CPF - Unit 5
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Federal Insurance Contributions Act
A U.S. payroll tax collected to fund the social security and medicare programs.
Who is medicare for?
Senior Citizens
Social Security
A federal program in the U.S. that provides retirement benefits and disability income to qualified individuals and their spouses, children, and survivors.
What is the total and split Social Security Contributions though OASDI?
12.4% - 6.2%
Who Contributes to Social Security?
Employer and Employee
Is there a cutoff for Social Security?
When making over $176,100 in 2025 you can stop contributing.
How do you qualify for Social Security?
Worked a total of 40 quarters/seasons and you contributed to the system.
What affects/calculates you Social Security Benefits?
Your highest 35 years of wage earning, your birth year, the percentage contributions, and the age you claim retirement.
Early Retirment
Age 62, Benefits Decrease by 30%
Full Retirement
Age 65-67
Delayed Retirement
Age 70, Benefits Increase by 24% (*% per Year)
The year you retire is affected by
Tax Rates, Capital Gains, IRA withdrawals, Life expectancy in your family history.
Social Security Benefits
Pre-determined steady income, income you can’t outlive, annual inflation adjustments, spousal and survivor benefits.
Does Social Security Increase with Inflation?
Yes, through Cost-of-Living Adjustments (COLAs)
Other fundings for Retirment
Personal Savings, Pension, Part-Time Work, Delaying Benefits, and Budgeting Well.
How much does social security replace.
40%
What % does retirees need of their preretirement?
70-80%
Social Security Covers all Retirement Expenses
False
What percentage is social security increased by inflation.
2.8%
Who is Medicare for?
People 65 and older or who have a qualifying disability.
Part A of Medicare
covers hospital insurance and inpatient care.
Part B of Medicare
covers outpatient care and medical services.
Part C of Medicare
A Medicare Advantage plan that combines the benefits of Part A and Part B
Part D of Medicare
provides prescription drug coverage.
Medicare Tax Percentages
2.90% - 1.45%
Higher Wage Earners and Medicare
My see an additional .9% taken out. $250,000 - Married, $125,000 - Married filling separately, $200,000 - Single
Retirement Planning
Determining retirement income goals and what’s need to achieve those goals.
What affects your retirement planning?
WLE, RWLE, RLE
Work Life Expectancy (WLE)
Number of years that you work in your life time.
Remaining Work Life Expectancy (RWLE)
How much time does someone have before they retire to work.
Retirement Life Expectancy (RLE)
How many years will you be retired (Not predictable).
Savings Concepts
Amount, Rate, Investments, Inflation
Time…
affects your savings percentage.
Retirement Income Sources
Social Security, Private Pensions, Savings, Work
Wage Replacement Ratio (WRR)
Estimate of retirement income based on employment income. Calculation compares employment income and retirement budget.
Top-down Approach
Used with younger clients where expenditure patterns are likely to change dramatically over time.
Budgeting Approach
Used with older clients because, as a person nears retirement, it is possible to examine the actual expenditure patterns of the person.
401(k)
A defined-contribution, tax-advantaged retirement savings plan that is sponsored by one’s employer.
403(b)
A tax-advantaged retirement account for certain employees of tax-exempt organizations.
What happens when you switch jobs?
You can roll it over or cash it out with potential tax penalties.
ROTH IRA
Individual owned, you contribute after you pay income tax, where it grows tax free.
Simplified Employee Pensions
IRA for someone who is self-employeed or a business owner.
Tax Free vs Tax Deferred Accounts
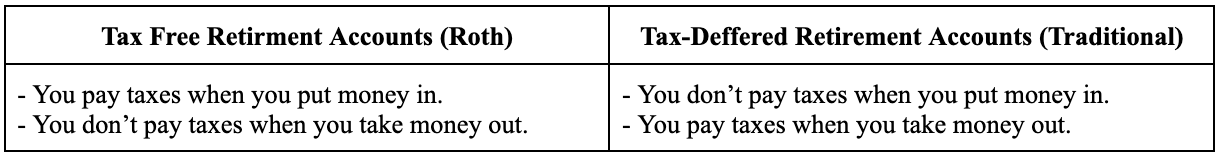
Pension Plan
employer-sponsored retirement program that provides guaranteed income for life (or a set period) after you stop working, funded by employer contributions and investments.
Are there retirement plan limits?
Yes
Will
A legal document communicating a person's final wishes about their possessions. Interstate is where courts decide the actions of your stuff if you do not have a will.
Power of Attorney
Can legally act as another person. Paperwork must be signed to grant this.
Living Will
A legal document expressing your wishes about medical treatment if you cannot make your own decisions.
Beneficiary
Who receives an asset.
Executor
The person who is willing to perform what is stated in the will. They divide assets, collect owed money, pay off debts, make decisions about selling and investing.
Probate
Legal process with court involvement, it costs money, and lengthens the time to recieve the proceeds. To avoide propate use of a trust, naming beneficiaries on financial accounts, joint property ownership, and gifts.
Trusts
A legal arrangement in which property is transferred. Revocable trusts can be changed. Irrevocable trusts cannot be changed.
- Grantor: Who owns the stuff
- Trustee: Who manages and dowels items out to beneficiaries.
Revocable vs. Irrevocable
Can Change vs. Cannot Change
Gift Tax
A federal tax applied to gifts of money or property over a certain sum.