BIPN 100 - Lecture 8 Efferent Division of the PNS
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the efferent divisions of the PNS and what do they control? Are they mostly voluntary or involuntary?
Somatic Motor Neurons
control skeletal muscles
mostly voluntary (exceptions: cranial and spinal reflexes)
Autonomic Neurons
Control smooth and cardiac muscle, many glands, some adipose tissue
Mostly involuntary (exception: breathing and heart rate - divers can be trained to bypass)
Works with endocrine and behavioral state system to maintain homostasis.
What are the two branches of the autonomic nervous system? What do they control?
Parasympathetic (rest and digest) and sympathetic (fight or flight)
_____ is a dynamic balance between the autonomic branches.
Homeostasis
Most internal organs are under what kind of control?
Antagonistic control
One autoomic branch is excitatory and the other branch is inhibitory.
What are the exceptions to antagonistic innervation (control)? Where are these exceptions controlled?
Exceptions: Only innervted by the sympathetic branch (tonic control)
Sweat glands
smooth muscle in most blood vessels
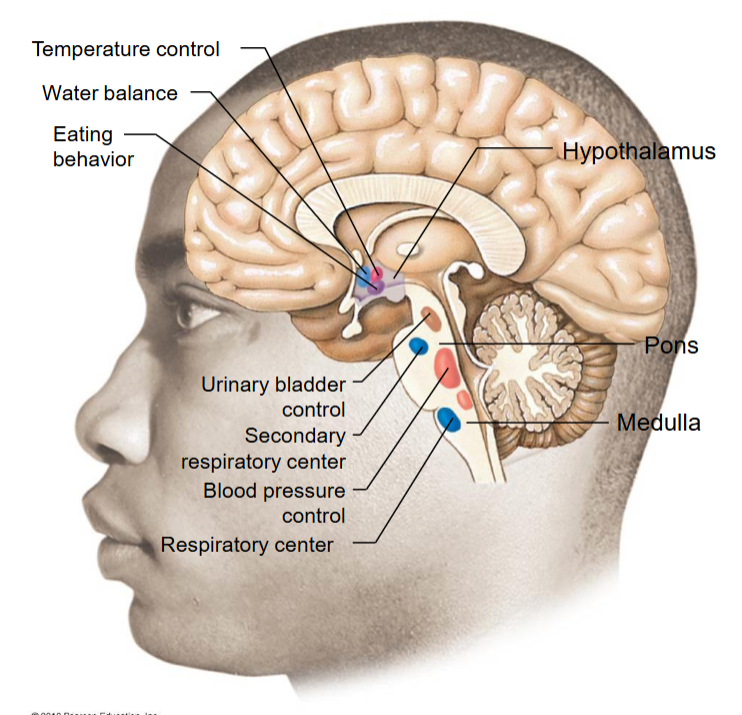
Where are the autonomic control centers? Describe their characteristics.
Hypothalamus
Homeostatic center of the brain
Sends input into the autonomic nervous system (both sympathetic and parasympathetic)
Brainstem
Nuclei in the brainstem regulates the autonomic nervous system
Note: Nuclei are a group of cell bodies where information gets integrated.
