6. LO6: Vascular System
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
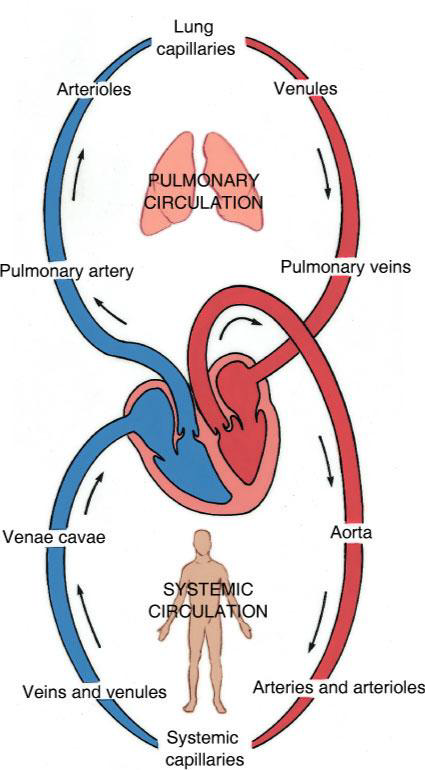
What are the three main components of the vascular system of the head and neck?
An arterial blood supply, a capillary network, and a venous drainage.
What is a vascular plexus?
A large network of blood vessels within the system.
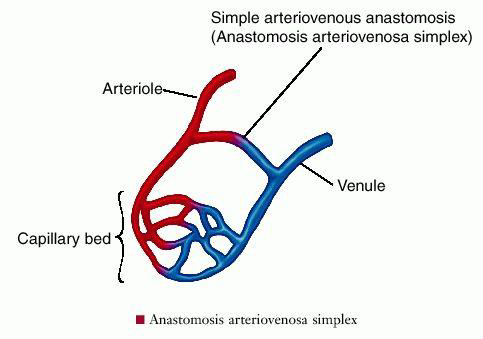
What is an anastomosis?
A connecting channel (or communication) among blood vessels.
What is an artery?
A vessel that begins at the heart and carries blood away from it.
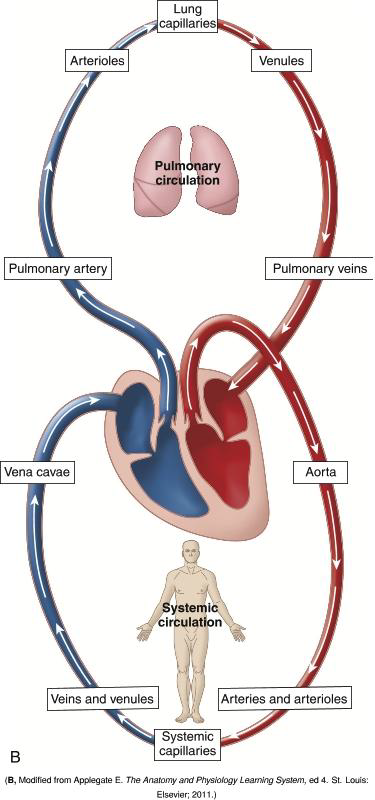
What is an arteriole?
A smaller diameter artery.
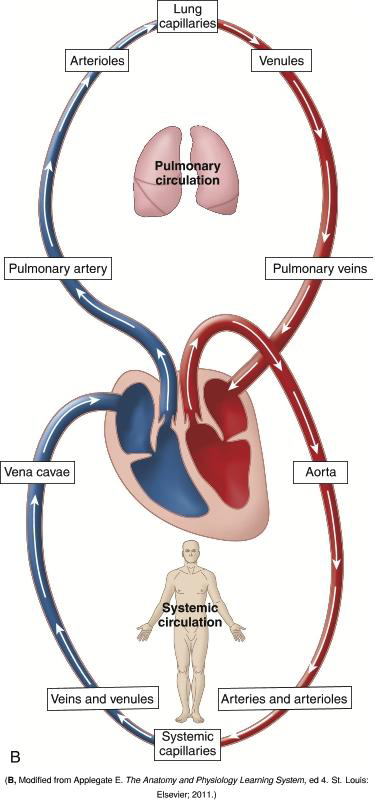
What function do smaller diameter arteries and arterioles serve?
They control the filling of capillaries and the arterial pressure.
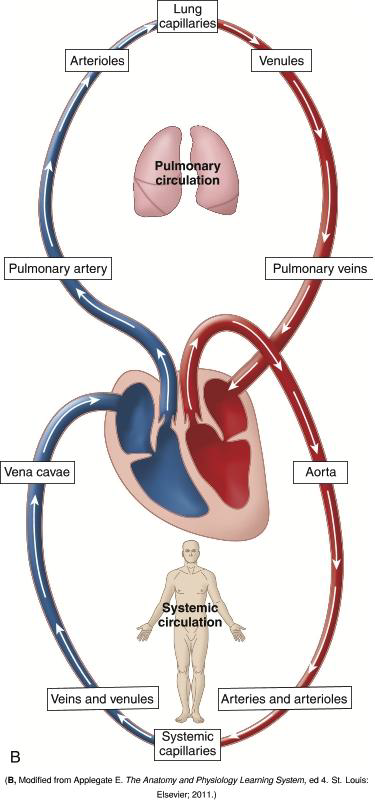
How does a capillary compare to an arteriole in size?
It has a smaller diameter. Can supply blood to a larger area
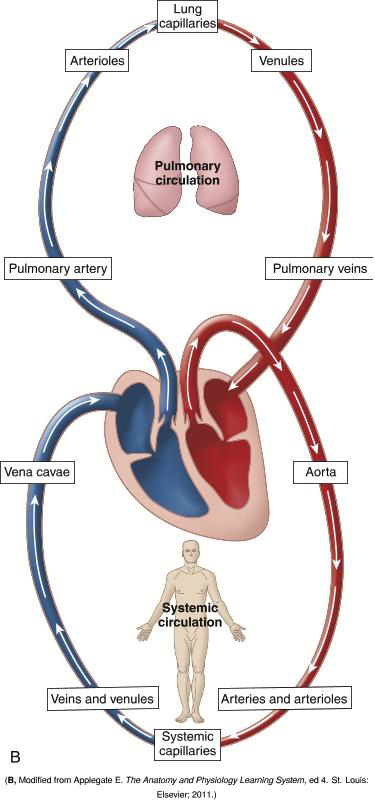
What is the function of the capillary network?
The exchange of oxygen, metabolic waste products, and carbon dioxide.
What is a vein?
A vessel that drains blood from an area and carries it to the heart.
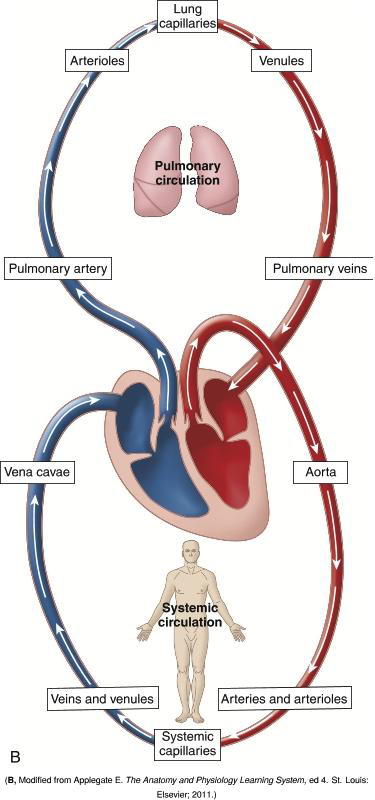
How do veins differ from arteries in terms of structure?
They have a larger diameter, are more numerous, and have valves to prevent backflow.
What is a venous sinus?
A blood-filled space between two layers of tissue.
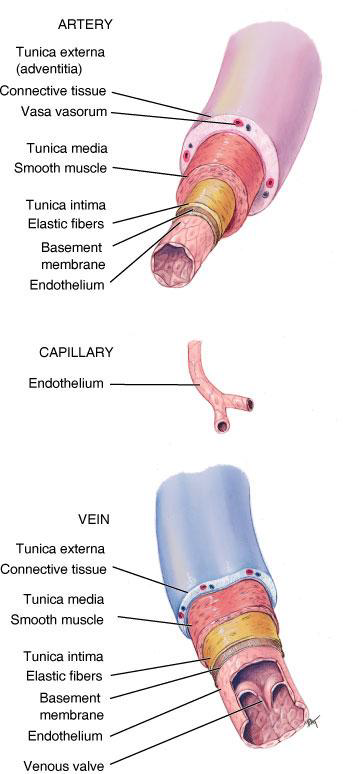
What are the three layers (tunics) of a blood vessel?
Tunica externa, Tunica media, and Tunica interna (intima).
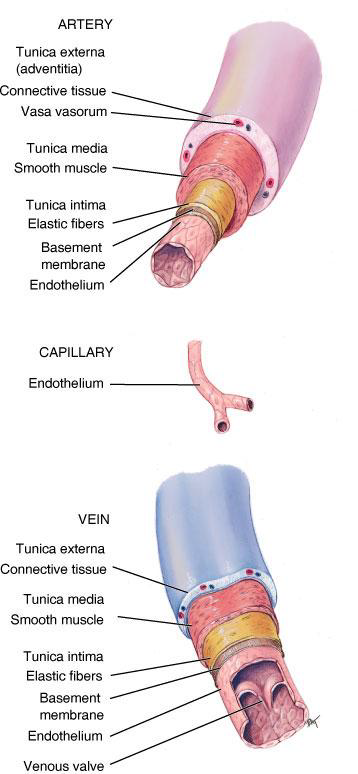
What is the Tunica externa composed of?
Connective tissue.
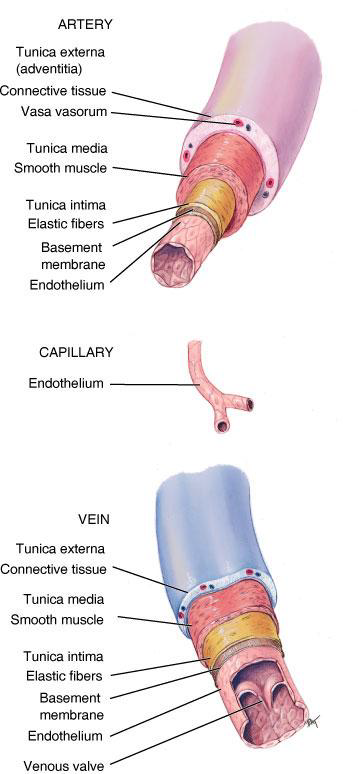
What is the Tunica media composed of?
Smooth muscle and elastic fibers.
What is the Tunica interna composed of?
Endothelium (lining the vessel).
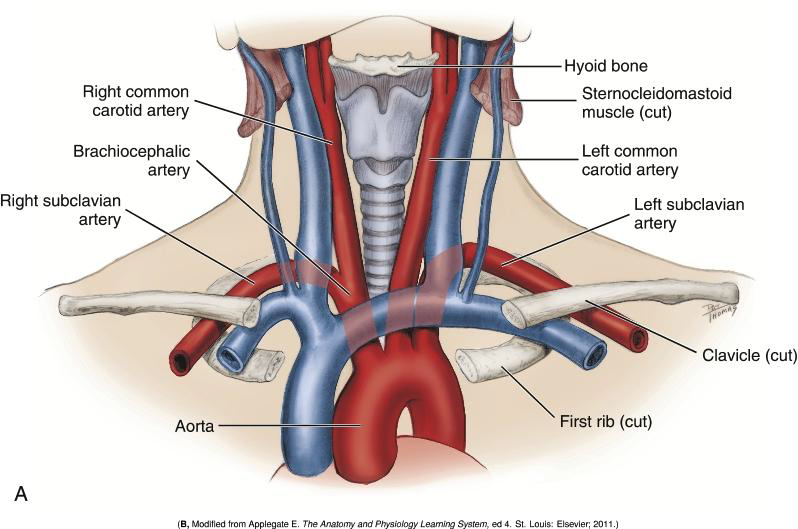
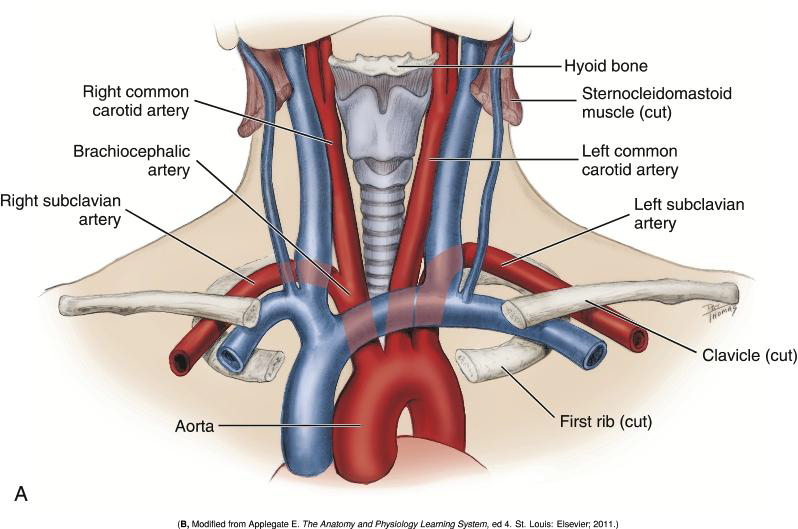
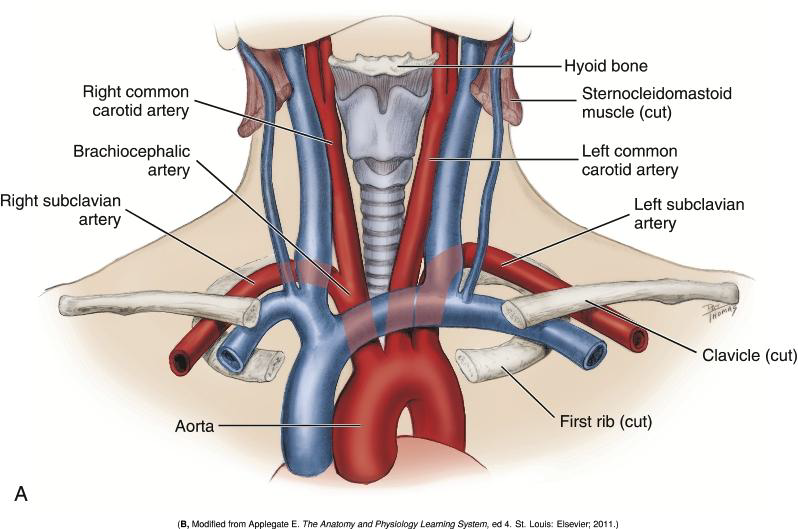
What are the two major arteries that supply the head and neck?
