Clin Med Derm Bacterial, Viral, and Fungal Infections
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Impetigo
Bacterial Skin Infections:
infection of the epidermis which may extend into the dermis (Ecthyma)
- occurs from either minor superficial breaks in the skin OR secondary infection from other derm conditions (eczema)
- more common in children!
- often asymptomatic, but can be itchy or painful
S. aureus
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What bacteria causes impetigo?
1. nonbullous
2. bullous
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are the 2 forms of impetigo?
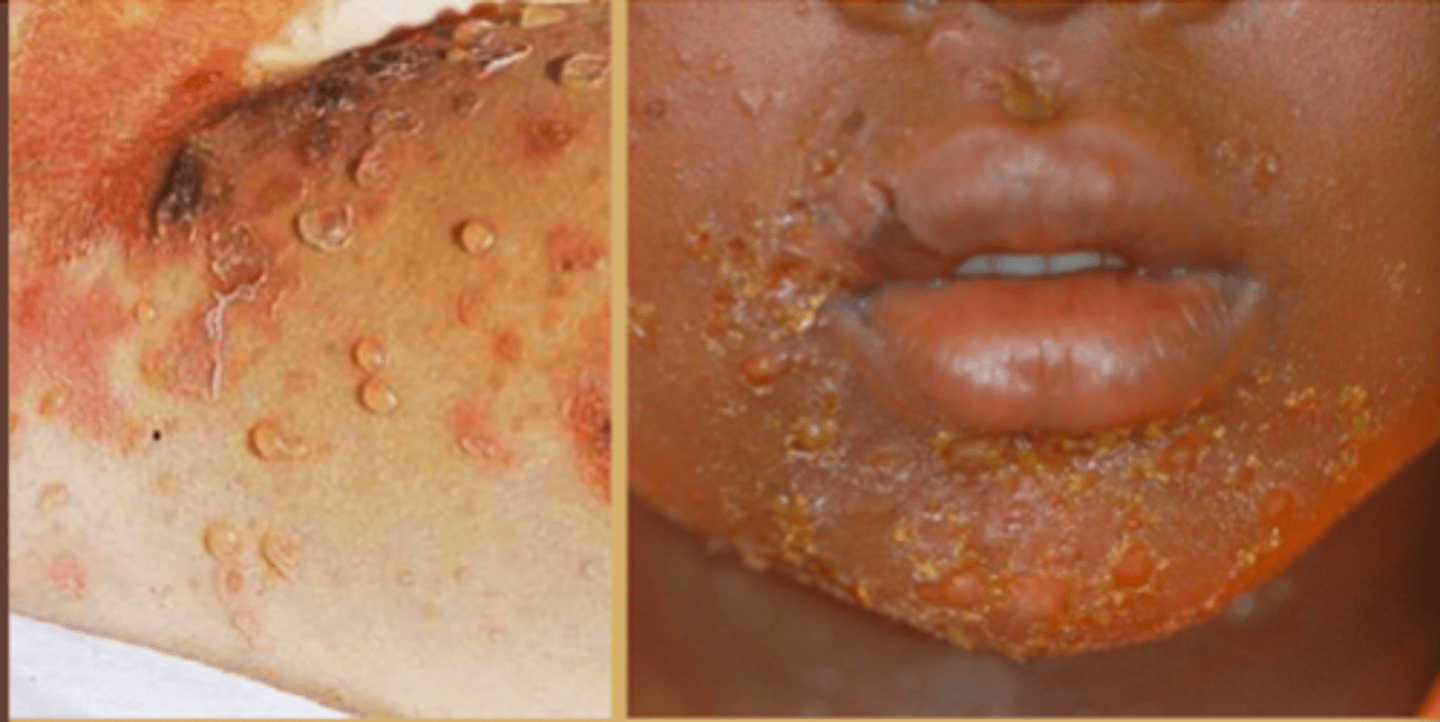
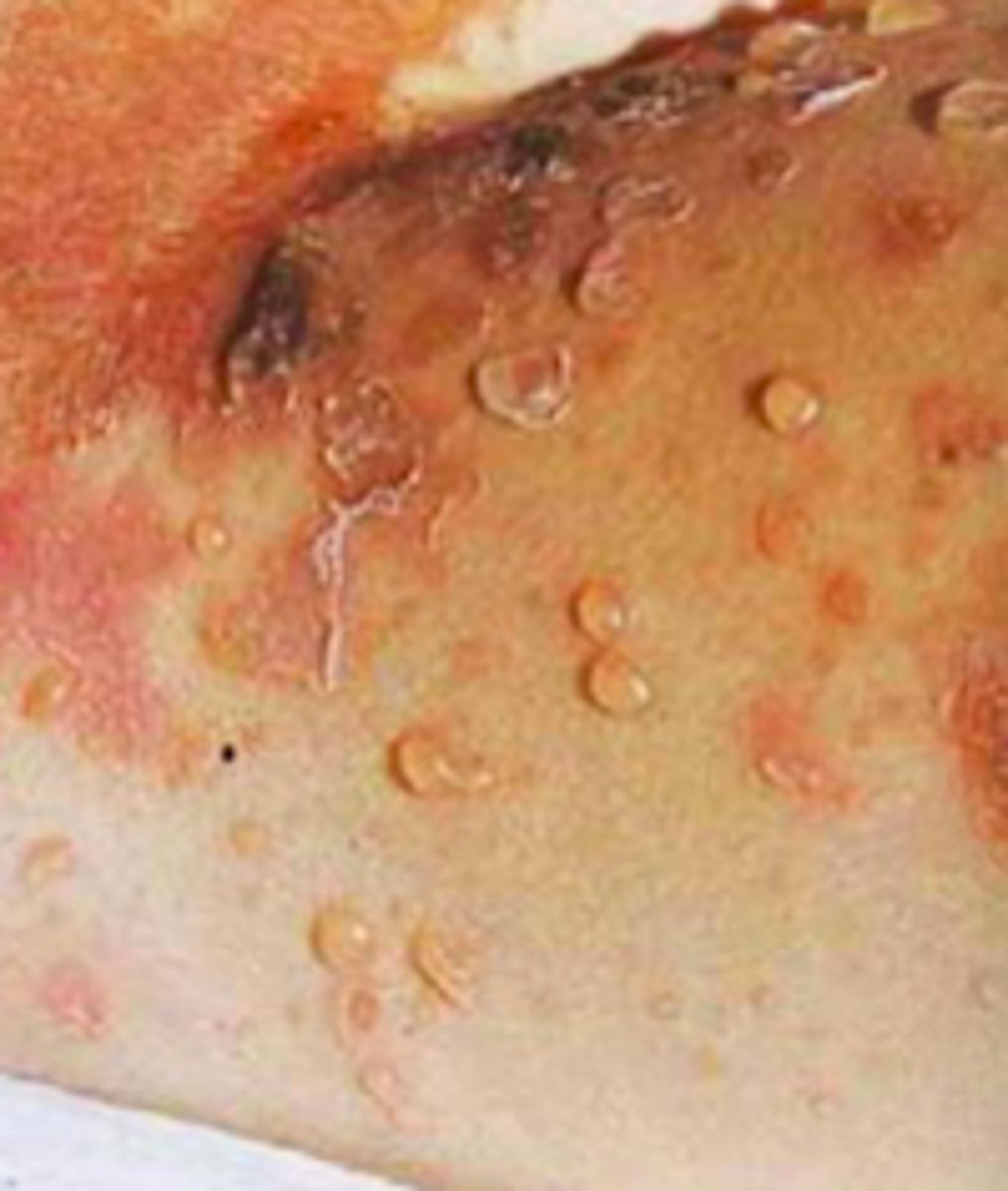
nonbullous impetigo
Bacterial Skin Infections:
erosions with "honey-colored crusts" and surrounding erythema
bullous impetigo
Bacterial Skin Infections:
impetigo including blisters containing clear, yellow, or slightly purulent fluid with an erythematous base
- gram stain (gram + cocci)
- swab serous drainage & culture (S. aureus)
Bacterial Skin Infections:
When we are Dx'ing impetigo, what are the methods we can do? What would we find with each of these methods?
MRSA must be suspected if certain ABX fail!!
Bacterial Skin Infections:
When we are Dx'ing impetigo, if antibiotics fail, what do we suspect?
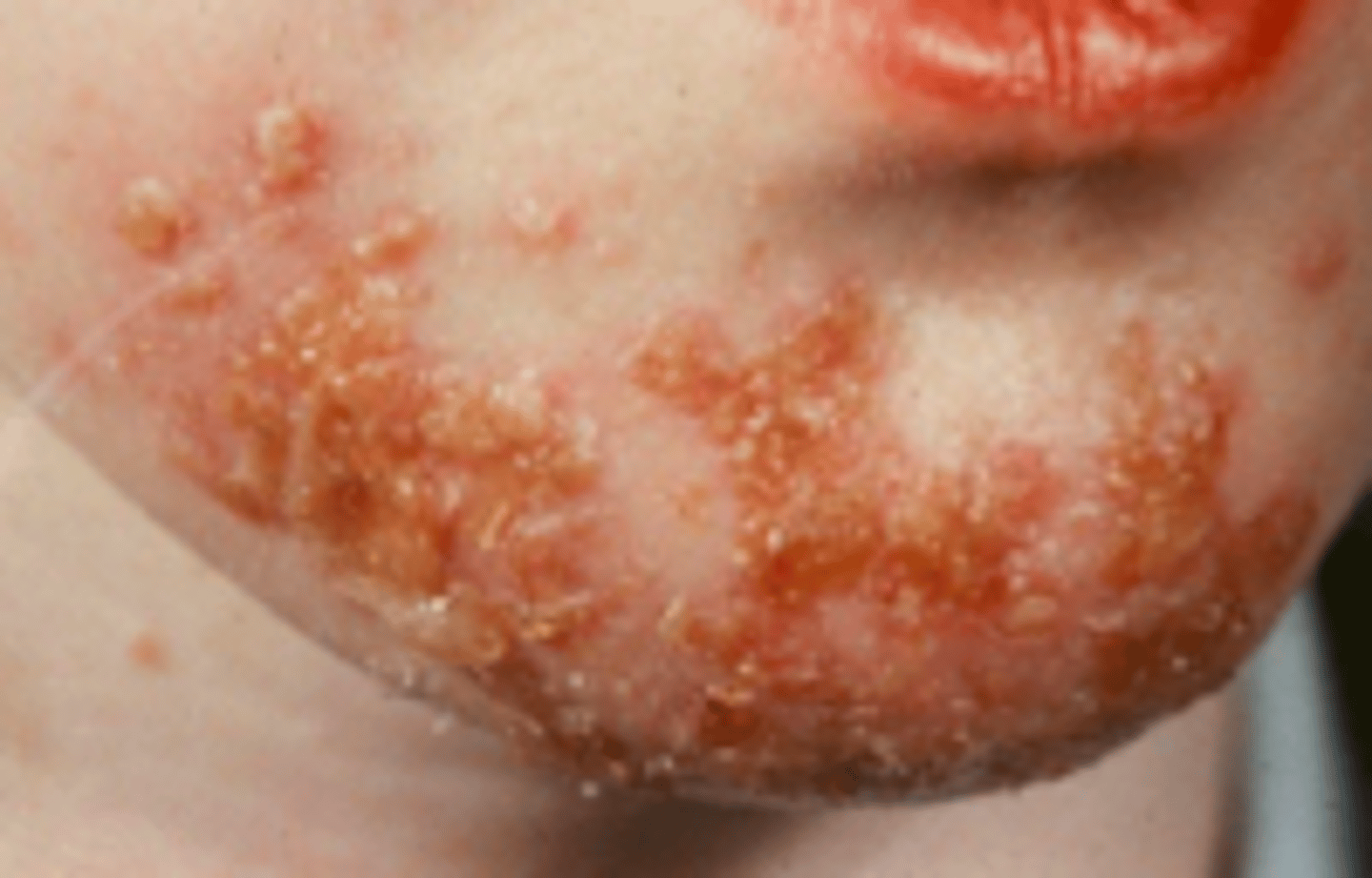
ecthyma
Bacterial Skin Infections:
deeper impetigo (down to dermis (takes weeks to occur)
impetigo
Bacterial Skin Infections:
All of the following are possible complications of what bacterial skin disorder:
- can lead to ecthyma if untreated
- may lead to cellulitis, sepsis
- recurrent!!
- MRSA if antibiotics fail
- mupirocin ointment (bactroban) at night - use for 7-10 days and is highly effective
- cephalosporin, clindamycin
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are the preferred treatments for impetigo?
benzoyl peroxide for family members, frequently wash the shared items (i.e. towels)
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What do we advise family members of people infected with impetigo to use as prevention?
impetigo
Bacterial Skin Infections:
If a patient presented w the following S/S, what may you suspect they have:
- honey-colored crusts
- surrounding erythema
- pt describes limited itching
folliculitis
Bacterial Skin Infections:
- bacterial infection that occurs in the upper part of the hair follicle
- may extend deeper into the follicle if left untreated, may become chronic
- shaving/waxing/plucking, and tight clothing are predisposing factors
- can be usually non-tender; may be pruritic
- will see multiple, small, erythematous follicular papules & pustules scattered in areas of hair growth
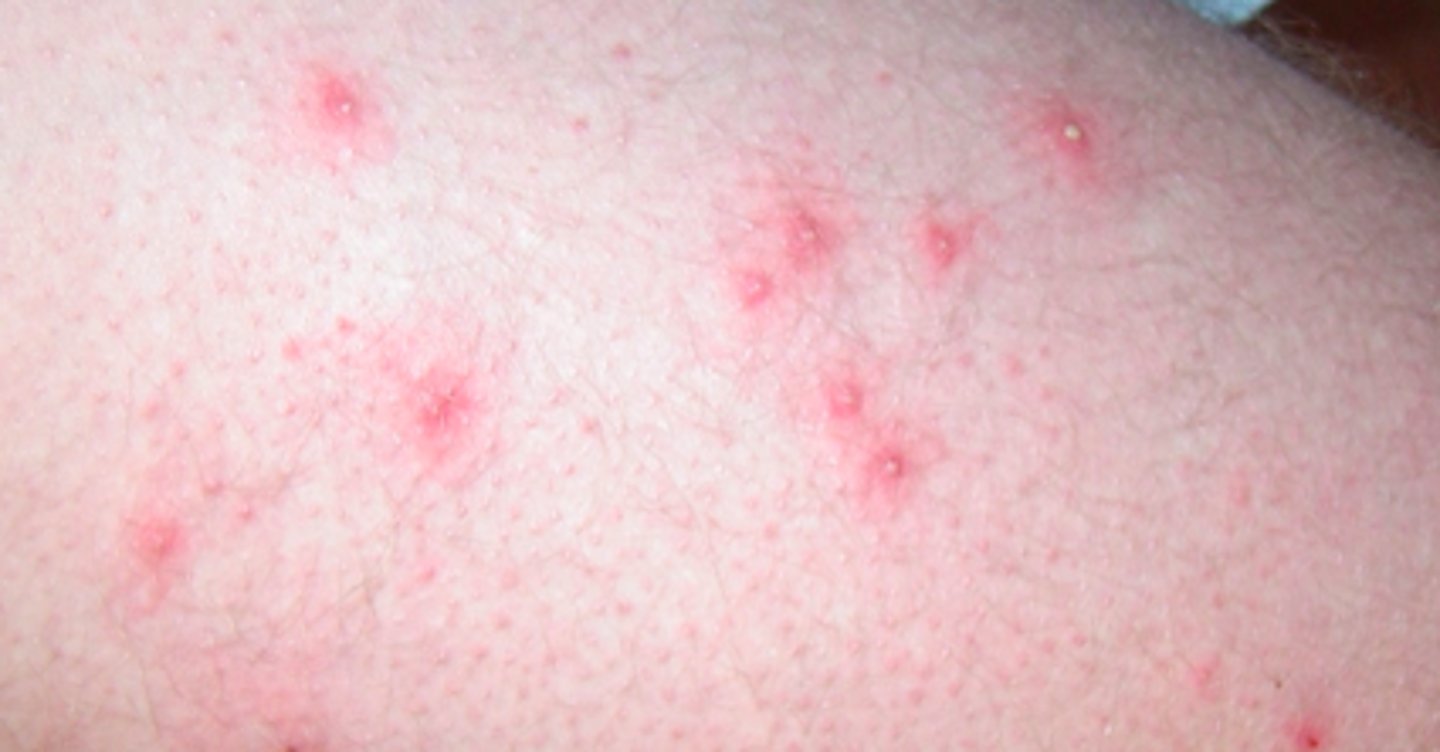
folliculitis
Bacterial Skin Infections:
If a patient presented w/ the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
- multiple erythematous papules and some pustules
- found in areas of hair growth
- Usual non-tenderness, some pruritic
Staph aureus
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What is the bacteria that causes folliculitis?