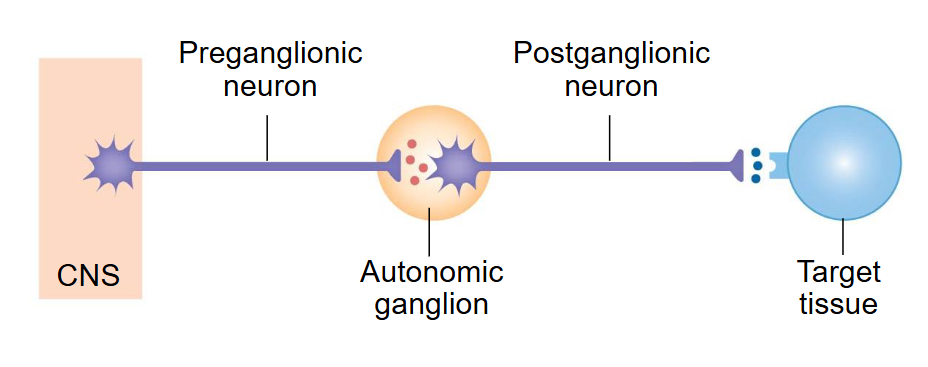
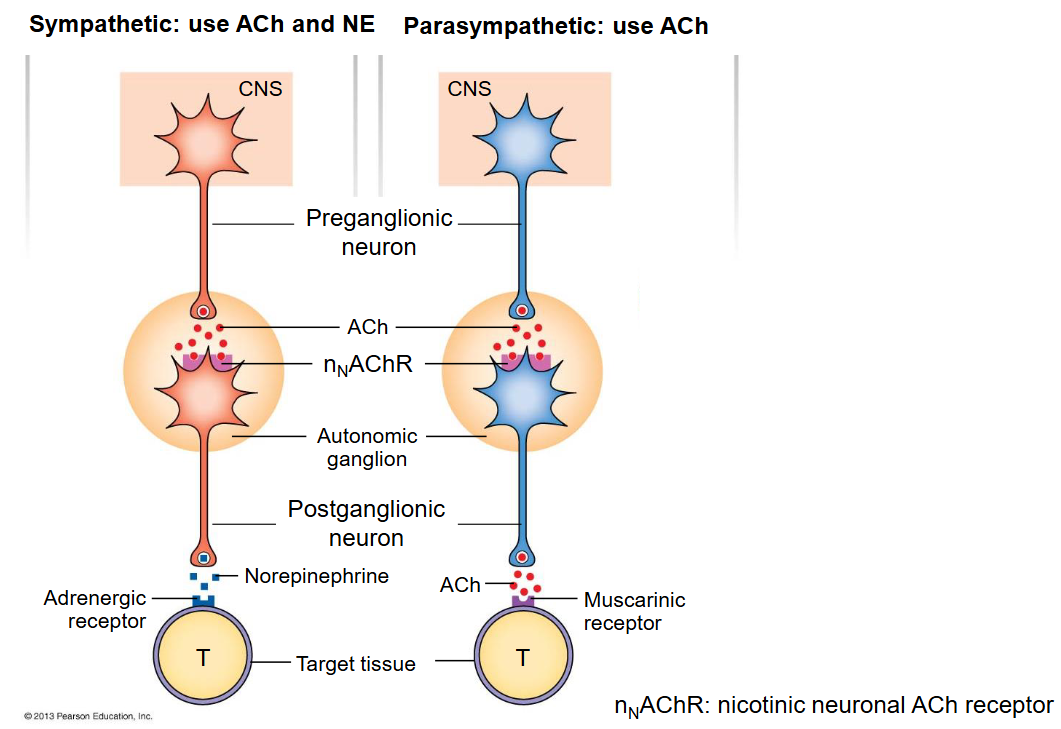
Draw a picture of autonomic pathways (sympathetic and parasympathetic). How does this differ from a somatic pathway?
Somatic pathway only consist of one neuron (Aa motor neuron) which synapses with skeletal muscle. Autonomic pathways consist of two neurons that synapse in an autonomic ganglion.
Draw a sympathetic pathway into the spinal cord. Label the neurons and structures.
Notes:
Paravertebral Sympathetic ganglia - contains postganglionic cell bodies. The preganglionic neuron is short since the ganglia is close to the spinal cord.
Exception: Prevertebral sympathetic ganglia - ganglia are not near the spin (scattered int he abdomen) resulting in longer preganglionic axons
Don’t Need to Know Much:
White Ramus: contains preganglionic axons (B fibers) myelinated (white)
Gray Ramus: contains postganglionic axons (C fibers) not myelinated (grey)
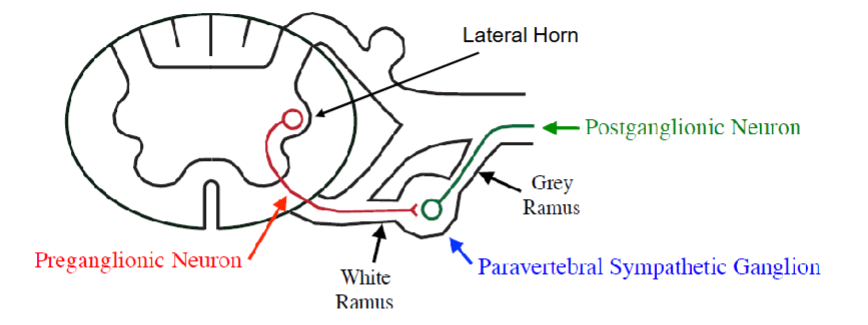
In the paravertebral sympathetic ganglion is the preganglionic neuron longer or shorter than the prevertebral sympathetic ganglia?