The common carotid and subclavian arteries.
How do the origins of the common carotid and subclavian arteries differ on the right and left sides?
On the right side, they are branches of the brachiocephalic artery;
on the left side, the 2 arteries arise directly from the aorta.
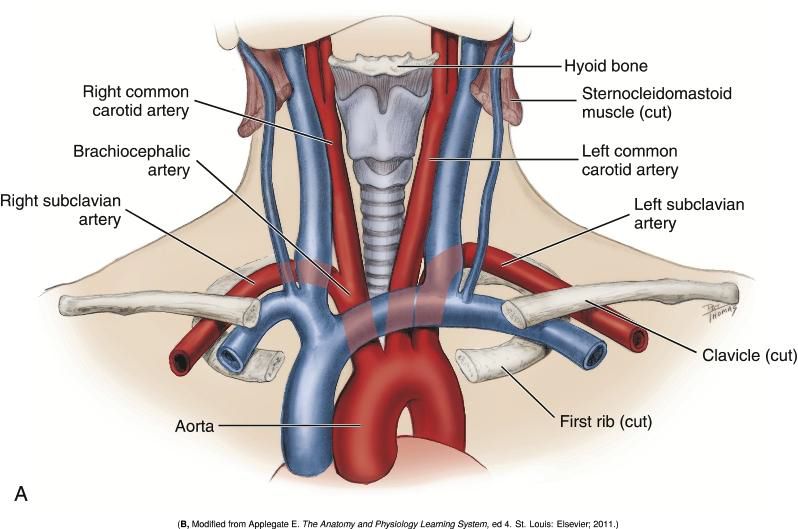
What is the brachiocephalic artery a direct branch of?
The aorta.
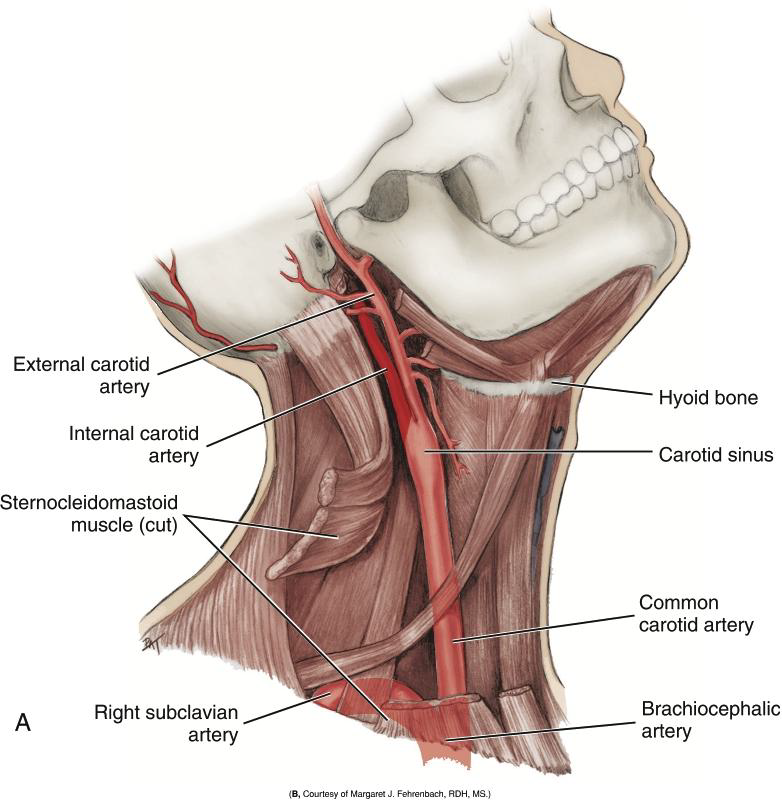
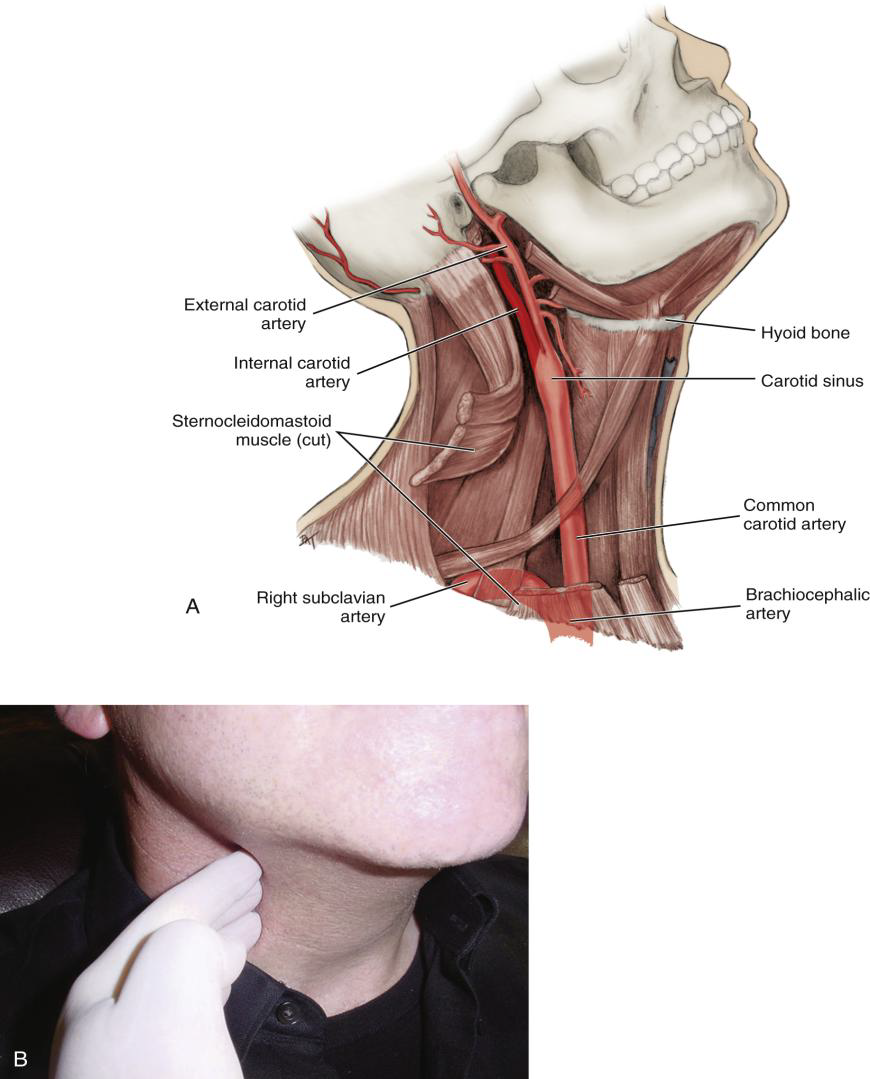
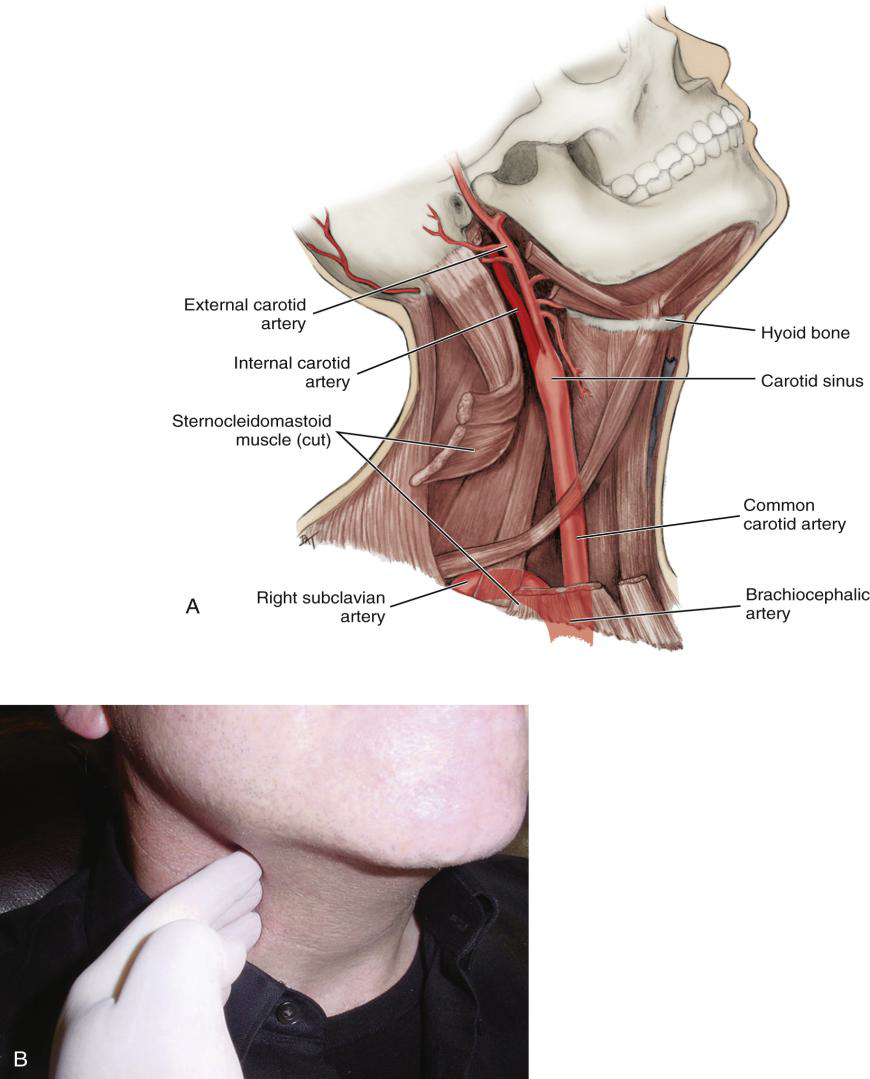
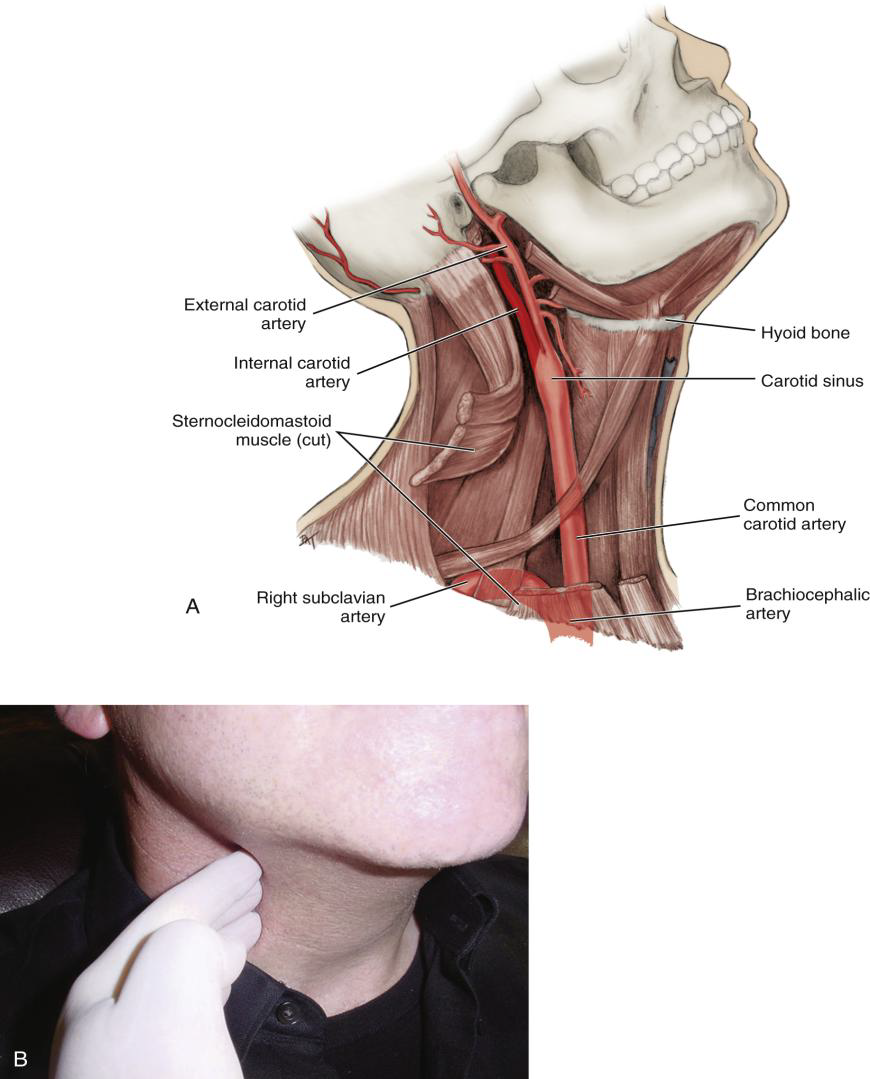
Describe the path of the Common Carotid Artery in the neck.
It travels superiorly along the neck, lateral to the trachea and larynx, to the superior border of the thyroid cartilage.
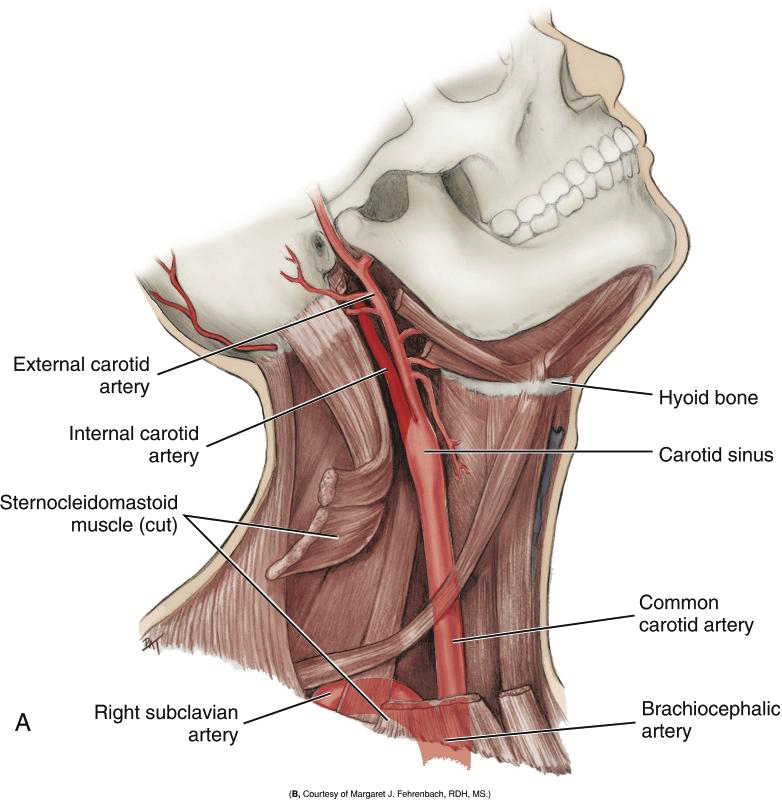
Does the Common Carotid Artery have branches in the neck?
