Anxiety Disorders
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Fear
Immediate response to a real threat. Short-lived and adaptive, helps keep us safe.
Anxiety
Focuses on future threats. Long-lasting with cognitive symptoms like tension and worry. Can be adaptive
HPA Axis
Hypothalamus detects threat → signals pituitary gland → releases ACTH → adrenal glands release cortisol & adrenaline → triggers fight or flight response
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions like breathing and digestion. Includes:
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): Activates anxiety response.
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS): Calms the body.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Activates the body's alarm response during anxiety. Increases heart rate and prepares for fight or flight
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Calms the body after a threat. Slows down heart rate and restores normal function
Rumination (Cognitive component of anxiety)
Repetitive thinking about past events in a negative way.
Transient
Short-lived or temporary.: anxiety can be transient or long lived
Functional Impairment
When anxiety interferes with daily functioning, it may be considered a disorder.
Developmental Consideration
Age and developmental stage affect how anxiety manifests and is diagnosed.
Sociodemographic Factors
Anxiety is more common in women. Social factors influence prevalence and experience.
Phobia
An irrational fear of a specific object or situation that interferes with functioning.
Types of Phobias
Blood-Injury-Injection Phobia
Parasympathetic nervous system increases rapidly shutting everything down and they faint (vasovagal syncope)
Situational phobia
using public transport, driving through tunnels, etc
Natural environment phobia
Animal phobia
other phobia
Other phobias are statistically rare and need to be treated differently
Trypophobia
Biological revulsion (evolutionary fear response) to clustered holes or patterns. unofficial/proposed phobia
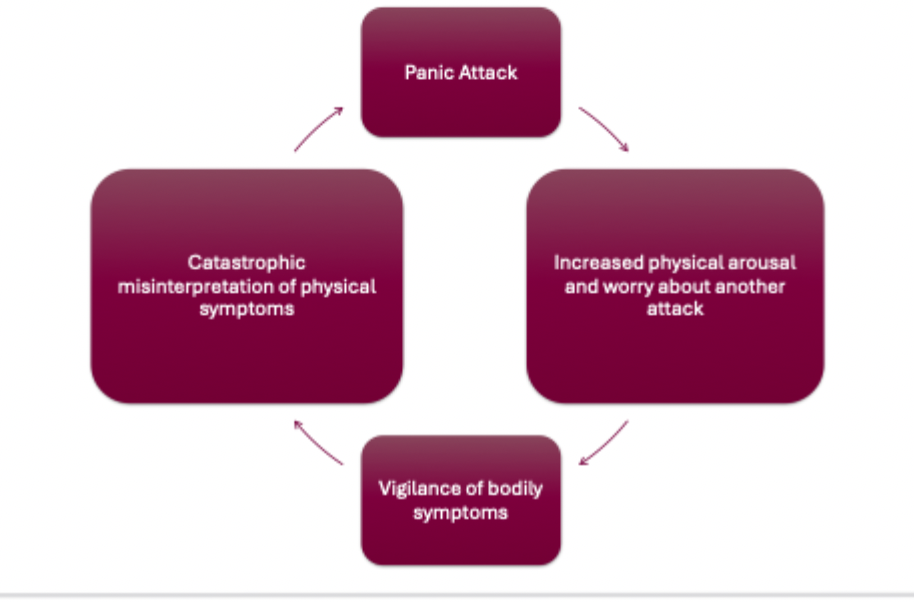
Panic Attack
Sudden intense fear with physical symptoms (e.g., heart palpitations, dizziness, choking). Peaks within minutes.
Agoraphobia
Fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult or help unavailable. May or may not involve panic attacks. Leads to avoidance and dysfunction.
Social Isolation
Can lead to depression. Often associated with anxiety disorders.
Splashing Water Technique
Splashing water on the face signals safety to the body, activating the parasympathetic system.
Elements of Anxiety
Anxiety consists of three components:
Physiological: Increased heart rate, shortness of breath, muscle tension.
Cognitive: Worry, rumination, future-focused thoughts.
Behavioral: Avoidance and safety behaviors.
DSM-5 Overview: Specific Phobia
Marked fear or anxiety about a specific object or situation. Fear is excessive and leads to avoidance or distress.
DSM-5 Overview: Panic Disorder
Recurrent unexpected panic attacks followed by persistent worry about future attacks or behavioral changes to avoid them.
DSM-5 Overview: Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Excessive anxiety and worry on most days for at least 6 months. Difficult to control and associated with symptoms like fatigue, irritability, and sleep disturbance.
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
Marked fear or anxiety about social situations where one may be judged. Often begins around age 11 and can be comorbid with depression or substance abuse.
