Chemical Bonding Unit Test
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set might have more than necessary bc I was trying to make it fast, currently unreviewed/edited in terms of amnt of content (refer to the posted study guide for topics) *what he said in jan.* Metallic bonding = 5% test Covalent bonding= 75% test Ionic bonding= 20% test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Central atom
Atom in the center of the lewis structure, forms most bonds, is the least EN (NEVER H)
How to know a central atom in a lewis structure
USUALLY the first element listed in the chemical formula OR look for least EN
exceptions:
- diatomic compounds (2 atoms)
-Hydrogen is the starting element
Single dots (lone e-) on a Lewis structure show…
Bonding sites & if you count them up the ideal # of bonds
Can you reduce the formula of a covalent compound
NO, NEVER.
Formal charge equation
FC= VE-CB-NE
The # of valence electrons (from periodic table) - # of covalent bonds on the atom (on the LS) - # of non-bonded e- (on the LS)
-Do this for each atom in the compound and then add up their charges to see the compounds overall charge
-Most stable is zero UNLESS it’s a polyatomic in which case it would be the charge of the polyatomic that is most stable
Polyatomic ions
Polyatomic’s have both ionic and covalent character (covalently bonded cluster of atoms with an ionic charge)
How to show polyatomic ions lewis structure
Put the compound in parentheses and put the charge on it’s upper right corner
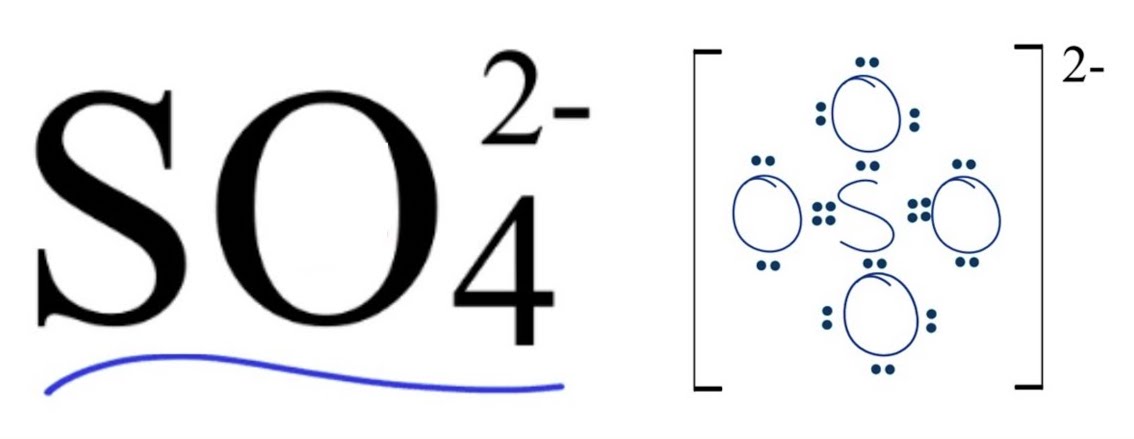
Things that have multiple bonds are more ___ than single bonds
Conductive
this is bc the transfer of e- is quicker & more efficient
Resonance structures
Resonance structures show the multiple ways bonding can occur in a compound
Why are resonance structures caused
They are caused when there is more than one way to place double bonds and lone pairs on atoms
Coordinate bond
When both bonding e- are donated by a single atom
ie. this happens when one atom is satisfied and another isn’t, the satisfied atom will share 2 of it’s e with the other atom, forming a bond, to satisfy it so the whole compound can be more stable
Multiple bonding
Double or Triple bonds
-these occur to satisfy atoms that do not fulfill the octet rule
Why are excess atoms theorized to happen
The D sub-level acts like a trunk where extra e- can be stored if need be, this is why we can fit 10 e- on some atoms instead of only eight, bc 2 would be in the “trunk”
The bonds are SPD hybrids when this happens
How many e- can Sulfur hold?
12*
*only when acting as a central atom!
How many e- can Phosphorus hold?
10*
*only when acting as a central atom!
How many e- can Hydrogen hold?
2
How many e- can Boron hold?
6*
*only when acting as a central atom!
How many e- can Beryllium hold?
4*
*only when acting as a central atom!