No, it is branchless until it terminates.
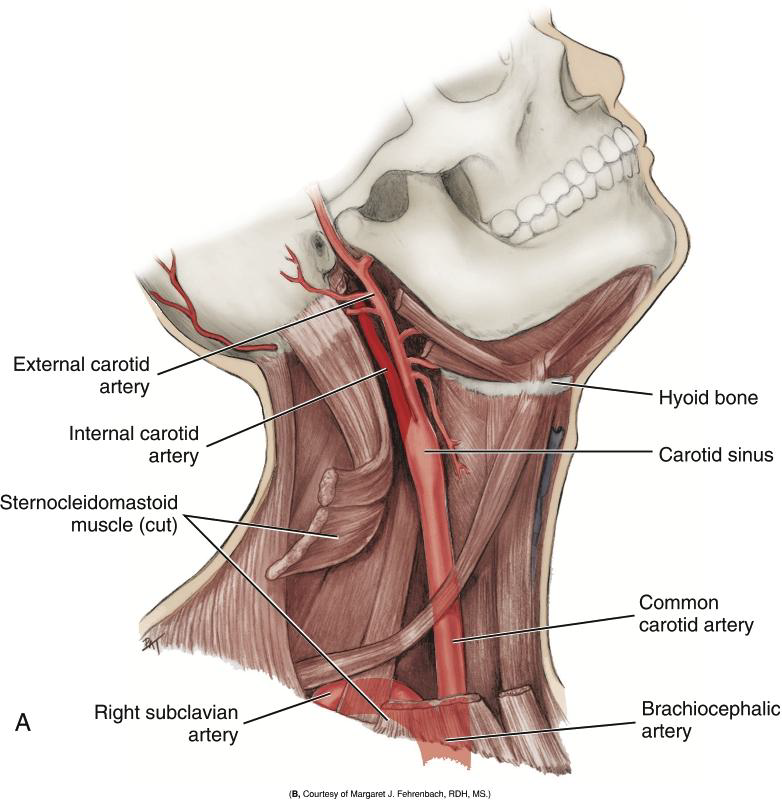
Where does the Common Carotid Artery divide?
At the superior border of the thyroid cartilage (level of the larynx). After the Carotid sinus
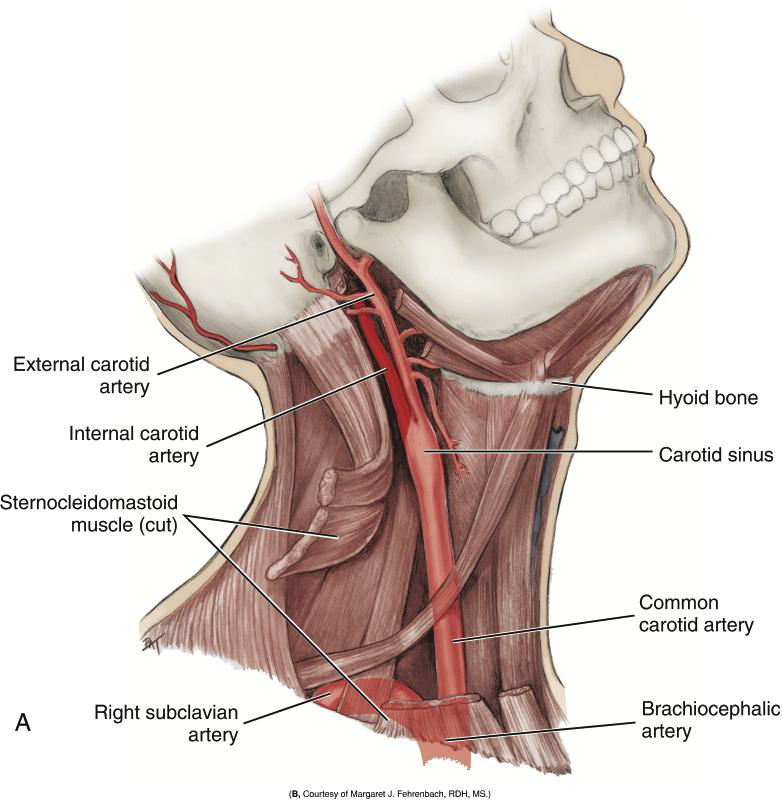
Into what two arteries does the Common Carotid Artery divide?
The internal and external carotid arteries.
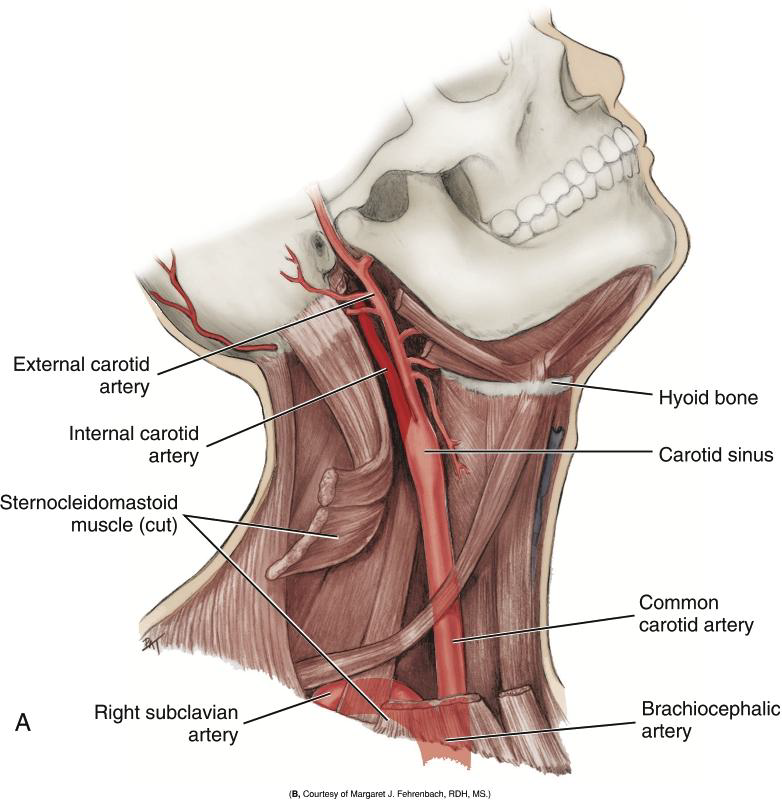
What is the Carotid Sinus?
A swelling just before the bifurcation of the common carotid artery.
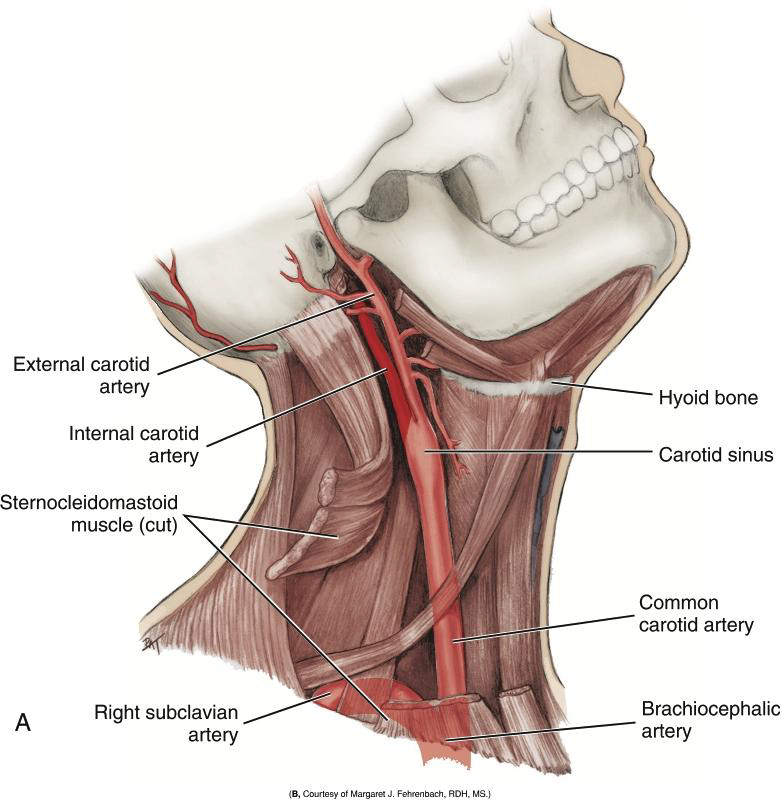
Where is the carotid pulse palpated?
Against the larynx.
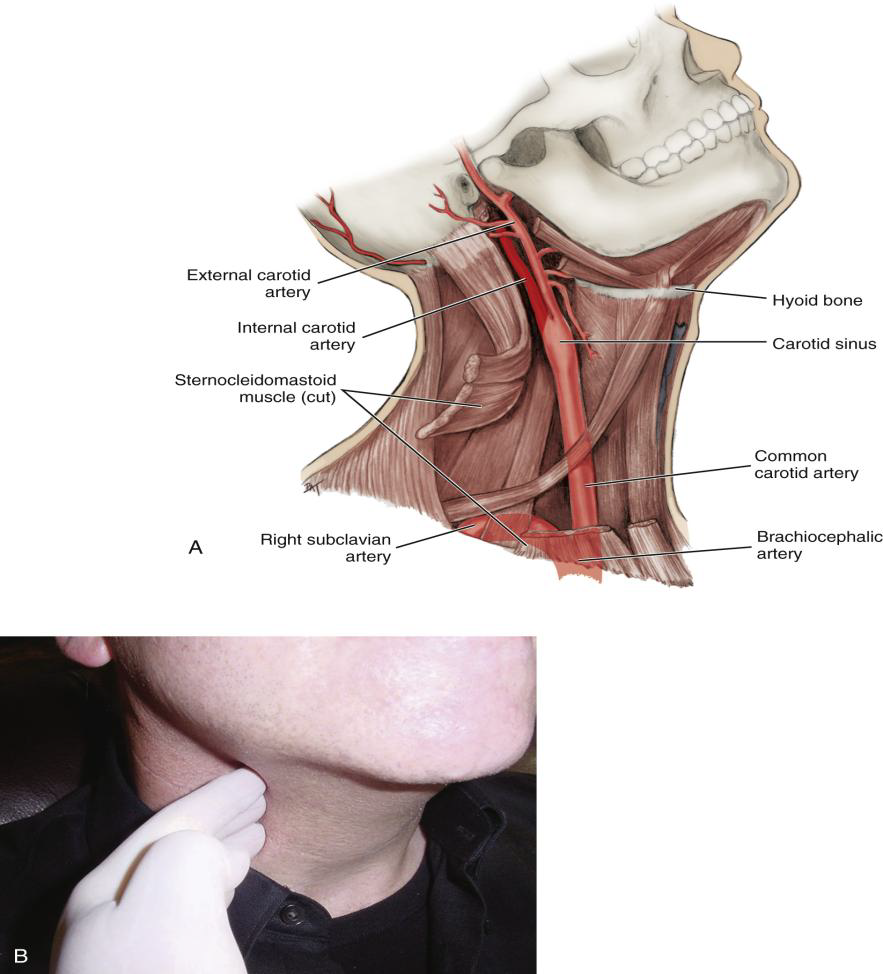
Which is the most reliable arterial pulse?
