AP Chemistry Exam
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
What is an isotope?
Atom that can have varying neutron counts
What are the 3 suffixes for organic compounds and what do they mean?
-ene CnXa (a=2n)
-ane CnXa (a=2n+2)
-yne CnXa (a=2n-2)
Describe empirical vs. molecular formulas
Empirical- smallest whole number ratio of elements in a molecule
Molecular- Exact number of atoms of each element in a molecule
What is the formula to find the mass percent of an element in a molecule?
Mass of substance/Total mass of mixture * 100
What are all of the electron orbitals, and how are they numbered?
S orbital
Inner-most orbital
Holds 2 electrons
Prefix is the row number you are in
P orbital
After S orbital
Holds 6 electrons
Prefix is the row number you are in
D orbital
After P orbital
Holds 10 electrons
Prefix is the row number you are in -1
F orbital
After D orbital
Holds 14 electrons
Prefix is the row number you are in -2
When are electron orbitals most stable?
When they are half or fully filled
Which orbitals hold the valence electrons?
The S and P orbitals
What is Coulombs Law?
Like charges attract and opposite charges repel.
The closer 2 molecules are, the more they will attract (because force is indirectly proportional to distance)
What is photoelectron spectroscopy?
Technique used to determine the different energy sublevels occupied by electrons in an atom
Contains a graph that shows energy on the x-axis and relative number of electrons on the y-axis
High peaks mean a large amount of electrons are present in this sublevel
Peaks should match up with ,P,D and F orbitals
What does isoelectric mean?
Containing the same number of electrons
What is a saturated carbon?
A carbon with all single bonds
What is an unsaturated carbon?
A carbon with a double bond or triple bond
Which are more stable, saturated or unsaturated carbons?
Saturated because they are generally more stable and less reactive
Name all diatomic molecules.
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Fluorine
Oxygen
Iodine
Chlorine
Bromine
What is shielding?
Having ore orbitals of electrons means that some of the attractive energy from the valence electrons to the core protons is shielded and decreased slightly
Describe the 4 main periodic trends.
Increases left to right and down to up
Electronegativity
Since proton number is increasing but atomic radius is decreasing as you move left to right across a period, electrons are becoming increasingly attracted to the center protons, increasing electronegativity. The same occurs as you move up: atomic radius is decreasing because electrons are more attracted to the center protons
Ionization energy
As you move left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases because electrons are more attracted to the center protons. This makes it more difficult to remove electrons from atoms with these smaller radii. The same occurs as you move up: atomic radius is decreasing because electrons are more attracted to the center protons
Increased right to left, up to down
Atomic radius
As you move left, proton number decreases which will decreases the attraction of electrons to the nucleus. As you move down electron orbitals are being added which increases shielding and causes radius to increase
Metallic character
As you move left, atoms become more readily available to lose electrons, a characteristic of metals. As you move down, atomic radius is increasing, meaning valence electrons are further from the positive nucleus. This means that removing electrons is easier
What is the formula for incomplete combustion?
Fuel + O₂ → CO + C + H₂O
What is the formula for complete combustion?
Fuel + O2→ CO2 + H2O
What is electron affinity?
How strongly an atom wants to gain an electron
What is mass spectroscopy?
Process used to help determine the abundance of each mass number of the different natural occurring isotopes of an element
UNIT 1 END
Describe the 3 types of compounds?
Ionic
Between a metal and a nonmetal
Electron transfer
Covalent
Between a nonmetal and a nonmetal
Electron sharing
Metallic
Between a metal and a metal
“Sea” of free flowing electrons
How does bond length differ in covalent bonds?
Triple bonds are the strongest types of bonds, followed by double and then single bonds. Since the bond is so strong, electrons will be pulled closest together in triple bonds, making them have the shortest bond length. Bond length increases as bond strength decreases.
How does atomic radius affect bond length?
Atoms with greater atomic radii will have longer bond lengths since electrons have a greater distance from the center of the atom.
What is lattice energy?
Energy required to separate ions in an ionic compound (change compound into a gaseous state)
What type of molecules have the greatest lattice energy?
Small molecules. This is because they are held more tightly together in ionic compounds, so it is more difficult break their intermolecular forces
Name the most electronegative atoms in decreasing electronegativity.
Fluorine
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Chlorine

How do you determine bond length from a covalent bond graph showing potential energy and internuclear distance
Atoms to the left of the “Goldilocks Zone” (the dip shown in the middle of the graph) will repel. This is because they are too close together to bond. At the Goldilocks Zone, atoms are the most optimal distance to bond with each other. Past this zone, atoms will be too far away to bond effectively. Atoms with larger bond lengths will appear further to the right on this graph due to their larger size. The distance between two large atoms needs to be greater in order for them to bond effectively.
What is an alloy are what are the two types?
