Mark 201 Chapter 4: Market Research
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is marketing research?
•the process of…
…defining a marketing problem and opportunity, systematically collecting and analyzing information, and recommending actions
–Purpose?
ensuring we do “evidence based decision making”
*understand process of HOW to do it
Customer Insights
–Understanding of customers and the marketplace *you need to understand your customer to be successful!
–Basis for creating customer value, competitive advantage, and relationships
Market Research and Metrics: What is the greatest resource in the marketing research (MR) process?
you and I! (general consumers have the information that organizations need)
Market Research and Metrics: What do we want most out of the research process?
The truth, but, the truth is hard to find (how do we get the information from people and ensure it’s truthful?)
Types of Market Research (3)
1) Exploratory – clarifies the scope and nature of a marketing problem or opportunity
Do I need to draw a survey of X amount of peopple, do I need a focus group of X amount of people? (quality response/data > quantity)
2) Descriptive – describes basic characteristics of a given population or clarifies its usage and attitudes
Who, What, Where, When, Why
context matters! we need to focus on a particular group/target market
3) Causal – identifies cause-and-effect relationships among variables
only possible through a formal study (hard to prove otherwise)
Competitor Analysis System
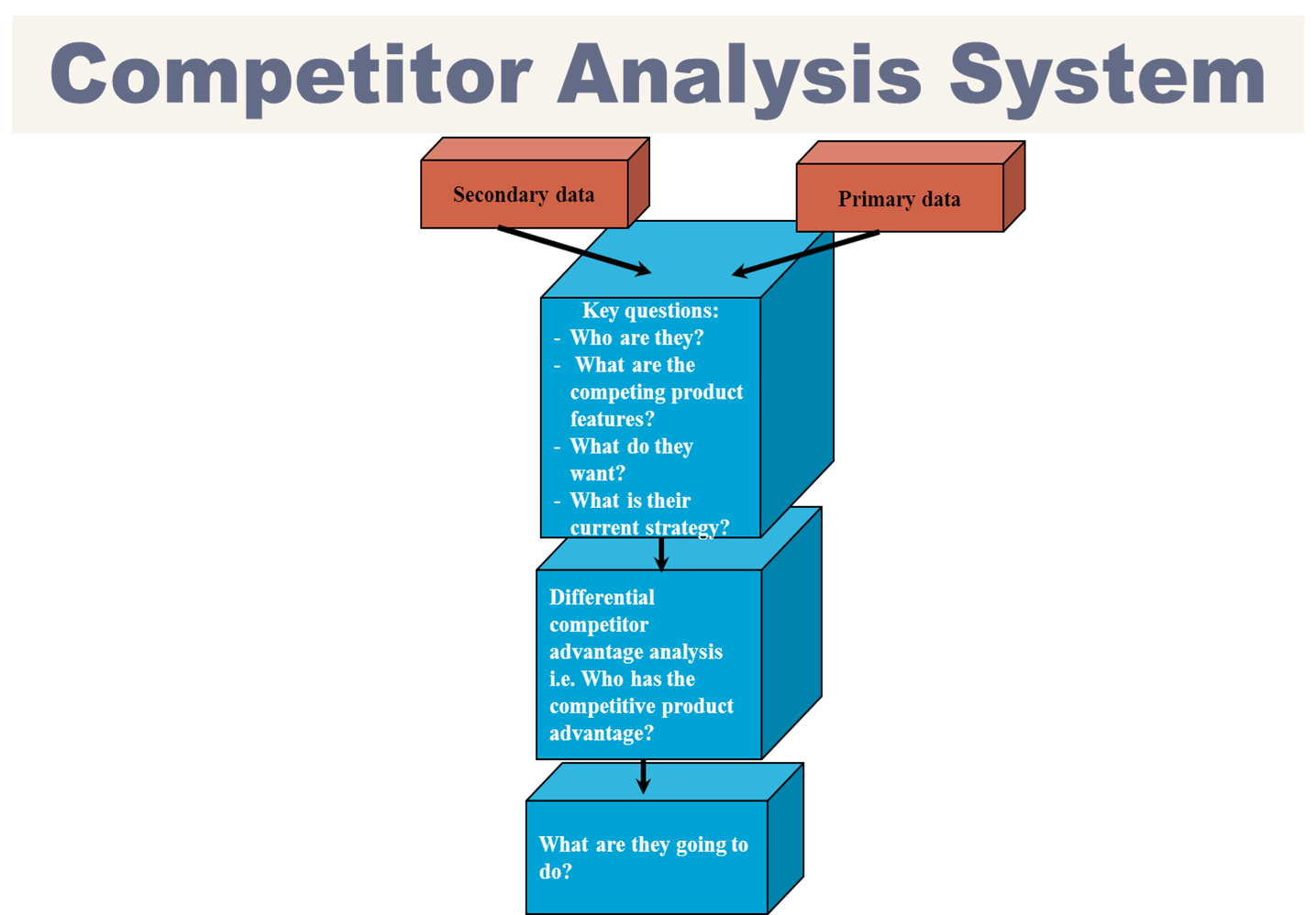
Secondary data: data developed for another purpose other then what you’re studying, but is relevant to you
Primary data: data you find/come up with for your specific study