- oral antibiotics based on culture
- topical clindamycin
- benzoyl peroxide wash (to prevent Abx resistance)
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are some treatments for S. aureus folliculitis?
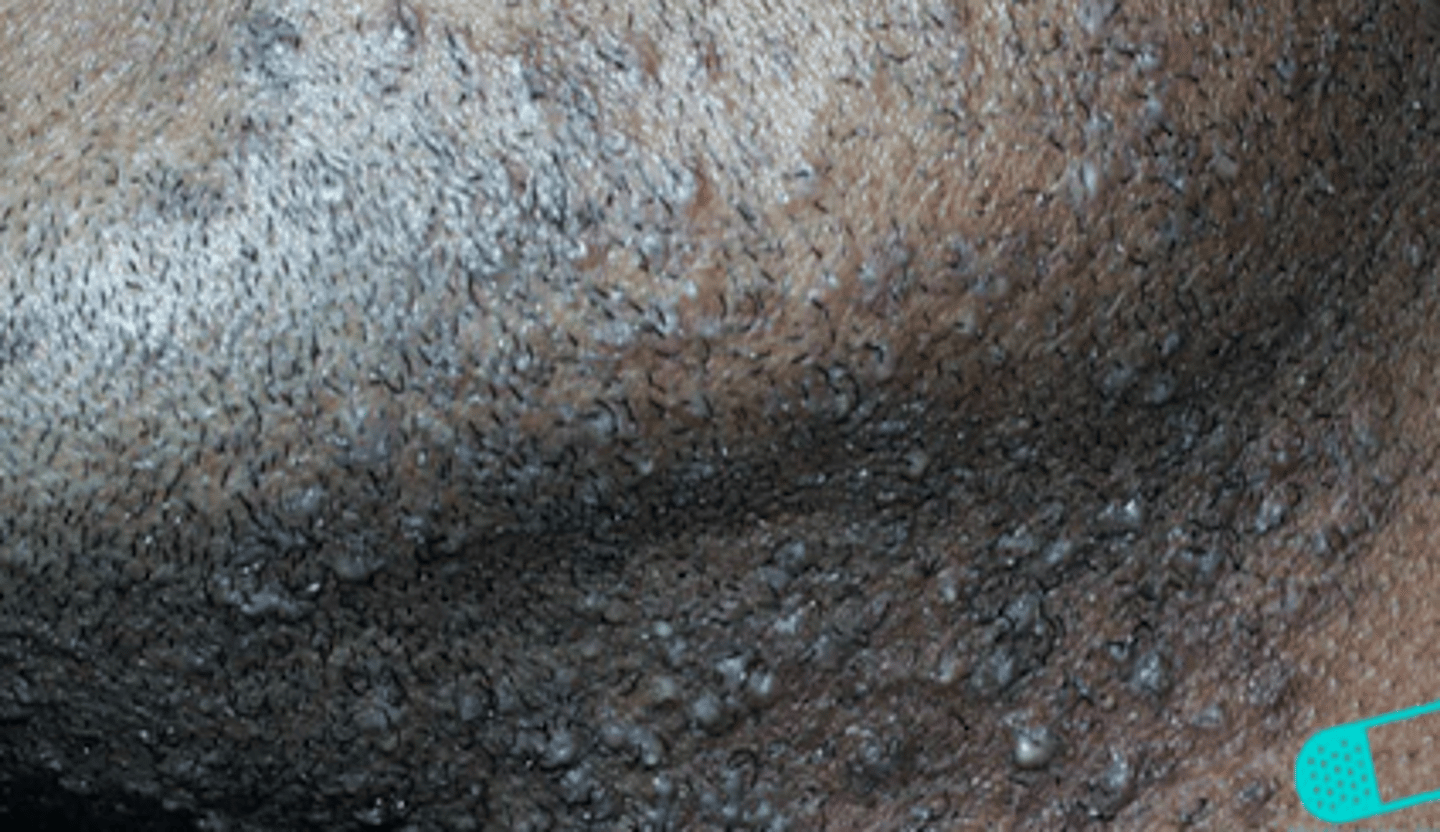
hot tub folliculitis
Bacterial Skin Infections:
- occurs on trunk and extremities after immersion in a hot tub
- caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa
pseudomonas aeruginosa
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What is the bacteria that causes hot-tub folliculitis?
self-limiting
- if not, fluoroqinolone
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What is the treatment for hot-tub folliculitis?
pseudofolliculitis barbae
Bacterial Skin Infections:
- aka razor bumps
- foreign body inflammatory reaction surrounding ingrown hairs from shaving/plucking
- can be seen in anyone but most commonly in black men

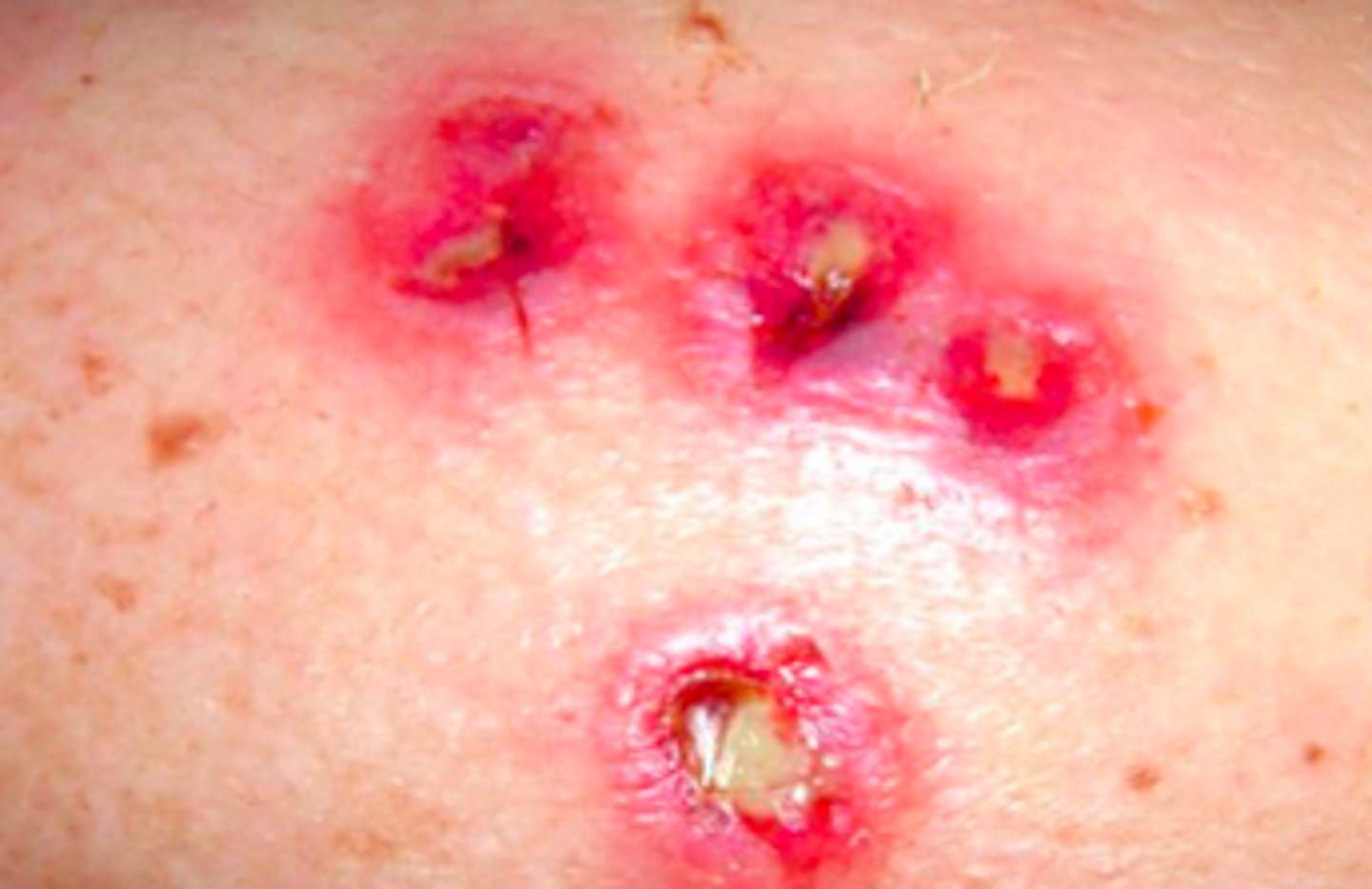
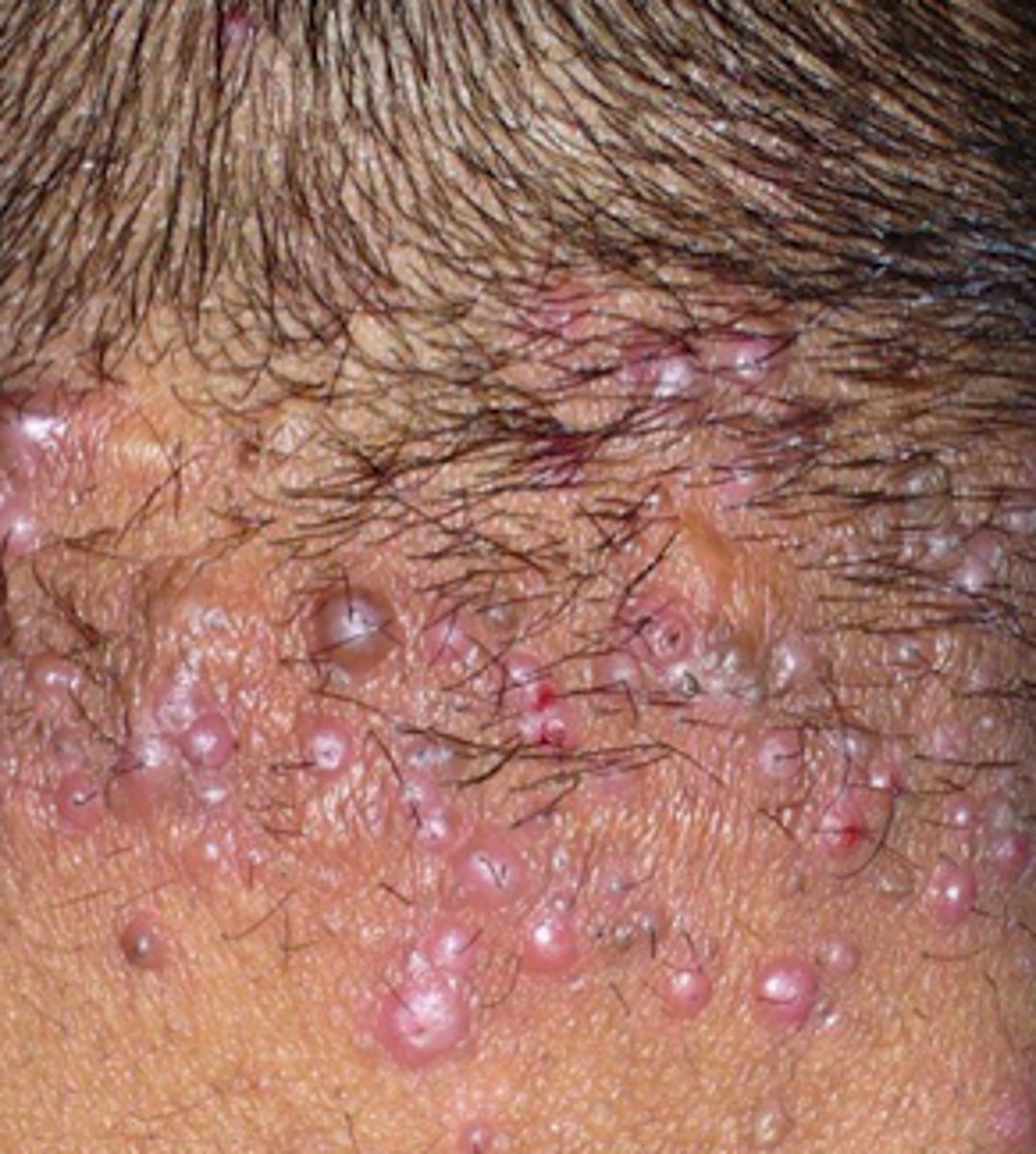
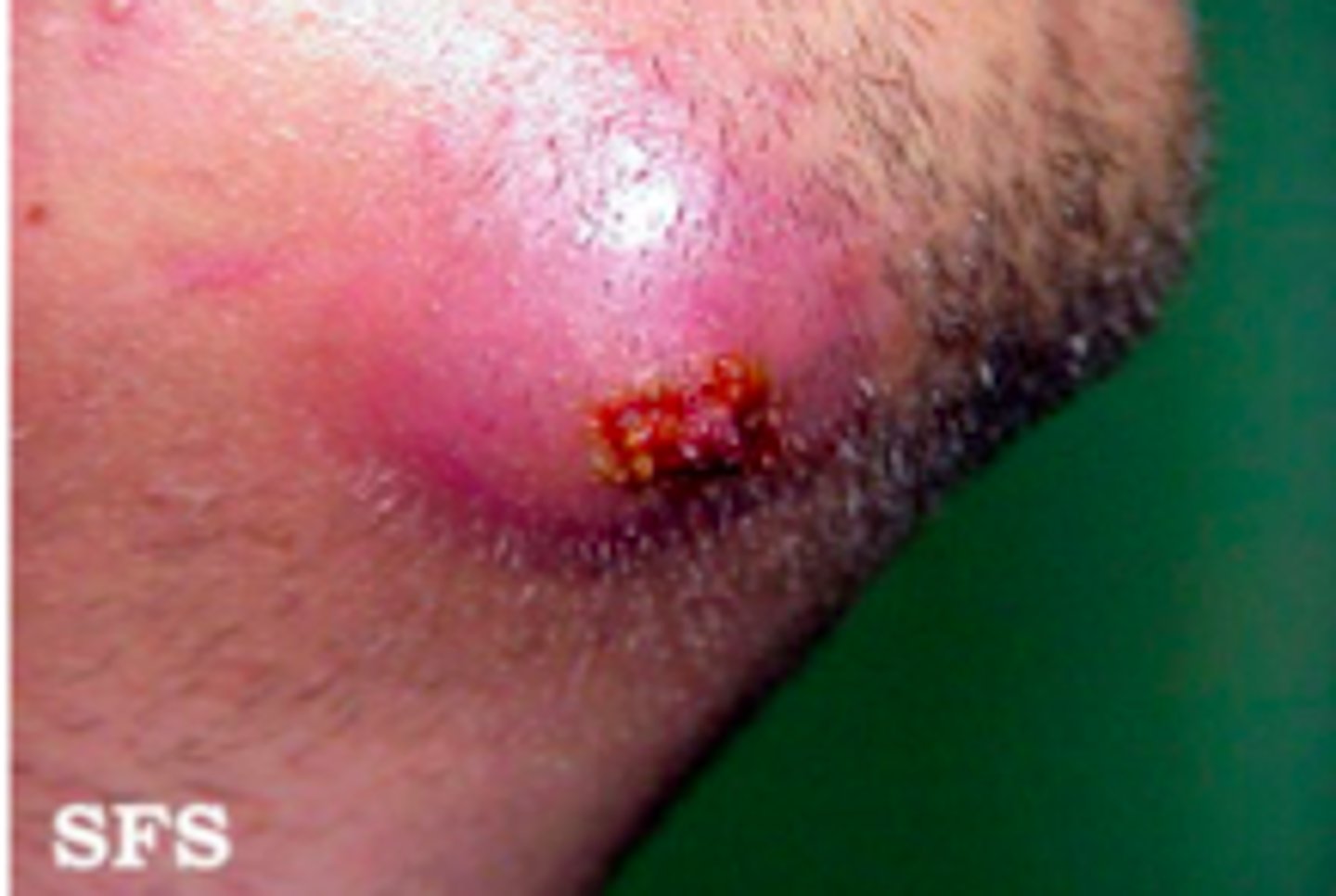
furuncle/carbuncle
Bacterial Skin Infections:
- lasts days/months
- throbbing pain, very tender to the touch
- possible fever, malaise
- regional lymphadenopathy!!!!