Carotid pulse
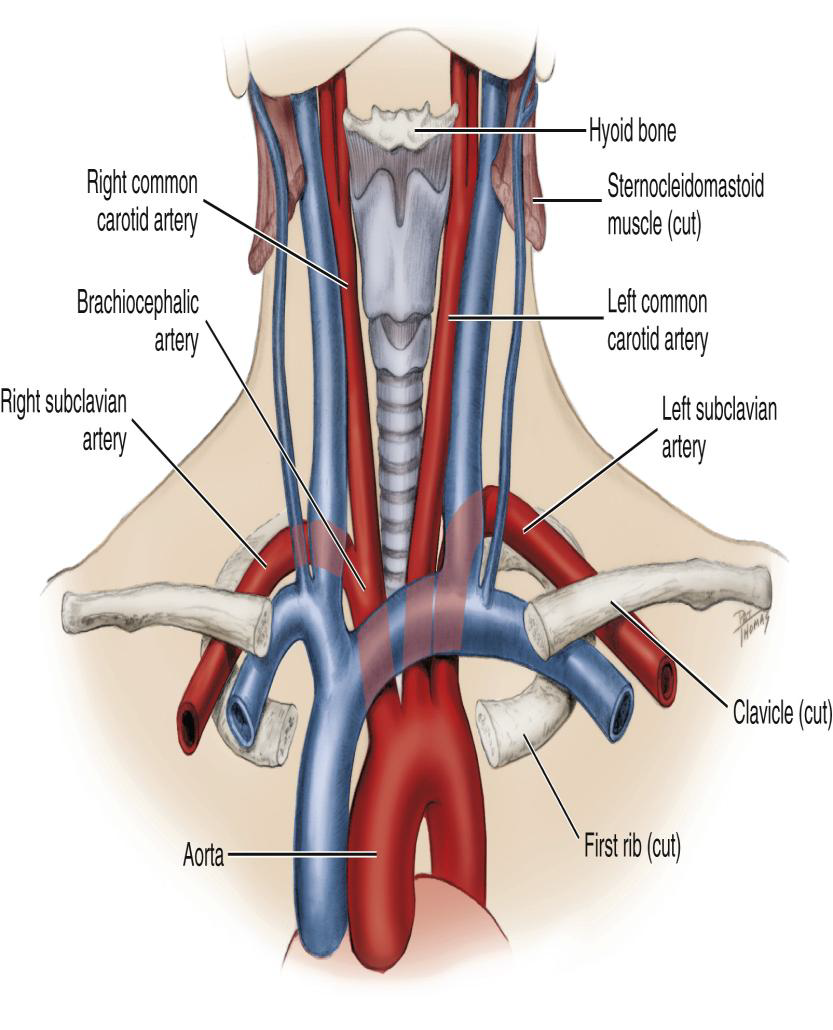
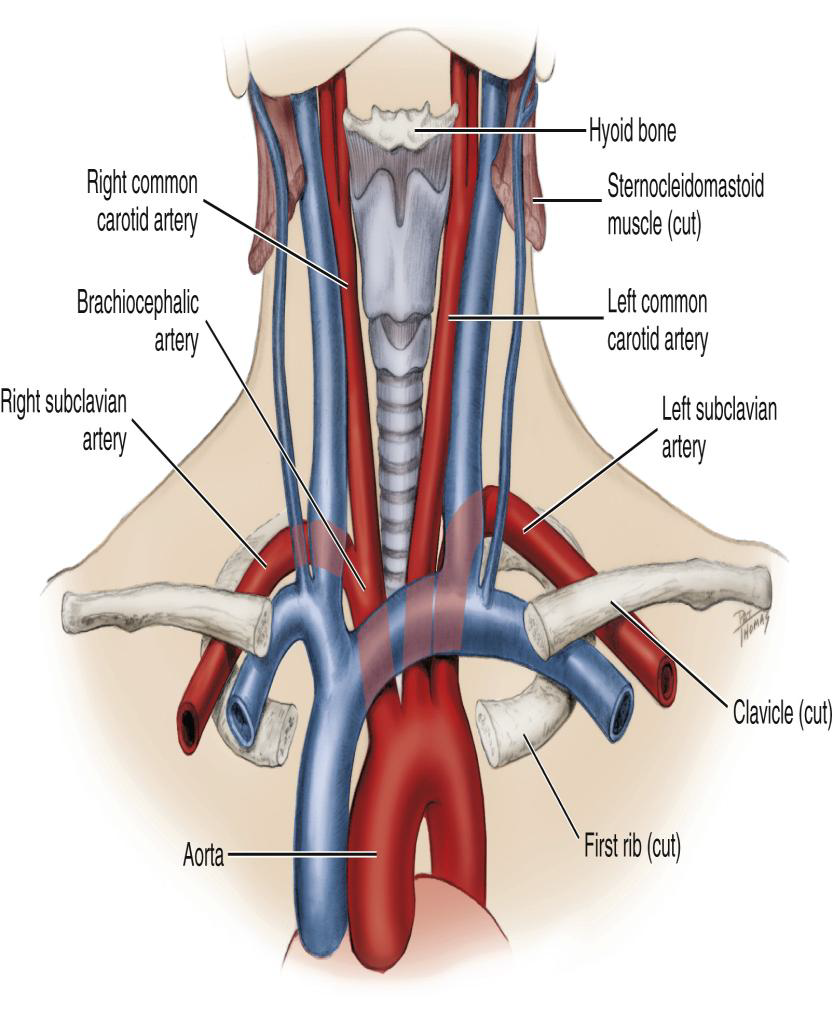
Where does the Subclavian artery arise relative to the common carotid?
Lateral to the common carotid artery.
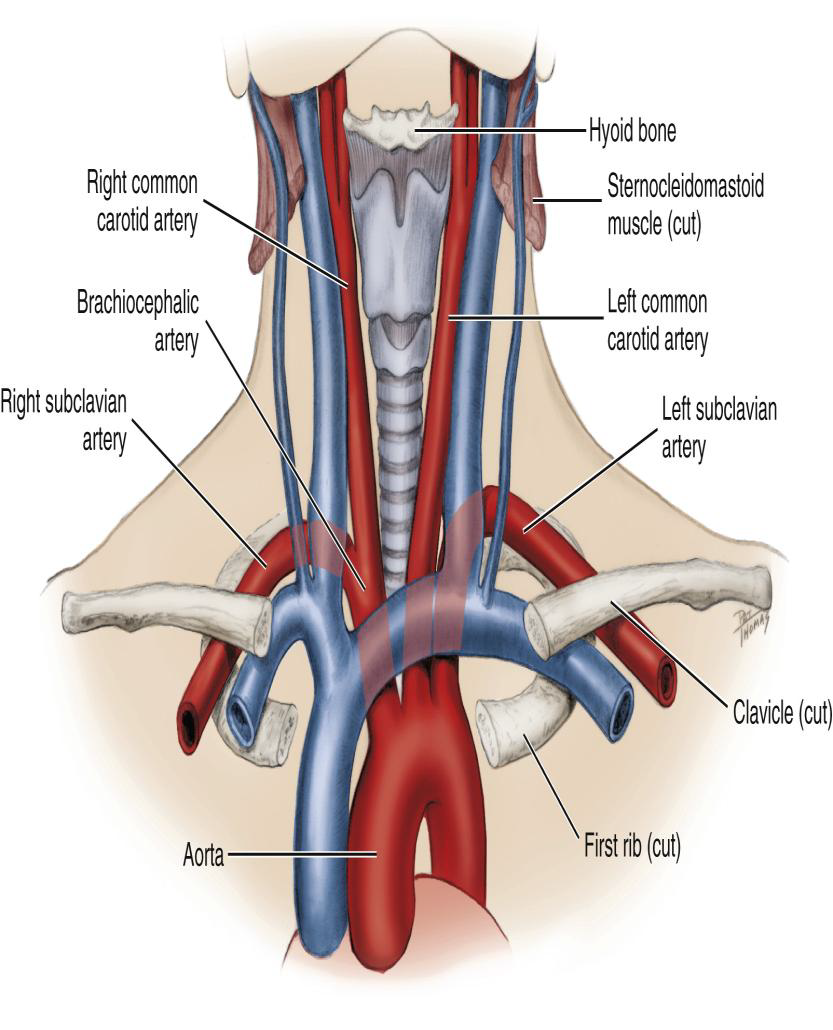
What is the major destination of the Subclavian artery?
The upper extremity (arm).
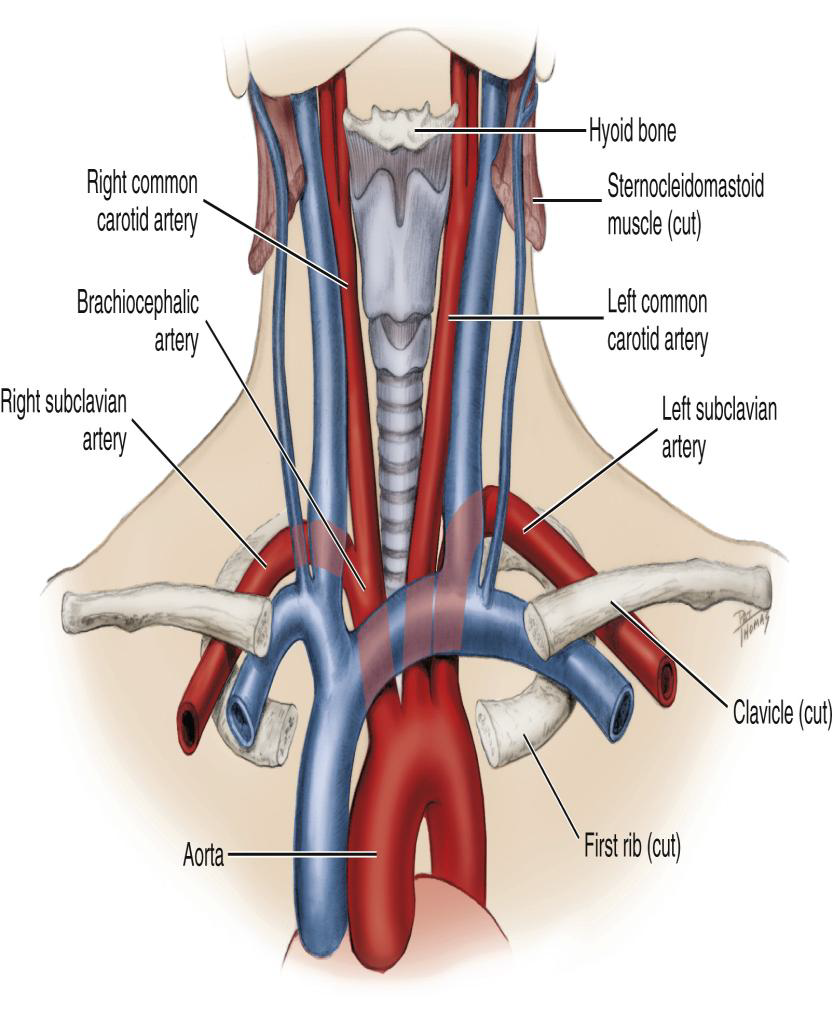
Subclavian artery supplies which structures?
Supplies intracranial and extracranial structures
Where does the Internal Carotid Artery travel after the bifurcation?
Superiorly in a slightly lateral position to the external carotid artery.
Does the Internal Carotid Artery supply the neck?
No, it supplies intracranial structures.
What is the source of the Ophthalmic Artery?
The Internal Carotid Artery.
What does the Ophthalmic Artery supply?
The eye, orbit, lacrimal gland, and much of the forehead.
What covers the opthalmic artery?
