4. Fluids Formulas (10%)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms

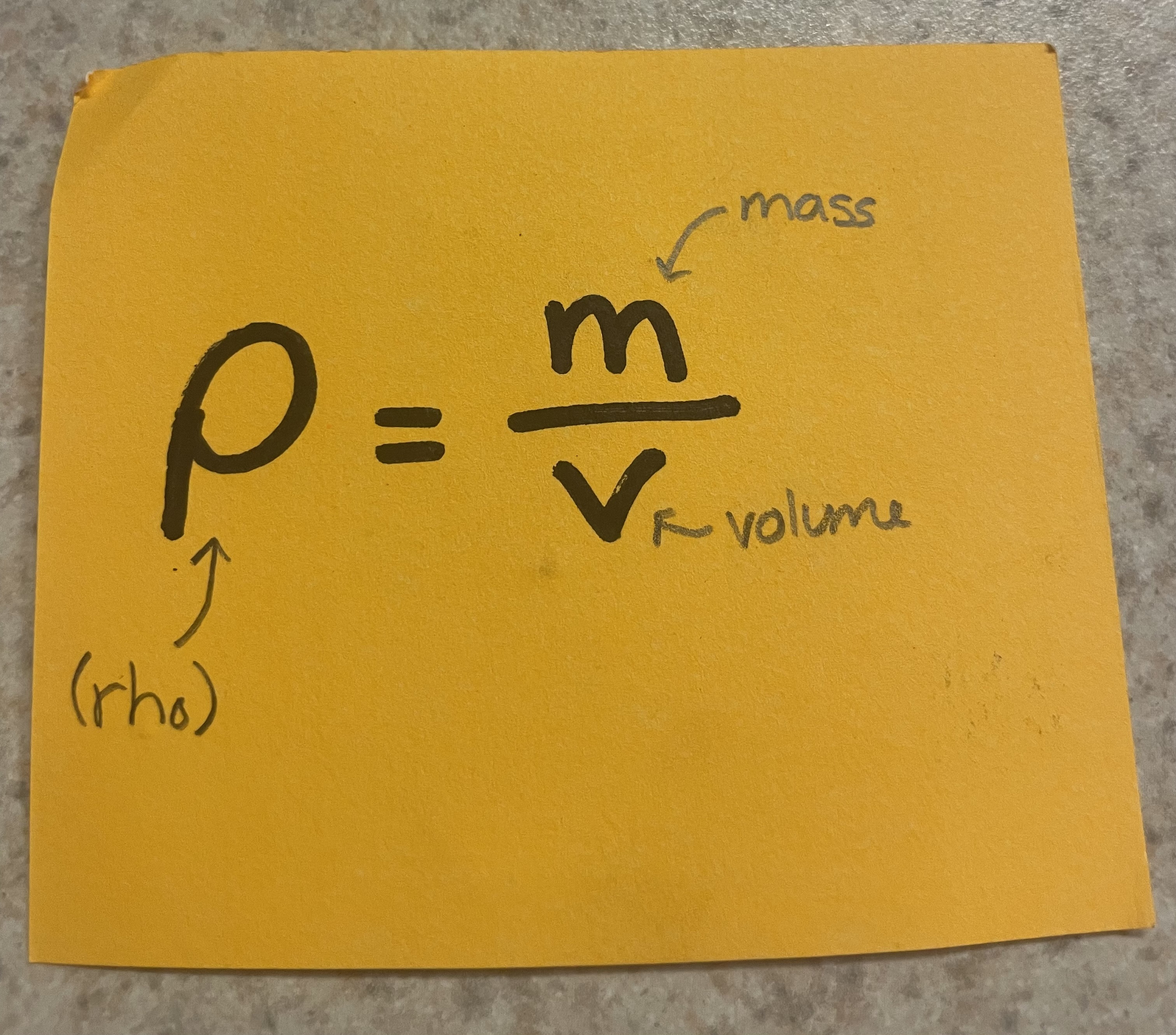
Density
variables: mass, volume

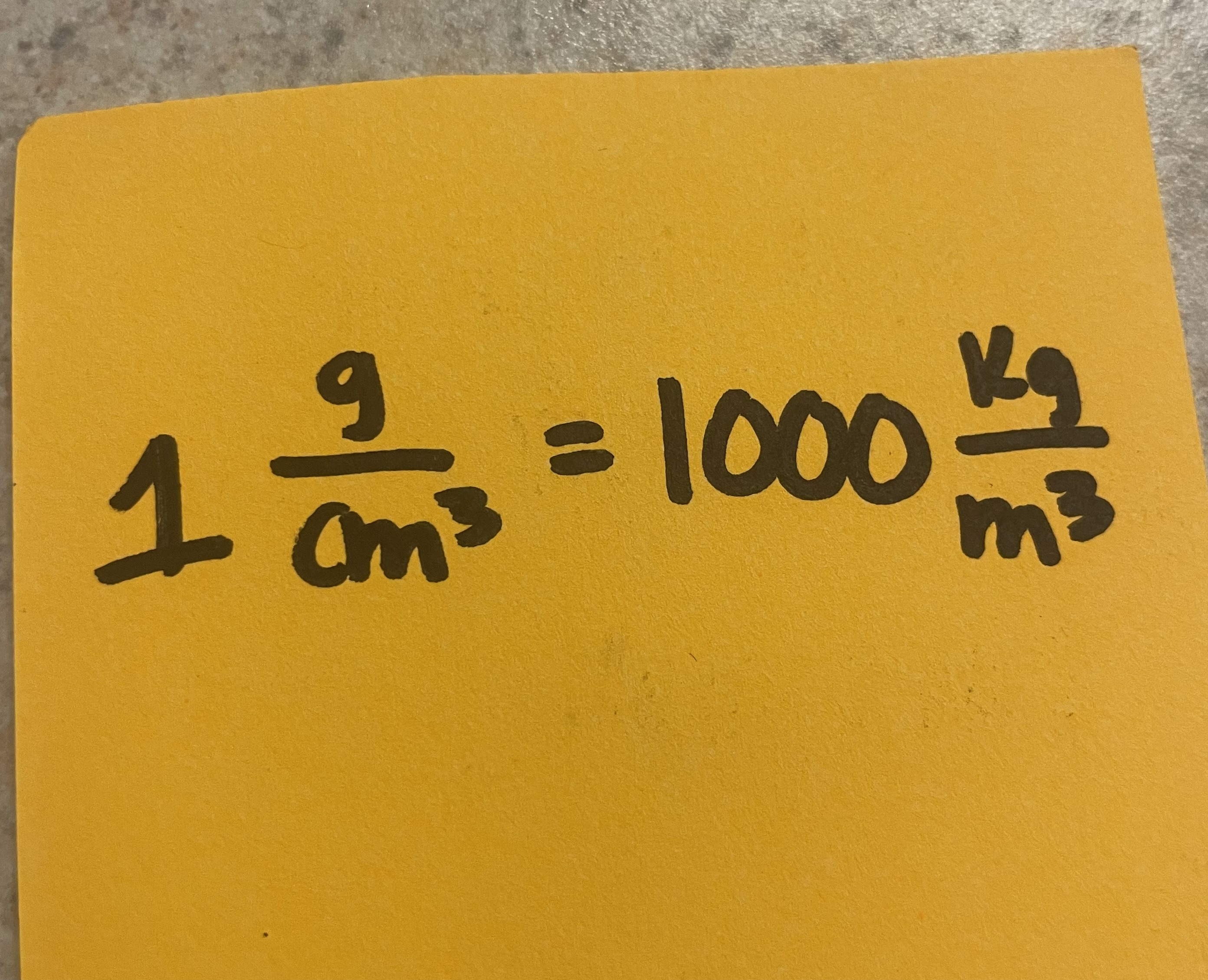
Density of Water (2)

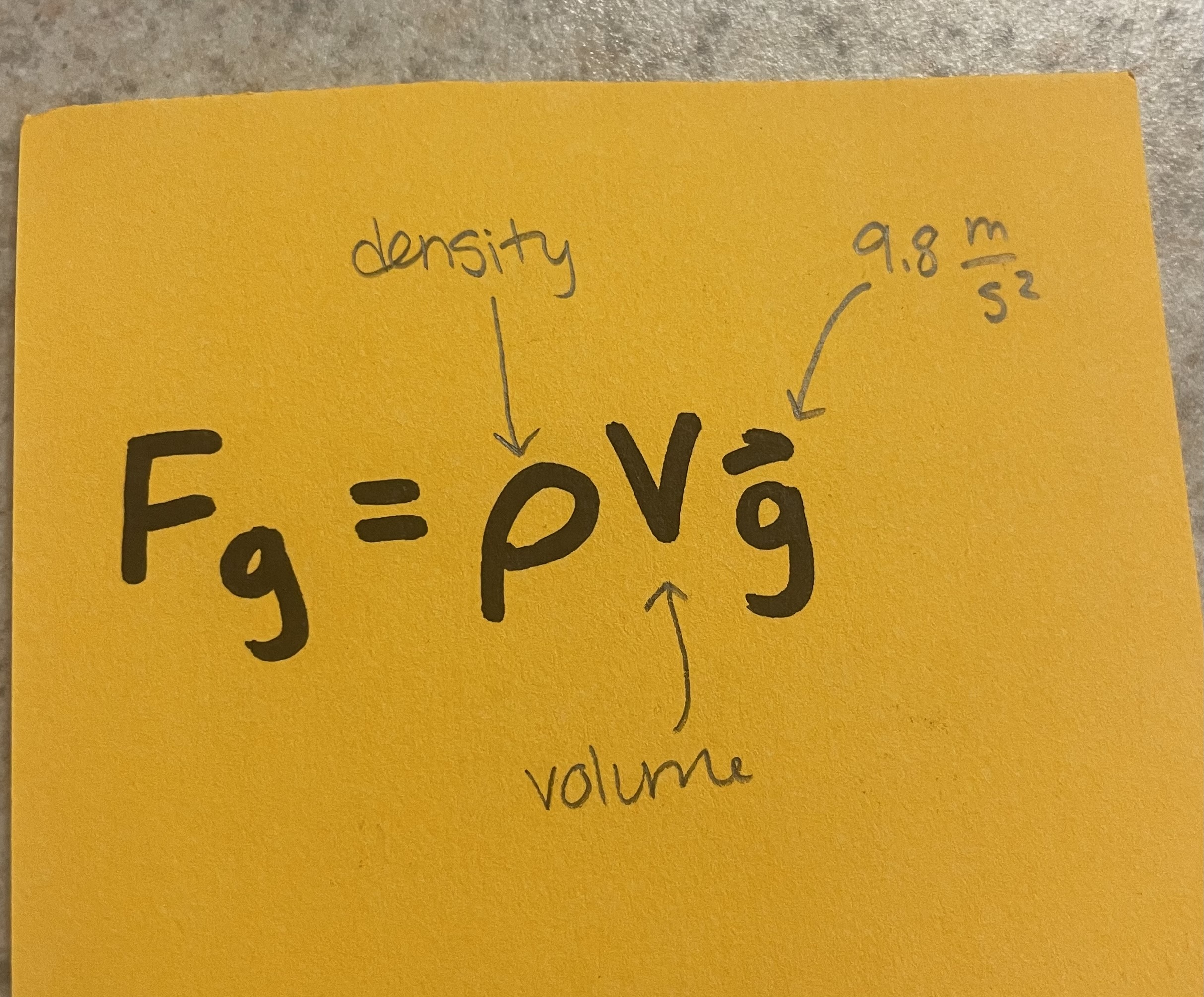
