Microeconomics Unit 6
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Government role in private sector
Provide legal and social framework
Market failure #1
public goods: products that most people want but nobody wants to buy. So, the market doesn’t produce them.
Ex: Firehouse
Private goods
Rivalry: my use automatically precludes yours Ex: Clothes
Excludable: I can keep you from getting the benefit of my good Ex: Locking your car and keeping the key
Publics goods
Non-rivalry and non-excludable
Free riders: people who enjoy the benefit of a public good but don’t pay for it
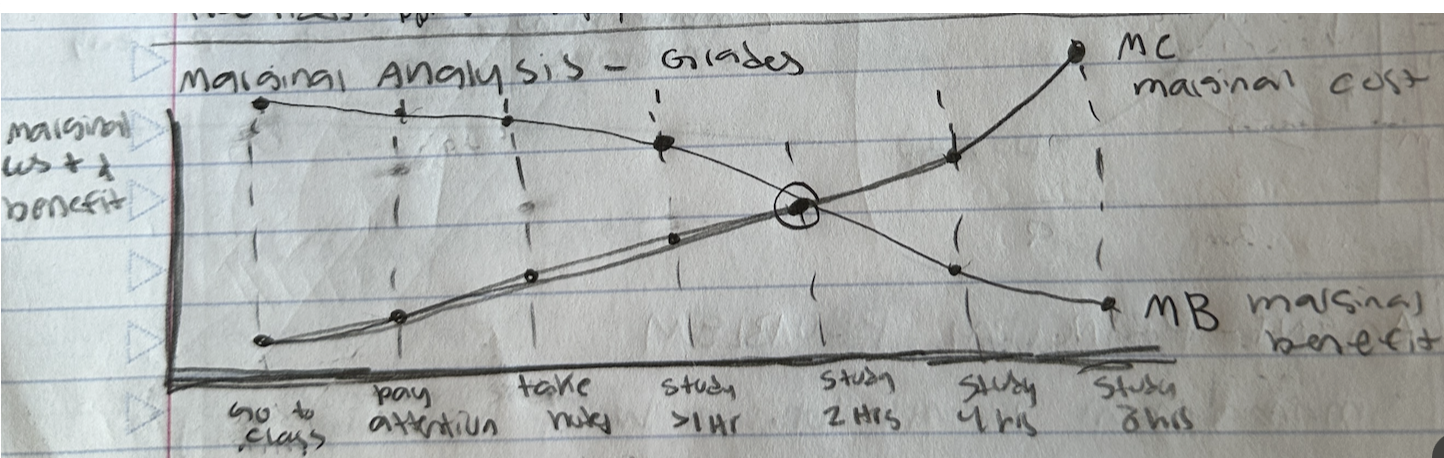
Marginal analysis
Marginal benefit vs marginal cost
Externalities (spillovers)
The positive or negative impact on a 3rd party that results when someone purchases a product
Result: overallocation or underallocation of the product purchased b/c the effect is outside the buyers and sellers
Negative externalities
Impact on others is bad: government wants to decrease output Ex: Cigarettes
How does the government discourage negative externalities?
Supply: Tax product
Demand: Warning labels, age limit, can’t advertise
Positive externalities
Impact on others is good: government wants to increase output Ex: college education
How does the government incorage positive externalities?
Supply: State subsidy
Demand: Financial aid
Supply
(MPC) Marginal Private Cost: the cost to the firm of making one more unit