⭐The 5-Step Market Research Approach⭐
Systematic approach ensures that market research is done thoroughly, that all elements are considered, and that results are accurate
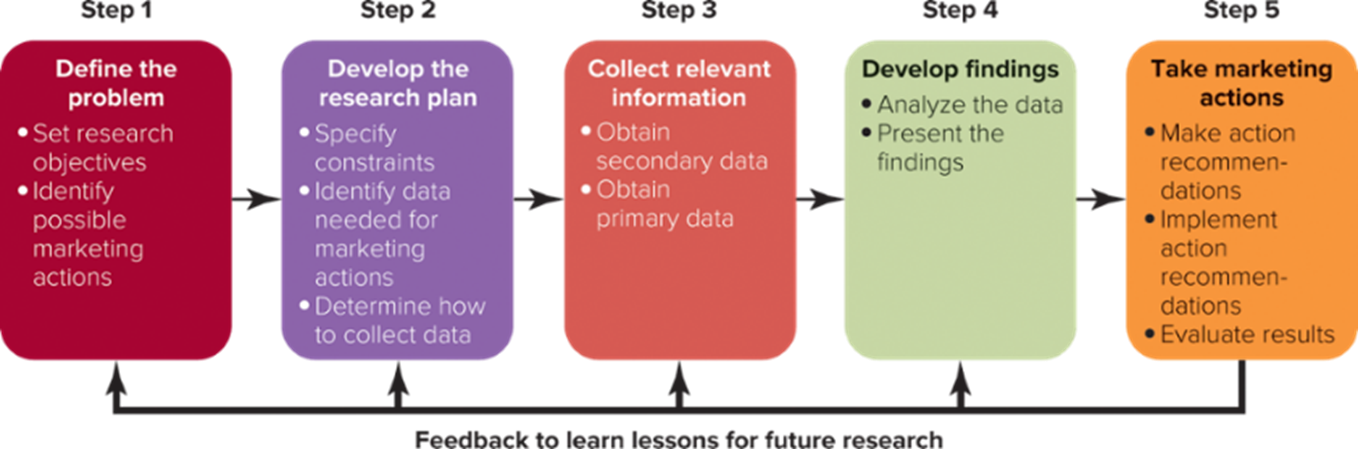
The 5-Step Market Research Approach- Step 1: Define the Problem/Issue/ Opportunity
*this is where alot of mental energy is used because it is a key step!
Two key elements:
1) Set the research objectives
–Objectives – specific, measurable, and achievable goals that the decision maker seeks to achieve
Common research objectives are to discover consumer needs and wants, and to determine why a product is not selling
2) Identify possible marketing actions
has to be usable, needs to have a ‘return on investment’
–Measures of success – criteria or standards used in evaluation proposed solutions to the problem
then you need to see if there was a change, if it did anything
The 5-Step Market Research Approach- Step 2: Develop the Research Plan
*it’s important to understand what this means and whether or not you can rely on what the data says
specify constraints: In a decision, the restrictions placed on potential solutions to a problem.
•Special methods vital to marketing are:
1)Sampling - the process of gathering data from a subset of the total population rather than from all members of that particular group; selecting a group of distributors, customers, or prospects, asking them questions and treating their answers as typical of all of those in whom they are interested
probability sampling: Selecting a sample so that each element of a population has a specific known chance of being selected.
nonprobability sampling: Selecting a sample so that the chance of selecting a particular element of a population is either unknown or zero.
