Types of Maps
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
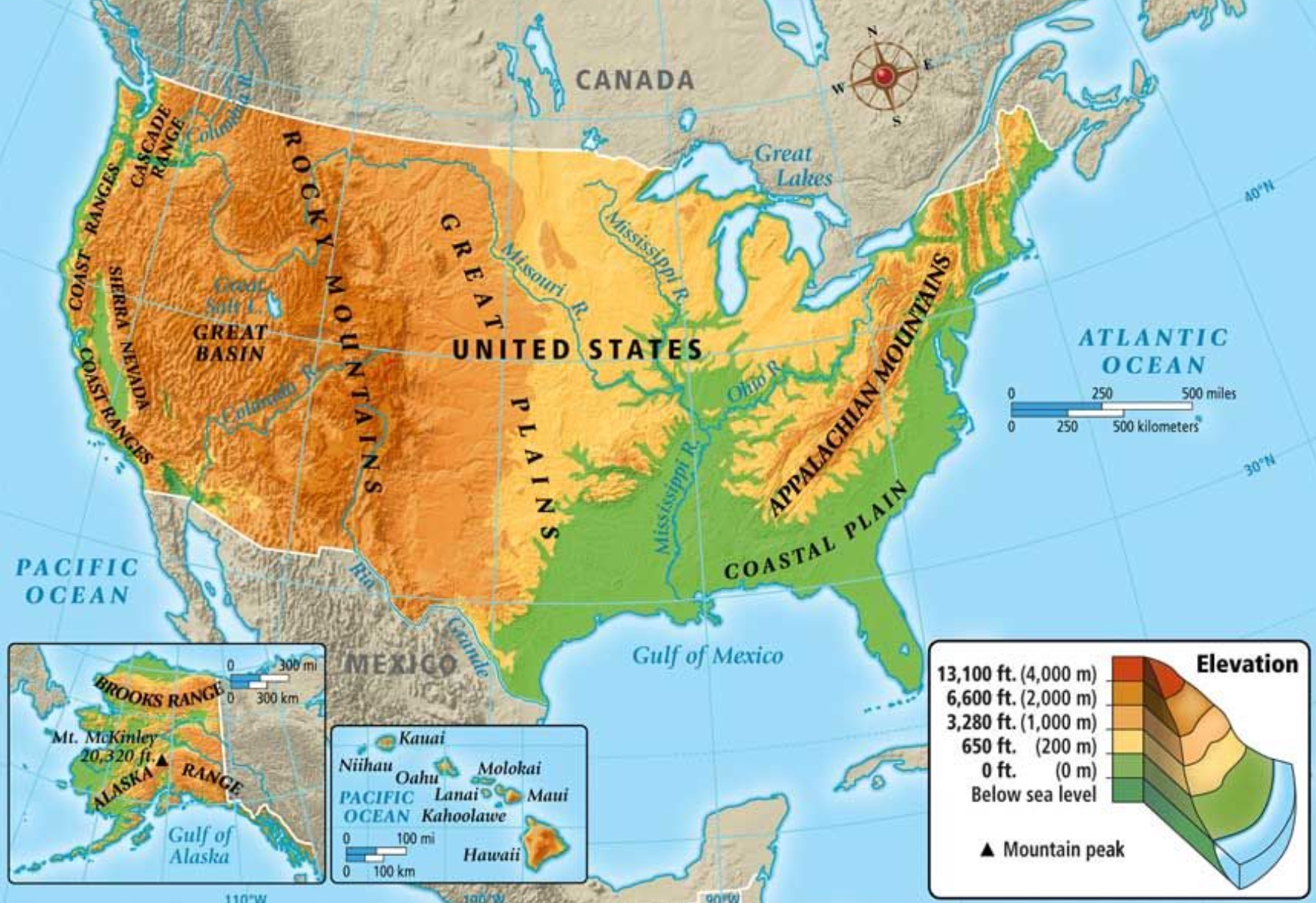
Physical Map
A two-dimensional representation of a region's physical features.
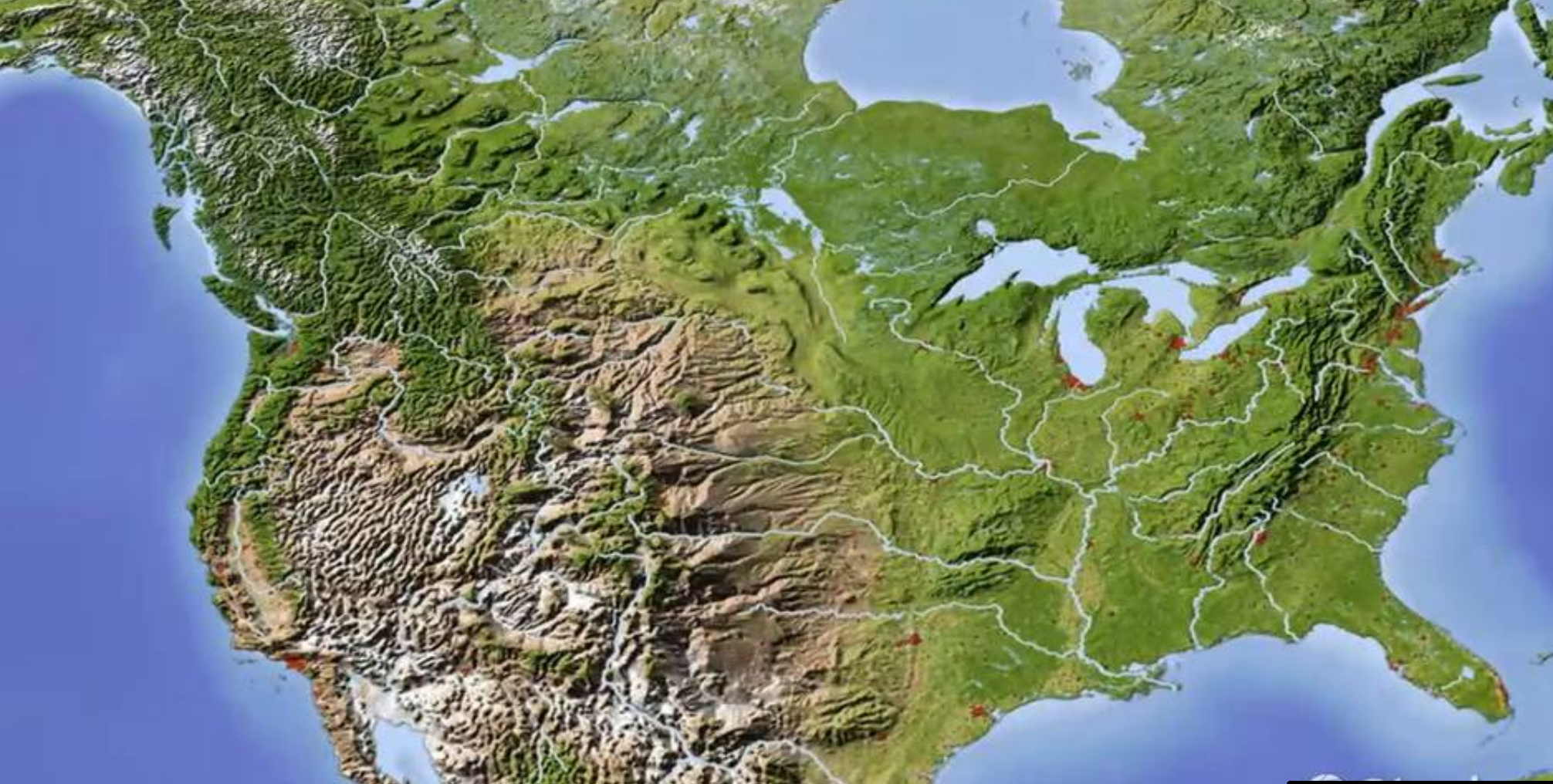

Relief Map
A representation of the terrain features of the ground above sea level.
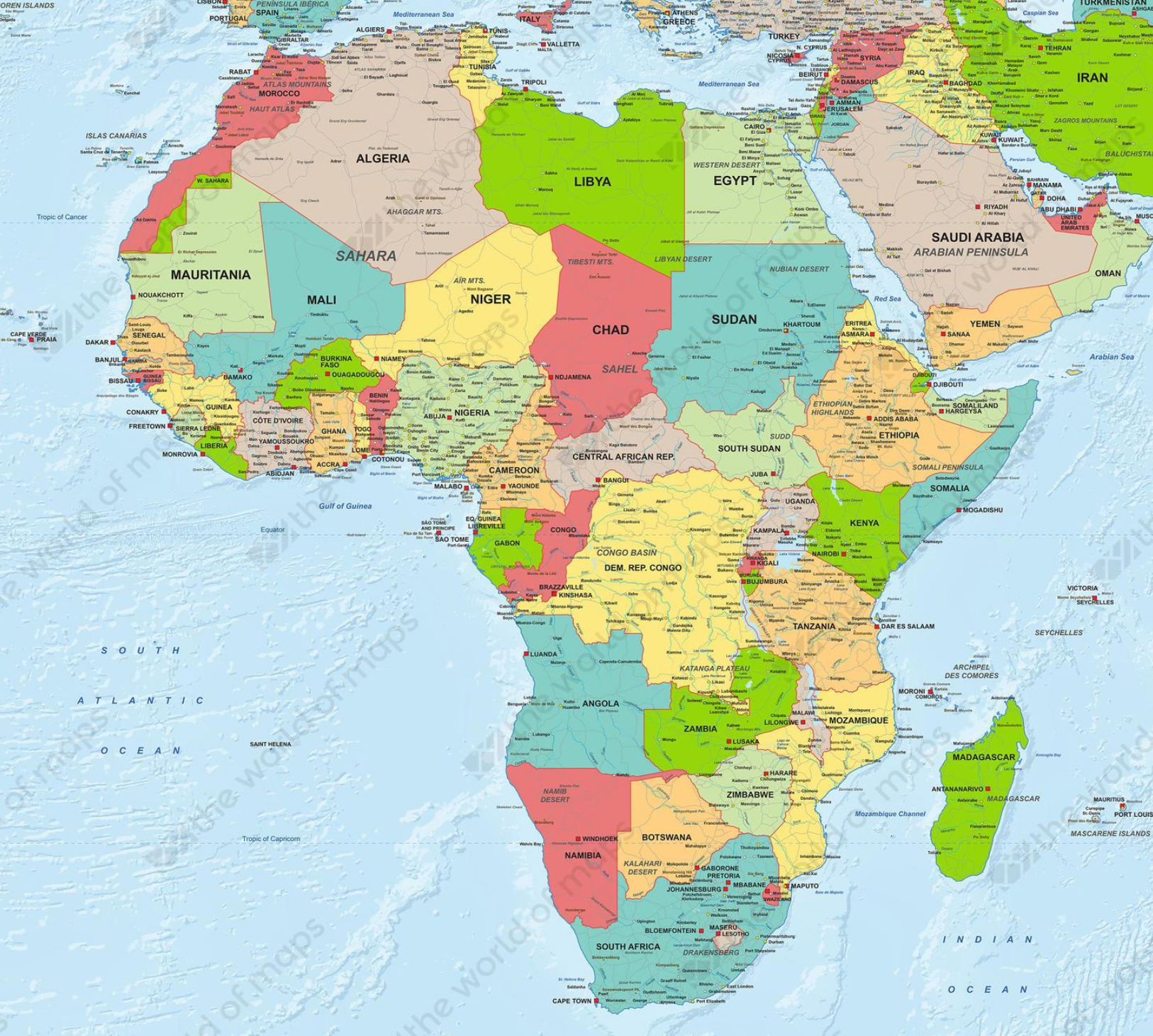
Political Map
A map that shows political divisions and administrative boundaries (names and borders).