Developmental Trajectory
Childhood fears may persist into adulthood, leading to increased dysfunction over time in SAD.
Introversion vs Social Anxiety
Introverts prefer solitude but are not fearful of social situations. SAD involves fear and avoidance due to anxiety.
Cognitive Patterns in SAD
Includes intrusive automatic negative thoughts and lack of positive feedback processing. Safety behaviors worsen anxiety.
Temperamental Factors
Behavioral inhibition in infancy (e.g., difficult temperament) may predispose individuals to SAD.
Freudian View of Anxiety
Anxiety arises from conflict between the id (instinctual desires) and ego (reality constraints).
Classical Conditioning and Phobia
Phobias can be learned through association, such as pairing a neutral stimulus (e.g., bunny) with a loud noise.
Modeling and Transmission
Fear can be internalized by observing anxious behavior in parents or through explicit instructions (information transmission).
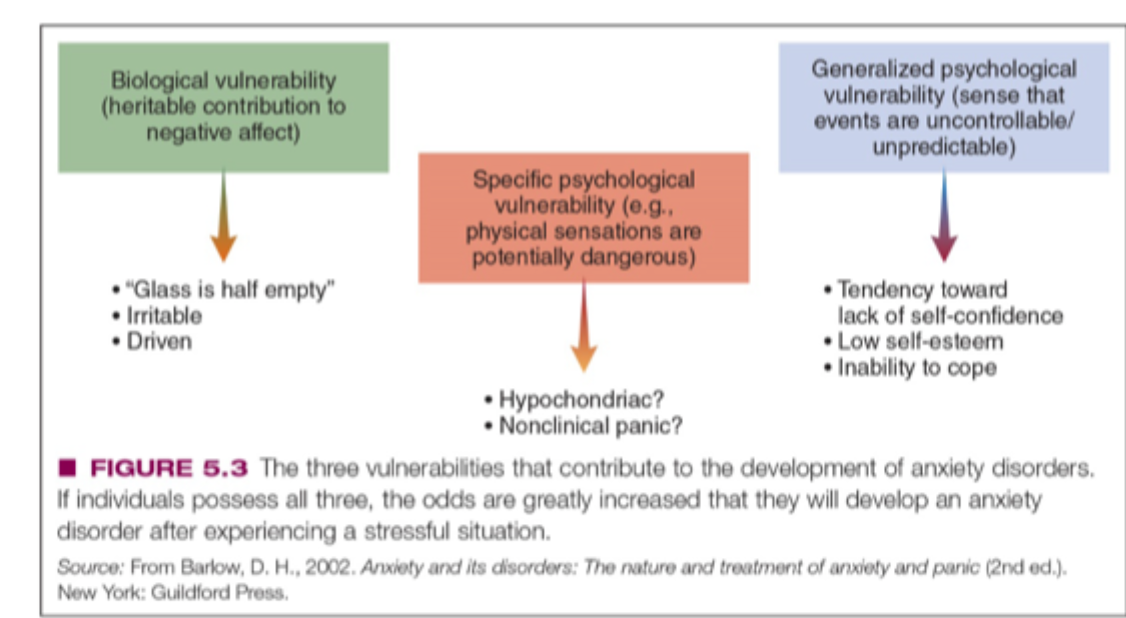
Diathesis-Stress Model
Anxiety disorders result from a combination of genetic vulnerability and environmental stressors.
Fear of Fear
Describes panic disorder where individuals fear the physical symptoms of anxiety, believing they signal danger.
Biological Vulnerability
Genetic predisposition to negative affect or pessimism increases risk for anxiety disorders
Generalized Psychological Vulnerability
Belief that the world is uncontrollable, often learned through adverse life events
Specific Psychological Vulnerability
Specific experiences (e.g., bullying) may lead to particular anxiety disorders like SAD
Serotonin and SSRIs
Serotonin depletion or receptor dysfunction is linked to anxiety. SSRIs can help but may have side effects and are not effective for all.
Medication Limitations
Long-term use may lead to side effects or symptom relapse. SSRIs may increase suicidal thoughts in depressed patients.
GABA
Increased GABA activity reduces anxiety.
TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation)
Non-invasive technique that modulates brain activity to treat anxiety.
Psychodynamic Therapy
Includes techniques like free association and dream interpretation to uncover unconscious conflicts.
CBT for SAD
Targets automatic negative thoughts and safety behaviors. Effective in reducing symptoms.
Interceptive Exercises
Expose individuals to feared physical sensations to reduce fear response and build tolerance.
Etiology of Anxiety Disorders
Direct conditioning theory
little albert
Observational learning
fear comes by watching someone
Information Transmission
explicitly told to fear
Triple Vulnerability Model
Treatments
Biological treatments
psychosocial perspective