2)Statistical inference – used to generalize the results from the sample to larger groups
•When determining the way in which data will be collected, methodology, cost, efficiency, and accuracy of results are important considerations
•The Internet provides numerous online tools to facilitate the gathering of information example surveys
•To ensure the accurate answers are obtained researchers carefully select research methodologies that encourage honesty
*in the marketing research world, we often calculate the Margin of Error (MOE) ex. 75% ± 3% ; for this we have to have a random sample; this is a mangerial tool, studies have to be useful in terms of somebody making a decision
Qualitative vs Quantitative Methodology

Quantitative: used to make decisions considered more heavy in weight
Qualitative: more exploratory
focus group: group of people talking, have a moderator; talkative, informal, where people can gain information, can help answer the “WHY?” question; very expensive (more likely to do online to reduce costs); timely
The 5-Step Market Research Approach- Step 3: Collect Relevant Information
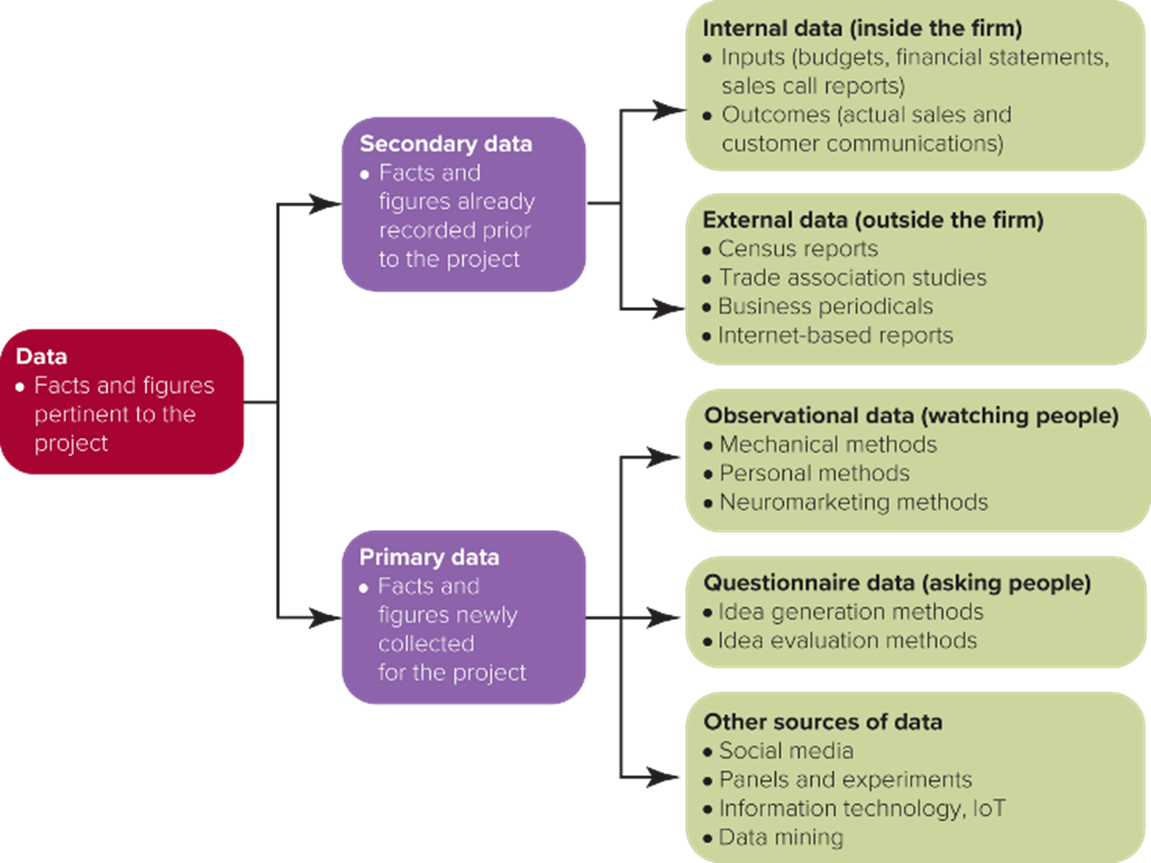
•Secondary data is lower in cost and easier to obtain
somebody already did the research and obtained it; results, target audience, general subject, etc.; facts and figures that have already been recorded by a third party
ex. Statista, Stats Canada (higher quality data)
•Internal data exists within a company and can include data derived from big data analytics, or simpler approaches that review basic sales reports, profitability data, and costing information.
