Learning aim A - The effects of exercise and sports performance on the skeletal system
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/141
Last updated 12:16 PM on 3/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 2 types of skeletons called?
axial and appendicular
2
New cards
name the 6 main bones from head/waist (not arms)
cranium, vertebrae, clavicle, scapula, sternum, ribs
3
New cards
what are the 3 bones in your arm called?
humerus, ulna, radius
4
New cards
what are the 3 bones in your hand called?
carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
5
New cards
name the 2 bones found at your hip
sacrum and pelvis
6
New cards
name the 4 bones found in your leg
femur, patella, tibia, fibula
7
New cards
what are the 3 bones found in your feet?
tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
8
New cards
what bones are part of the axial skeleton?
cranium, vertebrae, ribs, sacrum
9
New cards
what are the 5 different bone types?
long, short, sesamoid, flat, irregular
10
New cards
what are long bones?
Bones that are longer than they are wide (femur, ulna, phalanges)
11
New cards
what are short bones?
Short bones - Bones that are as short as they are wide (carpals and tarsals)
12
New cards
what are flat bones?
broad, flat and usually thin bones (pelvis, sternum, ribs)
13
New cards
what are sesamoid bones?
bones that are held within tendons and covered in cartilage (patella)
14
New cards
what are irregular bones?
bones that are irregular in shape (vertebrae)
15
New cards
what’s the neutral spine alignment?
* Should naturally form an S shape (3 slight curves) when viewed from the side
* should be straight when viewed from the back
* should be straight when viewed from the back
16
New cards
what’s a convex curve?
* kyphotic curve (outward)
* thoracic and sacral areas have gentle convex curves
* thoracic and sacral areas have gentle convex curves
17
New cards
what’s a concave curve?
* lordotic curve (inward)
* cervical and lumbar areas
* cervical and lumbar areas
18
New cards
what is a posterior view?
Back
19
New cards
what are the functions of the curves in your spine?
* acts as a coil spring
* absorbs shock
* allows a range of movement
* keeps you balanced and upright
* absorbs shock
* allows a range of movement
* keeps you balanced and upright
20
New cards
name the 5 parts of the vertebrae column
cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
21
New cards
what is the cervical vertebrae?
* from base of skull to the top of shoulders (7 vertebrae)
* protect the spinal chord
* work with muscles, tendons, ligaments and joints
* provides support, structure and flexibility to the neck.
* protect the spinal chord
* work with muscles, tendons, ligaments and joints
* provides support, structure and flexibility to the neck.
22
New cards
what is the thoracic vertebrae?
* from shoulders to ribs (12 vertebrae)
* provides rib attachment to protect heart and lungs
* allows movement for the body
* provides rib attachment to protect heart and lungs
* allows movement for the body
23
New cards
what is the lumbar vertebrae?
* from ribs to pelvis (5 vertebrae)
* supports the body’s weight
* allows movement
* protects spinal chord and nerves
* supports the body’s weight
* allows movement
* protects spinal chord and nerves
24
New cards
what is the sacrum?
* single bone in pelvis (5 separate vertebrae)
* creates an anchor point where spinal chord can attach to the pelvis
* provides stability to bodies core
* creates an anchor point where spinal chord can attach to the pelvis
* provides stability to bodies core
25
New cards
what is the coccyx?
* in pelvis (3-5 vertebrae)
* several pelvic muscles attach to this
* several pelvic muscles attach to this
26
New cards
what is scoliosis?
* genetic condition
* abnormal curve of spine to L or R
* abnormal curve of spine to L or R
27
New cards
what is kyphosis?
* excessive outward curve of the upper spine
* hunchback
* caused by poor posture
* hunchback
* caused by poor posture
28
New cards
what is the process by which bones form?
ossification
29
New cards
what do Osteoblasts do?
synthesise and build the bone whilst bringing calcium to them, which increases bone matrix.
30
New cards
what do osteoclasts do?
absorb bone tissues and clears extra calcium away from the bones.
31
New cards
what are epiphyseal plates?
areas located at ends of long bones, where new bone growth takes place.
32
New cards
name the 8 functions of the skeleton
* support
* protection
* attachment of muscles
* produces blood cells
* storage of minerals
* leverage
* weight bearing
* reduces friction across joints
* protection
* attachment of muscles
* produces blood cells
* storage of minerals
* leverage
* weight bearing
* reduces friction across joints
33
New cards
how does the skeleton provide support?
* gives the body its shape
* supporting framework for soft tissues
* supporting framework for soft tissues
34
New cards
how does the skeleton provide protection?
* surrounds vital tissues and organs
35
New cards
how does the skeleton provide attachment of skeletal muscles?
* surface for muscles to attach to - allows movement
* movements occur at joints
* movements occur at joints
36
New cards
ligament
fibres that link bone to bone
37
New cards
tendon
fibres that link muscle to bone
38
New cards
how does the skeleton produce blood cells?
* blood cells are produced in bone marrow
* continuously produces red and white blood cells
* continuously produces red and white blood cells
39
New cards
how does the skeleton store minerals?
* bones are made of minerals
* store calcium and phosphorus
* essential for bone growth and maintaining bone health
* released into blood stream when needed
* store calcium and phosphorus
* essential for bone growth and maintaining bone health
* released into blood stream when needed
40
New cards
how does the skeleton provide leverage?
* muscles attach to bone (tendon)
* provide power when moving
* provides a lever system - muscles can pull to create movement
* provide power when moving
* provides a lever system - muscles can pull to create movement
41
New cards
how does the skeleton weight bear?
* body weight is supported by skeleton
* bones are very strong and will support weight
* large forces applied during exercise, skeleton provides strength to prevent injury
* bones are very strong and will support weight
* large forces applied during exercise, skeleton provides strength to prevent injury
42
New cards
how does the skeleton reduce friction across joints?
* synovial joints secrete synovial fluid that prevents bones from rubbing against one another
* reduces friction, pain and discomfort
* reduces friction, pain and discomfort
43
New cards
what are the functions of long bones?
* Produce red blood cells, essential for o2 delivery.
* Produce white blood cells, fight off infections.
* Enable large movements, allowing increased speed or range of movement
* Acts as levers to generate more force on a system
* Produce white blood cells, fight off infections.
* Enable large movements, allowing increased speed or range of movement
* Acts as levers to generate more force on a system
44
New cards
what are the functions of short bones?
* Increase stability and reduce unwanted movement
* Weight bearing - help the body to hold balance and remain upright
* Absorb shock, such as when running
* Weight bearing - help the body to hold balance and remain upright
* Absorb shock, such as when running
45
New cards
what are the functions of sesamoid bones?
