Brand Management Exam 1
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Relativity
Branding as a means to distinguish goods of one producer from those of another
Differentiated Goods
Goods that are substitutes, but not perfect substitutes
Horizontal Differentiation
Choices are drive by preferences and circumstances
Vertical Differentiation
Goods are of different qualities
Relevance
Consumers buy products because of a brand's relevance in that moment
Five P's of Relevance
Purpose
Pride
Partnership
Protection
Personalization
Purpose
Customers feel like the company shared and advances their values
Pride
Customers feel accomplished and inspired to use the company's products and services
Partnership
Customers feel like the company relates to and works well with them
Protection
Customers feel secure when doing business with the company
Personalization
Customers feel their experiences with their company are continuously tailored to their needs and priorities
What is the difference between products and brands?
Products are anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a need, but a brand has dimensions that differentiate it in some way from other products designed to satisfy the same need
Customer Value Hierarchy
core benefit, generic product, expected product, augmented product, potential product
Core Benefit
First layer of the customer value hierarchy: the fundamental need that consumers satisfy by consuming the product
Generic Product
Second layer of the customer value hierarchy: a basic version of the product containing only those attributes that are absolutely necessary for its functioning
Expected Product
Third layer of the customer value hierarchy: a set of attributes that buyers reasonably expect and agree to when they purchase a product
Augmented Product
Fourth layer of the customer value hierarchy: Additional attributes, benefits, and related services that distinguish the product from competitors
Potential Product
Fifth and final layer of the customer value hierarchy: all of the augmentations and transformations that a product might ultimately undergo in the future.
Perceived Risk
Any action of a consumer may produce consequences which they cannot anticipate
Functional Risk
The risk that a product does not perform up to expectations
Solutions to Functional Risk
Total Quality Management (TQM), meaning (1) eliminating defects (2) waste elimination, or removing inefficiencies and (3) Just-in-time (JIT) production which minimizes inventory and reduces wasted by only producing what is needed
Physical Risk
Product poses a threat to the physical well being or health of the user or others
Solutions to Physical Risks
Product Warnings
Financial Risk
The risk that the product is not worth the price paid
Solution to Financial Risk
Price Sensitivity studies
Social Risk
The risk that the product results in embarrassment from others (stigmatized products)
Solution to Social Risk
Anti-Stigma Marketing Campaigns
Psychological Risk
The risk that the product affects the mental well-being of the user
Solution to Psychological Risks
Advanced Disclosure
Time Risk
The failure of the product results in an opportunity cost of finding another satisfactory product
Solution to Time Risks
Full satisfaction garuntees
Customer-Based Brand Equity (CBBE)
the differential effect that brand knowledge has on consumer response to the marketing of that brand
Associative Network Memory Model (ANMM)
Memory is a network of nodes (concepts) and associations linked tothe nodes
Core Brand Associations
abstract associations that characterize 5 to 10 most important aspects or dimensions of a brand
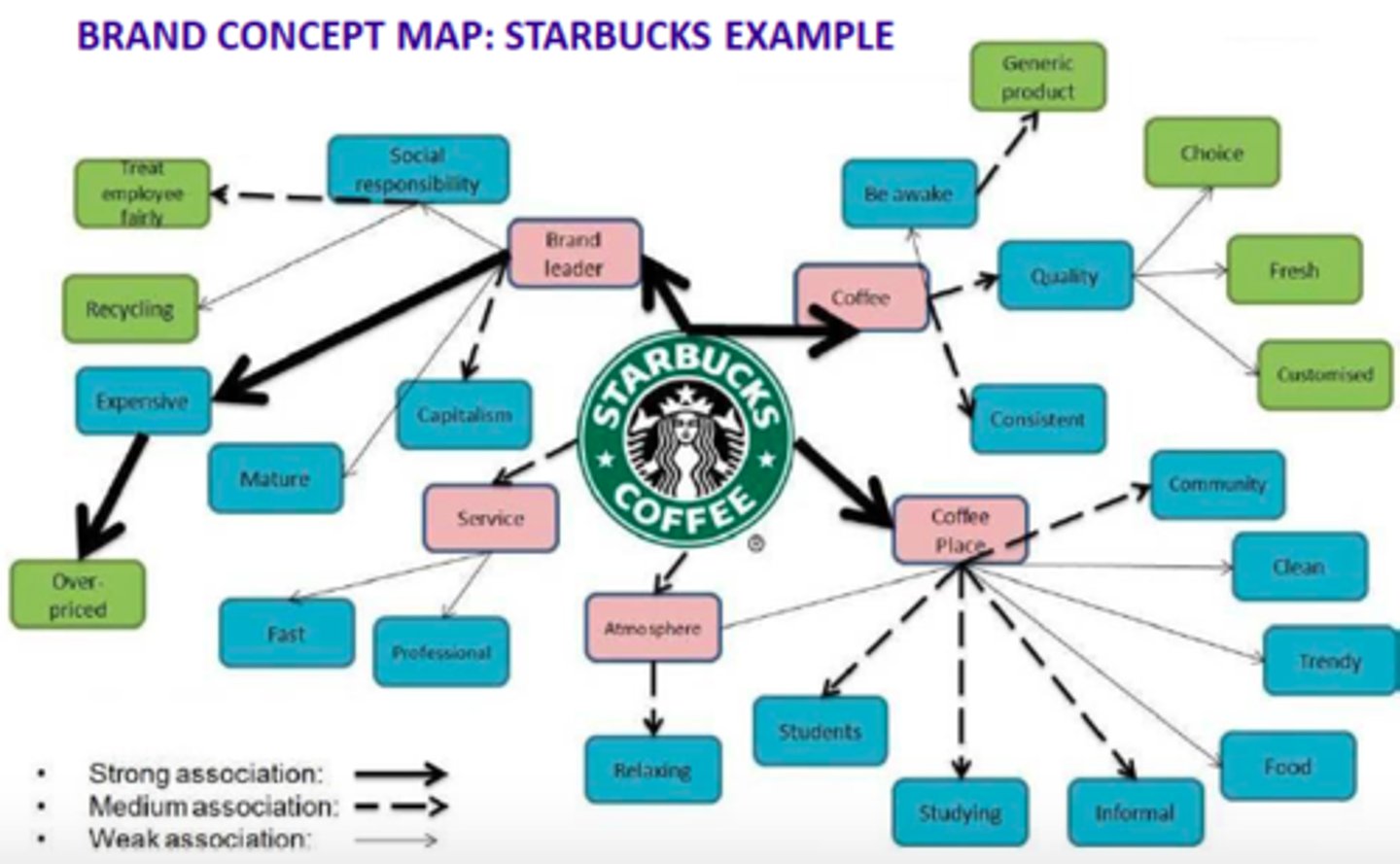
Brand's Mental Map
Accurately portrays in detail all salient brand associations and responses for a particular target market
When does CBBE occur?