- large, erythematous, warm, fluctuant nodule
- S. aureus (again)
staph aureus
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What is the bacteria that will cause a furuncle/carbununcle infection?
furuncle
Bacterial Skin Infections:
acute, red, hot, tender nodule or abscess that evolves from a folliculitis

carbuncle
Bacterial Skin Infections:
a deeper infection composed of interconnecting furuncles
- "boil," "abscess"
- gram stain (gram-positive cocci)
- bacterial culture (S. aureus)
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are the lab findings we see when we try to Dx furuncles/carbuncles?
- I & D w/packing
- systemic Abx based on culture (PCN, cephalosporin, fluoroqinolone)
- warm compresses/analgesics for pain
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are some treatments recommended for furuncles/carbuncles?
cellulitis
Bacterial Skin Infections:
- inflammation & infection of the dermal & subcutaneous tissues (deeper!!!)
- caused by S. aureus and B. hemolytic streptococci in adults (HiB in children)
- red, hot, tender area of skin originating at the site of bacterial entry
- may have a prodrome (malaise, anorexia, fever)
- will see erythema, warmth, and edema of the affected skin
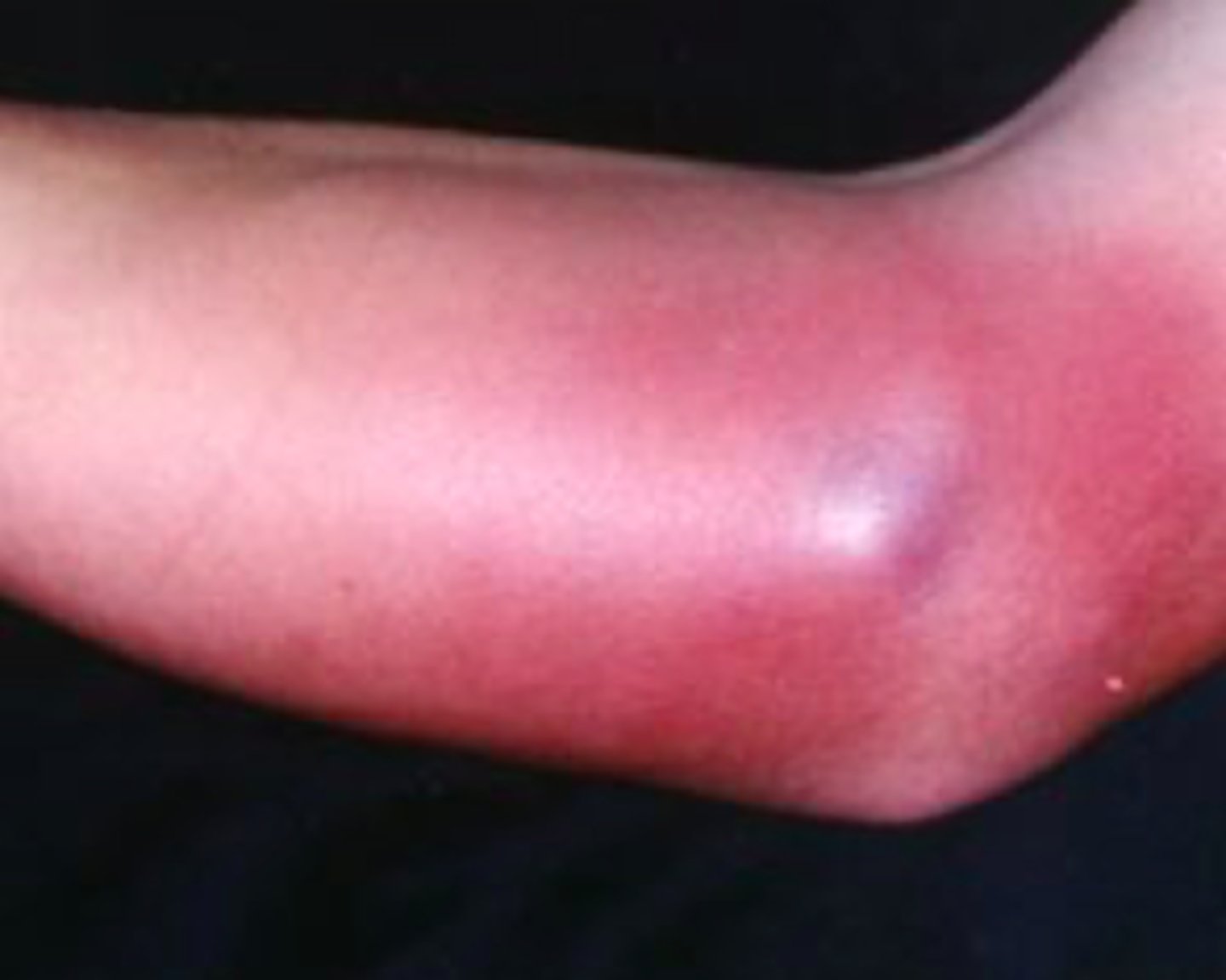
ersipelas
Bacterial Skin Infections:
- inflammation & infection of the upper layers of the skin (more superficial)
- caused by S. aureus and B. hemolytic streptococci in adults (HiB in children)
- red, hot, tender area of skin originating at the site of bacterial entry
- may have a prodrome (malaise, anorexia, fever)
- erythema, warmth, & edema of affected skin
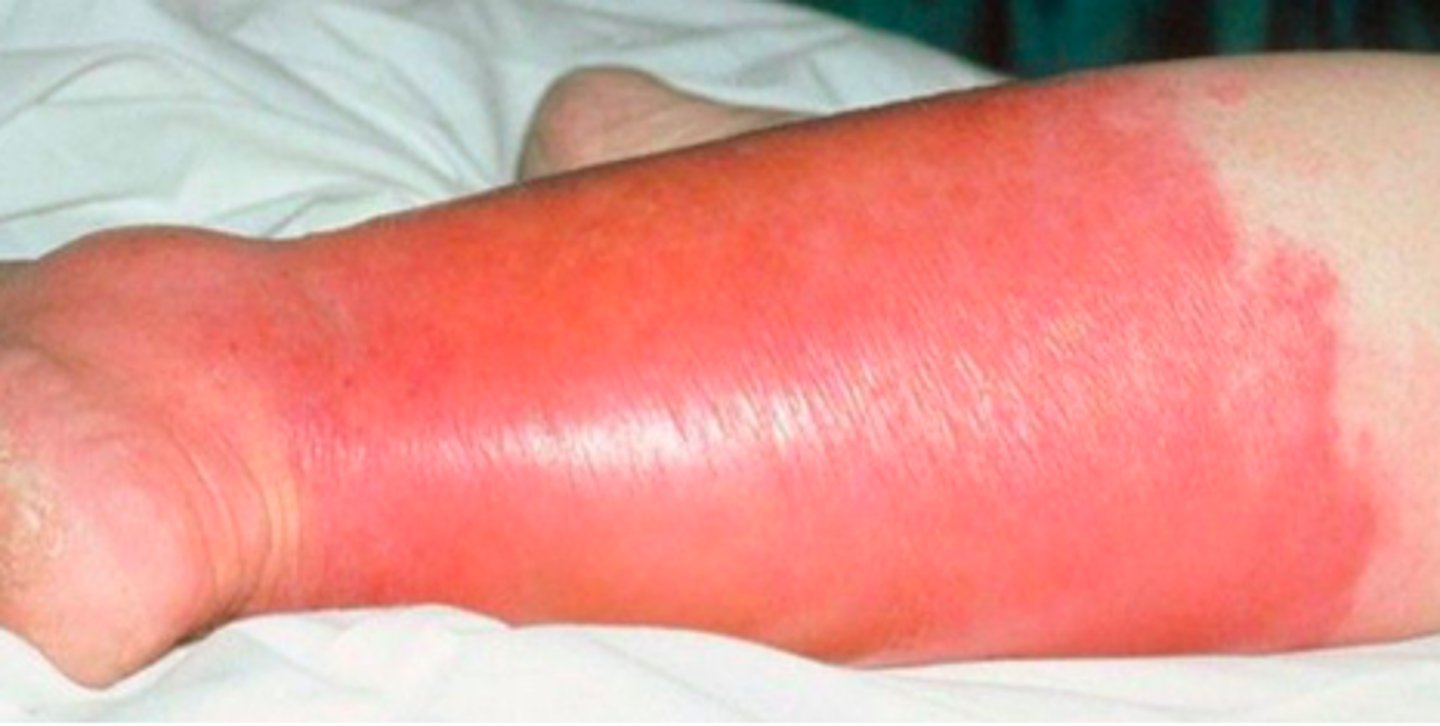
S. aureus, beta-hemolytic streptococci
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are some of the common bacteria that can cause cellulitis/erysipelas in adults?
S. aureus, beta-hemolytic streptococci, hemophilus influenza B
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are some of the common bacteria that can cause cellulitis/erysipelas in children?
cellulitis
Bacterial Skin Infections:
If a patient presented with the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
-effecting dermal and SQ layer
- prodrome of malaise, anorexia, fever
- blanchable, non bilateral acute infection
- erythema, warmth, and edema of 1 portion of skin; not very well-demarcated
- pain & tenderness at the site
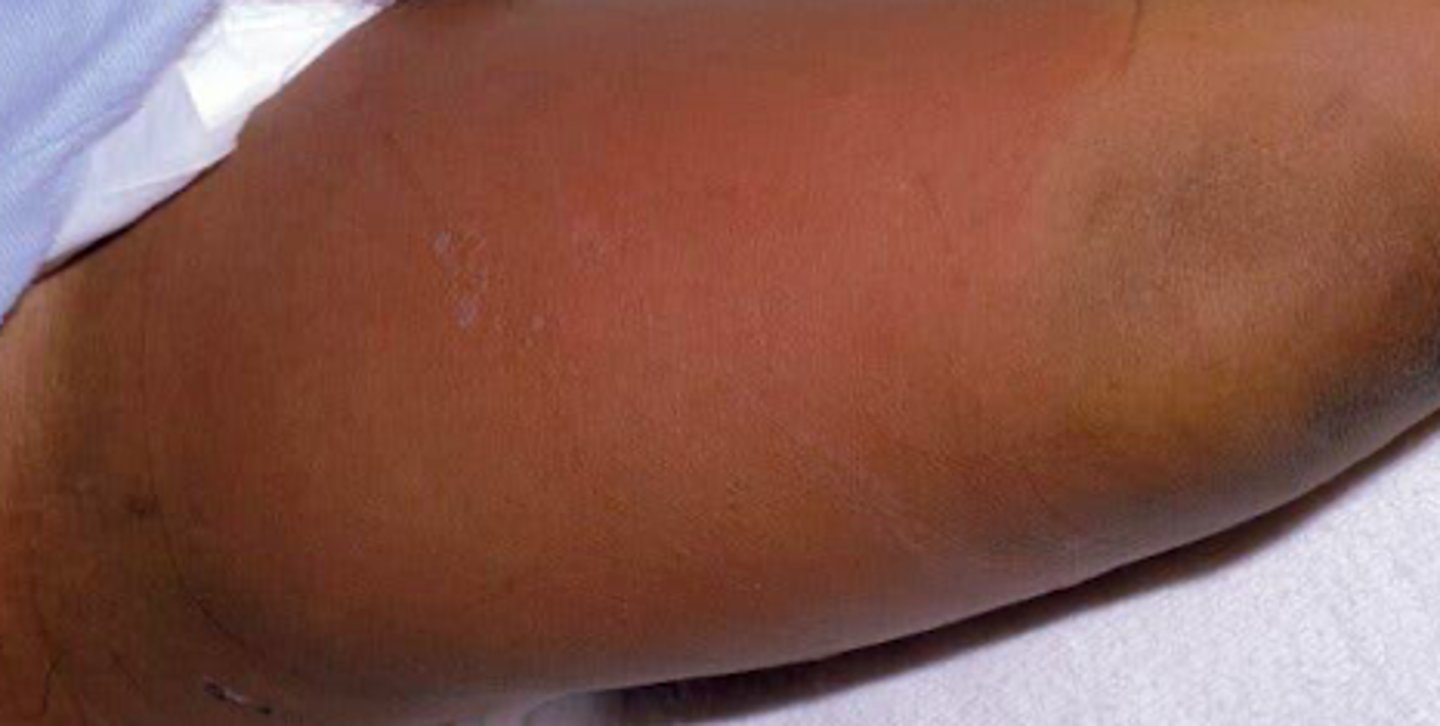
erysipelas
Bacterial Skin Infections:
If a pt presented w the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
-effecting epidermis layer
- prodrome of malaise, anorexia, fever
- erythema, warmth, shiny, and edematous plaques; very well-defined
- pain at site
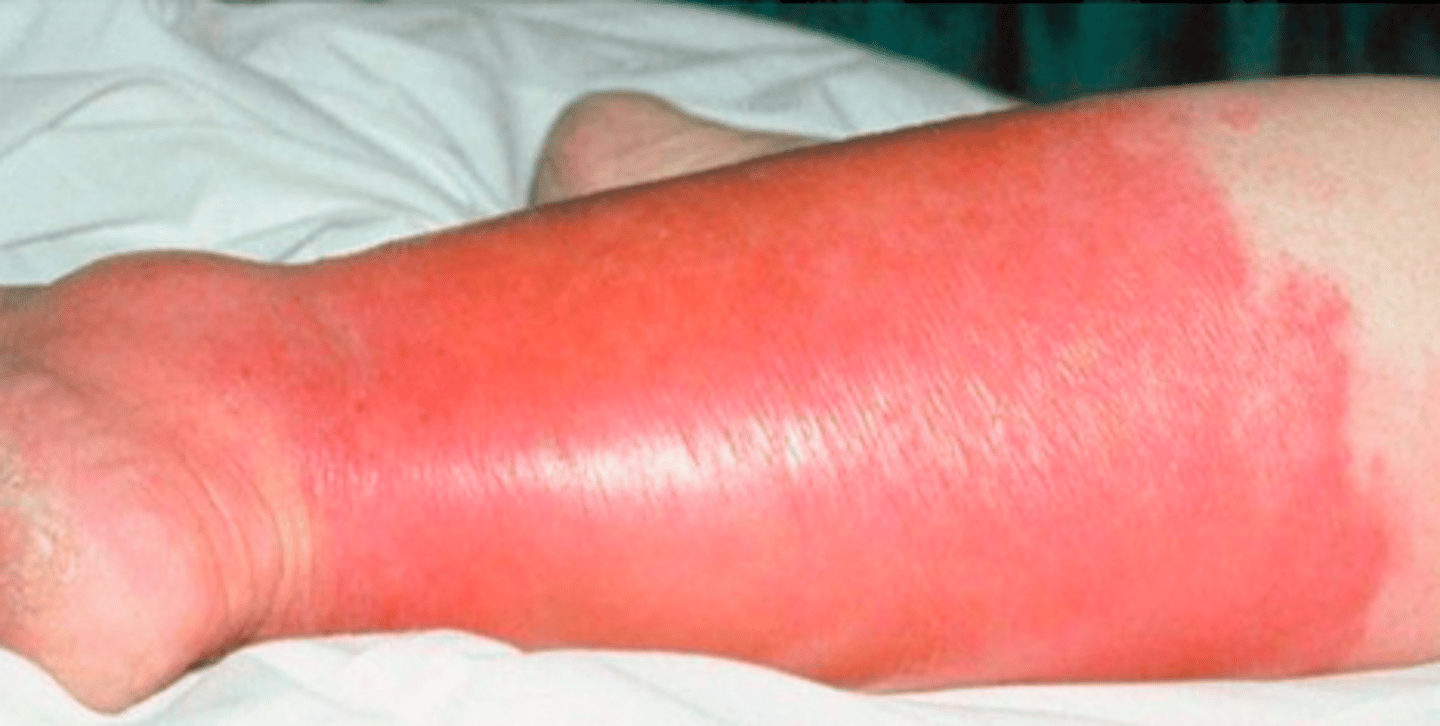
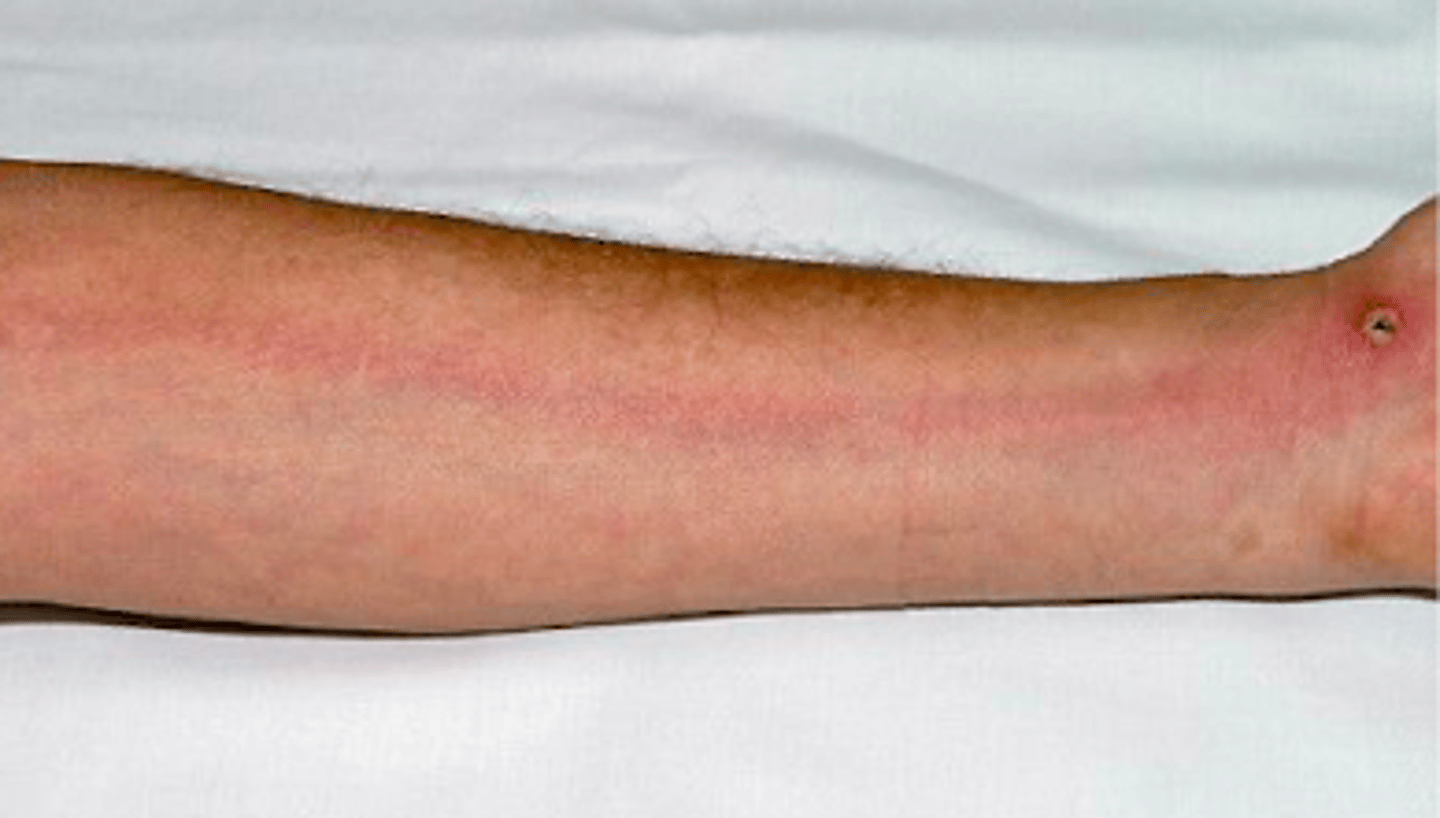
lymphangitis
Bacterial Skin Infections:
-also called cat scratched fever
described as "streaking" on PE - indicates development of cellulitis (deeper, so enters the lymph vessels) - NEED IV ABX
- supportive care (rest, elevation, analgesia)
- dressings: wet-to-dry, sterile saline dressings to remove purulent & necrotic material
- oral Abx (usually PCN-based and/or broad spectrum Abx)
- if severe, IV Abx (lymphangitis)
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are the recommended management and pharmacological treatments of cellulitis/erysipelas?
IV Abx
Bacterial Skin Infections:
If a patient with cellulitis that is on oral antibiotics, and they present with the following S/S, what is our next step of treatment:
- rapidly spreading lesions
- lymphangitis
- high fever
- comorbid Dx (diabetes mellitus, HIV, etc.)
mark the areas with permanent marker to observe worsening!!!
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What is an important aspect of cellulitis and erysipelas monitoring?
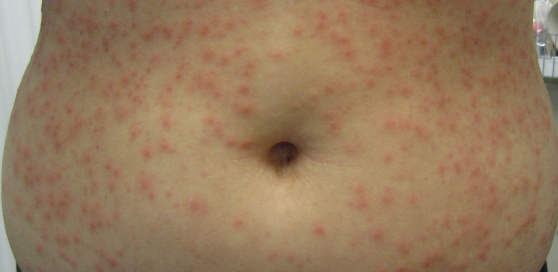
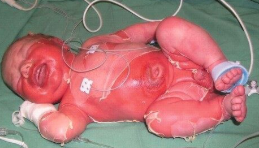
Staph-Scalded Skin Syndrome
Bacterial Skin Infections:
young babies/children affected!!
- S. aureus produces exfoliative toxins, usually secondary to conjunctivitis, otitis media, nasopharyngeal colonization, bullous impetigo
