Plate Tectonics Quiz 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Components of Earth System
Biosphere, Hydrosphere, Cryosphere (Whats around us)
Atmosphere (Above us)
Solid Earth (Below Us)
Main Elements of Earth
Iron (35%)
Oxygen (30%)
Silicon (15%)
Magnesium (13%)
Organic Chemicals
Carbon containing compounds (like skeletons)
Minerals
Solid, naturally occurring, orderly manner/composition
Glass
Not a mineral - not orderly arranged/composed
Melt
a solid material becomes hot and transforms into liquid
Rocks
Coherent aggregates of minerals, crystals, grains, or glass
Igneous Rocks
Formed when molten cools and solidifies
Sedimentary Rocks
rocks formed from sediments - formed from broken pieces of other rock types or from minerals out of water solutions (can have organic materials in it)
Metamorphic Rocks
When pre-existing rocks undergo changes due to response in temperature and pressure
What are Earth’s layers
Crust, Mantle (Upper, Lower), Outer Core, Inner Core
Continental Crust Characteristics
Thicker (25-70 km thick), Less dense, Granite in Composition
Oceanic Crust
Thinner (7-10 km thick), Denser, Basaltic in Composition
Mantle
Hot, Dense, Iron and Magnesium rich, some solid rock, some viscous areas (like honey)
Core
Outer Core is liquid (only true liquid layer), Inner Core is solid (pressure keeps atoms locked together in dense crystal) } both made of Nickel and Iron
Mechanical Layering of Earth
Lithosphere: Crust and top of mantle (solid, behaves elastically)
Asthenosphere: Region of the mantle that flows easily (plastic, 100km thick)
Mesosphere: Lower mantle (material flows, but slower than asthenosphere)
Outer Core
Inner Core
Explain Convection and what it can cause
Ridges, Trenches, (you know what convection is just make sure you say upwell and downwell)
Superposition
Undisturbed layers have the youngest on the top and oldest on the bottom
Principal of Original Horizontality
Layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally under the influence of gravity
Principle of Inclusion
Broken pieces of other rocks (inclusions) that are included in a rock layer need to exist before the rock layer
Principle of Original Lateral Continuity
sedimentary layers are initially deposited in continuous, horizontal sheets that extend in all directions until they taper out, thin, or encounter a barrier
Cross Cutting Relationships
any geologic feature—such as a fault, dike, or intrusion—that cuts across another rock body must be younger than the material it disrupts
Deformation
the change in a rock's shape, size, or position due to stress from tectonic forces (causes folds, faults, etc)
Uncomformities
gaps in geological record that may indicate episodes of crustal deformation, erosion, and/or sea level variations
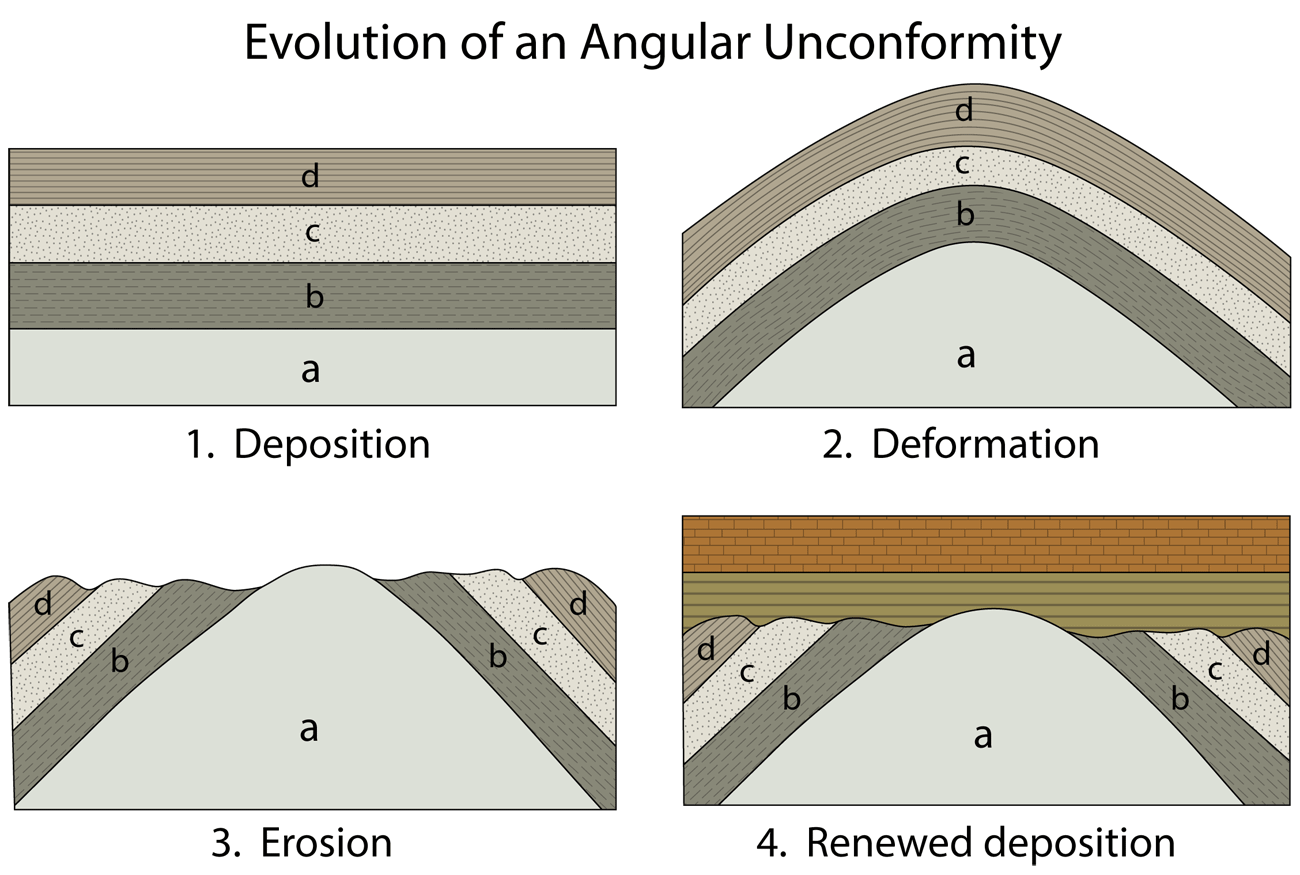
Angular Uncomformity
a type of geological unconformity where younger, horizontal sedimentary rock layers overlie older, tilted or folded sedimentary layers.