Force of Gravity Applied to an Object/Weight of a Volume of Fluid (aka the “force down” applied onto an object submerged in a fluid and is directly opposed by buoyant force)
variables: density of object/fluid, volume of object/fluid

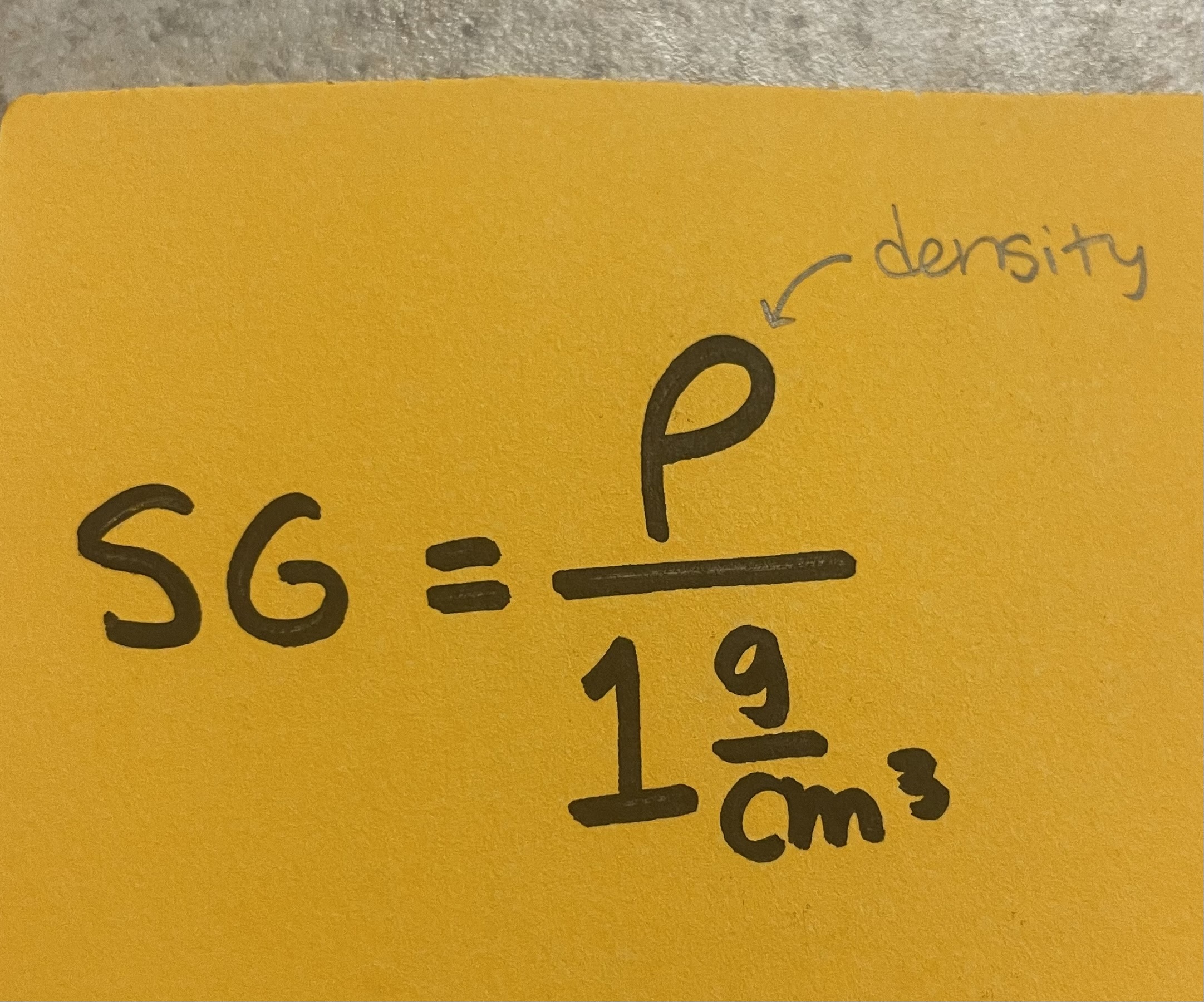
(density of liquid or object / density of water)
Specific Gravity (% of an object that is submerged in water)
if SG > 1, object will sink


Pressure
variables: normal force, area