Covered by the large SCM on each side
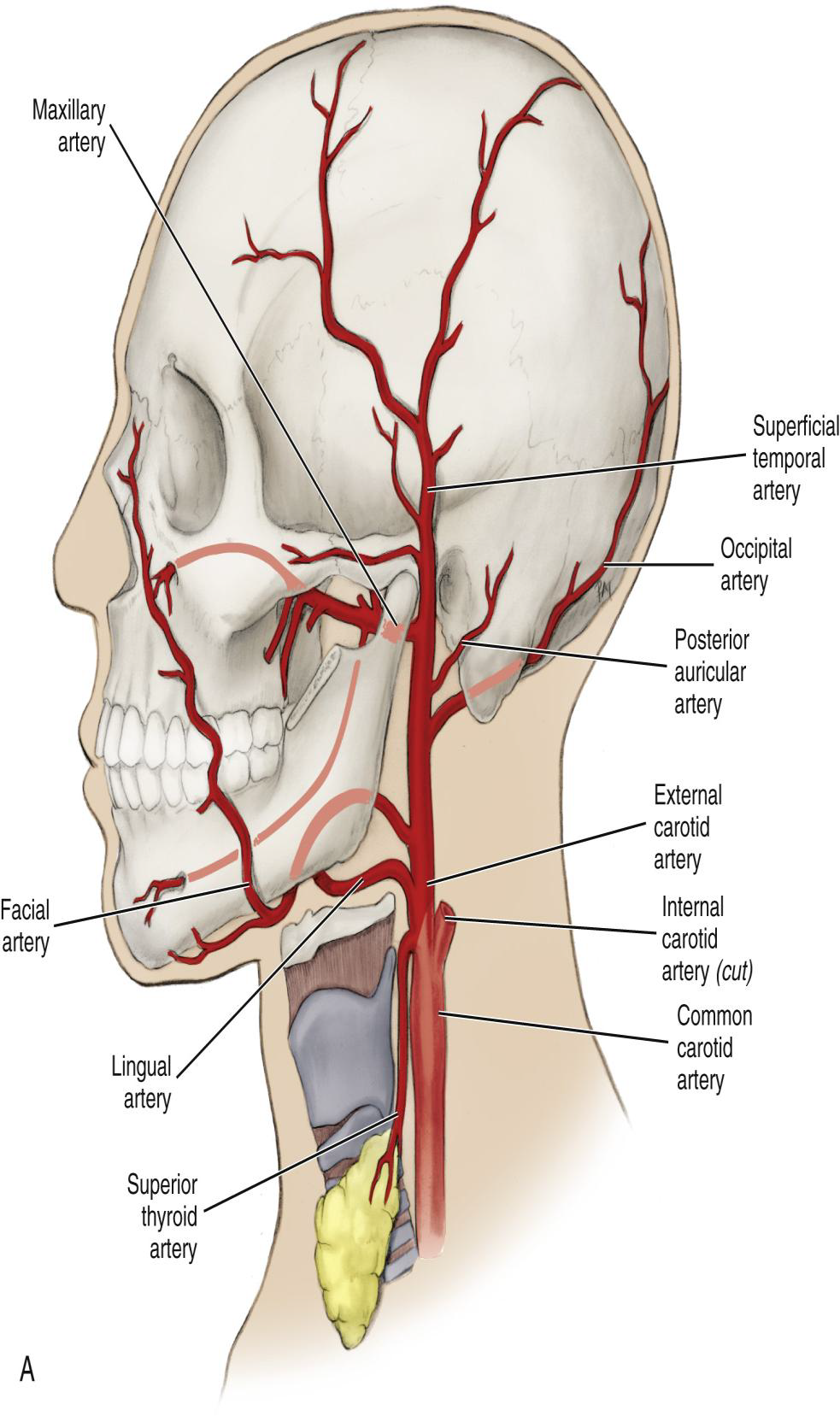
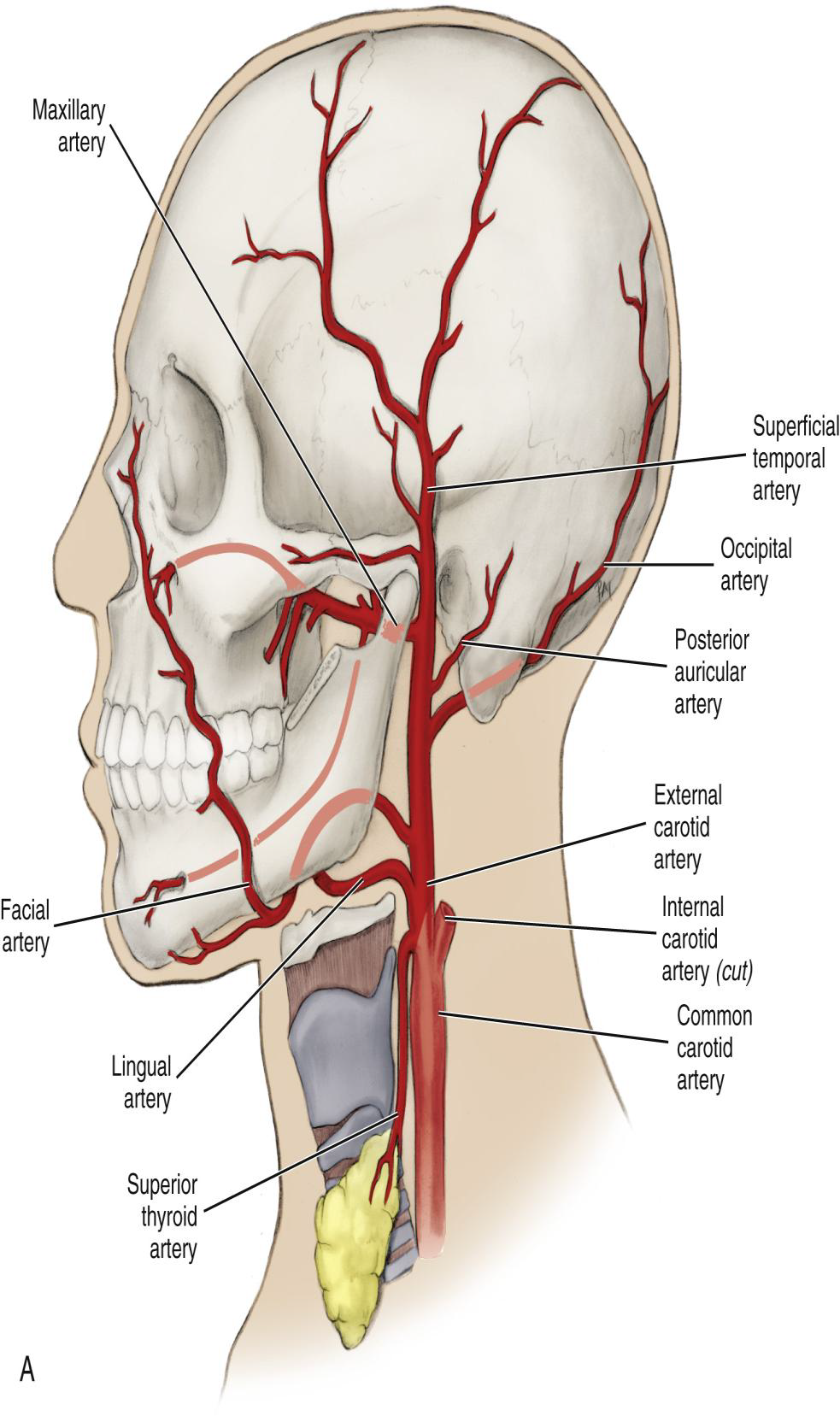
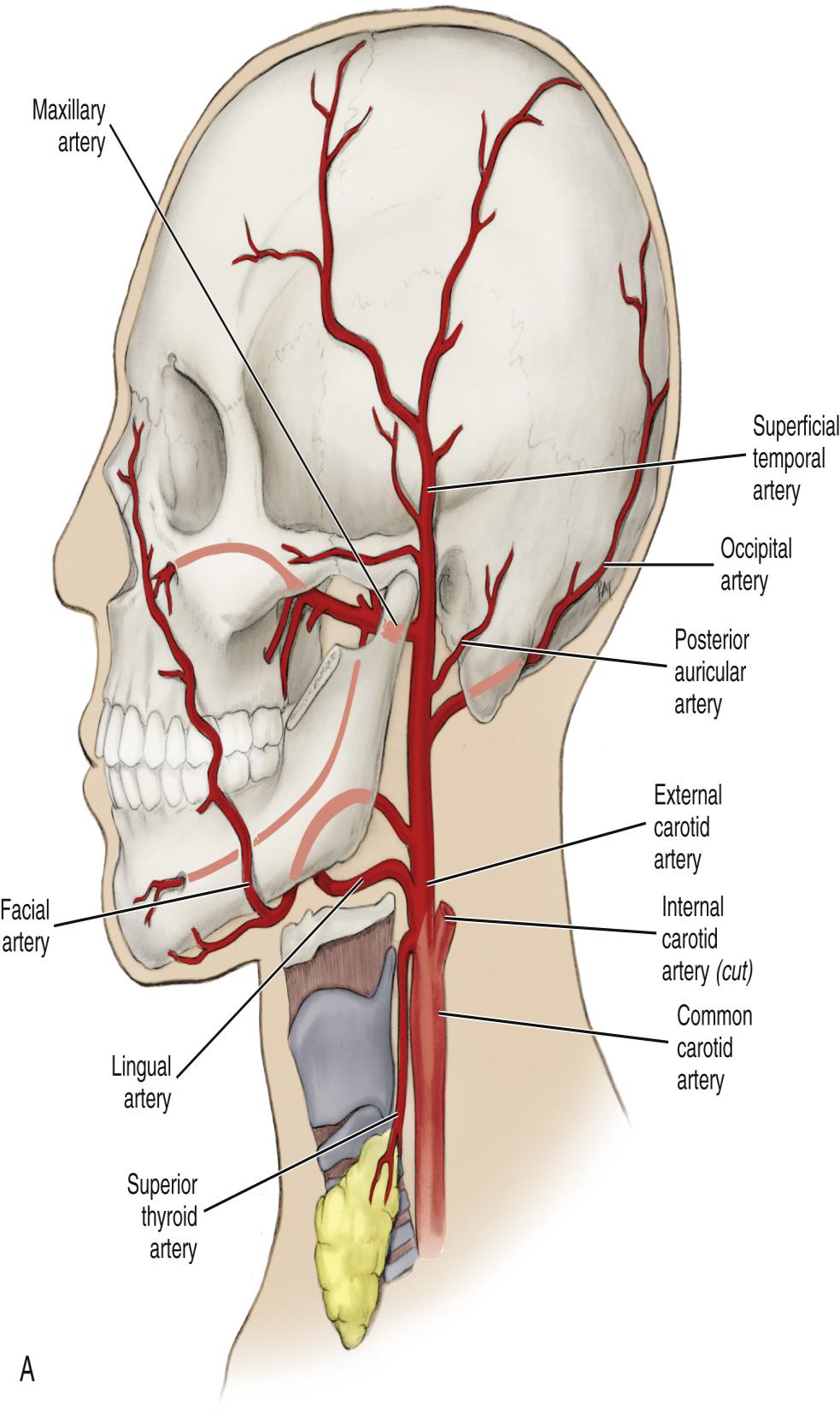
Where does the External Carotid Artery begin and arise from
Begins at the superior border of the thyroid cartilage.
Arises from common carotid artery
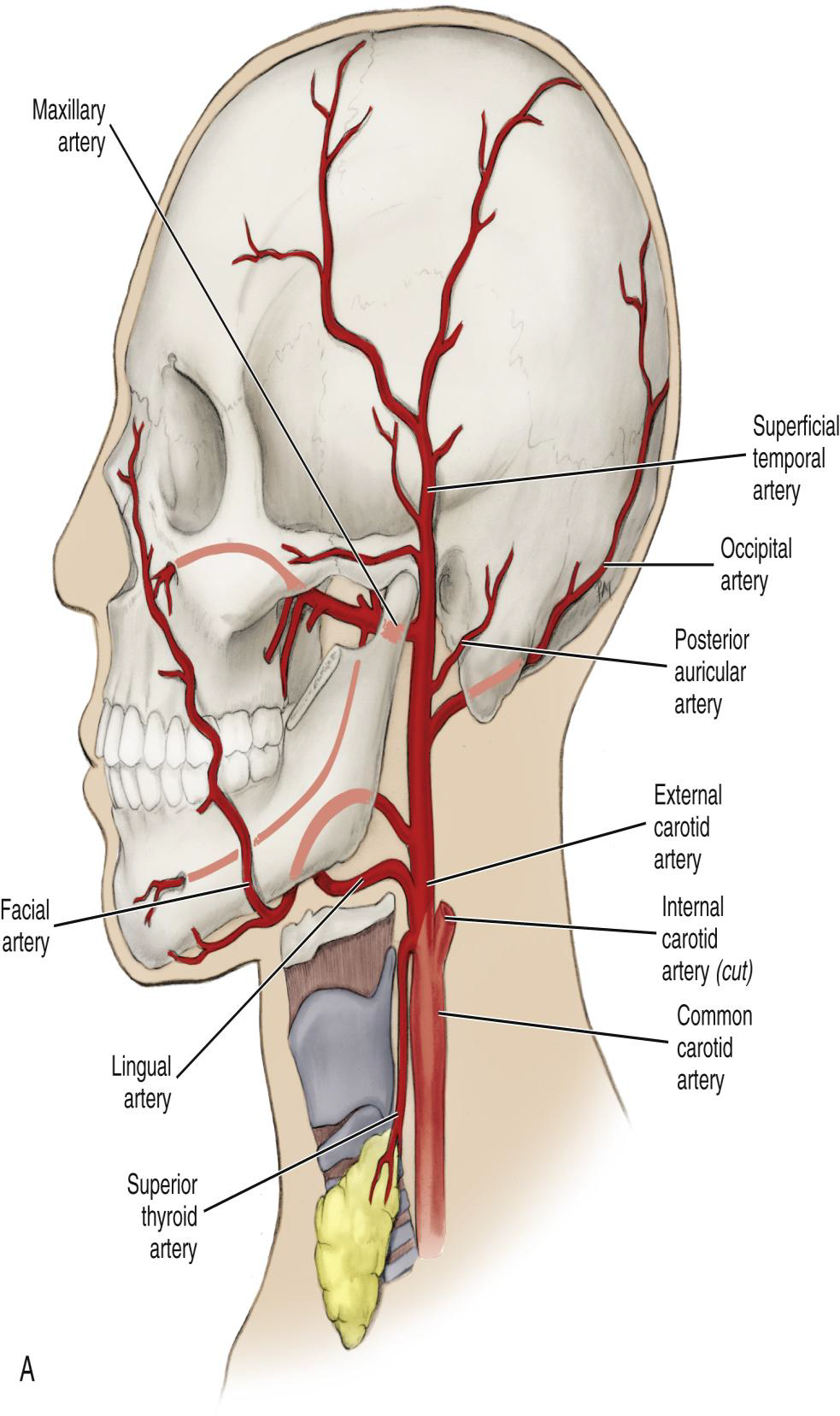
What is the position of the ECA relative to the Internal Carotid Artery?
It travels superiorly in a medial position to the internal carotid artery.
What does the ECA supply?
The extracranial tissue of the head and neck, including the oral cavity.
What are the four sets of ECA branches?
Anterior (3), Medial (1), Posterior (2), and Terminal (2).
Name the three anterior branches of the External Carotid Artery.
Superior thyroid, Lingual, and Facial arteries.
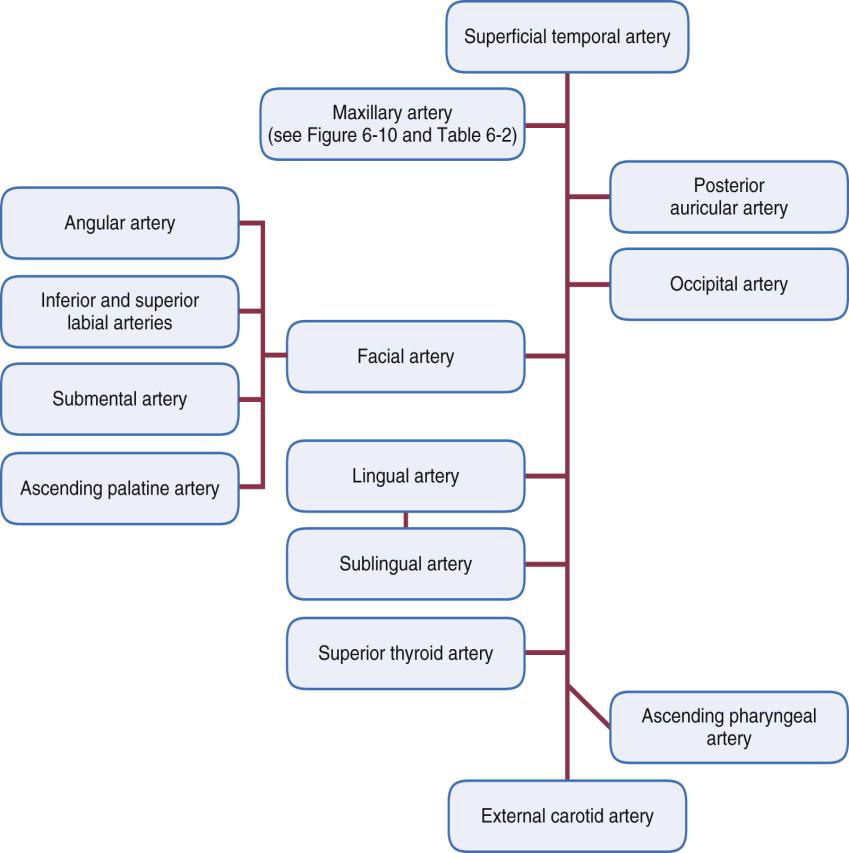
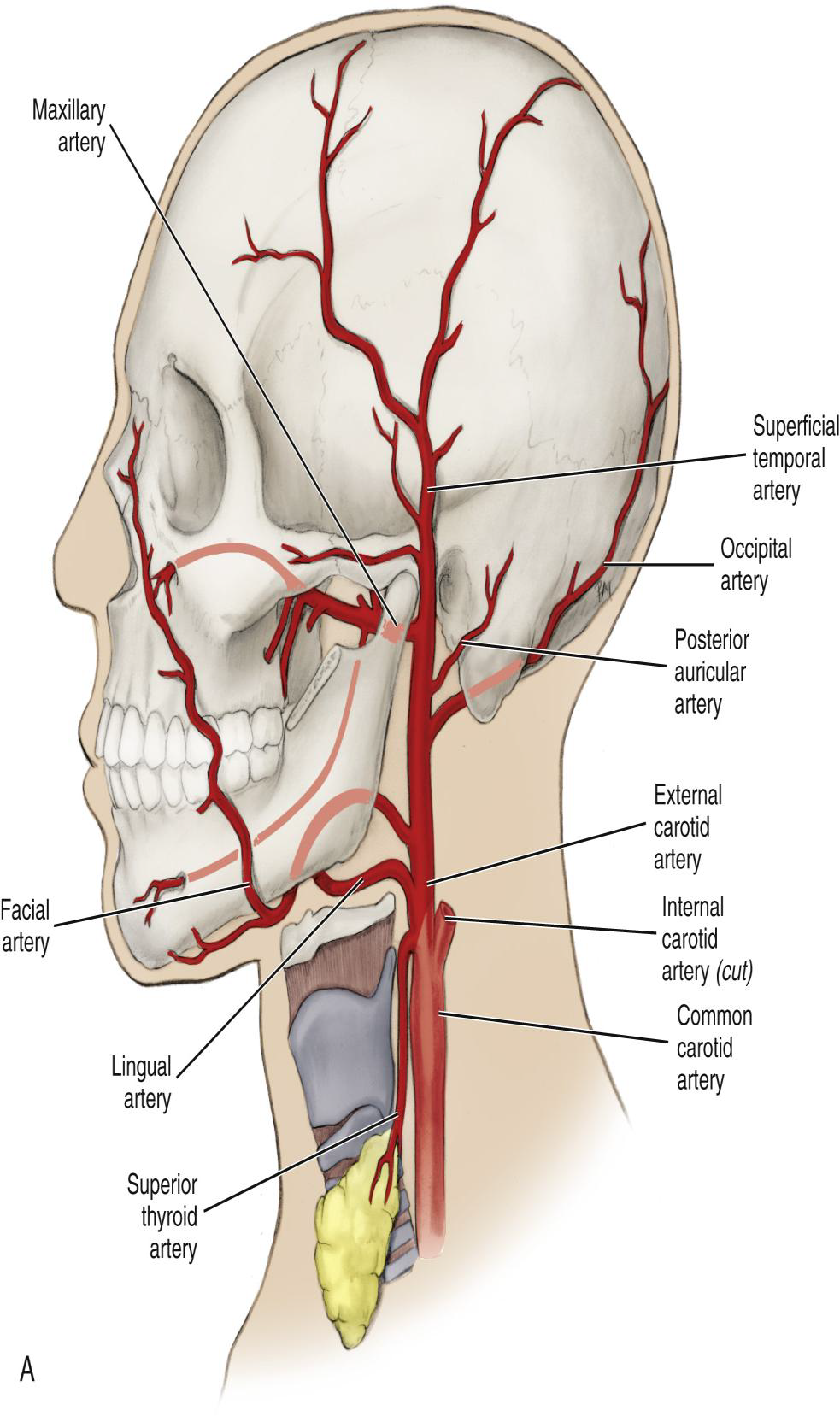
What does the Superior Thyroid Artery supply?