- will see tenderness to erythematous areas, fever, and irritability
- will have ill-defined erythema with fine, sandpaper appearance; eventually painful skin and superficial sloughing and skin appearing wrinkled
staph-scalded skin syndrome
Bacterial Skin Infections:
If an 8-month old patient presented w the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
- fever & irritability
- ill-defined, tender erythema with fine, sandpaper appearance on epidermis
- painful and superficial sloughing skin
- skin appears wrinkled
False!! actually resolves very quickly and leaves very little scarring (only takes about a week to heal)
Bacterial Skin Infections:
True/False:
In staph-scalded skin syndrome, babies and infants, even after treatment, often are affected in the long term by scarring and slow healing.
S. aureus
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What bacteria causes staph-scalded skin syndrome?
- oral Abx
- baths & cool compresses to make the babies feel better :((((
- hydration!!
- if severe, hospitalization w/ IV fluids/Abx if severe
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are the recommended treatments for patients with staph-scalded skin syndrome?
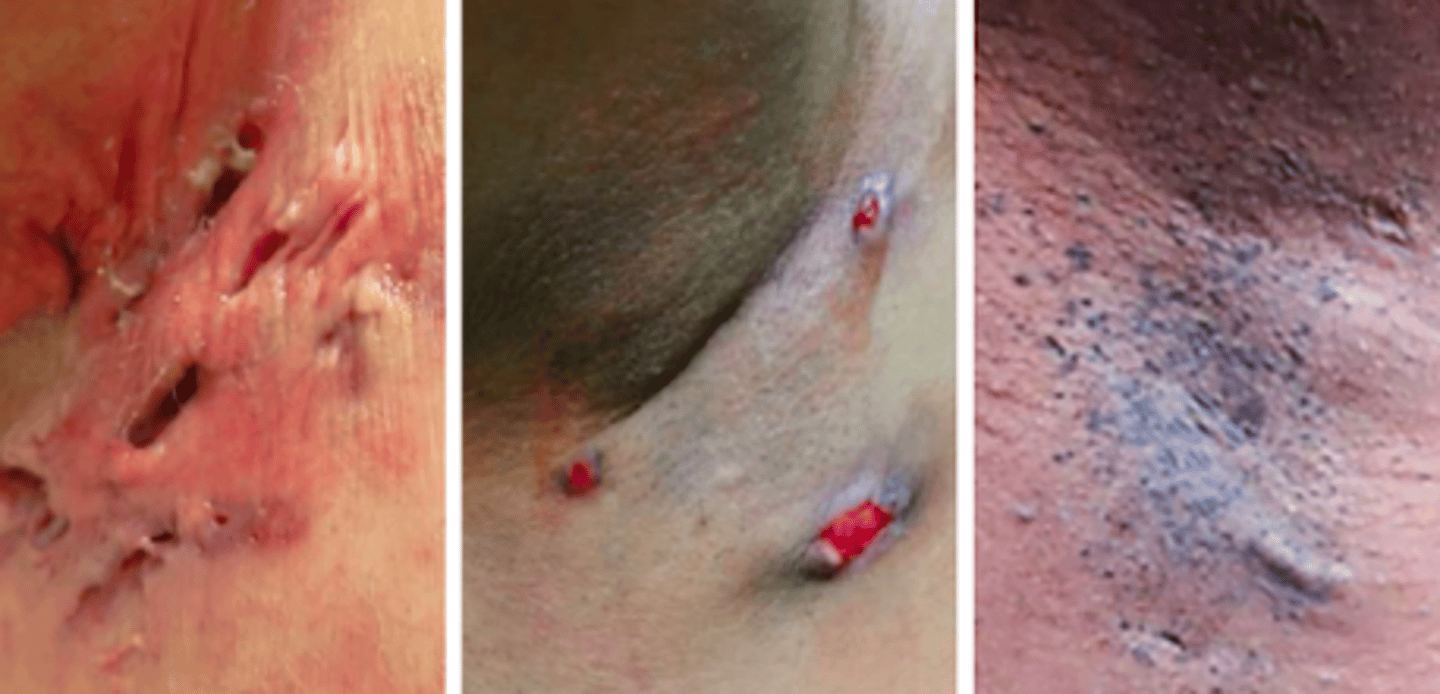
hidradenitis suppurativa
Bacterial Skin Infections:
- chronic, suppurative disease of apocrine gland-bearing skin
- involves mostly the axillae & anogenital region
- common predisposing factors include obesity, women, black patients, cigarette smoking
- onset: puberty
- will have intermittent pain & marked point tenderness related to abscess
- initial lesion is very tender, red, inflammatory nodule/abscess
hidradenitis suppurativa
Bacterial Skin Infections:
If a patient presented w the following S/S, what may you suspect they have:
- initial lesion that is very tender, red, inflammatory nodule/abscess
- open comedones or double comedones (giant dilated pores)
- tender sinus tract
- smelly pus drains from the opening of the abscesses & sinus tract
- hypertrophied, keloided scars from old lesions
various pathogens!! S. aureus, strep, E. coli, proteus, pseudomonas
Bacterial Skin Infections:
When we are trying to Dx hidradenitis suppurativa, what are the common pathogens we may find on lab findings?
Very mild disease to severe all possible
will usually go into remission in mid-30s
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What is the course/prognosis of HS? When do we start to see remission?
- I & D
- intralesional triamcinolone injections
Bacterial Skin Infections:
For acute painful lesions, what are the recommended treatments for HS?
- oral Abx (erythromycin, tetracycline, minocycline, clindamycin)
- prednisone tapers to calm it down
- accutane? may stop oil production
- Biologics!!!! (Infliximab, Humira, Enbrel)
Bacterial Skin Infections:
For chronic lesions, what are the recommended treatments for HS? (really mostly just need to know 1)
- I & D (okay for 1-2 acute lesions)
- excise nodules & sinus tracts
- complete excision of axilla/anogenital region
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are some common surgical treatments for HS?
(not always recommended)
pilonidal cyst
Bacterial Skin Infections:
- abnormal pocket of skin that usually contains hair & skin debris
- located at the superior gluteal cleft
- PCs usually occur from an inflammatory reaction that contains a foreign body (usually hair)
- resulting abscess is VERY PAINFUL
- recurrent (if no surgery) and common in people who sit for long periods of time
pilonidal cyst
Bacterial Skin Infections:
If a pt presented w the following S/S, what may you suspect they have:
- erythematous, painful nodule with smelly drainage of pus/blood from an opening in the skin above the gluteal cleft
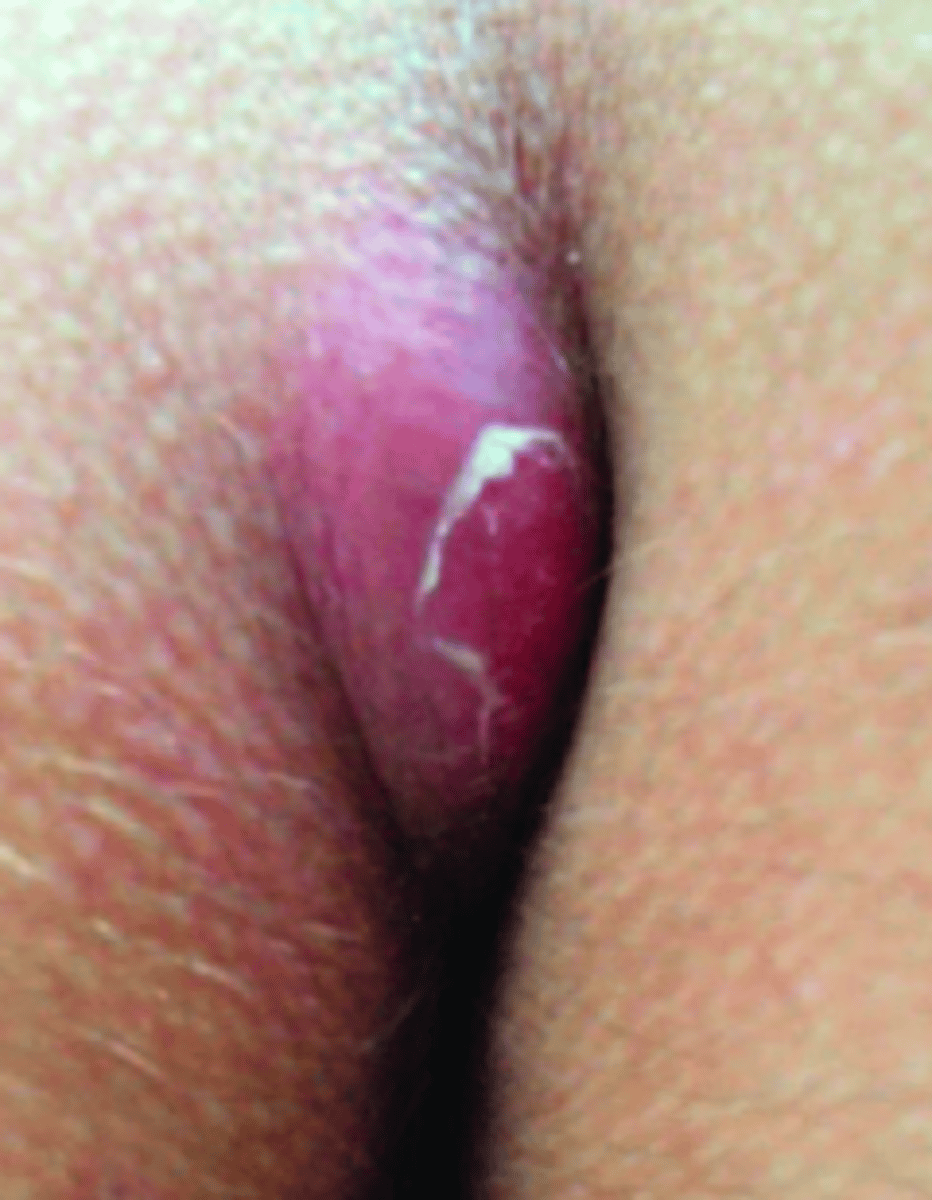
- I & D and packing bc they are deep
- surgical excision!!! (without this, will COME BAAACKKKKK)
Bacterial Skin Infections:
What are the recommended treatments for pilonidal cysts?