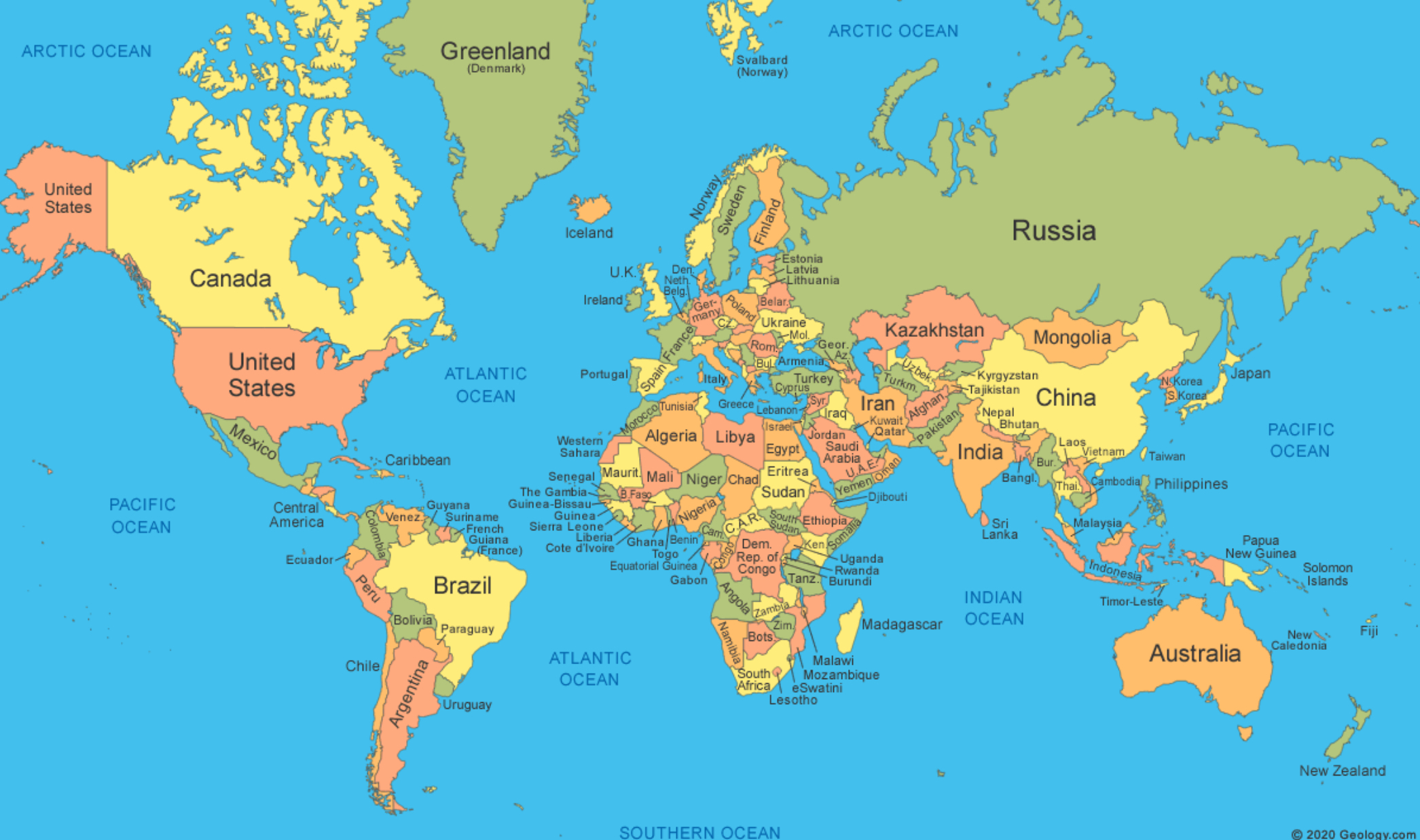
World Map
A graphical representation that depicts Earth's exterior on a flat surface.
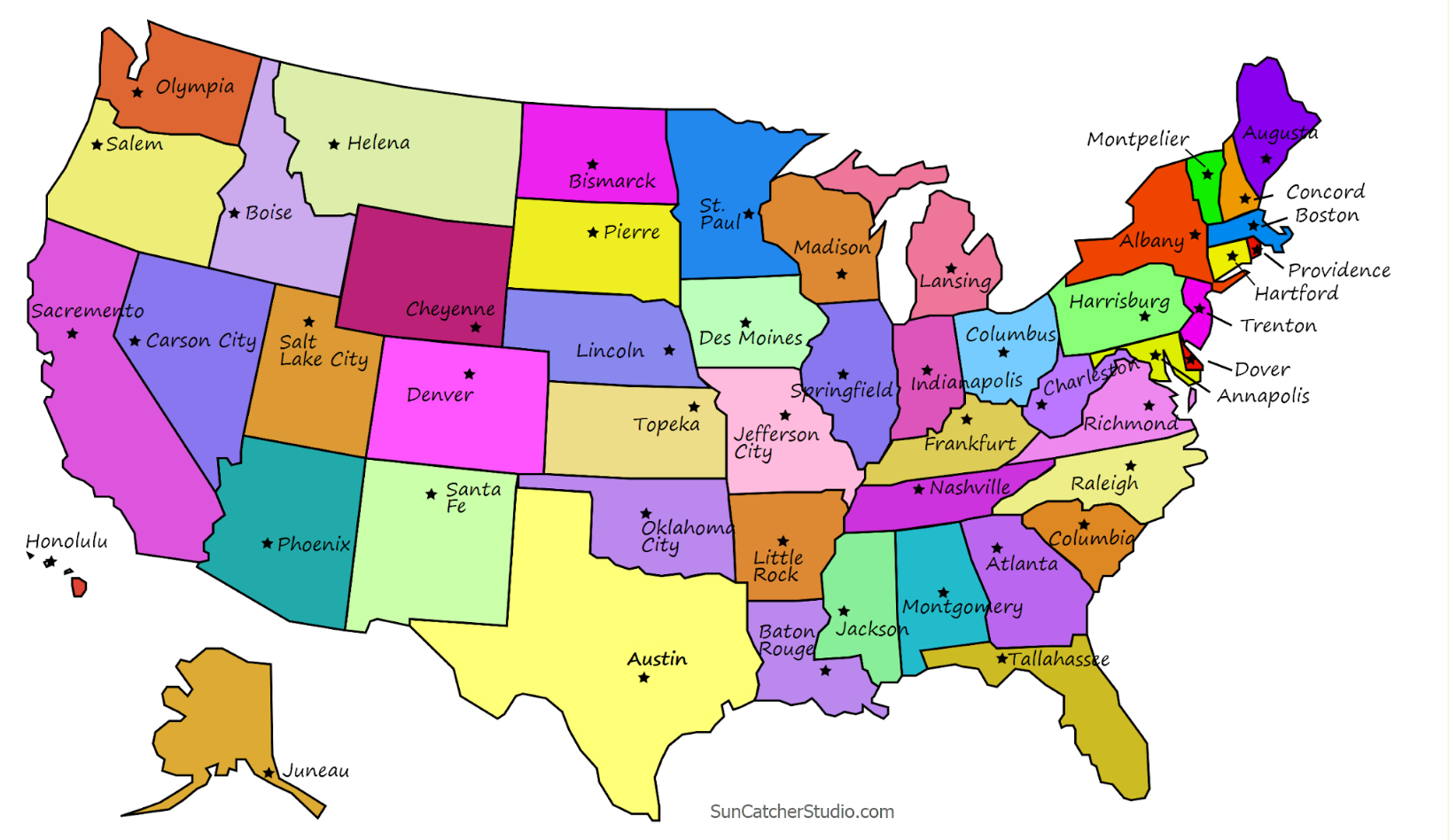
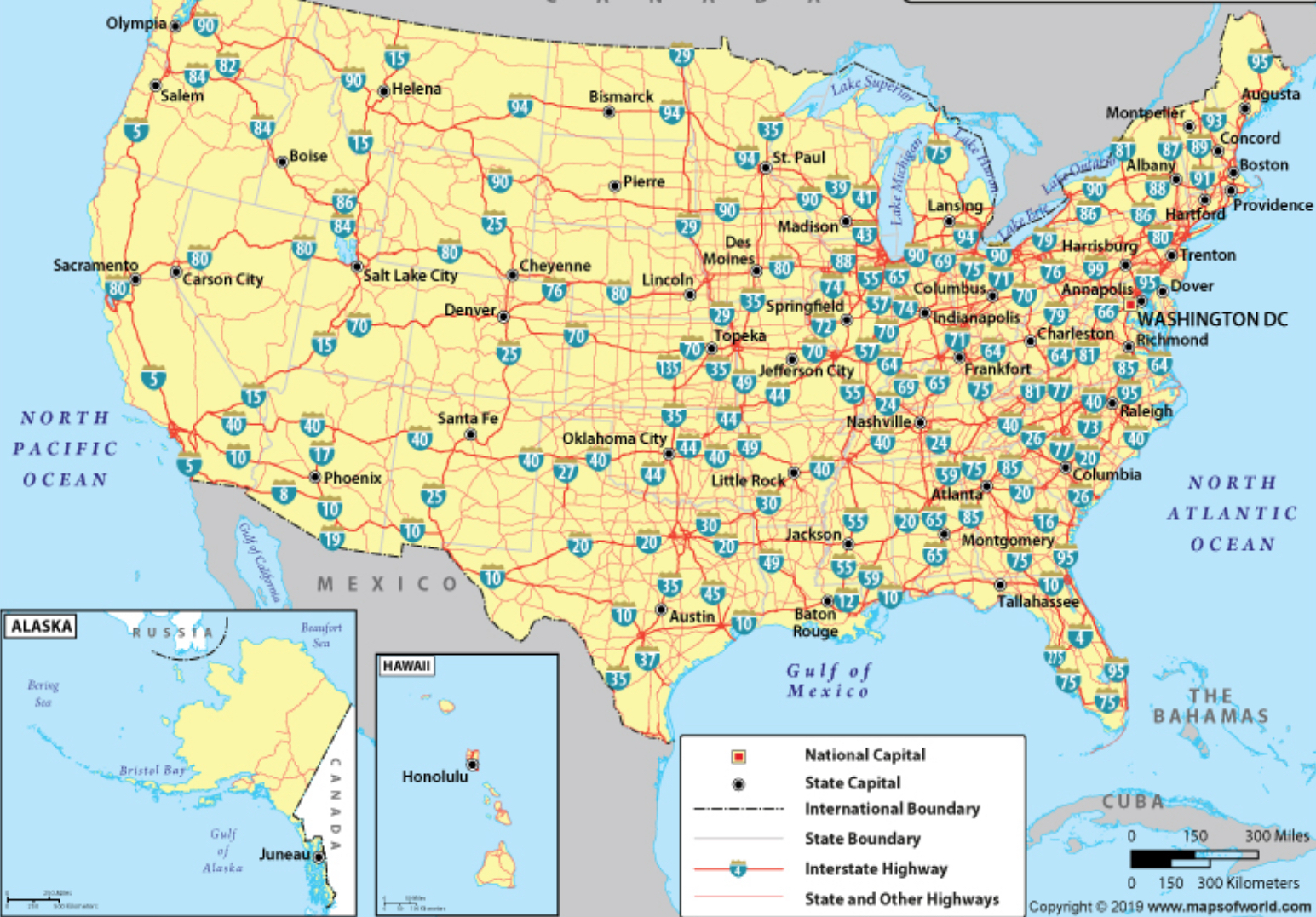
National Map
A collection of topographic information and boundaries relating to the whole of a country.
