Gross Anatomy I - Exam 3 - Palmer (Yarbrough)
1/338
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
339 Terms
the lower limb is anchored to the axial skeleton by ______ joint & associated ligaments
sacroiliac joint
what are the 3 transitional areas of the lower limb? (3)
femoral triangle, popliteal fossa, tarsal tunnel
what are the 2 main functions of the lower limb? (2)
support the body weight
locomotion
when standing erect, how does the vertical line pass through the center of gravity at the hip joint?
slightly posterior to the hip joint
when standing erect, the vertical line through the center of gravity is anterior to:
the knees and ankle joints
the knee & hip joints are in _________ when standing; this reduces the amount of energy required to stand
extension
what components help produce a smooth & efficient gait?
pelvic tilt (coronal plane), pelvic rotation (transverse plane), knees toward midline, flexion of the knees
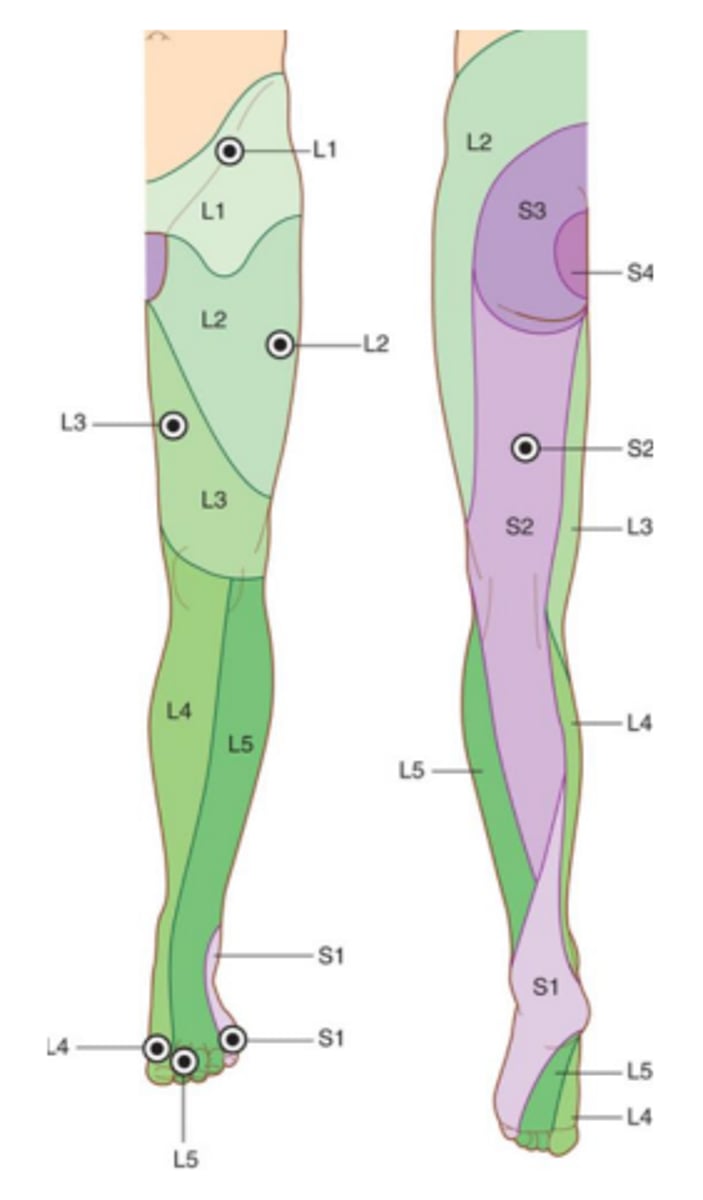
testable image #1! (leg dermatomes)
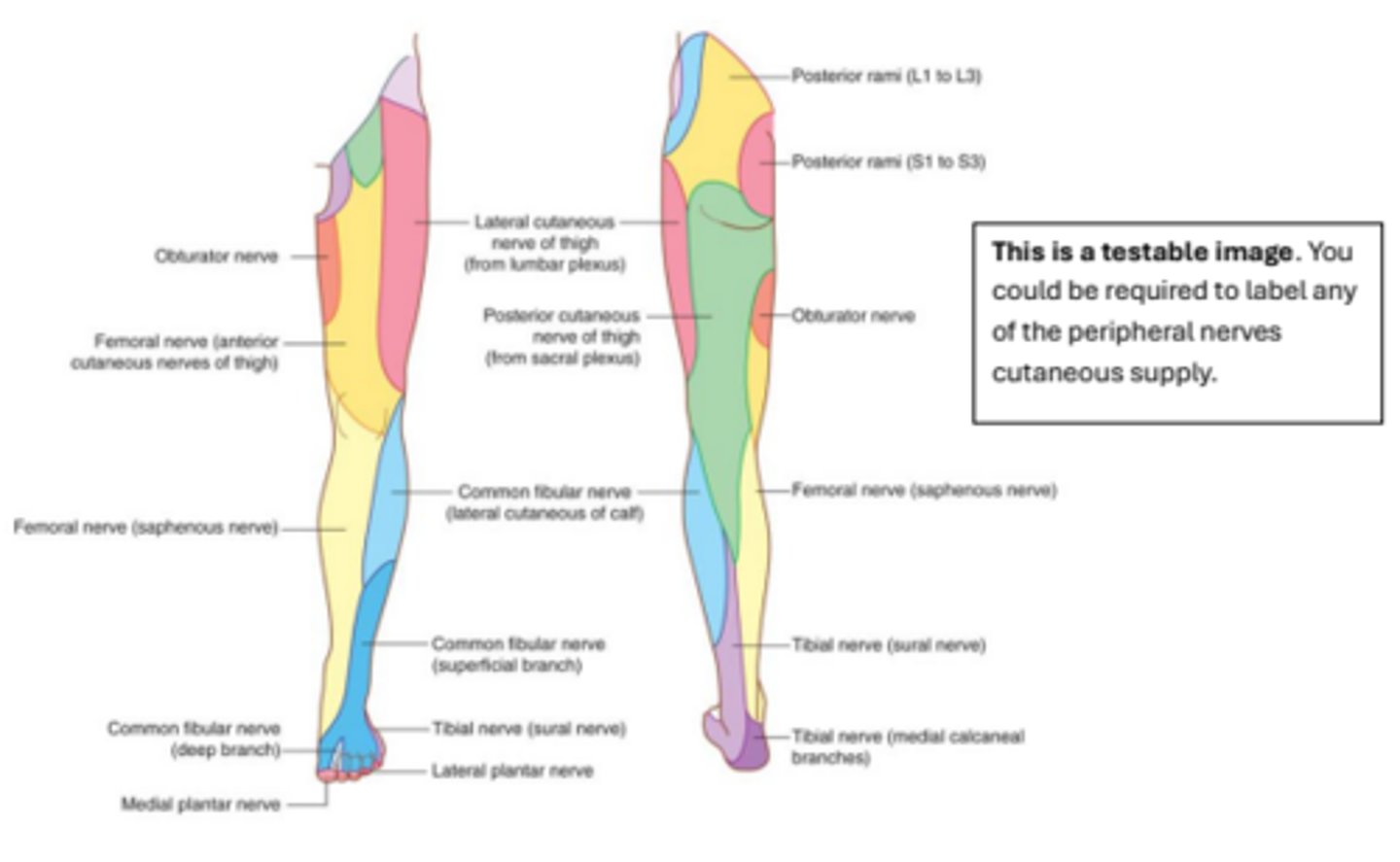
testable image #2! (peripheral nerves/cutaneous supply)
the pelvis is formed by which 3 bones? (3)
ilium, ischium, pubis
when do the ischium & pubis fuse?
4-8 years old
when does the ilium fuse to the other bones?
11-17 years old
Which features are included in linea terminalis?
pubic crest
pecten pubis
arcuate line
pectineal line
The _________ is where the ilium, pubis &
ischium fuse.
acetabulum
Difference between true pelvis & false pelvis.