A mixture of two or more metals
Typically have superior properties to that of the individual metals present
Two types
Substitutional alloys: two atoms that are about the same size (one can “substitute” in)
Interstitial alloys: Two atoms with very different sizes (smaller atom goes in between larger atoms
IT IS POSSIBLE to have a combination of both kinds of alloys
What is bond order?
The number of bonding pairs of electrons between two atoms
What is formal charge?
# of valence electrons - # of lone pairs electrons - # of bonds
Remember: Val Likes Bread
0 is the most stable formal charge
What is Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR)?
Model that assumes electrons orient themselves to experience as little repulsion as possible (why molecular geometry and Lewis Structures exist)
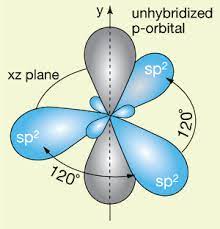
What is hybridization?
The mixing of several atomic orbitals to form the same total number of equivalent hybrid orbitals
When sigma and pi bonds are used
When counting areas of hybridization, count where there is a bond between atoms AND where lone pairs are present
What is a sigma bond?
The first and strongest type of covalent bond
What is a pi bond?
Covalent bond that is weaker than the sigma bond
Restrict movement in molecules
Describe the hybridization of the following bonds:
Single
Double
Triple
Single- s
Double- sp
Triple- sp2
UNIT 2 END
What is polarizability?
Ability of an atom to form a temporary or induced dipole
More electrons increases polarizability
More surface area increases polarizability
What are London Dispersion Forces?
Present in all covalent molecules
Very weak bonds because they are temporary
Result of the Coulombic interactions between temporary, fluctuating dipoles caused by an unequal distribution of electrons
Larger molecules (more surface area/contact area) exhibit stronger LDFs
The more polarizable an atom is, the greater it’s LDF’s (and vice versa)
What are Dipole-Dipole forces?
Present between polar molecules because of their partial positives and partial negatives
Strength depends on:
Magnitude of the dipoles (molecules with larger dipole moments experience stronger dipole-dipole interactions)
Relative orientation (when oppositely-charged poles are close, the interaction is stronger; when like-charged poles are close, the interaction is weak/repulsive)
What are Dipole-Induced Dipole forces?
Present between a polar and nonpolar molecule
A greater dipole moment (difference in charges) of the polar molecule and greater polarizability of the nonpolar molecule increases strength of dipole-induced dipole interactions
What are Ion-Dipole forces?
Forces between ions and polar molecules
What is Hydrogen Bonding?
Special type of dipole-dipole interaction between molecules
Results from the attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (F, O, or N) and another electronegative atom
(F, O, or N) in a different molecule
List the intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest.
Hydrogen bonding
Dipole-Dipole
London Dispersion Forces
What is an ionic solid?
Network of ions held together by electrostatic attraction
Tend to be brittle (due to repulsion of like charges when 1 layer slides across another layer)
What is a covalent network solid?
Network of atoms that are covalently bonded together
Can be 3D network (e.g. diamond)
Can be layers of 2D network (e.g. graphite)
What are molecular solids?
Network of covalently-bonded molecules
Attracted to each other through weak intermolecular forces
Do not conduct electricity
What are metallic solids?
Made of alloys
Tend to have the following properties:
Great conductors of heat and electricity
Malleable
Ductile
What is Kinetic Molecular Theory?
5 part model that explains the properties of ideal gasses
Since the particles are extremely small and have a great distance between them, their volumes individually can be assumed to be zero
Particles are in constant motion and their collisions with the walls of their container are caused by the pressure exerted by the gas
Particles are assumed to exert no forces on each other. They are neither attracting or repelling each other
The average kinetic energy of the particles as a collective is assumed to be directly proportional to the temperature of the gas in Kelvin. This is represented by the formula KE=½MV2
Ideal gasses experience elastic collisions. This means that no kinetic energy is lost or gained when particles collide. All energy is conserved before and after collisions.
Explain when gases deviate from ideal behavior.
Kinetic Molecular Theory states that gases have to be at a high temperature and low pressure, but that is not possible since the 2 are directly related
Gases have few interactions, but they still exist
Elastic collisions are not possible
What is a Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution?
Diagram that shows the distribution of the speed of particles at any given temperature
What is effusion and what is the main idea?
Process in which a gas escapes from one vessel to another through a small opening. Lighter molecules will move faster than larger molecules!!!
Describe how interactions of the solute and solvent must be in a mixture in order for a solution to form.
Solvent-solute interactions must be relatively equal or greater than solute-solute or solvent-solvent interactions in order for a solution to form because these new interactions must be more favorable than the initial conditions
What is filtration?
Method of separation for heterogenous mixtures
What is chromatography?
