Honors Biology - Chapter 9 Photosynthesis Test
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Heterotroph definition
Organisms that get energy by eating food
Heterotroph example
Animals, human, fungi
Autotroph definition
Organisms that make their own food
Autotroph example
Plants/algae
What is ATP
Principle compound cells use for energy
How is energy stored/released in ATP
Through phosphate bonds; if the bonds break energy is released, and if the bond is reconnected the energy is given back
What are the different parts of an ATP molecule
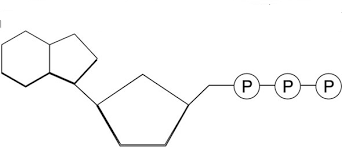
Adenine → ribose → phosphate
Where does the energy used to turn ADP → ATP come from
Food
What cellular activities do cells do to use ATP
Muscle contraction
Active transport
Photosynthesis
Transport
What is the symbol equation for photosynthesis
6 CO2 + 6 H2O [with light]→ C6H12O6 + 6 O2
What are pigments
Light absorbing molecules
What is chlorophyll
Main pigment/molecule plants use in photosynthesis
What colors of the light spectrum does chlorophyll reflect and absorb
Absorbs:
Red
Blue
Reflects:
Green
Where is chlorophyll found in the chloroplast
Photosystems within the thylakoid membrane
What are the parts of a chloroplast
Thylakoid
Granum
Photosystems
Stroma
What is the thylakoid in a chloroplast
Disc-like molecule
What is the granum in a chloroplast
A stack of flat discs with pigment
What are the photosystems in a chloroplast
Small spherical molecules near the connecting points of a stack of thylakoids
What is the stroma in a chloroplast
A jelly-like substance, essentially the cytoplasm of this organelle
What is NADP+
An electron carrier
How does NADP+ work
Transports high energy electrons from light-dependent reactions to light-independent reactions
What does NADP+ become when it grabs electrons
NADPH
Where in the chloroplast do light-dependent reactions occur
in the thylakoid membrane
What products come from light-dependent reactions
ATP
NADPH
Oxygen
What does ETC stand for
Electron transport chain
What does the ETC do
Transports high energy electrons to turn NADP+ into NADPH
What does ATP synthase do
H+ ions escape across the thylakoid membrane to make ATP
What parts does a water molecule get broken into during light dependent reactions
H2O → H+ + O2 + e-
What is the order of the ETC
Photosystem II → electron carriers → photosystem I → ATP synthase
Describe the 4 main events that happen in the ETC
Light goes through the cytoplasm and into the second photosystem → High energy electrons are made + water molecules are split into H+ and O2
These electrons move down to photosystem one, generating energy to pump H+ ions across the thylakoid membrane and into the thylakoid space
In photosystem one, electrons are reenergized. A second ETC transfers the electrons to NADP+ in order to make it NADPH
Once enough H+ ions are in the thylakoid space to make it positively charged, H+ ions pass back across the thylakoid membrane through ATP synthase. The ATP synthase molecule rotates as this happens, and energy produced converts ADP into ATP
Where is the chloroplast does the Calvin Cycle occur
In the stroma
What does the Calvin Cycle produce
Glucose
NADP+
ADP
Why do two sets of three molecules need to leave the cycle to make glucose
Glucose needs six total carbon molecules, 2 × 3 = 6
What three factors affect photosynthesis
Light intensity
Temperature
Water
What are the 4 main steps in the Calvin Cycle
Six CO2 molecules combine with 6 5-carbon molecules → makes twelve different 3-carbon compounds
ATP and NADPH turn all twelve of the 3-carbon molecules into higher energy forms, turning ATP → ADP and NADPH → NAPH+
Two of the 3-carbon molecules leave the cycle to produce sugars, lipids, etc.
The ten remaining 3-carbon molecules convert back into six separate 5-carbon molecules using ATP, once more turning to into ADP. The cycle now repeats.
Photosynthesis takes place in the…
Chloroplasts
The function of chlorophyll is to…
Capture energy from the sun
What reactants are needed for light-dependent reactions?
Light and water
What reactions are needed for light-independent reactions?
Carbon dioxide and energy-rich compounds