False pelvis are the iliac crests and above, whereas true pelvis is the area below the pelvic brim, containing the pelvic cavity, the opening
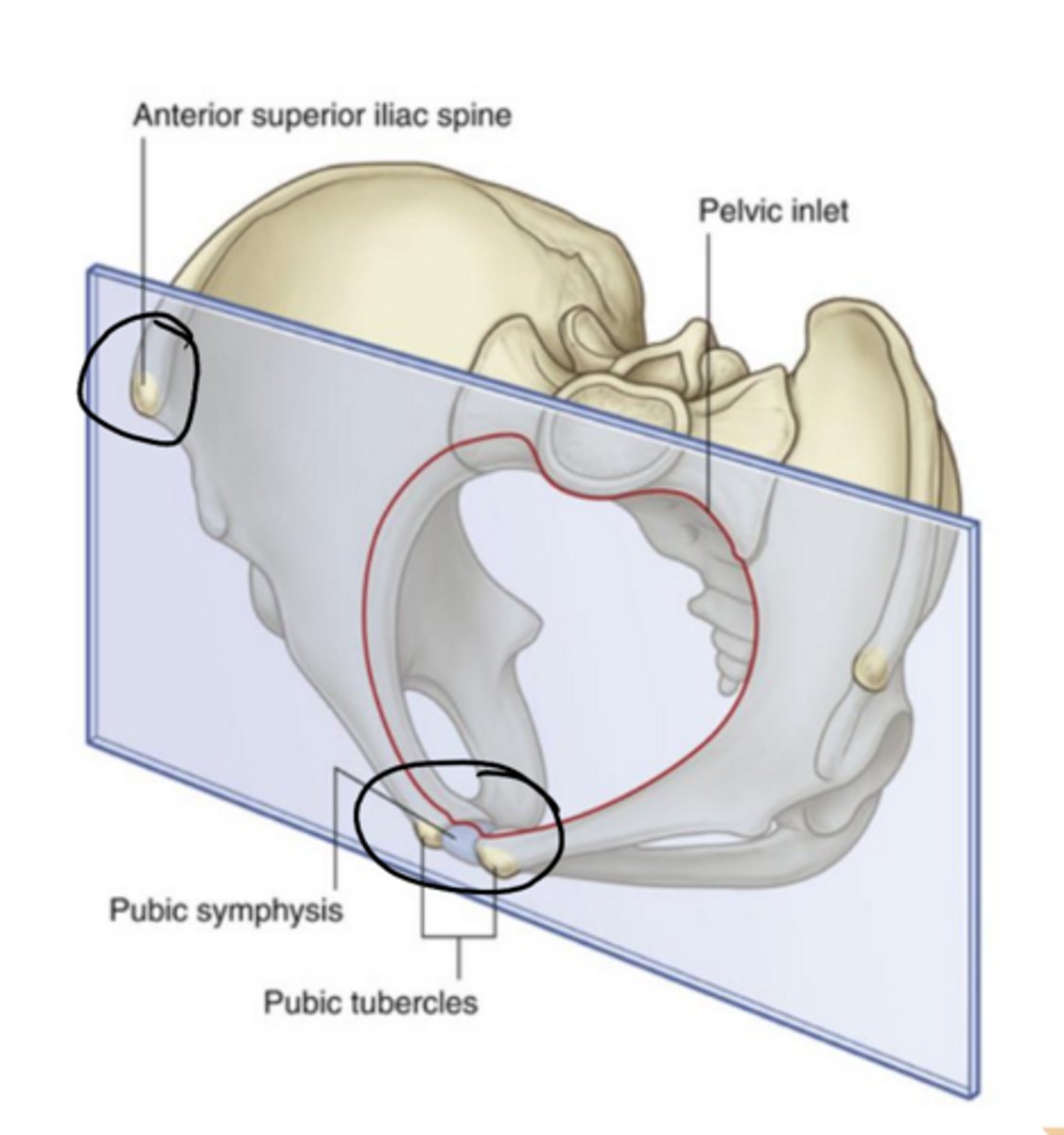
In anatomical position, the pubic symphysis & the
_________ lie in the same vertical
plane.
anterior superior iliac spine
What makes up the pelvic walls?
sacrum
coccyx
ilium
ischium
pubis
piriformis
obturator internus
sacrospinous ligament
sacrotuberous ligament
What makes up the pelvic outlet?
pubic symphysis
ischiopubic ramus
sacrum
sacrotuberous ligament
coccyx
ischial tuberosity
The adjacent surfaces of the pubic bones are linked by the________.
pubic symphysis
What type of joint is the pubic symphysis?