* Ease joint movement, reduces friction
* Resist friction so movement isn’t slowed
* Resist friction so movement isn’t slowed
46
New cards
what are the functions of flat bones?
* Protect vital organs to reduce injury
* Enable muscle attachments to create movement
* Produce blood cells (adults only)
* Enable muscle attachments to create movement
* Produce blood cells (adults only)
47
New cards

describe the function of bone types when kicking a football.
* Long bone (femur) allows a large movement to increase force as the ball is kicked
* Sesamoid bone (patella) allows ease of movement at the knee
* Short bones (tarsals) support the body weight so the player remains upright
* Flat bone (pelvis) provides larger areas for muscle attachment
* Sesamoid bone (patella) allows ease of movement at the knee
* Short bones (tarsals) support the body weight so the player remains upright
* Flat bone (pelvis) provides larger areas for muscle attachment
48
New cards
name the 3 different joint types
* fibrous
* cartilaginous
* synovial
* cartilaginous
* synovial
49
New cards
what are fibrous joints?
* Joints that are fixed and allow no movements
* Sacrum, coccyx, cranium
* Sacrum, coccyx, cranium
50
New cards
what are cartilaginous joints?
* Slightly moveable joints
* Between the thoracic, lumbar and cervical vertebrae
* Between the thoracic, lumbar and cervical vertebrae
51
New cards
what are synovial joints?
* Freely moveable
* Important in sport
* Shape of bone determines range of movement
* Important in sport
* Shape of bone determines range of movement
52
New cards
what are the 6 different synovial joints?
hinge
condyloid
ball and socket
gliding
pivot
saddle
condyloid
ball and socket
gliding
pivot
saddle
53
New cards
what is a hinge joint?
* Only allow forwards and backwards movement
* Examples : elbow and knee joint
* Sporting example : bicep curl
* Examples : elbow and knee joint
* Sporting example : bicep curl
54
New cards
what is a condyloid joint?
* Allow forwards, backwards, side to side
* Examples : wrist joint
* Sporting example : dribbling a basketball
* Examples : wrist joint
* Sporting example : dribbling a basketball
55
New cards
what is a ball and socket joint?
* Allows movement in all directions
* Example : hip and shoulder joint
* Sporting example : running and throwing a javelin
* Example : hip and shoulder joint
* Sporting example : running and throwing a javelin
56
New cards
what is a gliding joint?
* Allows movement over a flat surface in all directions but is restricted by ligaments
* Examples : carpals and tarsals
* Sporting example : netball jump when foot is pointing downwards
* Examples : carpals and tarsals
* Sporting example : netball jump when foot is pointing downwards
57
New cards
what is a pivot joint?
* Allows side to side, circle motions
* Example : kneck
* Sporting example : swimming
* Example : kneck
* Sporting example : swimming
58
New cards
what is a saddle joint?
* Has concave (inward) and convex (outward) surfaces
* Allows back and forward movement
* Example : base of thumb
* Sporting example : gripping a tennis racket
* Allows back and forward movement
* Example : base of thumb
* Sporting example : gripping a tennis racket
59
New cards
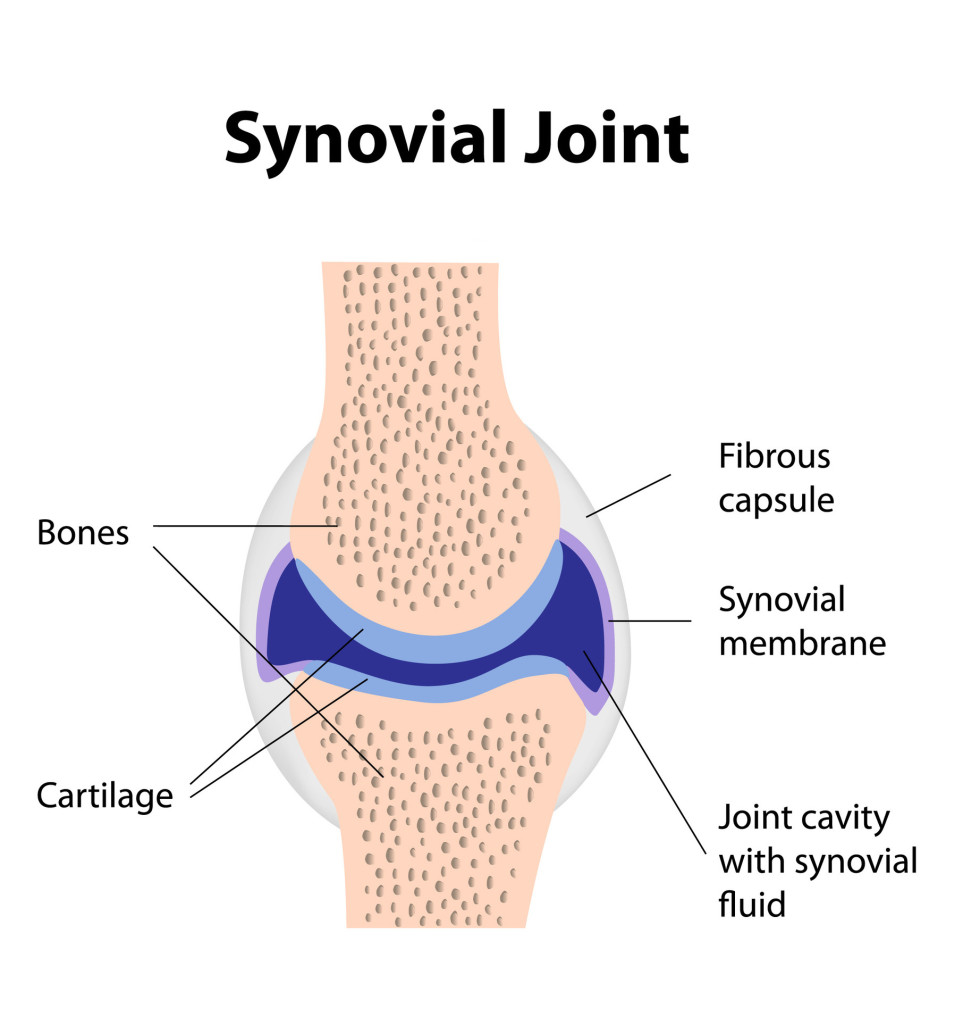
what’s the function of the fibrous capsule?