(MSC) Marginal Social Cost: the cost to the firm & society of making one more unit
Demand
(MPB) Marginal Private Benefit: the benefit to the buyer of a product from purchasing one more unit
(MSB) Marginal Social Benefit: the benefit to the buyers & society when purchasing one more unit
Consumer tax incidence
The rectangle above the equilibrium price
Producer tax incidence
The rectangle below the equilibrium price
If the D curve is inelastic
the producers can push more tax incidence onto the buyers, they are not sensitive to price
D inelastic; change in Q is small
Government revenues will be higher
D elastic; change in Q is large
Government revenues will be lower
If D curve is elastic
producers can’t push more tax incidence onto the buyers, they are sensitive to change in price. Producers must pay more of the tax
DWL on PC market graph
SOP: S=D

DWL on monopoly graph
SOP: MC = D

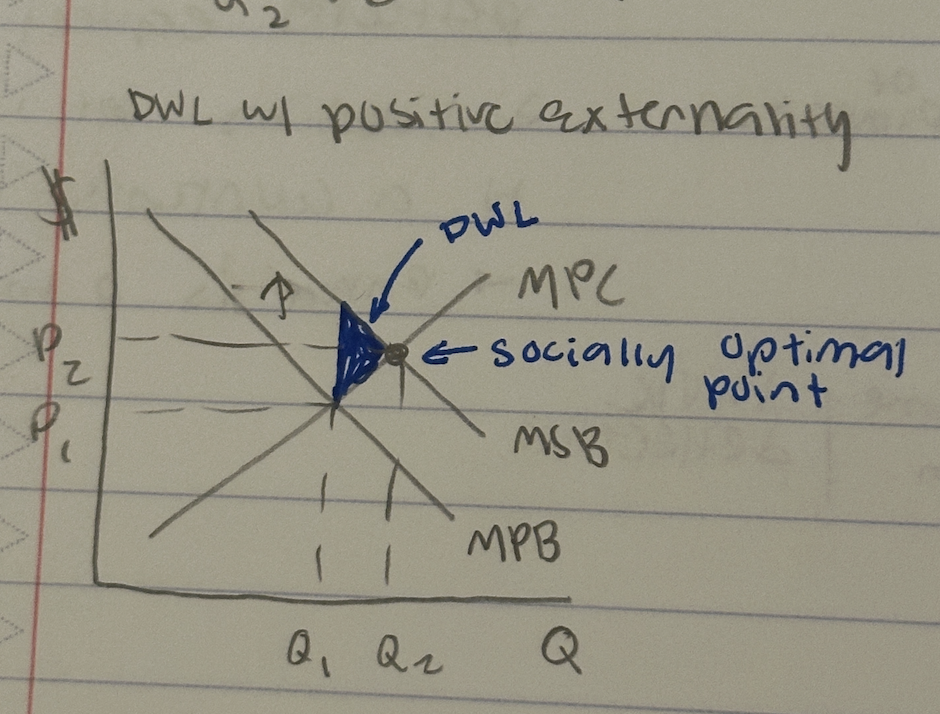
DWL w/ positive externality
SOP: MPC = MSB
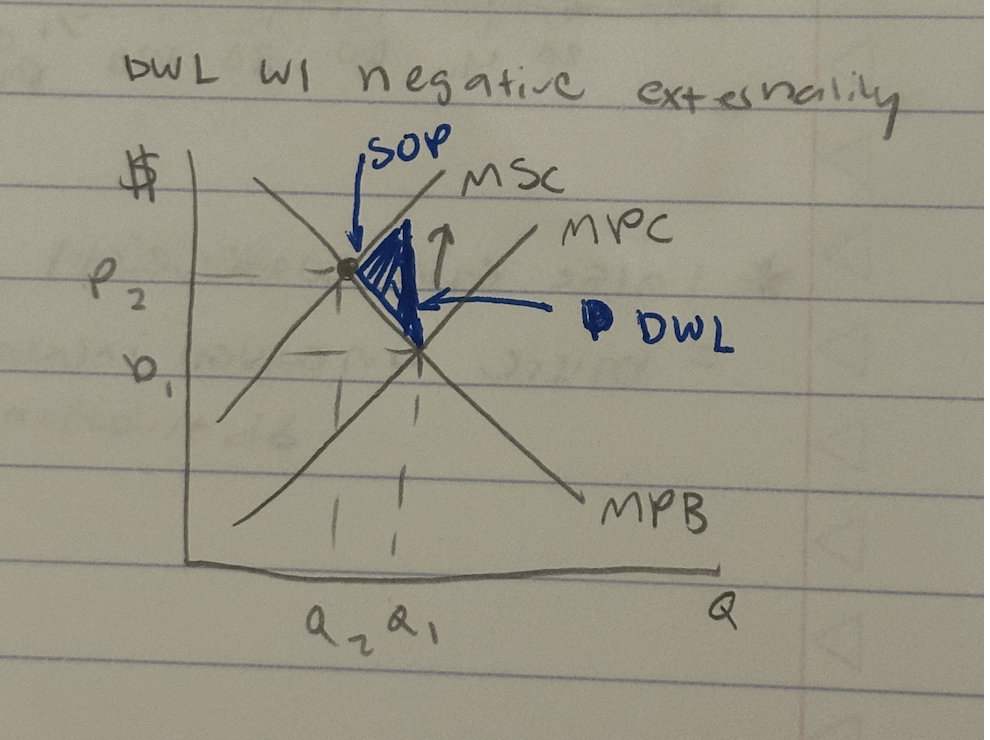
DWL w/ negative externality
SOP: MPB = MSC
Anti-trust laws
against collusion in oligopolies
against interstate monopolies
Price regulation
ATC pricing (fair returns) p=ATC
MC pricing (Socially optimal) p = MC
Disclosure laws
removing info failures
Lorenz curve
graphically demonstrates a country’s income inequality
Gini coefficient
measures the degrees of deflection from a perfectly equal distribution of income to a countries population
ranges from 0 (best) to 1 (worst)