Tissue inferior to the hyoid bone, including infrahyoid muscles, SCM, laryngeal muscles, and the thyroid gland.
How many branches does the Superior Thyroid Artery have?
4
• infrahyoid
• SCM
• superior laryngeal
• cricothyroid
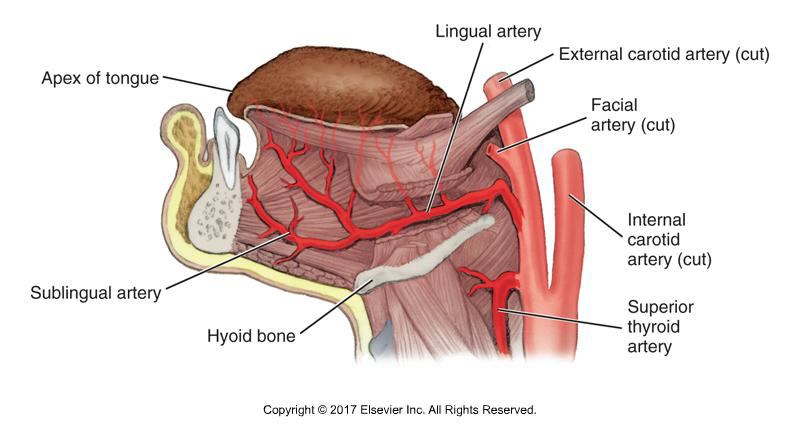
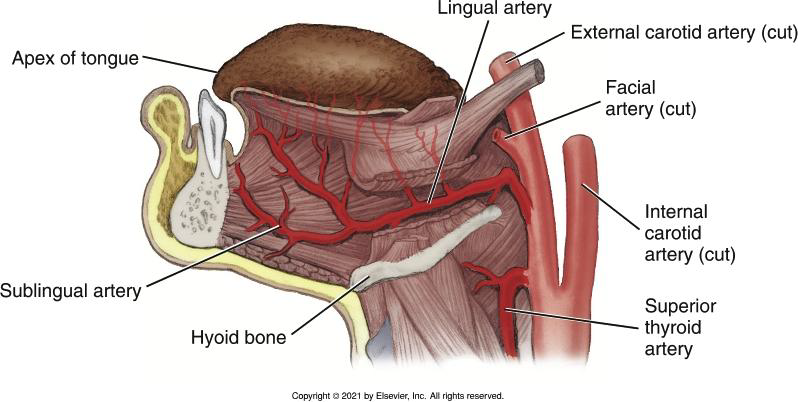
Where does the Lingual Artery branch off?
Below the facial artery.
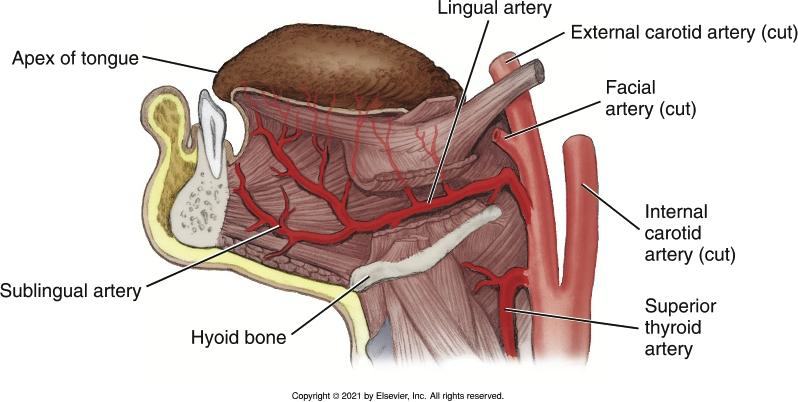
What does the Lingual Artery supply?
Tissue superior to the hyoid bone, including suprahyoid muscles, floor of the mouth, and the tongue.
Provides well-developed blood supply to tongue
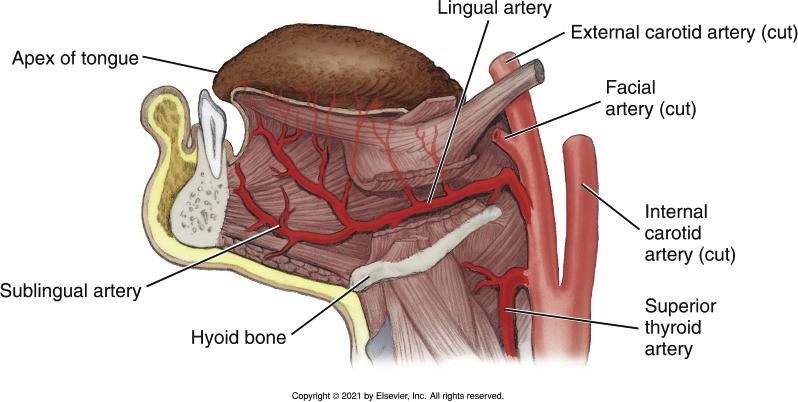
What are the three terminal branches of the Lingual Artery?
Dorsal lingual, deep lingual, and sublingual arteries.
What structures do the three terminal branches of the Lingual Artery supply?
• dorsal lingual artery- deep posterior part of the tongue
• deep lingual artery-deep anterior part of the tongue
• sublingual artery-mylohyoid muscle / ventral surface of the tongue / FOM
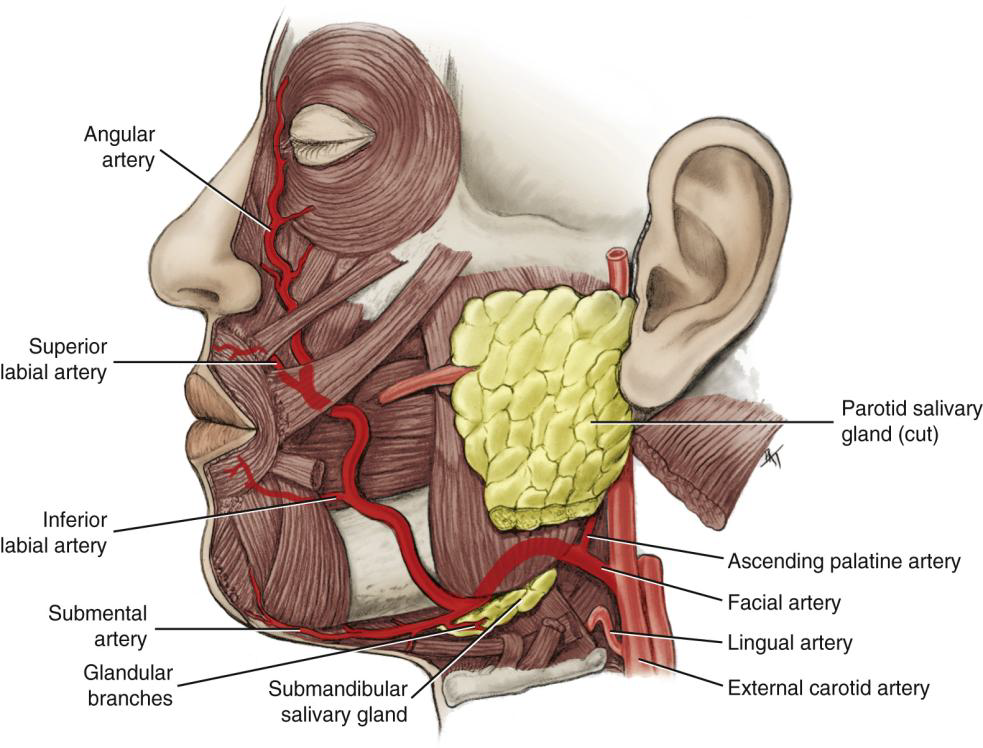
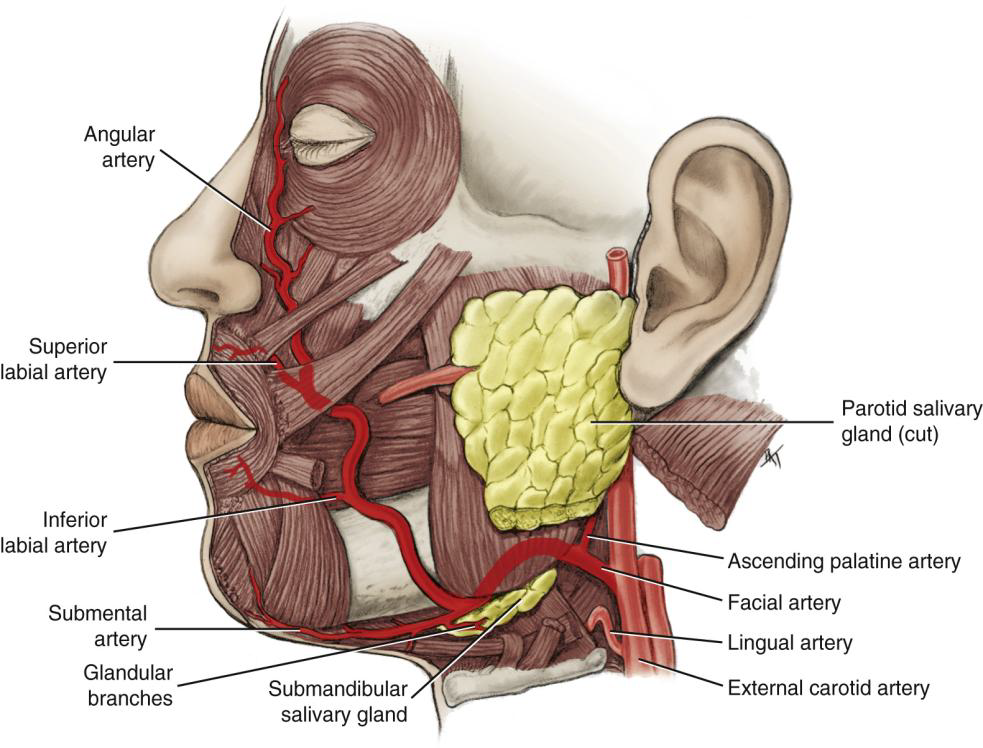
Where does the Facial Artery run relative to the submandibular gland?
Deep to the gland.
Where does the Facial Artery cross the mandible?
Just in front of the angle of the mandible (inferior border) ascending the side of the neck
Where does the Facial Artery terminate?
At the medial canthus of the eye.
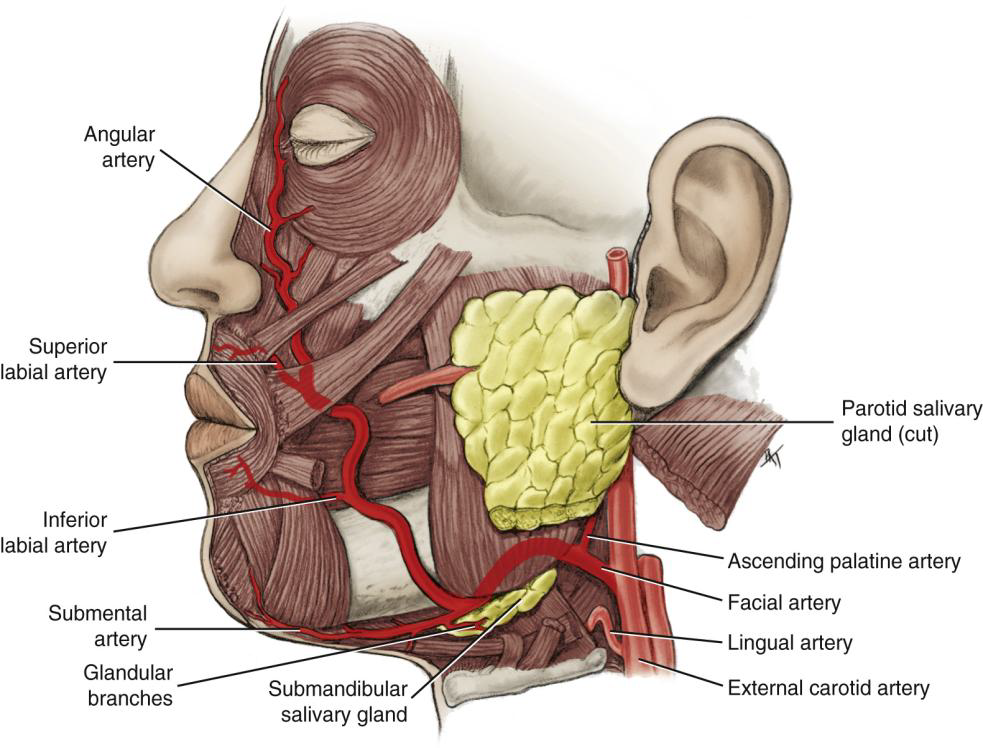
Name the branches of the Facial Artery.