An outer sleeve to help hold the bones in place and protect the joint
60
New cards
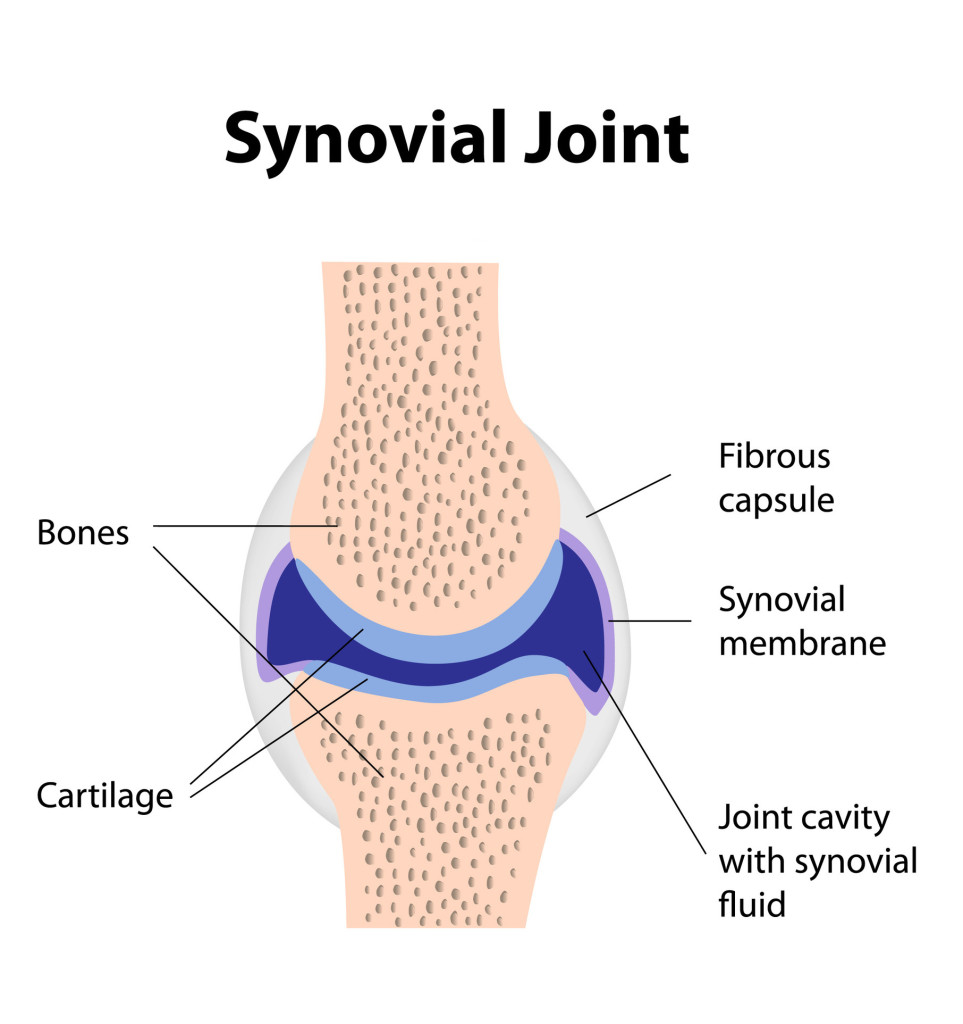
what’s the function of the synovial membrane?
Capsule lining that secretes synovial fluid to prevent bones rubbing
61
New cards
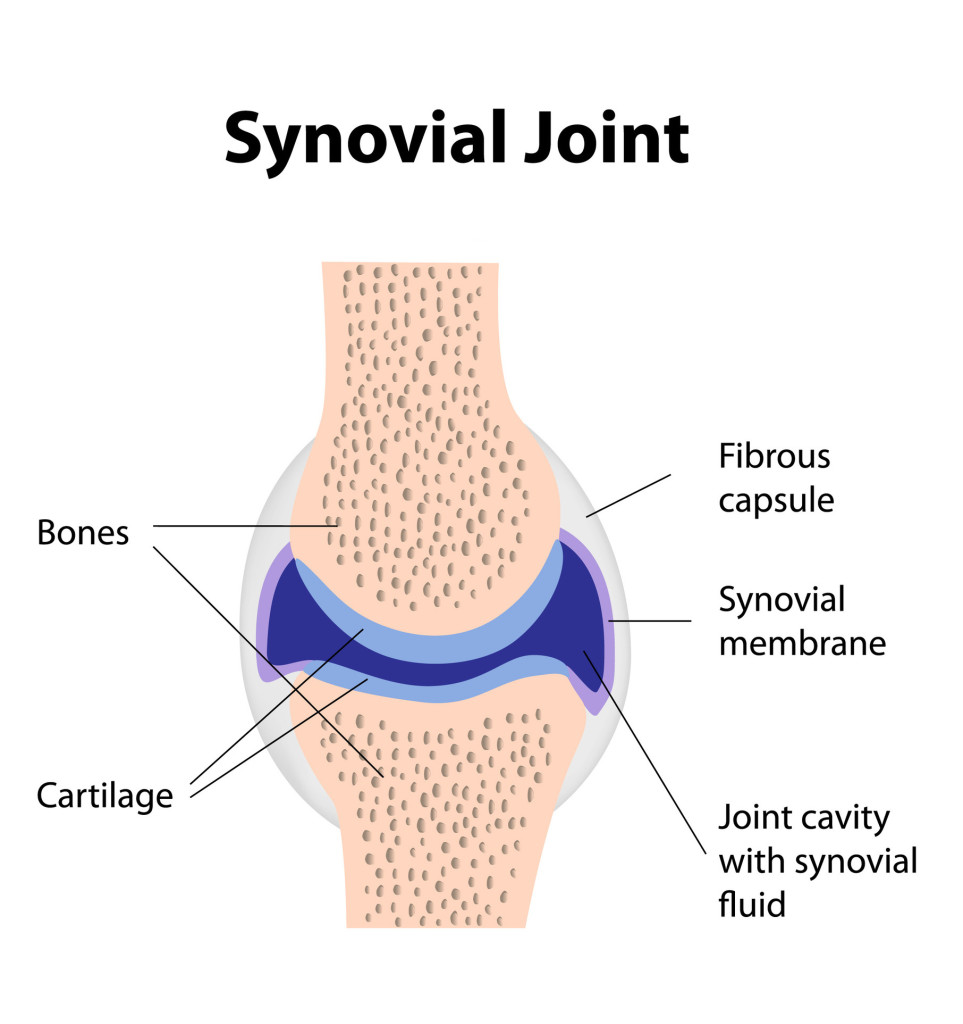
what is synovial fluid?