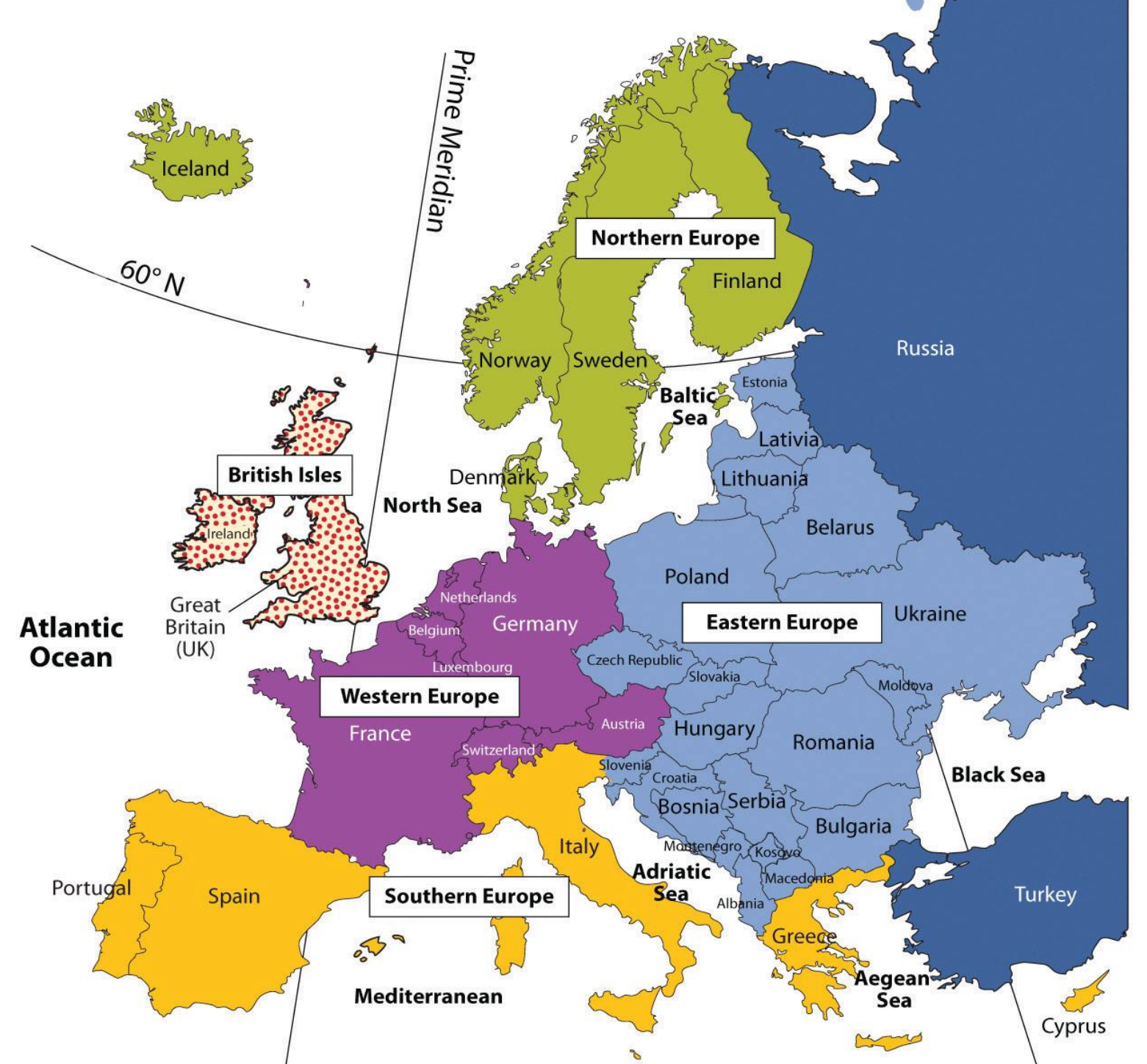
Regional Map
A map that shows the boundary of a particular landmass (of considerable extent) within a larger area.
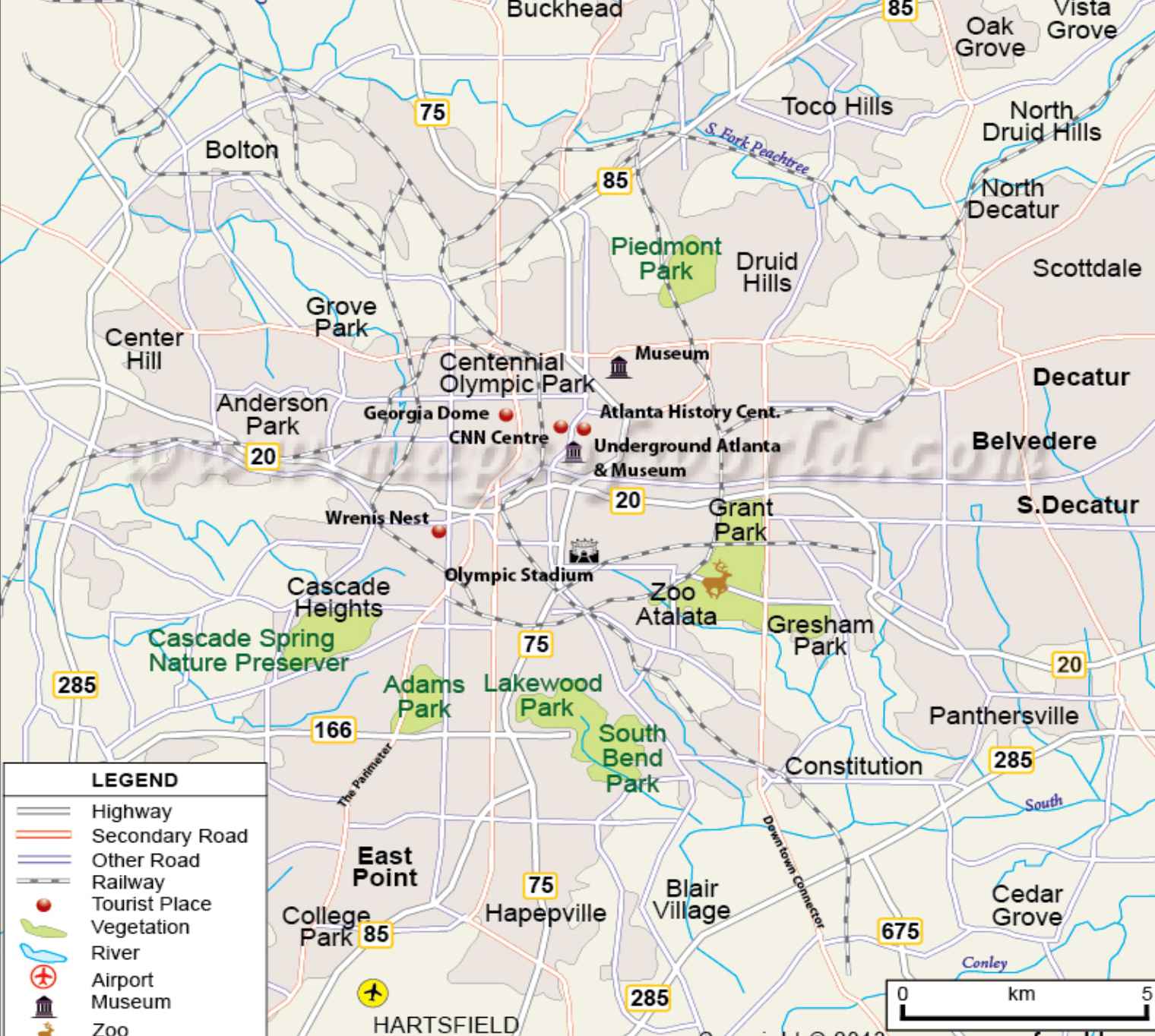
Local Map
A partial view of a larger map intended to show links and nodes to process complex elements.