molluscum contagiosum
Viral Skin Infections:
- self-limited epidermal viral infection
- skin-to-skin contact
- asymptomatic, but (mostly parents) concerned about cosmetic disfigurement, painful if infected
- presents as pearly white or skin-colored papules or nodules, round and umbilicated
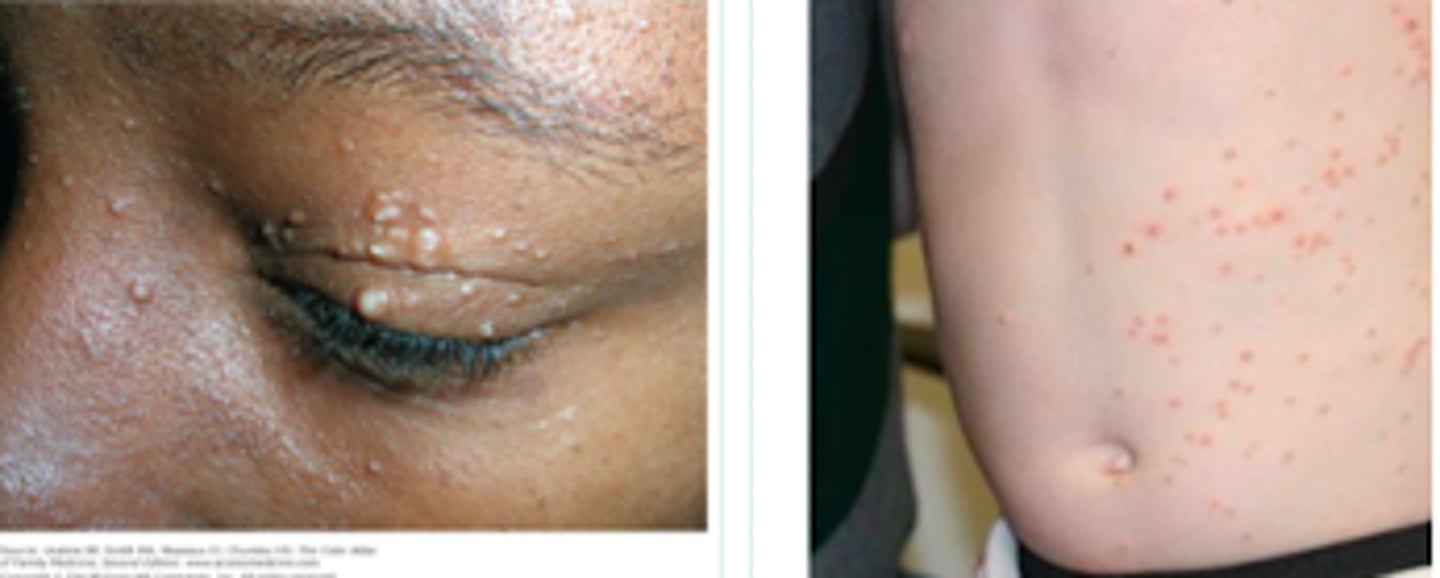
Children, Sexually active adults, and immunocompromised pts
Viral Skin Infections:
What are the risk groups for Molluscum Contagiosum?
molluscum contagiosum
Viral Skin Infections:
If a pt presented w the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
- history of wrestling (skin-to-skin contact)
- asymptomatic, but interesting skin findings
- pearly white or skin-colored papules/nodules that are round & umbilicated
- larger lesions have a central necrotic plug
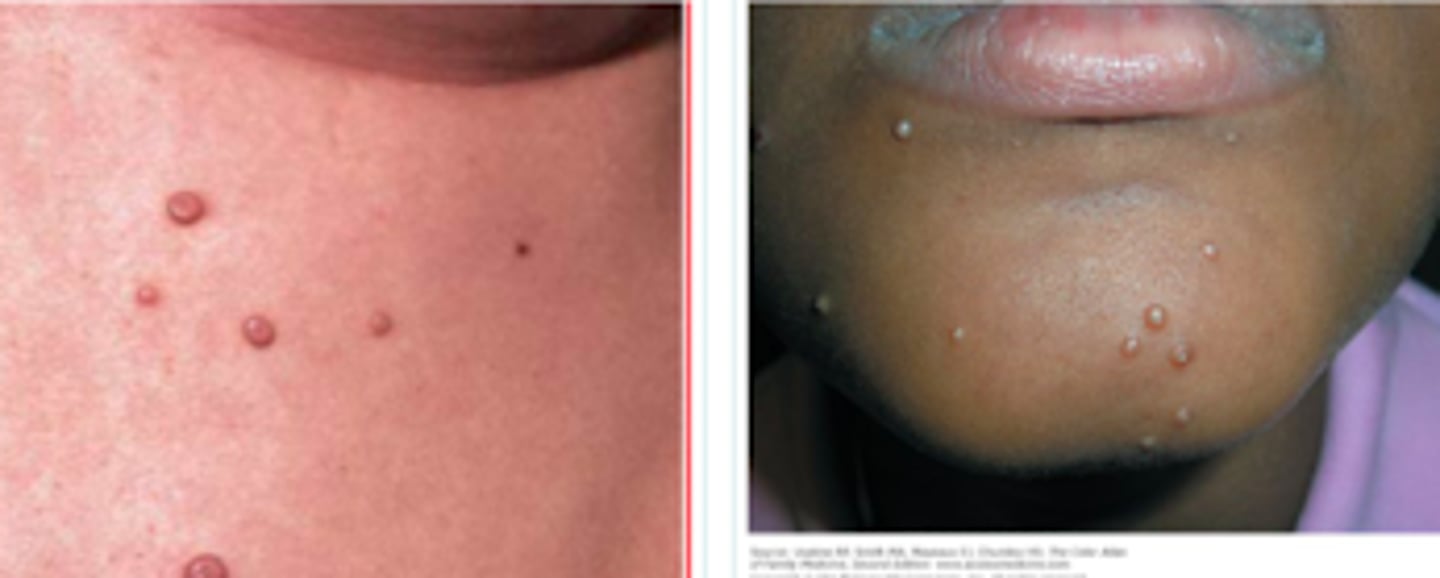
clinical Dx!!
Viral Skin Infections:
How do we Dx molluscum contagiosum?
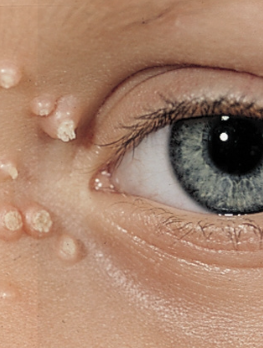
no management/treatment usually!!
self limited (take months to years though)
- avoid skin-to-skin contact
- for cosmetic reasons, can perform curettage (painful), cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen), topical therapies (salicylic acid, imiquimod, apple cider vinegar, retinoid)
Viral Skin Infections:
What are the management methods for molluscum contagiosum?
verruca
Viral Skin Infections:
aka warts
- discrete, benign epithelial hyperplasia w surface hyperkeratosis
- caused by human papillomavirus (HPV)
- skin-to-skin contact transmission
- don't usually get healed easily (can last for years if untreated)
human papillomavirus (HPV)
Viral Skin Infections:
What is the virus that causes verruca?
Verruca vulgaris: common wart
Verruca plantaris: plantar wart
Verruca plana: flat wart
Filiform verruca: finger-like projections
Viral Skin Infections:
What are the different types of Verruca?
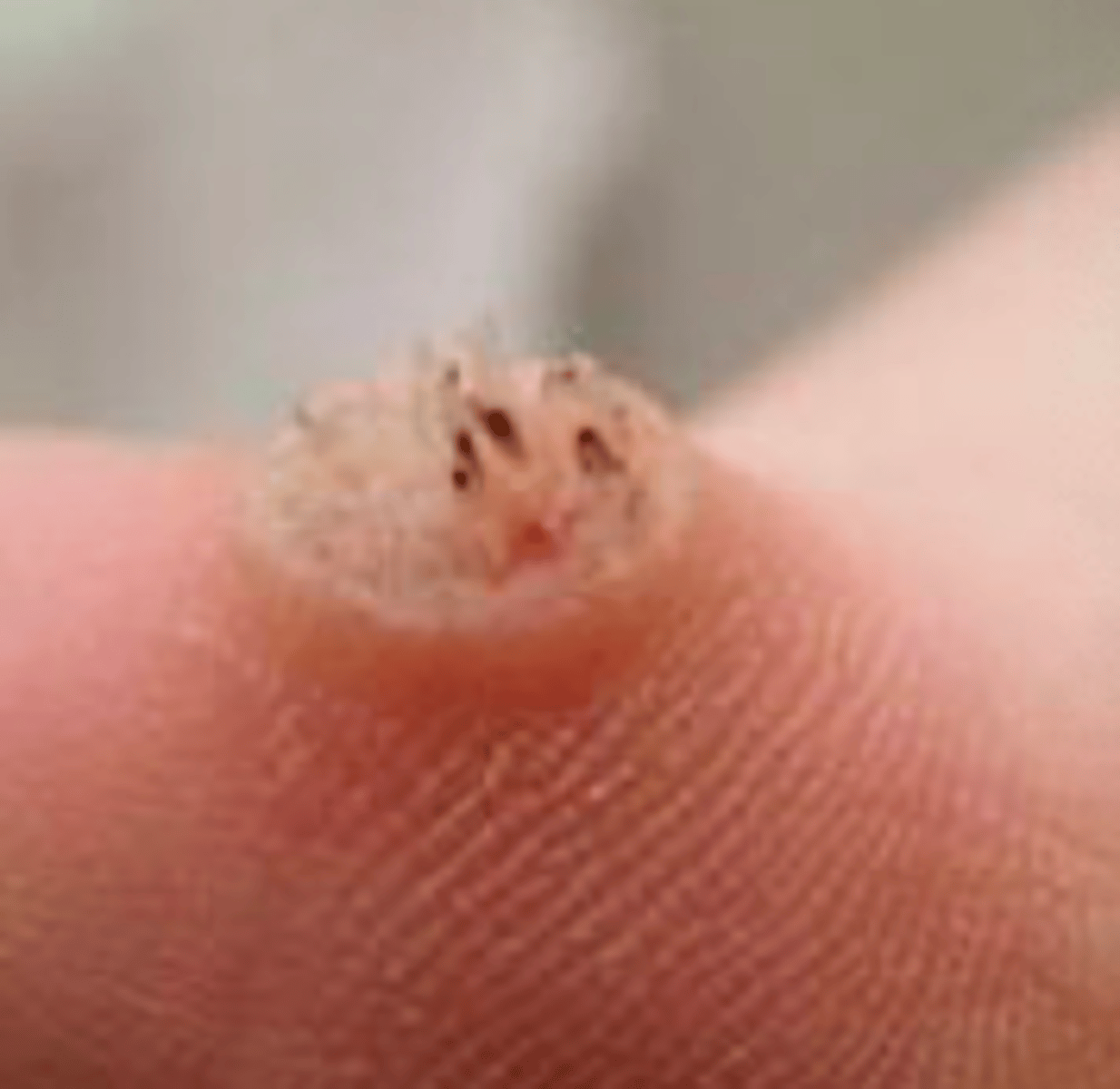
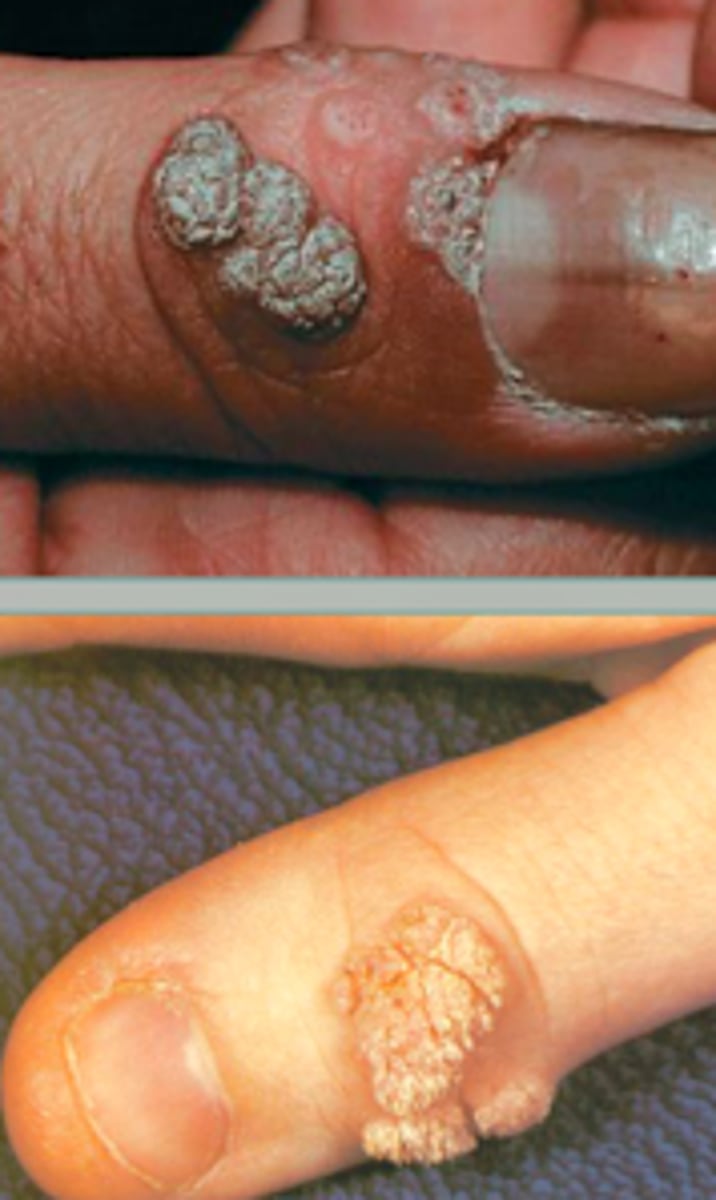
verruca vulgaris
Viral Skin Infections:
a common wart
- hyperkeratotic, firm papules
- clefted surface with vegetations
- red/brown dots: thrombosed capillaries
-when on palms, it can disrupt fingerprints
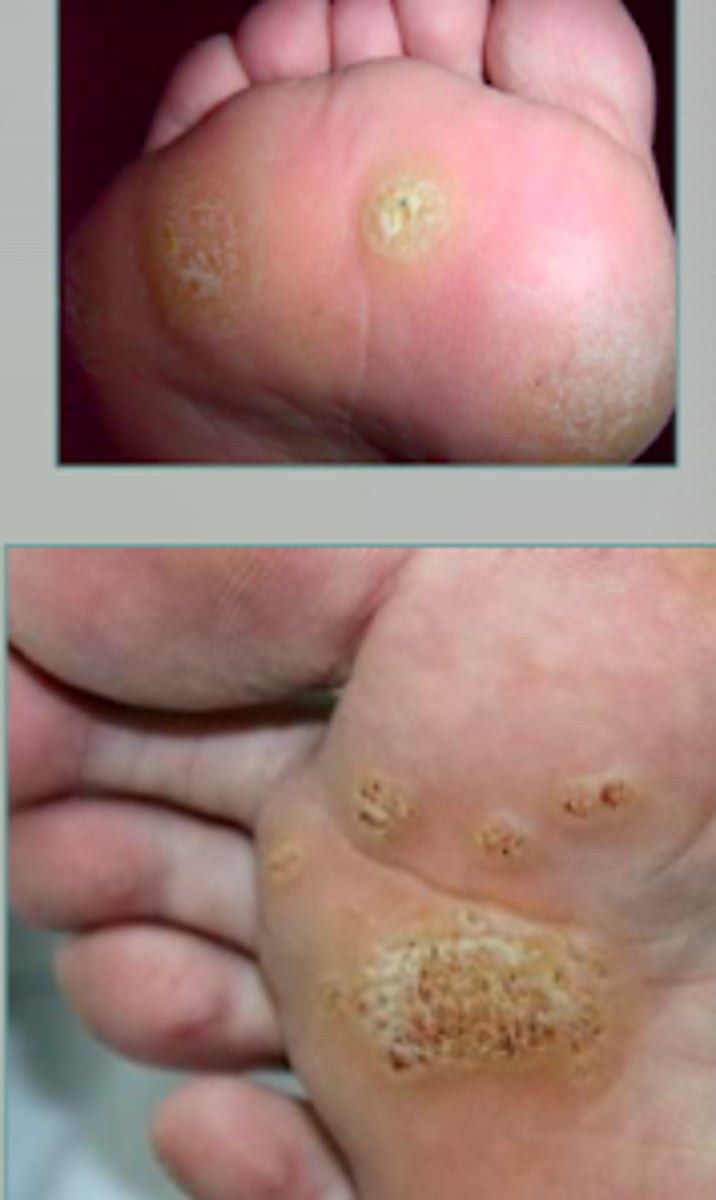
verruca plantaris
Viral Skin Infections:
plantar wart
- skin-colored verrucous papules
- marked tenderness to palpation
- found on plantar surface of feet usually
- tend to coalesce
hard to treat
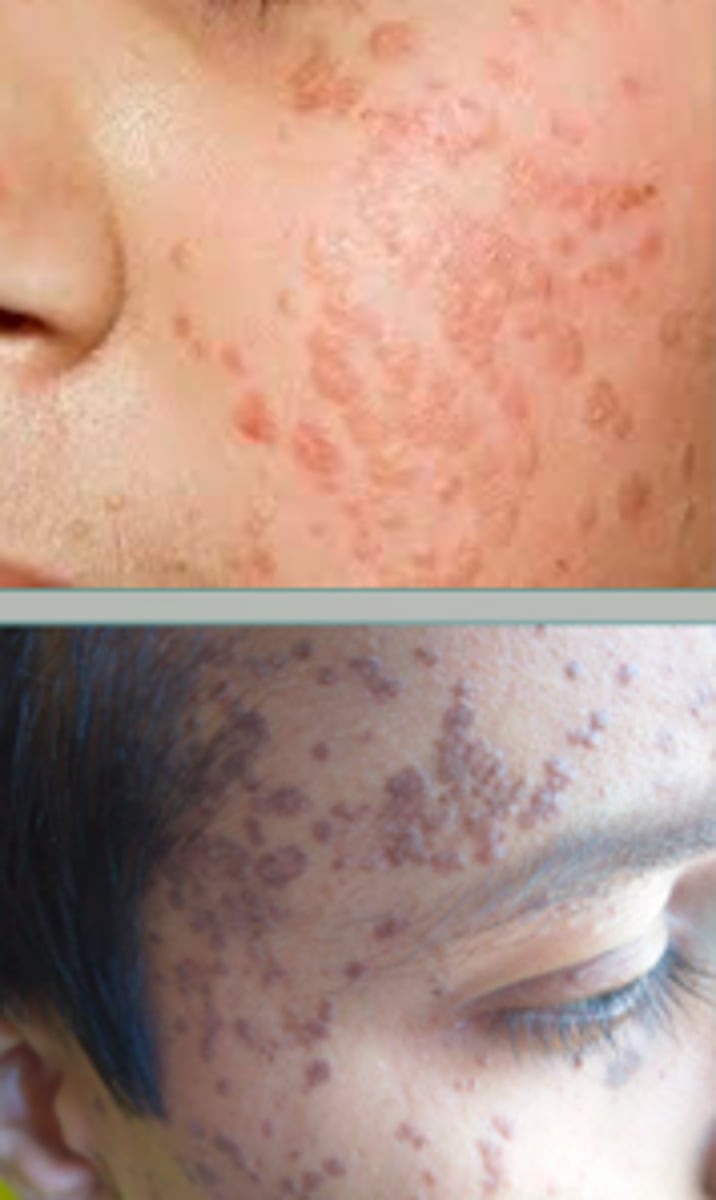
verruca plana
Viral Skin Infections:
- sharply defined, flat-topped papules
- skin-colored to brown
- occur on face, bear area, dorsa of hands, shins
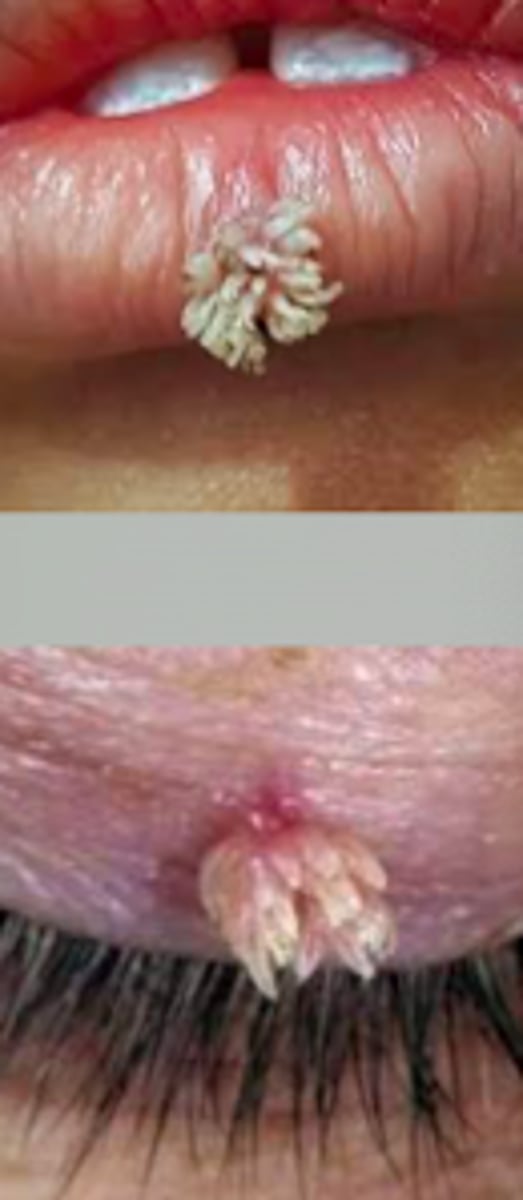
filiform verruca
Viral Skin Infections:
- long, narrow projections 1-2 mm from the skin
- skin-colored to brown
- typically found on eyelids, ears, and lips
- resemble coral reef
- rarely form in clusters