* Thick liquid
* Lubricates
* Reduces friction
* Lubricates
* Reduces friction
62
New cards
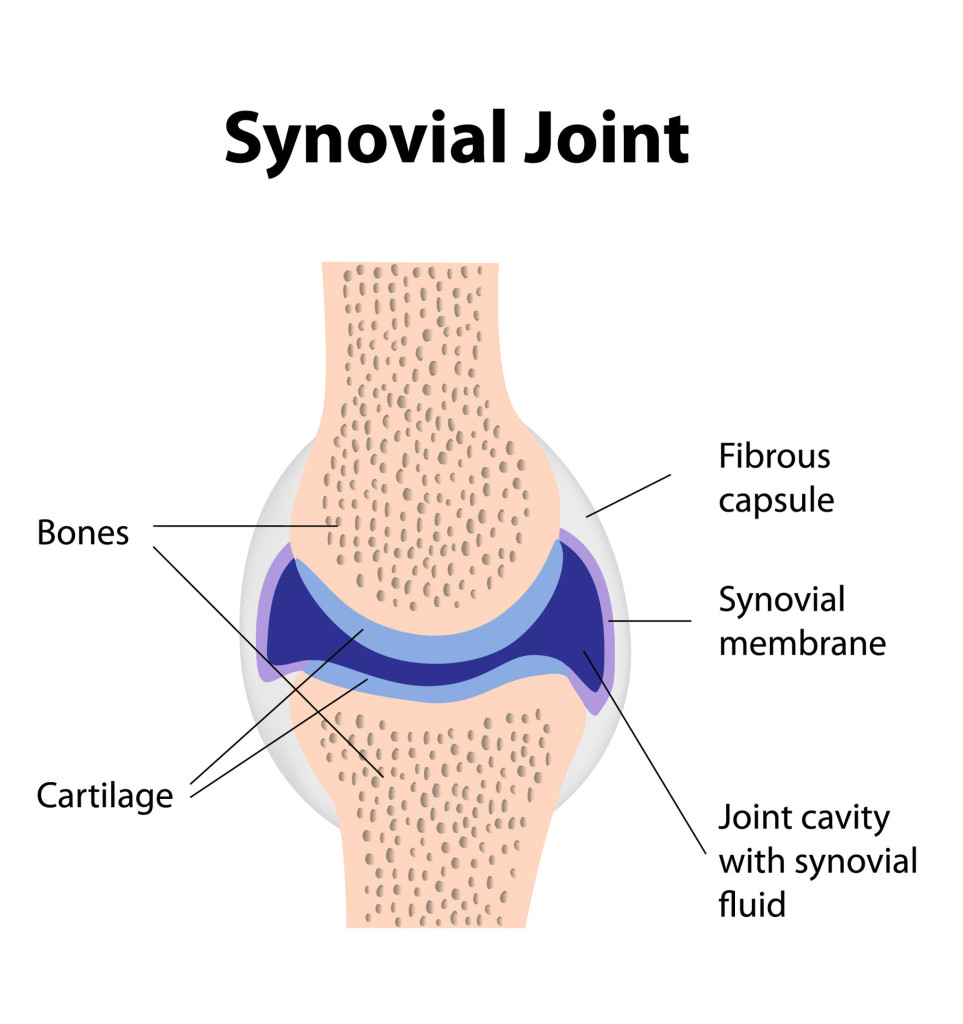
what’s the function of the joint cavity / bursa?
Aka bursa, small fluid filled sac lined by synovial membrane and provides a cushion between tendons and bones
63
New cards
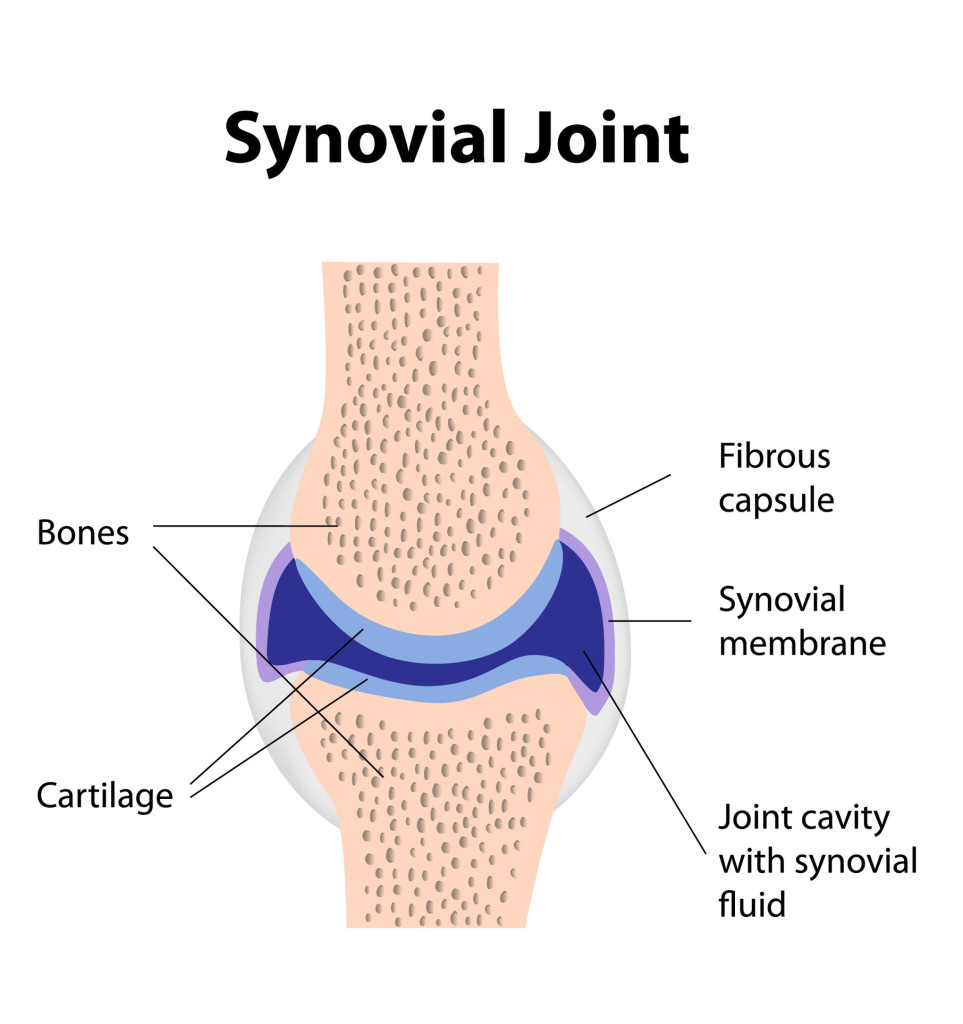
what’s the function of the articular cartilage?