•External data comes from published sources outside the organization, which can track what consumers watch on television, on mobile devices, or online, as well as what they buy from online or offline retailers
•“Why not use secondary data?”
•Data may be out of date
•Definitions or categories of preexisting data may not be right for the project
•Data may not be accurate or specific to the study
•Primary Data – data that is originally and specifically collected for the project at hand
go out and get yourself
•Observational data: (observing people) Facts and figures obtained by watching how people actually behave, which can be collected by mechanical (including electronic), personal, or neuromarketing methods; we want to know the truth, shows you what people do, but doesn’t tell you WHY
•Questionnaire data: Facts and figures obtained by asking people about their attitudes, awareness, intentions, and behaviours.
•Other sources of data
ex. in-depth interviews: Detailed interviews where a researcher questions an individual at length in a free-flowing conversational style in order to discover information that may help solve a marketing problem.
ex. focus groups: A qualitative research technique where a small group of people (usually six to ten) meet for a few hours with a trained moderator to discuss predetermined areas.
ex. panel: A large sample of respondents that voluntarily complete questionnaires on a regular basis so that researchers can assess changes in behaviour and attitudes.
ex. omnibus survey: The voluntary participation of respondents in routine research surveys that allow marketers to add a small number of questions to an existing survey to receive cost-effective data.
ex. experiment: In marketing, changing a variable involved in a customer purchase to find out what happens.
Nature and Scope of Secondary Data
Use and Evaluation of Secondary Data (5)
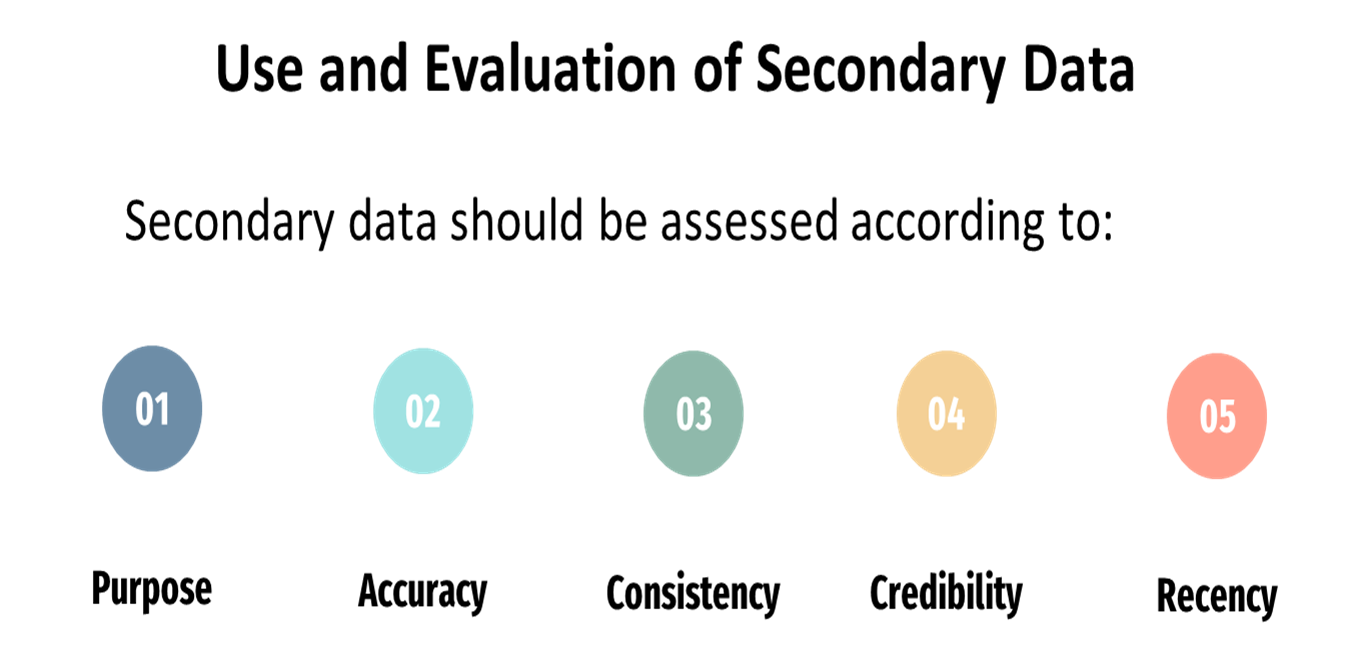
purpose: what was the purpose of this particular information? why did somebody go out and want this information?
accuracy: go back and look at how data was collected; was a random sample done? how were the focus groups done?; want to ensure it was done properly, that the data has a certain amount of integrity
consistency: is this consistent with what I already know? is it the same/similar to results as other similar studies?
credibility: who did the study? were they certified people? is this an accredited agency that did this work for us?
recency: how recent is this information?