- 10-20% salicylic acid
- imiquimod cream (chemo so be CAREFUL)
- cryosurgery (liquid nitrogen)
- electrosurgery
- surgery
Viral Skin Infections:
What is the treatment recommendation for verruca?
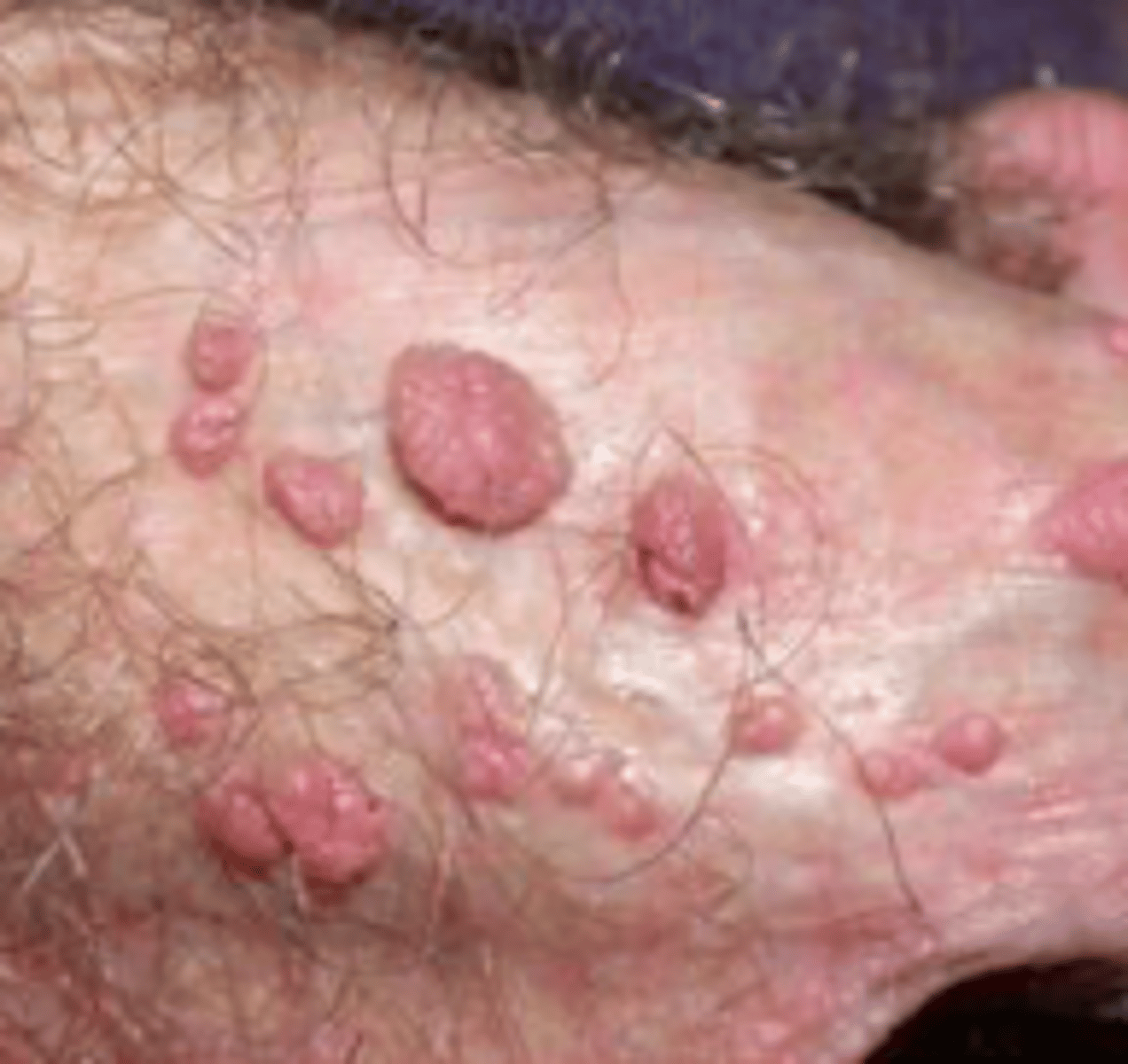
condyloma acuminata
Viral Skin Infections:
aka genital warts
- caused by HPV 6 and 11
- small papules that are "cauliflower-like"
- keratotic, flat-topped, skin-colored to pink
- can be solitary or clustered
prevented by using condoms and getting PAP smears yearly
- cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen)
- topical imiquimod cream (Mon-Wed-Fri at night, wash off in AM)
Viral Skin Infections:
What are the treatments recommended for condyloma acuminata?
HPV Types 6 and 11
Viral Skin Infections:
What are the common strains of HPV that cause condyloma acuminata?
biopsy
Viral Skin Infections:
How do we HAVE TO diagnose condyloma acuminata?
Herpes Simplex
Viral Skin Infections:
- can have Type 1 or Type 2
- usually affects young adults
- skin-to-skin transmission; usually when the person is shedding the virus but lacks the lesion
HSV Type 1: Labialis “cold sore”
Viral Skin Infections:
Type of Herpes Simplex:
causes labialis herpes
- "cold sore"
HSV Type 2: Genital
Viral Skin Infections:
Type of Herpes Simplex:
causes genital herpes
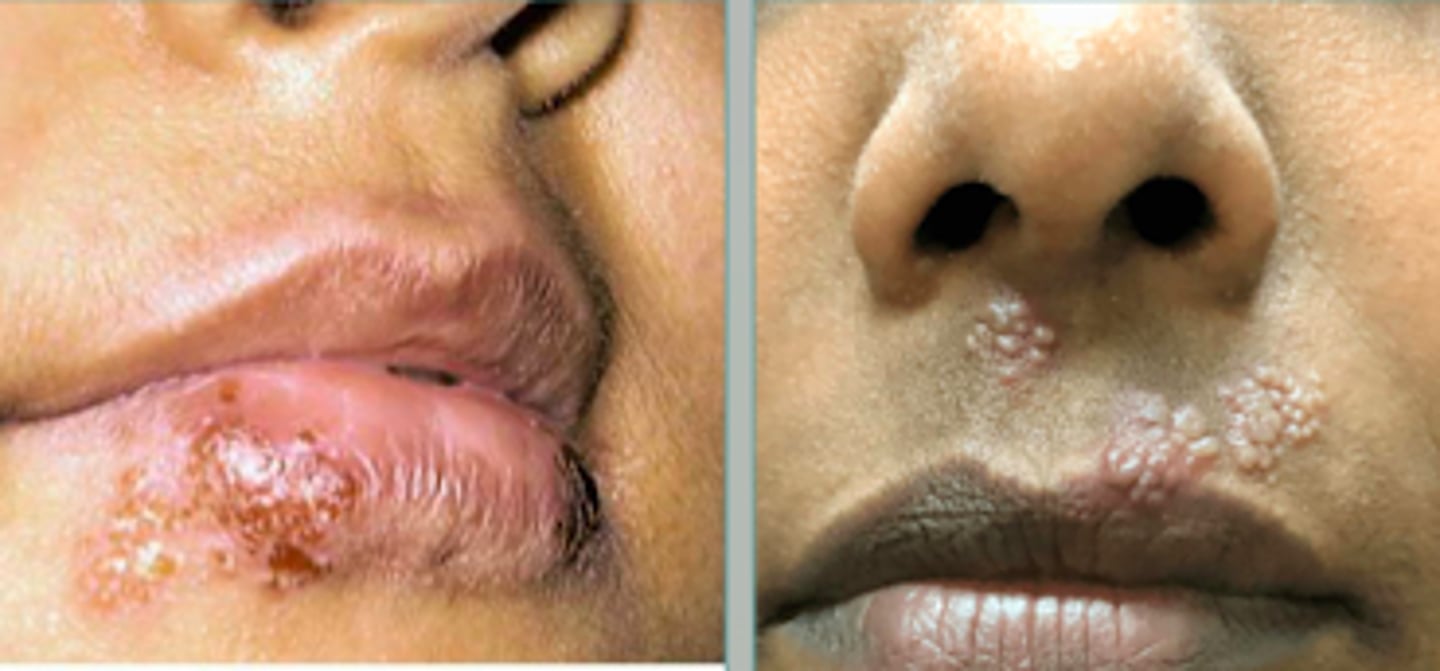
herpes simplex primary infection (specifically HSV Type 1)
Viral Skin Infections:
If a pt presented w the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
- 2-20 day incubation
- often asymptomatic, but this patient has vesicles on their lip
- regional lymphadenopathy
- fever, headache, malaise, myalgia
- resolves in 3-4 days
recurrent herpes
Viral Skin Infections:
If a pt presented w the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
- prodrome of tingling, aching, or burning sensation that precedes the lesion by ~24 hours
- grouped vesicles on erythematous base
- can lead to erosions or crusts
- Tzanck smear (see multinucleated keratinocytes) - fluid from a vesicle smeared on microscope slide, dried, and stained
- viral culture from swabbing lesion fluid
- IgM and IgG Abs
Viral Skin Infections:
How do we diagnose herpes simplex?
multinucleated keratinocytes
Viral Skin Infections:
When we are diagnosing herpes simplex, and we perform a Tzank smear, what will we see on the smear?
- topical antiviral therapy (acyclovir 5%, penciclovir 1%) - minimal efficacy
- oral antiviral therapy (acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir)
heavier dosage for primary episodes rather than recurrent episodes
Viral Skin Infections:
When we are treating herpes simplex, what do we prescribe? What is the difference between the first episode and the recurrent episodes?
Varicella: chickenpox
Herpes Zoster: Shingles
Viral Skin Infections:
What are the 2 different Varicella-Zoster Virus’s?