Articular cartilage, located on ends of bones, smooth covering to stop bones from moving and keeps them in place
64
New cards
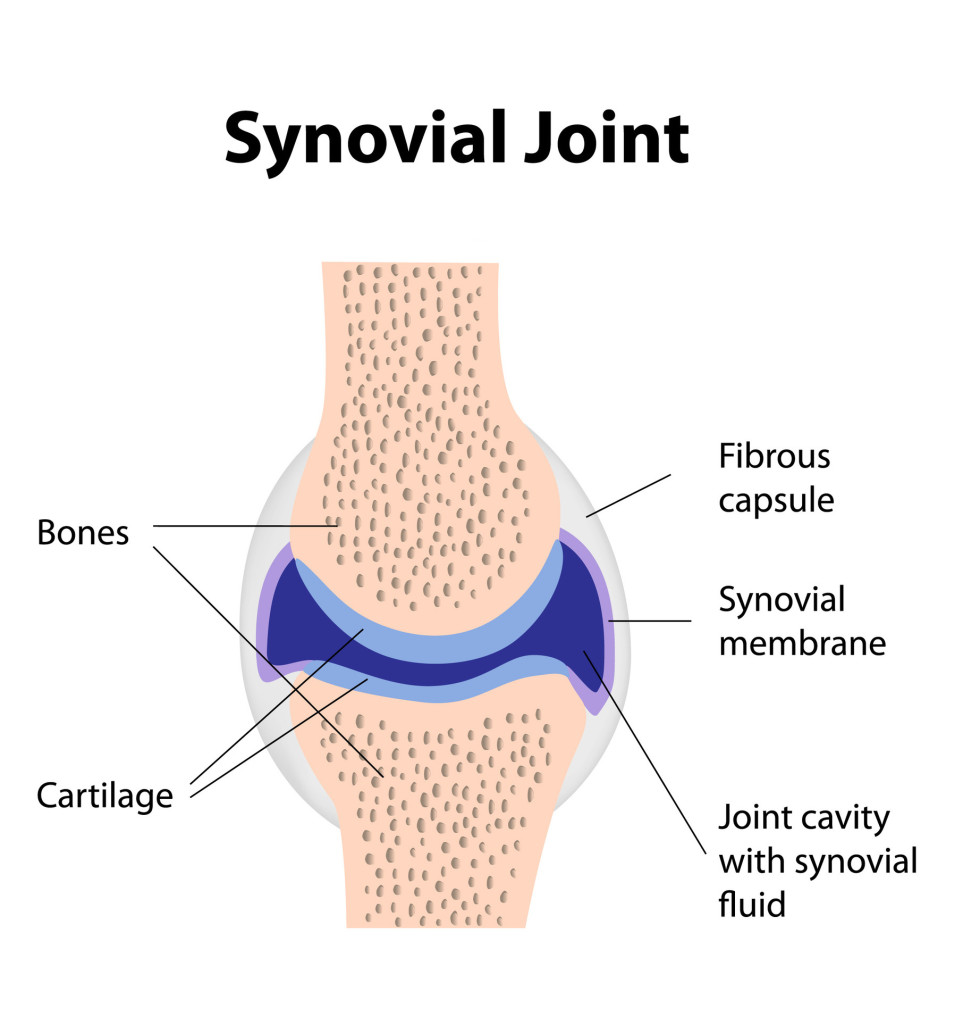
what’s the purpose of ligaments in relation to articulating bones?
offers stability
65
New cards
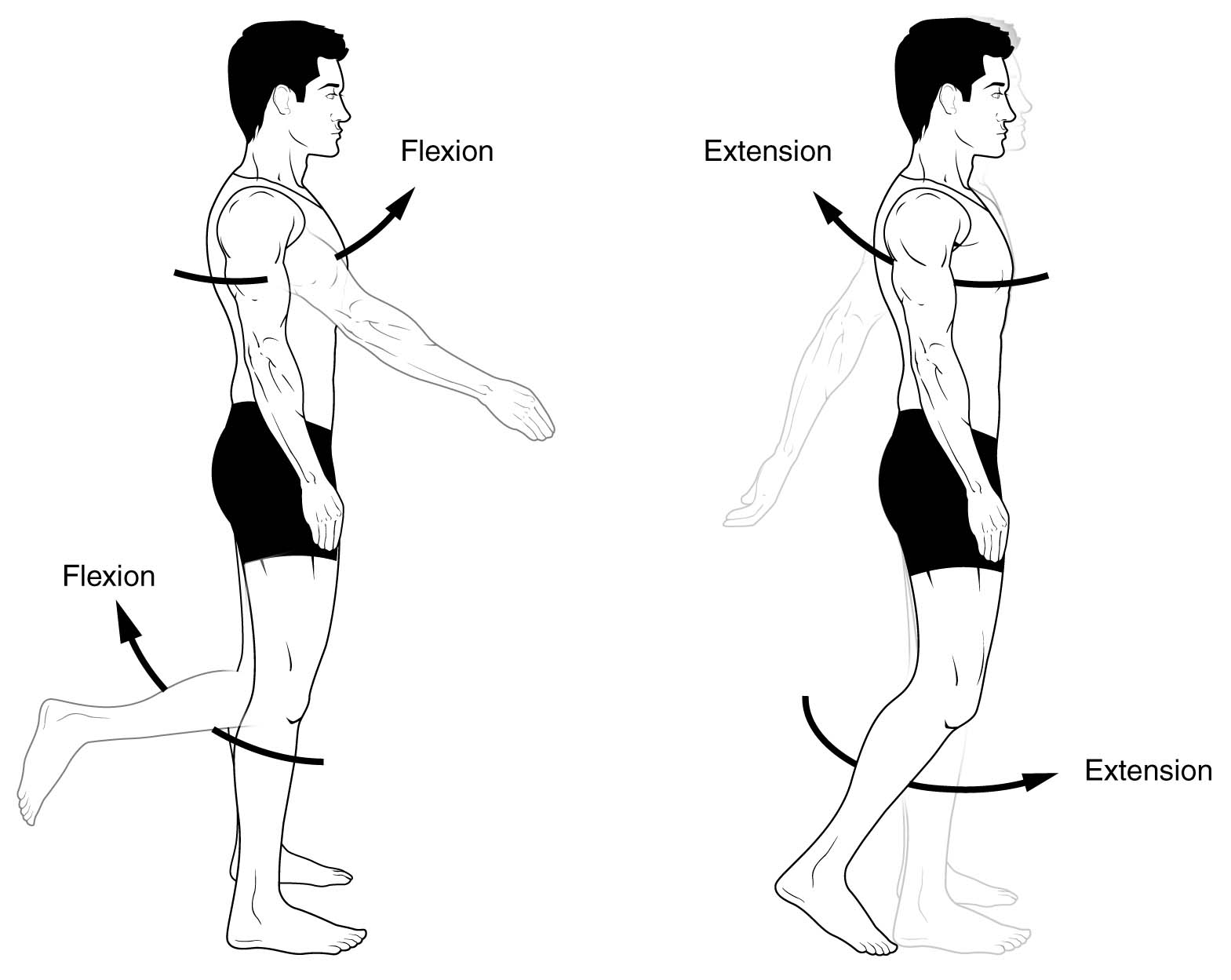
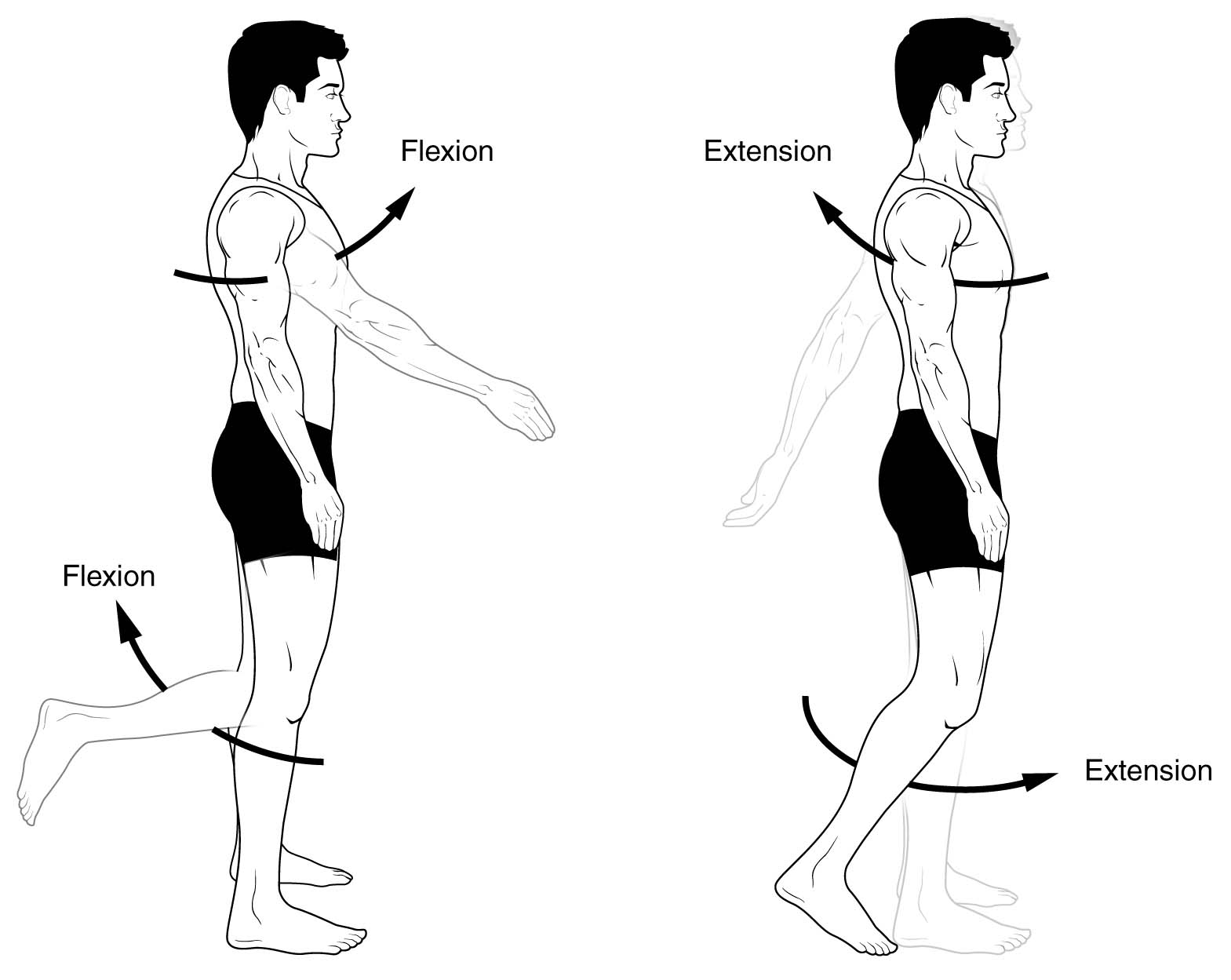
what is flexion? give some examples.
* Flexion is reducing the angle between the bone of a limb at a joint.
* The muscles contract, moving joint into a bent position.
* Examples include bending arm into a bicep curl and bending knee to kick a ball.
* The muscles contract, moving joint into a bent position.