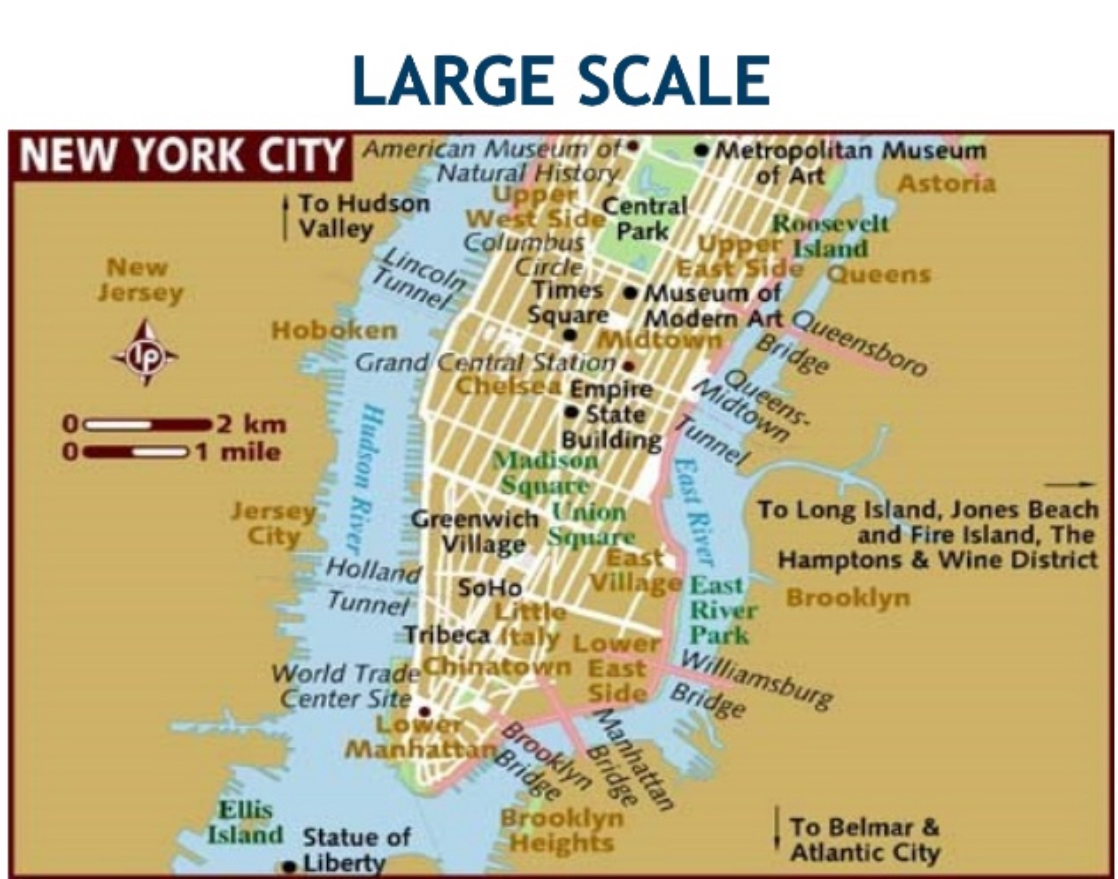
Reference Map
A map that shows the location of geographic areas for the purpose of orienteering, land use, and infrastructure (unique identifiers).
Mobility Map
A method used to explore the movement patterns of an individual, group, or a community.
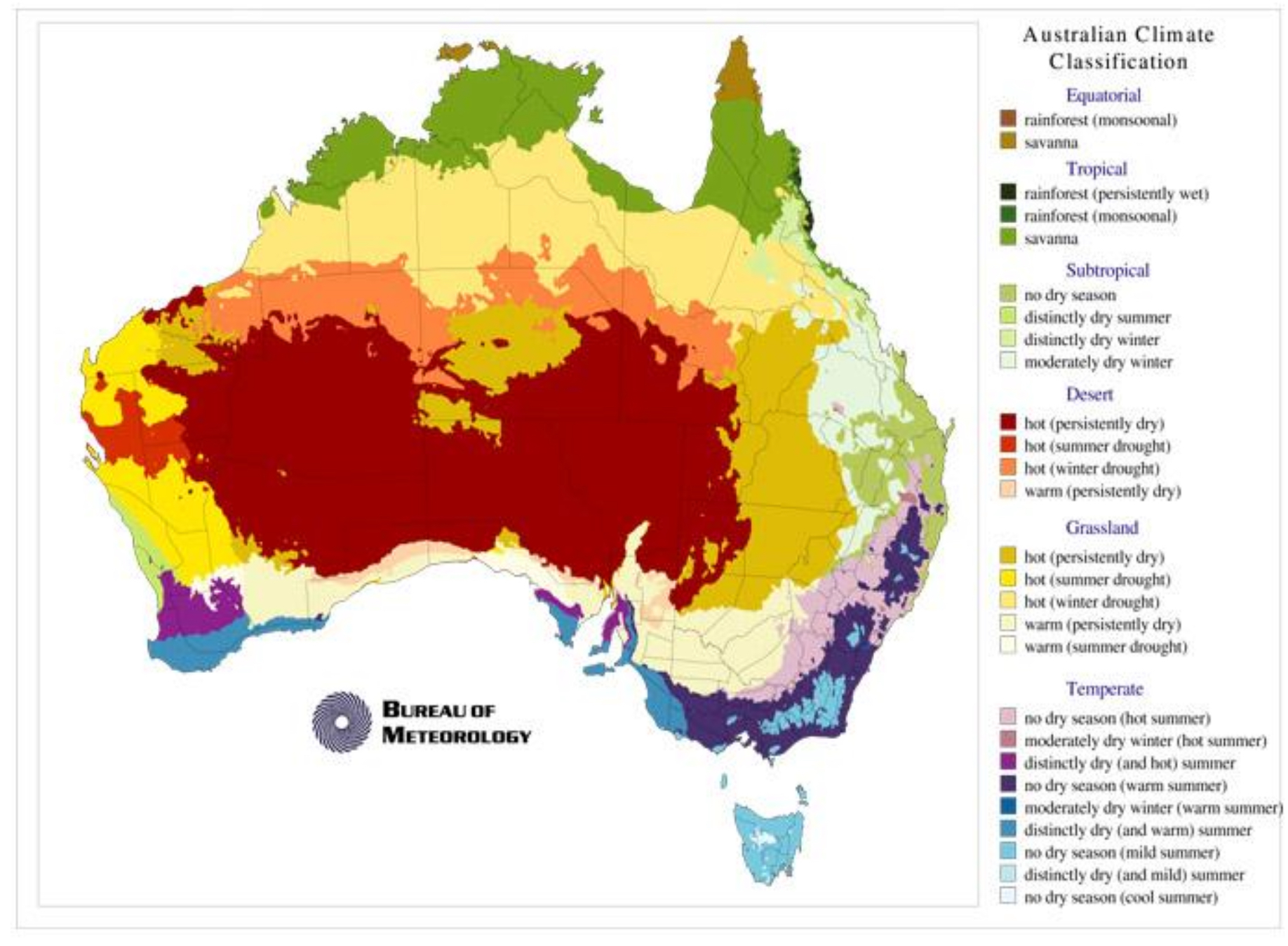
Choropleth Map
A map that uses color or shading to represent statistical data for geographic areas.