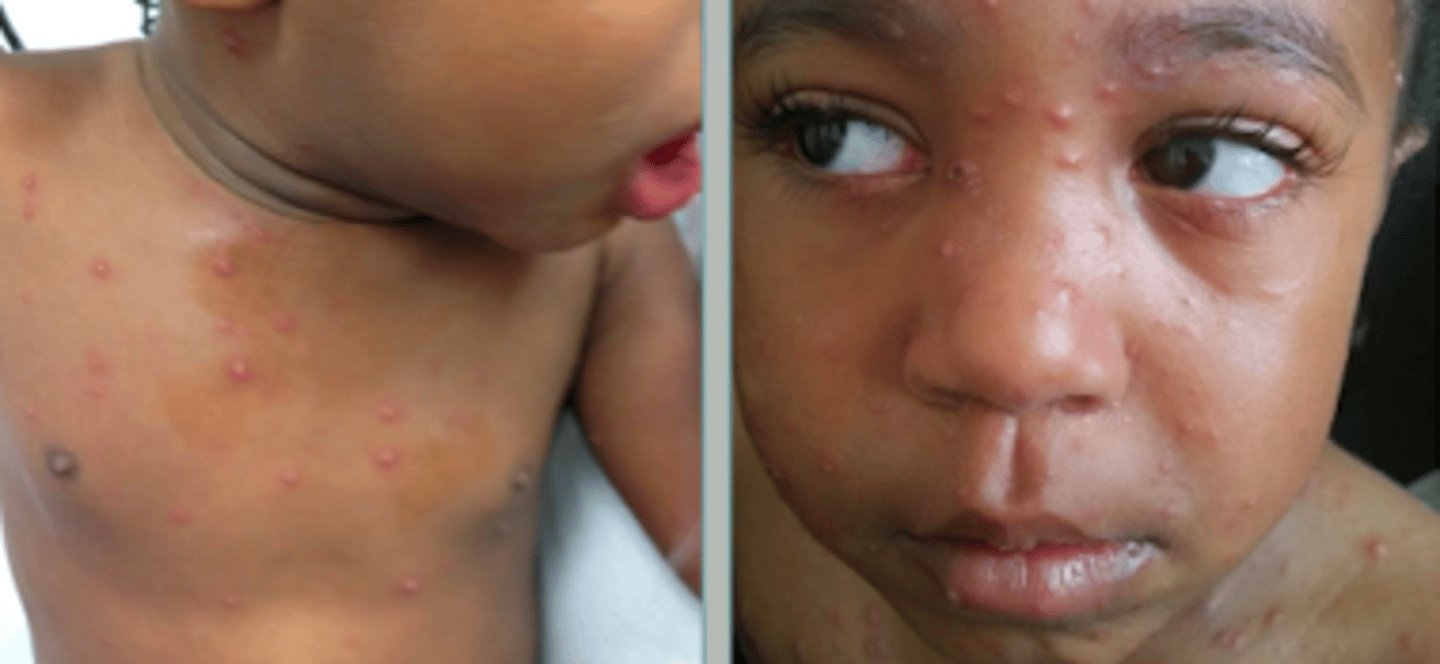
varicella: chickenpox
Viral Skin Infections:
- highly contagious primary infection characterized by pruritic vesicles that evolve into crusts & scars
- mostly affects <10 y/o
- transmission includes direct contact & airborne droplets (VERY contagious even before rash & until the last crop of vesicles crust over)
once the last crop of vesicles scab over
Viral Skin Infections:
When do people become non-contagious anymore in varicella?
varicella: chickenpox
Viral Skin Infections:
If a pt presented w the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
- mild prodrome in children
- papules --> vesicles --> pustules --> crusts --> scars (seeing all stages of evolution simultaneously)
- dew drop on rose petal = vesicle on red base
- started on face & scalp; then spread inferiorly and focus on trunk
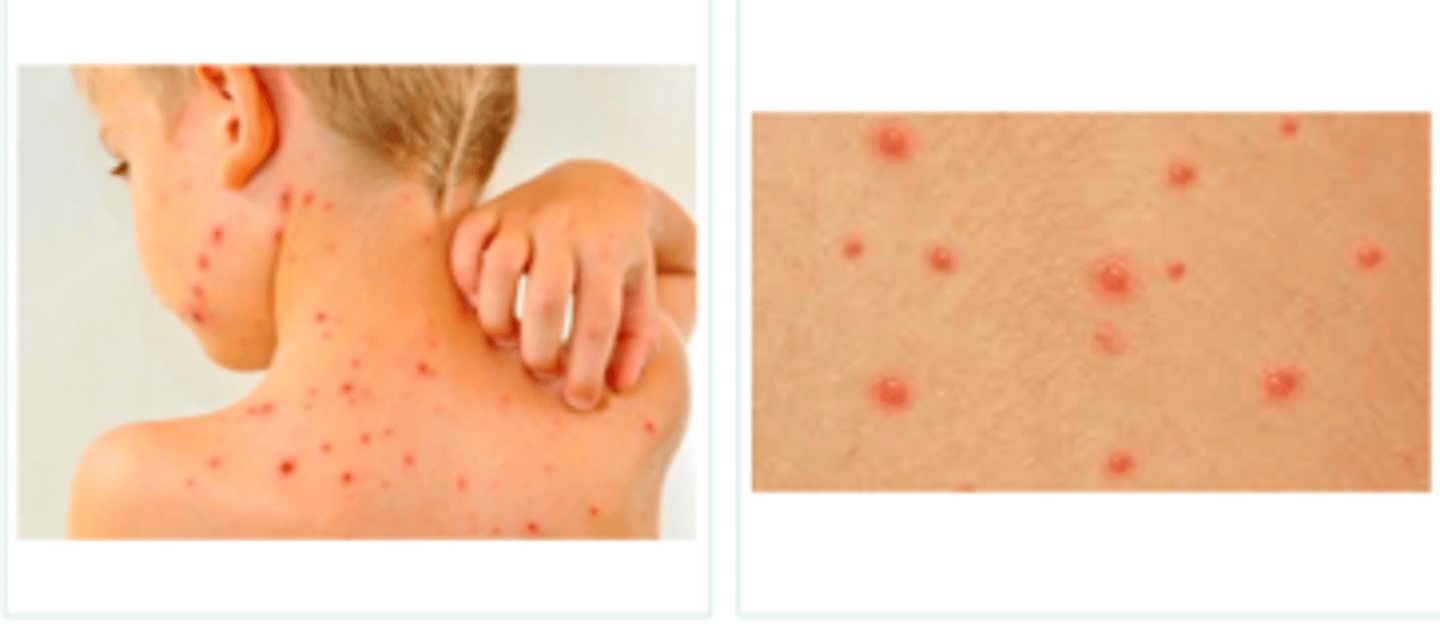
clinical Dx and self-limiting Tx! (may do some symptomatic relief - benadryl, hydrocortisone, calamine lotion, hydration)
May develop secondary bacterial infection from scratching
Viral Skin Infections:
What are the diagnostic and treatment methods in varicella?
herpes zoster: Shingles
Viral Skin Infections:
- active dermatomal infection associated w the reactivation of varicella zoster virus
- characterized by unilateral pain & a vesicular eruption limited to a dermatome innervated by a corresponding sensory ganglia
- can ONLY occur in someone that has previously had chicken pox (>50)
Prodrome: Neurotic pain or paresthesia for 2-3 weeks prior. Allodynia: Heightened sensation to mild sensation
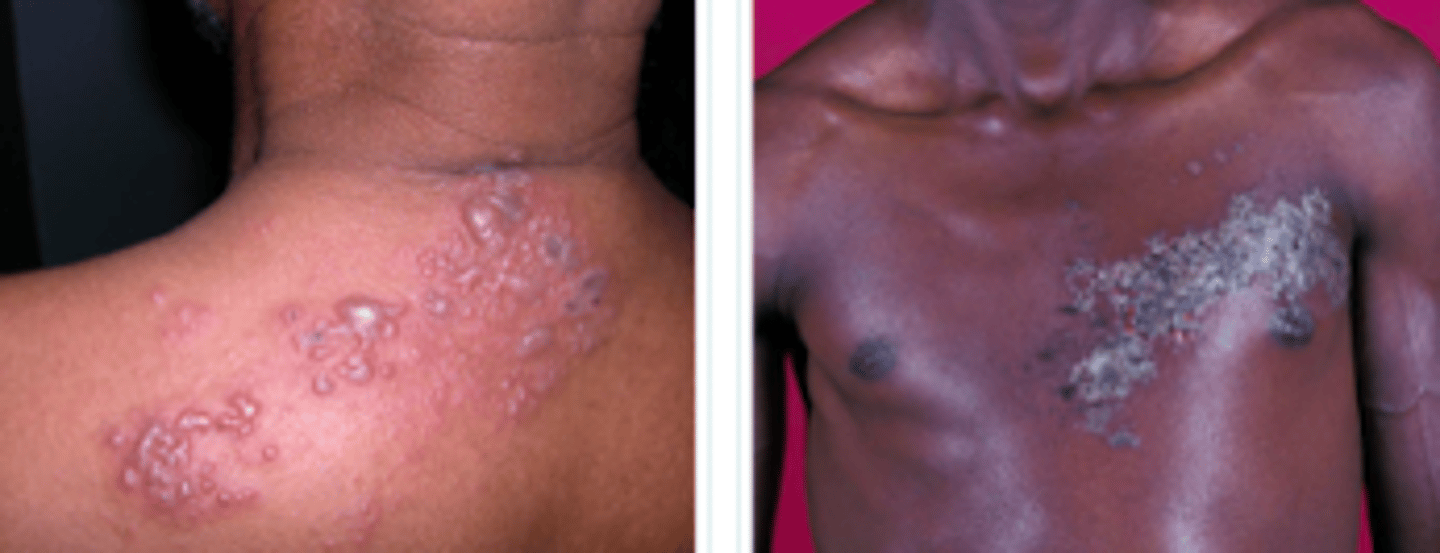
increasing age, immunocompromised, physical/emotional stress
Viral Skin Infections:
What are some common risk factors for the reactivation of herpes zoster, aka shingles?
herpes zoster (aka shingles)
Viral Skin Infections:
If a pt presented w the following S/S, what may we suspect they have:
- neuritic pain or paresthesias for 2-3 weeks prior
- allodynia (heightened sensation to mild stimuli)
- headache, malaise, fever
- papules (24h) --> vesicles/bullae (48h) --> pustules (96h) --> crusts (7-10 days) forming over 1 week within 1 unilateral, dermatomal distribution
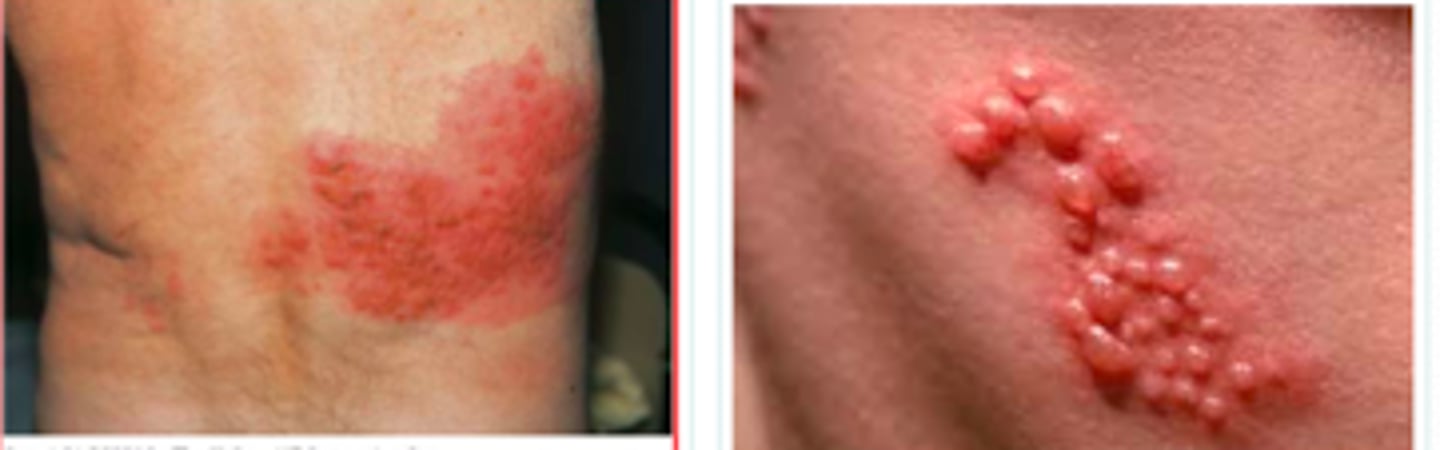
Post-Herpetic Neuralgia
Viral Skin Infections:
the terrible nerve pain that can live with patients after the rash goes away in herpes zoster
- risk of 40% in patients >60 y/o
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
Viral Skin Infections:
type of Herpes Zoster complication:
- involvement of facial and auditory nerves
- can cause lesions in the ear/tympanic membrane, facial paralysis, severe ear pain
- may lead to permanent deafness, vertigo, and facial muscle weakness
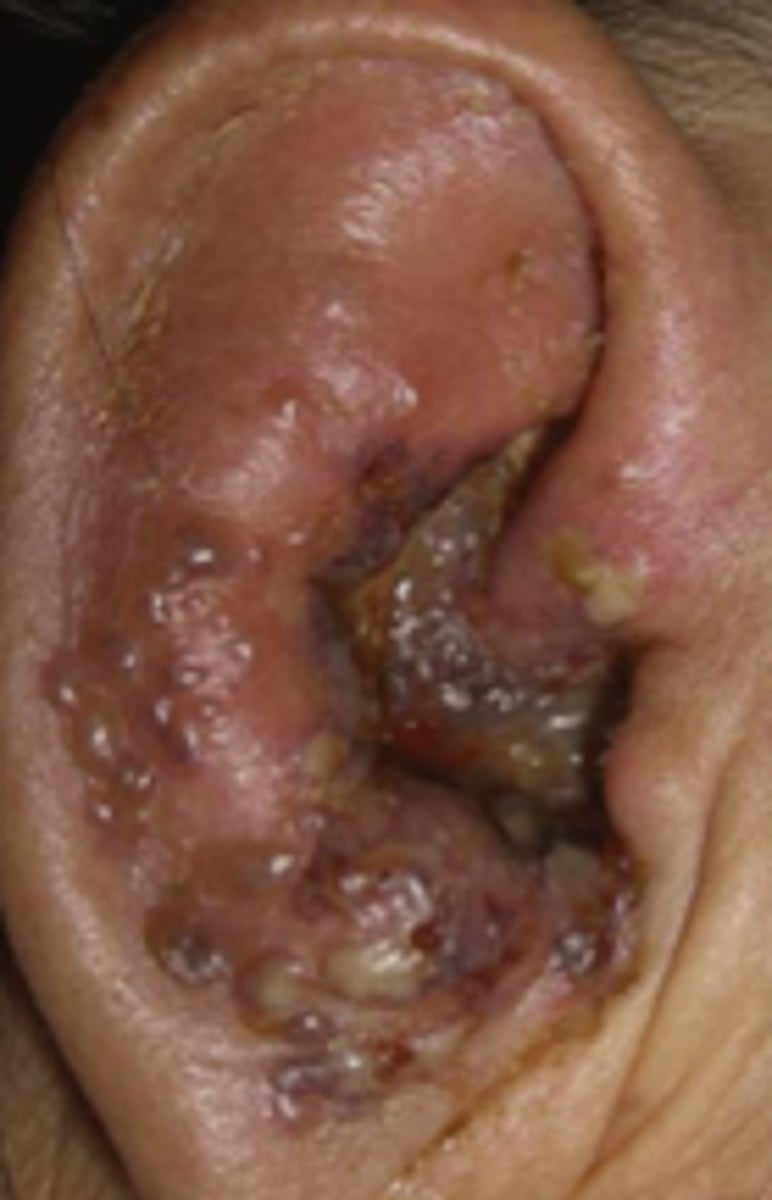
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
Viral Skin Infections:
type of Herpes Zoster complication
- Hutchinson’s Sign: vesicles on tip of nose. eye involvement
- always do fluorescein stain eye when zoster affects face
- can lead to blindness
- REFER TO OPHTHALMOLOGY
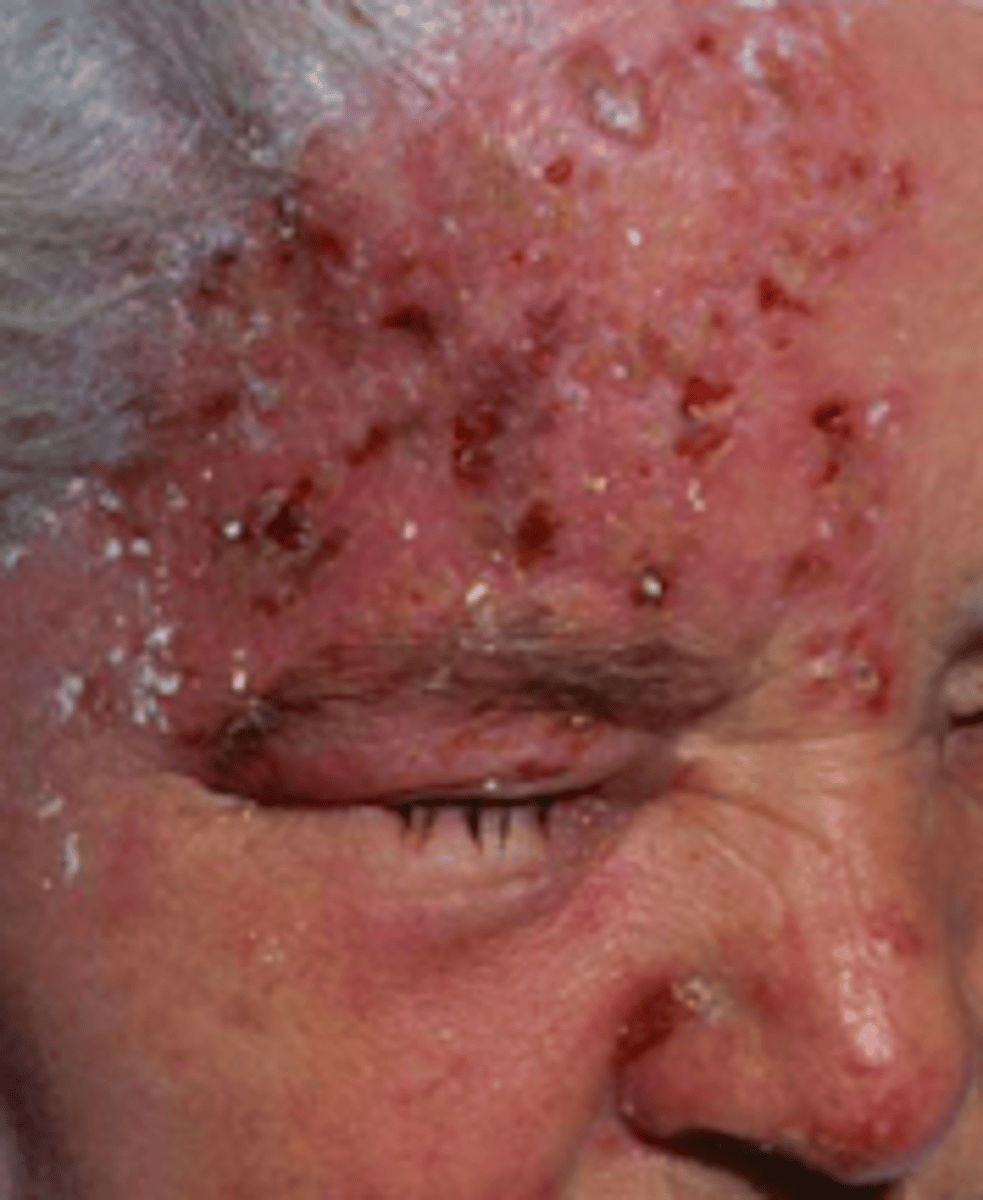
Hutchinson's Sign
Viral Skin Infections:
Herpes Zoster complication (Herpes Zoster Ophthaalmicus)
- vesicles on tip of nose
- suggests eye involvement!!!