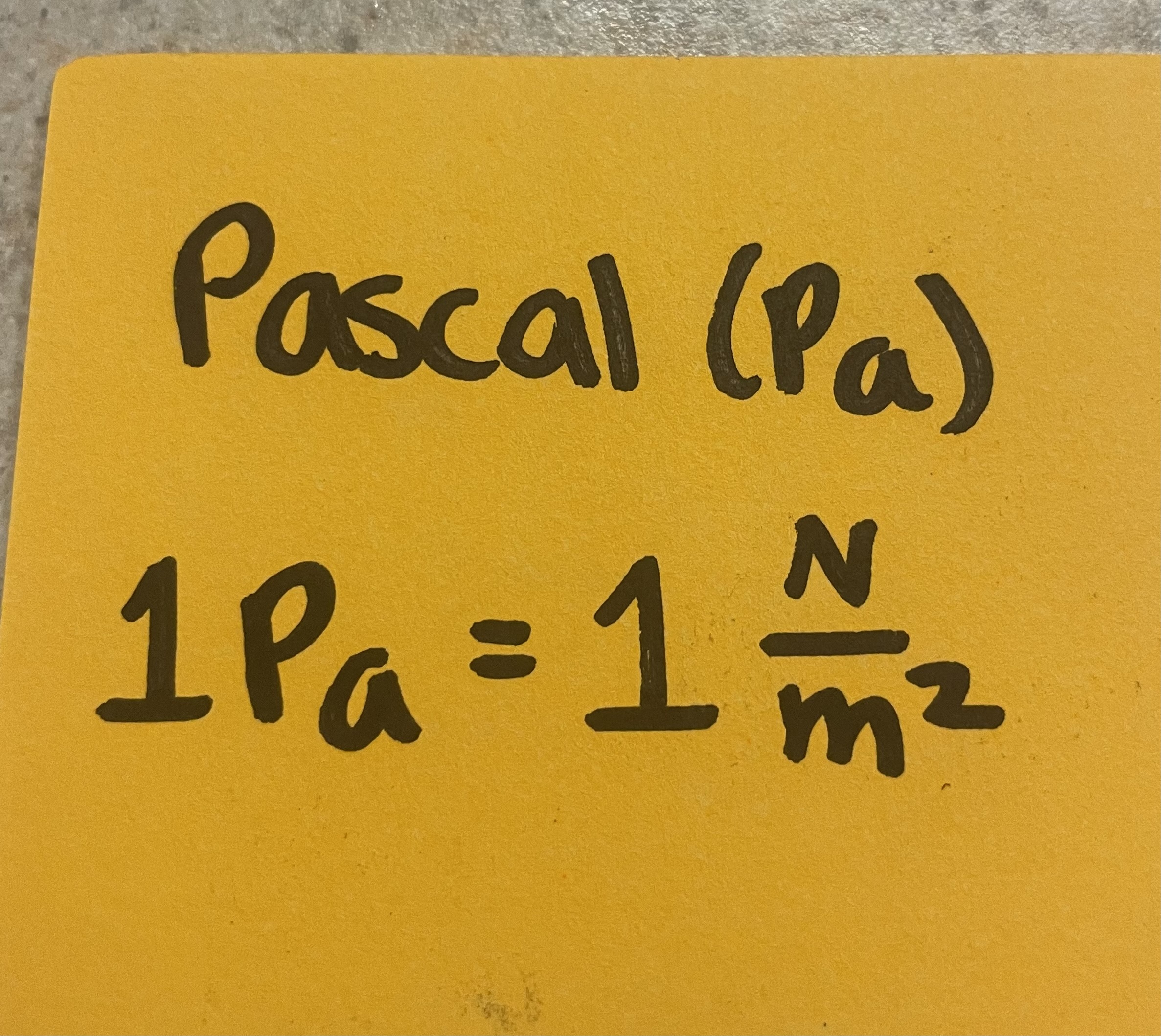
Pressure units

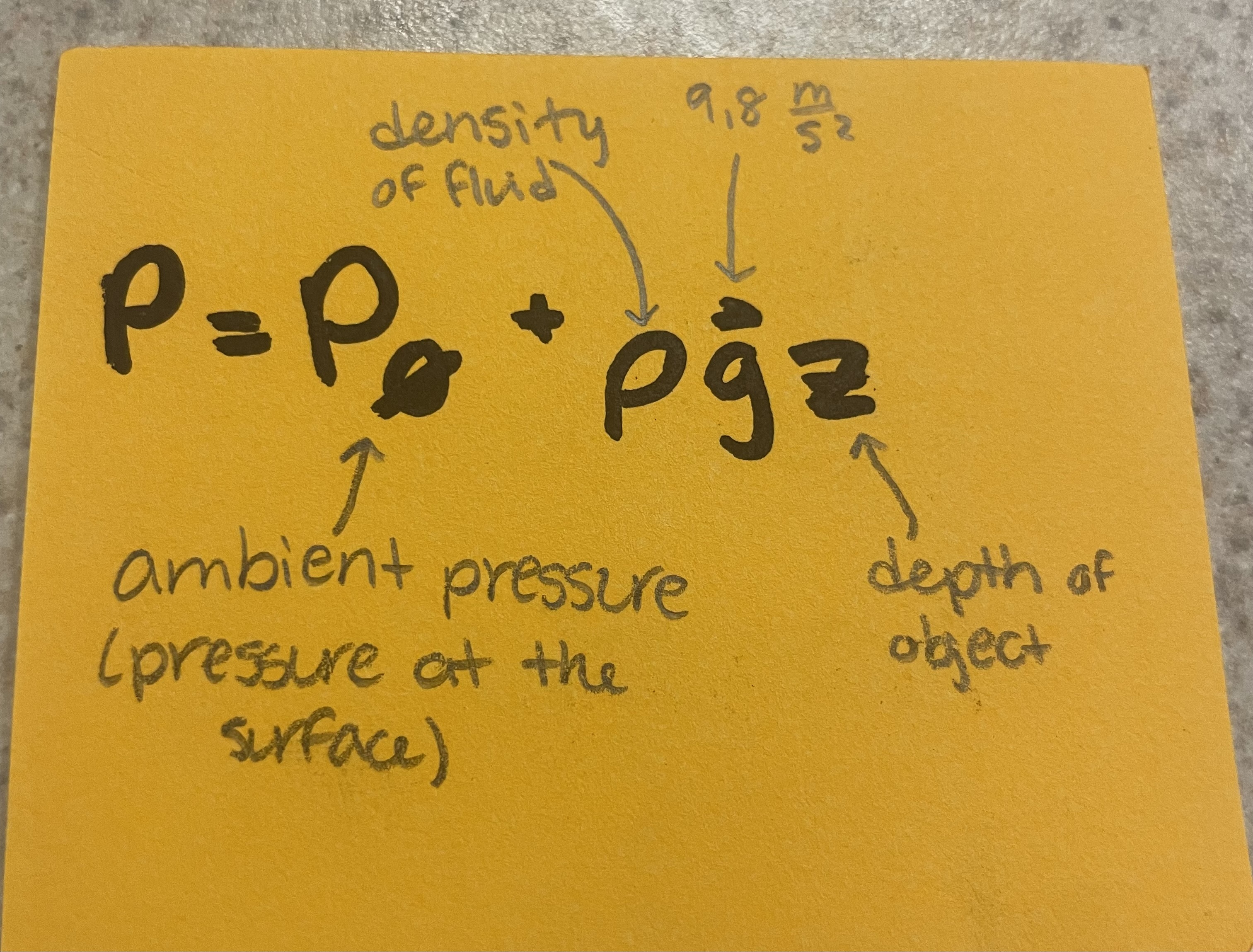
Absolute Pressure
variables: ambient/surface pressure, fluid density, depth of object


Gauge Pressure
variables: absolute pressure, atmospheric pressure