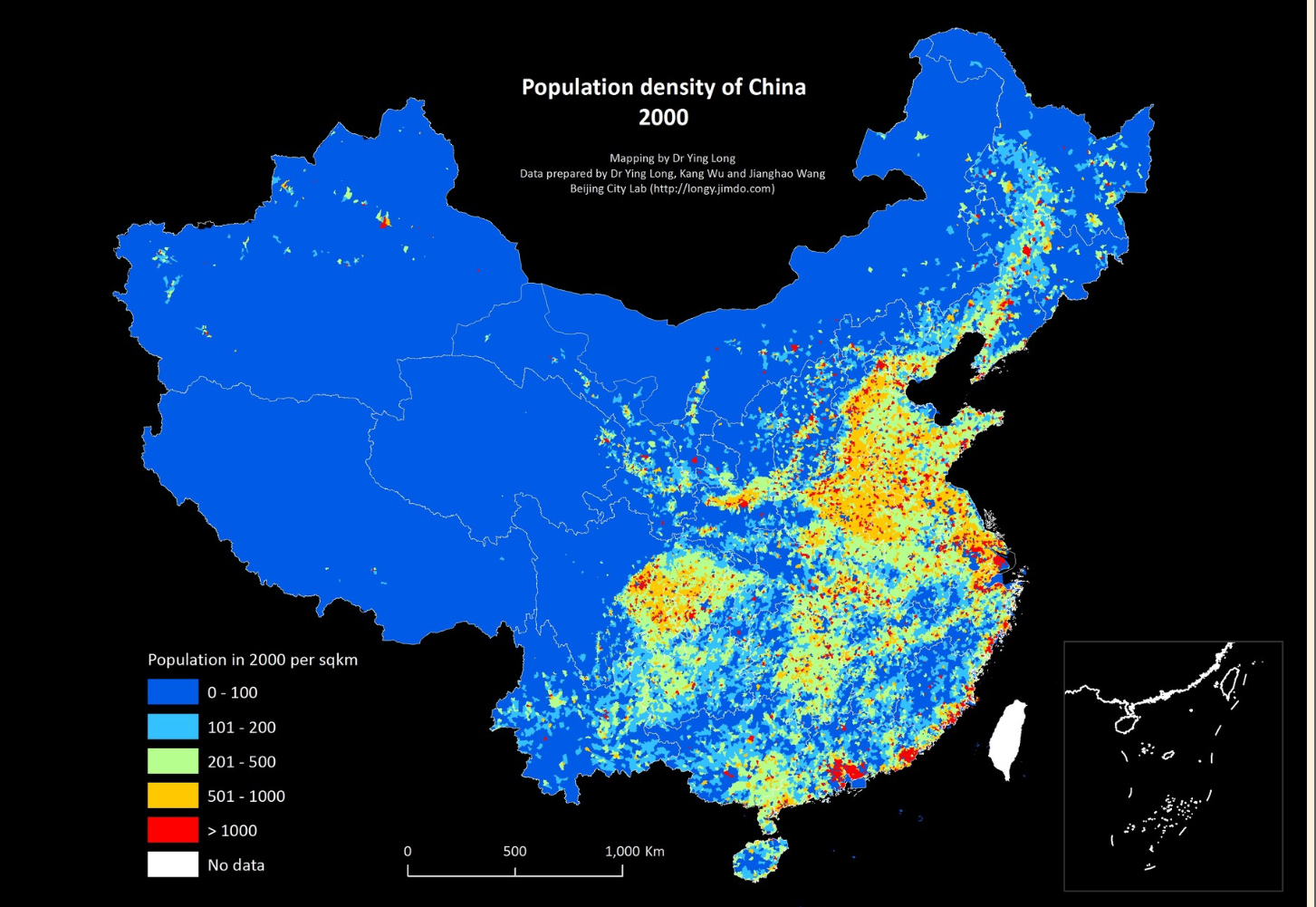

Dot Map
A type of map that uses a point symbol to indicate the distribution of many related phenomena (population). Density is a secondary indication.
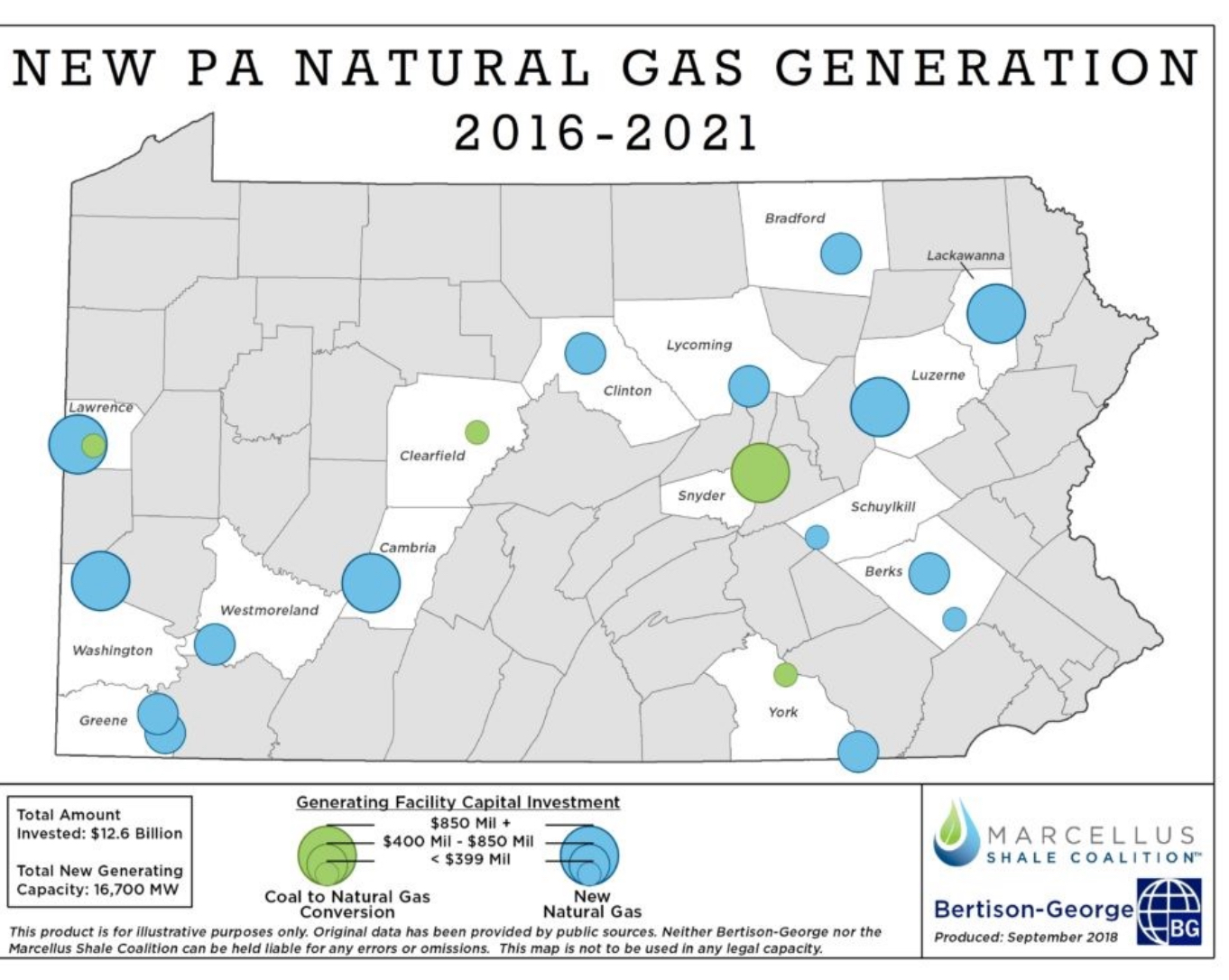
Gradient Map
A map that displays the mood of an image by changing the value of a variable (size or color).
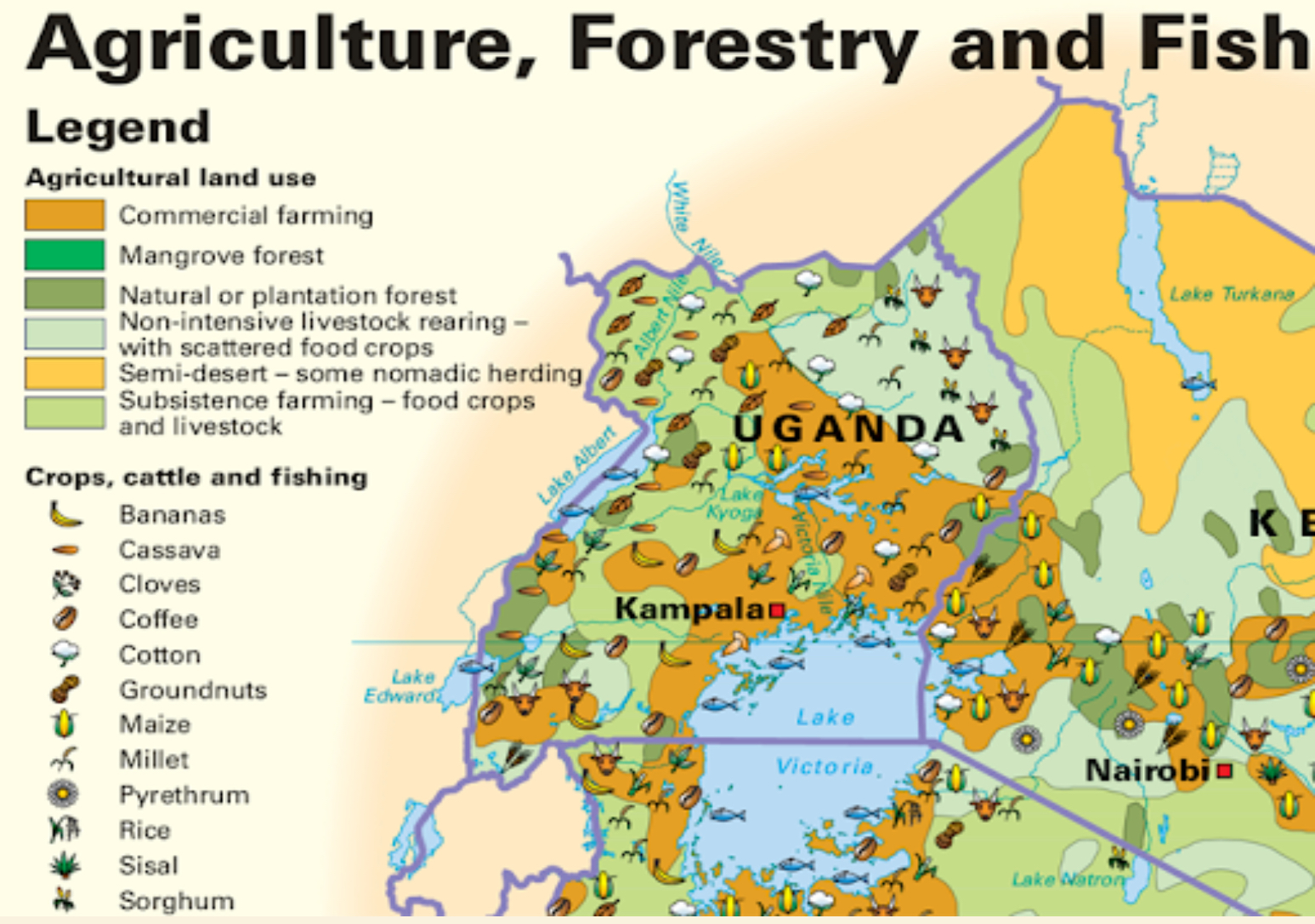
Thematic Map
A map that portrays the geographic pattern of a particular subject (theme) in a geographic area using map symbols.