Shorter because the ganglion is closer to the spinal cord.
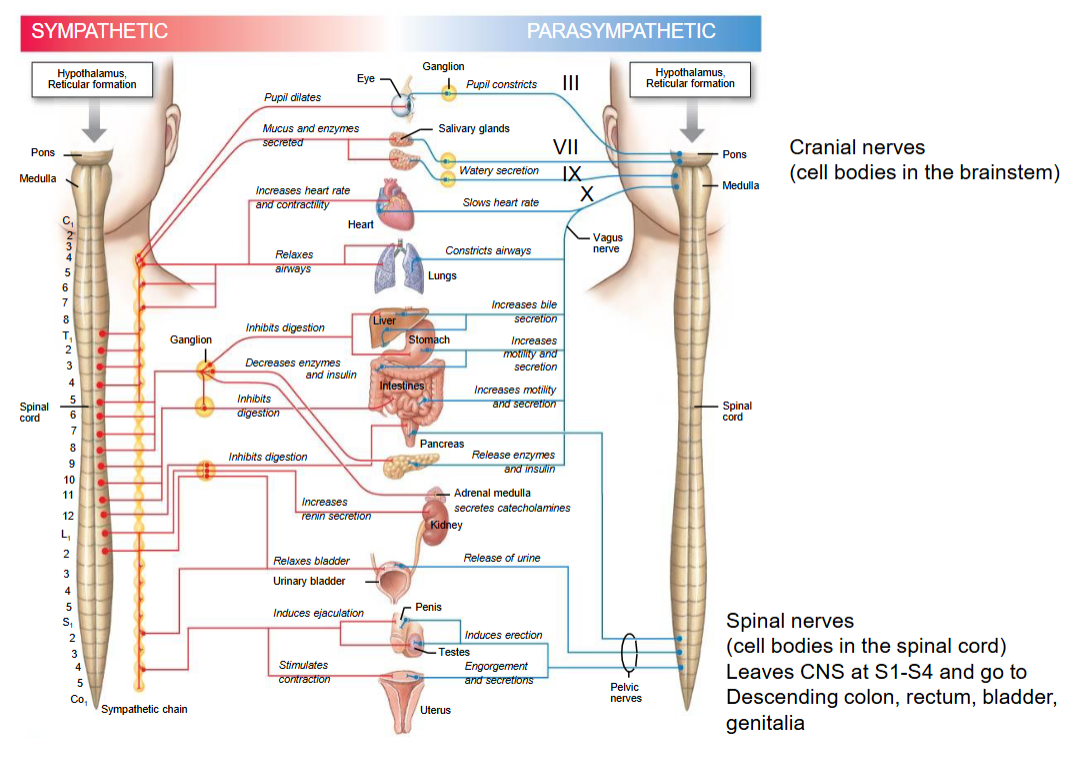
How can you differentiate between sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways.
Location
Sympathetic: The preganglionic neuron comes out only in the thoracic and lumbar region of the spine.
Parasympathetic: The preganglionic neuron only comes out in the brainstem and sacral region of the spine.
How close the ganglia is
Sympathetic: The autonomic ganglion is very close to the spinal cord (with few exceptions)
Parasympathetic: The autonomic ganglia is very close to the tissues (further from the spinal cord).
Length of preganglionic neuron
Sympathetic: The preganglionic neuron is very short and the post-ganglionic neuron is long (with exceptions)
Parasympathetic: Preganglionic neuron is very long and postganglionic neuron is short.
Draw and differentiate the receptors and neurotransmitters of sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways.