* Examples include bending arm into a bicep curl and bending knee to kick a ball.
66
New cards
what is extension? give some examples.
* The act of straightening limb to increase the angle at a joint
* Examples include straightening arm in a bicep curl and straightening knee after kicking a ball.
* Examples include straightening arm in a bicep curl and straightening knee after kicking a ball.
67
New cards
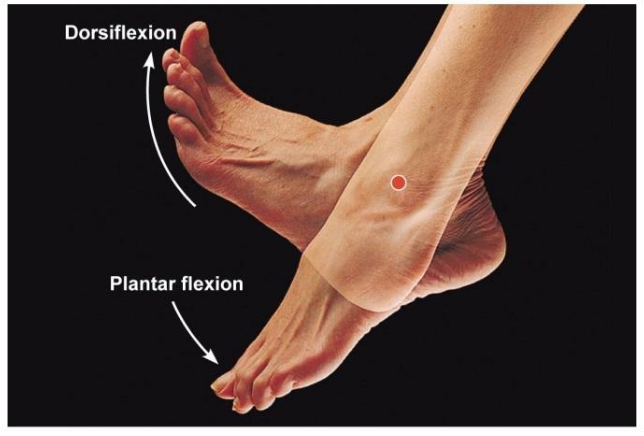
what is dorsiflexion? give some examples.
* An upward movement that occurs only at the ankle.
* Reduces angle at the ankle, pulls toes up towards lower leg
* Examples are helping to control a ball, pulling toes upward in a stretch and walking.