cartilaginous joint; symphysis
What is present on the pubic symphysis joint's bony surfaces? (only on the bone)
hyaline cartilage
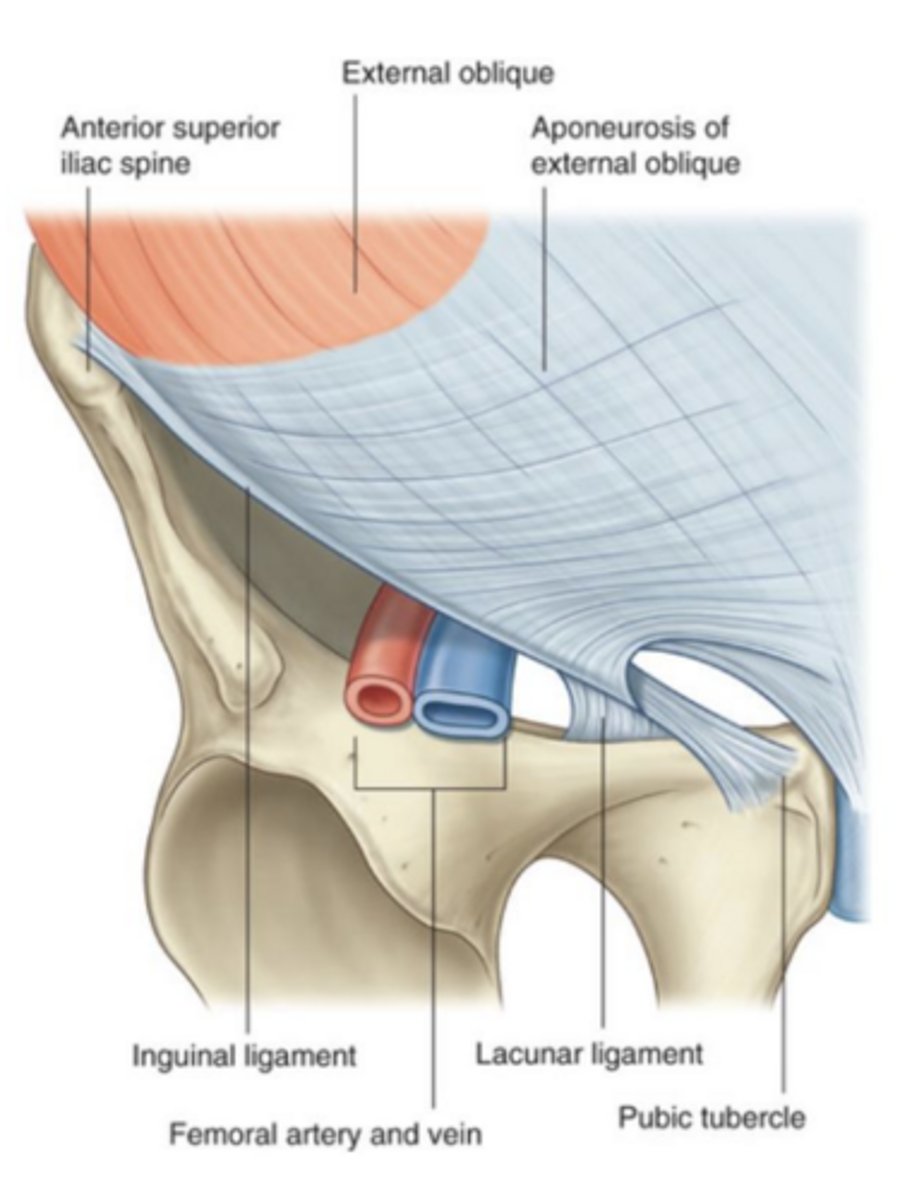
The inguinal ligament is a thickened, reinforced edge of __________
external oblique aponeurosis
The lateral attachment of the inguinal ligament:
anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
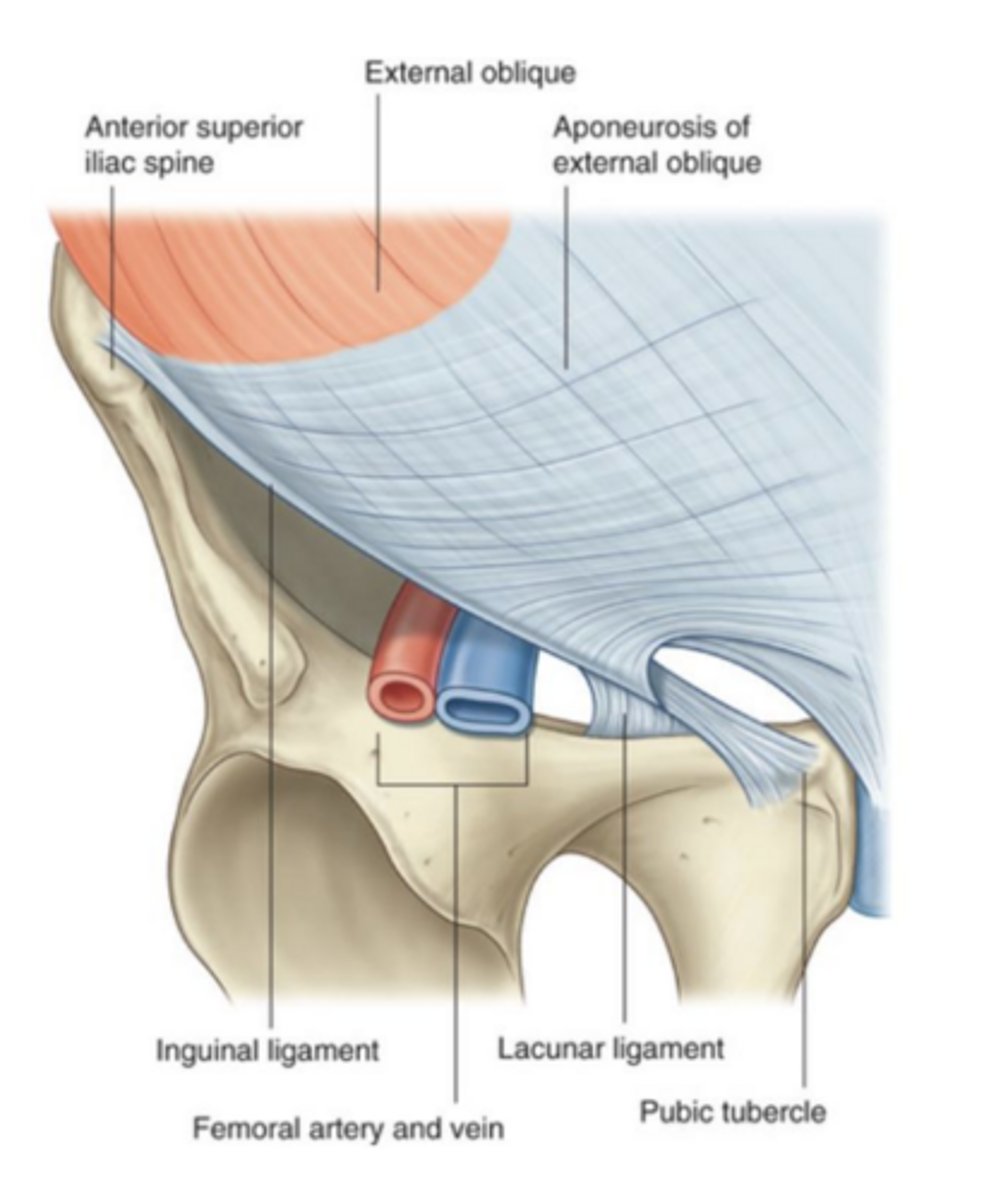
The medial attachment of the inguinal ligament:
the pubic tubercle
pelvic inlet shape (male pelvis)
heart-shaped
pelvic inlet shape (female pelvis)
circular
subpubic arch (male pelvis)
narrower angle (50-60°)
subpubic arch (female pelvis)
wider angle (80-85°)
ischial spines (male pelvis)
prominent; medially projected
ischial spines (female pelvis)
less prominent; further apart
obturator foramen (male pelvis)
round, smaller
obturator foramen (female pelvis)
oval, larger
iliac crests (male pelvis)
higher; more vertical
iliac crests (female pelvis)
lower; flare outward
The ____________ is a common site for bone
marrow biopsy.
iliac crest
Where does a subcapital happen? risks?
line through femoral head-neck junction;
high risk of necrosis in femoral head
transcervical (femur fracture)
fracture line through mid-portion of femoral neck;
more common in older individuals with osteoporosis;
following low-energy fall (i.e. from standing height)
basicervical (femur fracture)
fracture through base of the femoral neck;
lowest risk of necrosis;
more common in younger individuals;
following high-energy trauma (i.e. fall from a great height)
The hip joint involves articulation between:
head of the femur & the acetabulum (of pelvic bone)
what is the name of the surface of hip joint articulation?
lunate surface
Hip joint classification:
synovial; ball-and-socket
Acetabular labrum: (details)
the rim of the acetabulum is raised slightly by a fibrocartilaginous collar (the acetabular labrum)
Transverse acetabular ligament: (details)
labrum bridges across the acetabular notch
Acetabular foramen: (details)
formed when the transverse acetabular ligament bridges the acetabular notch, allowing nerves and blood vessels to pass into the joint
Ligament of the head of the femur:
aka ligamentum teres
attaches to the: fovea, acetabular fossa, acetabular ligament, margins of the acetabular notch
what does the artery of the ligamentum teres (acetabular branch of obturator artery) supply?