Online Consumer Panels (+ and -)
Advantages
speed (quick turn-around), higher response rates (pre-targeted individuals (we know they will respond to questionnaires, etc.)
Disadvantages
costly to set up, control
not a random sample therefore we can’t assign a margin of error (step down in terms of quality)
Digital Tools
we choose these based on cost, time, etc.
all available to carry out research (lots of choice and opportunity)

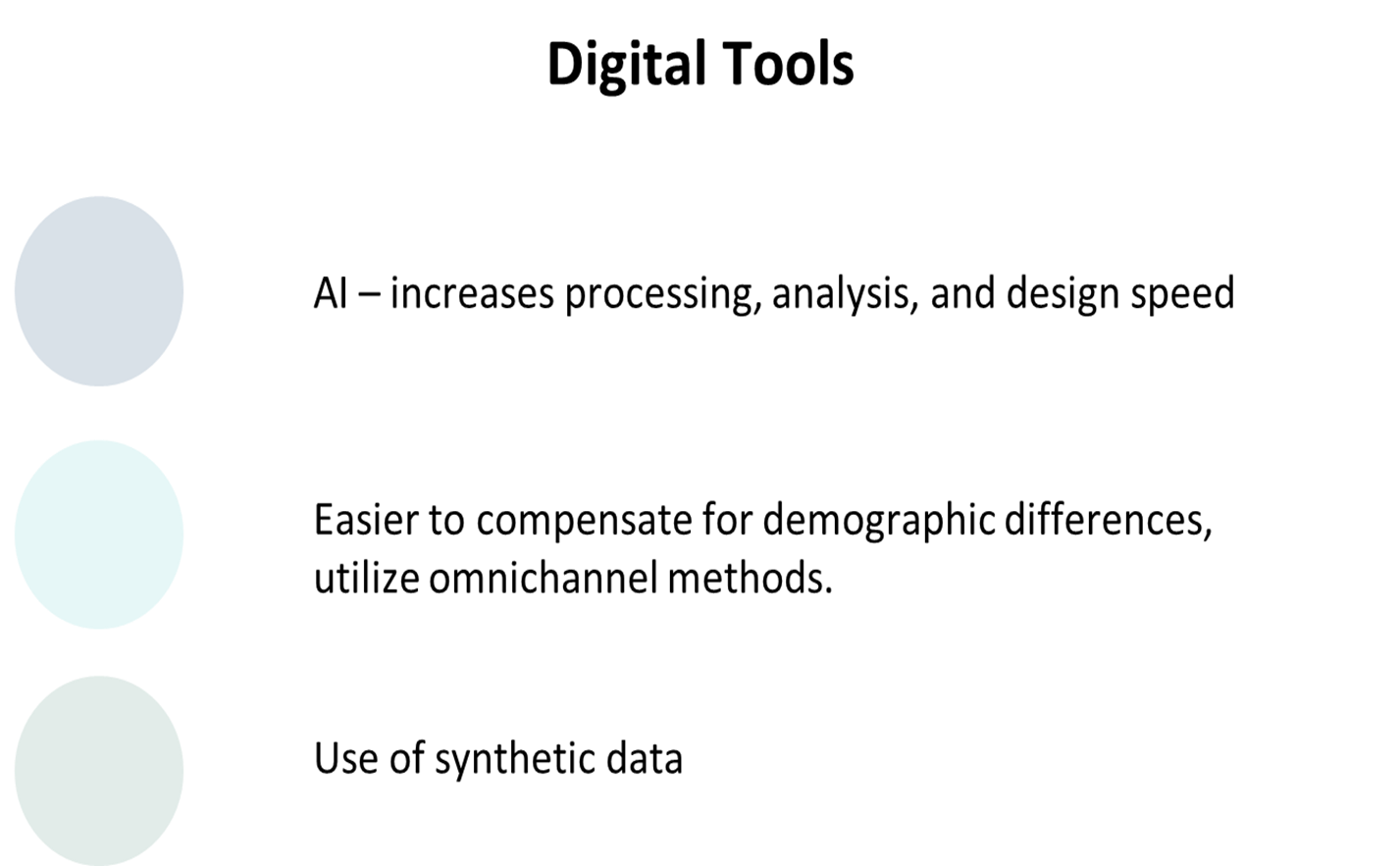
these tools are more subjective compared to numbers themselves
Public Engagement
this is the governments form of research
Metrics
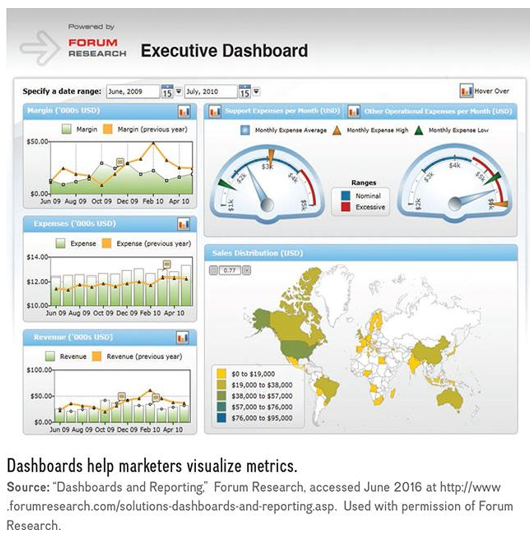