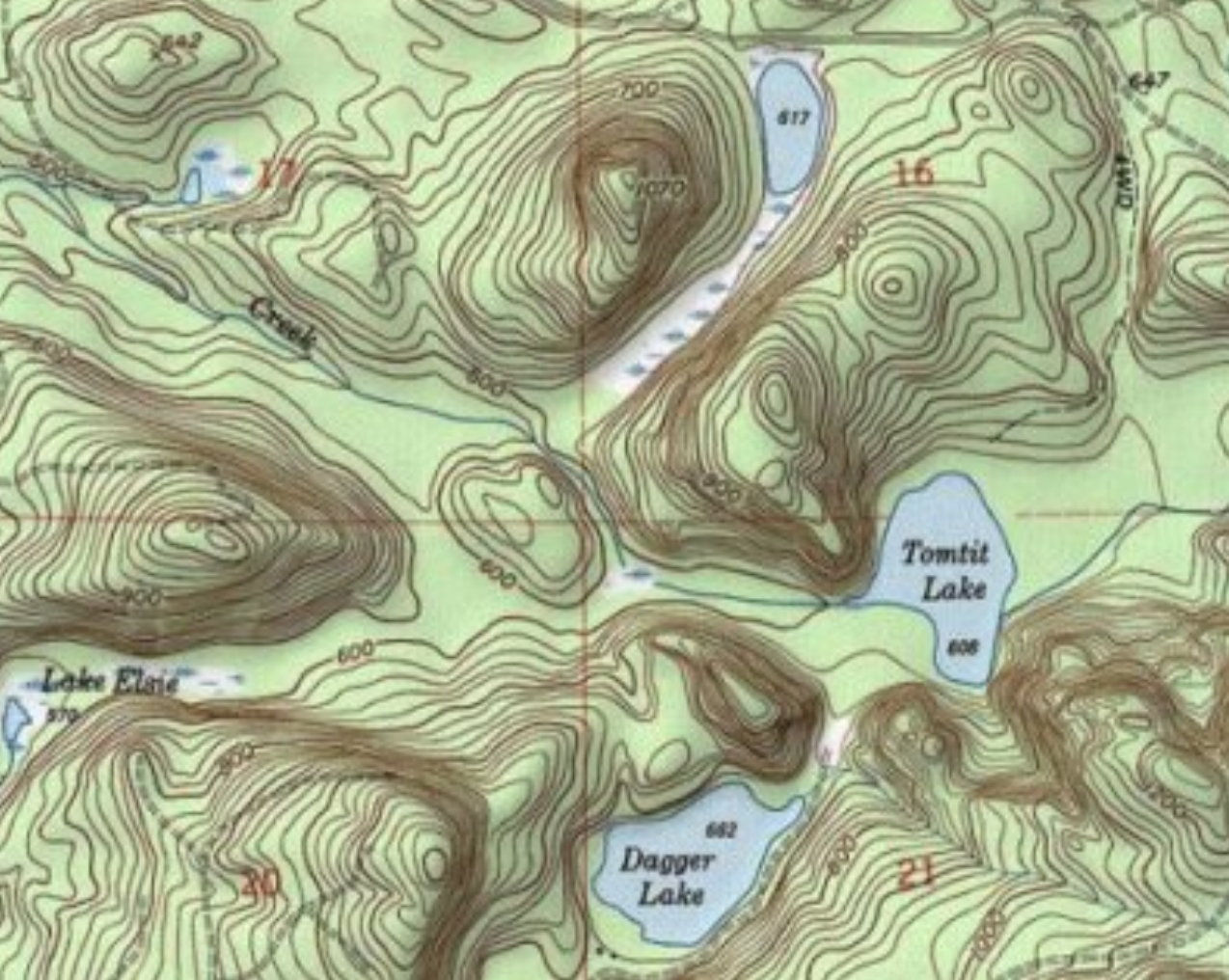
Topographic Map
A detailed and accurate illustration of man-made and natural features on the ground of a specific area.
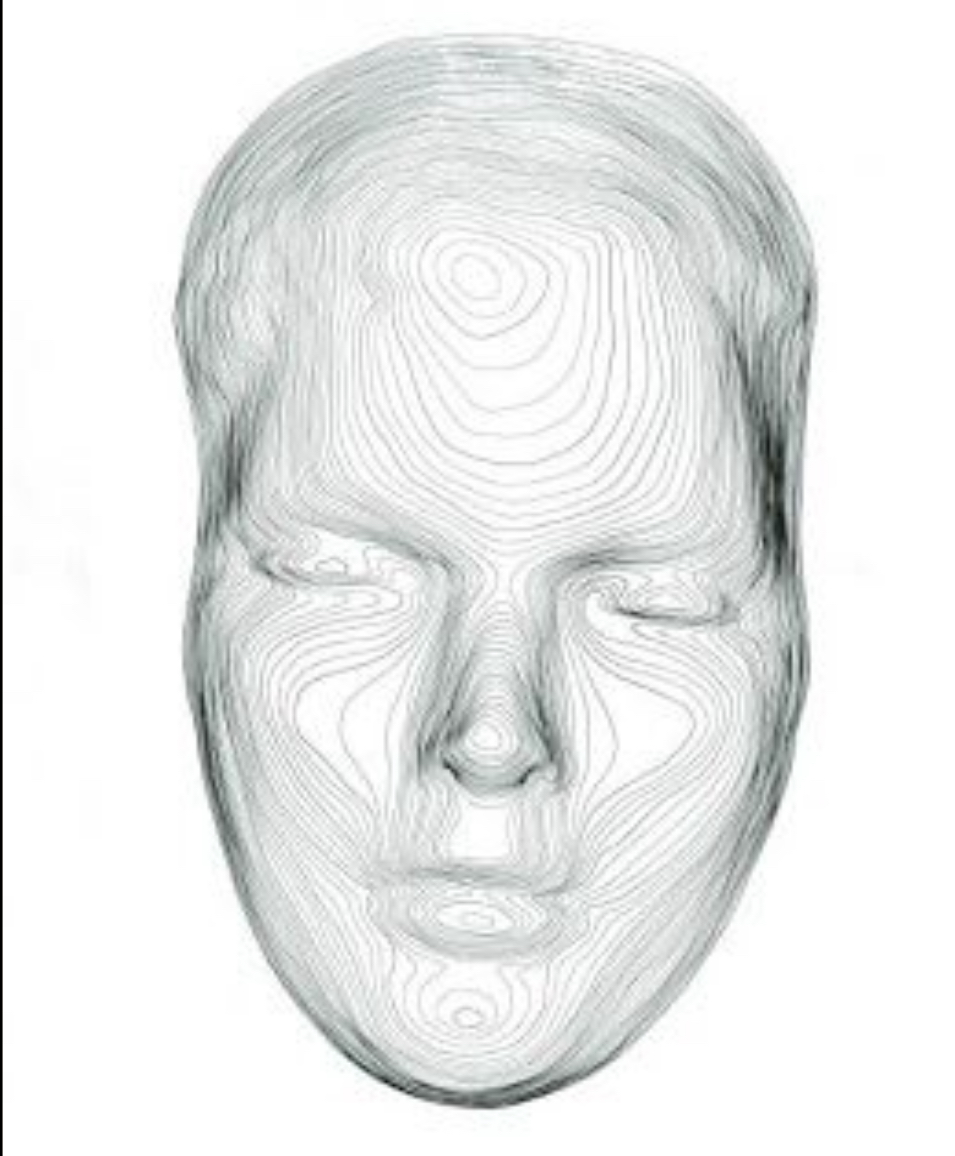
Contour Map
A map that shows elevations above sea level and surface features of the land by means of contour lines (curved lines).
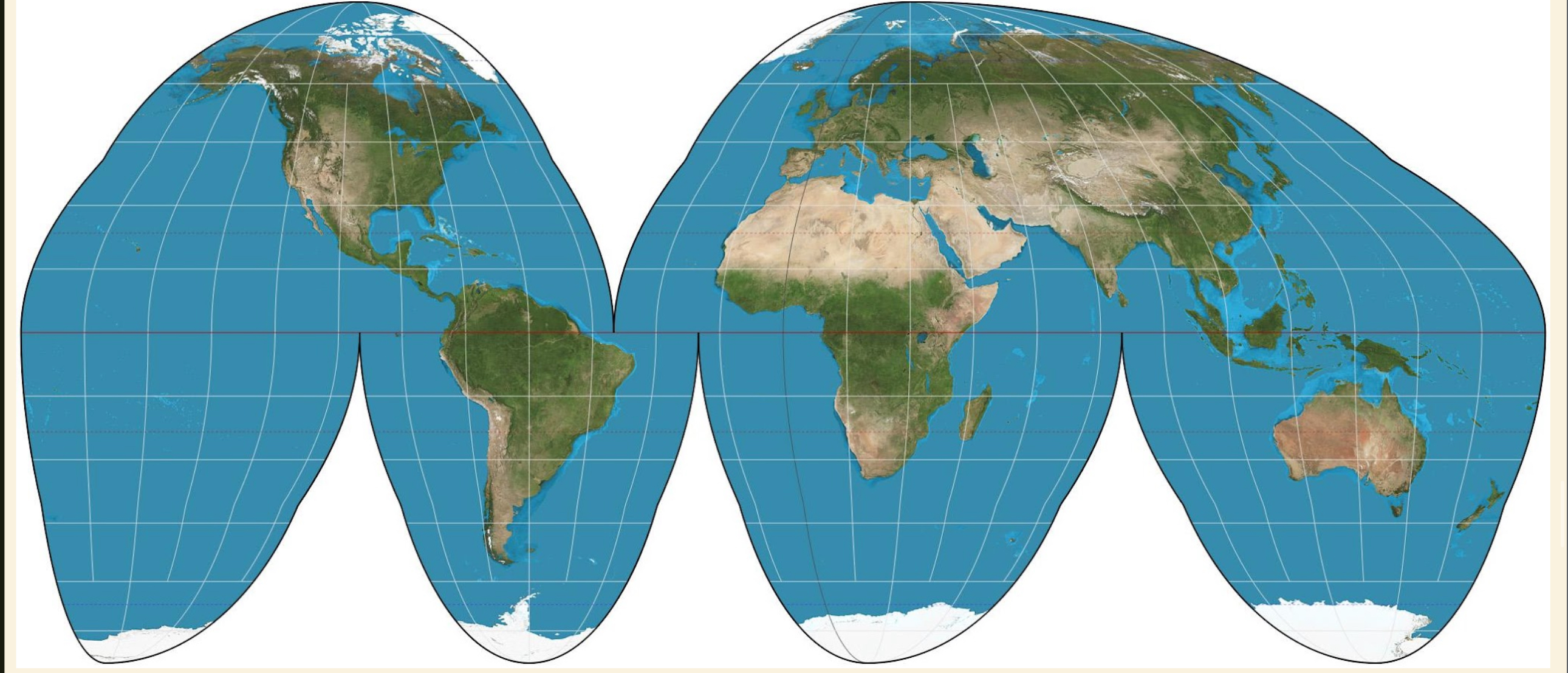
Homolosine Map
An interrupted, equal-area composite map projection of the entire world with discontinuity in the ocean regions.