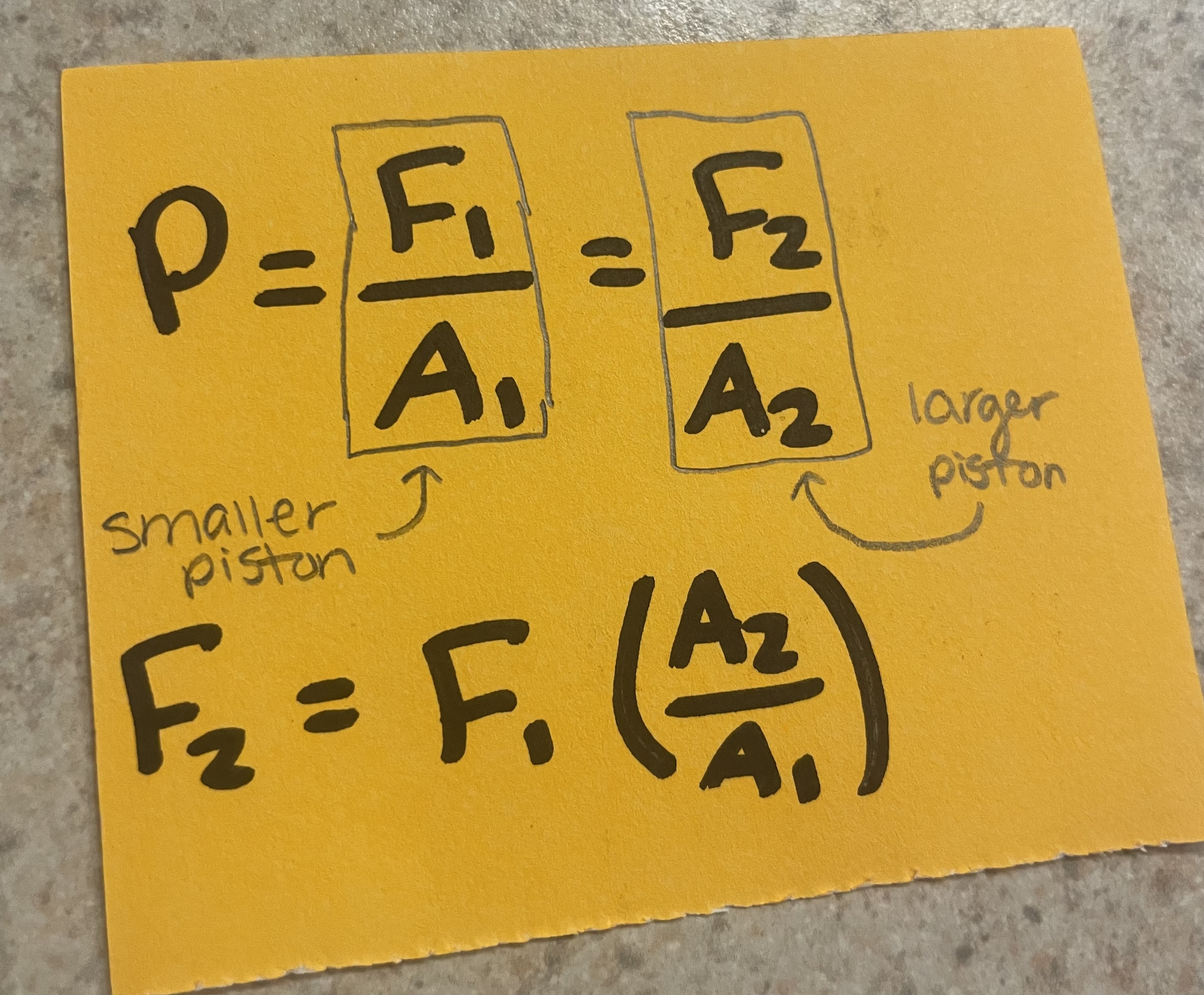
Pascal’s Principle (2)


(remember volume = area x height)
Buoyant Force // Upward Force Applied to a Submerged Object as Exerted by the Fluid (which opposes the object’s weight, causing