Angular, superior labial, inferior labial, ascending palatine, submental, and glandular branches.
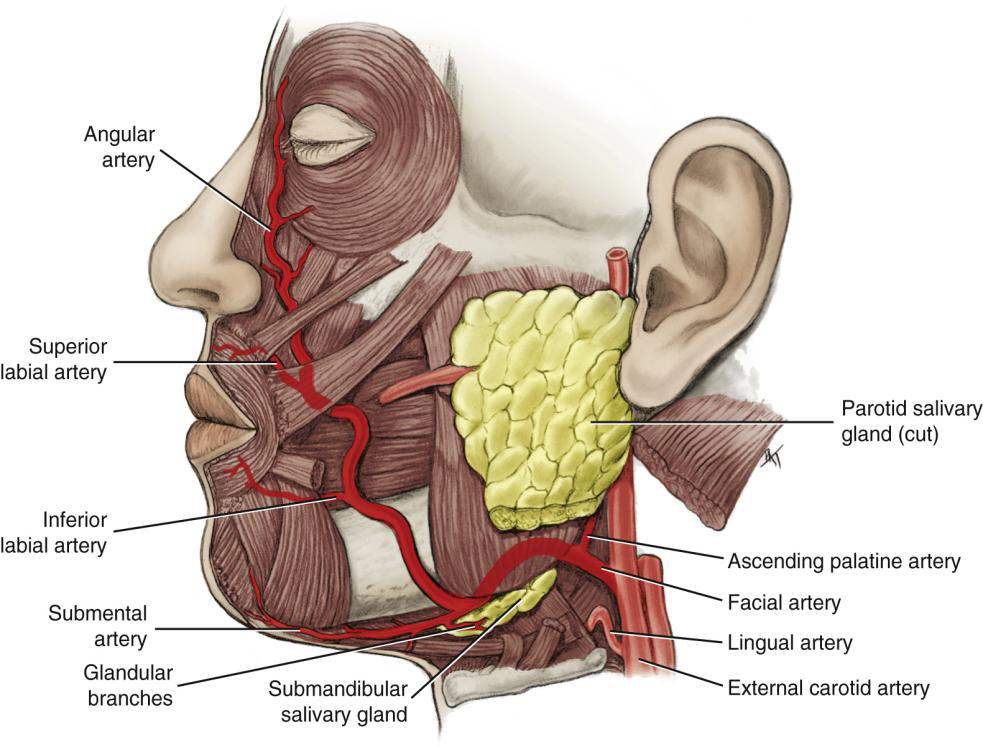
What is the first branch off the Facial Artery?
The Ascending Palatine Artery.
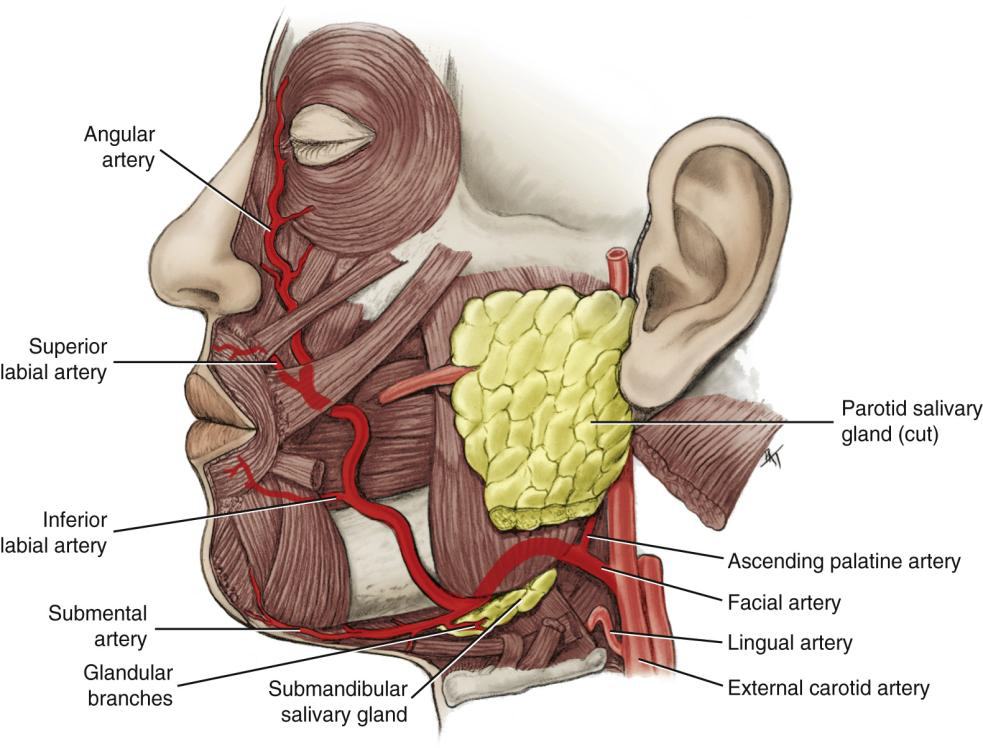
What is the clinical significance of the Ascending Palatine Artery?
It supplies the tonsils and can be a source of hemorrhage during tonsillectomy.
Wht does the Ascending Palatine Artery supply?
supplies the soft palate, palatine muscles,
and palatine tonsils
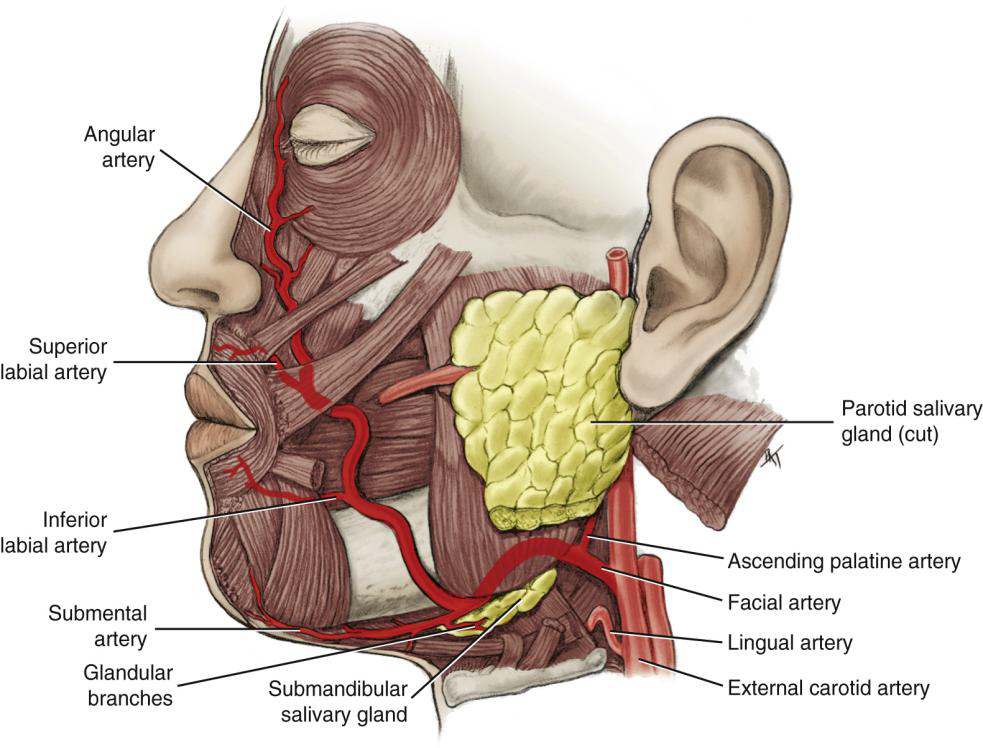
What does the Submental Artery supply?
Submandibular lymph nodes, submandibular salivary gland, mylohyoid, and digastric muscles.
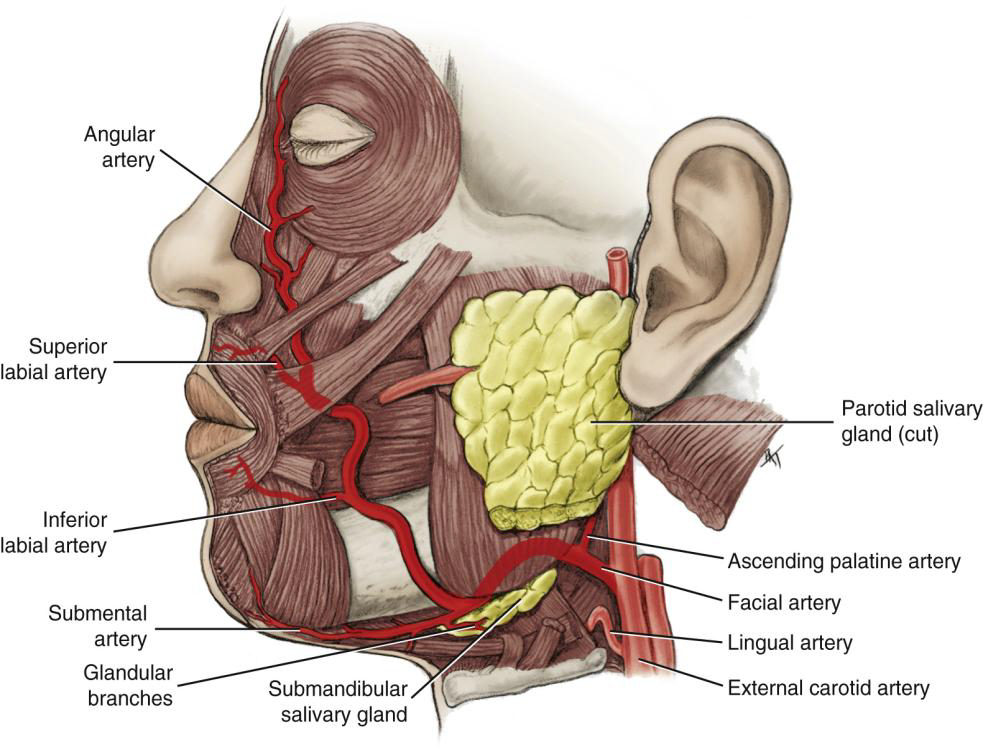
What does the Angular artery supply?
The lateral side of the naris (nose).
What is the only medial branch of the External Carotid Artery?
The Ascending Pharyngeal Artery.
Can the Ascending Pharyngeal Artery be seen in most lateral views?
No.
What are the (3 main) ascending Pharyngeal Artery branches?
pharyngeal
meningeal
and tonsillar branches
Name the two posterior branches of the External Carotid Artery.
The Occipital artery and Posterior Auricular artery.
Where does the Occipital Artery arise?
Just deep to the ascending ramus of mandible, traveling to the posterior scalp.
Which cranial nerve is adjacent to the Occipital Artery at its origin?
The hypoglossal nerve (12th).
What does the Posterior Auricular Artery supply?
The inner ear (auricular branch) and mastoid air cells (stylomastoid branch).
What are the 4 branches of the occipital artery?
• sternocleidomastoid – SCM mucle
• auricular – scalp in the occipital region
• meningeal – meninges in the occipital area
• muscular – suprahyoid muscles
What does the postauricular artery branch into and what do they supply?
auricular branch – inner ear
Stylomastoid branch – mastoid air cells
Name the two terminal branches of the External Carotid Artery.
The Superficial Temporal Artery and the Maxillary Artery.
Where does the ECA split into these terminal branches?
Within the parotid salivary gland.
Is the Superficial Temporal Artery visible?
Yes, it can sometimes be visible under the skin in the temporal region.
What re the 4 branches of the superficial Temporal artery?
• transverse facial
• middle temporal artery
• frontal branch
• parietal branch
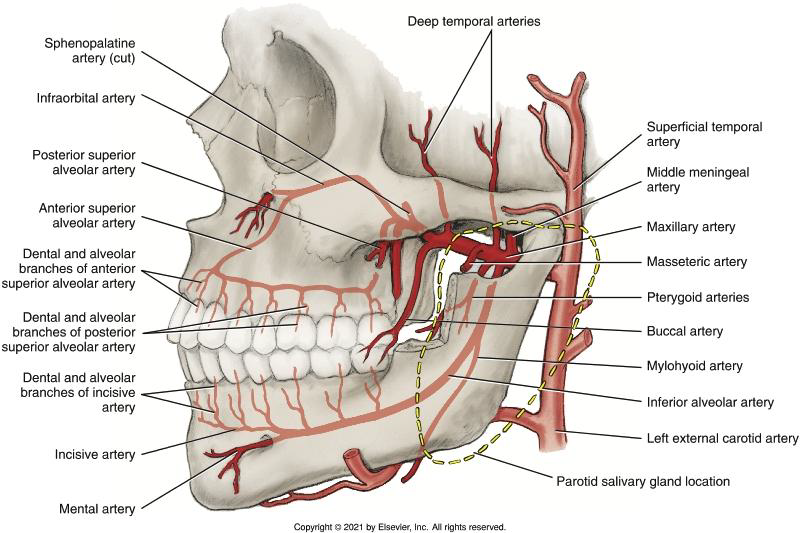
What is the larger terminal branch of the ECA?
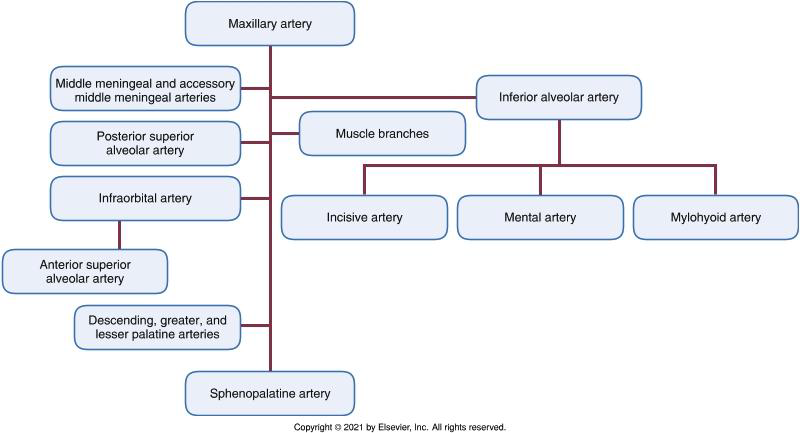
The Maxillary Artery.