- antiviral therapy EARLY (acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir)
- pain management (gabapentin, lidocaine patch 5%, Narcotic pain management)
Viral Skin Infections:
What are some common treatments for herpes zoster?
vaccine available for patients 50+
Viral Skin Infections:
What is the best prevention for herpes zoster?
dermatophytes
Fungal Skin Infections:
a group of fungi that synthesize keratinases that digest keratin & sustain existence of fungi
topical and systemic chronic steroid use!!!
Fungal Skin Infections:
What is a host factor that facilitates dermatophyte infections, which means we often see fungal infections in patients that use these?
sweating, occlusive clothes, occupational exposure, high humidity
Fungal Skin Infections:
What are some local factors that facilitate dermatophyte infections?
tinea pedis
Fungal Skin Infections:
- dermatophyte infection of the foot characterized by erythema, scaling, and maceration
- can start in feet and spread to inguinal areas, trunk, or hands
- can cause breaks in the skin & allow secondary bacterial infections
-ages 20-50 and more common in males
walking barefoot on contaminated floors
Fungal Skin Infections:
How do we transmit tinea pedia (aka athlete's foot) from one person to another?
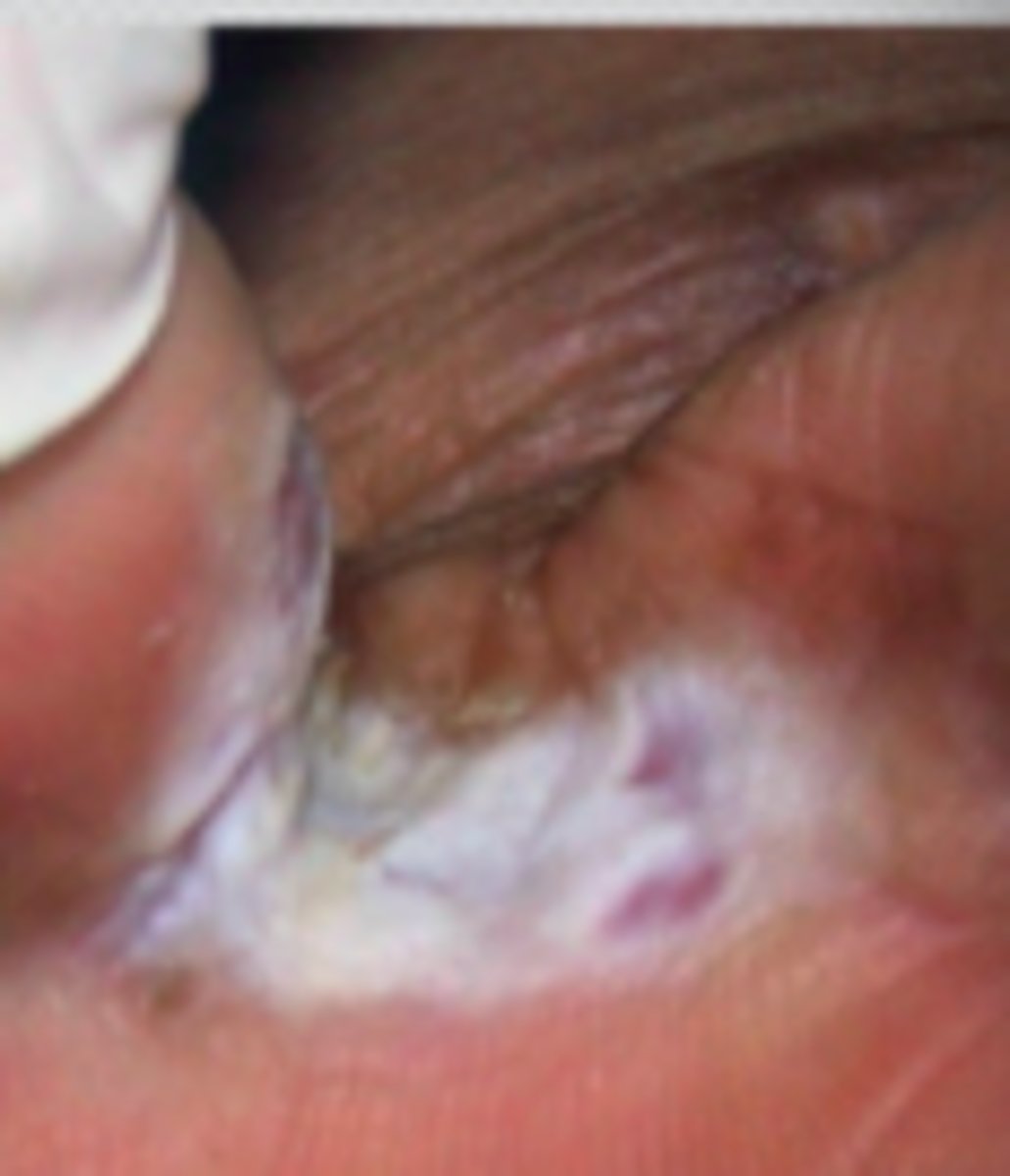
interdigital type
Fungal Skin Infections:
Type of Tinea Pedis:
- maceration, peeling, fissuring of toe webs
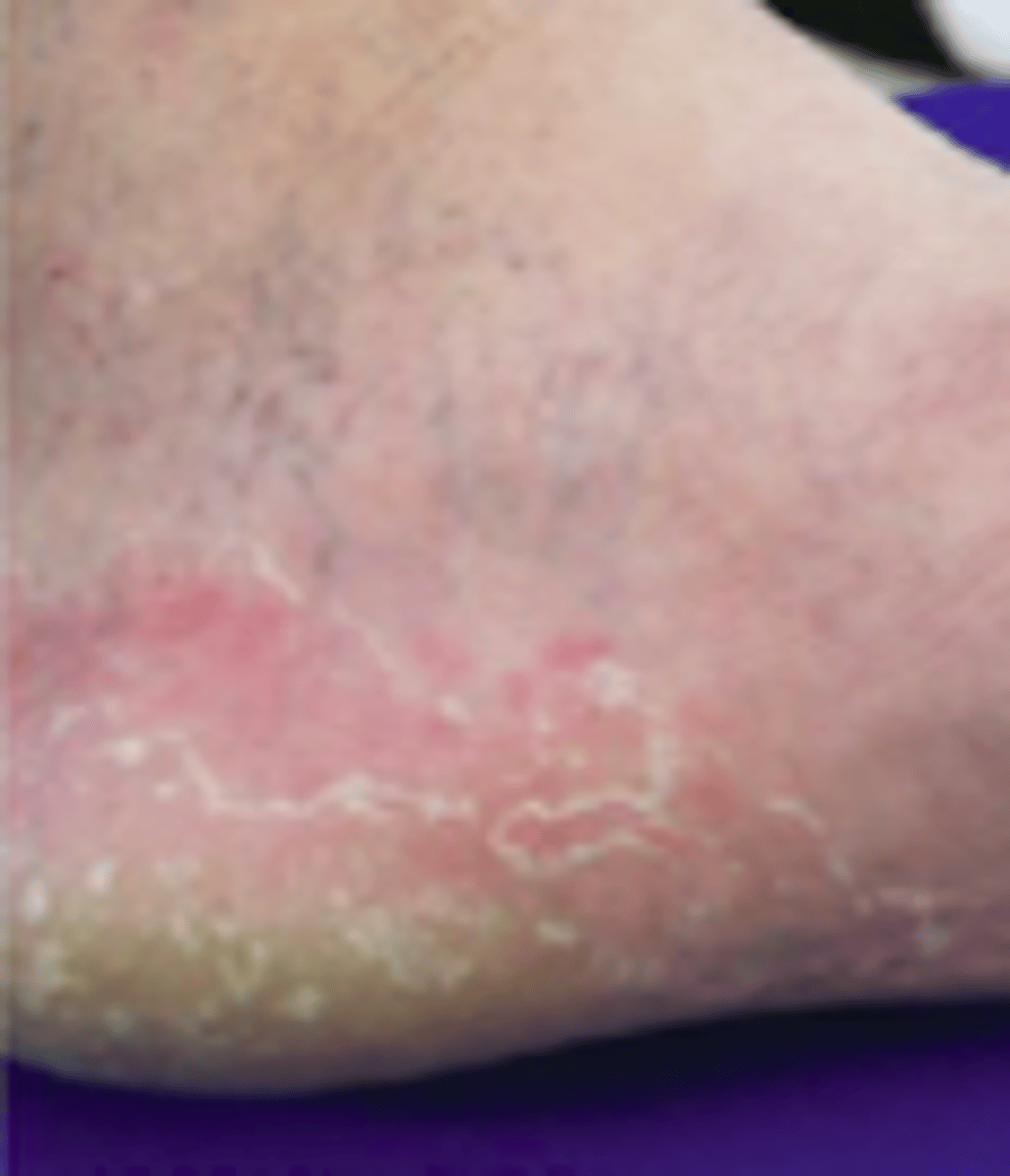
moccasin type
Fungal Skin Infections:
Type of Tinea Pedis:
- well-demarcated erythema with OR without papules at the margins, fine white scaling, hyperkeratosis
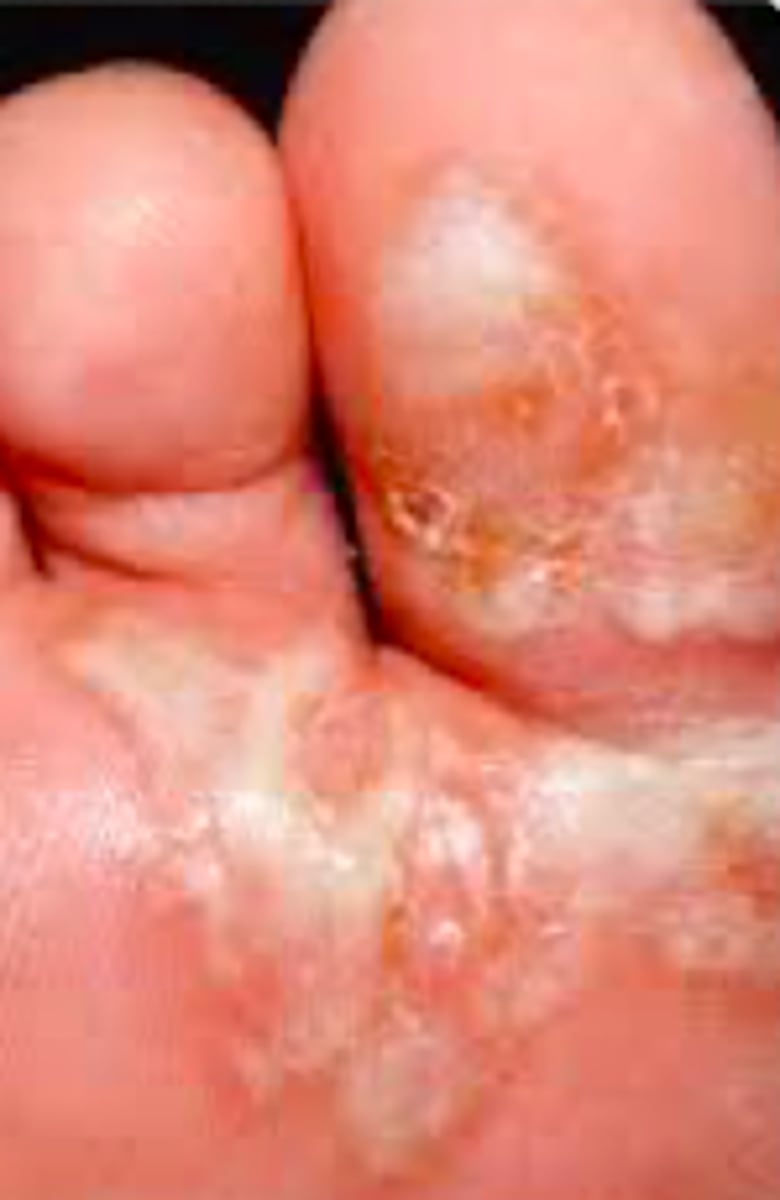
bullous type
Fungal Skin Infections:
Type of Tinea Pedis
- ruptured vesicles/bullae, erythema
usually a clinical Dx, BUT
- KOH prep shows hyphae
- fungal culture shows dermatophytes
Fungal Skin Infections:
How do we Dx tinea pedis?
topical antifungals x2-4 weeks
- if those don't work: systemic antifungals
Fungal Skin Infections:
What are the treatments for tinea pedis?