* Reduces angle at the ankle, pulls toes up towards lower leg
* Examples are helping to control a ball, pulling toes upward in a stretch and walking.
68
New cards
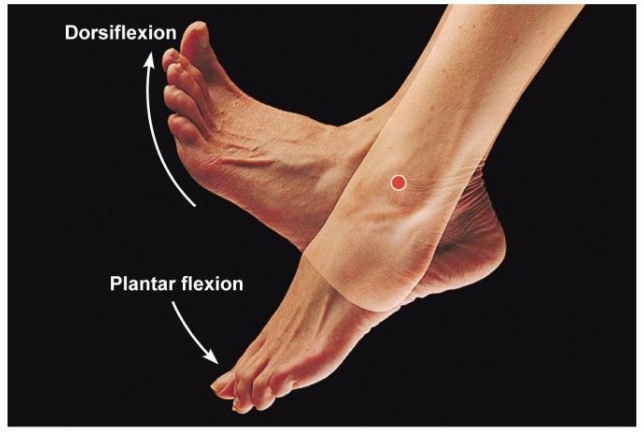
what is plantar flexion? give some examples.
* Increasing the angle at the ankle
* A movement that points the toes downward by straightening the ankle.
* Examples include jumping to shoot in netball, pointing the toes in a trampoline or dance routine and pointing toes to produce a good dive in swimming.
* A movement that points the toes downward by straightening the ankle.
* Examples include jumping to shoot in netball, pointing the toes in a trampoline or dance routine and pointing toes to produce a good dive in swimming.
69
New cards
what is lateral flexion? give some examples
* Movement away from the body’s midline to allow the spine to move side to side.
* Increasing the angle between a joint and body part (side movement)
* Examples include moving neck sideways toward shoulder in warm up, side and hip stretch, and moving upper body sideways when performing a cartwheel.
* Increasing the angle between a joint and body part (side movement)
* Examples include moving neck sideways toward shoulder in warm up, side and hip stretch, and moving upper body sideways when performing a cartwheel.

70
New cards
what is horizontal flexion? give some examples
* Movement towards the midline of the body but the elbows face out to the sides (palms facing down).
* Examples include stretching the arms out, a discus thrower bringing the arm through to release the discus
* Examples include stretching the arms out, a discus thrower bringing the arm through to release the discus
71
New cards
what is horizontal extension? give some examples.
* Movements away from the midline of the body horizontally with elbows facing outwards (palms facing down).
* Examples include stretching the arms out, a discus thrower bringing the arm out to aid power to the release of the discus
* Examples include stretching the arms out, a discus thrower bringing the arm out to aid power to the release of the discus
72
New cards
what is hyperextension? give some examples.
* Outward movement beyond the normal anatomical position.
* Neck moves further away from chest, spine moves further away from pelvis.
* Examples could be when performing a dance or trampoline routine.
* Neck moves further away from chest, spine moves further away from pelvis.
* Examples could be when performing a dance or trampoline routine.

73
New cards
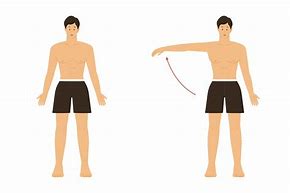
what is abduction? give some examples.
* Movement away from the body’s vertical midline.
* Examples could be performing a crucifix in a gymnastics routine or c completing a star jump.
* Examples could be performing a crucifix in a gymnastics routine or c completing a star jump.
74
New cards
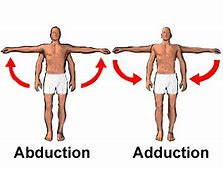
what is adduction? give some examples.
* Movement towards the body’s vertical midline
* Examples could be returning to a standing position after a martial arts kick to the side of the body or pulling oars in rowing.
* Examples could be returning to a standing position after a martial arts kick to the side of the body or pulling oars in rowing.
75
New cards
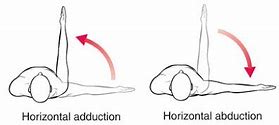
what is horizontal abduction? give some examples.
* Movement away from the midline of the body horizontally rather than vertically.
* Examples include cartwheels, preparing to throw a discus.
* Examples include cartwheels, preparing to throw a discus.
76
New cards
what is horizontal adduction? give some examples.
* Movement towards the midline horizontally rather than vertically.
* Examples include bringing arms in front of chest.
* Examples include bringing arms in front of chest.
77
New cards
what is circumduction? give some examples.
* Circular conocial movement (controlled)
* Example, shoulder joint during an overarm throw in cricket
* Example, shoulder joint during an overarm throw in cricket
78
New cards
what is rotation? give some examples.
* Circular movement of a limb where the limb turns round its long axis
* Example, rotation of neck when a swimmer comes up for a breath.
* Example, rotation of neck when a swimmer comes up for a breath.
79
New cards
what are the 5 short term (acute) responses of the skeletal system to exercise?
* Produces more synovial fluid : joints are lubricated and protects bones during increased demands that are put on the skeletal system.
* Synovial fluid becomes less viscous (becomes thinner) : increases range of movement at a joint
* Synovial fluid produces increased nutrients to the articular cartilage.
* Bones increase mineral uptake
* Body absorbs calcium : increases bone density. Important as when more force is applied to bones they need to be strong enough to cope with the demands.
* Synovial fluid becomes less viscous (becomes thinner) : increases range of movement at a joint
* Synovial fluid produces increased nutrients to the articular cartilage.
* Bones increase mineral uptake
* Body absorbs calcium : increases bone density. Important as when more force is applied to bones they need to be strong enough to cope with the demands.
80
New cards
what are the 4 long term (chronic) responses of the skeletal system to exercise?
* Improved fitness and reduced health risks
* Increase in bone density, overtime will be more resistant to forces
* Ligaments will get stronger
* Ligaments stretch, more flexibility
* Increase in bone density, overtime will be more resistant to forces
* Ligaments will get stronger
* Ligaments stretch, more flexibility
81
New cards
what is arthritis?
Arthritis
* Inflammation of the synovial joint causing pain and stiffness.
* Osteoarthritis - reduces cartilage tissue, bones rub together
* Exercise can help prevent arthritis, joints produce more synovial fluid - improves lubrication and reduces friction
* Stretching improves range of motion at a joint as it lengthens ligaments
* Inflammation of the synovial joint causing pain and stiffness.