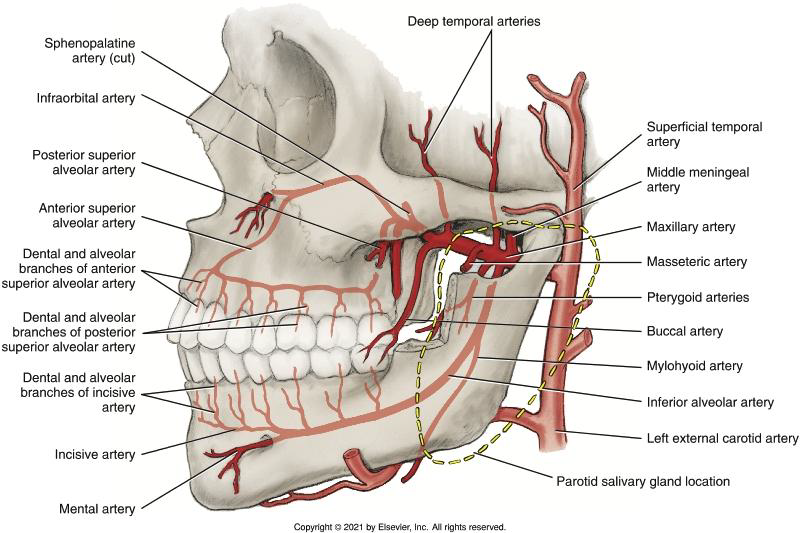
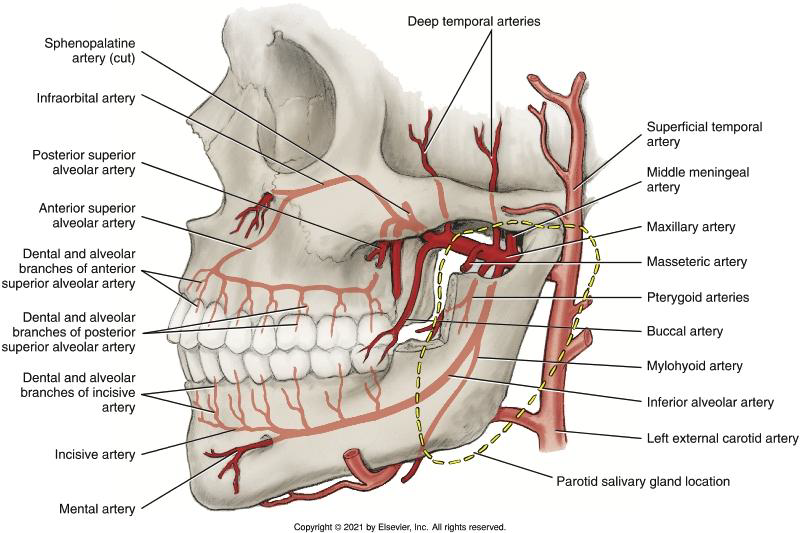
What are the three parts of the Maxillary Artery defined by?
Location (Mandibular, Pterygoid, Pterygopalatine).
Where is the First Part (Mandibular part) located?
Between the neck of the mandibular condyle and the sphenomandibular ligament.
Where is the Second Part (Pterygoid part) located?
between the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament anteriorly and superiorly through the infratemporal fossa
Where is the Third Part (Pterygopalatine part) located?
In the pterygopalatine fossa. (deep and inf. to the eye)
Which artery from the First Part supplies the meninges and skull bones?
The Middle Meningeal Artery.
Which artery from the First Part of the mandibular branch of maxillary artery enters the mandibular canal to supply the mandibular posterior teeth and gingiva?
The Inferior Alveolar (IA) Artery.
What branches arise from the IA artery before it enters the canal?
The Mylohyoid Artery.
Supplies the mylohyoid muscle and FOM
What branch arises from the IA artery and exits the mental foramen?
The Mental Artery.
supplies the tissue of the chin
anastomoses with the inferior labial artery
What artery remains in the mandibular canal to supply anterior teeth?
The Incisive Artery.
Supply the pulp of the mandibular anterior teeth by way of each tooth’s apical foramen
the periodontium (including the gingiva) of the mandibular anterior teeth
The Incisive Artery supplies?
Supply the pulp of the mandibular anterior teeth by way of each tooth’s apical foramen
the periodontium (including the gingiva) of the mandibular anterior teeth
What do the arteries of the Second Part (Pterygoid) of the maxillary artery supply?
Muscles of mastication (Deep temporal, Pterygoid, Masseteric, Buccal arteries).
• deep temporal arteries: supply the temporalis muscle
• pterygoid arteries: supply the lateral and medial pterygoid muscles
• masseteric artery: supplies the masseter muscle
• buccal artery: supplies the buccinator muscle and other soft tissues of the cheek
Which arteries accompany branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (5th)?
Second Part (Pterygoid) of the maxillary artery
Which artery arises as the Maxillary artery enters the pterygopalatine fossa from the infratemporal fossa?
The Posterior Superior Alveolar (PSA) Artery.
Where does the Posterior superior alveolar artery (PSA) enter the posterior superior alveolar foramina?
on the maxillary tuberosity,
What does the PSA artery supply?
Maxillary posterior teeth pulp, periodontium, and maxillary sinus.
Which artery travels in the infraorbital canal?
The Infraorbital Artery.
The infraorbital artery can share a common trunk with?
May share a common trunk with the posterior superior alveolar artery
What branch arises from the Infraorbital Artery?
The Anterior Superior Alveolar (ASA) Artery.
which then branches into dental and alveolar branches
The Anterior Superior Alveolar (ASA) Artery anastomoses wit which artery?
anastomoses with the posterior superior alveolar artery.
The Anterior Superior Alveolar (ASA) Artery supply which structures?
• the pulp of the maxillary anterior teeth via each tooth’s apical foramen
• the periodontium (including the gingiva) of the maxillary anterior teeth
The infraorbital artery travels in the infraorbital canal and emerges onto
the infraorbital artery travels in the infraorbital canal and emerges onto the face from the infraorbital foramen
What does the Middle Superior Alveolar (MSA) artery supply (if present)?
Maxillary premolars and buccal periodontium.
Which artery does the Middle Superior Alveolar (MSA) artery anastomose wtih?
ASA and PSA arteries
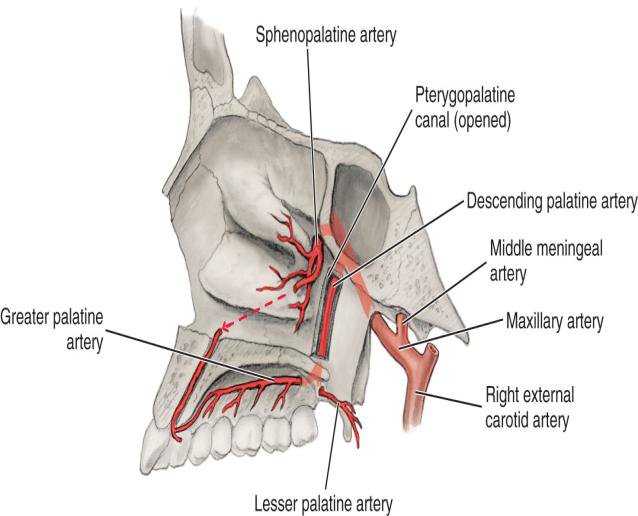
What does the Descending Palatine Artery divide into?
The Greater and Lesser Palatine arteries.
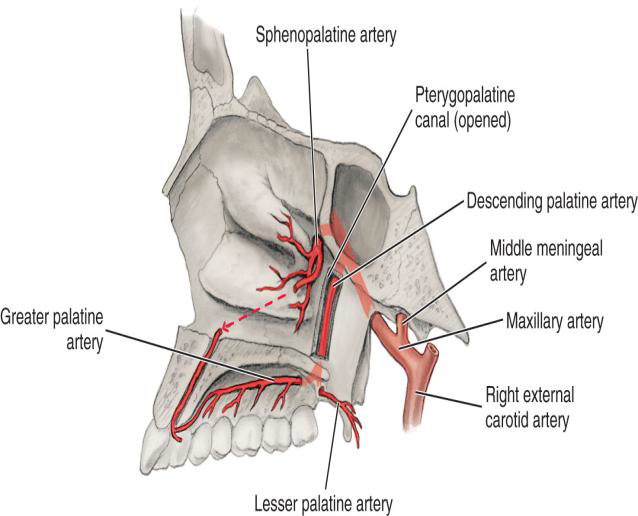
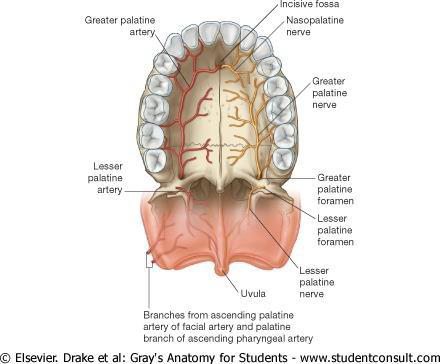
What does the Greater Palatine Artery supply?
The hard palate via the greater palatine foramina
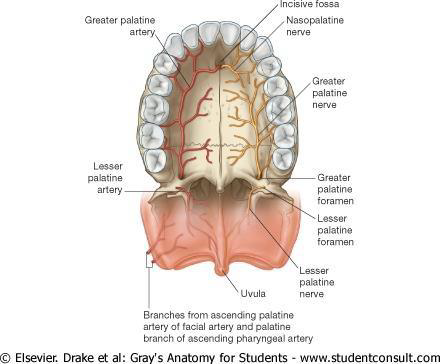
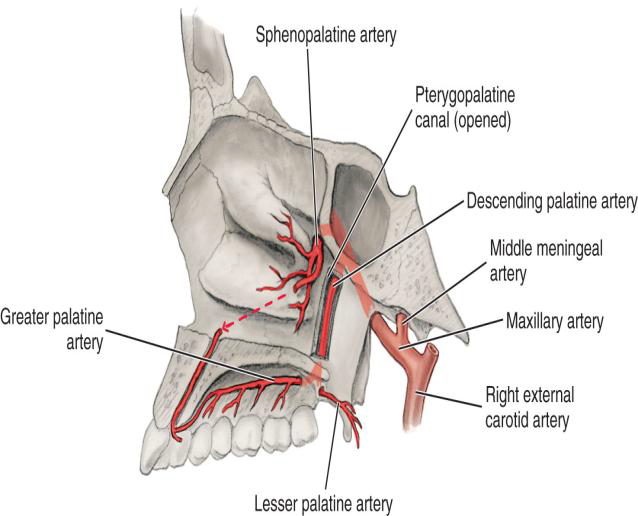
What does the Lesser Palatine Artery supply?
The soft palate via lesser palatine foramina
What is the terminal branch of the Maxillary Artery?
The Sphenopalatine Artery.
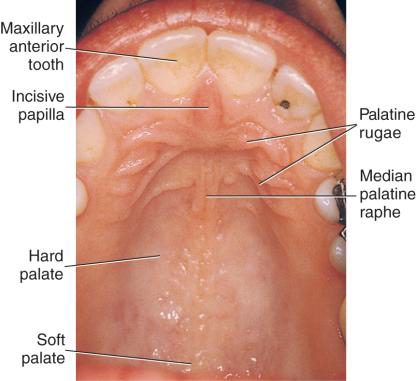
What branch of the Sphenopalatine artery travels through the incisive foramen?
The Nasopalatine branch.
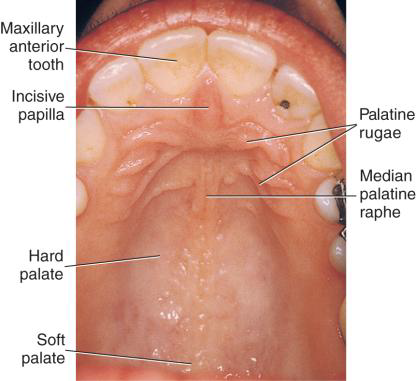
The Nasopalatine branch accompanies which nerve through the incisive foramen on the maxillae?
accompanies the nasopalatine nerve through the incisive foramen on the maxillae
Supplies the nasal cavity via the sphenopalatine foramen
Where does all venous drainage from the head and neck eventually terminate?
In the Internal Jugular Vein which then joins the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein behind the medial end of the clavicle.
What drainage starts out as small, freely anastomosing venules in the brain and get bigger as they near the neck and descend toward the heart?
Venous Drainage
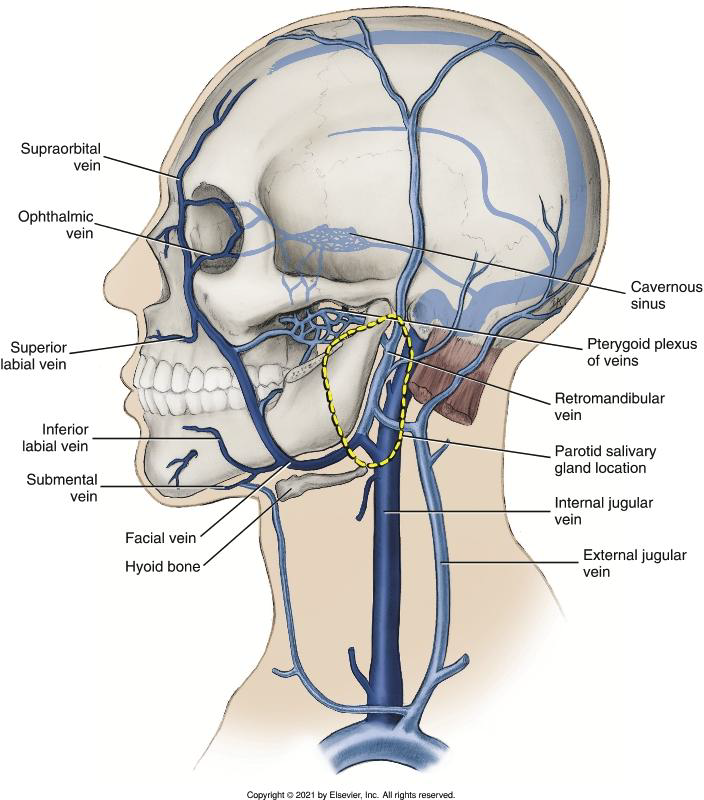
Is it true that in general, veins follow the same pathways as arteries and, in most instances, have the same names?
Yes, it is true
How is the Facial Vein formed?
By the union of the supratrochlear and supraorbital veins at the medial canthus.