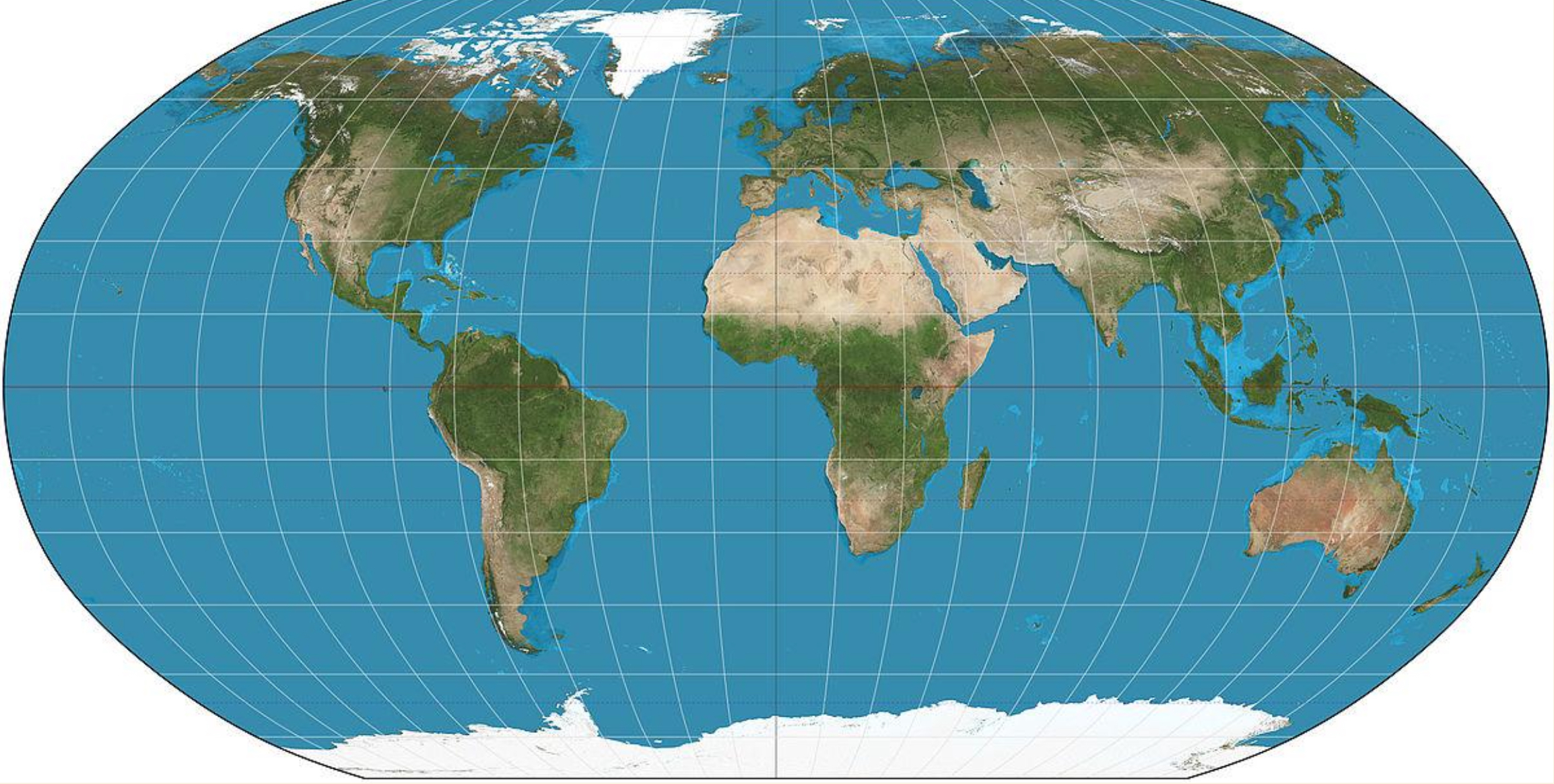
Robinson Projection
A compromise map projection that readily shows the whole globe as a flat map and accurately portrays the water to land ratio. Distorts distance and direction.
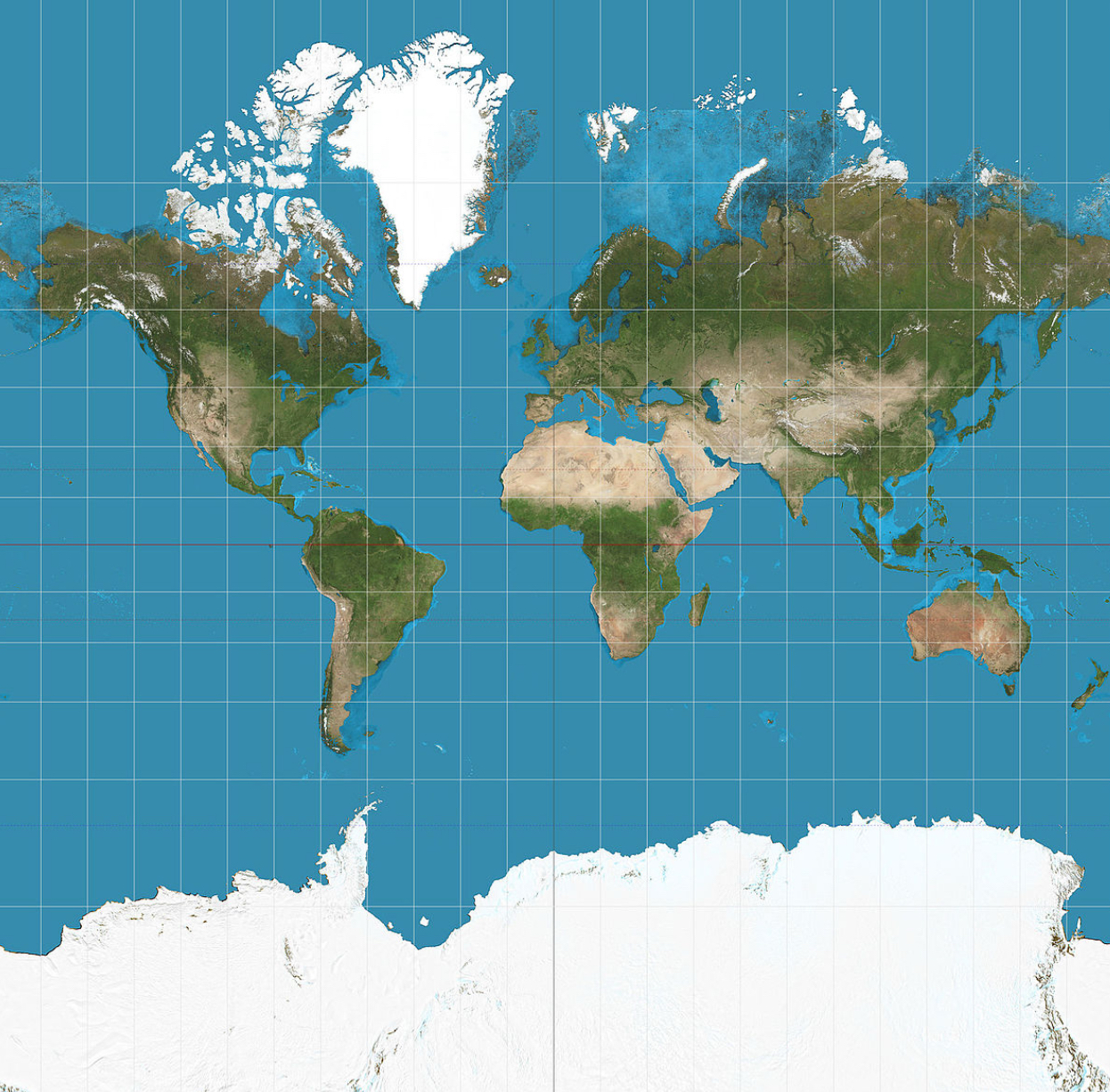
Mercator Projection
A conformal map projection where meridians are equally spaced straight lines that extend beyond the poles and parallel lines are farther apart as their distance from the Equator increases. It is used as a navigation tool that allows navigators to get their 'true bearings'. Distorts size and shape.