Sympathetic:
Neurotransmitters: ACh and Norepinephrine
Receptors: nNAChR (nicotinic neuronal ACh receptor)
Parasympathetic:
Neurotransmitters: Ach (both)
Receptors: nNAChR and muscarinic receptors (5 subtypes)
Note: The second receptor for both pathways dictates response on tissue (whether it is excitatory or inhibitory)
Draw and explain hormone release in the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
Adrenal Sympathetic Pathway
Hormone: Epinephrine
Function of Hormone: Circulate in bloodstream and bind to adrenergic receptor and cause change in function of the tissue.
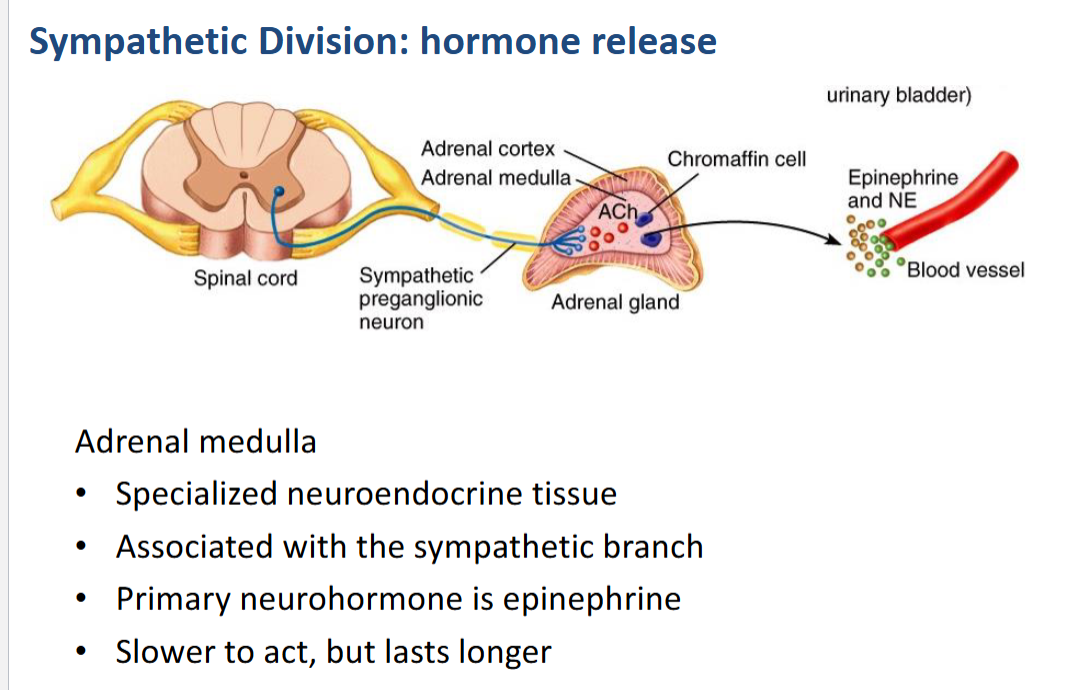
What are the characteristics of the adrenal medulla?