* Osteoarthritis - reduces cartilage tissue, bones rub together
* Exercise can help prevent arthritis, joints produce more synovial fluid - improves lubrication and reduces friction
* Stretching improves range of motion at a joint as it lengthens ligaments
82
New cards
what is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis
* Weakening of bones caused by lack of vitamin D
* As you age, bones become less dense and become brittle and fragile, more likely to break
* Exercise provides increased bone density, can help prevent
* Resistance training can also help prevent it - overloading skeletal system increases bone density
* Weakening of bones caused by lack of vitamin D
* As you age, bones become less dense and become brittle and fragile, more likely to break
* Exercise provides increased bone density, can help prevent
* Resistance training can also help prevent it - overloading skeletal system increases bone density
83
New cards
how does age affect the skeletal system?
Age
* Skeletal system is a living tissue, constantly growing and repairing
* Exercising benefits you, however could cause harm in some children
* Child’s bones are still growing, too much force can damage epiphyseal plates that are found in the ends of long bones
* Damage can result in stunted growth
* Skeletal system is a living tissue, constantly growing and repairing
* Exercising benefits you, however could cause harm in some children
* Child’s bones are still growing, too much force can damage epiphyseal plates that are found in the ends of long bones
* Damage can result in stunted growth
84
New cards
what is skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle
* Attached to bones
* Striped
* Voluntary muscle - under conscious and in your control
* Important for sport - attach to tendons and are responsible for movement
* Can contract - pull bones to create movement (lever system)
* Subject to fatigue during exercise
* Attached to bones
* Striped
* Voluntary muscle - under conscious and in your control
* Important for sport - attach to tendons and are responsible for movement
* Can contract - pull bones to create movement (lever system)
* Subject to fatigue during exercise
85
New cards
what is cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle
* Muscle tissue that is found in the walls of your heart
* Works continuously and is involuntary - controlled by the autonomic nervous system
* Has its own blood supply (coronary arteries)
* Contracts to help pump blood around the body
* Can get stronger
* Doesn’t fatigue during exercise
* Muscle tissue that is found in the walls of your heart
* Works continuously and is involuntary - controlled by the autonomic nervous system
* Has its own blood supply (coronary arteries)
* Contracts to help pump blood around the body
* Can get stronger
* Doesn’t fatigue during exercise
86
New cards
what is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle
* Involuntary, controlled by autonomic nervous system
* Located in walls of digestive system and blood vessels
* Helps to regulate digestion and blood pressure
* Slow-contracting
* Can dilate and constrict vessels
* Involuntary, controlled by autonomic nervous system
* Located in walls of digestive system and blood vessels
* Helps to regulate digestion and blood pressure
* Slow-contracting
* Can dilate and constrict vessels
87
New cards
name all the muscles.
.
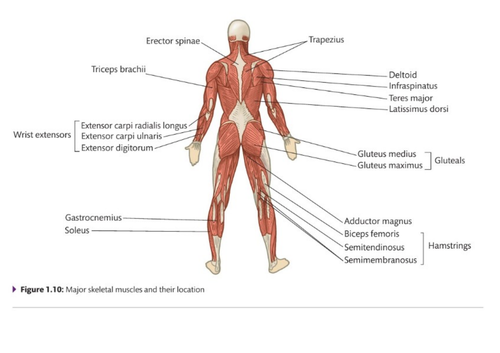
88
New cards
what’s the agonist?
contracting muscle
89
New cards
what’s the antagonist?
relaxing muscle
90
New cards
what’s a synergist?
muscle assisting the agonist
91
New cards
whats a fixator?
eliminates unwanted movement
92
New cards
what are antagonistic muscle pairs and give some examples
Antagonistic muscle pairs are muscles that work together in pairs to create movement, examples of antagonistic muscle pairs are-
\n
* Deltoid and latissimus dorsi at the shoulder
* Biceps and triceps at the elbow
* Glutes and hip flexors at the hip
* Quadriceps and hamstrings at the knee
* Gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior at the ankle.
* Internal and external intercostal muscles when ventilating
\n
* Deltoid and latissimus dorsi at the shoulder
* Biceps and triceps at the elbow
* Glutes and hip flexors at the hip
* Quadriceps and hamstrings at the knee
* Gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior at the ankle.
* Internal and external intercostal muscles when ventilating
93
New cards
what happens during the pulling phase of a row?
* Agonist = posterior deltoid
* Antagonist = anterior deltoid
* Fixators = abdominals and obliques
* Synergists = pectorals
* Antagonist = anterior deltoid
* Fixators = abdominals and obliques
* Synergists = pectorals
94
New cards
what happens during the upward phase of a bicep curl?
During the upward phase of a bicep curl, the antagonistic muscle pairs are as follows
* Agonist = biceps
* Antagonist = triceps
* Fixator = rotator cuffs
* Synergists = brachialis
* Agonist = biceps
* Antagonist = triceps
* Fixator = rotator cuffs
* Synergists = brachialis
95
New cards
what happens during the kicking phase of a football?
During the kicking phase of a football, the antagonistic muscle pairs are as follows
\n
* Agonist = hamstring
\n
* Antagonist = quadriceps
\n
* Fixator = glutes
\n
* Synergists = gastrocnemius
\n
* Agonist = hamstring
\n
* Antagonist = quadriceps
\n
* Fixator = glutes
\n
* Synergists = gastrocnemius
96
New cards
what happens during the downward phase of a press up?
During the downward phase of a press up, the antagonistic muscle pairs are as follows
\n
* Agonist = triceps
\n
* Antagonist = biceps
\n
* Fixator = latissimus dorsi
\n
* Synergists = deltoids
\n
* Agonist = triceps
\n
* Antagonist = biceps
\n
* Fixator = latissimus dorsi
\n
* Synergists = deltoids
97
New cards
biceps (1.where, 2.what it acts on, 3.action, 4.example)
found in front upper arm
acts on elbow
flexion (bend arm)
bicep curl + pull up
acts on elbow
flexion (bend arm)
bicep curl + pull up
98
New cards
triceps (1.where, 2.what it acts on, 3.action, 4.example)
found in back upper arm
acts on elbow
extension (straighten)
passing a netball
acts on elbow
extension (straighten)
passing a netball
99
New cards
deltoid (1.where, 2.what it acts on, 3.action, 4.example)
Covers shoulder
Shoulder \n Abduction (raises arm sideways)
First part of star jump
Shoulder \n Abduction (raises arm sideways)
First part of star jump
100
New cards
pectorals (1.where, 2.what it acts on, 3.action, 4.example)
Upper chest
Shoulder
Adduction (brings arm across chest)
Breaststroke
Shoulder
Adduction (brings arm across chest)
Breaststroke