supplies the head of the femur
Artery of ligament of head of the femur supplies blood to the ______
head of the femur
Iliofemoral ligament (characteristics)
anterior, triangular shaped; Y appearance; part of hip joint
Pubofemoral ligament (characteristics)
anteroinferior, triangular shaped; blends with fibrous membrane & deep surface of the iliofemoral ligament
Ischiofemoral ligament (characteristics)
reinforces the posterior aspect of the fibrous membrane
Which structures primarily provide blood supply to the hip joint? (6)
obturator artery
medial femoral circumflex artery
lateral femoral circumflex artery
superior gluteal artery
inferior gluteal artery
first perforating branch of the deep artery of the thigh
Which structures primarily provide nerve supply to the hip joint? (4)
femoral nerve
obturator nerve
superior gluteal nerve
nerve to the quadratus femoris
Greater sciatic foramen superior to piriformis (gateway contents)
superior gluteal nerve, artery, & vein
Greater sciatic
foramen inferior to
piriformis (gateway contents)
sciatic nerve
inferior gluteal nerve, artery, and vein
pudendal nerve
internal pudendal artery & vein
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
nerve to obturator internus
nerve to quadratus femoris
lesser sciatic foramen (gateway contents)
obturator internus muscle
pudendal nerve
internal pudendal artery & vein
obturator canal (gateway contents)
obturator nerve
obturator artery & vein
gap between inguinal ligament & pelvic bone (gateway contents)
psoas major
iliacus
pectineus
femoral artery & vein
femoral nerve
femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve
lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh
lymphatics
The lumbar plexus is formed by the anterior rami of spinal nerves:
L1-L4 (most of L4)
The lumbosacral trunk is formed by:
L4/L5 (the rest of L4)
The lumbosacral trunk joins with the anterior rami of
________________________ to form the sacral plexus.
S1-S3