*Note, this is a metal but it’s EN is close to NM so it can covalently bond
What are the deficit atoms
Atoms that are stable with less than 8 e-
These are H, B, Be
What are the excess atoms
Atoms that can hold 8+ e- but can be stable @ 8
These are P, S, Noble gases & Halogens (NG and Halogens are VERY rare)
Why are covalent bonds NOT conductive
Bc they do not have charged particles capable of transporting e-
Melting and boiling point increases with…
Molar mass
more mass= more substance to melt
State of matter @ room temp for covalent bonds
Can be solid, liquid, or gas
Why do covalent bonds have low MP/BP
Bc they have weak forces of attraction btwn them. Since covalent bonds form btwn NM’s there is no opposite charges & therefore no coulombic attraction, this makes the force weaker. The e- are also shared, not transferred, making a weaker bond which is easier to break and therefore a lower MP/BP
Properties of covalent bonds
-low melting/boiling point
-soluble (dissociates in water)
-non-conductive
-share e- to achieve octet
How does e- sharing work
Covalent bonds share e- via. orbital overlap
-more overlap (ie. double & triple bonding) = stonger bond
Covalent bonds occur so that…
They can act like noble gases (and be stable)
What is the rep. particle name for covalently bonded atoms
Molecule
Covalent bonds are formed btwn…
Non-metals only*
They share electrons
*Some metalloids bond with nonmetals and tend to form covalent bonds
Lone pair/unshared pair
pair of e- that are NOT shared btwn atoms
Where does hybridization occur
ONLY on the central atom
e- in metallic bonds are located in…
in an e- sea (have to explain on the test what it means), the e- are free-flowing throughout (delocalized) the space btwn each atom
the size of the e- cloud is dependent on the number of VE contributed
How are the nuclei/cations ordered in a metallic bond
They are in a “crystal lattice” (this is super ordered)
Metallic substances properties
malleable and ductile
the delocalized e- are a constant presence and are why metallic substances are malleable… the delocalized e- hold together any shifting cations through the electrostatic attraction that exists btwn the e- and the cations
high melting points
more delocalized e- = tougher metal and higher melting point
conductive
bc the flow of e- in the electron cloud
ionic bonding have high melting and boiling points bc…
-charge diff. btwn bonded atoms
- stronger charge diff = stronger attraction (= higher mp)
structure of ionic compounds
crystalline solid @ room temp (this is a highly ordered pattern in 3d space)
“Criss Cross” rule
(chemical formula formation)
the charge becomes the subscript for the other element (if you don’t get it idk what to tell you)
ex. K2O is potassium oxide
Reverse “Criss Cross” rule*
(how to determine charge of d-block/non-rep. elements)
ex. What is the charge of lead in TcO2
The compound must have a net zero charge, we know how many of each element, and oxygen has a charge of 2- so we can write this into algebra
1x + 2(-2) = 0
1x-4=0
x=4
The charge of technetium would be 4+
How do you tell which ionic compound has a higher melting point
The charge diff. between the bonded atoms in each compound. The stronger the charge diff. the stronger the attraction.
ex. N2H4 or H2O
N2H4 has a charge diff. of 4 and H2O has a charge difference of 3 so N2H4 would have a higher melting point
How do you tell which ionic compound is more conductive from the chemical formula
the number of ions in the compound, the more ions the better
ex. N2H4 or H2O
N2H4 would have 6 ions and H2O would have 3 so N2H4 would be more conductive
Name into chemical formula
Just do the criss cross with the names given
ex. Magnesium fluoride —> MgF2
how: Mg2+ + F1- —> MgF2
Name break down
(metal’s name) (non-metal)oid
ex. Magnesium fluoride
Name break down with roman numerals
“metal’s name” (charge) “non-metal”oid
Roman numeral in parentheses follows the name of the metal to specify its charge
ex. FeCl2 is iron(II) chloride
ex. Cu2S is copper(I) sulfide
How to know molecular geometry
The number of domains on the central atom and amount of lone pairs on the central atom
How to tell if a molecule is polar
bonded e- are shared unequally
How to tell if a molecule is nonpolar
ANY diatomic molecule (bc the atoms have the same EN and so they pull the e- the same amnt)
Perfectly symmetric molecules
If two atoms are on opposite sides of a central atom and are pulling w/ the same EN then the pulls cancel out and the molecule is NP
!! Carbon and Hydrogen bonded is considered NP bc they have EN that are super close !!
How to tell if a molecule has polar bonds vs is polar
Most every molecule has polar bonds except for diatomics (this is bc diatomics have the same EN)
Molecules can have polar bonds but be nonpolar
ex. if two atoms are on opposite sides of a central atom, they would have polar bonds w/ the central atom, but since they and are pulling w/ the same EN then the pulls cancel out and the molecule is NP
How to show bond dipoles
Two options
a. with arrows
the arrow points toward the more EN atom and the dash in the line goes on the less EN side
b. with the delta symbol (δ+ and δ-)
The more EN atom would get the δ- (bc it would get more e-) and the less EN atom would get the δ+ (bc it loses the e-)
Why things dissolve
Like dissolves like bc…
nonpolar solutes don’t have dipoles so the dipoles in the polar solvent won’t pull apart the molecules but with polar solutes and polar solvents the positive and negative dipoles are attracted to each other and pull molecules apart
London Dispersion Forces (LDF)
weakest of all IMF
!! ALL SUBSTANCES/MOLECULES EXPERIENCE LDF !!
