible for photosynthesis
Lysosomes
Specialised vesicles containing hydrolytic enzymes - responsible for breaking down waste material
Plasma membrane
Controls entry + exit to cell etc.
Centrioles
Composed of microtubules, 2 together from a centrosome involved in assembly + organisation of spindle fibres during cell division
Cell wall
Rigid - holds shape. Supports cell and plant as a whole and acts as defense against pathogens
Flagella/cilia
Move cell, move mucus/eggs etc. Outside cell can be sensory
State similarities and differences between plant and animal cells
Both have nucleus, golgi, mitochondria, membrane etc.
Only plant: Chloroplasts, permanent vacuole, cell wall
Mitochondria - diagram and labels
Chloroplast - diagram and labels
Process of protein synthesis (step by step)
RNA leaves nucleus through nuclear pore
Proteins synthesised on ribosomes on R.E.R.
Pass into cisternae and packaged into vesicles
Vesicles move to golgi apparatus using cytoskeleton
Vesicles fuse with cis face of golgi (proteins enter)
Proteins structurally modified. Leave in vesicles from trans face.
Secretory vesicles carry proteins to cell membrane
Vesicles fuse with cell surface membrane releasing contents by exocytosis
Outline the structure of the 3 components of the cytoskeleton
Microfilaments - contractile fibres formed form protein actin. Responsible for cell movement + contraction during cytokinesis
Microtubules - globular tubulin proteins polymerise to form tubes that form scaffold-like structure. Determine shape of cell + are tracks for organelle movement e.g. vesicles (Spindle fibres are microtubules)
Intermediate fibres - mechanical strength + help maintain integrity
Describe the functions of the cytoskeleton in a cell
Strength, Shape, Movement
Describe importance of the cytoskeleton in movements of cilia
Cilia/Flagella - 9+2 arrangement
2 central microtubules + 9 pairs
Pairs of parallel microtubules slide over one another - beating motion
Describe the importance of the cytoskeleton in the shape and behaviour of neutrophils
Neutrophils have multilobed nucleus and are very flexible to squeeze though small gaps to get to site of infection
Define Prokaryotic cell
Cells with no membrane-bound nucleus or organelles