•numerical data that is collected and grouped to track performance
–Dashboards: visualize data and key performance indicators (KPIs; types of metric that are used to evaluate performance) using graphs, charts, and numbers so that numerical information tells a story that is insightful, easy to use and understand
want to do it in a business sense with as much recency as possible
we need to choose which metrics are going to be the ones that give us the information we really need
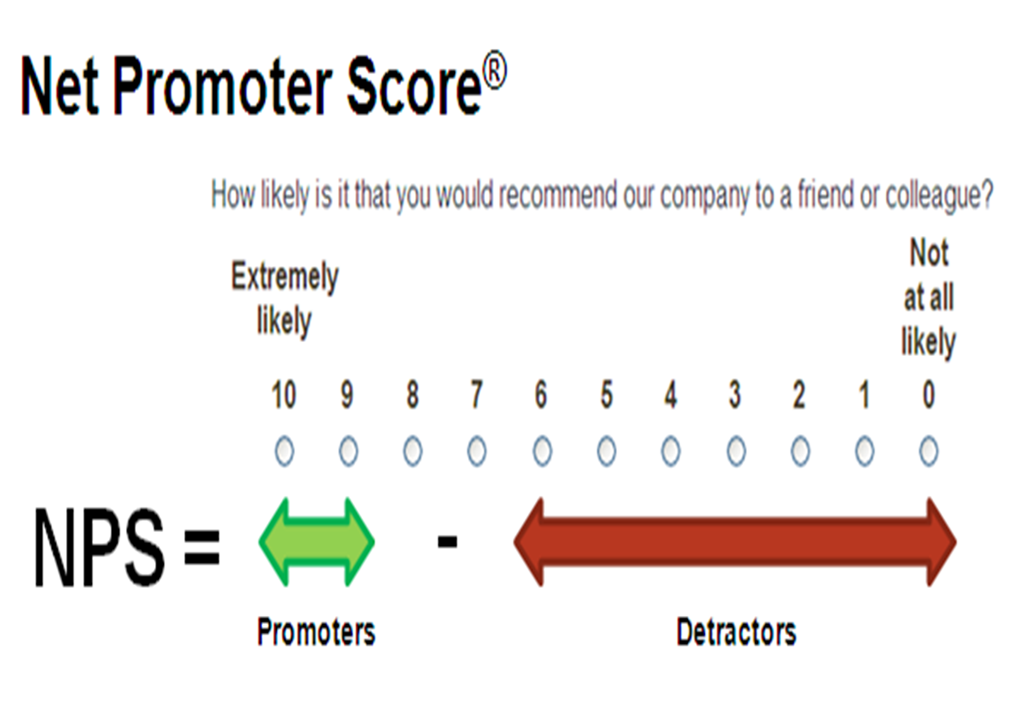
Metrics Example: Net Promoter Score (NPS)
done on an ongoing basis to create a continuous base of information that we make decisions from
What’s it for?