When consumers have (1) a high level of awareness, (2) strong and unique brand associations, and (3) are loyal to the brand
Brand Awareness
Measures how many consumers in a market are familiar with the brand and what it stands for, made up of brand recognition and recall
Brand Recognition
consumers' ability to confirm prior exposure to the brand when given the brand as a cue
Brand Recall
Consumer's ability to retrieve the brand from memory when given the product category
Brand Awareness Pyramid
Complete Market Set > Awareness Set > Consideration Set > Choice Set
Brand Image
Consumers' perceptions about a brand, as reflected by brand associations held in consumer memory
Brand Attributes
Physical characteristics; descriptive features that characterize a product/service
Brand Advantages
What a brand's products/services do, performance characteristics
Brand Benefits
The personal value and meaning that consumers attach to the product/service attributes
Brand Loyalty
A favorable attitude toward and consistent purchase of a single brand over time, created using attitudinal and behavioral marketing focus
Attitudinal Metrics
Liking, Word of Mouth
Behavioral Metrics
Recency of purchase, frequency of purchase, monetary average order size
Size of Wallet
Buyer's total spending in a category
Share of Wallet
The percentage of the customer's purchases made from a particular retailer
How to establish brand positioning?
Know who the target customer is, who the main competitors are, and how the brand is similar to or different from those competitors
Market Segment
a group of consumers who respond similarly to a firm's marketing efforts
Target Market
A group of people or organizations for which an organization designs their products (see 2-17)
Funnel Stages
The idea that companies are trying to funnel people through the different stages of purchase, and you can identify the bottleneck
Points of Parity
Features not necessarily unique to the brand; may be shared with other brands (core benefit, generic product, expected product)
Points of Difference
attributes, advantages, and benefits that consumers strongly associate with a brand, positively evaluate (augmented product)
Benefit Laddering
The idea that some brands position with one point of difference while others have a holistic product benefit (like Tylenol)
Non Comparative Positioning Statement
[Offering] is the best [product category] for [target customers]because [primary reason (i.e., the most strongly relevant POD)]
Four Fundamental Brand Questions
Who are you? (brand identity)
What are you? (brand meaning)
What do I think or feel about you? (brand responses)
What kind of association and how much of aconnection would I like to have with you? (brand relationships)
Brand Resonance Pyramid
salience > [performance, imagery] > [judgements, feelings] > resonance
![<p>salience > [performance, imagery] > [judgements, feelings] > resonance</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1f8473d4-b0a3-4b54-82e1-55b75f5927e9.jpg)
Stages of Brand Development
Identity > Meaning > Response > Relationships
Brand Salience
Brand Recognition, Depth of Brand Recall (how likely it is for a brand to come to mind), Breadth of Brand Recall (in what situations a brand is likely to come to mind)
Product Category Structure
Product class > Product category > product type > brand
Brand Performance
Describes how well the product/service meets customer's more functional needs
What does Brand Performance rely on?
Reliability
Durability
Serviceability
Service Effectiveness
Service Efficiency
Service Empathy
Style and Design
Price
Brand Imagery
The way people think about a brand abstractly, rather than what they think the brand actually does
What does Brand Imagery rely on?
User Imagery
Purchase Imagery
Brand Personality and Values
Brand History, Heritage
Brand Judgements
Personal Opinions and Evaluations of the brand
What does Brand Judgements rely on?
Brand Quality
Brand Credibility
Brand Consideration
Brand Superiority
What makes a brand credible?
Brand Expertise: how competent and innovative
Trustworthy: dependable and keeping customers interests
Likeability: fun, interesting
Brand Feelings
Customers emotional responses and reactions to the brand
Six brand feelings
warmth
fun
excitement
security
social approval
self-respect
Brand Resonance
a consumer's intense and actively loyal relationship with a brand
What does brand resonance depend on?
Behavioral Loyalty
Attitudinal Attachment
Sense of Community
Active Engagement