Examples of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
Eukaryotic - Plant, Animal, Fungi
Prokaryotic - Bacteria
Prokaryotic cell - diagram and lables
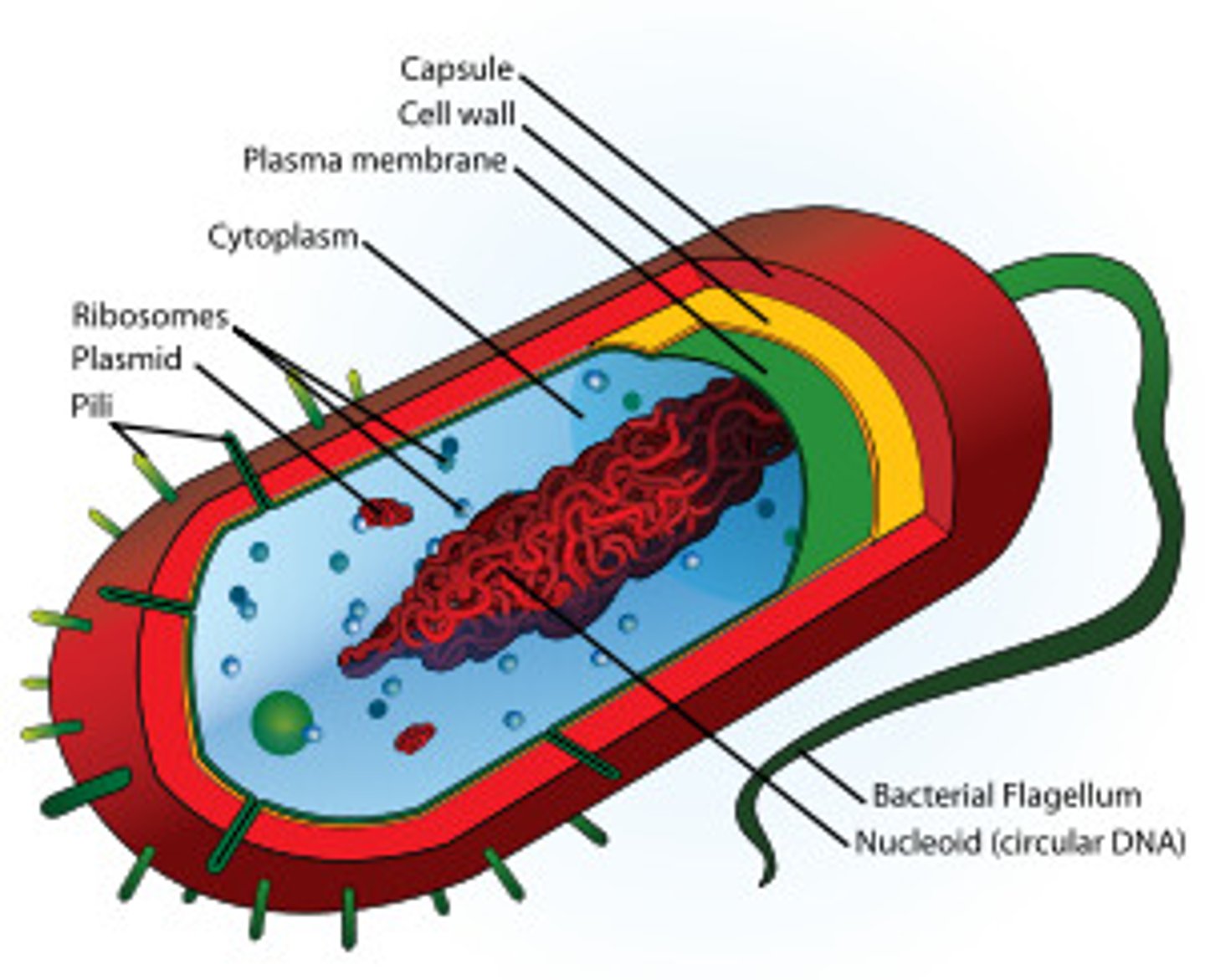
Cell wall (P)
Made of peptidoglycan/murein
Maintains structure
Ribosomes (P)
Smaller - 70s
Protein synthesis
Bacterial flagellum
Thinner, no 9+2, Rotates with whip like movement to propel cell along
Plasma membrane (P)
Controls entry/exit of cell
Plasmid (P)
Rings of DNA in cytoplasm
Bacterial Chromosome
Supercoiled to make it compact. Genes are grouped into operons so turned on/off together
Pili
Organelles of adhesion allowing bacteria to colonize environmental surfaces or cells and resist flushing
Slime capsule
Defense, Moisture
Comparison of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
Nucleus |
DNA |
DNA organisation |
Extra chromosomal DNA |
Organelles |
Cell wall |
Ribosomes |
Cytoskeleton |
Reproduction |
Cell type |
Cell surface membrane |
| Prokaryotic | Eukaryotic |
Nucleus | Present | Not present |
DNA | Circular | Linear |
DNA organisation | Proteins fold and condense DNA | Associated with proteins called histones |
Extra chromosomal DNA | Circular | Only present in certain chloroplasts and mitochondria |
Organelles | Non-membrane bound | Both with/without membranes |
Cell wall | Peptidoglycan | Fungi = chitin Plant = cellulose |
Ribosomes | 70S | 80S |
Cytoskeleton | Present | More complex |
Reproduction | Binary fission | Asexual or sexual |
Cell type | Unicellular | multicellular |
Cell surface membrane | Present | Present |
Describe endosymbiotic theory
There is compelling evidence that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once primitive bacterial cells.
Symbiosis occurs when two different species benefit from living and working together. When one organism actually lives inside the other it's called endosymbiosis. The endosymbiotic theory describes how a large host cell and ingested bacteria could easily become dependent on one another for survival, resulting in a permanent relationship. Over millions of years of evolution, mitochondria and chloroplasts have become more specialized and today they cannot live outside the cell.