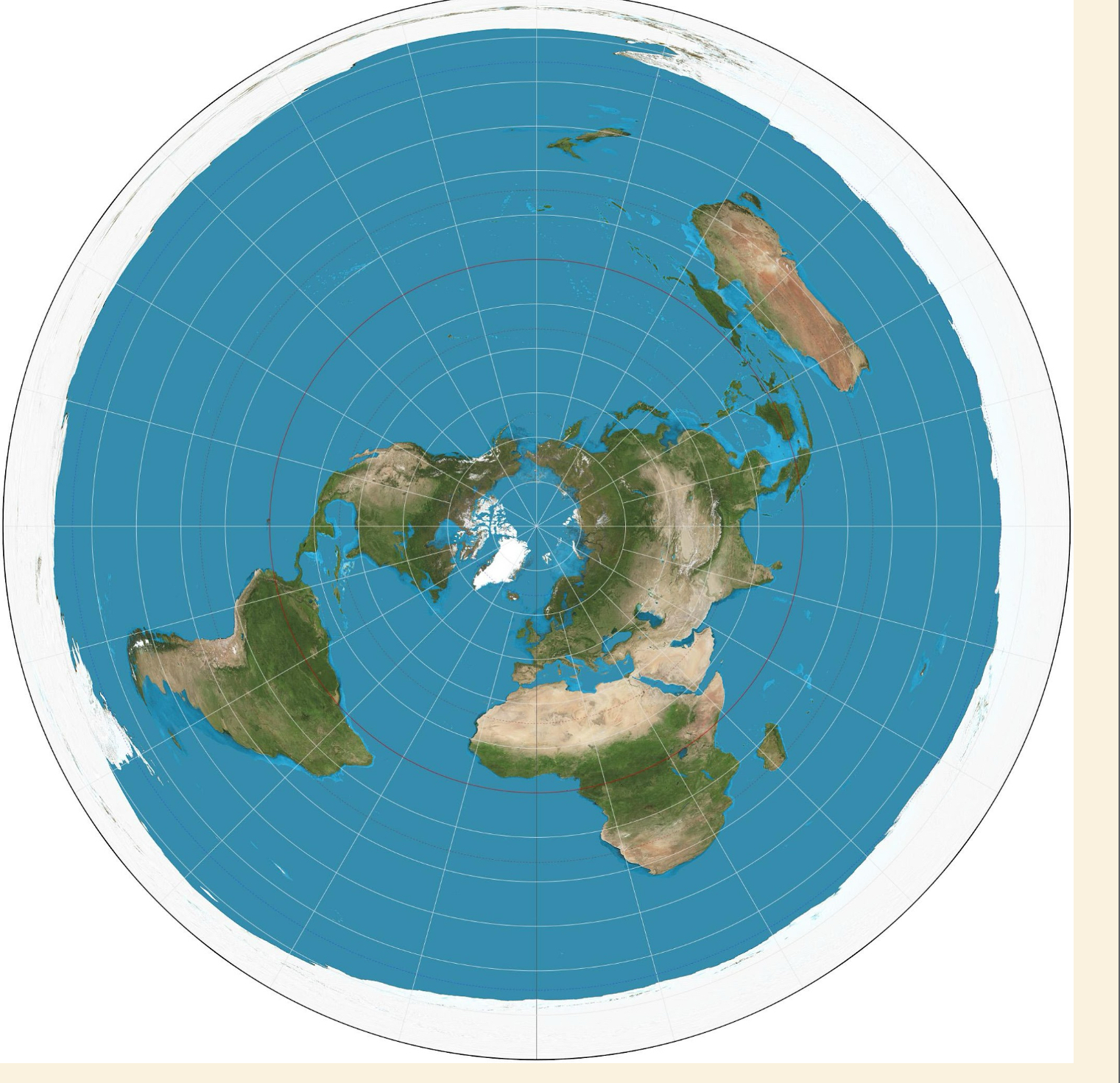
Azimuthal Projection
An equidistance projection where all points on the map are at proportionally correct distances from the center point.
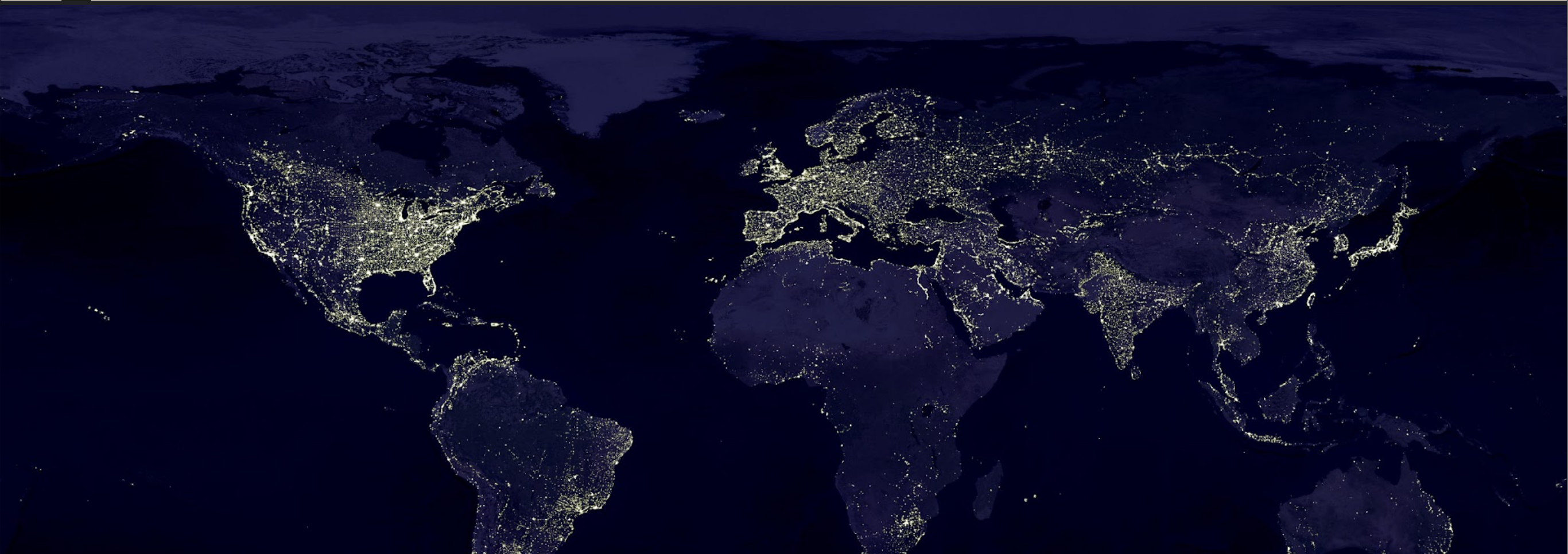
Landsat Map
Spatial-resolution imagery that provides large areas of repeated data at a scale that enables users to see detailed human-scale processes.
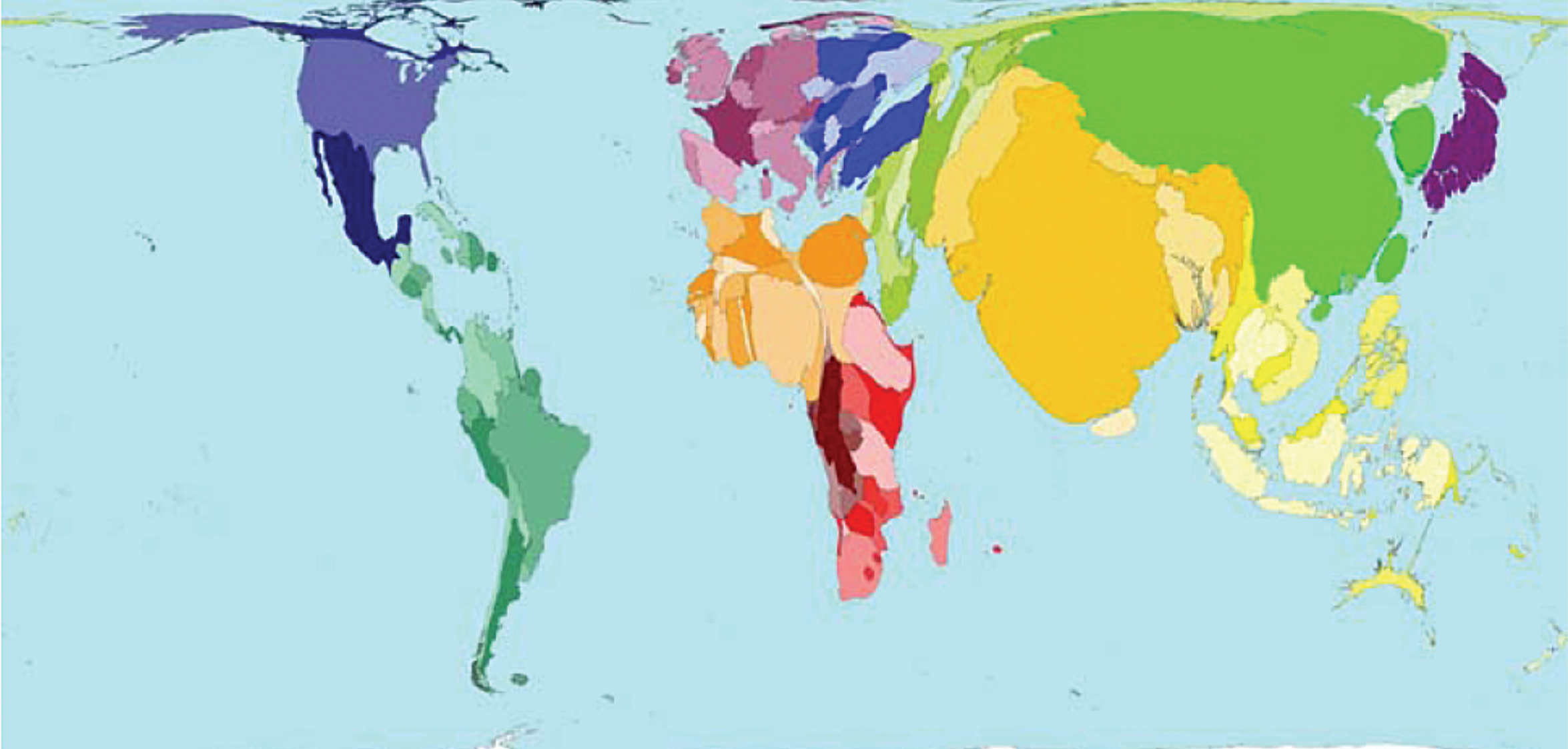
Cartogram
A map that uses distorted geometry to represent a thematic variable.