testable image #3 (lumbar plexus)
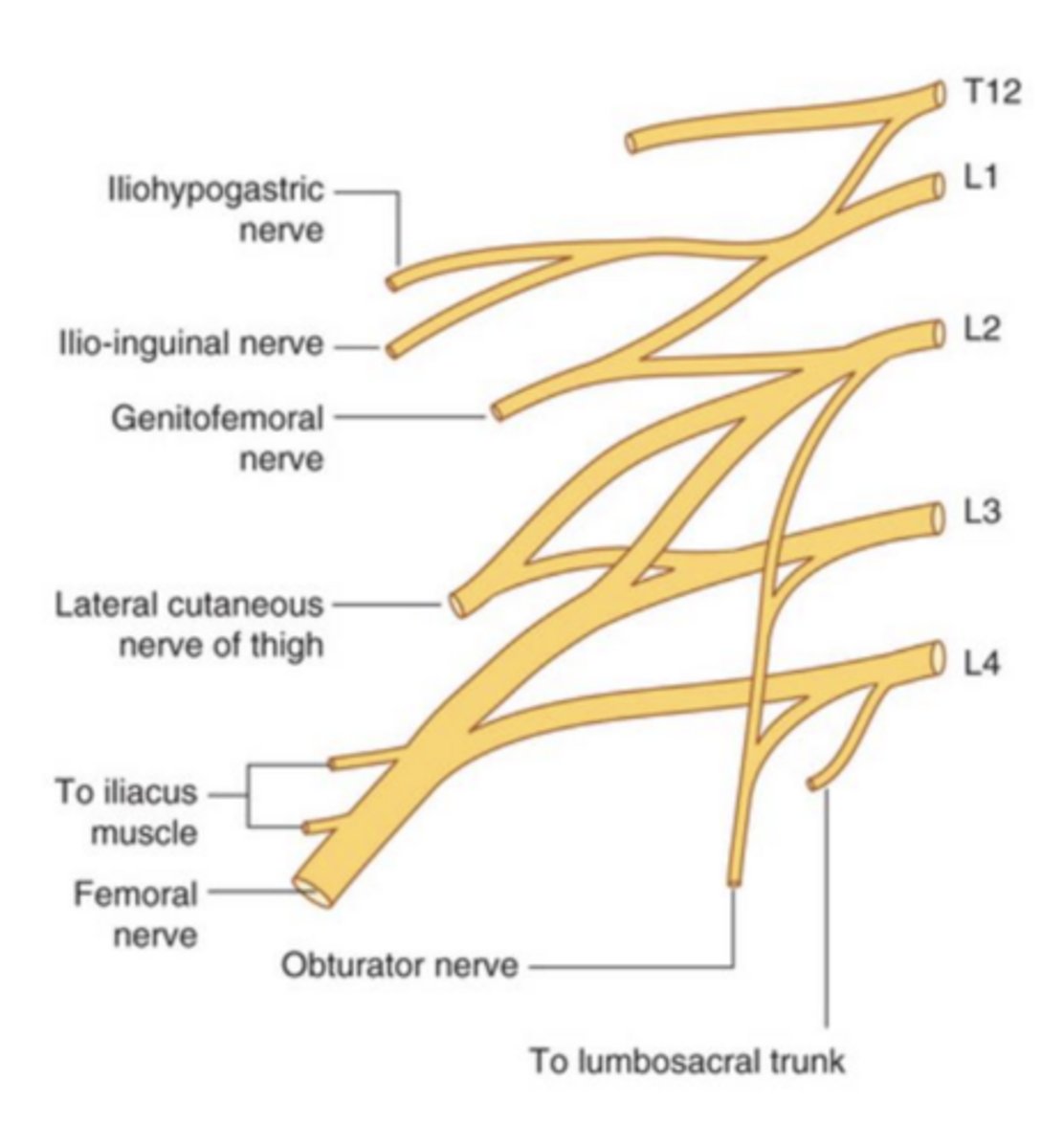
Iliohypogastric nerve (spinal segments, motor/sensory)
L1
motor: muscles of abdominal wall
sensory: posterolateral gluteal skin & skin in pubic region
Iliohypogastric nerve (spinal segment)
L1
Iliohypogastric nerve (motor innervation)
muscles of the abdominal wall
Iliohypogastric nerve (sensory innervation)
posterolateral gluteal skin
skin in pubic region
Ilioinguinal nerve (spinal segments, motor/sensory)
L1
motor: muscles of the abdominal wall
sensory: skin in the anterior medial part of the upper thigh
Ilioinguinal nerve (spinal segment)
L1
ilioinguinal nerve (motor innervation)
muscles of the abdominal wall
Ilio-inguinal nerve (sensory innervation)
skin in the anterior medial part of the upper thigh
ilioinguinal nerve passes through ___________
inguinal canal; leaves the abdominal wall through the superficial inguinal ring
iliohypogastric nerve & ilioinguinal nerve arise as a single trunk from _________
the anterior ramus of L1
genitofemoral nerve (spinal segment, motor/sensory)
L1, L2
motor: genital branch-cremaster muscle in males
sensory: femoral branch -> skin of upper anterior thigh
genital branch -> genital region
genitofemoral nerve (spinal segment)
L1, L2
genitofemoral nerve (motor innervation)
genital branch: cremaster muscle in males
genitofemoral nerve (sensory innervation)
femoral branch: skin of upper anterior thigh
genital branch: genital region
lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (spinal segment, motor/sensory)
L2, L3
no motor
sensory: skin over the anterolateral thigh; parietal peritoneum in iliac fossa
lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (spinal segments)
L2, L3
lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (motor innervation)
none
lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (sensory innervation)
skin over the anterolateral thigh; parietal peritoneum in iliac fossa
Femoral nerve (spinal segment, motor/sensory)