Adrenal Medulla
Specialized neuroendocrine tissue
Associated with the sympathetic branch
Primary neurohormone is epinephrine
Slower to act, but lasts longer
_____ release neurotransmitter over the surface of target cells.
Autonomic varicosities
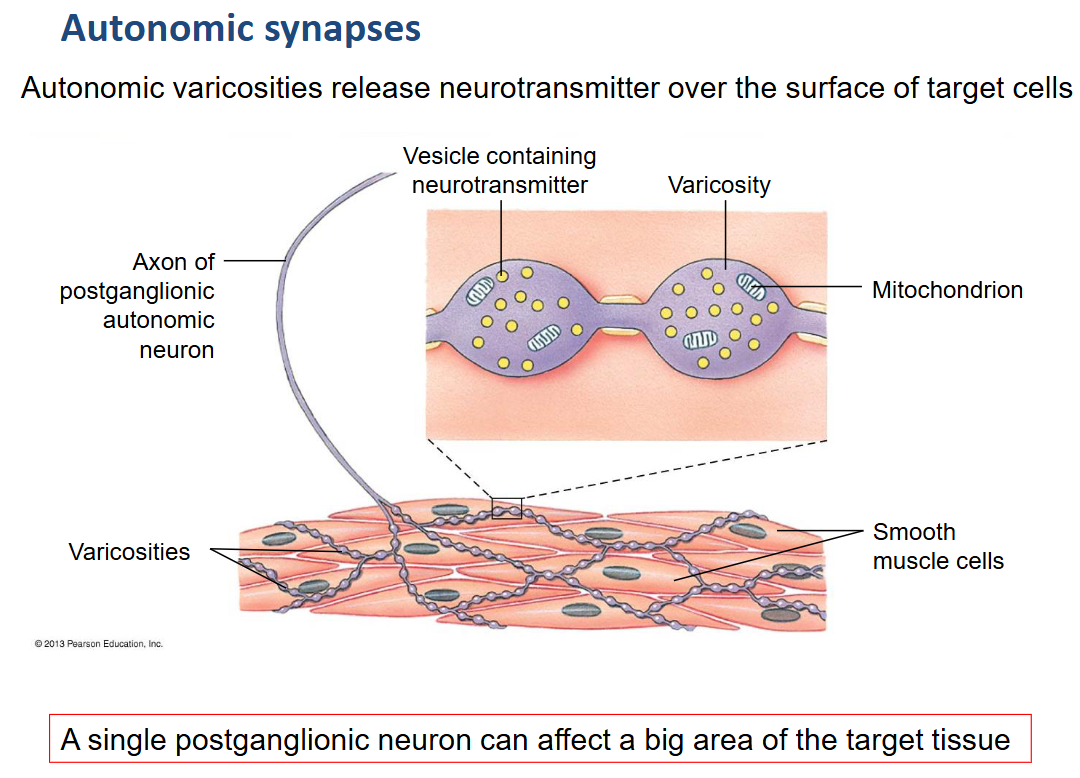
What are varicosities?
A vesicle containing neurotransmitter.
A _______________ can affect a big area of target tissue due to autonomic varicosities.
single postganglionic neuron
What division of the autonomic nervous sytem has adrenergic receptors? What are the types of adrenergic receptors?
Sympathetic Nervous System
Adrenergic Receptors: Consists of two subtypes
Alpha and Beta
Odd subtypes are excitatory
Even subtypes are inhibitory
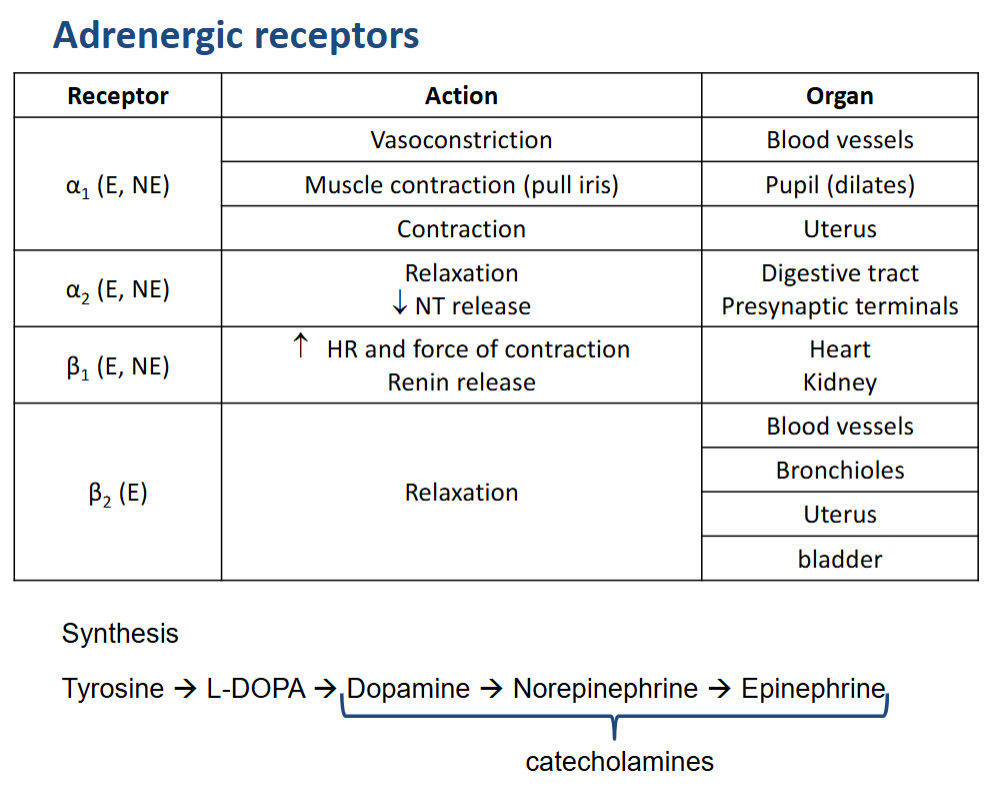
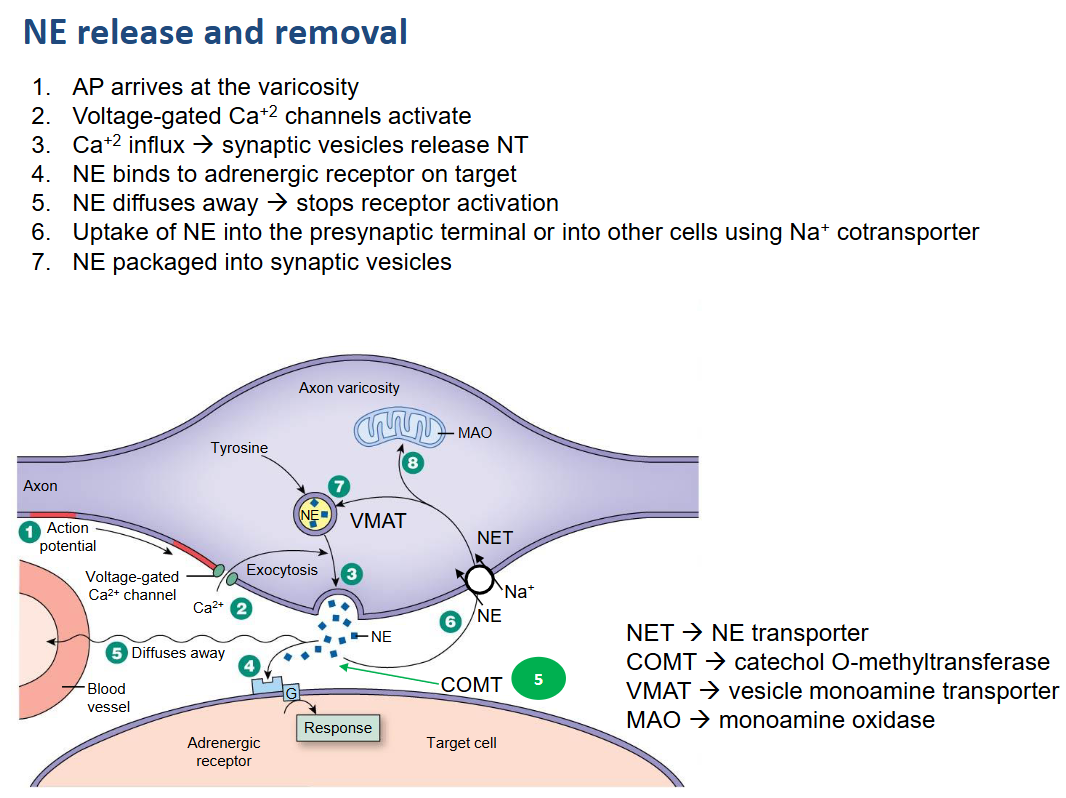
Explain how norephinephrine is released and removed.
AP (Action Potential) arrives at the varicosity.
Voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels activate.
Ca²⁺ influx triggers synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitter (NE).
NE binds to adrenergic receptors on the target cell.
NE diffuses away from the receptor, stopping receptor activation.
Uptake of NE into the presynaptic terminal or other cells occurs via Na⁺ cotransporter (NET).
NE is packaged into synaptic vesicles for reuse.
or NE is oxidized in the mitochondria.
What division of the autonomic nervous sytem has muscarinic receptors? How many subtypes are there?
Parasympathetic branch
Muscarinic receptors (metabotropic)
5 subtypes (m1-5)
Odd is excitatory
Even is inhibitory