it to float/rise) (aka the “force up” applied onto an object submerged in a fluid and is directly opposed by the force of gravity)
variables: fluid density, volume of fluid displaced/submerged


Critical Velocity/Speed [the flow speed at which the fluid's movement transitions from smooth, orderly (laminar) flow to chaotic, irregular (turbulent) flow]
variables: fluid viscosity, fluid density, diameter of the tube

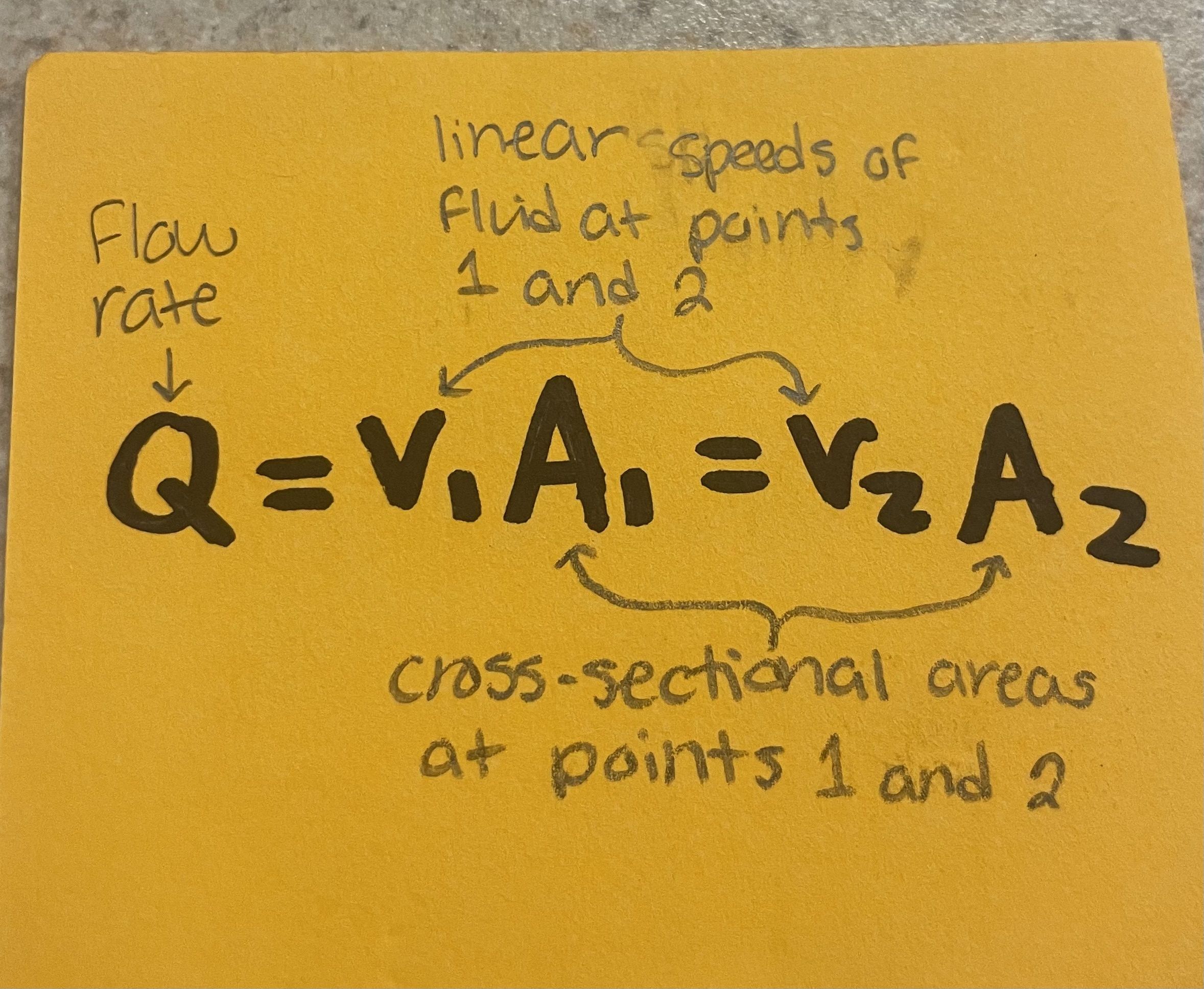