the more e- a molecule has, the stronger the LDF’s are
Dipole-Dipole Forces
occur when the partially + charged part of a molecule interacts w/ the partially - charged part of another molecule
strong relative strength
Hydrogen Bonding
special kind of dipole-dipole bonding
Occurs btwn a Hydrogen atom and a Oxygen, Nitrogen, or Fluorine atom
The partially positive end of the H in one atom is attracted to the partially negative end of the O,N, or F of another atom
STRONGEST of dipole-dipole attractions
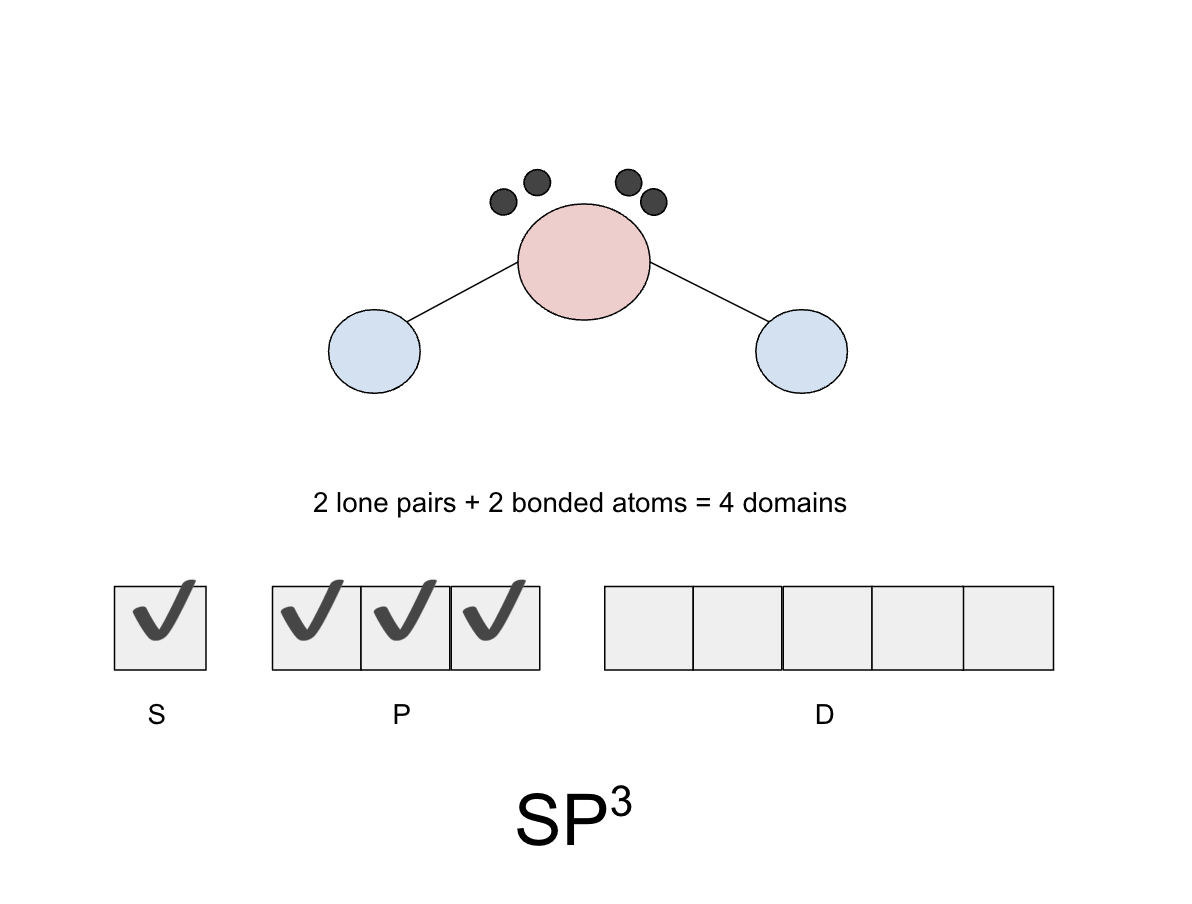
How to tell a central atom’s hybridization
You count the amount of domains a central atom has and then you fill in the boxes to see how many levels it has (makes more sense with the example)
Bond order & length
The length of the bond is determined by the number of bonded electrons (the bond order). The higher the bond order (more e- in a bond ie. double or triple), the stronger the pull between the two atoms and the shorter the bond length.
Relationship between bond length and strength of bond
If the bond length decreases, the bond energy would increase. If the two atoms bonded are closer together, then by coulomb's law, there should be a stronger force due to a smaller distance. Therefore, a shorter bond length would make it harder to break the bond, resulting in a higher bond energy.
The diatomics
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Fluorine, Oxygen, Iodine, Chlorine, and Bromine