good score = good customer satisfaction
used for evidence based decision making
The 5-Step Market Research Approach- Step 4: Develop Findings
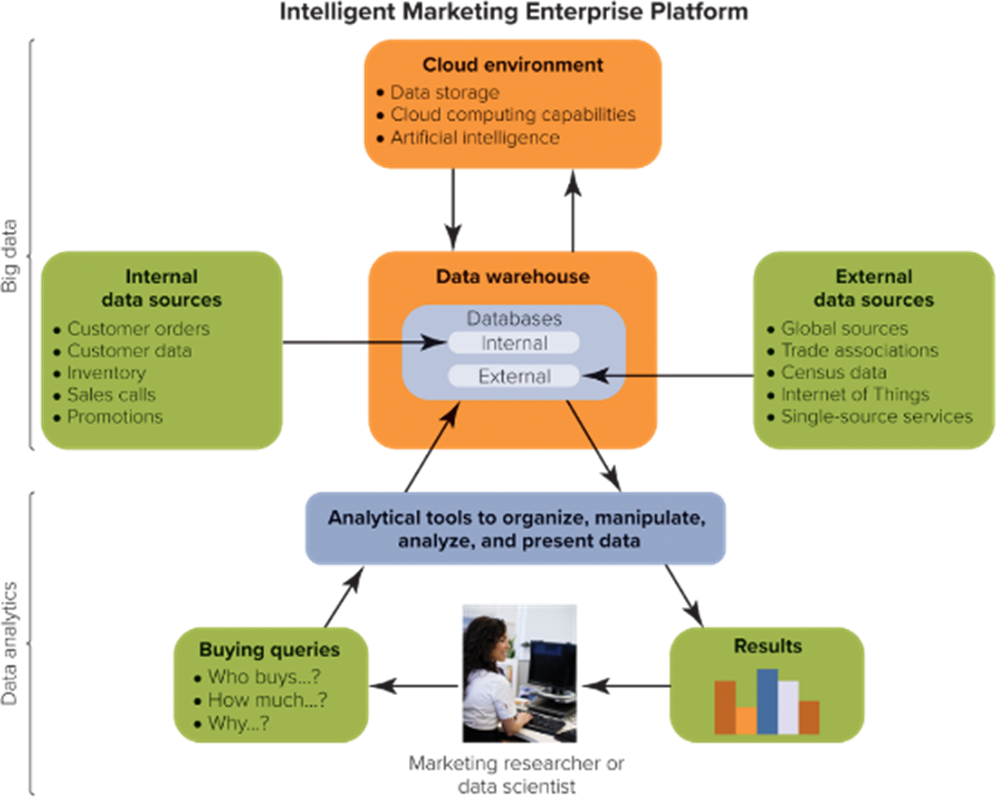
analyze the data; information technology includes all of the computing resources that collect, store, and analyze data.
data mining and predictive modelling; data mining is the processing of large amounts of data using sophisticated software to find insightful correlations and patterns that lead to better business decisions and predictive modelling is based on statistical models that use data mining and probability analysis to foretell outcomes.
analytics; descriptive analytics is a type of analytics that focuses on what has happened; web analytics is the measurement and analysis of website data, looking at elements such as page views, time on site, bounce rate, new visitors, returning visitors, and referral traffic; social analytics is the real-time measurement, interaction, and analysis of social media to assess social media campaign performance, message resonation and amplification, consumer sentiment, and common themes; social listening is research that monitors public online consumer conversations on social media sites such as social networks, blogs, and forums; RFM analysis is the rating of customers on the basis of how recently products were purchased (recency), how often products were purchased (frequency), and the dollar value of the transactions (monetary value).
predictive analytics is the combination of data from varied sources to reveal patterns that are modelled to predict what might happen in the future.
The 5-Step Market Research Approach- Step 5: Take Marketing Actions
Make action recommendations
Implement the action recommendations – storytelling is important
Evaluate the results:
The decision itself: this involves monitoring the marketplace to determine if action is necessary in the future
The decision process used: was the marketing research and analysis used to develop the recommendations effective? was it flawed? could it be improved for similar situations in the future?
Market Research – Regulatory Considerations
•Ethically and legally, privacy should be top-of-mind:
Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), PIPA in Alberta
Canada’s anti-spam legislation (CASL)
Canadian Marketing Association (CMA)
Privacy Commissioner of Canada
Canadian Research Insights Council (CRIC)