Continuity Equation // Flow Rate/Flux
variables: velocity at 2 points, cross-sectional areas at 2 points

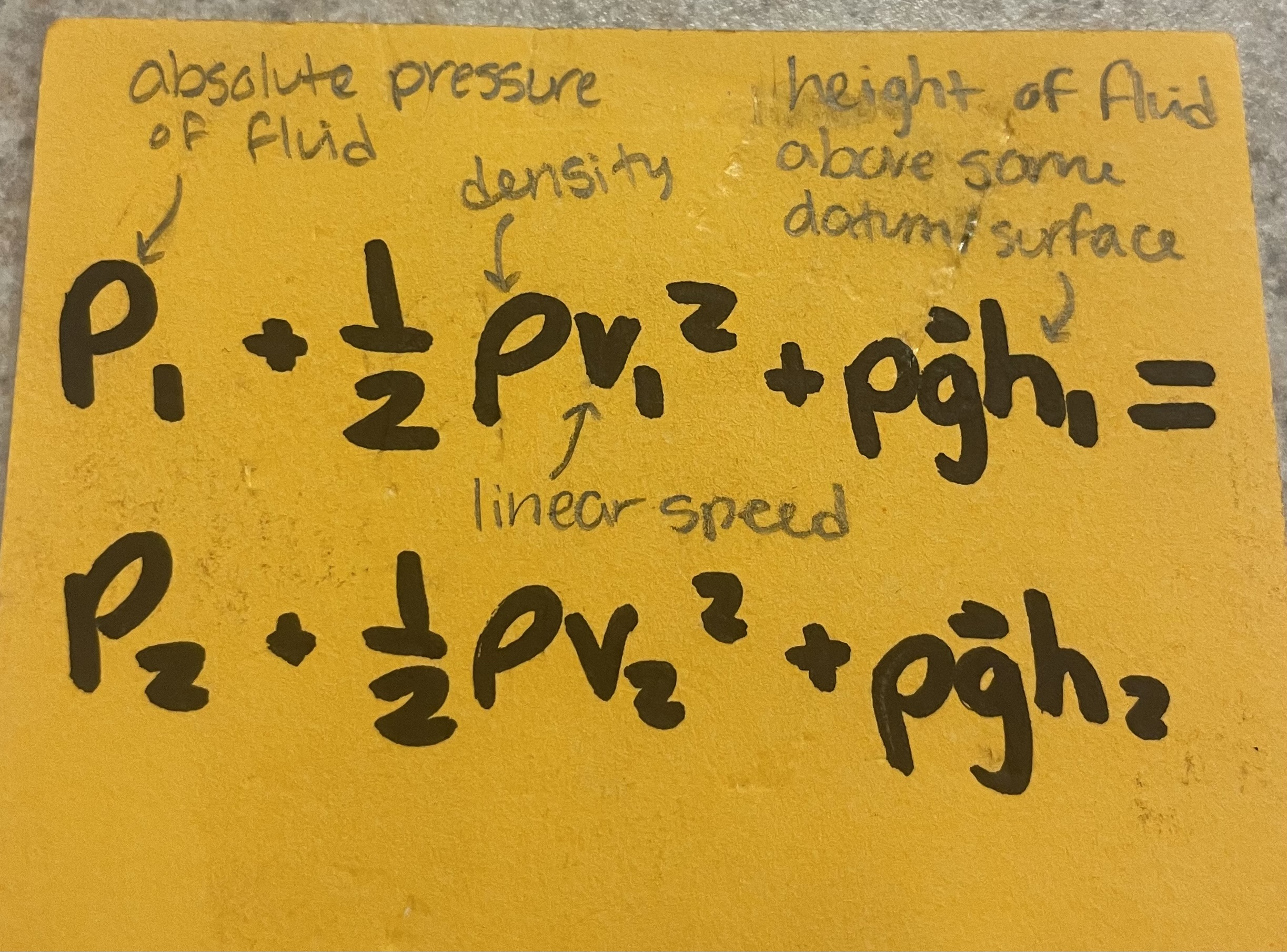
(essentially PE1 + KE1 = PE2 + KE2 except you add pressure and replace mass with density)
Bernoulli’s Equation