L2-L4
motor: all muscles in anterior compartment of the thigh; gives rise to branches that supply iliacus & pectineus
sensory: skin over the anterior thigh, anteromedial knee, medial side of the leg, medial side of the foot
Femoral nerve (spinal segment)
L2-L4
Femoral nerve (motor)
motor: all muscles in anterior compartment of the thigh; gives rise to branches that supply iliacus & pectineus
Femoral nerve (sensory)
sensory: skin over the anterior thigh, anteromedial knee, medial side of the leg, medial side of the foot
Obturator nerve (spinal segment, motor/sensory)
L2-L4
motor: all muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh (except pectineus & part of adductor magnus); obturator externus
sensory: skin over upper medial aspect of the thigh
Obturator nerve (spinal segment)
L2-L4
Obturator nerve (motor)
all muscles in the medial compartment of the thigh (except pectineus & part of adductor magnus); obturator externus
Obturator nerve (sensory)
skin over upper medial aspect of the thigh
testable image #4! (sacral plexus)
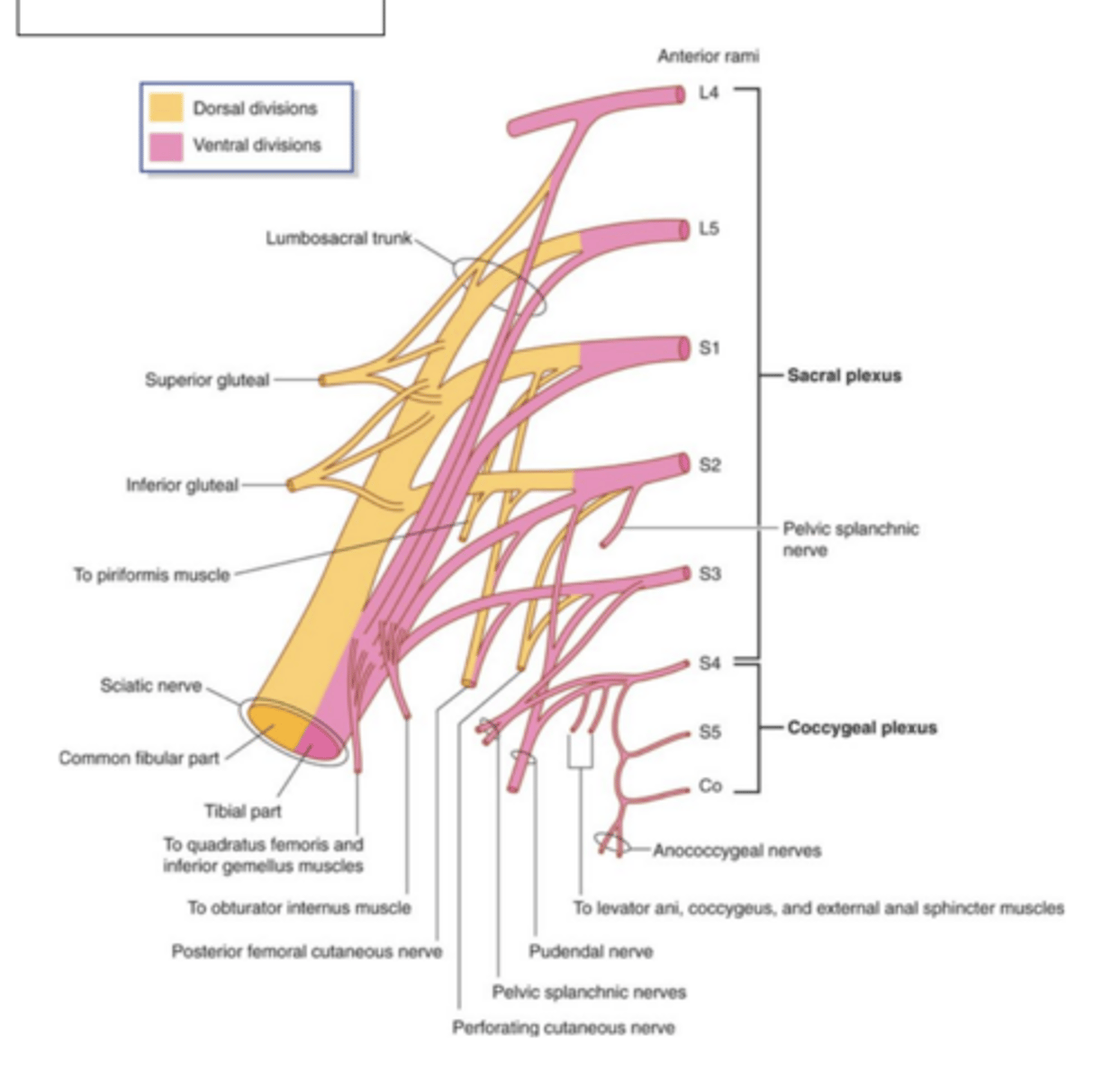
Superior gluteal nerve (spinal segment, motor/sensory)
L4-S1
motor: gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae
sensory: none
Superior gluteal nerve (spinal segment)
L4-S1
Superior gluteal nerve (motor innervation)
motor: gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae
Superior gluteal nerve (sensory innervation)
sensory: none
Inferior gluteal nerve (spinal segment, motor/sensory)
L5-S2
motor: gluteus maximus
sensory: none
Inferior gluteal nerve (spinal segment)
L5-S2
Inferior gluteal nerve (motor innervation)
motor: gluteus maximus
Inferior gluteal nerve (sensory innveration)
sensory: none
Nerve to the piriformis (spinal segment, motor/sensory)
S1-S2
motor: piriformis
sensory: none
Nerve to the piriformis (spinal segment)
S1-S2
Nerve to the piriformis (motor innervation)
piriformis
Nerve to the piriformis (sensory innervation)
none