Method of separation where a solution (called the mobile phase) is allowed to flow on a stationary substance. This separates molecules by their structure/polarity
Assuming the stationary phase is non-polar and the mobile phase is moderately polar, polar molecules will travel far as the liquid moves up the stationary phase while nonpolar molecules will travel less far since they are attracted to the nonpolar stationary phase
What are the types of chromatography and when should they be used? NORDIN
Paper- separating a mixture of different colors. The liquid soaks through the paper and carries the mixture with it. Some substances are carried faster than others so the substances are separated along the paper
Thin layer- separation of small molecules as they move through a silica gel
Column- separated substances are introduced onto the top of a column packed with an adsorbent (as silica gel or alumina), pass through the column at different rates (depending on the affinity of each substance for the adsorbent and for the solvent or solvent mixture) and are usually collected in solution as they pass from the column at different times
What is distillation?
Method of separation utilizing molecules different boiling points
What molecules are always soluble?
Sodium- Na
Nitrate- NO3-
Ammonium- NH4+
Potassium- K
What is photoelectron spectroscopy?
An experimental methos that uses photons to investigate the properties of matter
What color will a sample appear when using a spectrophotometer?
The complimentary color of the wavelength being absorbed
Ex. If a sample absorbs red light, we will see it as green
What are the 3 types of radiation emissions and what do they tell us about molecular motion
Microwave- Molecular rotation
Infrared- Molecular vibration
Ultraviolet/Visible- Transition in electron energy level
Name the types of radiation in decreasing wavelength (increasing frequency)
Radio
Microwave
Infrared
Visible
Ultraviolet
X-Ray
Gamma Ray
Rich Men In Vegas Use Xpensive Gambling
What factors increase boiling point?
High polarity (stronger intermolecular forces)
Increased surface area (more intermolecular forces present)
What is a solubility curve?
Graph that shows the maximum amount of solute a substance can hold at a specific temperature
Anything above the gasses line on the graph means the solution is over-saturated
UNIT 3 END
What is an equivalence point?
Point where all of the acid and base have been neutralized (moles will be equal!)
What is an end point?
Point where the indicator changes color in a nuetralization reaction
What is a redox reaction?
Reaction where a transfer of electrons takes place
What is reduction?
Gain of electrons
What is oxidation?
Loss of electrons
What is an oxidation number?
The charge of an atom or compound
What are the oxidation number rules?
Atoms in elemental form have an oxidation number of zero
Oxygen is always -2
Hydrogen is always +1
Oxidation states in compounds must equal zero
Oxidation states in polyatomic ions must sum to the ion charge
UNIT 4 END
What factors affect reaction rate
Nature/state of matter (gases react faster than liquids)
Concentration (the higher the concentration the more collisions and faster reaction rate)
Surface area (the greater the surface area the faster the reaction rate)
Temperature (higher temperature increases collisions and reaction rate)
How do catalysts lower reaction rates?
By affecting the orientation of the particles
What is collision theory?
Theory that states the following must be true in order for a reaction to occur:
Only 2 particles may collide at one time
Particles must collide
Particles must be aligned properly when they collide
Particles collide with a certain amount of energy
Sequence of collisions is called reaction mechanism
What is an intermediate
Molecule produced in one step and reacted in a following step
What is a catalyst?
Molecule reacted in one step and produced in a following step
What are the possible order for a rate, what do they mean, and what are their units of K?
Zero order- No affect on rate (K0)
Unit: [A]
First order- Doubles rate (K1)
Unit: ln[A]
Second order- Quadruples rate (K2)
Unit: 1/[A]
What order are half lives?
First order
When looking at rate graphs, how cn you tell what order the rection is?
The graph will be linear when the x axis uses the appropriate unit of K
Which step in a chemical reaction determines the rate?
The slowest step
When given a graph, how can you tell which step is the slow step?
The step with the largest “hump” will be the slow step
What is the transition state?
A high-energy intermediate state of the reactants during a chemical reaction that must be achieved for the reaction to proceed
What is the difference between differential rate law and integrated rate law?
Differential rate law is dependent on concentrations while integrated rate law shows the concentration of reactants as a function of time
What is a reaction mechanism?
The step-by-step sequence of reactions by which the overall chemical change occurs
What is the formula for heat of formation?
Products - reactants
What is the formula for bond enthalpy?
Bonds broken- bonds formed
UNIT 5 END
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to raise one gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius
What type of reactions are more likely to be spontaneous?
Exothermic reactions?
What is a triple point?
Point where temperature and pressure exists so that the substance exists in gas, liquid, and solid phases at once
What is critical temperature?
Temperature above which a substance cannot exist in the liquid phase
What is critical pressure?
Pressure at the critical temperature
What is the critical point?
Intersection between the critical temperature and pressure
What formula is used in a heating and cooling curve when a solid is changing into a liquid?
ΔH=nΔHfus
What formula is used in a heating and cooling curve when a liquid is changing into a gas?
ΔH=nΔHvap
Where direction is heat flowing is a heating/cooling curve has a positive trajectory?
Into the reaction (endothermic)
Where direction is heat flowing is a heating/cooling curve has a positive trajectory?
Out of the reaction (exothermic)
What do the values of ΔG mean?
Positive ΔG= non-spontaneous
Negative ΔG= spontaneous